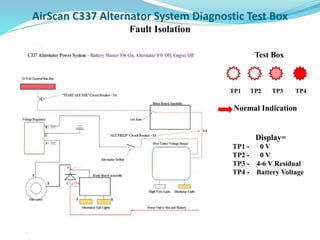
This training session overview provides details on troubleshooting the Cessna 337 alternator system. The classroom portion will last 45 minutes and cover an introduction, troubleshooting 101, a diagnostic test box, reviewing the alternator system, fault isolation, and helpful tips. The hands-on portion will last 20 minutes and involve connecting and operating the diagnostic test box. The goal is to efficiently diagnose alternator system malfunctions using structured procedural troubleshooting.