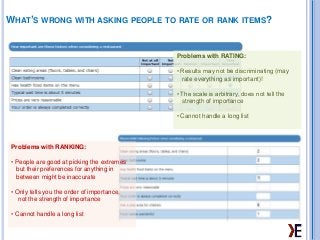
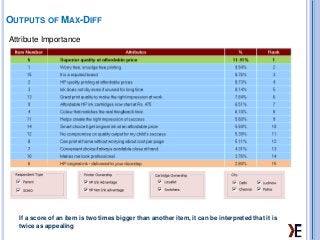
MaxDiff is an approach for obtaining preference/importance scores for multiple items. This presentation will help understanding why max diff is required, what are the types of max diff and outputs of max diff. We have also given our demo links in the end.