Antimicrobials General_MBBS.pptx
- 1. Antimicrobial Agents (General Considerations) Prof. R. K. Dixit Pharmacology and Therapeutics K.G.M.U. Lucknow dixitkumarrakesh@gmail.com 9415089880
- 4. Objectives • After this lecture students will be able to answer – What are antimicrobials, antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents (Terminologies used in antimicrobial treatment) – Classification of antimicrobials (chemicals, mechanism, spectrum) – Mechanisms of action of antimicrobials – Resistance development in antimicrobials – General adverse effects of antimicrobials – General drug interactions related to antimicrobials – Uses of antimicrobials (Therapeutic and Prophylaxis) – Selection of appropriate antimicrobials – Precautions while prescribing antimicrobials and failure
- 5. A naturopath tells “One should never take antibiotics Except in Pneumonia, GIT infections, boils, meningitis, encephalitis, osteomyelitis, occular infections, or other serious illness……………………………………….”
- 6. Allopath is Lucky to have the help of Antimicrobials But This Luck may not last long due to reasons…… –Inappropriate use,… –Overuse….. –Antimicrobial resistance –Reduced immunity –Worsening of environment –Co morbid illnesses like diabetes, malnutrition…… –Less interest of pharmaceuticals in this field –New antimicrobials generally expensive
- 7. Antimicrobials , Antimicrobials , Antimicrobials , Antimicrobials, Antimicrobials , Antimicrobials Antimicrobials!!! Penicillin, ampicillin, amoxycillin, ticarcillin, piperacillin, flucloxacillin, dicloxacillin, oxacillin, methicillin, nafcillin, carbenicillin, eryhtromycin, clindamycin, roxythromycin clarithromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline, vancomycin, teicoplanin, augmentin, gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, streptomycin, azithromycin, aztreonam, cephalexin, cefotaxime, cephamandole, cefepime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefpirome, imipenem, chloramphenicol, cotrimoxazole, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, trimethoprim,……. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………….. hundreds of different antimicrobial agents on the market.
- 8. What are the two basic causes of diseases • Abnormality in (Biochemistry, Anatomy and Physiology (BAP) of the body) the body’s self environment or cells or tissues or organs. Reasons may be anything including deficiency of essential elements, vitamins etc or abnormality in CNS, CVS, ANS etc. • Attack on the body by –Real invaders (Viruses, Bacteria, Protozoa, Helminthes, Fungus etc) –Pseudo invaders- Malignant cells
- 9. What are the two basic types of therapies in modern medical science • Pharmacotherapy against – Abnormality in (Anatomy, Biochemistry and Physiology of the body) the body’s self environment or cells or tissues or organs. Reasons may be anything including deficiency of essential elements, vitamins etc or abnormality in CNS, CVS, ANS etc. • Chemotherapy against – Real invaders (Viruses, Bacteria, Protozoa, Helminthes, Fungus etc) – Pseudo invaders- Malignant cells
- 10. Terminology 11 Chemotherapy – Use of drugs to treat infections and malignancy Antimicrobials and Antineoplastic agents (Beware of using this) Pharmacodynamic agents- Drugs regulating physiological process of body and act on the body cells. Chemotherapeutic agents- Selectively acting against microbes or malignant cells. (Don’t touch body cells) Prophylactic therapy- To prevent the occurrence of disease (May be chemo may be pharmacotherapy) Antimicrobials – Used in treating infectious microbial diseases. Antibiotics – Produced from microbes to inhibit or kill other microbes in low concentration (Antimicrobials from microbes) All antibiotics are antimicrobials But All antimicrobials are NOT antibiotics
- 11. Bacteriostatic- Stop the growth of bacteria Bactericidal- Kill the bacteria PAE- Post antibiotic effect Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)- Which stops the growth Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)- Which kills by 99.99% Which concentration will be more MIC or MBC What about MBC-MIC value regarding cidal or static activity MBC – MIC Less = Bactericidal MBC – MIC More = Bacteristatic What comes first •Stopping Or •Killing
- 12. • Bacteriostatic drugs –Kill (MBC) – This is your last chance to stop – Again I warn please stop – Please this is serious stop – Stop please I request – Please stop –Stop (MIC) • Bactericidal – if don’t obey Kill (MBC) – Stop (MIC) Bacteriostatic drugs (Police) show more patience Bactericidal are to kill (Commandos)
- 13. MBC – MIC is More MBC – MIC is Less What about MBC – MIC in this
- 14. • Prebiotics- –Chemicals which stimulate the growth of intestinal commensals and prevent multiplication and establishment of pathogenic bacteria • Inulin, Lactulose, Lactitol (ILL) • Probiotics- –Live microbs used as supplements to maintain the intestinal bacterial flora. • Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria
- 15. Terminology Summary Chemotherapy – Pharmacodynamic agents- Chemotherapeutic agents- Antimicrobials – Antibiotics – Bacteriostatic- Bactericidal- PAE- Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)- Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)- • Prebiotics- • Probiotics- • Prophylaxis-
- 16. Beware of term Chemotherapy Presently it is used only for Antineoplastic agents
- 18. Historical perspectives • Pasteur- (1877) – Phenomenon of antibiosis • Paul Ehrlich- (1906) – Father of Chemotherapy, – Coined term chemotherapy • Domagk- (1935) – Discovery of sulfonamides (Prontosil to sulphanilamide) • Fleming, Chain, Florey- – Penicillin (1929, 39, 41) from penicillium • Waksman- – Streptomycin, from actinomycetes, – Coined term antibiotic
- 20. Invaders And Agents Acting Against • Viruses • Bacteria – Gram Positive – Gram Negative – Acid fast • Fungi • Protozoa infections – Amoeba – Malarial parasite – Others • Helminthes • Neoplastic cells • Antiviral • Antibacterial – Against gram positive – Against gram negative – Antitubercular/Leprotic • Antifungal • Antiprotozoal – Antiamoebic – Antimalarial – Other antiprotozoals • Anthelmintics • Antineoplastic / Chemotherapeutic agents
- 21. What are the most important factors to be good Antimicrobial or Chemotherapeutic Agent? • Selectivity and Specificity (Don’t Touch Human Cells) • Safety • Stability • Availability • Feasibility & Affordability • Efficacy SAFE
- 22. Here onwards we will focus on Antibacterials only
- 23. How bacteria are identified • Gram staining • Developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884 • Based on structural characters of cell wall • Gram positive has thick layers of peptidoglycan and stain purple • Gram negative contains thin and stain pink • Reagents used are gention violet, iodine, alcohol, safarin • Acid fast or Ziehl-Neelsen staining • Described by Franz Ziehl and Friedrich Neelsen • Acid fast organisms contain large amounts of lipid substance within cell walls called MYCOLIC ACIDS which resist staining by gram stains. Reagents used are Ziehl- Neelsen carbol fuchsin, acid alcohol and metylene blue. Acid fast bacteria appear red – Mycobacteria – Nocardia By structure and culture and Colony characters
- 25. Human Vs Bacteria HUMAN CELLS ARE LAZY WHILE BACTERIAL CELLS ARE CRAZY Who’s Cells are more Lazy??? Exploring Selectivity and Specificity
- 26. Human Cell Vs Bacterial Cell Use Preformedfolic acid for synthesis of DNA Use precursor PABA of folic acid and synthesize Folic acid by themselves to be used for synthesis of DNA Topoisomerase II during DNA replication Topoisomerase IV and DNA Gyrase during DNA replication Sterols Hopanoids Different DNA dependent RNA Polymerase
- 27. Differences between human cells Vs Bacterial Cells (Makes the antibacterial selective) • Human cells don’t posses wall – (Peptidoglycans = peptides + sugar) • Human cell membrane is different – ( Bacteria Contain HOPANOIDS (with extra ring) in place of Sterol) • Human cells take preformed dihydrofolic acid – (no need of PABA in human) • Dihydrofolic acid reducatase enzyme is different • Topoisomerases are different – (in bacteria topoisomerase IV, DNA Gyrase) • DNA dependent RNA polymerase is different • Ribosome 60S subunit (in bacteria 50S) • Ribosome 40S subunit (in bacteria 30S) Human Cells are more lazy than Bacterial Cells
- 28. Gram Positive Gram Negative
- 29. Gram positive & Gram Negative • Gram positive bacteria have – Thick cell wall – Peptidoglycan directly accessible from environment • Gram negative bacteria have – Thin cell wall – Surrounded by inner and outer membrane – Of lipopolysaccharide, phospholipids, and proteins – Outer membrane is a barrier to diffusion of antibiotics • Limited antibiotics may diffuse through porins
- 30. Organism affected • Anti-viral • Anti-bacterial • Anti-fungal • Anti-protozoal • Anthelmintic • Antitubercular • Antileprotic Sources • Fungi- – Penicillin – Cephalosporins – Griseofulvin • Bacteria- – Polymyxin B – Colistin – Bacitracin • Actinomycetes- – Most common – Aminoglycosides – Tetracyclines – Chloramphenicol – Macrolides
- 31. Spectrum • Narrow – Penicillin G – Aminoglycosides – Isoniazide • Broad – Tetracycline – Chloramphenicol • Extended – Ampicillin – Amoxicillin – Sulphonamides – Fluoroquinolones – Most…….. Bacteristatic – Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim (alone) – Tetracyclines – Macrolides (Erythromycin) – Chloramphenicol – Ethambutol – Nitrofurantoin Bactericidal – Cotrimoxazol – Penicillins – Cephalosporins – Aminoglycosides – Vancomycin, Daptomycin – Fluroquinolones (ciprofloxacin) – INH, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide – Polymixins, Bacitracin – Metronidazole
- 32. Differences Between Human Cells Vs Bacterial Cells To Use As Selective Targets For The Antibacterial Agents
- 33. Differences between human cells Vs Bacterial Cells (Makes the antibacterial selective) • Human cells don’t posses wall – (Peptidoglycans = peptides + sugar) • Human cell membrane is different – ( Bacteria Contain HOPANOIDS (with extra ring) in place of Sterol) • Human cells take preformed dihydrofolic acid – (no need of PABA in human) • Dihydro folic acid reducatase enzyme is different – (thousand time affinity) • Topoisomerase II are different – (in bacteria topoisomerase IV, DNA Gyrase) • DNA dependent RNA polymerase is different • Ribosome 60S subunit (in bacteria 50S) • Ribosome 40S subunit (in bacteria 30S) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Human Cells are more lazy than Bacterial Cells
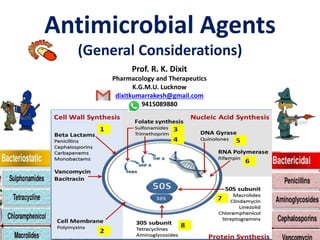
- 34. Mechanism of action (Targets) • Cell Wall synthesis inhibition- – Beta-lactams, Vancomycin, Cycloserines • Cell membrane Leakage- – Polypeptides, Polyenes • Folate Synthesis inhibition- – Sulfonamides – Pyrimethamine • DNA gyrase and Topoisomerase (IV) inhibition- – Fluroquinolones • RNA polymerase inhibition- – Rifampicin,, • Protein Synthesis Inhibition- (ATT) – Inhibition of 50S ribosome-Chloramphenicol, Macrolides, Clindamycin, Linezolid – Inhibition of 30S ribosome -Aminoglycosides, tetracyclines 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 Human Cells are more lazy than Bacterial Cells
- 35. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Human Cells are more lazy than Bacterial Cells
- 36. Folate Metabolism and sequence of Protein synthesis in bacteria
- 37. PABA Dihydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid Purines and Pyrimidines DNA And RNA DNA unwinding and thread separation (DNA gyrase / Topoisomerase IV) DNA dependent RNA Polymerase tRNA +Amino Acids Ribosome unit (50S) Ribosome unit (30S) Protein Synthesis Dihydro-folic acid Synthetase Dihydro-folic acid reductase DNA multiplication mRNA Sulphonamides (PABA analogue and inhibitor of DHFAS) Trimethoprim and Pyrimethamine (inhibitor of DHFAR) Quinolones (Inhibitor of DNA gyrase and Topoisomerase IV) Rifampicin (inhibitor of DNA dependant RNA Polymerase) Chloramphenicol, Macrolides (50S) Aminoglycosides, Tetracyclines (30S)
- 38. DNA unwinding and thread separation (DNA gyrase / Topoisomerase IV) PABA Dihydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid Purines and Pyrimidines DNA And RNA Dihydro-folic acid Synthetase Dihydro-folic acid reductase RNA Polymerase tRNA +Amino Acids Ribosome unit (50S) Ribosome unit (30S) Protein Synthesis mRNA Sulphonamides (PABA analogue and inhibitor of DHFAS) Trimethoprim and Pyrimethamine (inhibitor of DHFAR) Quinolones (Inhibitor of DNA gyrase and Topoisomerase IV) Rifampicin (inhibitor of DNA dependant RNA Polymerase) Chloramphenicol, Macrolides (50S) Aminoglycosides, Tetracyclines (30S) 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 39. Cell Wall synthesis inhibition- Beta-lactams, Vancomycin, Cycloserines Cell membrane Leakage- Polypeptides, Polyenes PABA Dihydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid Purines and Pyrimidines DNA And RNA DNA unwinding (DNA gyrase) Threads sepeartion (Topoisomerase IV) RNA Polymerase mRNA tRNA + Amino Acids Ribosome unit (50S) Ribosome unit (30S) Protein Synthesis Dihydro-folic acid Synthetase Dihydro-folic acid reductase DNA multiplication Sulphonamides (PABA analogue and inhibitor of DHFAS) Trimethoprim and Pyrimethamine (inhibitor of DHFAR) Quinolones (Inhibitor of DNA gyrase and Topoisomerase IV) Rifampicin (inhibitor of RNA Polymerase) Chloramphenicol, Macrolides (50S) Aminoglycosides, Tetracyclines (30S) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 40. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 41. Which of the following will have effect for longer time on the control of notorious activities of baby Post Pityai Effect (Post Antibiotic effect)
- 42. Post-Antibiotic Effect • Capacity to inhibit the growth of bacteria after removal of the drug from the culture (body) • Provides additional time for the immune system to remove bacteria that might have survived Post Pityai Effect
- 43. ANTIMICROBIALS Dose-dependent (With PAE) Time-dependent Antibacterial effect directly depends on their concentrations in the locus of infection (high doses 1-2 times/24h) •Aminoglycosides •Fluoroqinolones •Metronidazol •Amphotericin B Effectiveness depends on a period of time, during which concentration in blood overwhelms MIC for a particular causative agent (constant i.v. infusion or 3-6 times/24h) •Beta-lactames •Glycopeptides •Macrolides •Tetracyclines •Vancomycin Post Pityai Effect
- 44. Summary • Human cells are…………while bacterial cells are….. • Human cells use ………………………..folic acids • Gram positive cells contain ……………………. • Gram negative bacteria contain two……………….. • High quantity of Mycolic acid is present in………. • If Post antibiotic effect is more then frequency is • There are eight targets for Antibacterials to act. These are………….. • Antibacterials can be classified according to………………..
- 45. Relax and Revise
- 47. Antimicrobial Resistance Resistance Intrinsic Acquired Mutation Conjugation Transformation Transduction Not Dangerous/ less clinical importance Transmitted vertically only Dangerous/ clinical importance Can be transferred Horizontally and Vertically
- 48. Inherent Resistance (Not Much of clinical importance) • Bacteria naturally resistant – e.g., Gram-negative bacteria resistant to penicillins – Genes transferred to the bacterial progeny • Bacteria may be resistant because – No mechanism to transport the drug into the cell – Do not contain antibiotic’s target process or protein
- 49. Acquired Resistance • Due to exposure of antimicrobials • Horizontal evolution: –Resistance genes pass from resistant to nonresistant strain, –Antibiotics- a selective pressure. –Gene transfer mechanisms: • Conjugation. • Transduction. • Transformation.
- 51. Antibiotic Produces Selection Pressure
- 53. Resistance to Antibiotics 5. Adaptation of alternate metabolic pathway
- 54. Factors favoring Resistance •Prescription related factors: •Overuse and Underuse •Early discontinuation •Over continuation •Less dose, duration •Livestock doping: •Animals exposure
- 58. Adverse Drug Reactions of Antimicrobials • General – Hypersensitivity reactions – CNS – GIT – Injectable S/E – Vitamin Deficiency – Super infections – Teratogenic – Masking of infections – Intolerance – Drug induced fever • Specific
- 59. General-Adverse effects of antimicrobials •Hypersensitivity reaction- •Penicllins, Sulphonamides •Skin rashes , Angioedema, Bronchospasm •Anaphylaxis, •Management with OASIS •Oxygen, •Adrenaline {Physiological antagonist of histamine} •Antihistaminics •Steroid, •IV fluid •Supportive,
- 60. •Gastrointestinal symptoms- •Nausea, •Anorexia, •Gastric irritation, •Flatulence, indigestion, •Altered GI motility, •Mouth ulcers, Glossititis, Stomatitis, Chelitis •Esophagitis, •Mal-absorption syndrome •Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol, Quinolones, Ampicilline, Metronidazole
- 61. •Injectable Side effects- •Pain, Abscess formation, •Thrombo-phlebitis in case of IV •Flushing, redness in case of rapid IV
- 62. • Deficiency of Vitamins- • Vitamin Bcomplex and Vitamin K,
- 63. Reduced Efficacy of other drugs • Drugs which need entero- hepatic recirculation for their effect like Oral contraceptives
- 64. Super infections New infection • Most common organisms • Pseudomonas, Candida, Proteus • Clostridium difficle- Pseudomembranous Colitis • Due to removal of inhibitory mechanisms (Bacteriocins and competition for nutrition) – Common in immunocompromised, Diabetic, Surgical patients – Common drugs causing super infections (CAT) • Clindamycin, Cotrimoxazole, Chloramphenicol • Ampicillin • Tetracyclines Treated by Metronidazole, Vancomycin, Bacitracin
- 65. •CNS- •Headache, •Irritability, •Sedation, •Tinnitus , •Ataxia, •Forgetfulness •Slurred speech, •Blurring of vision •Convulsions in high dose of cephalosporins
- 66. •Masking of infections- •eg. Tt Gonorrhea mask Syphilis •Idiosyncratic and Intolerance- •Drug Fever- •Electrolyte imbalance-
- 67. • Teratogenic effects- • No antimicrobial is absolutely safe during pregnancy • No one is Category A • Category B, C and D can be given under special situation • Category X absolutely contraindicated to pregnant
- 68. Antibiotics in Pregnancy FDA Category Antibiotics in Category A B Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems (except Imipenem), Daptomycin, Vancomycin (oral), Clindamycin, Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Metronidazole (avoid first trimester), Nitrofurantoin, Acyclovir, Amphoterocin B, Ethambutol C Quinolones, Chloramphenicol, Clarithromycin, Imipenem, Linezolid, Trimethoprim/Sulfa (D if used near term), Vancomycin (IV), Rifampin, INH, PZA, PAS, Fluconazole, Caspofungin D Tetracyclines (Doxy, Tige, Mino), Voriconazole, Aminoglycosides (some put gentamicin as a category C) X Ribavarin Betalactam (Penicillins and Cephalosporins) Macrolides Quinolones Sulphonamides Tertracylines Aminoglycosides
- 69. Specific Side effects of antimicrobials •Bone marrow suppression- •Chloramphenicol (Aplastic Anaemia) •Thrombocytopenia- •Sulphonamides •Cephalosporins Cefamandole Cefoperazone Cefotetan Same which produce Disulfiram like reaction
- 70. • Renal toxicity- • Aminoglycosides, • Tetracyclines EXCEPT Doxycycline, • Cephalothin, • Talampicillin, • Nitrofurantoin, Nalidixic acid, Amphotericin B, • Vancomycin, Ethambutol, Flucytosine, Methacillin,
- 71. •Hepatotoxicity- •Rifampicin, •Isoniazide (in fast acetylators due to accumulation of Acetyl – isoniazide and acetyl – hydrazine) •Pyrazinamide •Tetracycline, •Erythromycin estolate, •Talampicillin, Nalidixic acid, Trovafloxacin •Oxacillin,
- 72. • Photoxicity- • Tetracyclines • Demeclocycline • Doxycycline • Quinolones •Sparfloxacin
- 73. •Ototoxicty- •Aminoglycosides, Vancomycin •Diabetes insipidus- •Demeclocycline Drugs producing Diabetes inspidus- Lithium, Demeclocycline Drug used in treatment of Lithium induced Diabetes inspidus- Amiloride
- 74. • Neuromuscular block- • Amino-glycosides • Polymyxin- B • Colistin • Gaping of wound • Respiratory paralysis in Myasthenia gravis
- 75. •Retinal damage- •Chloroquine •Neuropathy- •Polypeptides •Amphotericin B •Nitrofurantoin •Carbenicillin •Dapsone •Chloroquine •Isoniazid- in slow acetylators •Due to increased excretion of pyridoxine •Accumulated INH inhibits pyridoxine-kinase (Pyridoxine Kinase converts pyridoxine to active form) Isoniazid in •Slow Acetylators- Neuropathy •Fast Acetylators- Hepatotoxicity
- 76. Isoniazid Side effect depends on Acetylation status of Patient • North Indians are – 40% Fast – 45% Intermediate – 15% Slow Acetylators Neurotoxicity Hepatotoxicity Hydrazonation Acetylation
- 77. Haemolysis (G-6-PD deficiency), - •X-Linked recessive. •G-6-P-D is required for regeneration of NADPH. •NADPH is required for reduction of oxidized glutathione •Reduced glutathione protects –against oxidative injury •Precipitating pro-oxidants •Naphthalene, Methylene Blue, Beans (Favism) •Sulfa drugs, Primaquine, Isoniazide, Nitrofurantoin, Nalidixic acid, Dapsone, Furazolidione, Quinolones, Chloramphenicol, Chloroquine, •Haemolysis occurs during oxidative stress G-6-P-D Glutathion reductase Glutathione Glutathione disulphide NADP NADPH S P I N Delivery
- 78. •Discolouration of Teeth and bone damage- •Tetracyclines •Redman (Red neck) Syndrome- •Vancomycin, Teicoplanin, •Discolouration of secretions (saliva, sweat, urine)- • Rifampicin, Clofazimine, Nitrofurantoin
- 79. • Kernicterus- • Sulphonamides, Rifampicin • Flu-like syndrome- • Rifampicin • Antitestosterone effect- • Ketoconazole (reduces synthesis of testosterone leading to gynaecomastia)
- 81. • Optic neuritis- • Ethambutol • Tendon rupture- • Fluroquinolones
- 82. •Jarisch Herxheimer Reaction- •Penicillin in syphilis •Inflammatory reaction against endotoxins released by the death of spirochetes •Increased inflammatory cytokines •Manifest as fever, Chills, hypotension, headache, flushing, myalgia and skin lesions •Treatment by NSAIDS, Steroids, and general care •Other causes •Relapsing fever (louse or tick born) •Leptosporiosis •Q Fever •Brucellosis
- 83. •Alopecia- •All anti-cancer drugs •Fanconi’s Syndrome- (Renal toxicity)- •Expiry date tetracyclines- •due to toxic metabolites epitetracycline
- 84. •Pseudotumor cerebri- and bulging fontanelles- •Tetracyclines •Hyperuricemia- •Pyrazinamide (Gout) •Pulmonary eosonophilic syndrome- • Tetracylines •Vestibular toxicity- •Minocycline
- 85. •Disulfiram like reaction – (Good Chief Minister) •Griseofulvin, •Cefoperazone •Cefotetan •Cefamandole, •Metronidazole, Ethyl Alcohol – (Alcohol dehydrogenase or Acetaldehyde synthetase) Acetaldehyde- (Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) Acetic Acid- Kreb’s cycle- ATP + CO2+ H2O (Blocked by Disulfiram)- Accumulation of Acetaldehyde and precipitations of syndrome consisting of Headache, Vomiting, Flushing etc.
- 86. •Grey Baby Syndrome- (Ashen Grey Cyanosis)- •Chloramphenicol •Pulmonary Fibrosis- •Bleomycin, Nitrofurantoin
- 87. • Very Special- • Gatifloxacin • Prolongs QT interval and arrhythmia • Hypo or hyperglycemia in patients of diabetes. • Aminoglcosides have NOT side effects- • Neuromuscular block (more with Neomycin and Streptomycin), • Nephrotoxicity least with Streptomycin • Ototoxicity (Vestibular by Streptomycin, Gentamicin while Cochlear by Neomycin, Amikacin) • Teratogenic) • High dose of Ceftriaxone • Pseudo-lithiasis (Gall bladder sludge)
- 88. •Mafenide •Has carbonic anhydrase inhibitor activity •May alkalinize urine and cause acidosis •Hyperventilation •8-Hydroxy-quinoines (Iodochloro-hydroxyquinol,) •SMON (Subacute myelo-optic neuropathy) •Antianabolic effect (reduce protein synthesis)- •Tetracyclines
- 89. Important Drug Interactions of Antimicrobials •Synergism/Addition/ •Antagonism •Combinations of more than one antimicrobial •Combination of antimicrobial with other agents Pharmacodynamic Pharmacokinetic (ADME) •Chlelation /(Antacids, Milk)- Tetracyclines •Alteration of pH/ Ionization of drug- Penicillins •Alteration with Enterohepatic recirculation- (OCP) •Inducer (Barbiturates, Rifampicin, Griseofulvin, Carbamazepine) •Inhibitor (Cimetidine, Chlolramphenicol, Erythromycin, Quinolones) •Protein biding displacement of drug (Important with high protein binding drugs)- Sulphonamides Pharmaceutical •During manufacture, packaging, Storage •During drug administration •During Mixing and injecting drug •Mixing in oral solutions •Mixing in solvent, • In bottle, •No drug in •Blood, •Plasma and •Electrolyte solutions
- 90. Important Drug Interactions of Antimicrobials Pharmaceutical •During Manufacture, Packaging, Storage •During drug administration •During Mixing and injecting drug (If precipitate Reject) •Mixing in oral solutions (Not advisable) •Mixing in solvent (According to instructions) •No drug in •Blood, •Plasma •Albumin •Ringer lactate
- 91. Important Drug Interactions of Antimicrobials •Synergism/Addition(Cidal + Cidal, Static + Static) •Antagonism (Cidal + Static) When more sensitive to Cidal •Combination of antimicrobial with other agents •Best combo is Cidal + Cidal (Betalactam + Aminoglycoside) Pharmacodynamic
- 92. Important Drug Interactions of Antimicrobials Pharmacokinetic (ADME) •Chelation /(Antacids, Milk)- •Tetracyclines •Alteration with Enterohepatic recirculation- •OCP with antimicrobials •Inducers- •Rifampicin, Griseofulvin •Inhibitors- •Erythromycin, Chlolramphenicol, Quinolones (Grape fruit (Furanocoumarins) •Protein biding displacement of drug- •Sulphonamides
- 93. List of Important Interactions Related to Antimicrobials Sulphonamides Oral hypoglycaemics (Especially Sulphonylureas) Increased hypoglycemia Oral anticoagulants Increased anticoagulation (Protein binding displacement) Methotrexate (Inhibitor of Dihydrofolate Reducatase) Increased methotrexate toxicity (Folate deficiency) •Protein binding displacement •Folic acid depletion
- 94. Fluoroquinolone Antacids (Al, Mg, Ca), Zinc, Iron, Sucralfate, Milk Reduced absorption of Fluoroquinolone Theophylline Increased concentration due to decreased metabolism. (Least with Lome, Levo, Spar) Warfarin (Oral anti- coagulant) Enhanced effect due to decreased metabolism (least with Levo, Spar) Quinidine, Procainamide, Amidarone, Erythromycin, Cisapride, Astemizole, Terfenadine, Enhance Q-T interval leading to dangerous arrhythmia •Chelation •Enzyme inhibitor •Q-T prolongation
- 95. Ampicillin (Penicillin), (Cephalosporin) Contraceptive pills Failure of contraception (Inhibition of enterohepatic recirculation) Tetracycline, Chloramphenicol, Erythromycin Antagonism of bactericidal action (Cidal with Static) Aminoglycoside in same syringe Inactivation of both (Pharmaceutical) Hydrocortisone Inactivation of penicillin (Pharmaceutical) Allopurinol Increased incidence of non-urticarial maculo- papular rashes Probenecid Decreases tubular secretion of penicillin and increases action (Pk) Clavulanic acid, Sulbactam Inhibition of Betalactamase leading to better effect (Synergism) •Intestinal flora damage •Pharmaceutical incompatibility •Idiosyncratic •Secretion in renal tubule
- 96. Cephaloridine Furosemide Increased nephrotoxicity Rifampicin Warfarin and OCP Failure of anti-coagulation and contraception Griseofulvin Cefoperazone, Cefotetan, Cefamandole Metronidazole (Good Chief Minister) Alcohol Disulfiram like syndrome (Aldehyde Syndrome) Ethyl Alcohol – (Alcohol dehydrogenase or Acetaldehyde synthetase) Acetaldehyde- (Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) Acetic Acid- Kreb’s cycle- ATP + CO2+ H2O (Blocked by Disulfiram)- Accumulation of Acetaldehyde and precipitations of syndrome consisting of Headache, Vomiting, Flushing etc. •Enzyme Inducer •Nephrotoxic •Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor
- 97. Nalidixic acid Oral anticoagulants Enhanced anticoagulation Nitrofurantoin Nalidixic acid Antagonises action of nalidixic acid Probenecid Reduced tubular secretion leading to decreased concentration in urine Amphotericin-B Digitalis Amphotericin induced hypokalemia increases digitalis toxicity
- 98. Erythromycin Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Statins, Warfarin, Terfenadine, Inhibition of metabolism (Inhibit CYP3A4) Terfenadine Q-T prolongation leading to life threatening ventricular arrhythmias Linezolid MAO inhibitors Increased toxicity of MAO inhibitors (Linezolid is reversible inhibitor of MAO and may lead to cheese reaction with food containing tyramine and can precipitate Serotonin syndrome (confusion, hypertension, seizures, tachycardia and muscle rigidity) •Enzyme inhibitor •Q-T prolongation •MAO inhibitor property
- 99. Aminoglycosides Furosemide, Ethacrynic acid Increased Ototoxicity Skeletal muscle relaxants (curare like drugs) Enhanced and persistent neuromuscular blockade Tetracyclines Contraceptive pills Failure of contraception Antacids, Iron Milk , Food Decreased absorption due to Chelation •NOT •Damage of intestinal flora •Chelation
- 100. Chloramphenicol Oral hypoglycemic Increased hypoglycemic effect (due to enzyme inhibition by Chloramphenicol) Oral anti-coagulant Enhanced anticoagulant •Enzyme inhibitor
- 101. Ketoconazole Cisapride, Terfenadine, Astemizole, Quinidine, Warfarin, Cyclosporine Tacrolimus Statins Ketoconazole inhibits CYP3A4 leading to decreased metabolism and accumulation of other drug (Least with Fluconazole) H2 blockers, PPI, Antacids Decreased absorption of Ketoconazole due to decreased gastric acidity Amphotericin B Ketoconazole inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol and produces depletion of membrane ergosterol reducing the binding sites for Amphotericin B Griseofulvin Other drug Inducer of microsomal enzymes •Enzyme inhibitor •Enzyme inducer
- 102. Bacteriological Culture and Sensitivity Testing • Plate – –Kirby-Bauer test • Strip- –Epsilometer test • Dilution – –Test tubes
- 103. Culture and Sensitivity Results • Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) – The lowest concentration of drug that prevents visible bacterial growth after 24 hours of incubation – Organism and antimicrobial specific – Interpretation • Drug’s activity versus the organism • Site of infection • Drug resistance • Report organism(s) and susceptibilities –Susceptible (S) or ++++ –Intermediate (I) or + –Resistant (R) or -
- 104. Combination Therapy: Uses 1. Empirical therapy 2. Poly-microbial infections (Suspected mixed infection) 3. To prevent development of resistance Good combo is 2 bactericidal e.g. cell wall inhibitor & protein synthesis inhibitors e.g. Betalactam with Aminoglycosides Good Trio is 2 bactericidal with anti-anaerob Eg. Betalactam with Aminoglycoside with Metronidazole (BAM)
- 106. Selection of A Drug Selection ADR will govern ADR Agent, Dose, Dosage form, Duration, Route, Financial Condition Disease Site, Intensity, Previous Tt, Co-morbidities, Other Drugs taken by Patient Physiological condition, Conscious / Unconscious, DDI and DFI
- 107. Choice of antimicrobial agents Patient- •Age- Pediatric -----------General---------------------Geriatric •General condition (G.C)- Consciousness etc….. •Hepatic, Renal functions- •Other metabolic factors •Pregnancy- •Genetics- (G-6-PD deficiency) •Immune status of patient- •History of allergy •Financial condition- Infection- •Site •Type (Microbe)- Guess, Confirm with C/S •Intensity •Presence of pus, clot, Hematoma Drug- •Spectrum •Sensitivity •Dosage form availability •Relative Toxicity (selection depends on patient) •Acceptable pharmacokinetic profile •Price Selection ADR will govern ADR Agent, Dose, Dosage form, Duration, Route, Financial Condition Disease Site, Intensity, Previous Tt, Co-morbidities, Other Drugs taken by Patient Physiological condition, Conscious / Unconscious, DDI and DFI
- 108. Antimicrobial therapy • Emperical – Infecting organism(s) not yet identified – Experience based on Site, Size, Season, Spectrum – More “broad spectrum” • Definitive – Organism(s) identified – Specific therapy (“narrow” spectrum) • Prophylactic or preventative – Prevent an initial infection or its recurrence – Given in anticipation of infection
- 109. Empirical therapy • Know the common pathogens responsible for common infections • Know the antimicrobial spectrum of activity • Take sample before starting empirical therapy in complicated cases
- 110. Selecting a Therapeutic Regimen • Confirm presence of infection: – History signs and symptoms Investigations • Predisposing factors • Before selecting Emperic therapy get material for c/s or for microscopy • Consider the spectrum of activity; – Narrow vs broad spectrum • Special conditions like – Sepsis or meningitis, – Pt. with Diabetes, Immunosupression – Pt. with other co morbid illnesses
- 111. Prophylactic use of antimicrobials in important conditions •Rheumatic fever- •Benzathine Penicillin •Tuberculosis- •Isoniazid, Rifampicin •Mycobacterium avium complex- • Azithromycin, Clarithromycin •Pneumocystis – •Cotrimoxazole •HIV exposed person- •Zidovudine + Lamivudine + Indinavir •HIV in foetus – •Zidovudine to mother
- 112. •Meningococcal meningitis- •Rifampicin / Sulfadiazine •Gonorrhoea / Syphilis- •Ampicillin or Ceftrioxone •Genital herpes – • Acyclovir •Malaria- •Chloroquine, Mefloquine •Influenza A- •Amantadine •Cholera- •Tetracyclines •Whooping cough – •Erythromycin •Plaque- •Doxycycline •Bird flu- •Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
- 113. •Dental extraction, Tonsillectomy, Endoscopies- • Amoxicillin •Catherization- •Cotrimoxazole, Norfloxacin, Ampicillin, Gentamicin •COPD- •Ampicillin, Doxycycline •Immunocompromised- •Penicillin, Cephalosporins ± Aminoglycosides ± Fluroquinolones± Metronidazole •General Surgical prophylaxis- BAM or CAM or FAM
- 114. Monitoring Therapeutic Response • Clinical assessment – Improvement in signs and symptoms • Fever curve, WBC • Erythema, pain, cough, drainage, etc. • Laboratory tests
- 115. Antimicrobial Factors in Drug Selection
- 116. The Criteria of the Ideal Antibiotic: • Selectivity against microbes • Least toxic to the human cells • Ability to reach at the desired site(BBB) • Remains in body long enough to be effective • Shelf life good • Does not lead to resistance development • Less expensive, Less allergic • Microbiocidal rather than microbiostatic. • Less suppression of normal flora
- 117. Causes of failure of antimicrobial therapy •Improper selection of – •Drug, •Dose, •Duration •Dosage form and Route •Delay of treatment •Drug quality questionable •Failure to apply adjuvant measures •Immune-compromised status •Extra smart organism •Resistant, Dormant
- 118. Summary • Antimicrobials are among the most important advances of modern medicine. • The general concept regarding antimicrobials – Antibacterial spectrum, Classification of antimicrobials – Chemotherapeutic drugs Vs Pharmacodynamic drugs – Bacteriostatic drugs, Vs Bactericidal drugs – MIC Vs MBC – Post antibiotic effect, – General side effects of antimicrobials – General Mechanisms of actions of antimicrobials (1-8) – General Drug interactions of antimicrobials – Antimicrobial Resistance- – Selection of appropriate antimicrobial – Causes of failure
- 119. Summary • Appropriate selection of antimicrobials is complicated. • It is not only the matching a drug to a bug • Antimicrobial selection depends on – Clinical efficacy, – Adverse effect profile, – Pharmacokinetic disposition, and – Cost ultimately guide therapy • Once chosen, the dose, duration must be based on – Age, Sex (pregnancy) and weight of the patient, – Site, Severity of infection, – Route of elimination, – And other factors including co-morbid conditions • Use antimicrobials – Only when needed – For optimum time period as needed to treat the infection – Try to limit the emergence of bacterial resistance
- 120. Superbugs (Microorganisms with multiple resistance) • MRSA - Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus • VISA - Vancomycin intermediate resistant Staphylococcі • VRE - Vancomycin-resistant enterococci • ESBLs - Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (microorganisms – resistant to cephalosporins and monobactams) • PRSP - Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae • MRPA (MDR-PA)- Multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa • MRAB (MDR-AB) - Multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- 121. Why worry? MDRO are dangerous – Difficult to treat – More virulent – Increase mortality and morbidity Resource-intensive – More expensive and toxic antibiotics – Increase length of hospitalization – Increase demand for isolation-facilities
- 122. Why Worry???? Antibacterial Resistance is developing fast Newer Antibacterial entry is slow
- 123. E n d o f a n t i b i o t i c s - t h e u l t i m a t e c o n s e q u e n c e
- 124. THANKS