OLIGOPOLY
RP Pamplona
OLIGOPOLY
Etymology
Oligo meaning small number; few
Monopoly
OLIGOPOLY
An oligopoly is a market form in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers (oligopolists). Oligopolies can result from various forms of collusion which reduce competition and lead to higher prices for consumers. ©Wikipedia
OLIGOPOLY
Number of Sellers
“Few” – a “handful” of sellers.
There are so few firms that the actions of one firm can influence the actions of the other firms.
OLIGOPOLY
Nature of Product Differentiation
Homogenous (steel/aluminum)
Differentiated (automobiles)
OLIGOPOLY
Ability to Enter and Exit the Industry
Barriers to entry are high such as government licenses, economies of scale, access to expensive and complex technology, and strategic actions.
Additional sources of barriers to entry often result from government regulation favoring existing firms making it difficult for new firms to enter the market.
OLIGOPOLY
Degree of Control on Product Price
Oligopolies are price setters rather than price takers.
OLIGOPOLY
Promotions (Non-price competition)
Oligopolies tend to compete on terms other than price.
Loyalty schemes
Advertisements
Product Differentiation
OLIGOPOLY
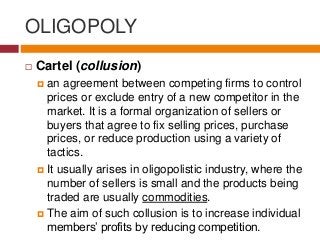
Cartel (collusion)
an agreement between competing firms to control prices or exclude entry of a new competitor in the market. It is a formal organization of sellers or buyers that agree to fix selling prices, purchase prices, or reduce production using a variety of tactics.
It usually arises in oligopolistic industry, where the number of sellers is small and the products being traded are usually commodities.
The aim of such collusion is to increase individual members’ profits by reducing competition.
OLIGOPOLY
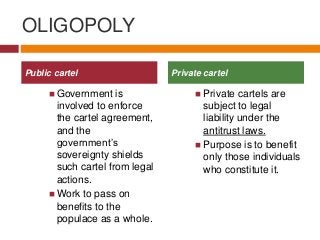
Public cartel
Government is involved to enforce the cartel agreement, and the government’s sovereignty shields such cartel from legal actions.
Work to pass on benefits to the populace as a whole.
Private cartel
Private cartels are subject to legal liability under the antitrust laws.
Purpose is to benefit only those individuals who constitute it.
OLIGOPOLY
Price Leadership
There may be an acknowledged market leader which informally sets prices to which other producers respond.
Interdependence
Oligopolies are typically composed of large firms that the actions of one firm affect market conditions.
Each firm must be intelligent enough to guess what will be the possible responses and countermoves of their competitors.
OLIGOPOLY
Examples
Worlwide
Kraft Foods, PepsiCo, and Nestlé – top three leading food processing companies
OLIGOPOLY
Nestlé, The Hershey Company, and Mars, Incorporated – make most of the confectionery made worldwide
OLIGOPOLY
Microsoft, Sony, and Nintendo – dominate the video game console market