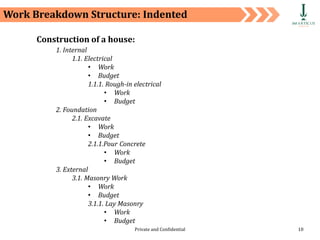
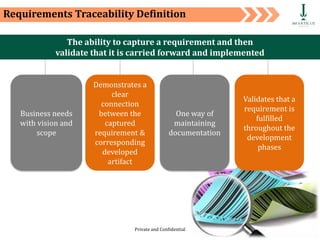
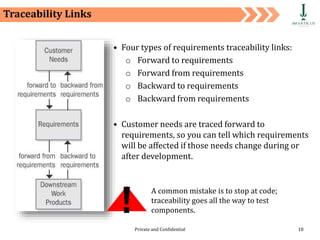
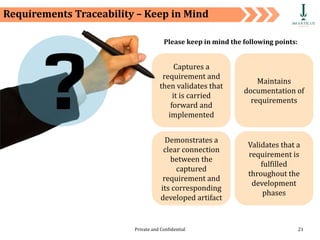
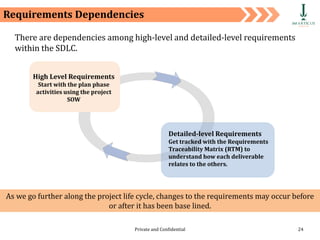
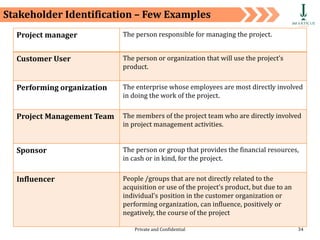
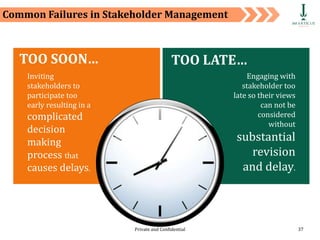
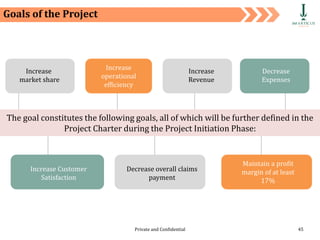
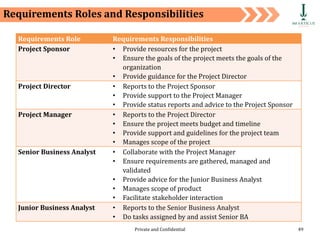
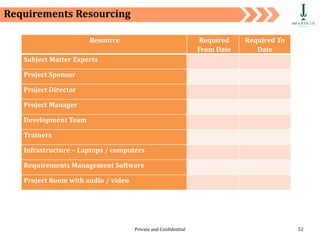
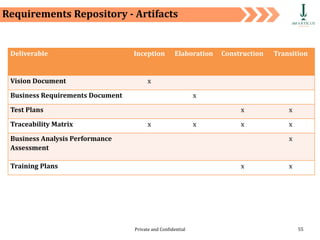
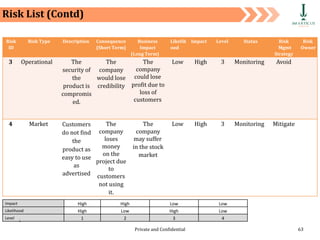
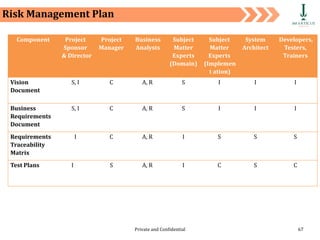
The document discusses requirement management and analysis. It covers creating and using a requirement work plan (RWP), the components and purpose of an RWP, and a case study on developing an RWP. It describes an RWP as a to-do list for requirement elicitation, documentation, and validation. The key components of an RWP include a work breakdown structure (WBS), which lists all tasks and activities, and identifies resources, skills, effort, and milestones. Traceability and managing requirement changes and dependencies throughout the project lifecycle are also addressed.