Report
Share
Recommended
S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370 

S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370 Steven Duplij (Stepan Douplii)
More Related Content
What's hot
S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370 

S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370 Steven Duplij (Stepan Douplii)
What's hot (19)
Lecture 6 Basic Transform: Translation, Rotation, Scaling

Lecture 6 Basic Transform: Translation, Rotation, Scaling
Implementing real-time transactional security property using timed edit automata

Implementing real-time transactional security property using timed edit automata
ORTHOGONAL, ORTHONORMAL VECTOR, GRAM SCHMIDT PROCESS, ORTHOGONALLY DIAGONALI...

ORTHOGONAL, ORTHONORMAL VECTOR, GRAM SCHMIDT PROCESS, ORTHOGONALLY DIAGONALI...
S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370 

S.Duplij, R.Vogl, "Membership amplitudes and obscure qudits", arXiv:2011.04370
A non-stiff boundary integral method for internal waves

A non-stiff boundary integral method for internal waves
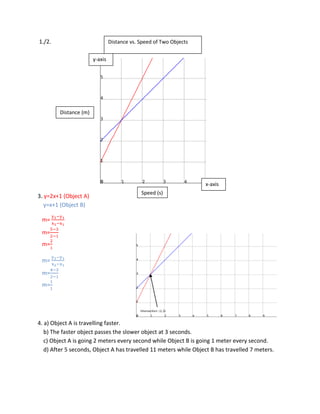
The Speed of Two Objects
- 1. Distance vs. Speed of Two Objects 1./2.<br />y-axis1514475154305<br />Distance (m)<br />x-axisSpeed (s)<br />3. y=2x+1 (Object A) y=x+1 (Object B) <br />2390775447675 m= y2-y1x2-x1 m=5-32-1 m=21<br /> m= y2-y1x2-x1 m=4-32-1 m=11<br />4. a) Object A is travelling faster. b) The faster object passes the slower object at 3 seconds. c) Object A is going 2 meters every second while Object B is going 1 meter every second. d) After 5 seconds, Object A has travelled 11 meters while Object B has travelled 7 meters.<br />
