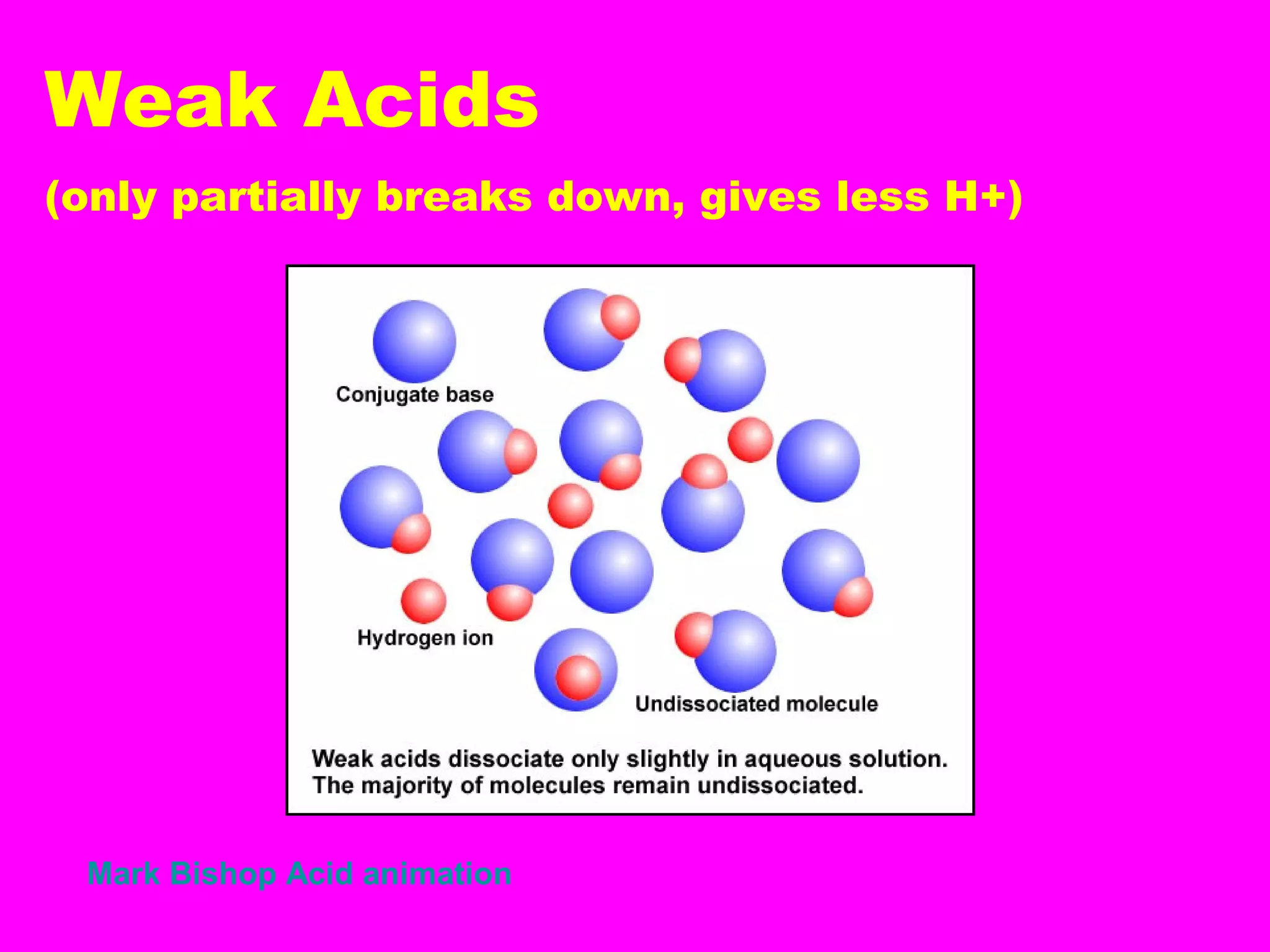
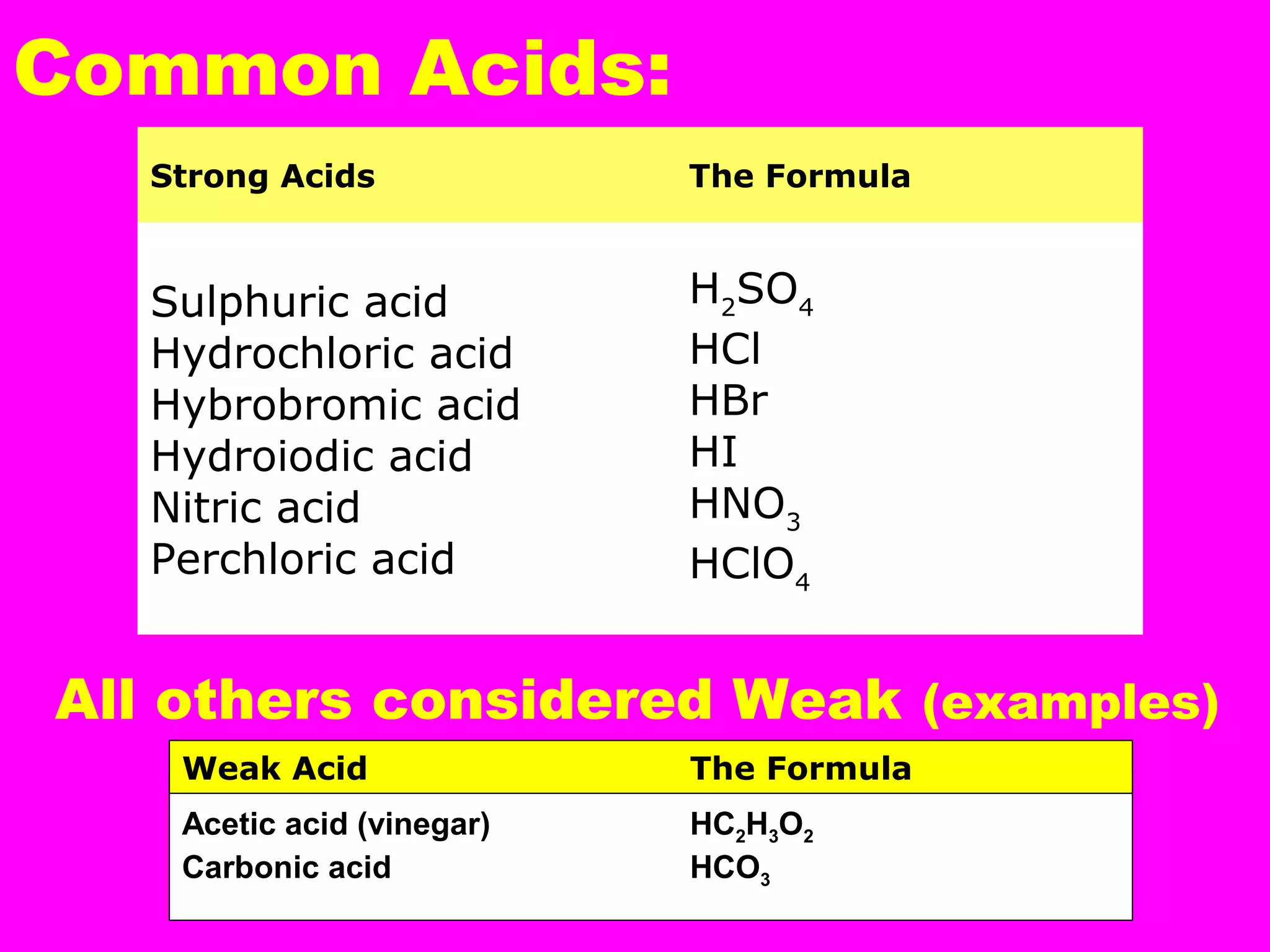
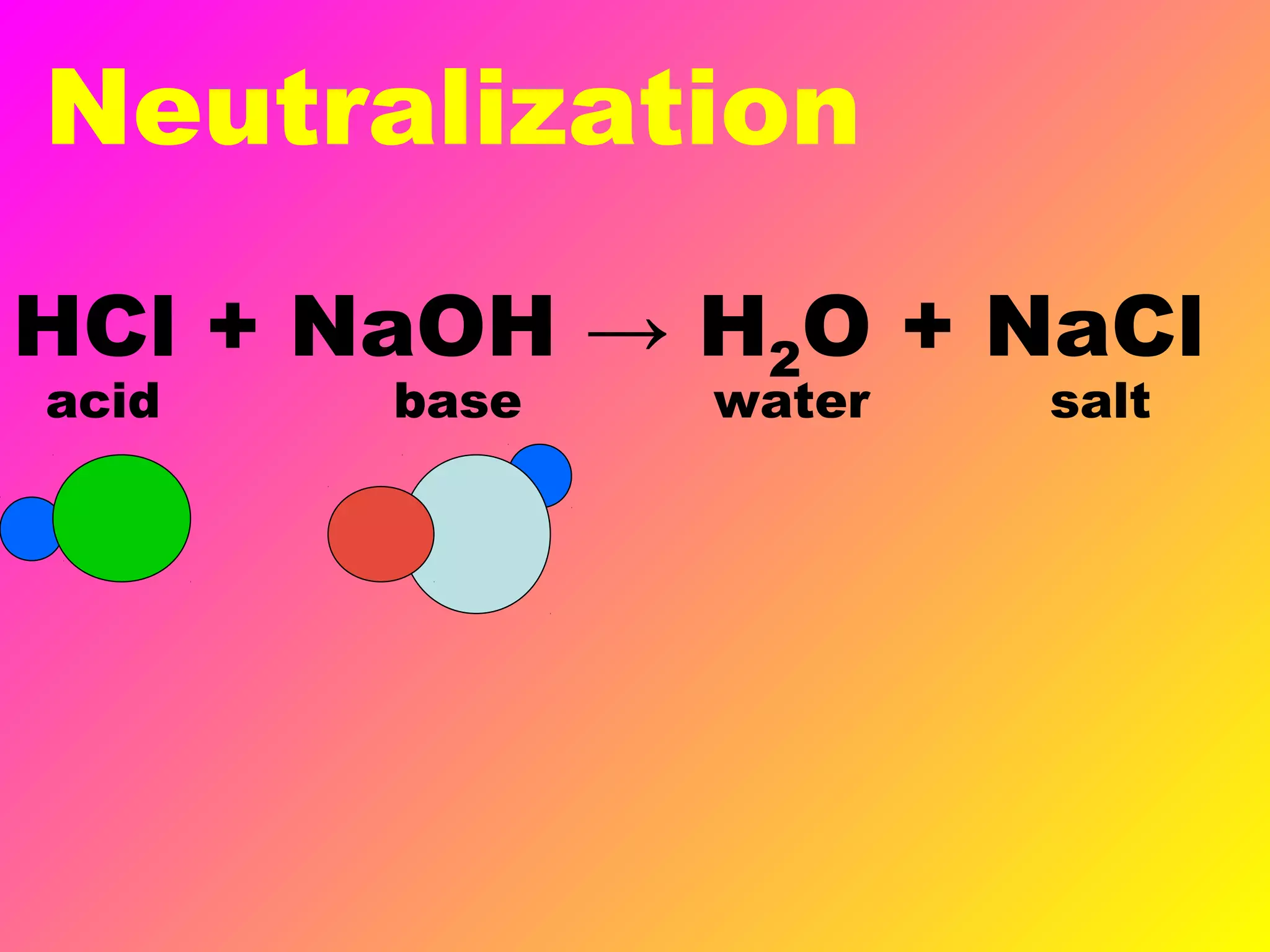
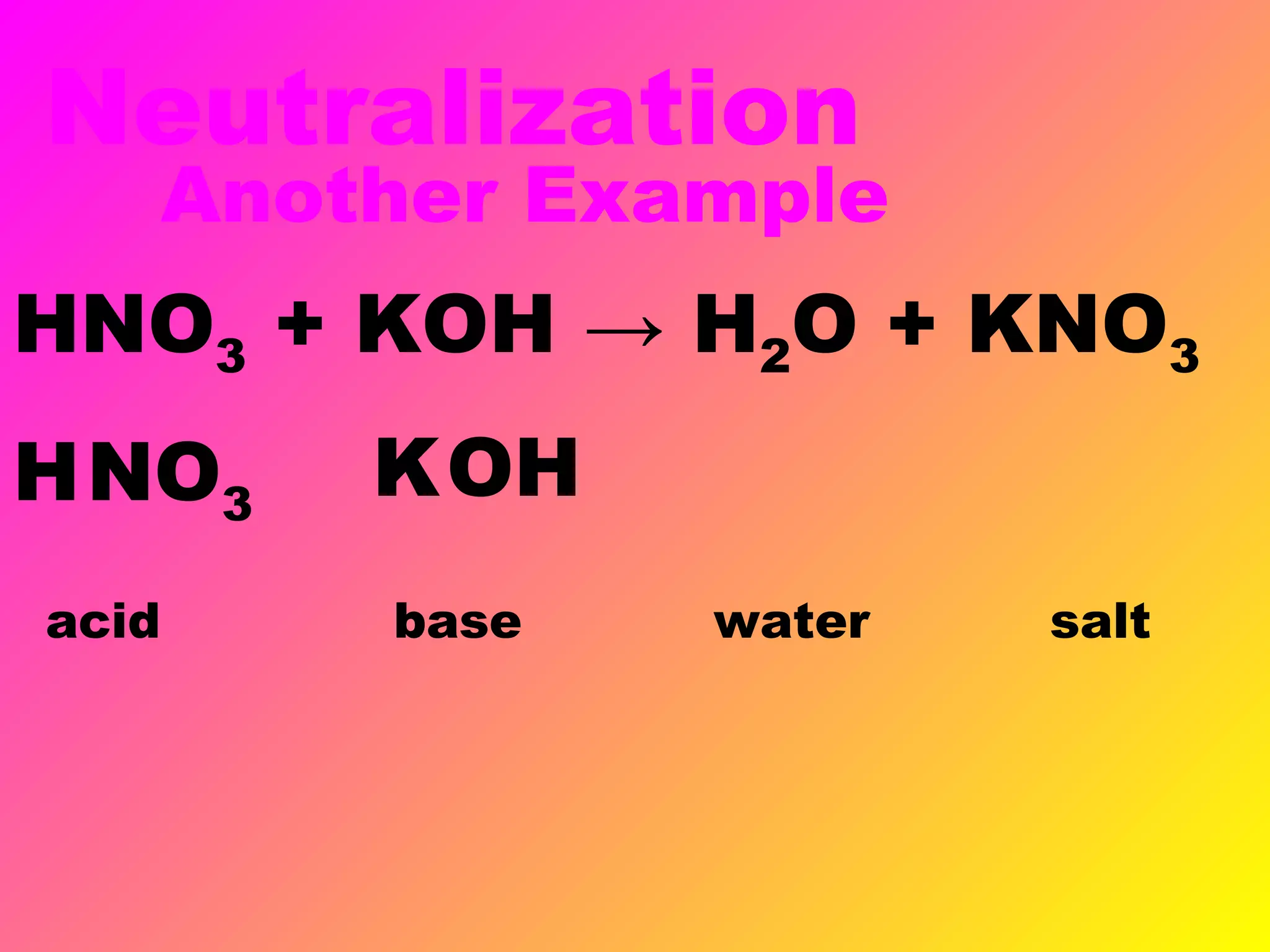
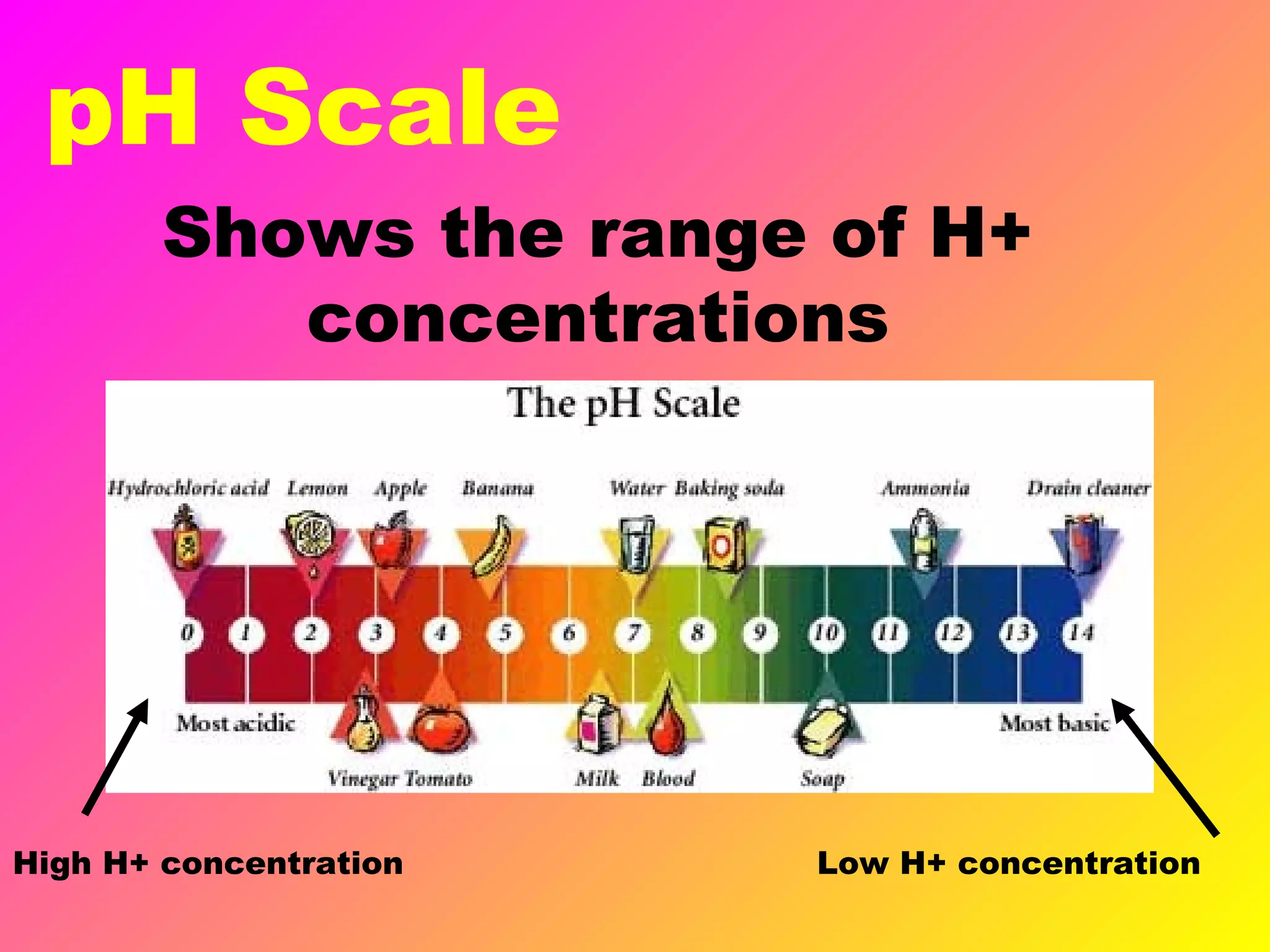
This document defines acids and bases and their key characteristics. Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, while bases release OH- ions in water and feel slippery. Strong acids and bases fully dissociate in water, while weak ones only partially dissociate. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. When acids and bases react, they undergo a neutralization reaction where water and a salt are formed. Indicators are used to test whether a solution is acidic or basic. The pH scale measures the concentration of H+ ions, with lower pH indicating more H+ ions and higher pH less H+ ions.