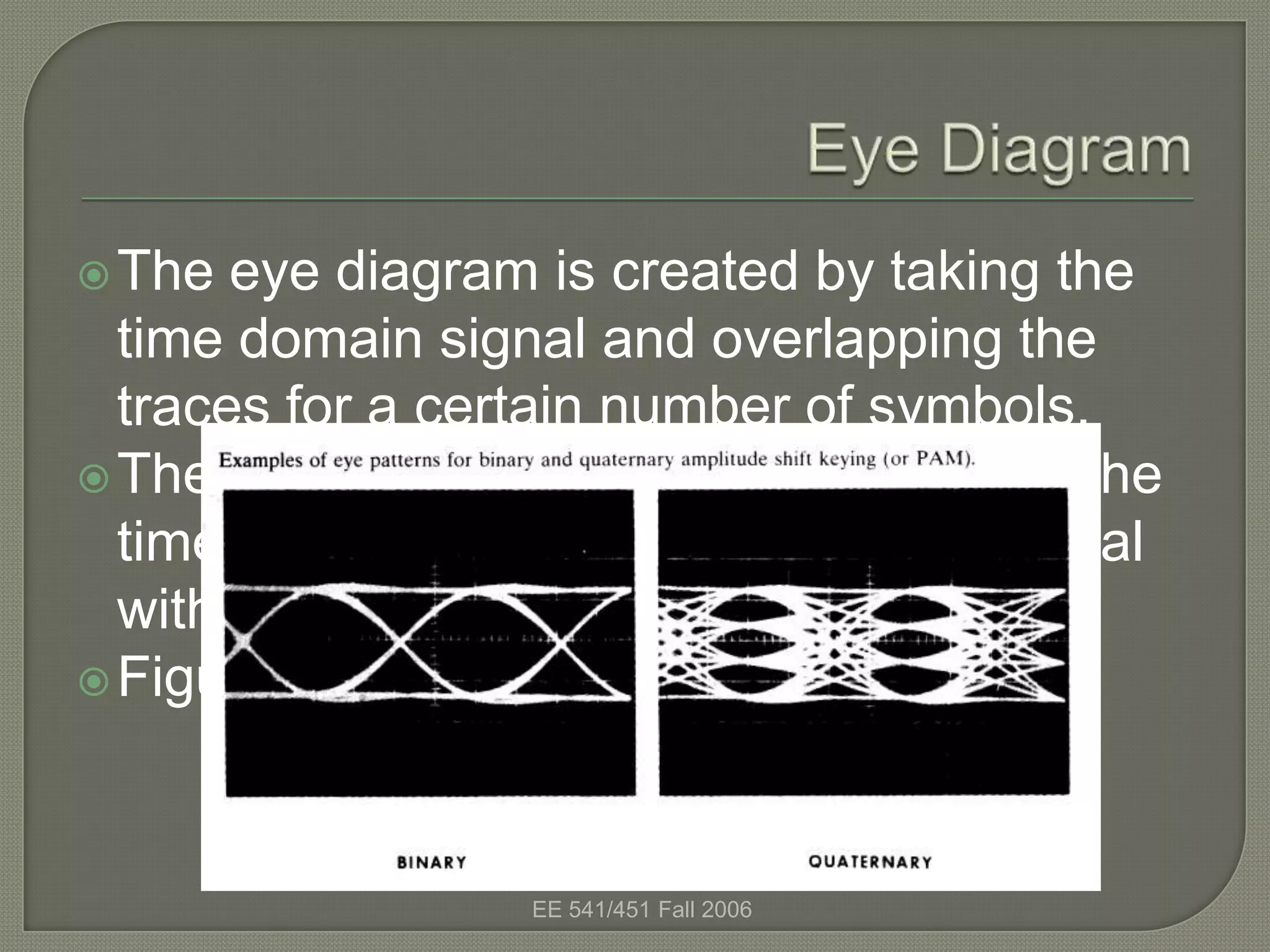
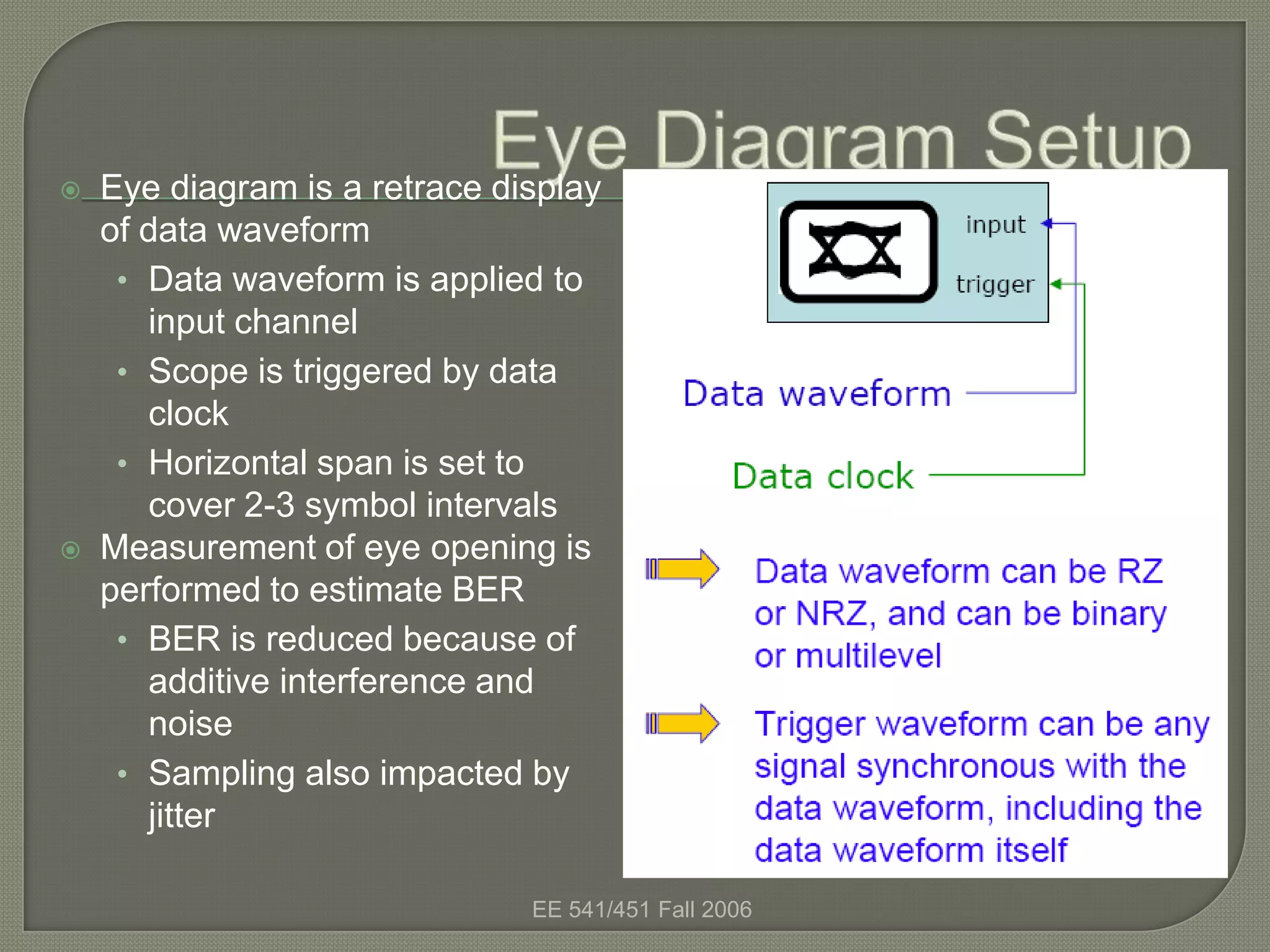
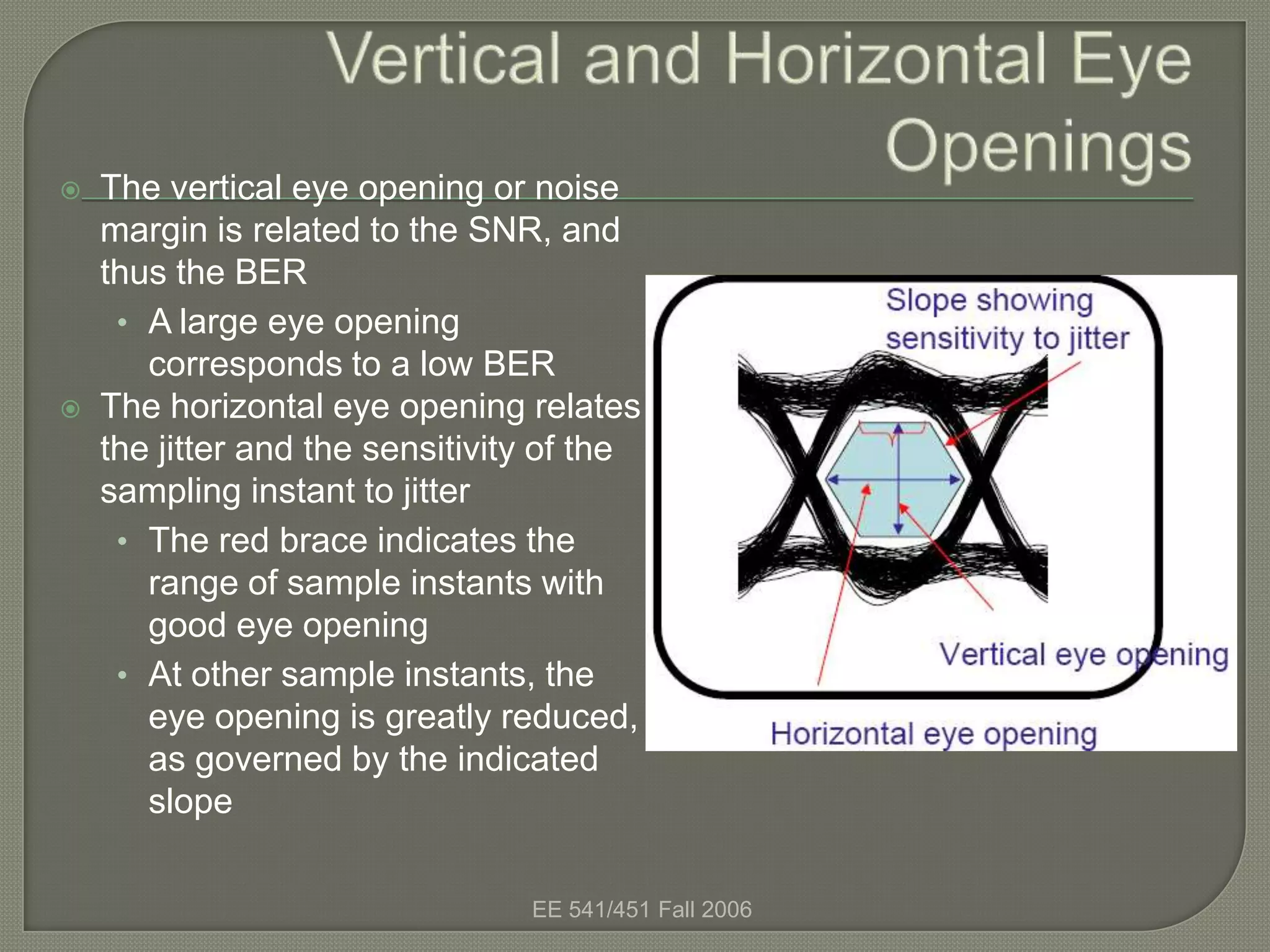
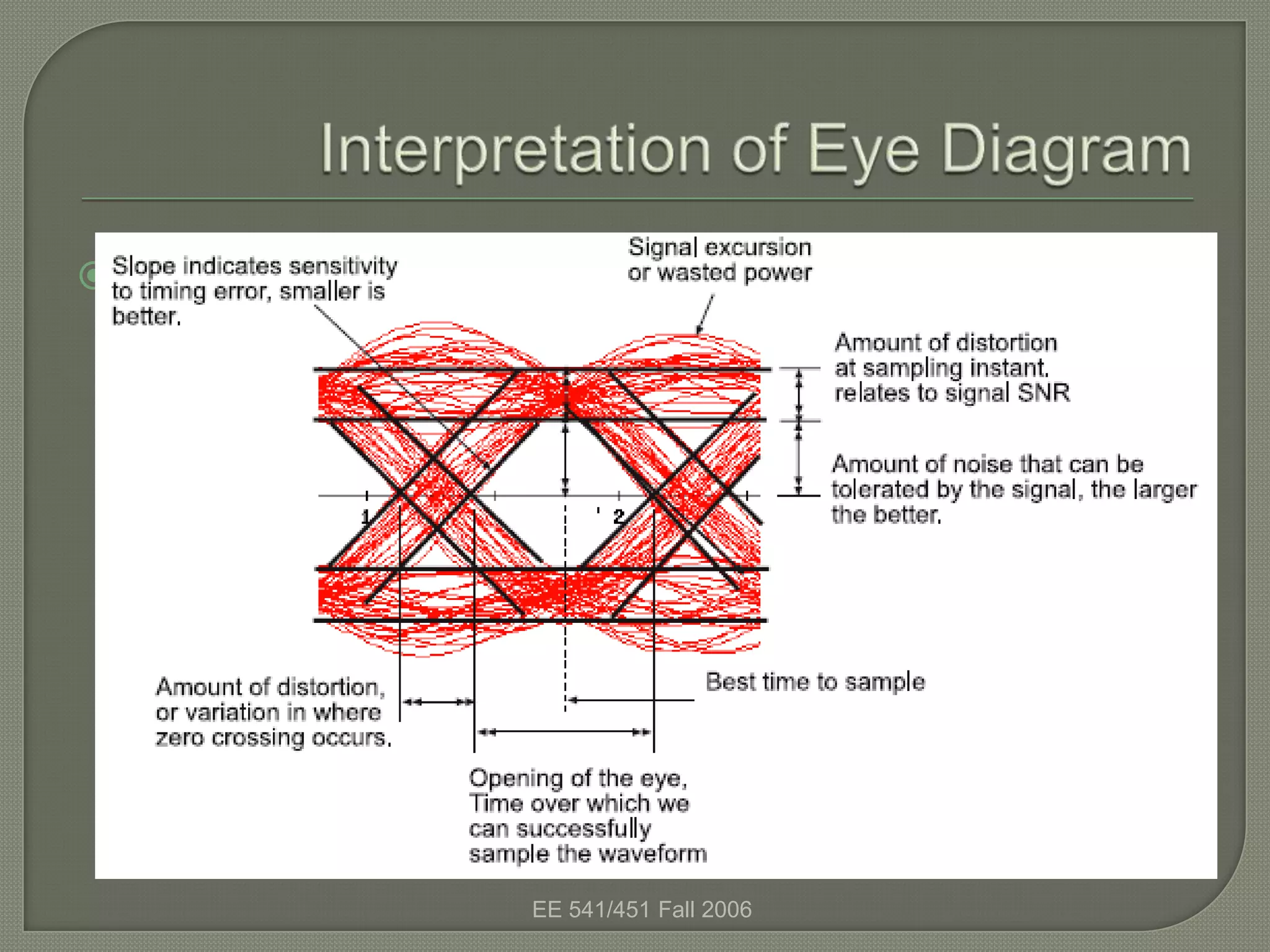
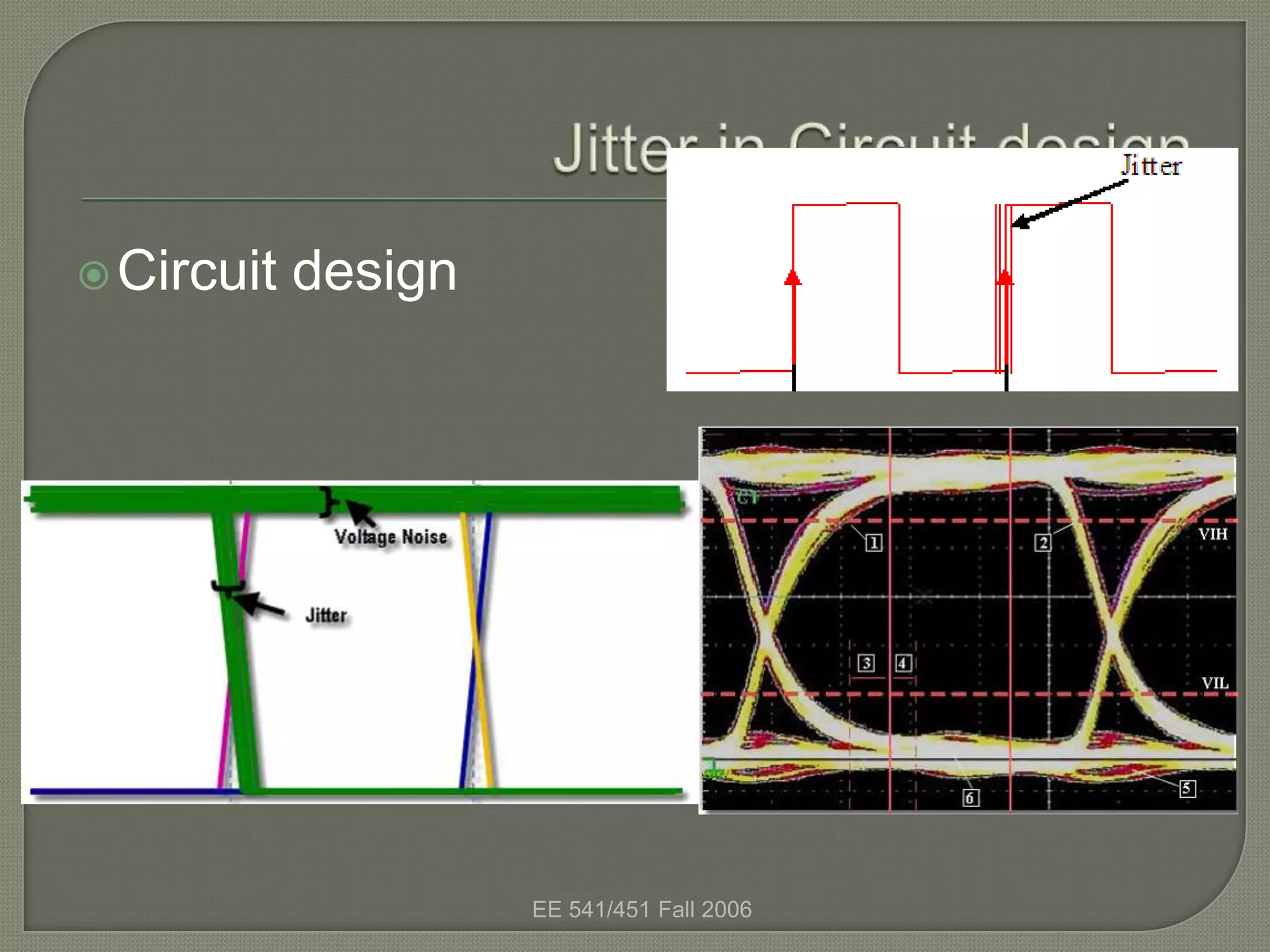
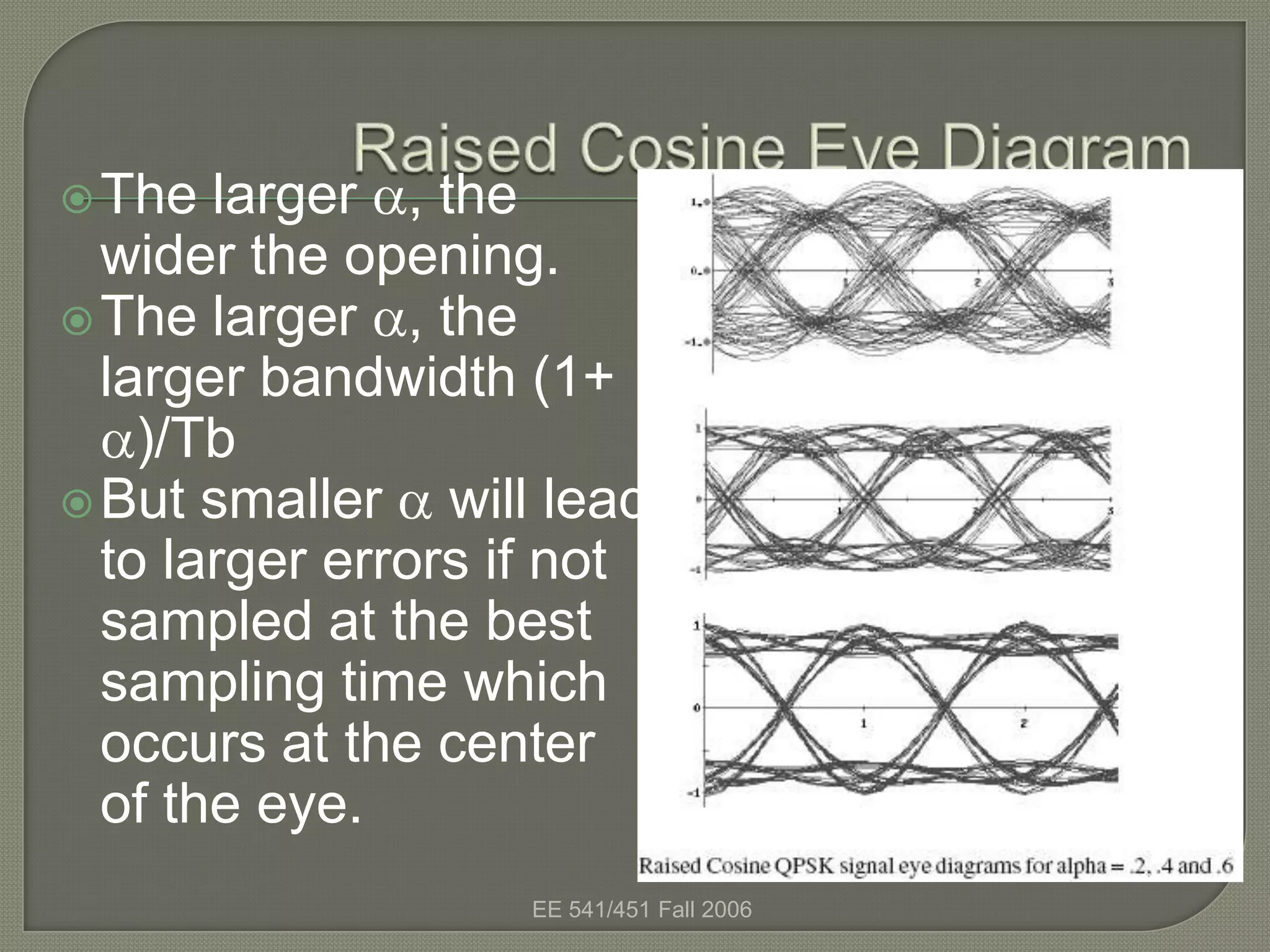
The eye diagram is a visualization technique used to evaluate the quality of a received digital signal. It reveals the impact of intersymbol interference and noise by showing the variation in sample values and jitter sensitivity of the sampling instant. The eye diagram is created by overlapping traces of symbols and the open part represents the safe sampling region. It allows estimating the bit error rate, with a larger eye opening corresponding to a lower bit error rate.