This document discusses object oriented programming concepts in C++ including file input/output modes, file pointers, reading and writing data to files, and reading/writing class objects to files. Key points covered include:
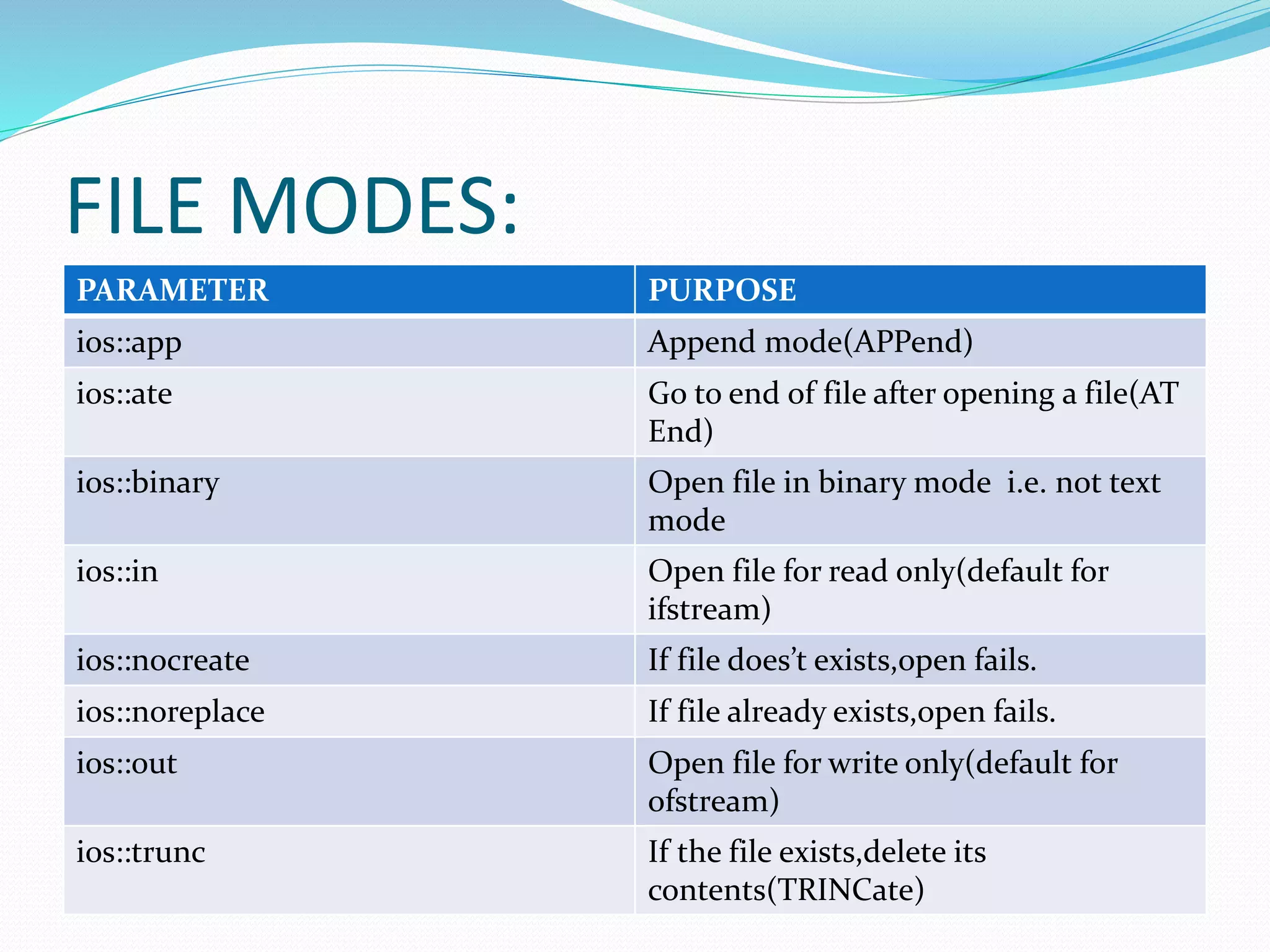
- Common file I/O modes like append, read/write, binary, and their purposes.
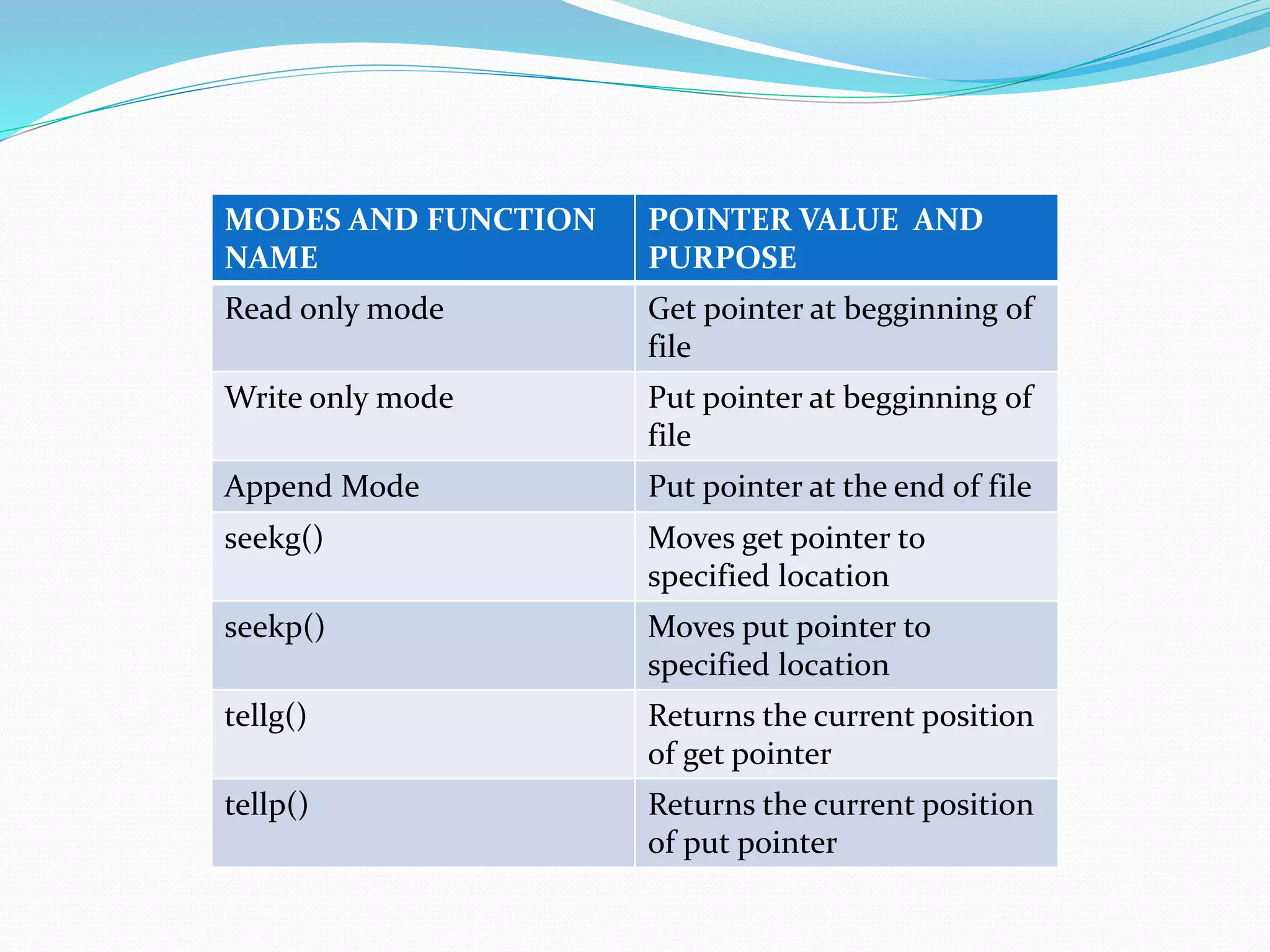
- File pointers (get and put) and how they track read/write locations and can be manipulated.
- Low-level file I/O functions like get(), put(), read(), write() for single characters and blocks.
- An example of reading/writing a class object to a file by writing/reading the entire object as a block.



![get() and put() functions
The get() and put() functions can be used with file stream classes.
Get() and put() functions handle one character at a time.
PROGRAM:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
#include<string.h>
Void main()
{
char line[]=“object oriented programming”;
fstream file;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwithfile354546-150504123857-conversion-gate02/75/Working-with-file-35-45-46-6-2048.jpg)
![file.open(“data”,ios::in|ios::out);
int len = strlen(line);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{file.put(line[i]);}
file.seekg(0);
char c;
while(file.eof()!=1)
{
file.get(c);
cout<<c;
}
}
OUTPUT: object oriented programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwithfile354546-150504123857-conversion-gate02/75/Working-with-file-35-45-46-7-2048.jpg)



![READING AND WRITING CLASS
OBJECTS
PROGRAM:
#include<iosream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
#include<string.h>
class person
{
private:
char name[30];
int age;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwithfile354546-150504123857-conversion-gate02/75/Working-with-file-35-45-46-11-2048.jpg)

