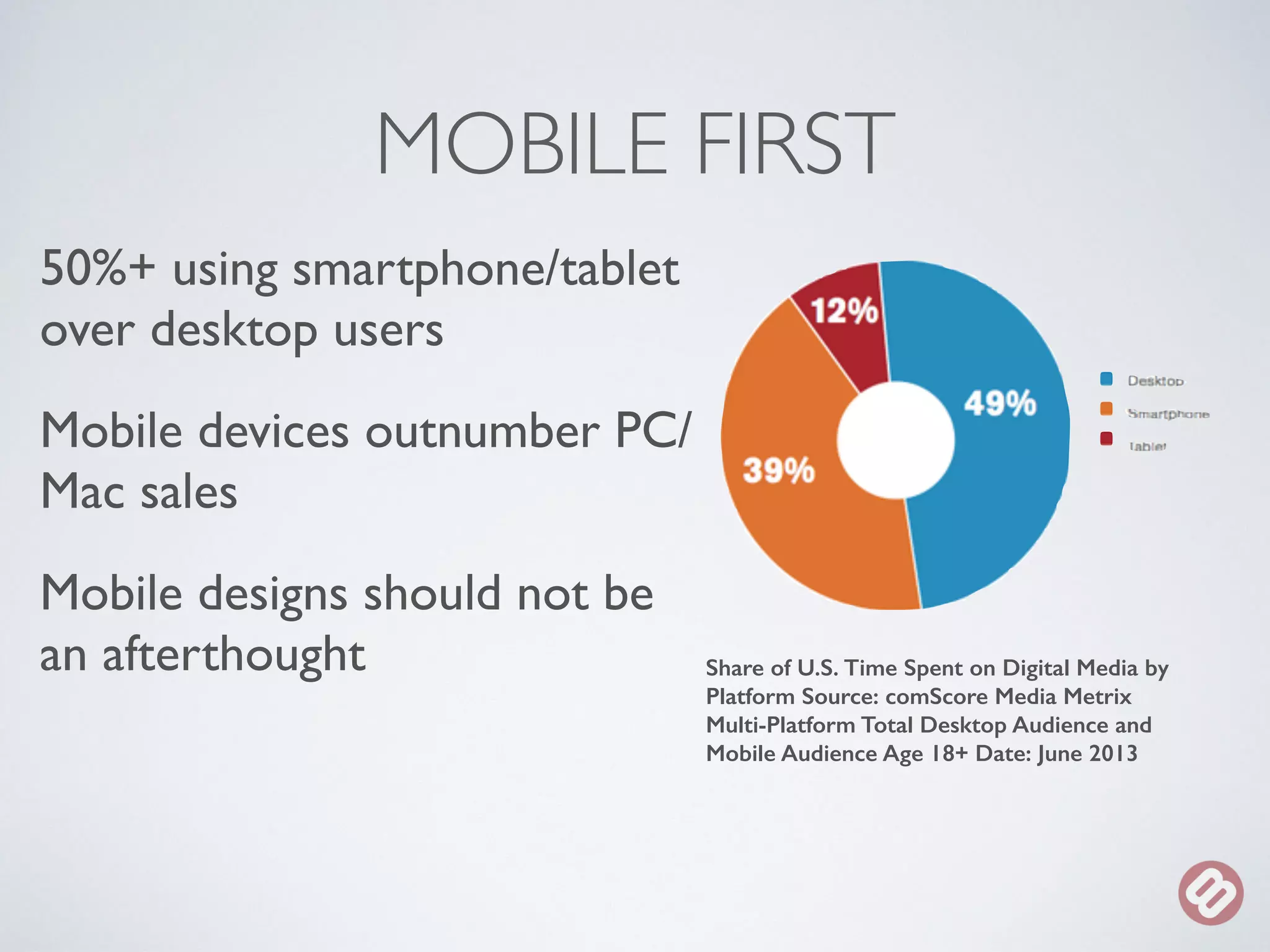
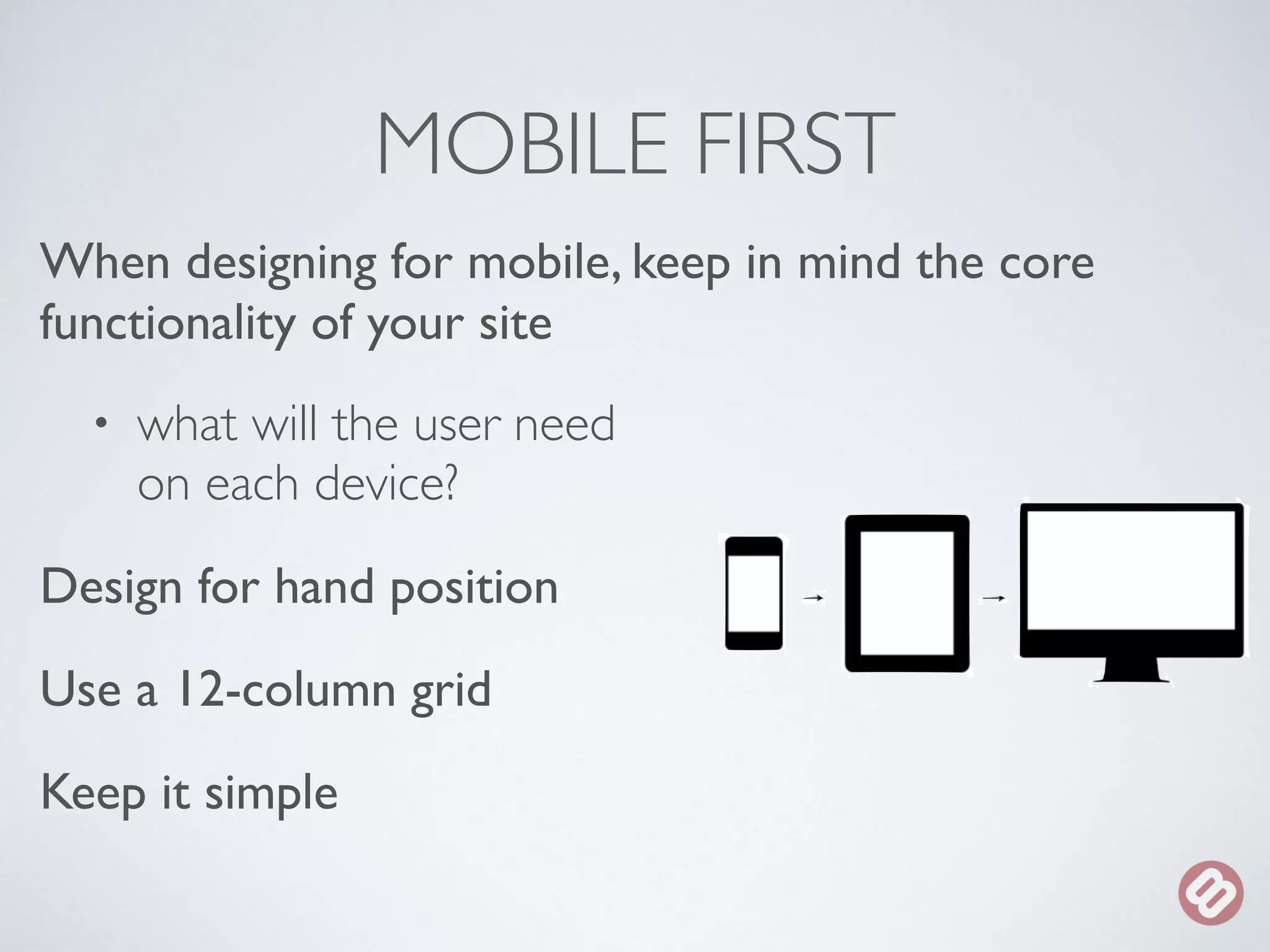
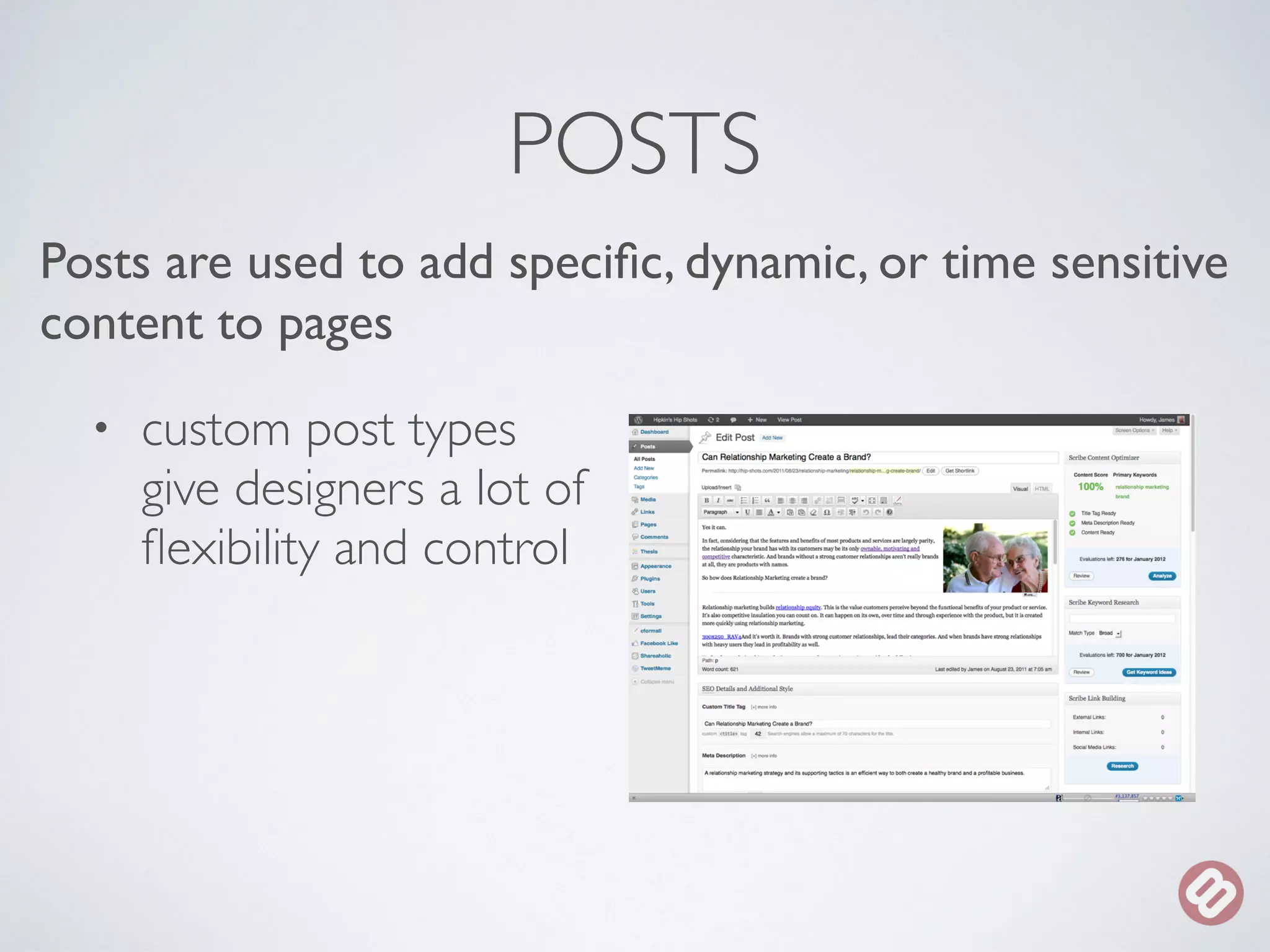
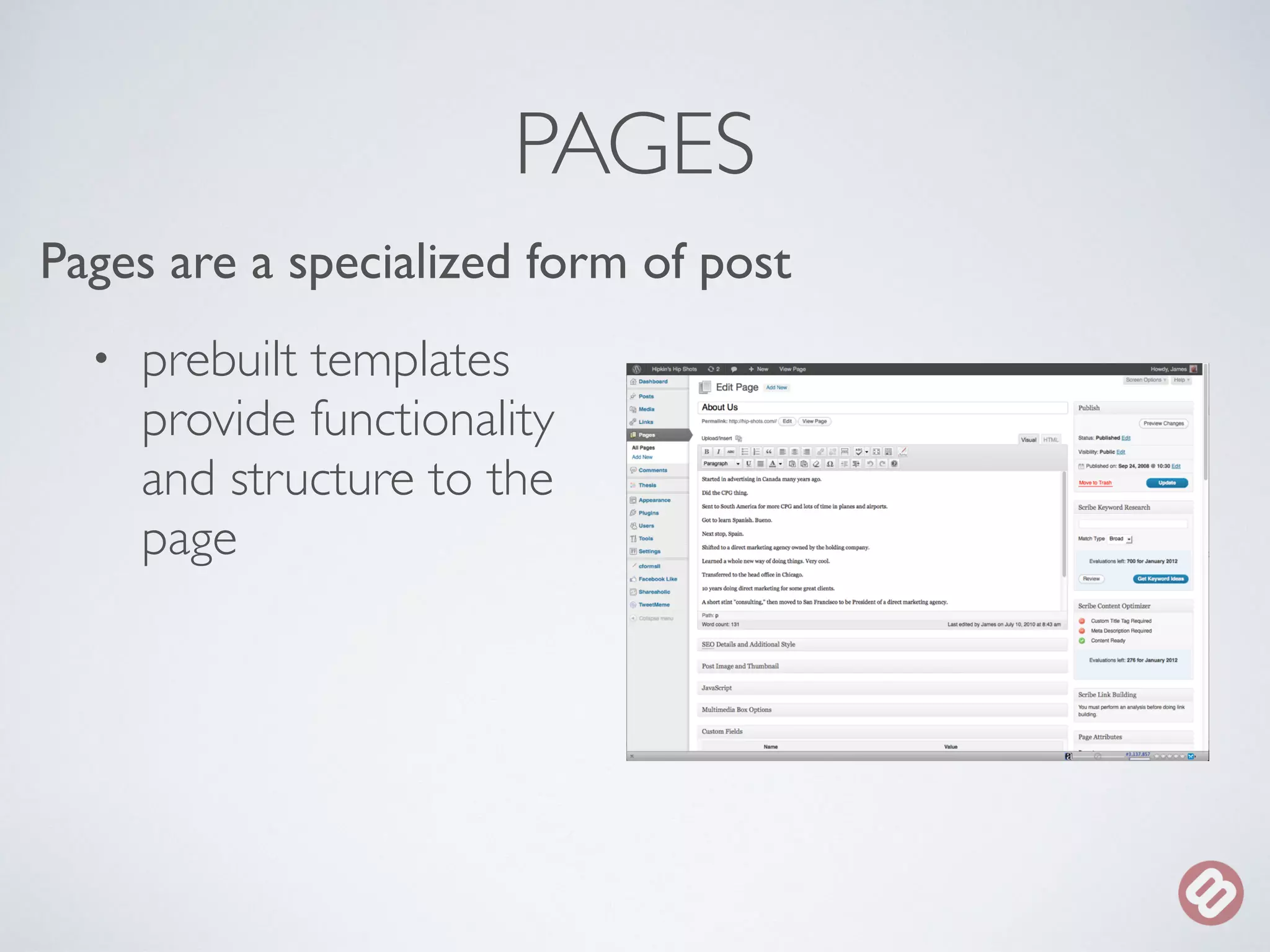
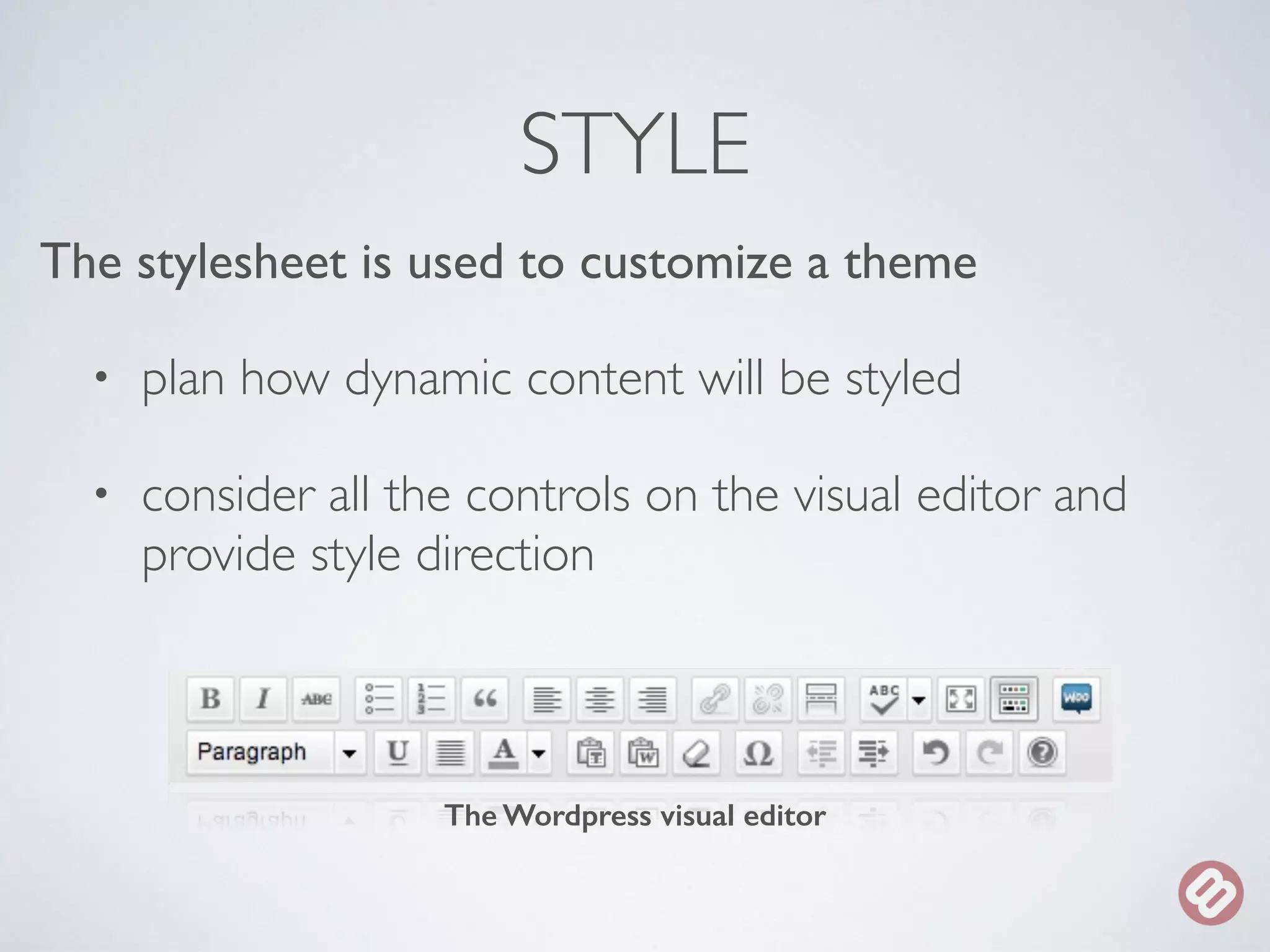
The document provides an overview of considerations for designers working on WordPress websites. It discusses website structure using HTML and CSS, fonts and mobile design. It also covers WordPress themes, templates, plugins and implications for designers, such as designing for navigation, footers, forms and more. Designers are advised to involve WordPress developers early in the process to understand template needs and functionality.