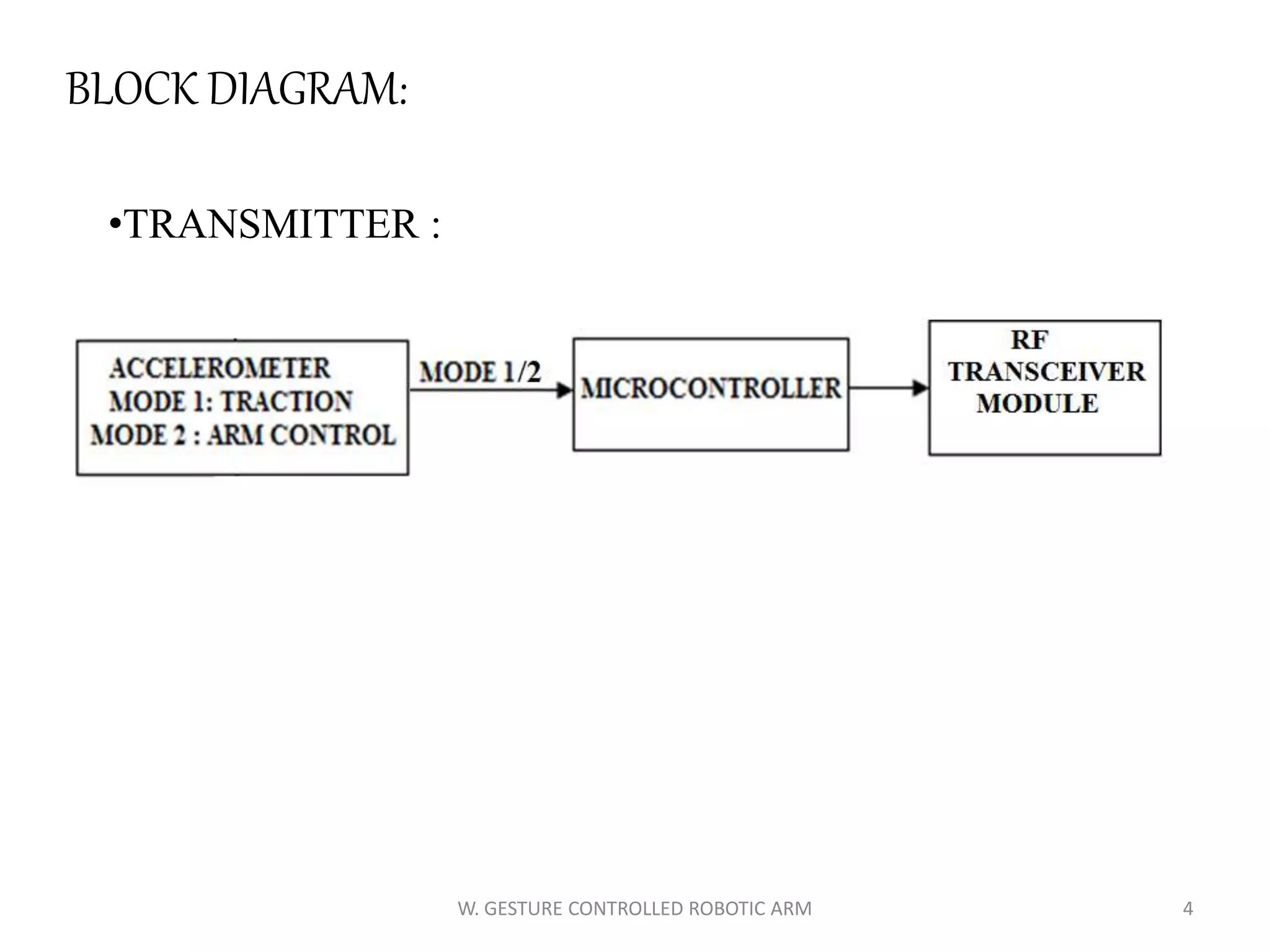
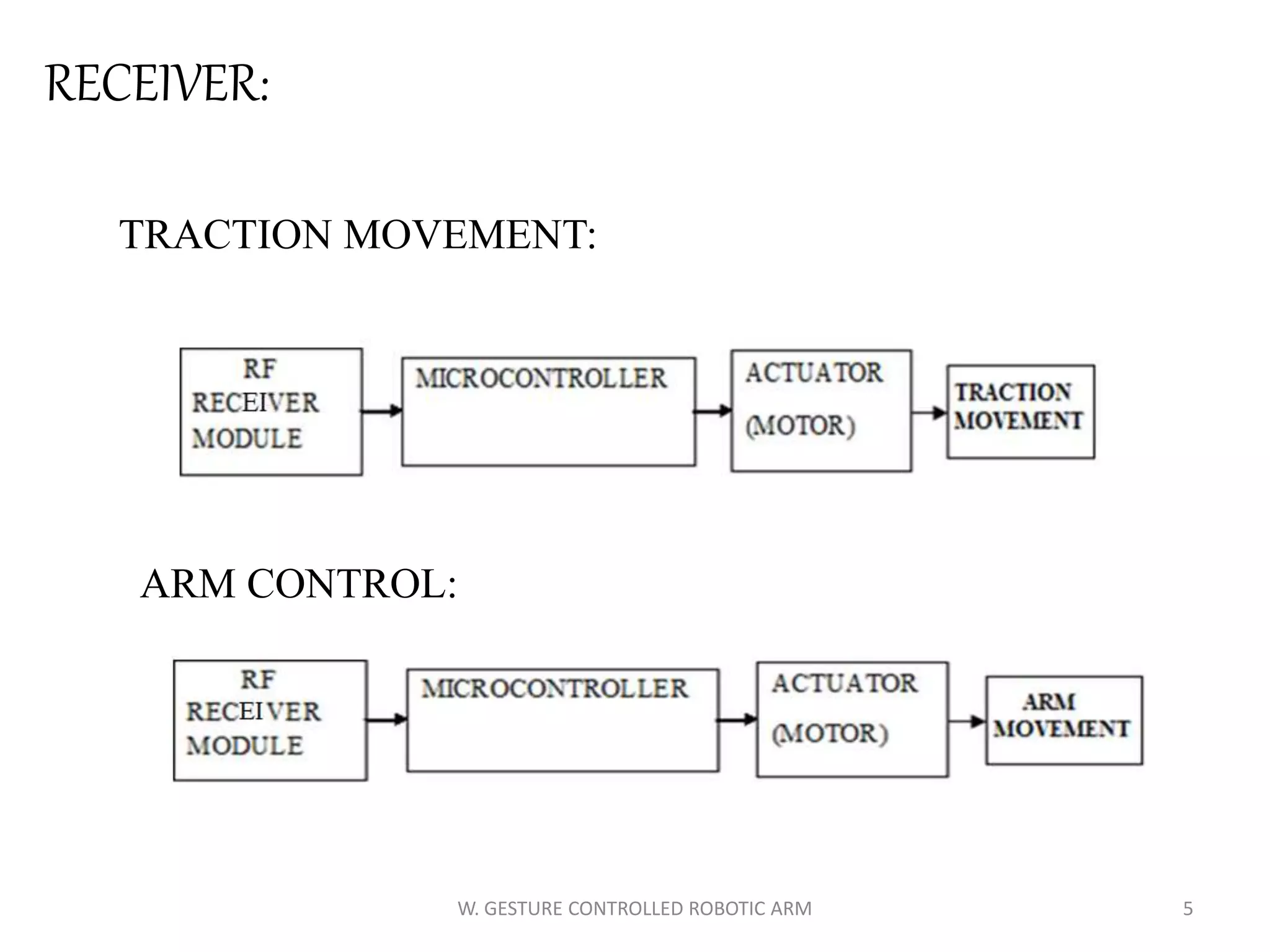
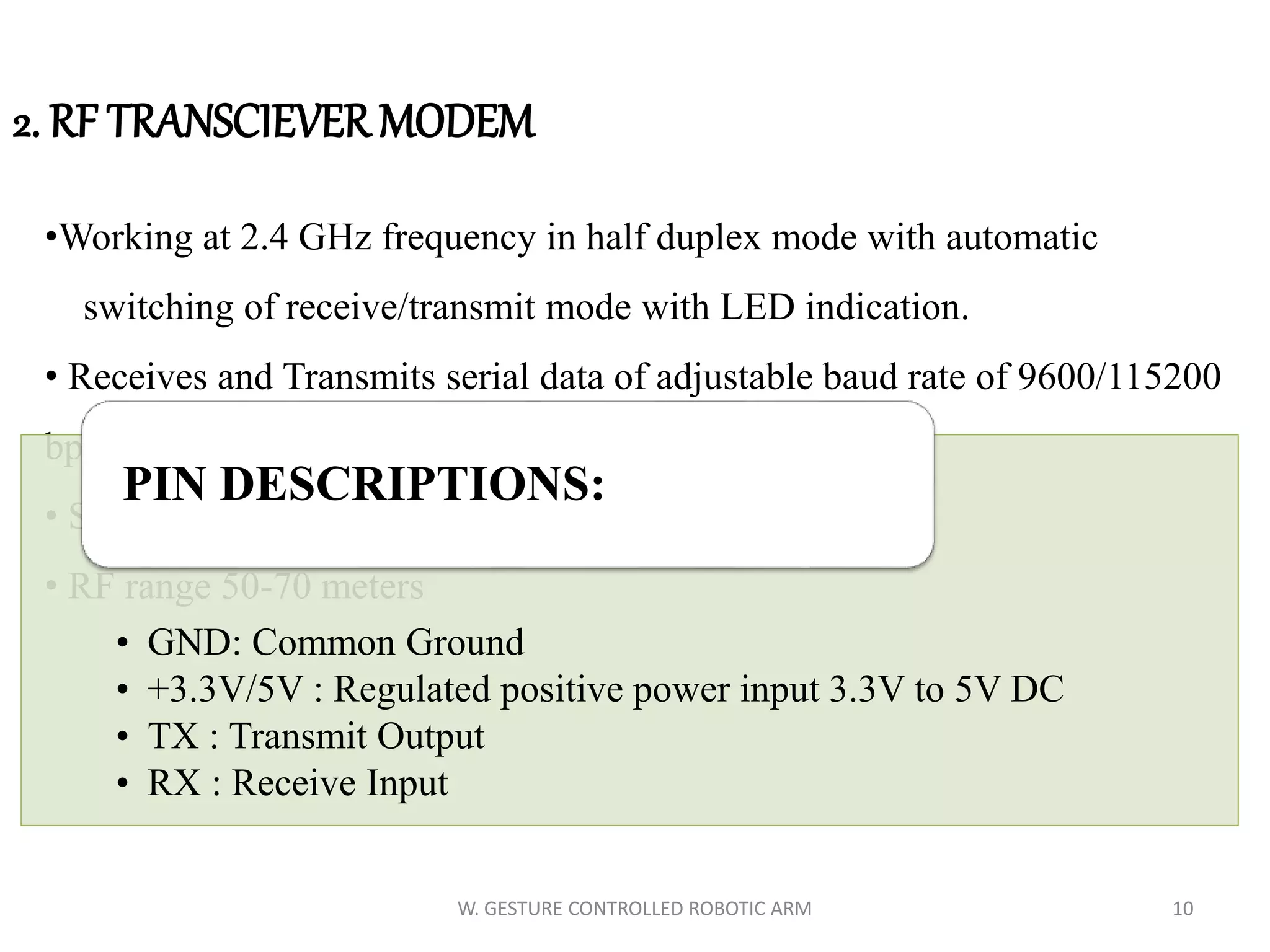
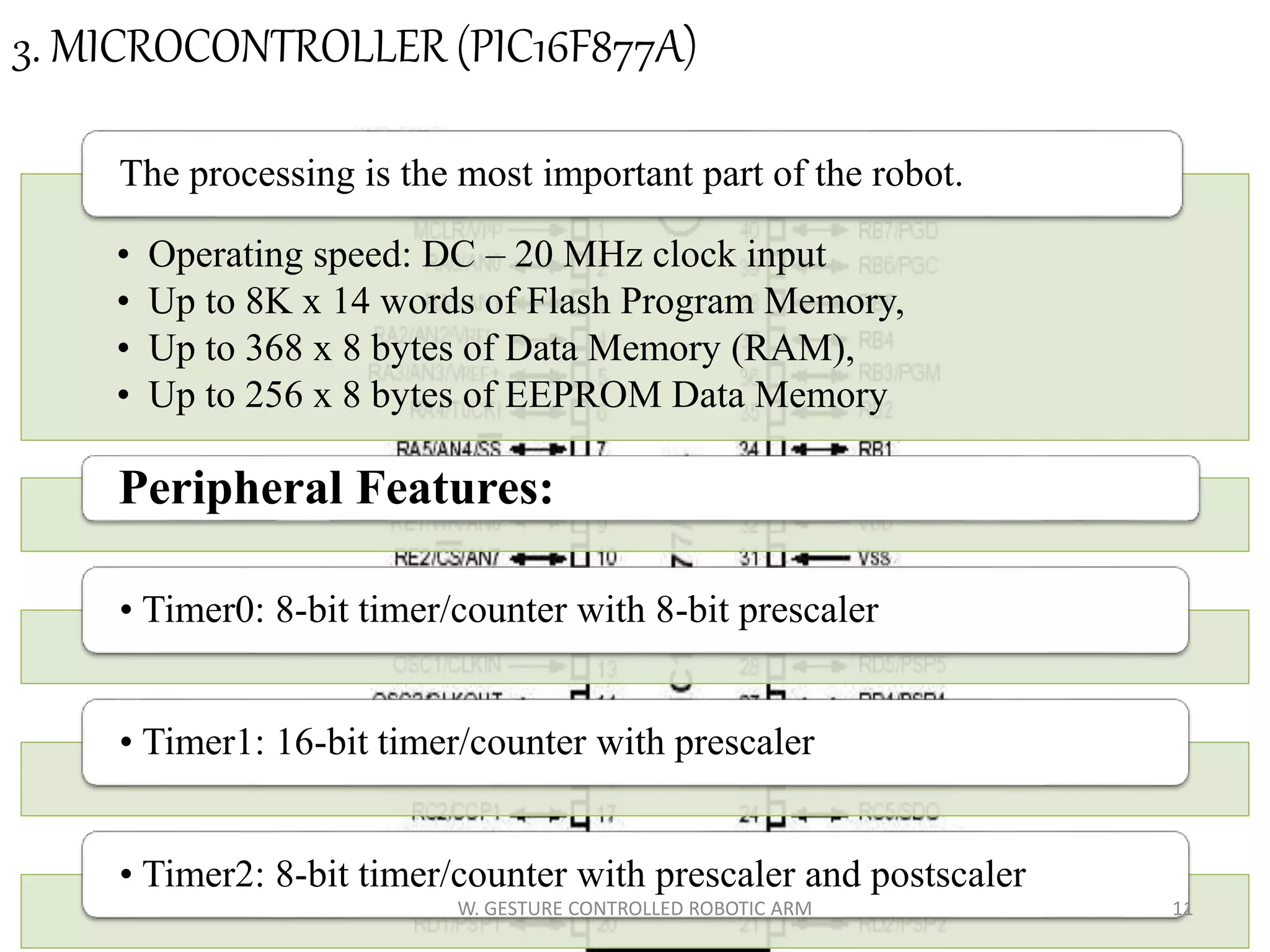
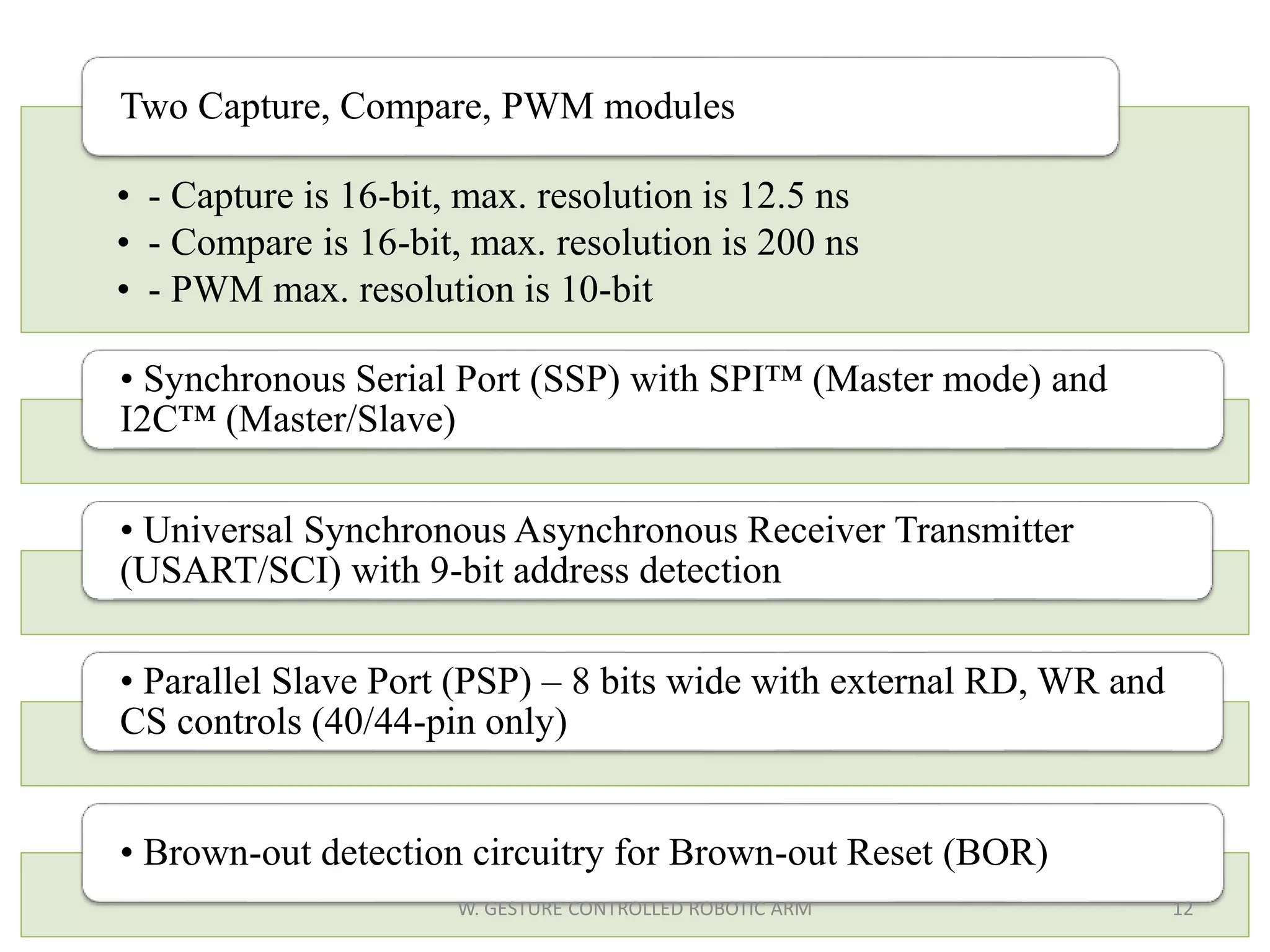
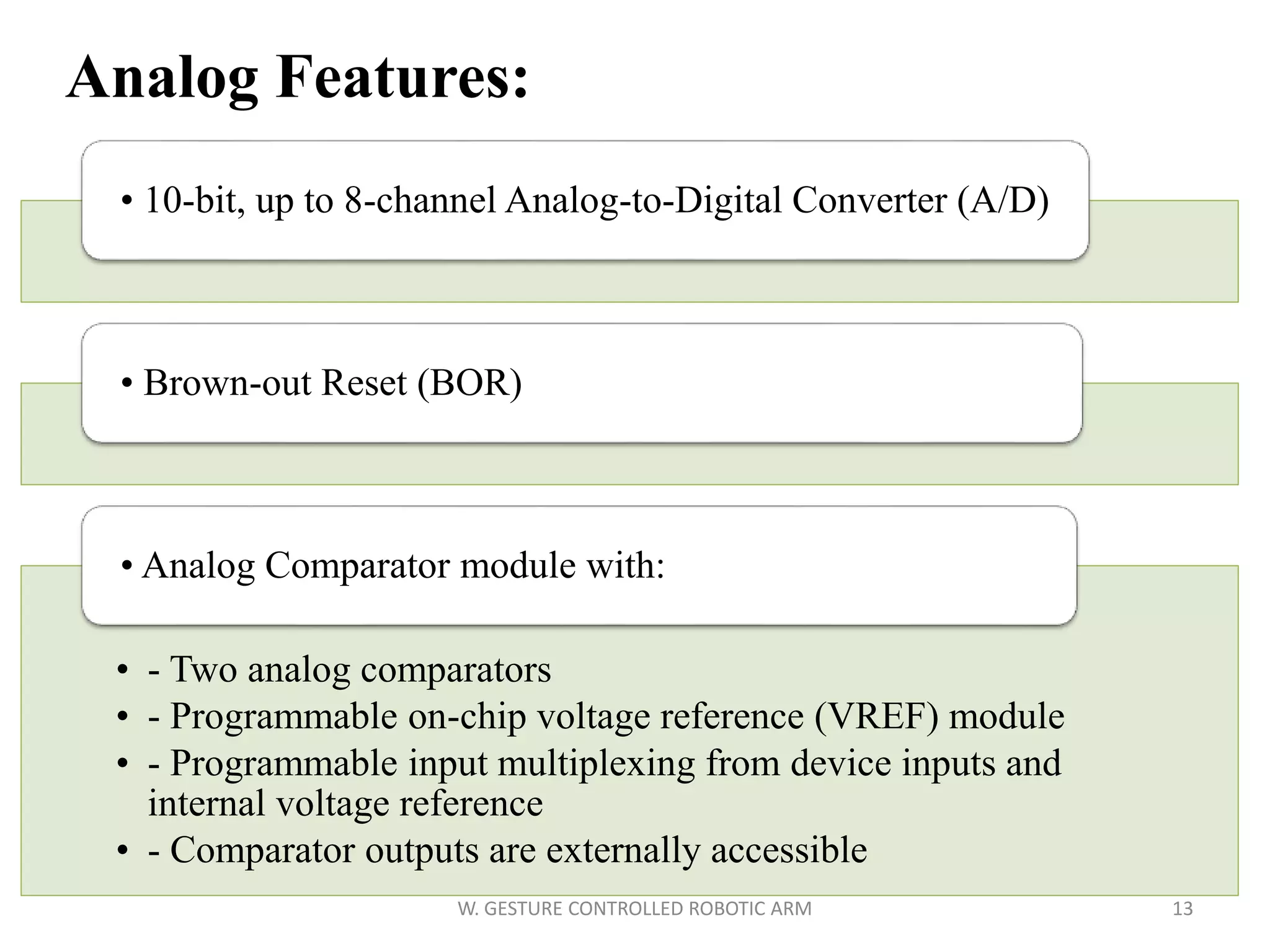
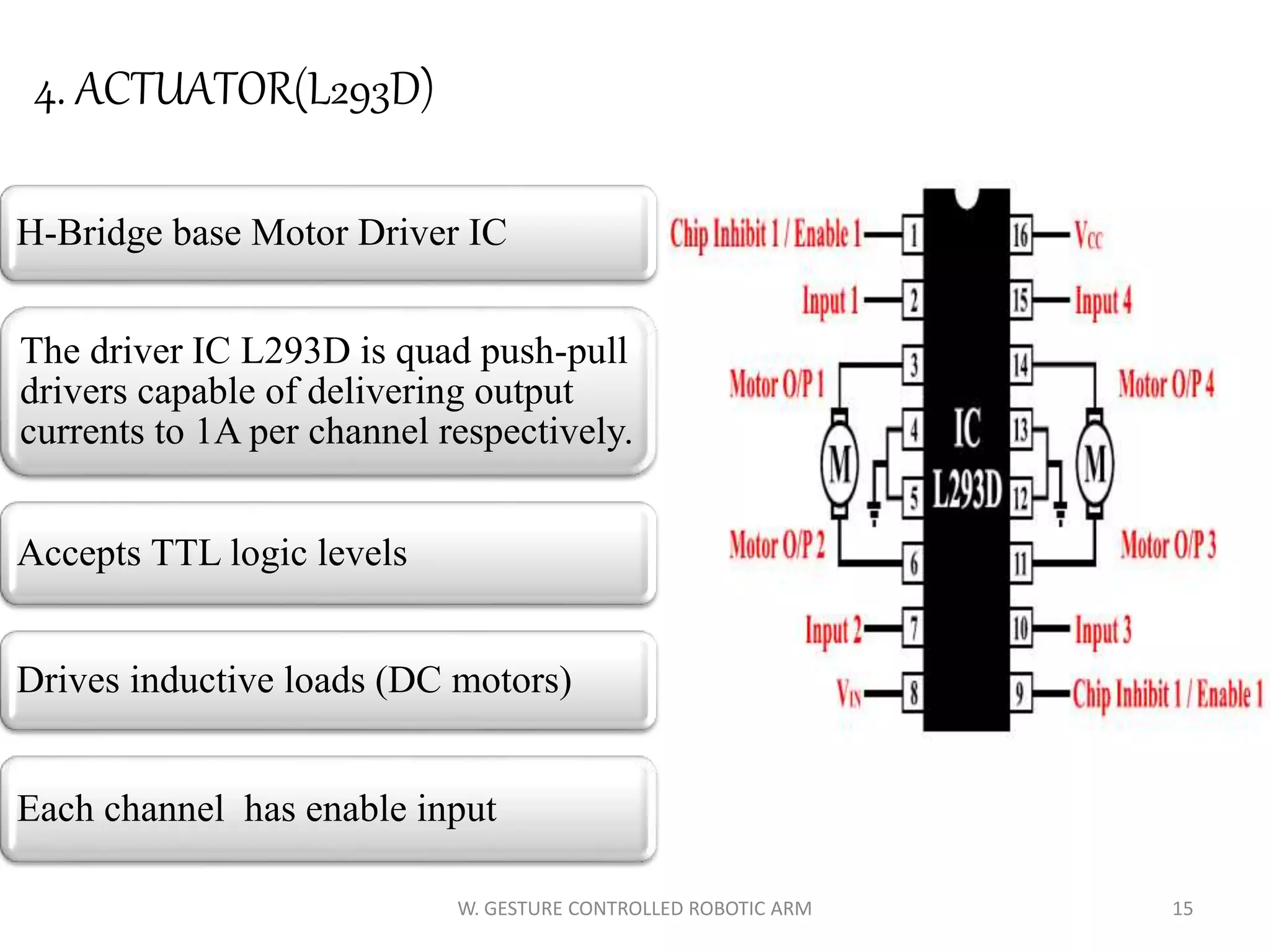
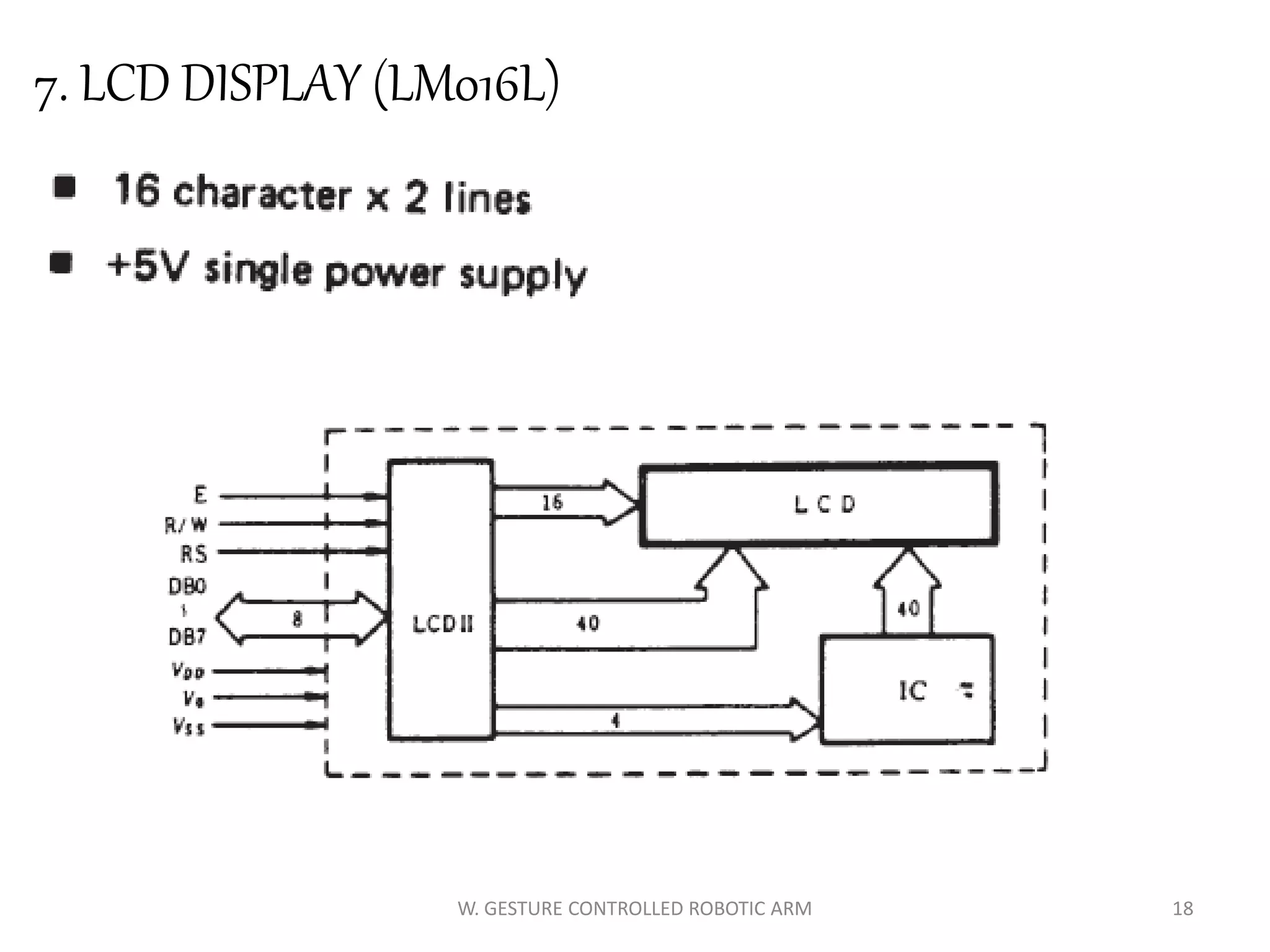
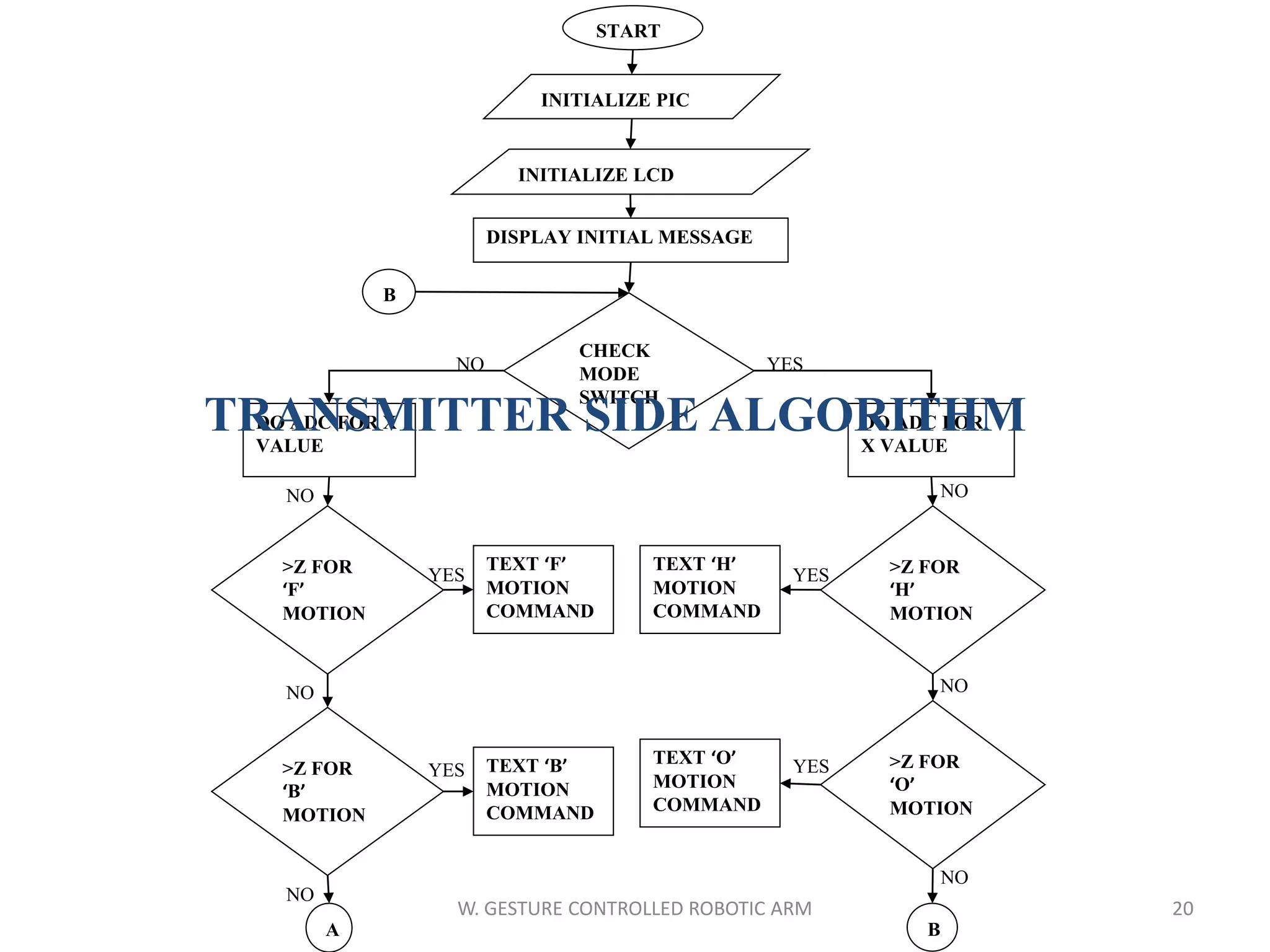
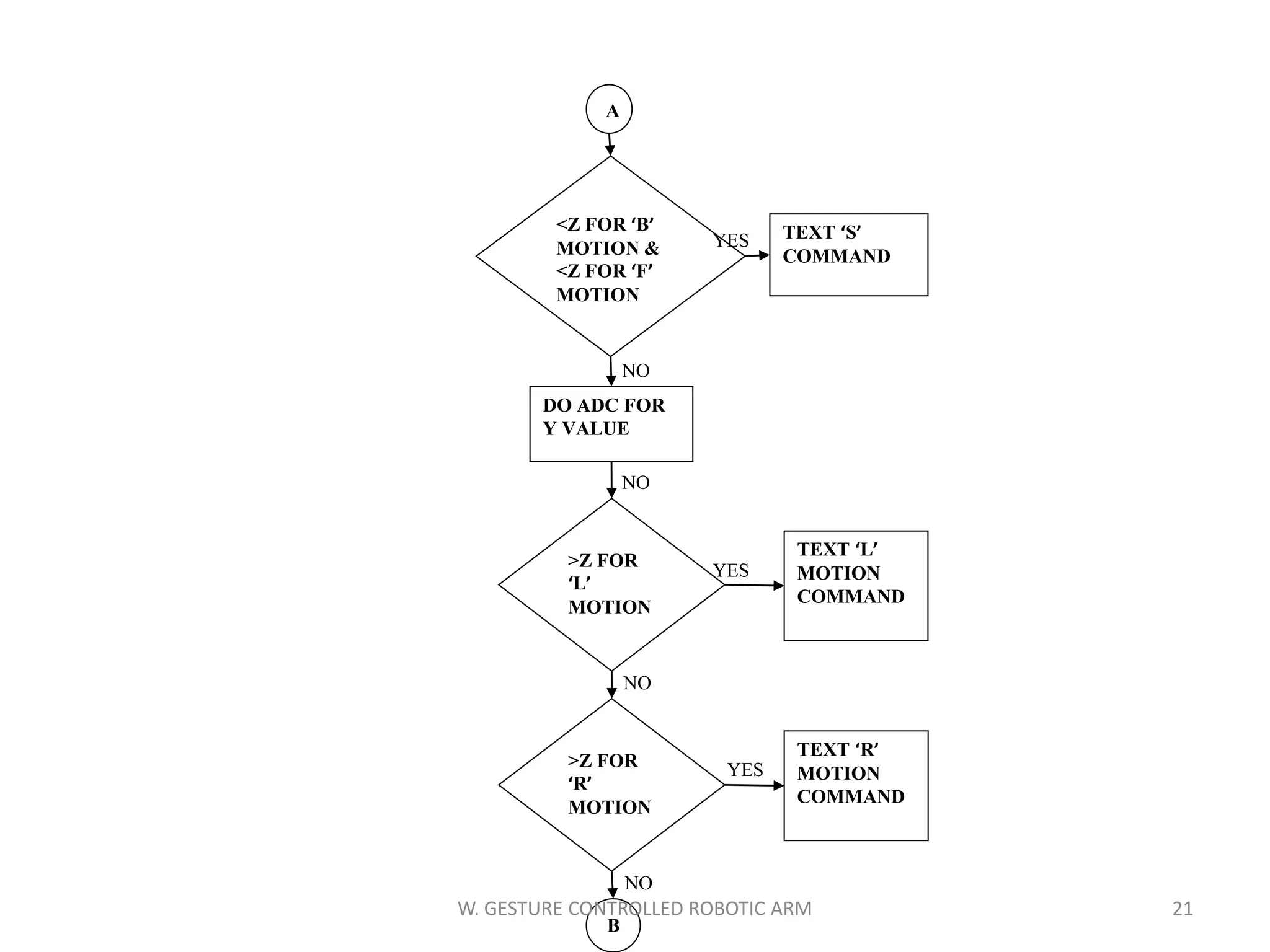
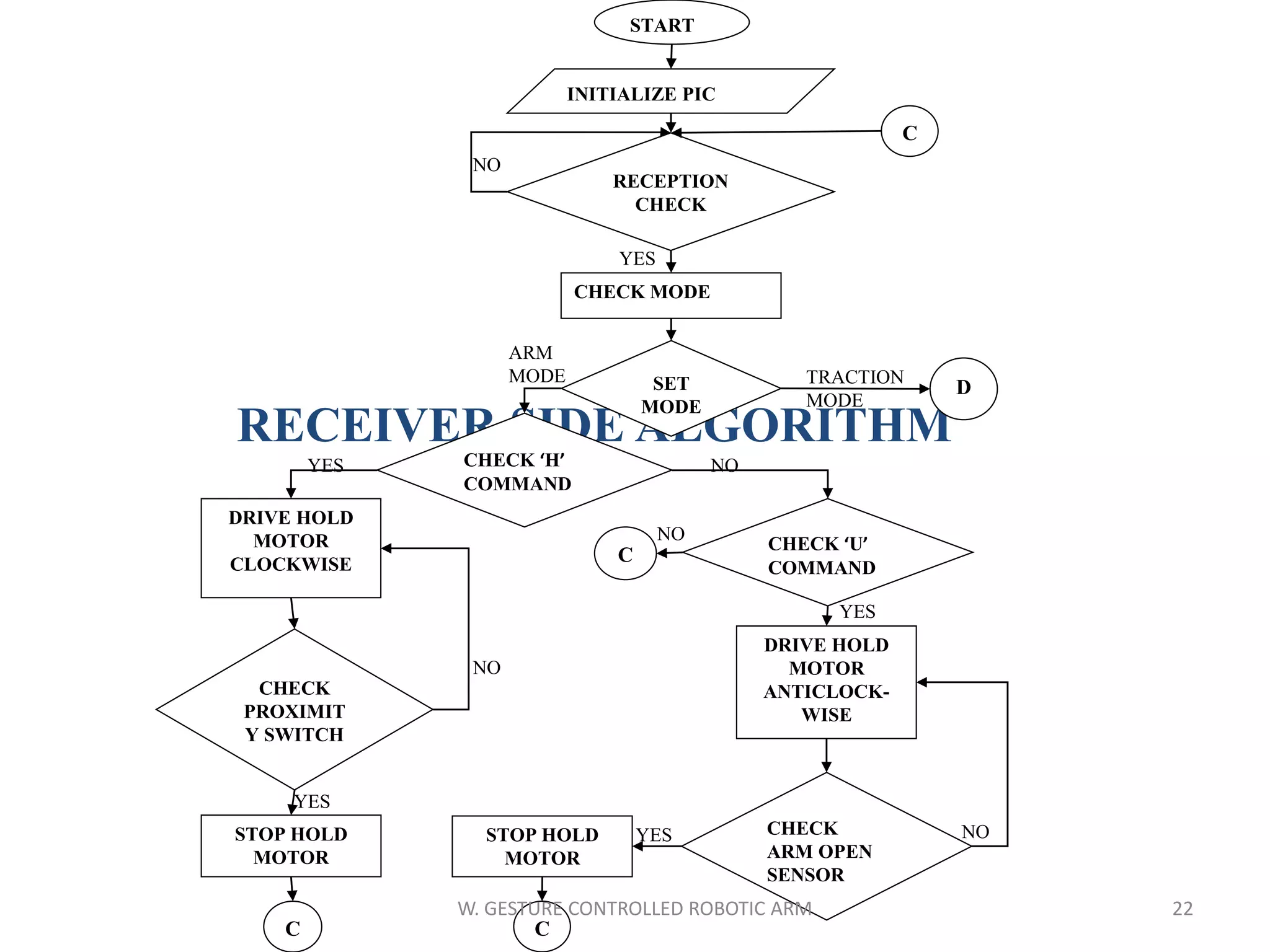
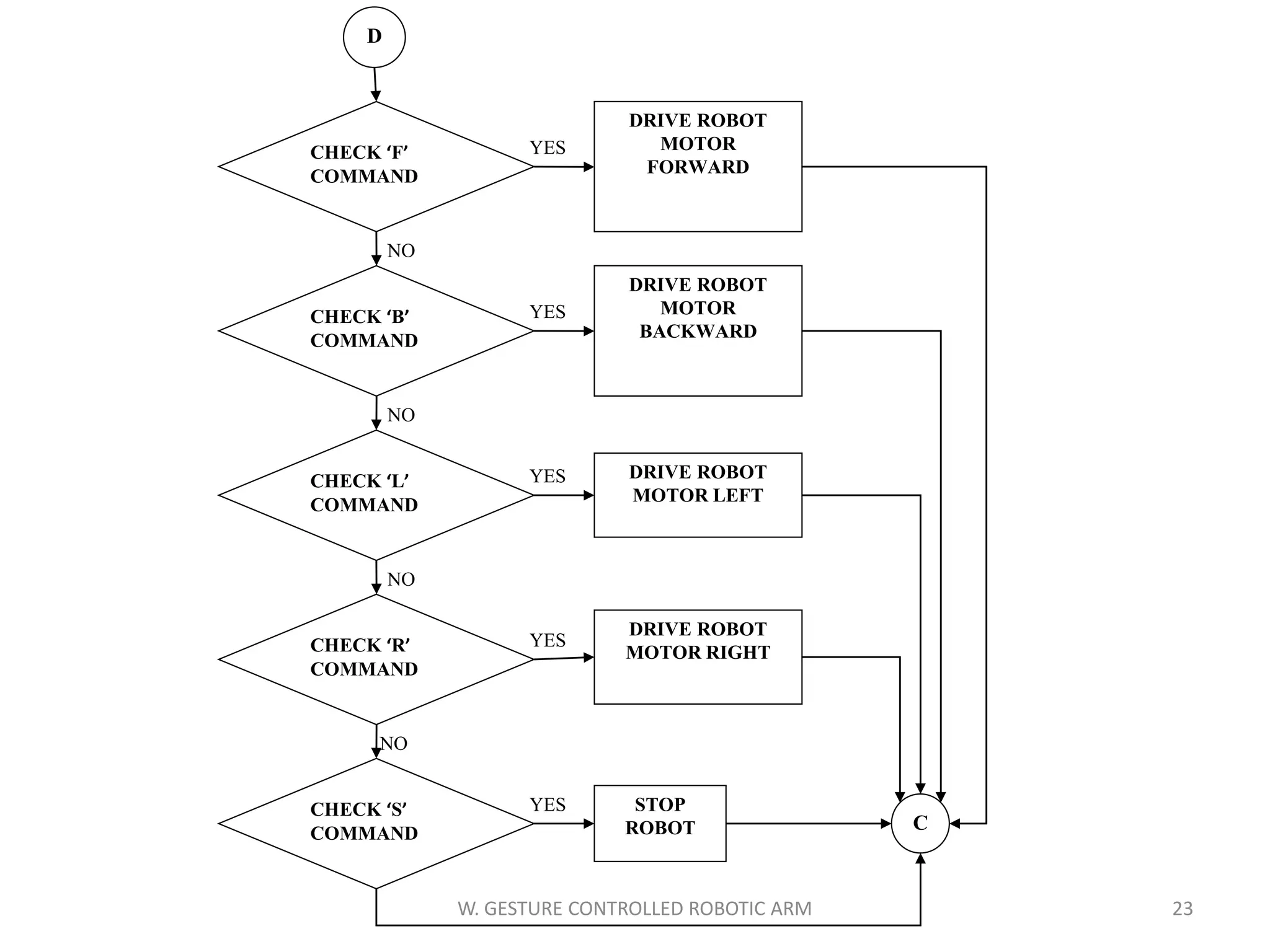
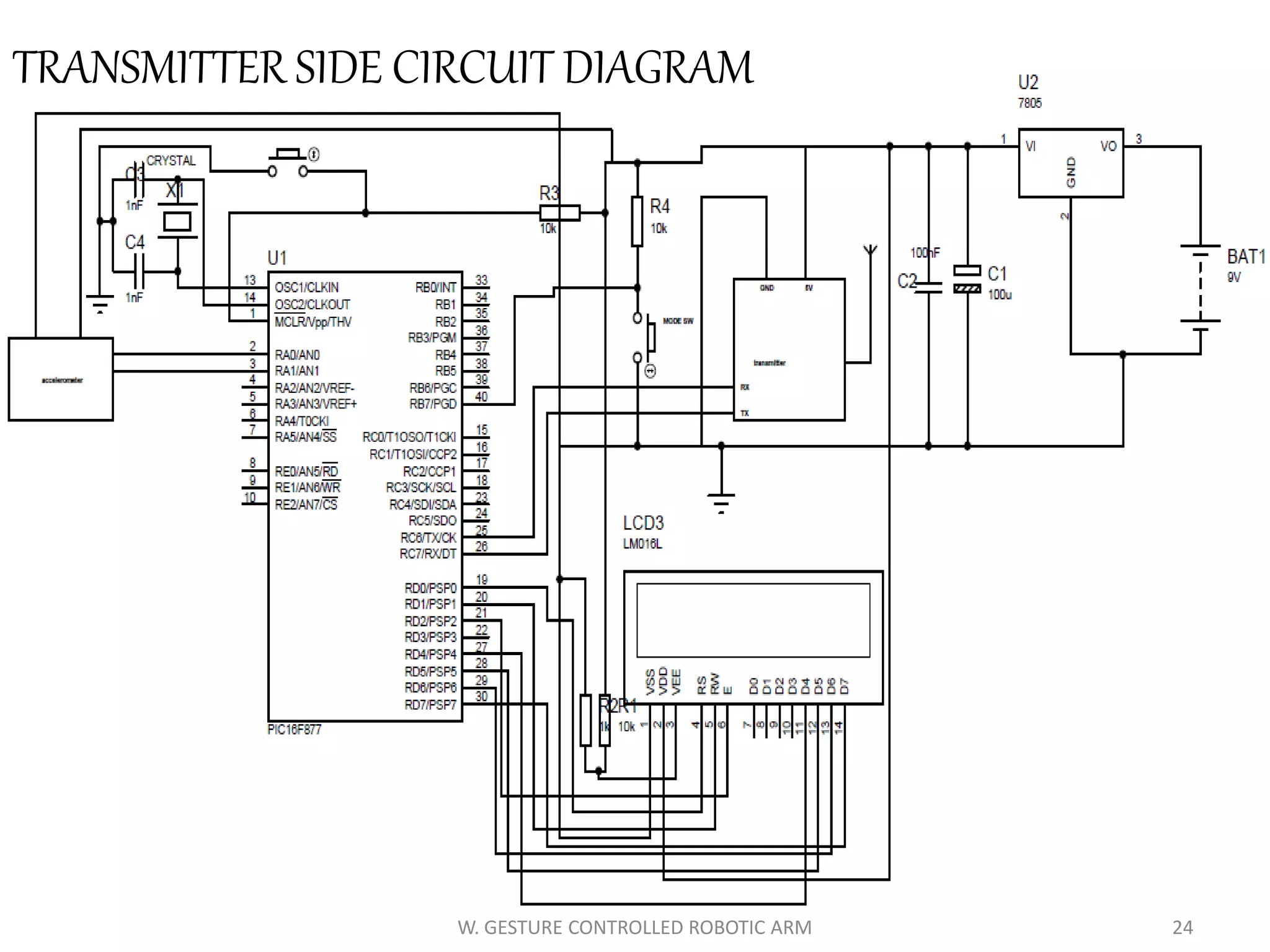
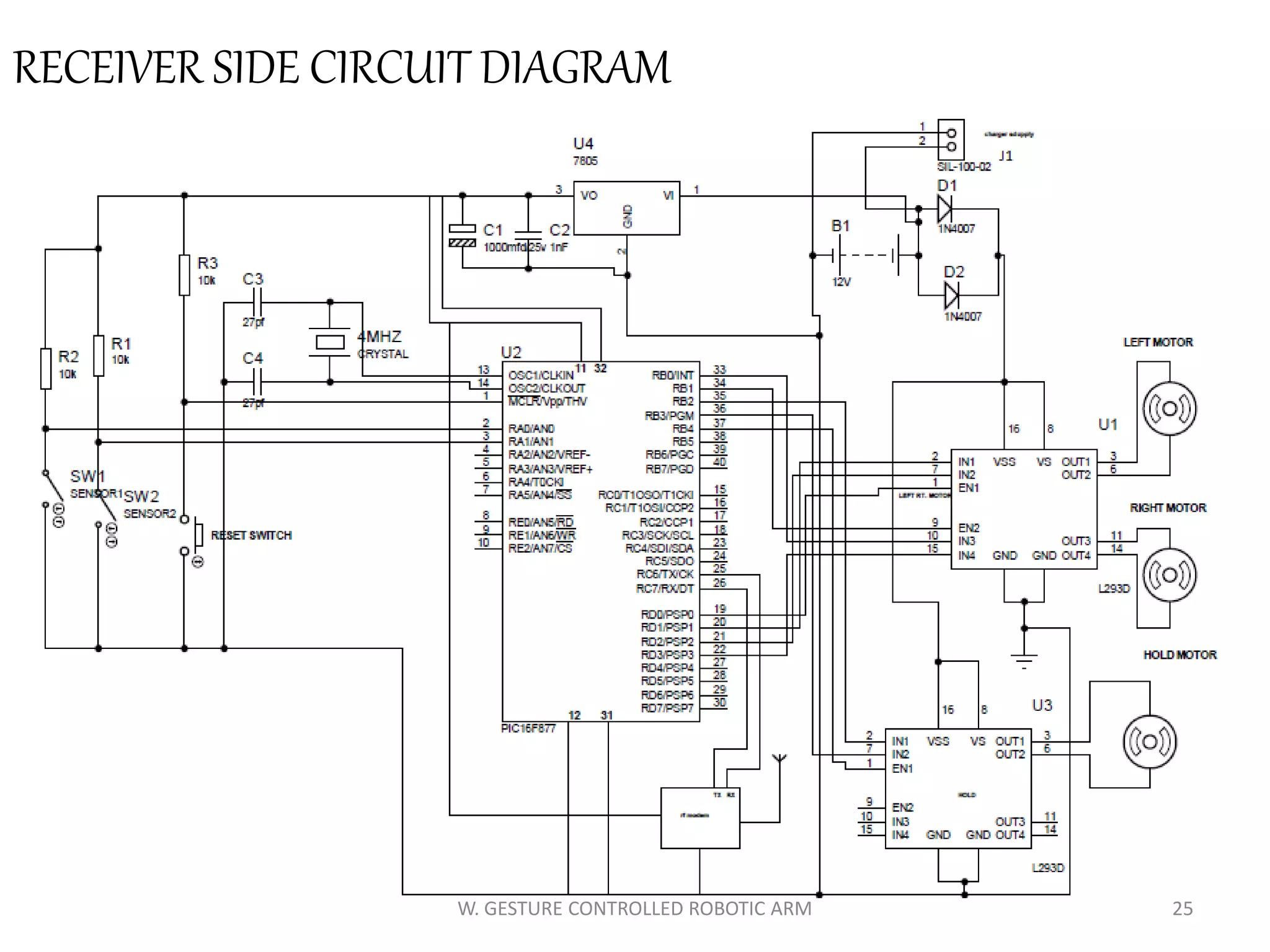
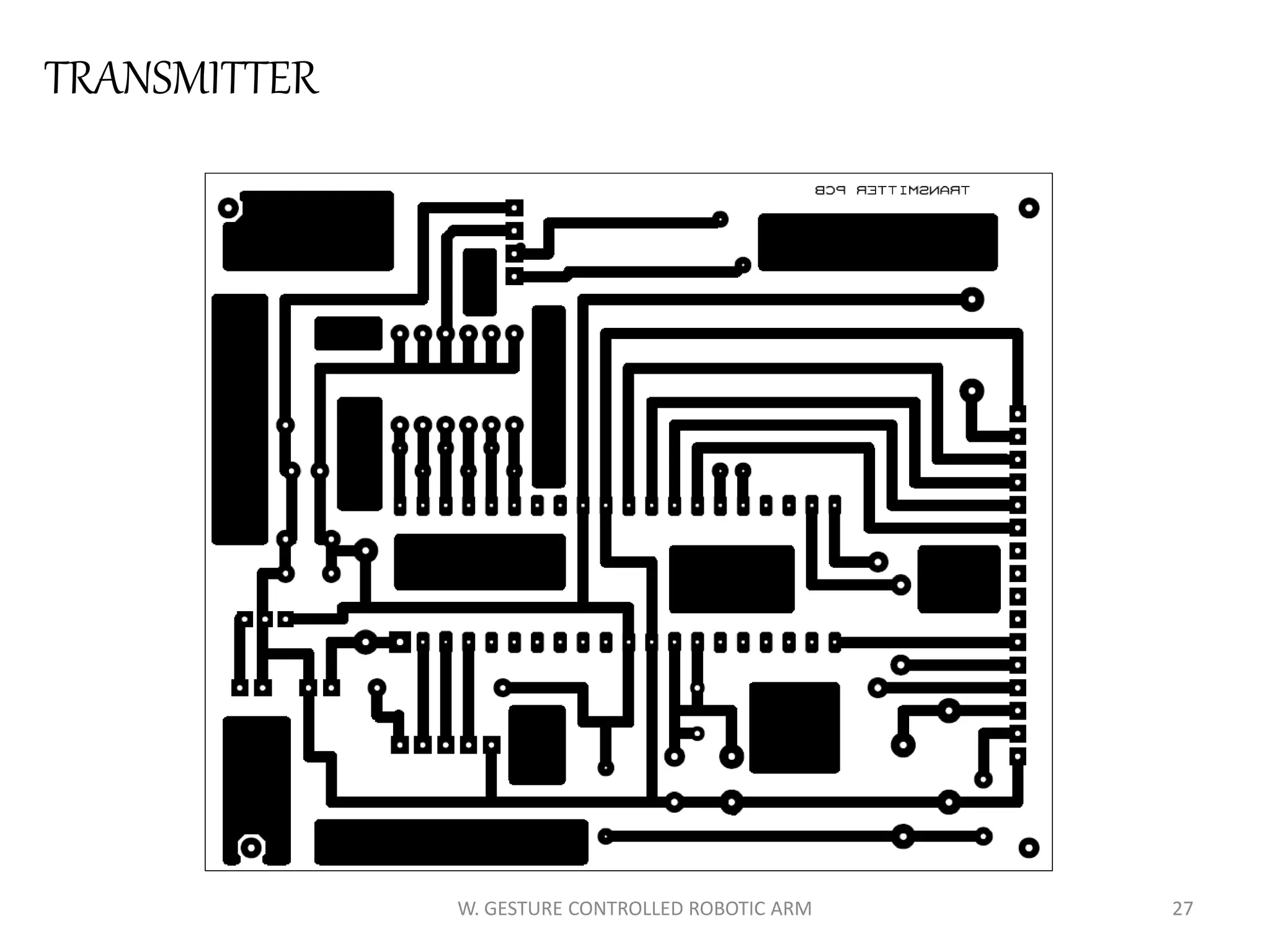
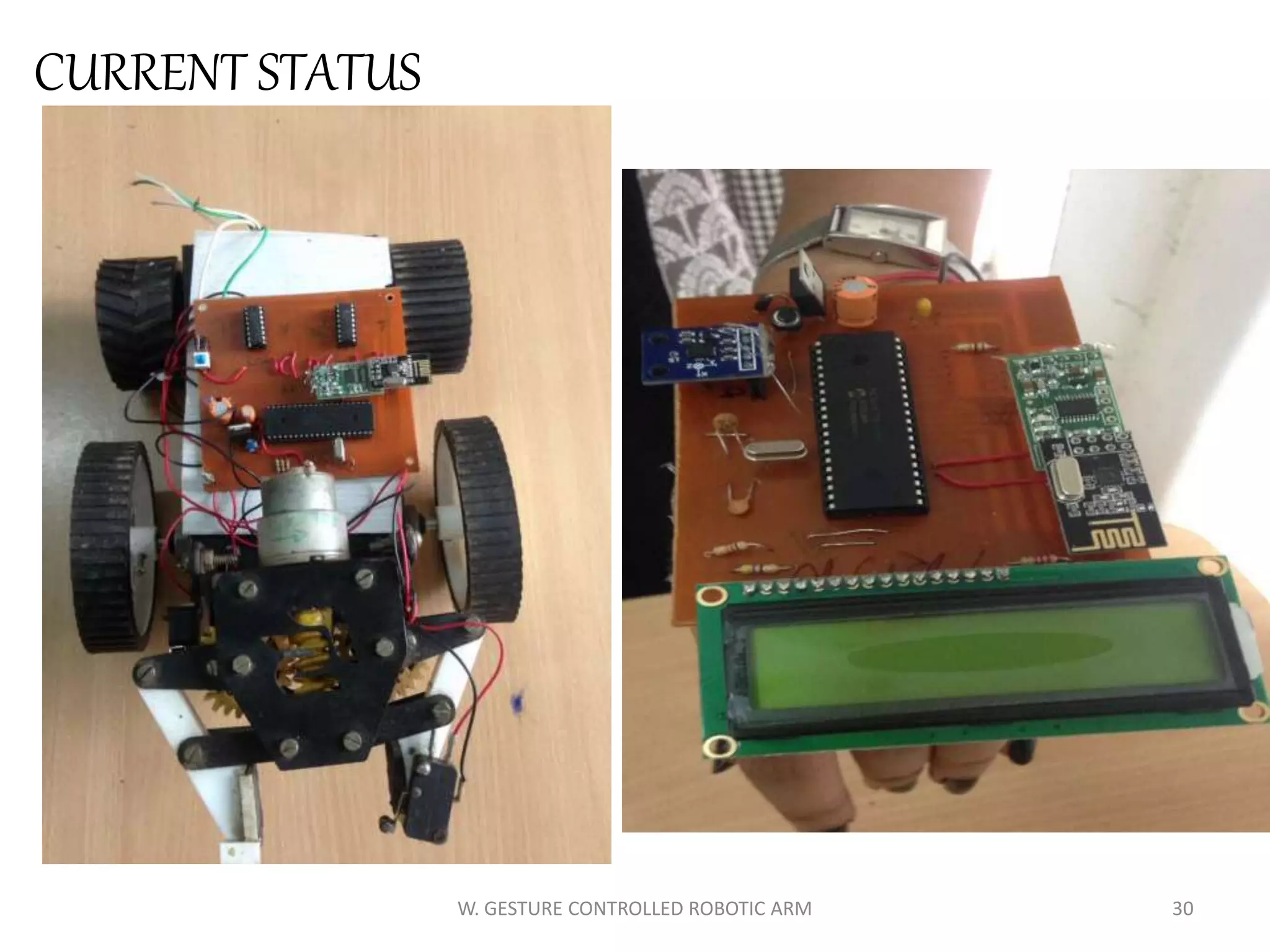
This document discusses a wireless gesture-controlled robotic arm, detailing its components, functionality, and applications in areas such as medical science and defense. It includes technical specifications for the accelerometer, RF transceiver, microcontroller, and actuators, along with descriptions of their wiring and algorithms for operation. The project emphasizes the convenience of using hand gestures to control robotic movements remotely.