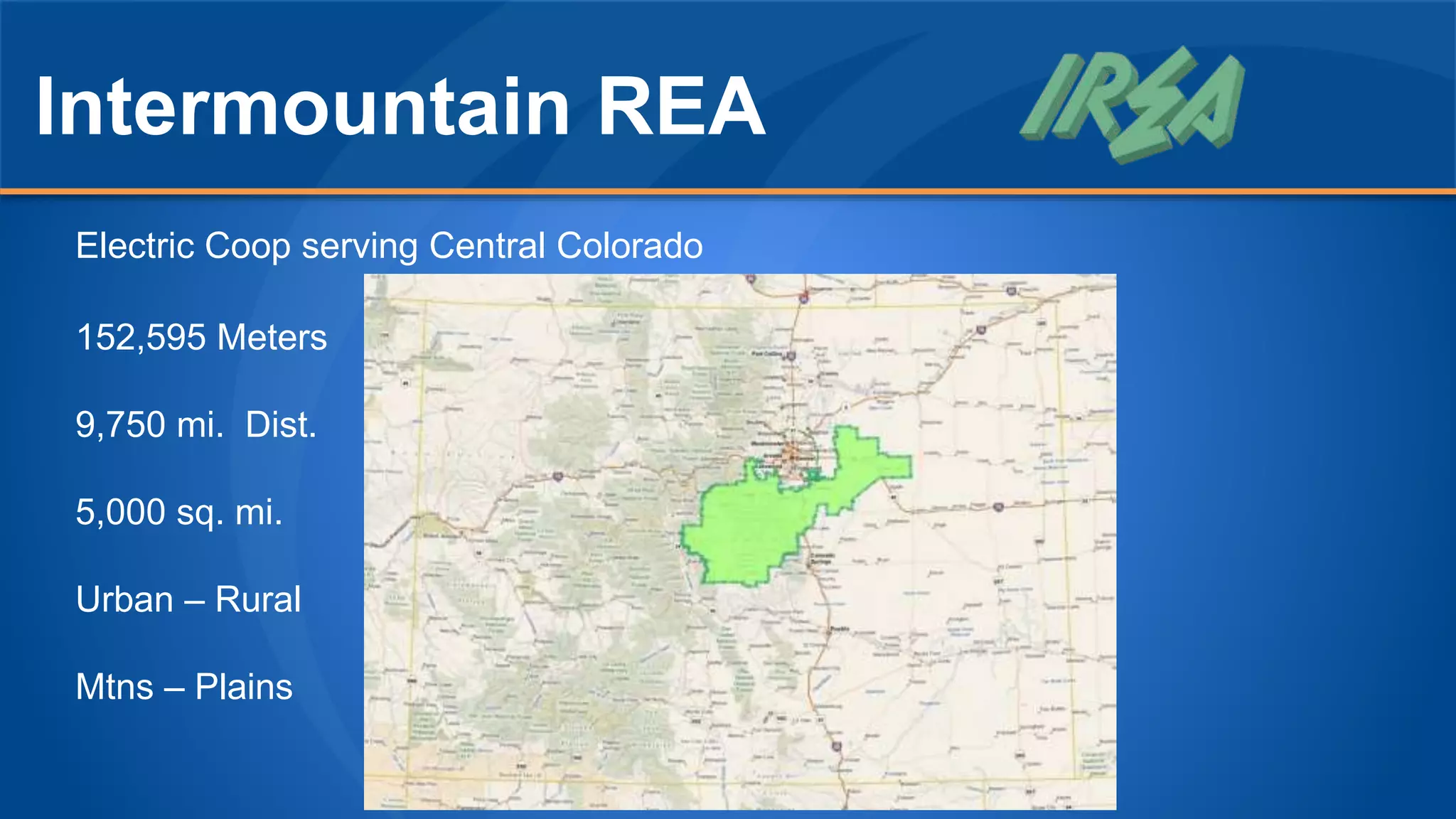
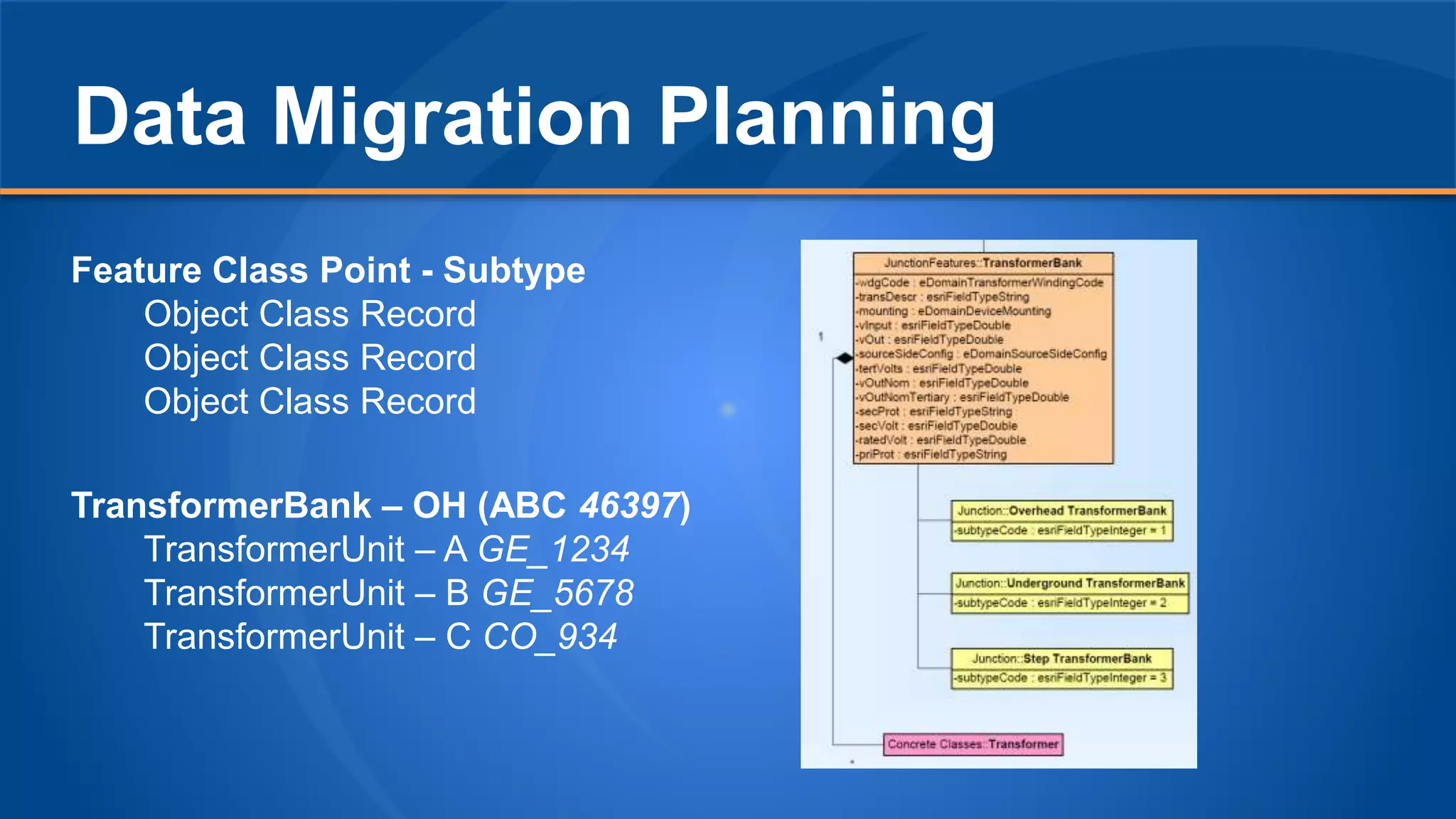
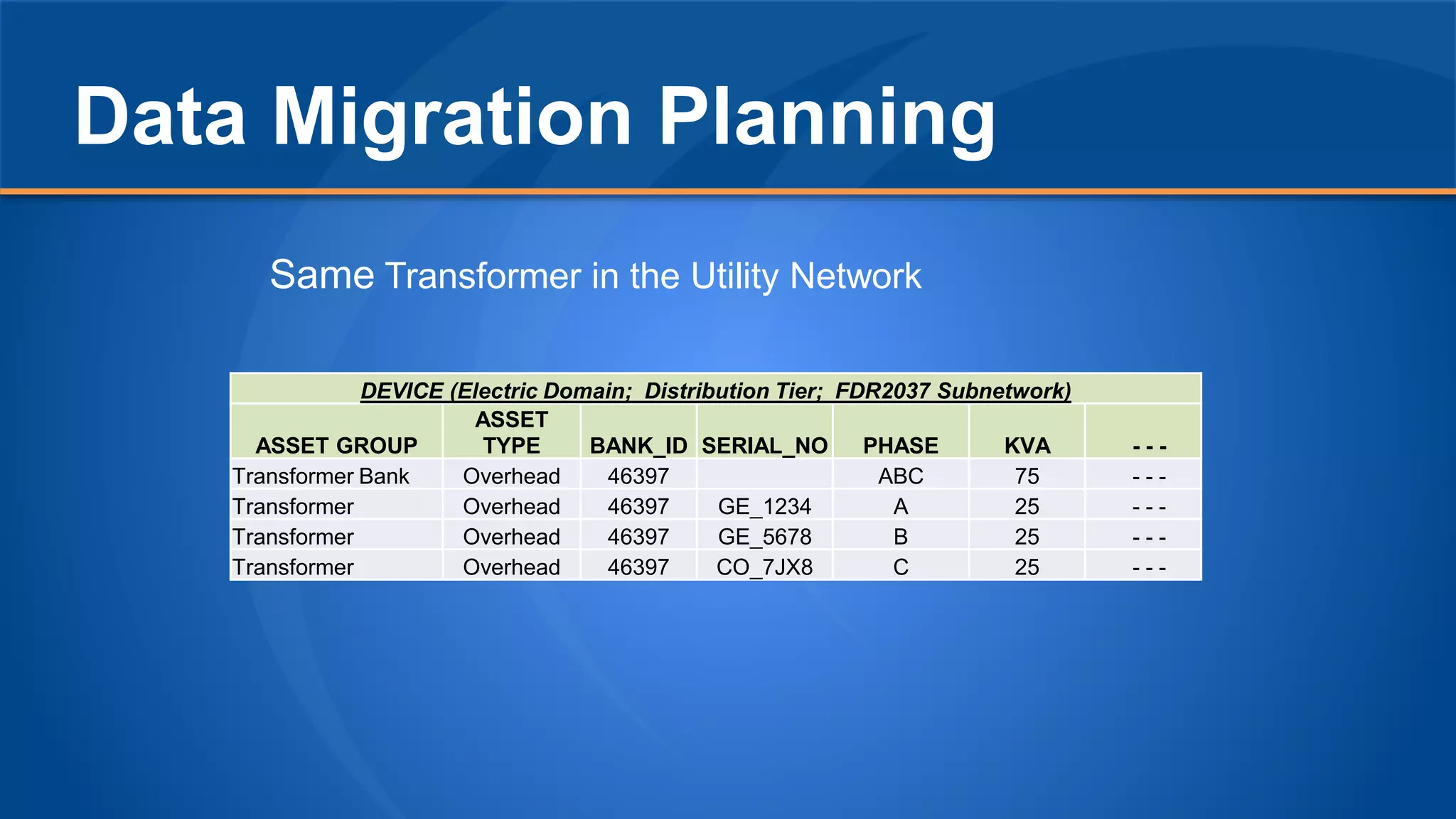
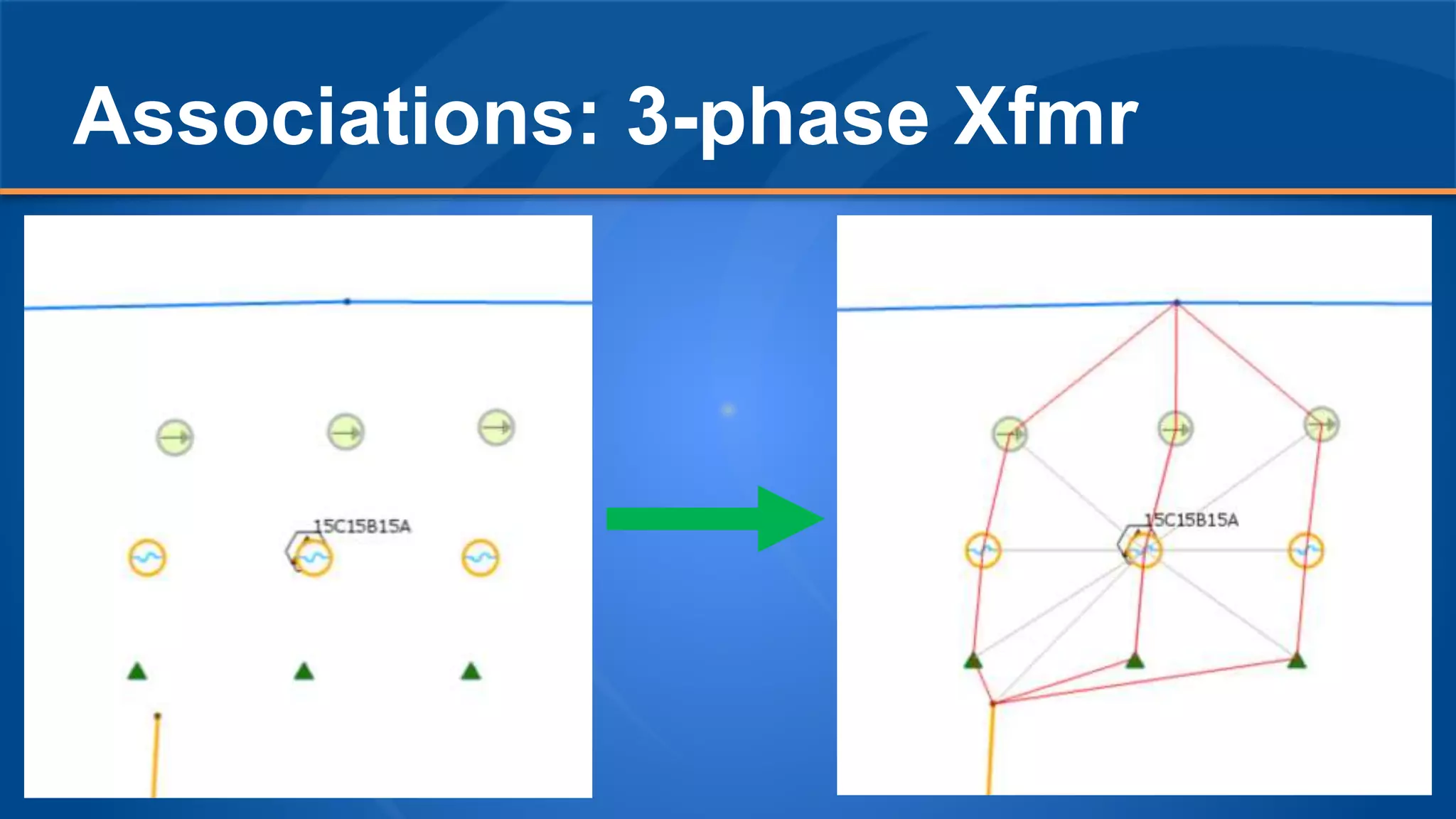
The document discusses the experiences of Duane Holt and John Coleman with the utility network used by Intermountain Rural Electric Association, detailing their current status, future steps, and challenges faced. Key topics include data migration planning, system architecture, and the benefits and concerns related to utility network operations. The emphasis is on enhancing productivity through improved tools for managing associations and connectivity in utility mapping.