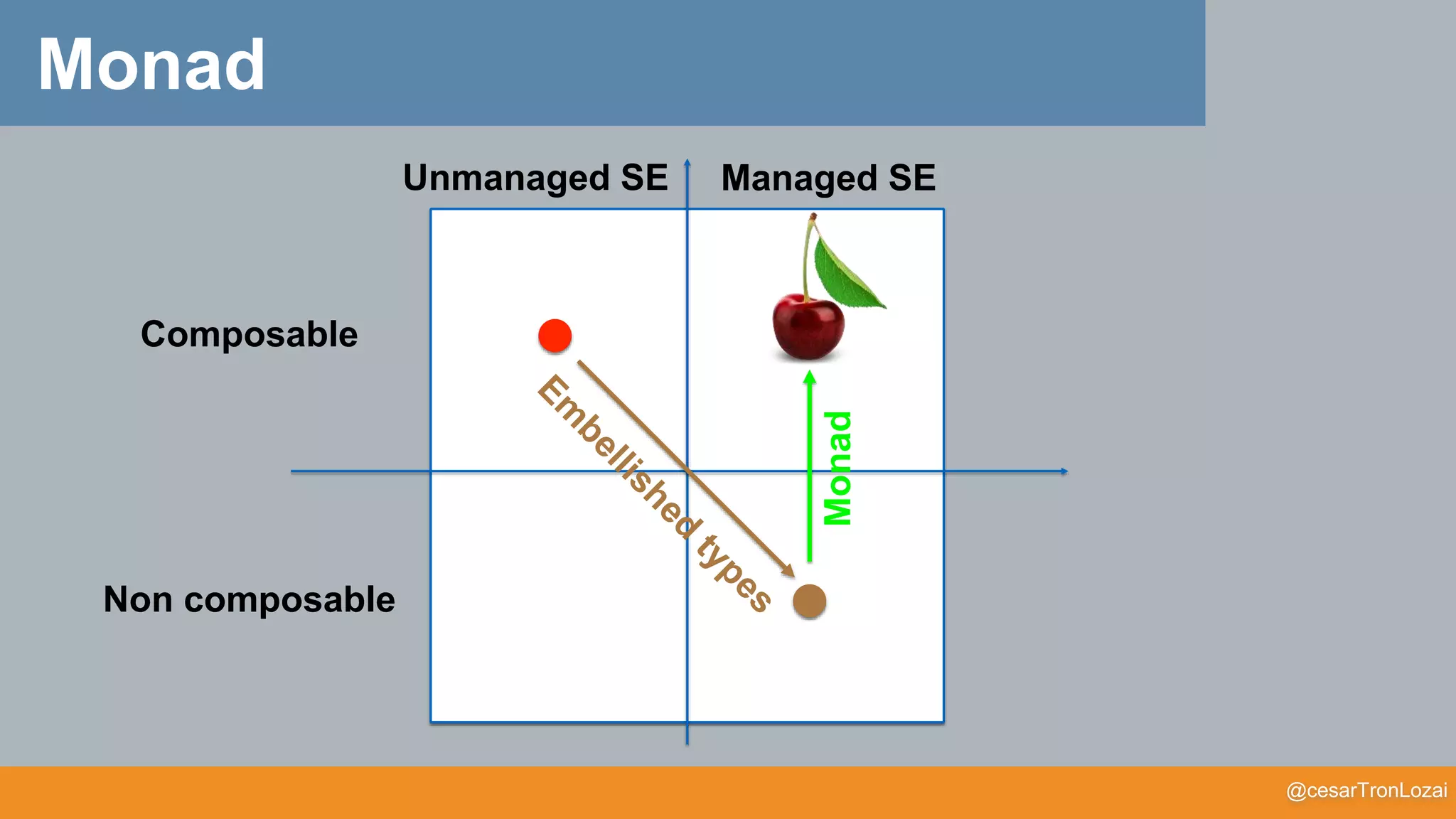
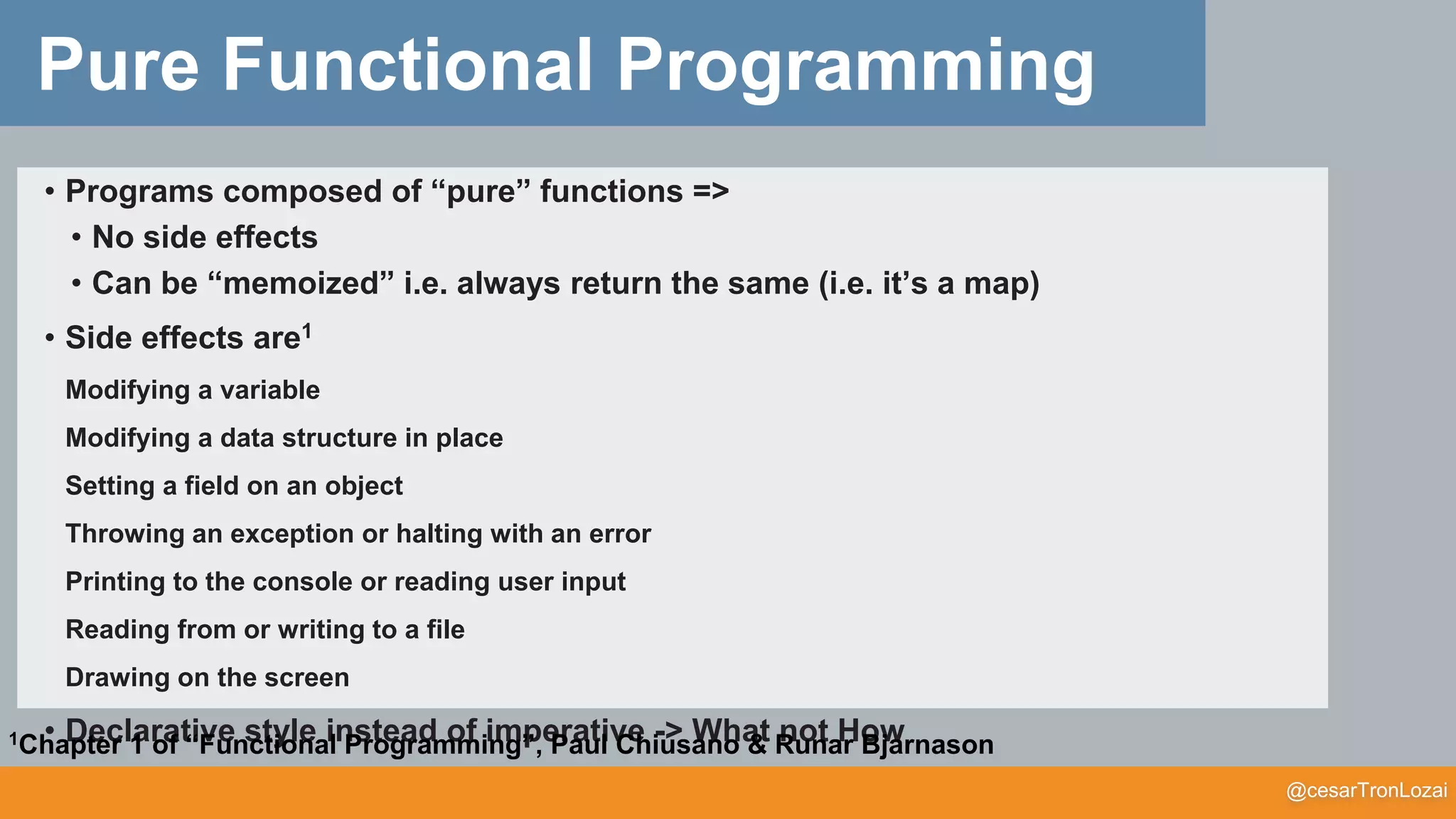
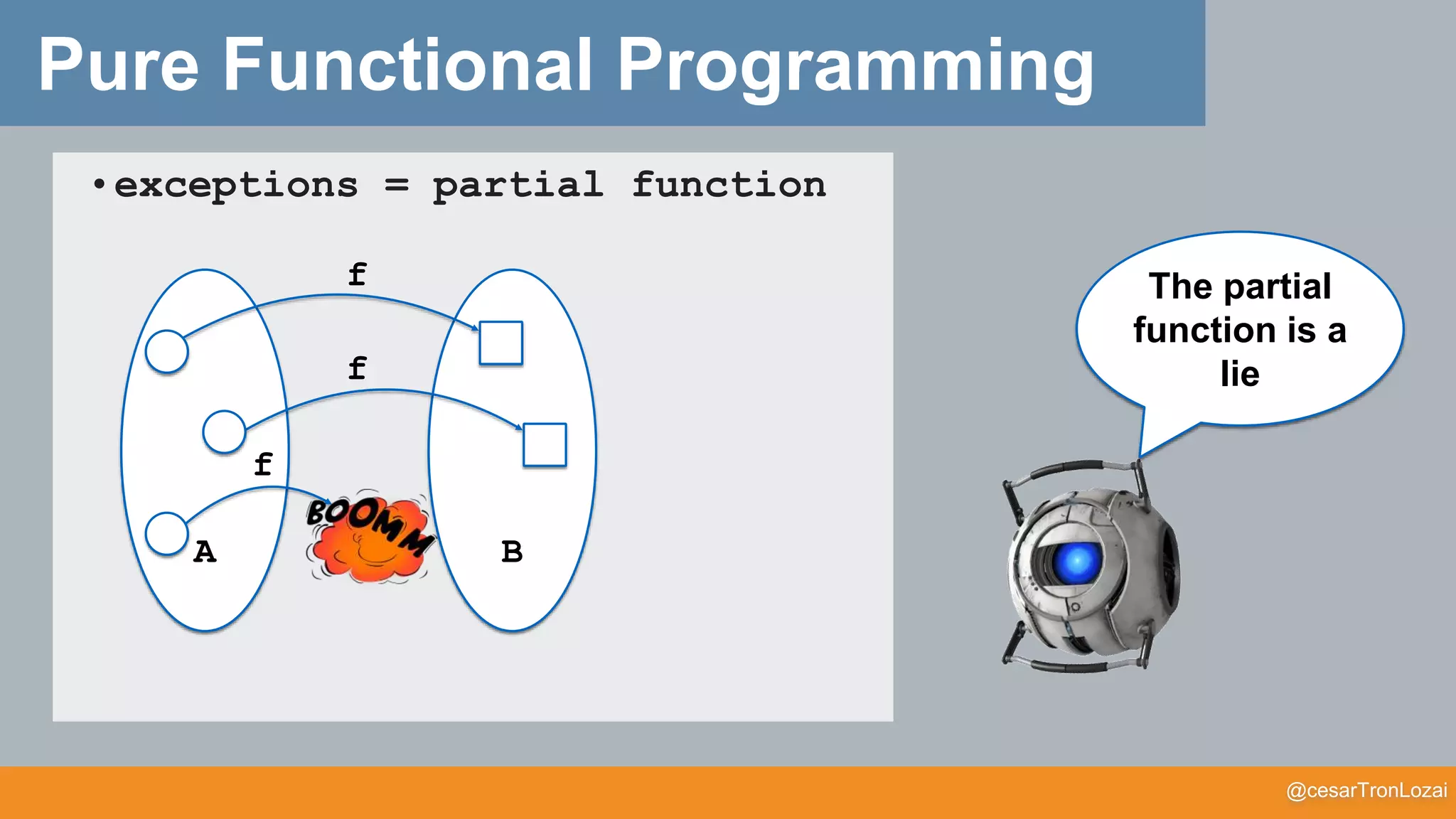
The document discusses the concept of monads in functional programming, emphasizing their importance in managing side effects and writing cleaner, more robust code. It explores the theoretical foundations of monads, comparing them to functors and illustrating their practical applications through various programming examples. The talk aims to simplify these concepts for better understanding and to encourage further exploration of functional programming principles.














![@cesarTronLozai
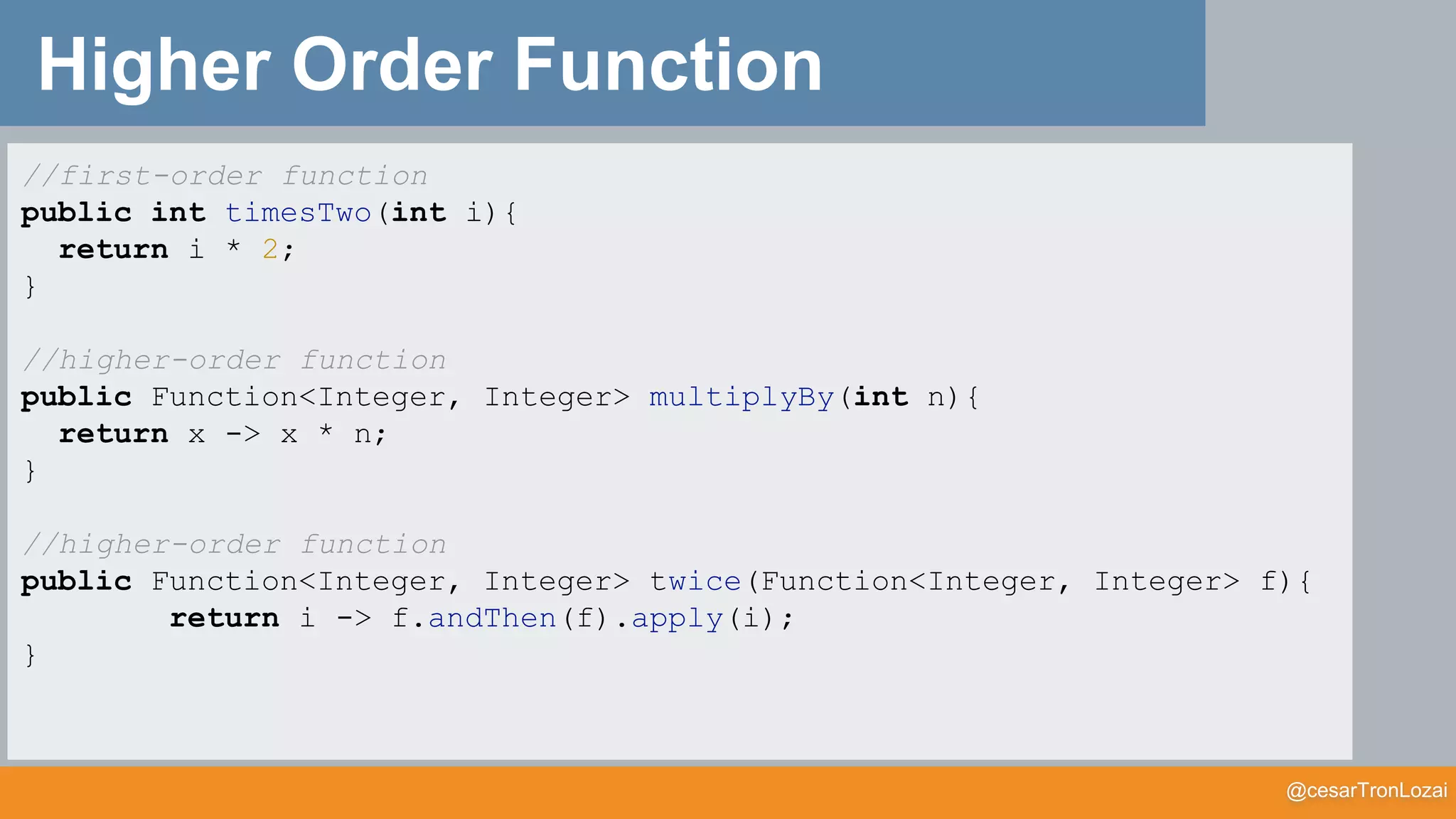
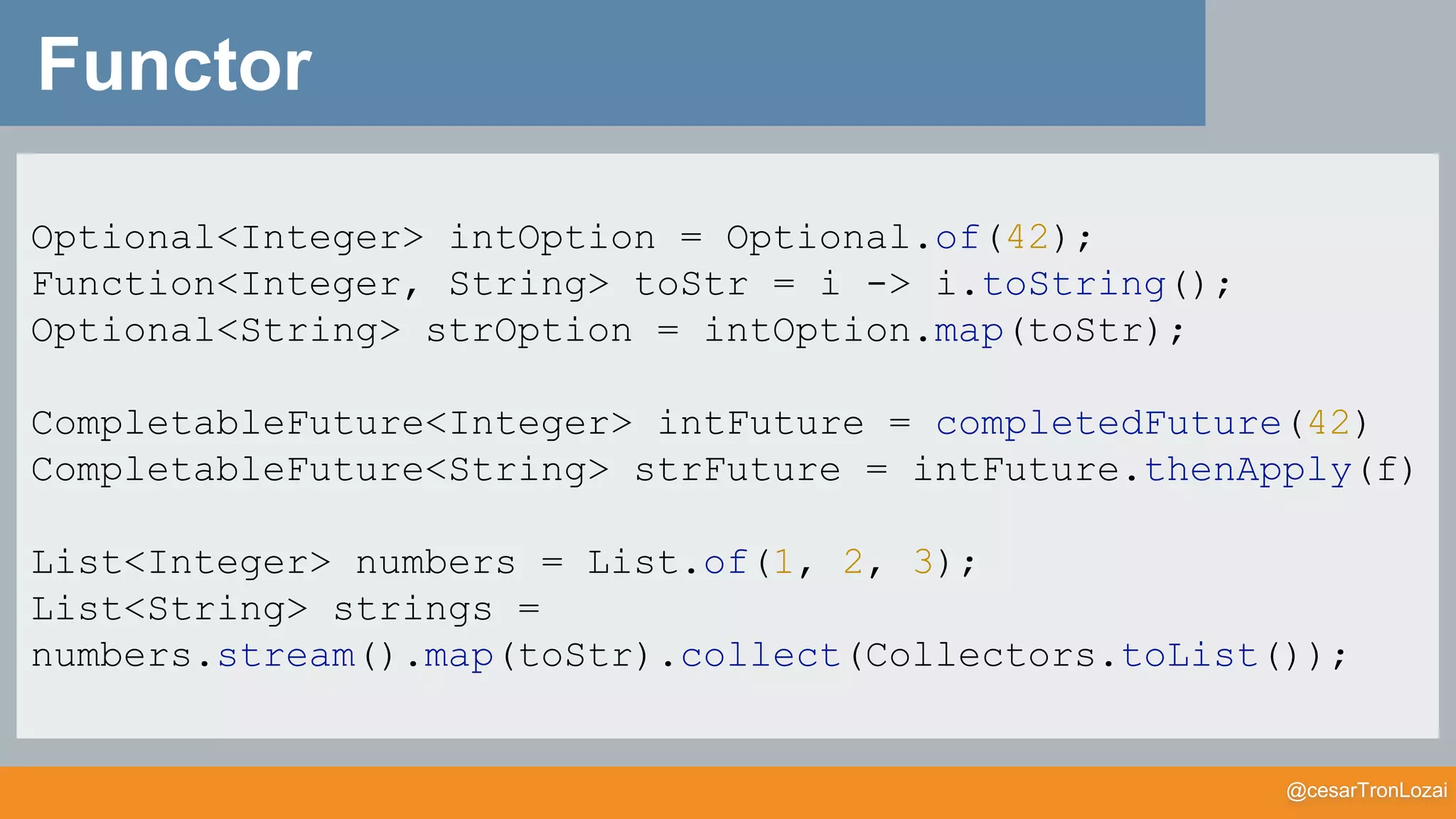
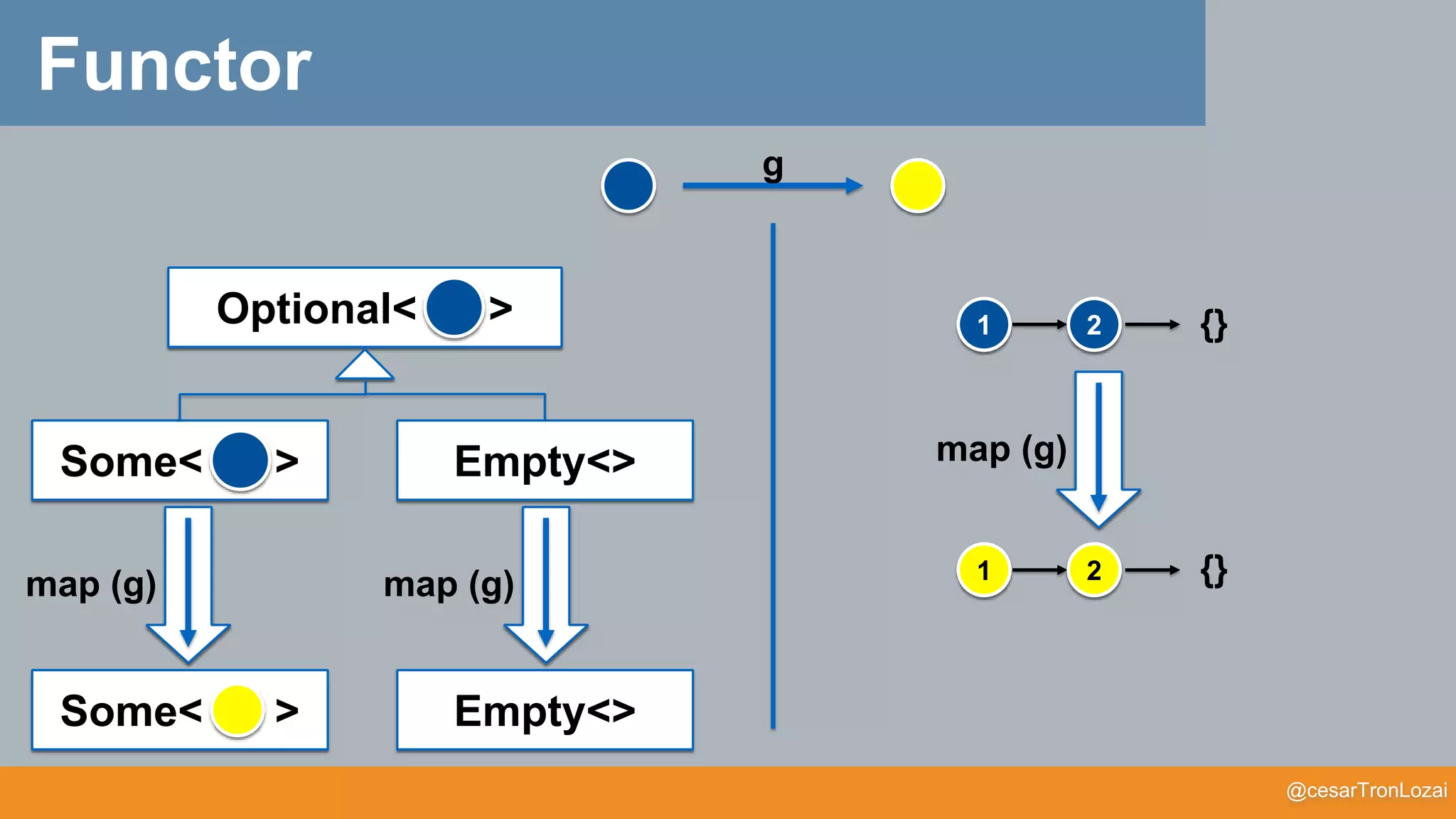
Functor
• The function that creates the lifted function is called map
map (g)
F :: A -> F[A]
g :: A -> B
map :: (A -> B) -> F[A] -> F[B]
map(g) :: F[A] -> F[B]
g
F
F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-21-2048.jpg)










![@cesarTronLozai
f :: A -> M[B]
g :: B -> M[C]
g >=> f :: A -> M[C]
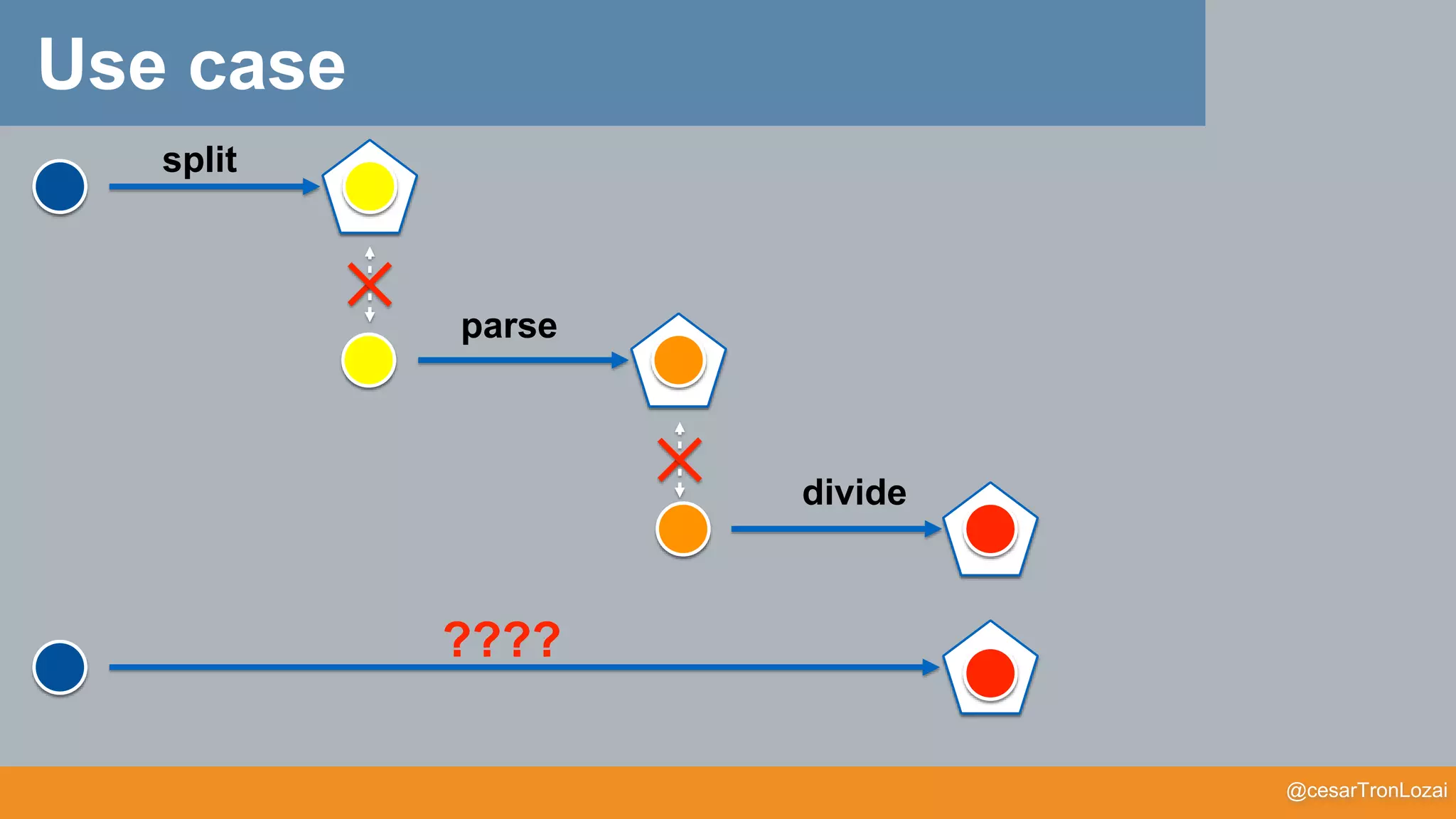
• How can we compose wrapped result types??
g
f
g >=> f
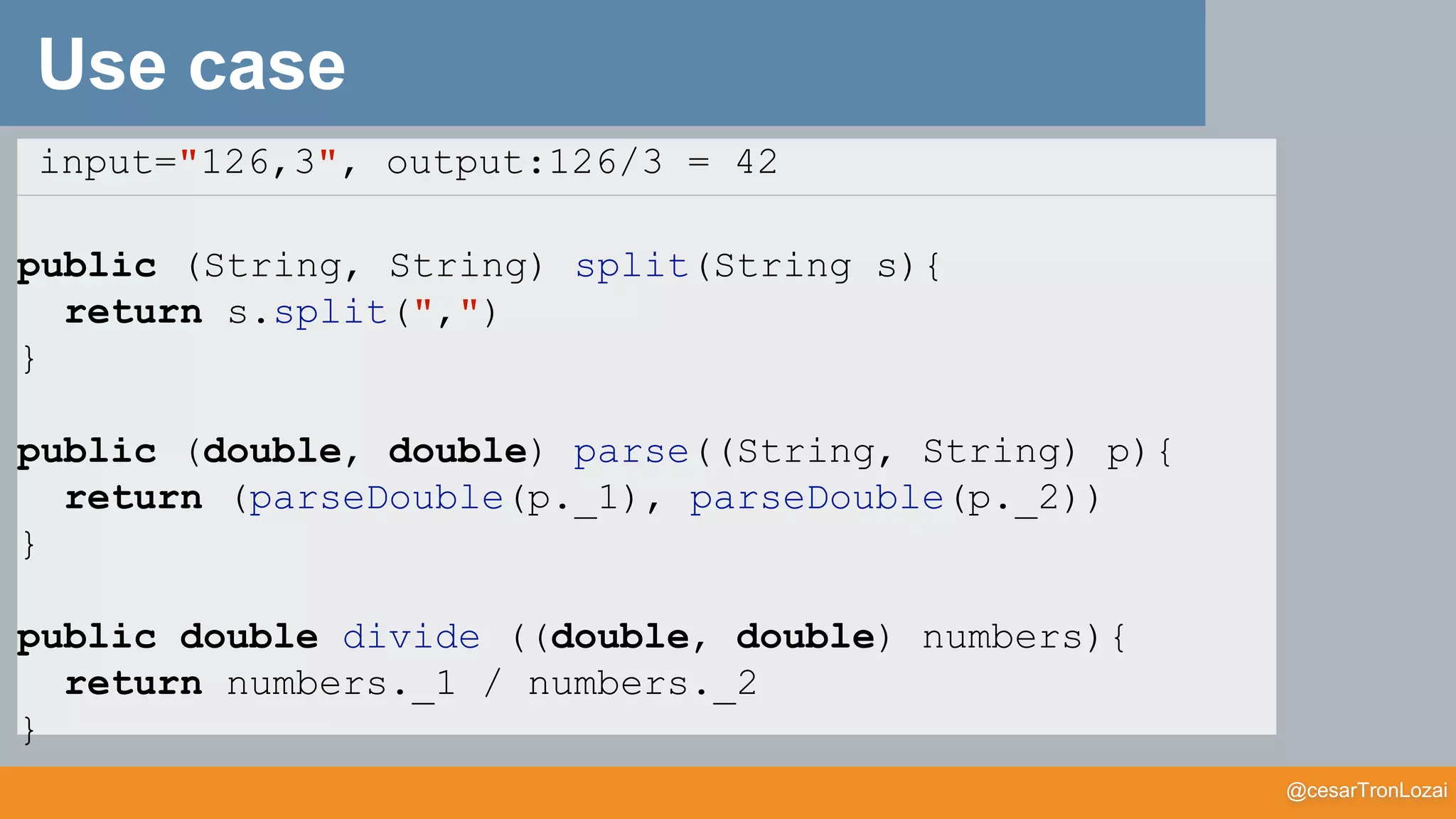
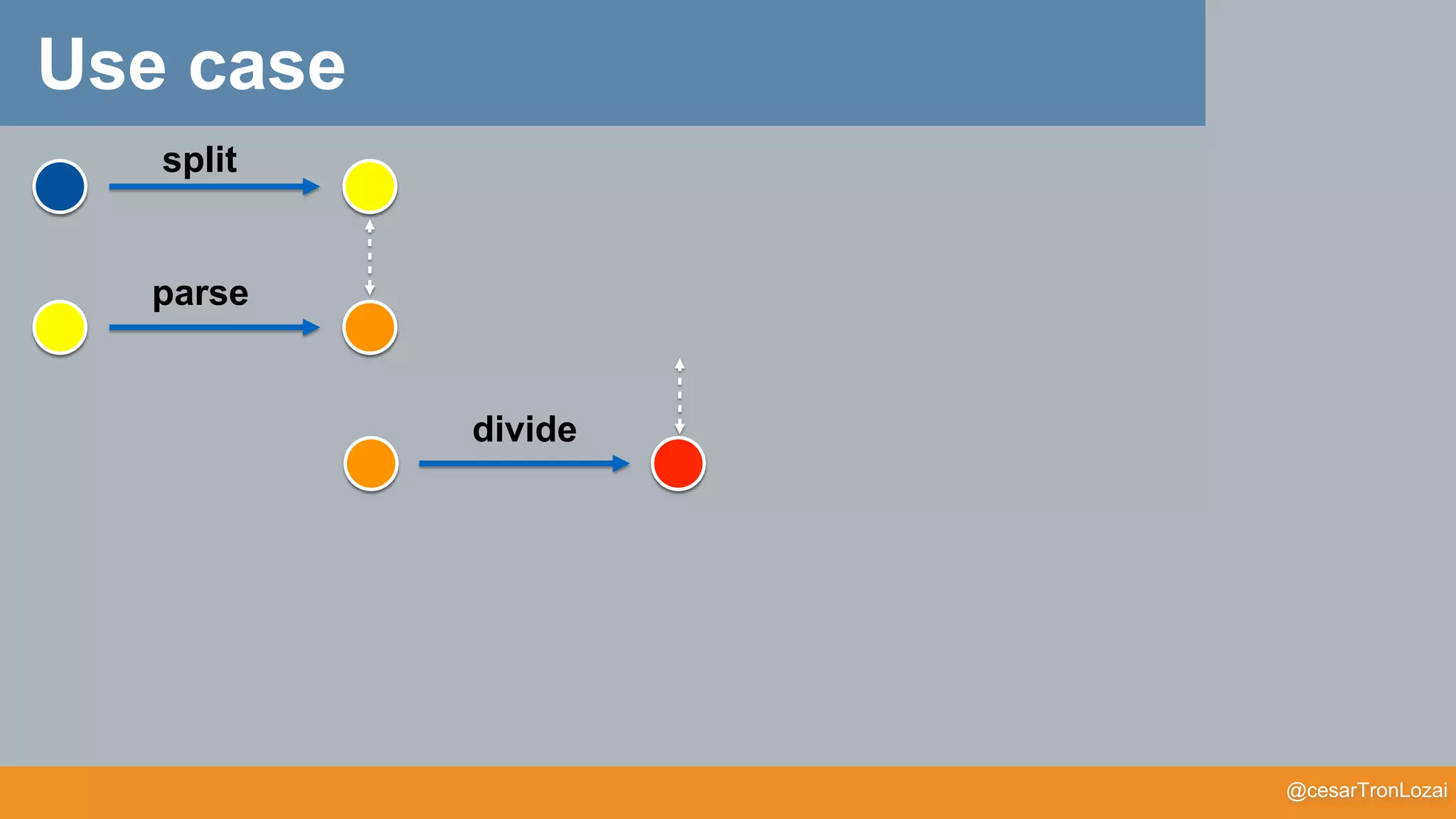
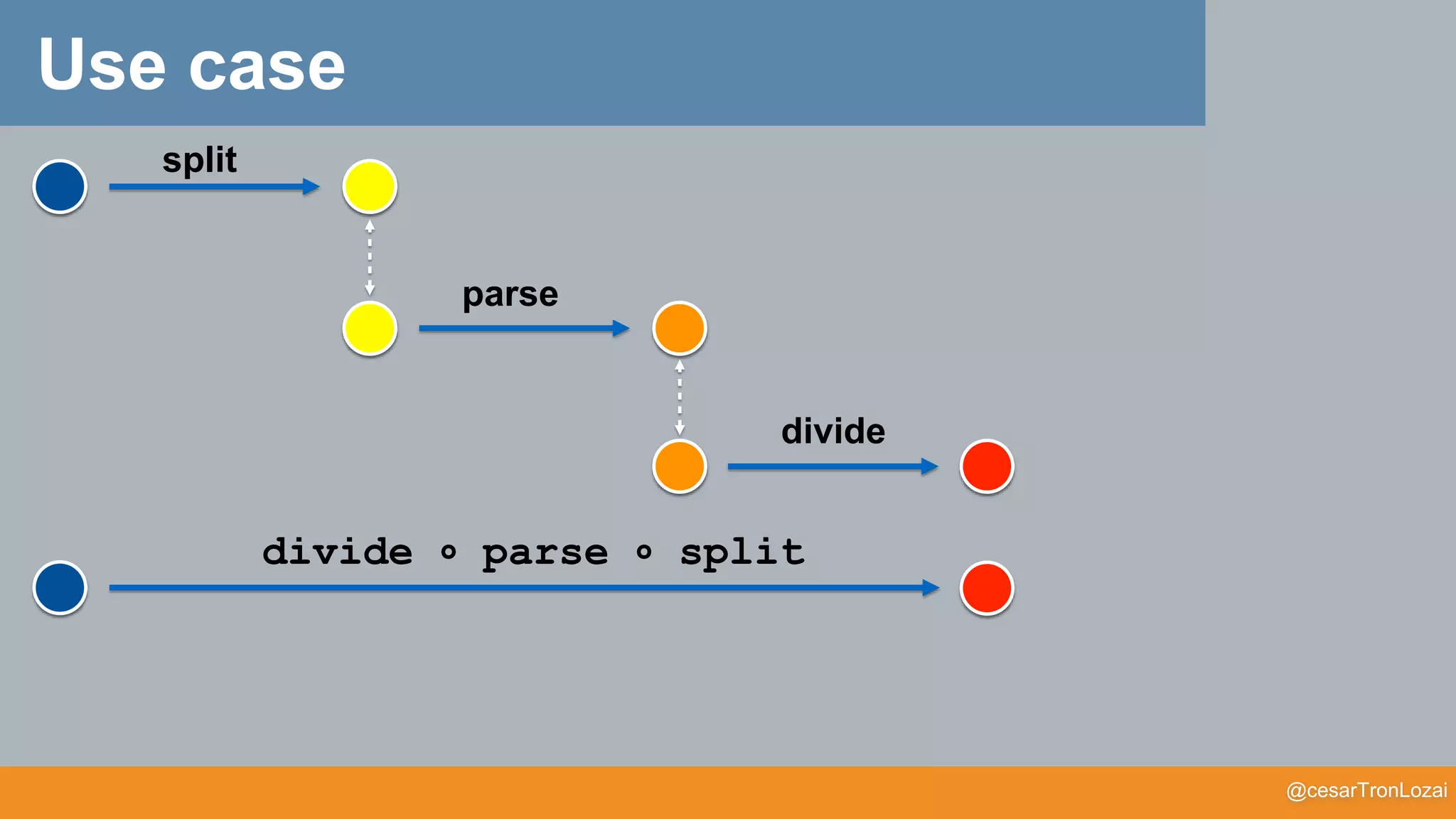
Use case](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-41-2048.jpg)
![@cesarTronLozai
f :: A -> M[B]
g :: B -> M[C]
map(g) o f :: A -> M[M[C]]
g >=> f :: A -> M[C]
Can we use a Functor??
map (g)
f
map (g) o f
We need something that can do M[M[T]] -> M[T]
g
Use case](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-42-2048.jpg)
![@cesarTronLozai
Monad
map g
f
flatten
flatten
flatten o map (g) o f
f :: A -> M[B]
g :: B -> M[C]
g >=> f :: A -> M[C]
g >=> f = flatten o map (g) o f
g](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-43-2048.jpg)

![@cesarTronLozai
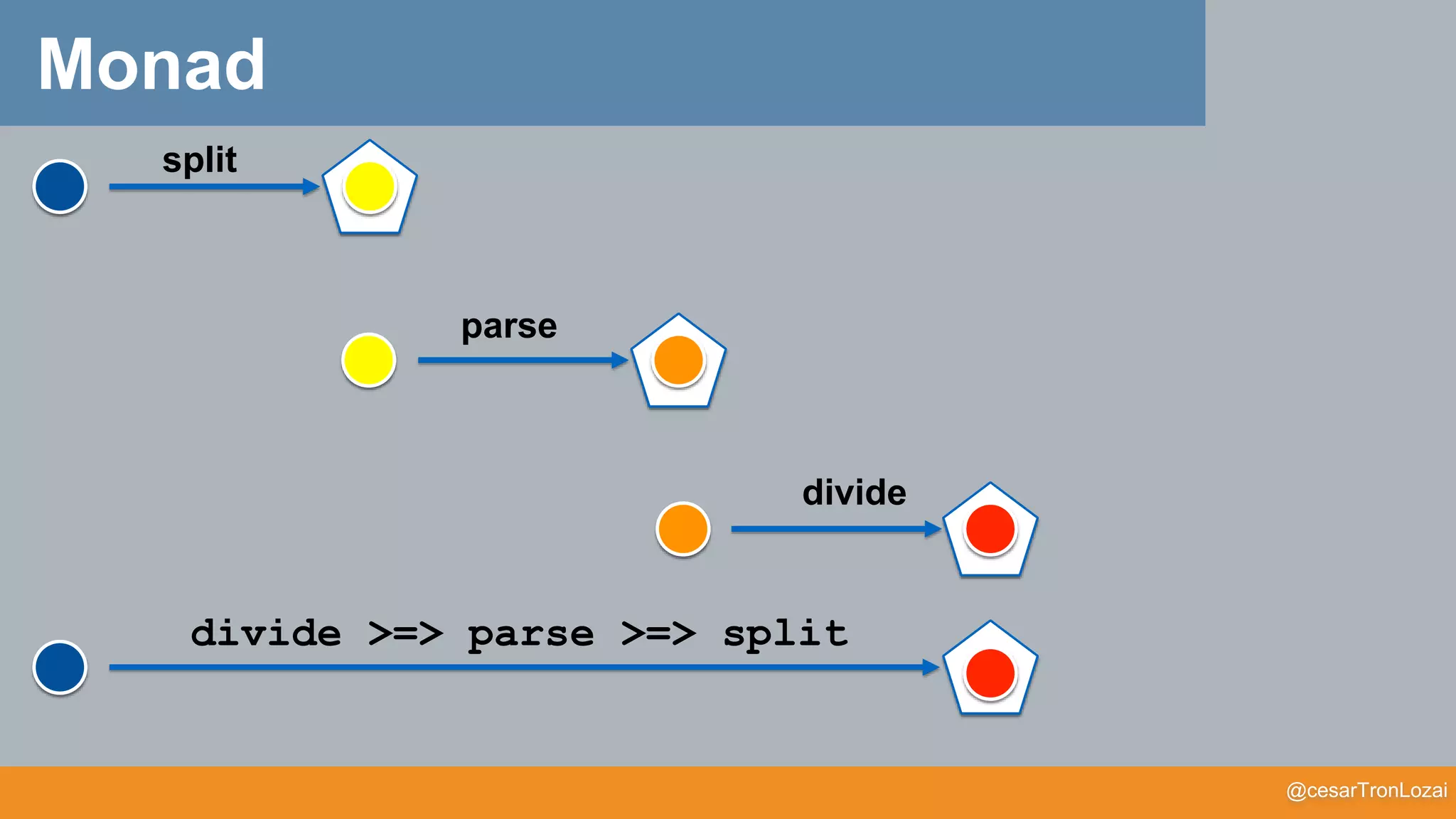
Monad
flatmap (g) = flatten o map (g)
M :: A -> M[A]
f :: A -> M[B]
map ::(A -> B) -> M[A] -> M[B]
flatmap ::(A -> M[B]) -> M[A] -> M[B]
g >=> f = x -> flatmap(g)(f(x))
flatten
g
map g](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-45-2048.jpg)



![@cesarTronLozai
Monad
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> completedFuture(T value)
public static <T> Optional<T> of(T value)
public static <T> Stream<T> of(T e)
flatmap ::(A -> M[B]) -> M[A] -> M[B]
pure :: A -> M[A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-50-2048.jpg)



![@cesarTronLozai
Monad
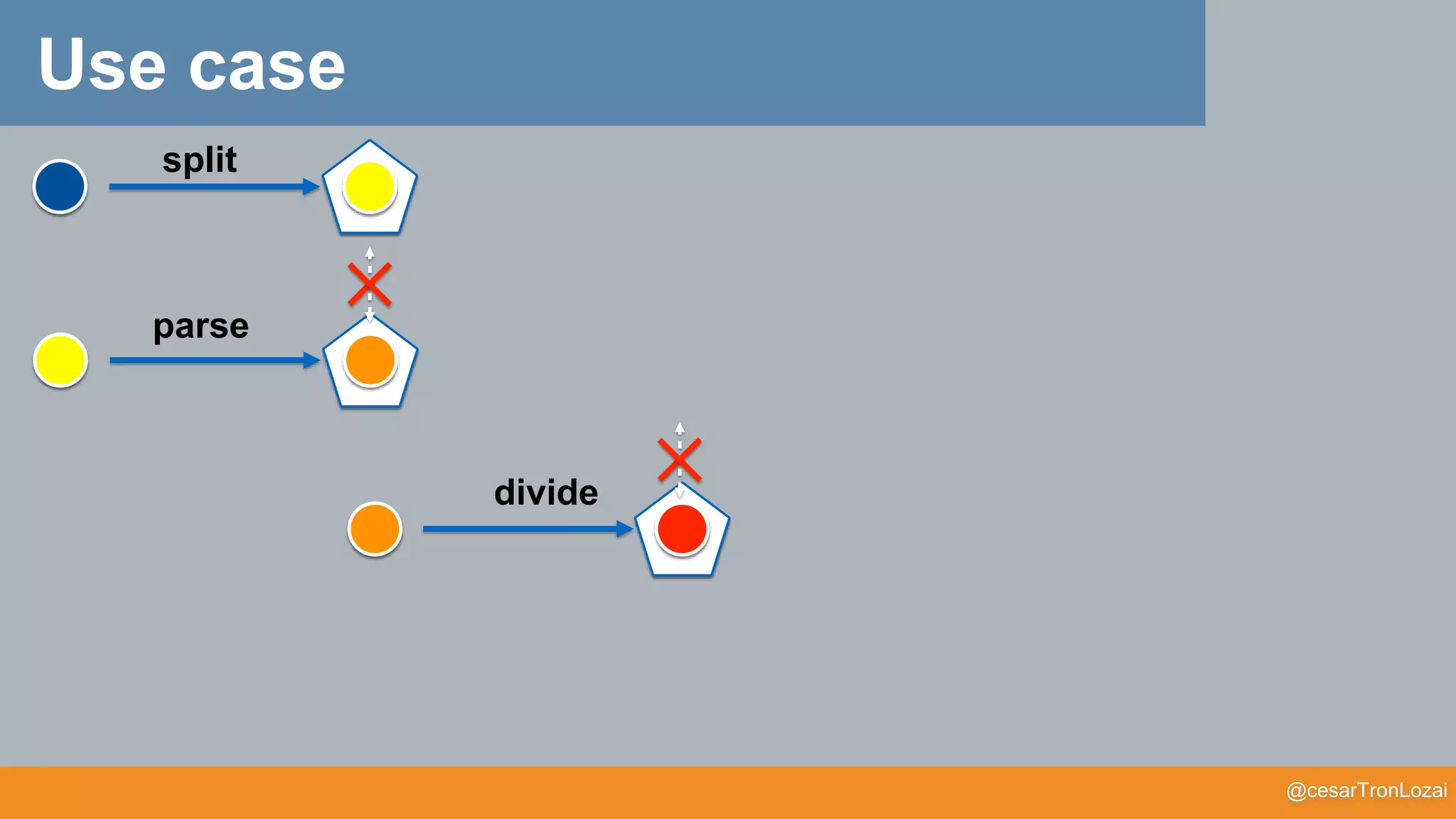
def split(s: String): Option[(String, String)] = ???
def parse(p: (String, String)): Option[(Double, Double)] = ???
def divide(n: (Double, Double)): Option[Double] = ???
def myProgram(s: String): Option[Double] = {
for {
split <- split(s)
parse <- parse(split)
divide <- divide(parse)
} yield divide
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatthefisamonadv7-191122145836/75/What-the-f-is-a-monad-54-2048.jpg)