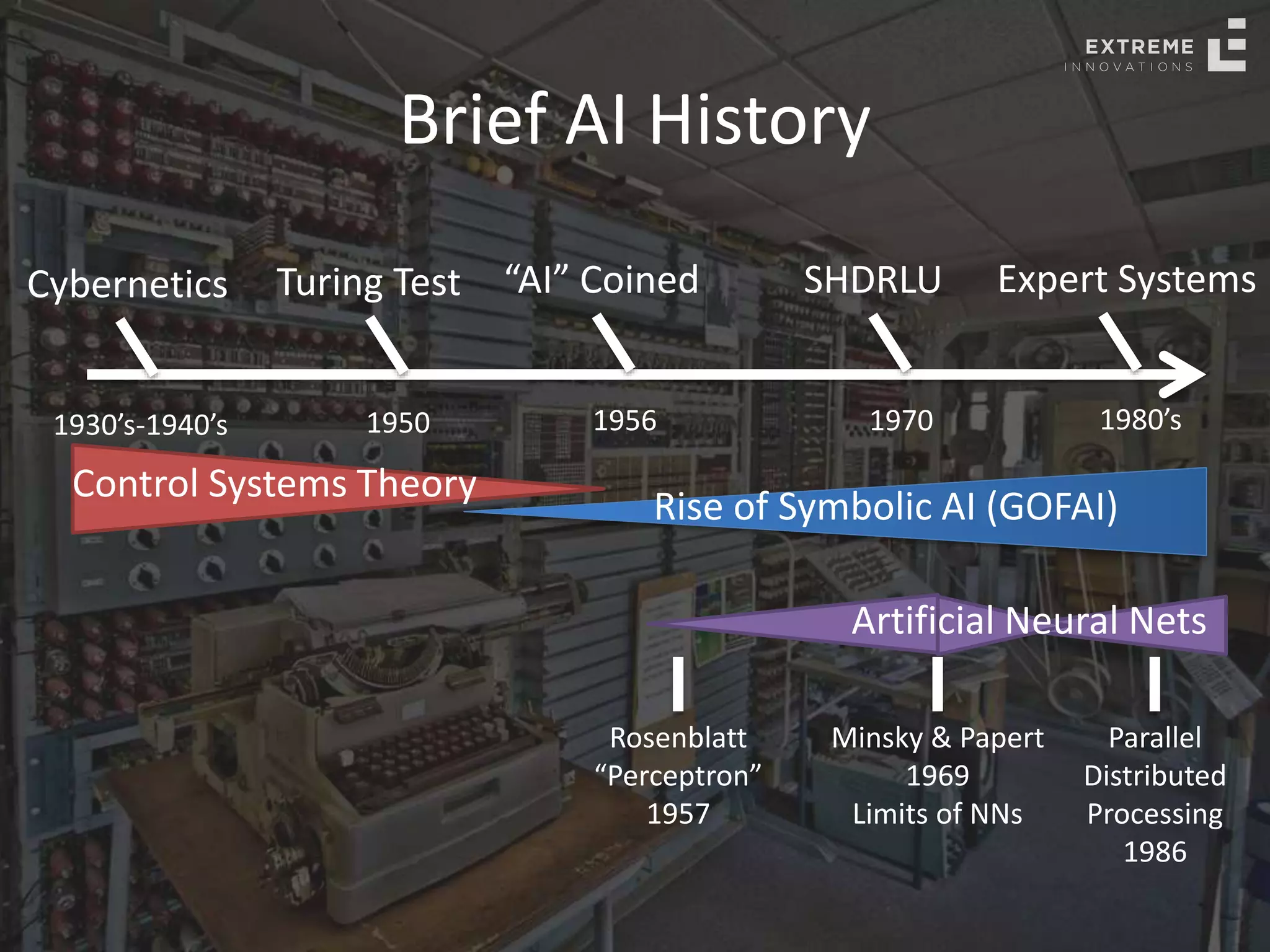
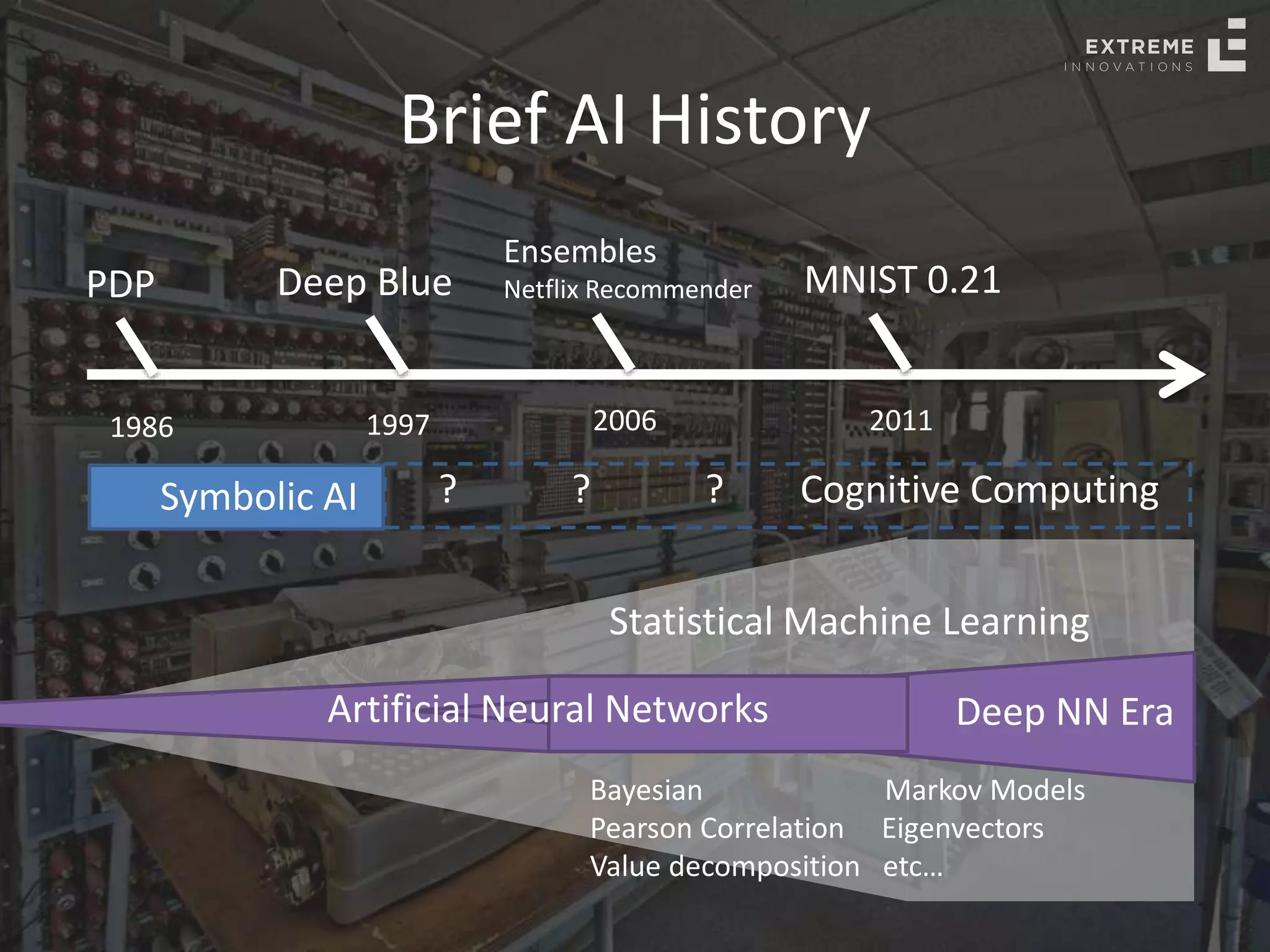
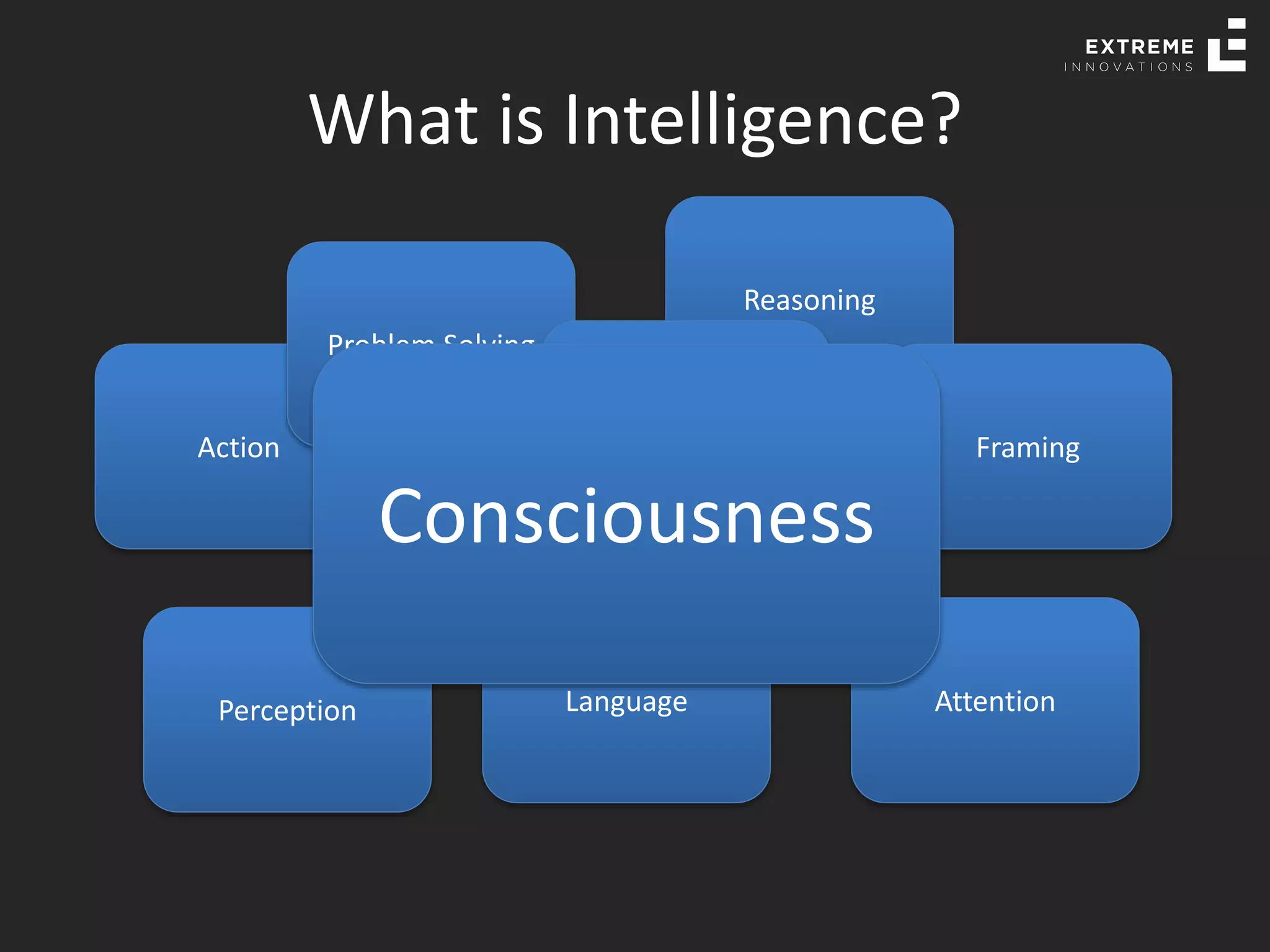
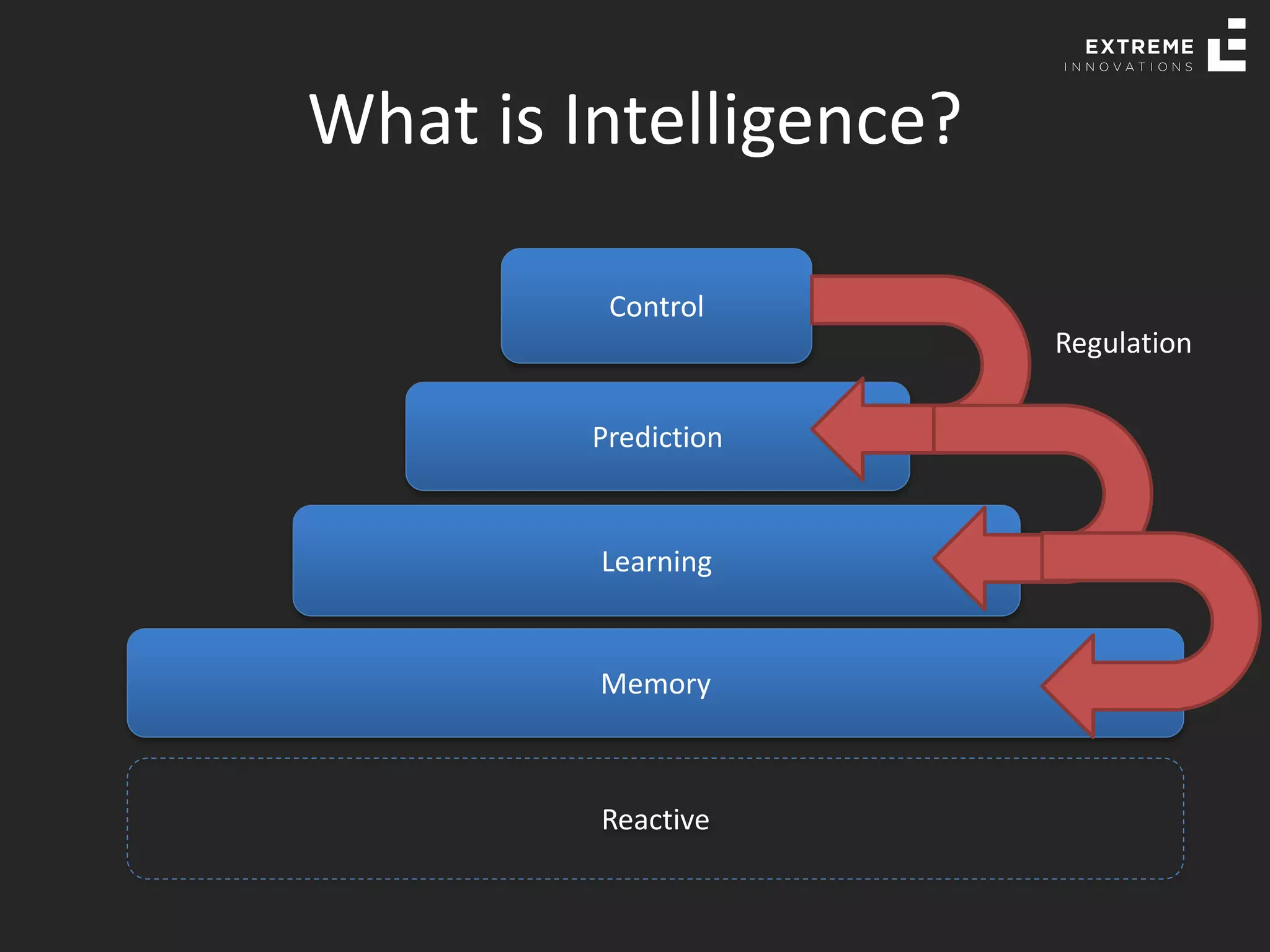
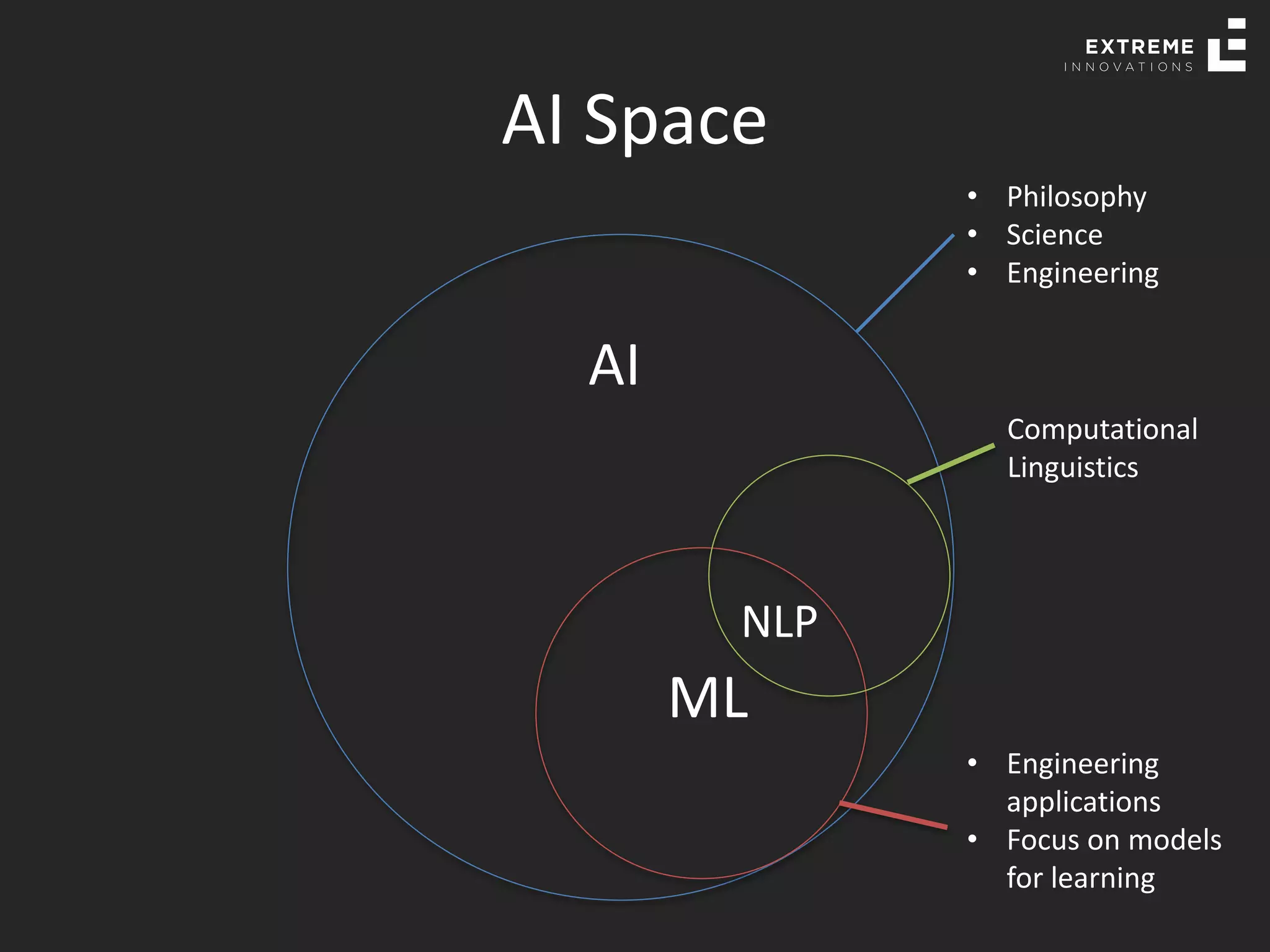
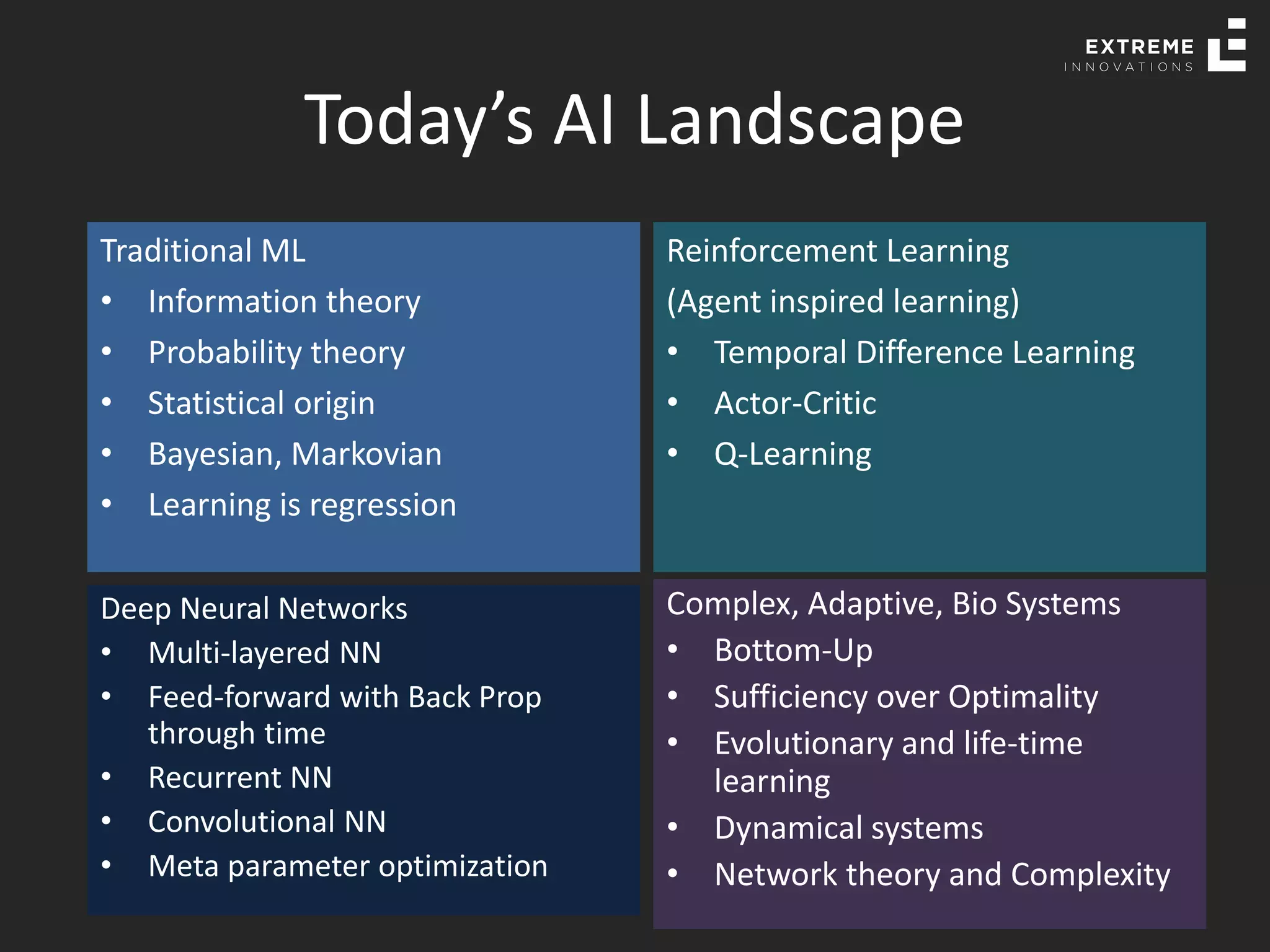
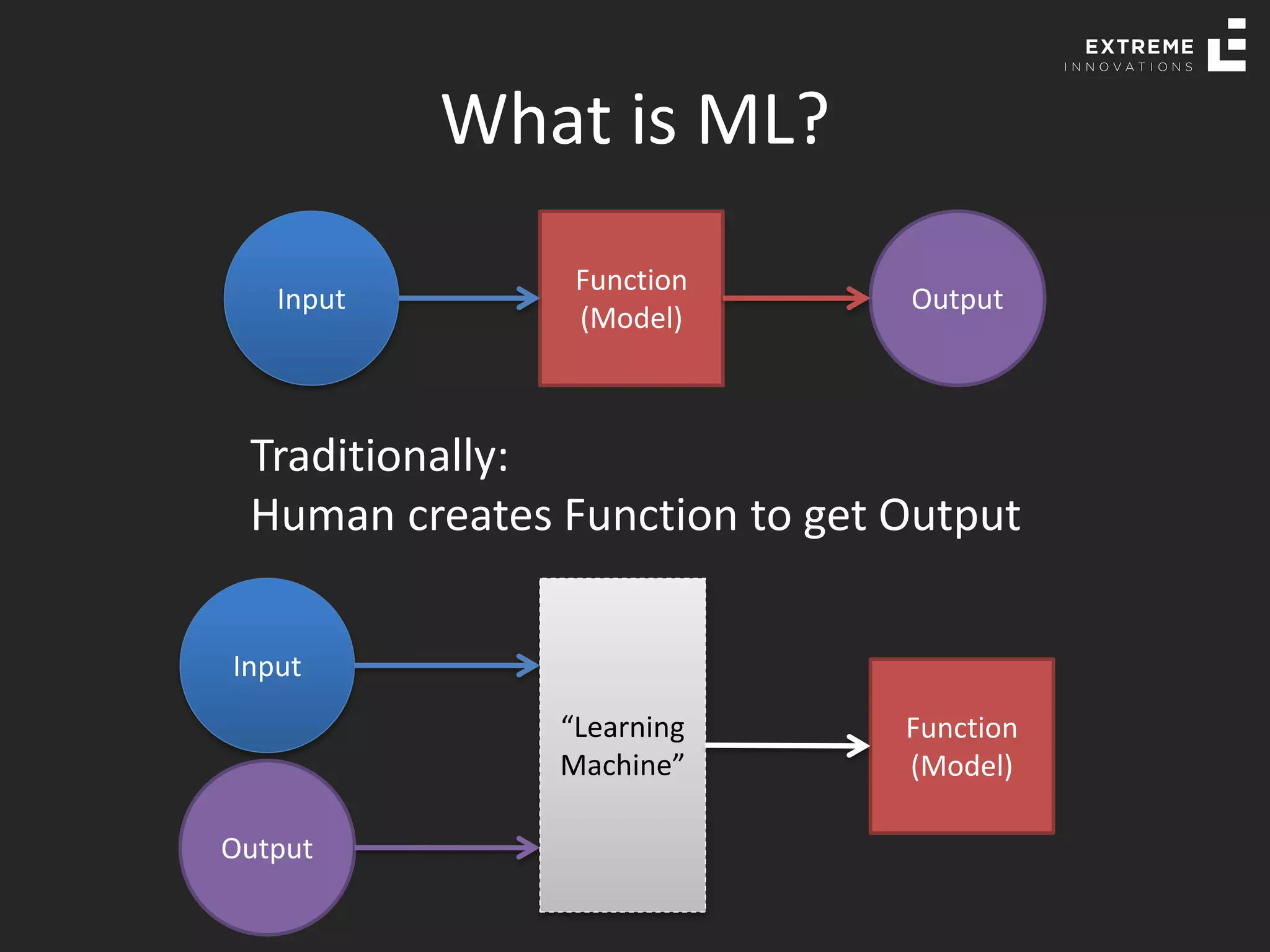
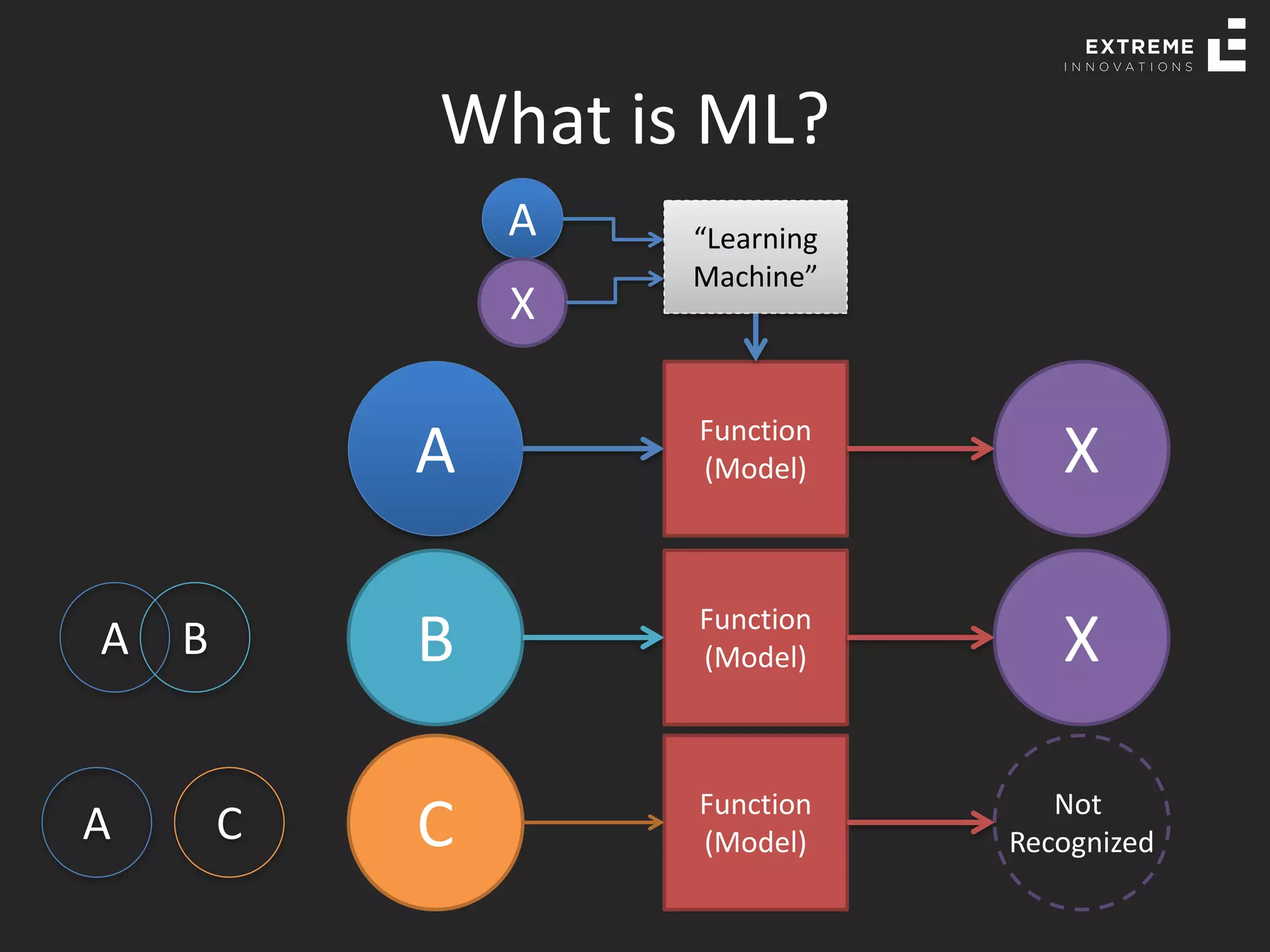
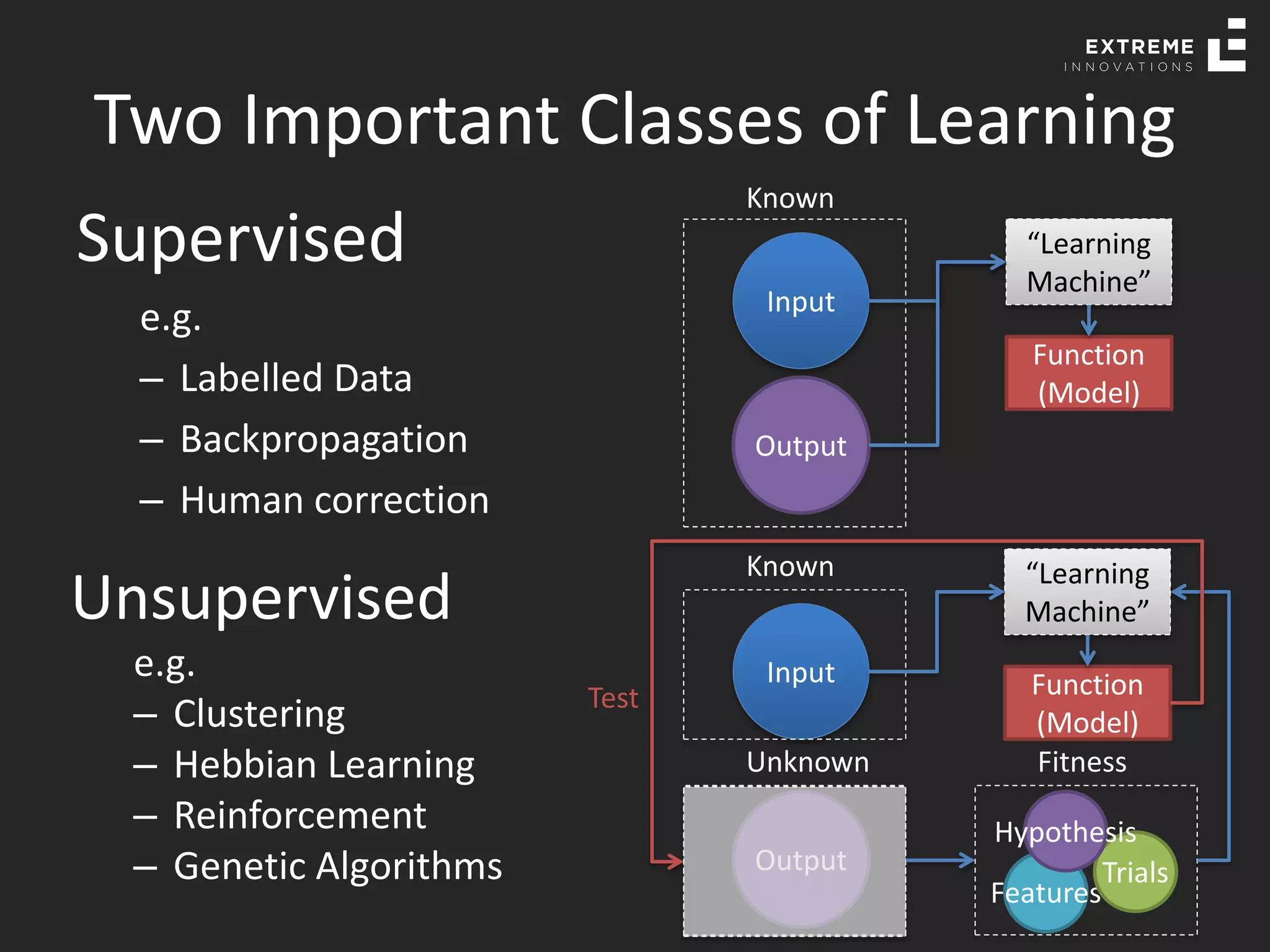
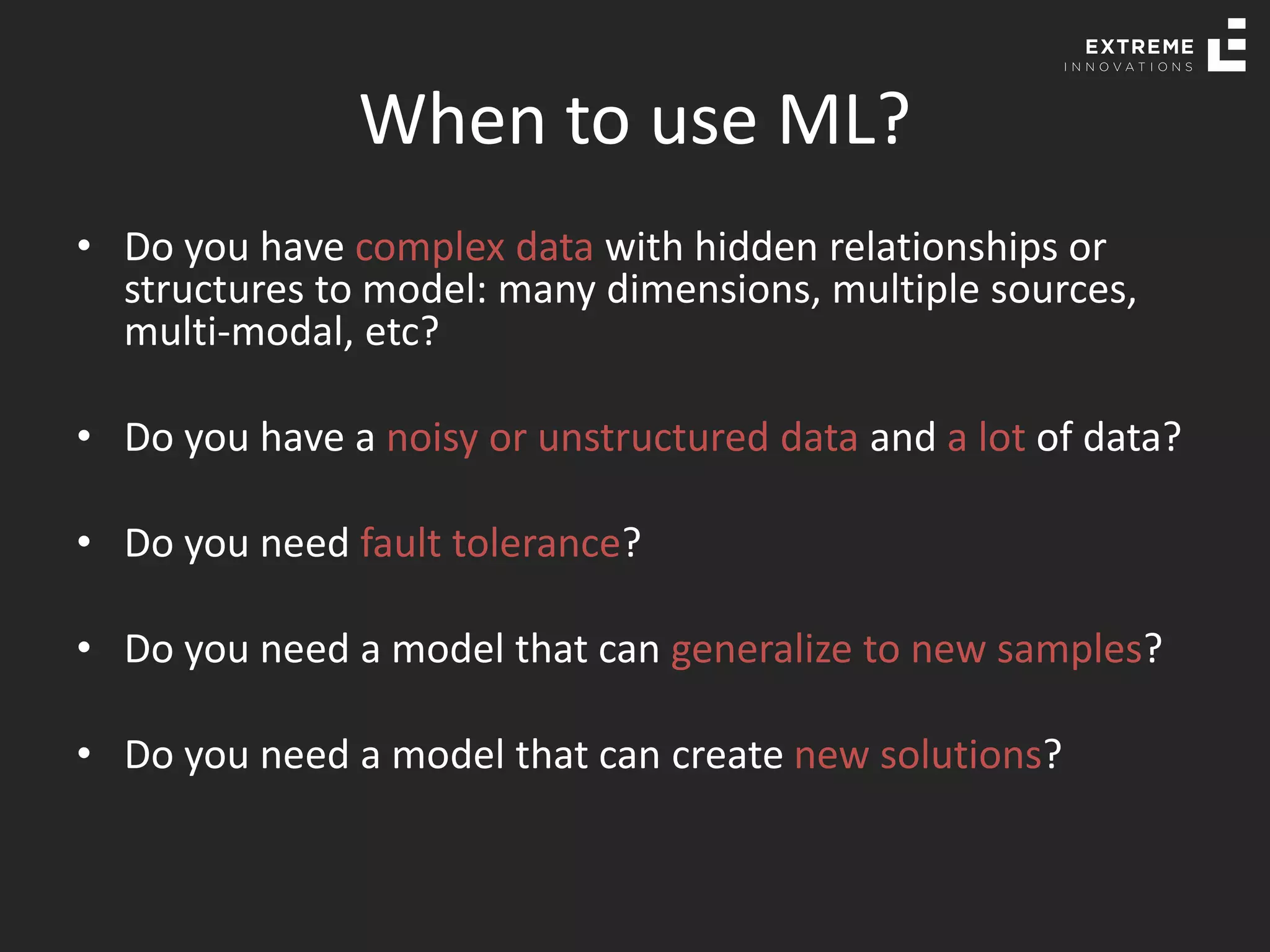
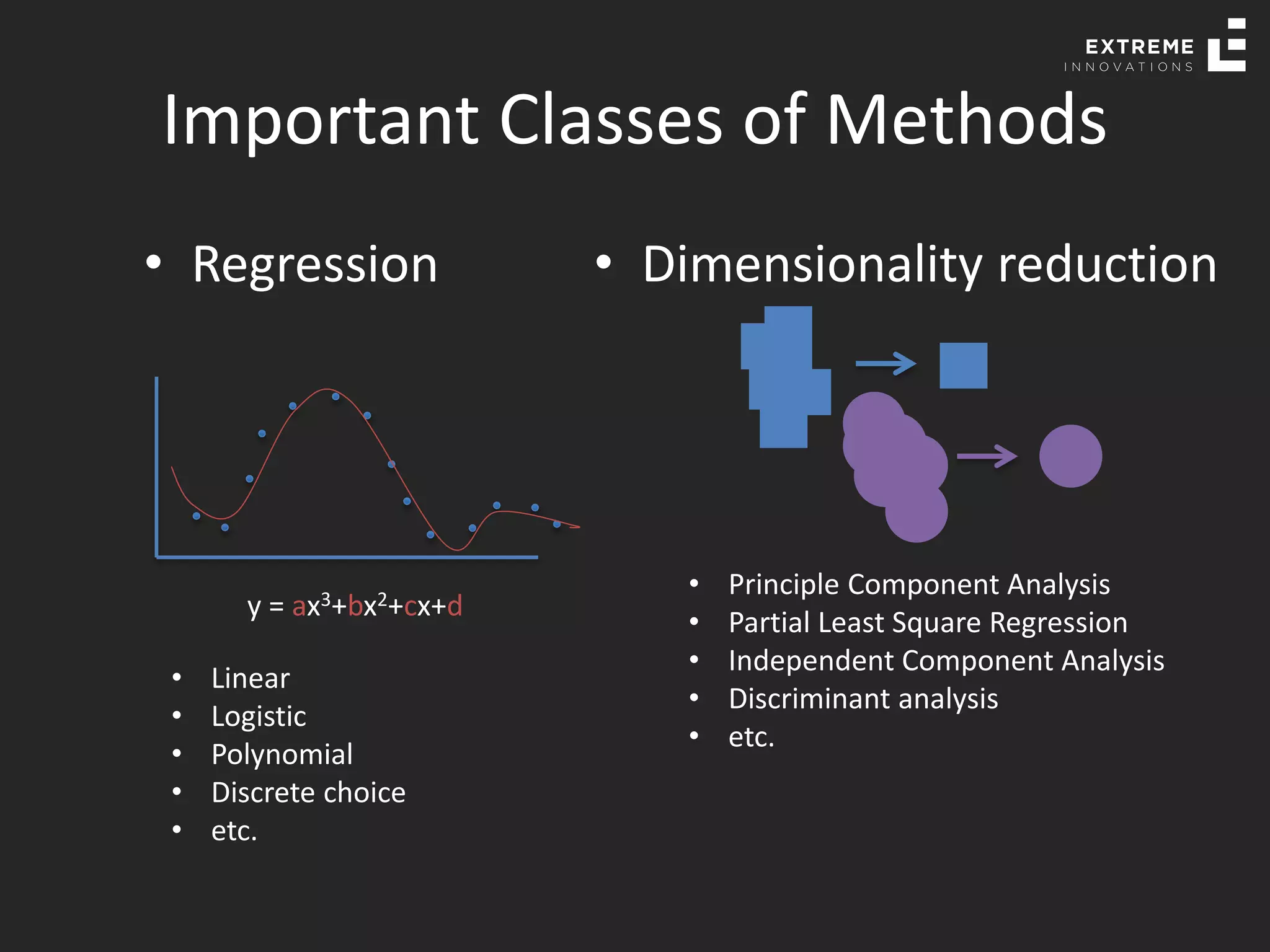
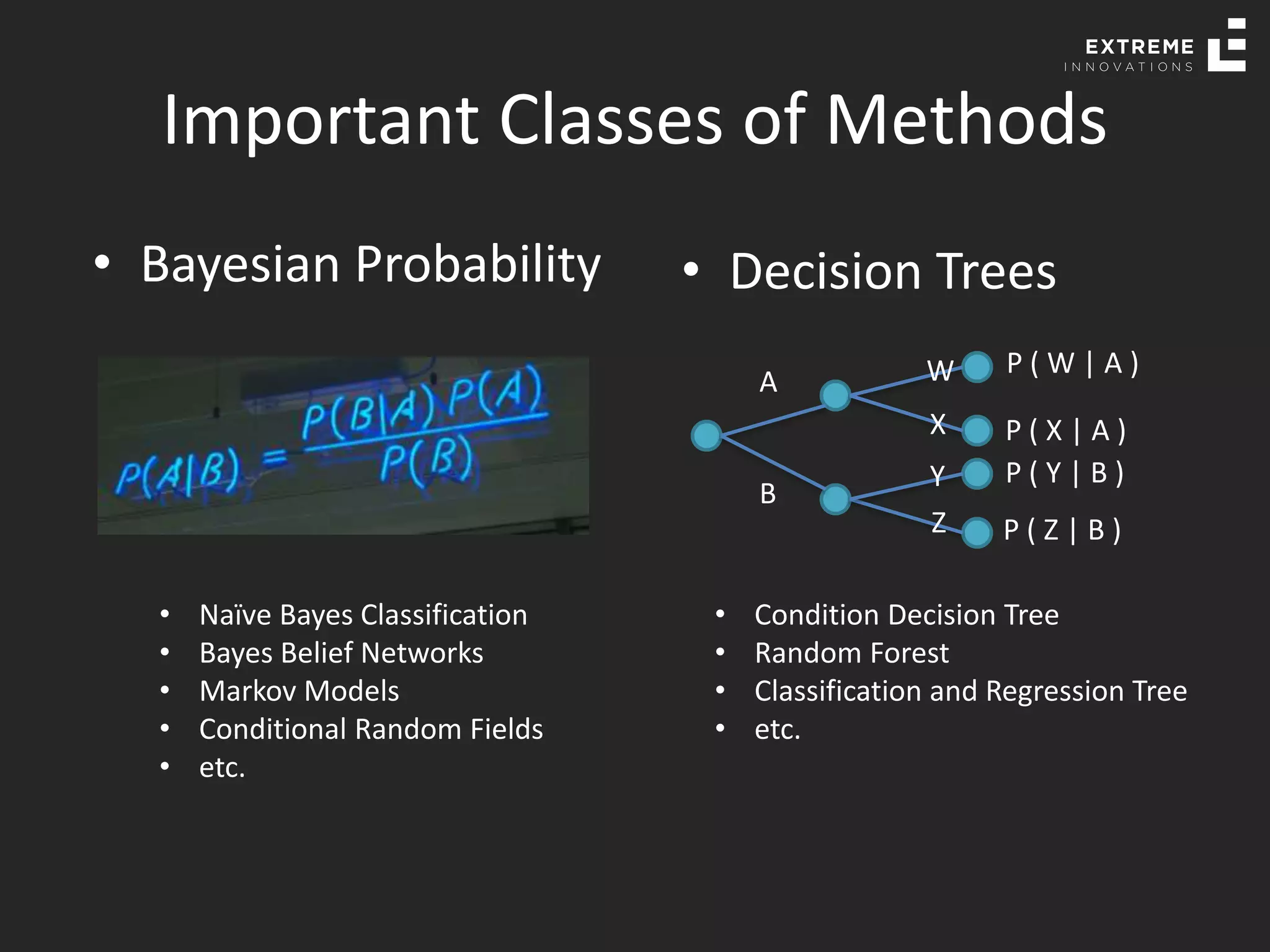
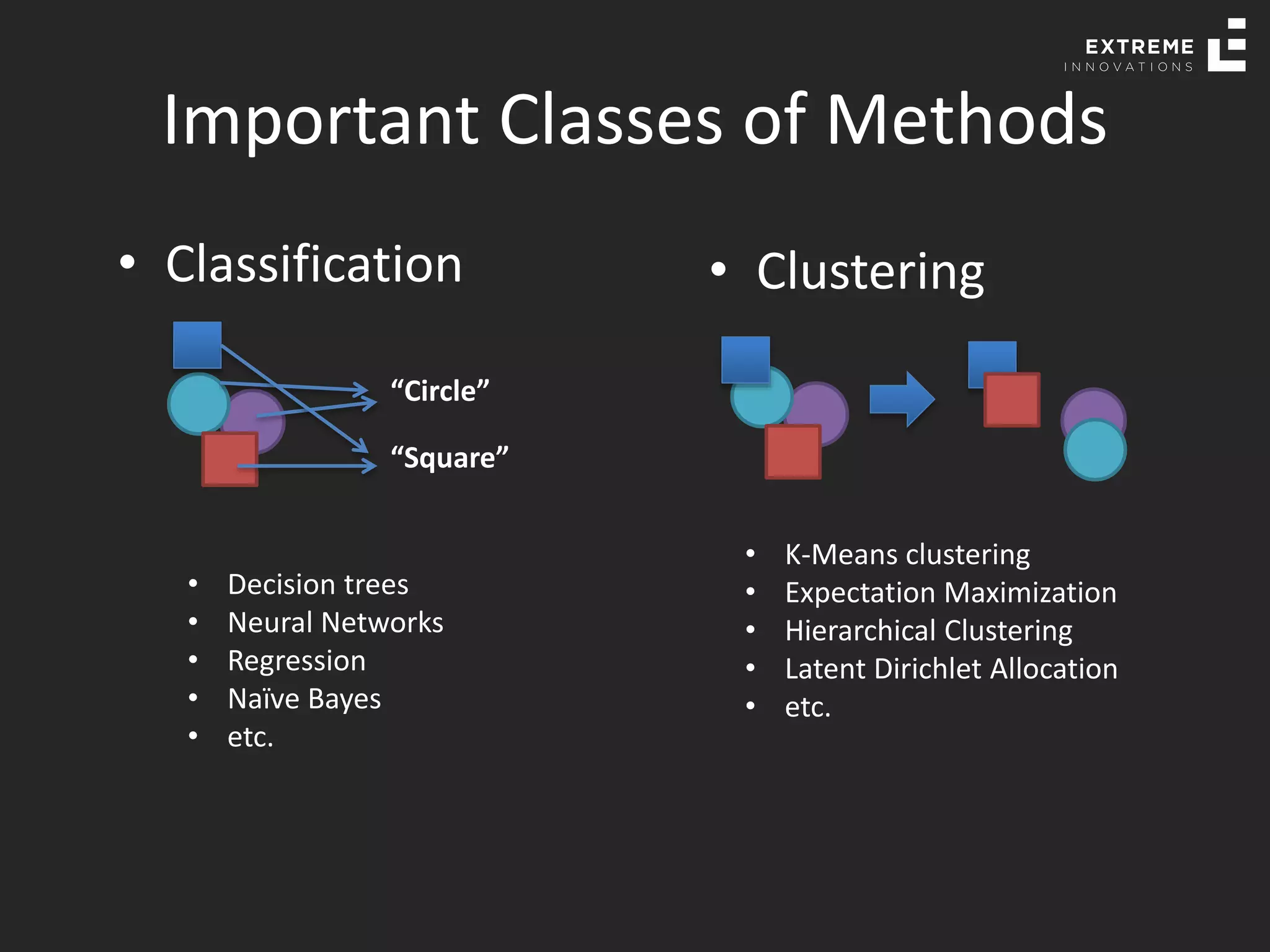
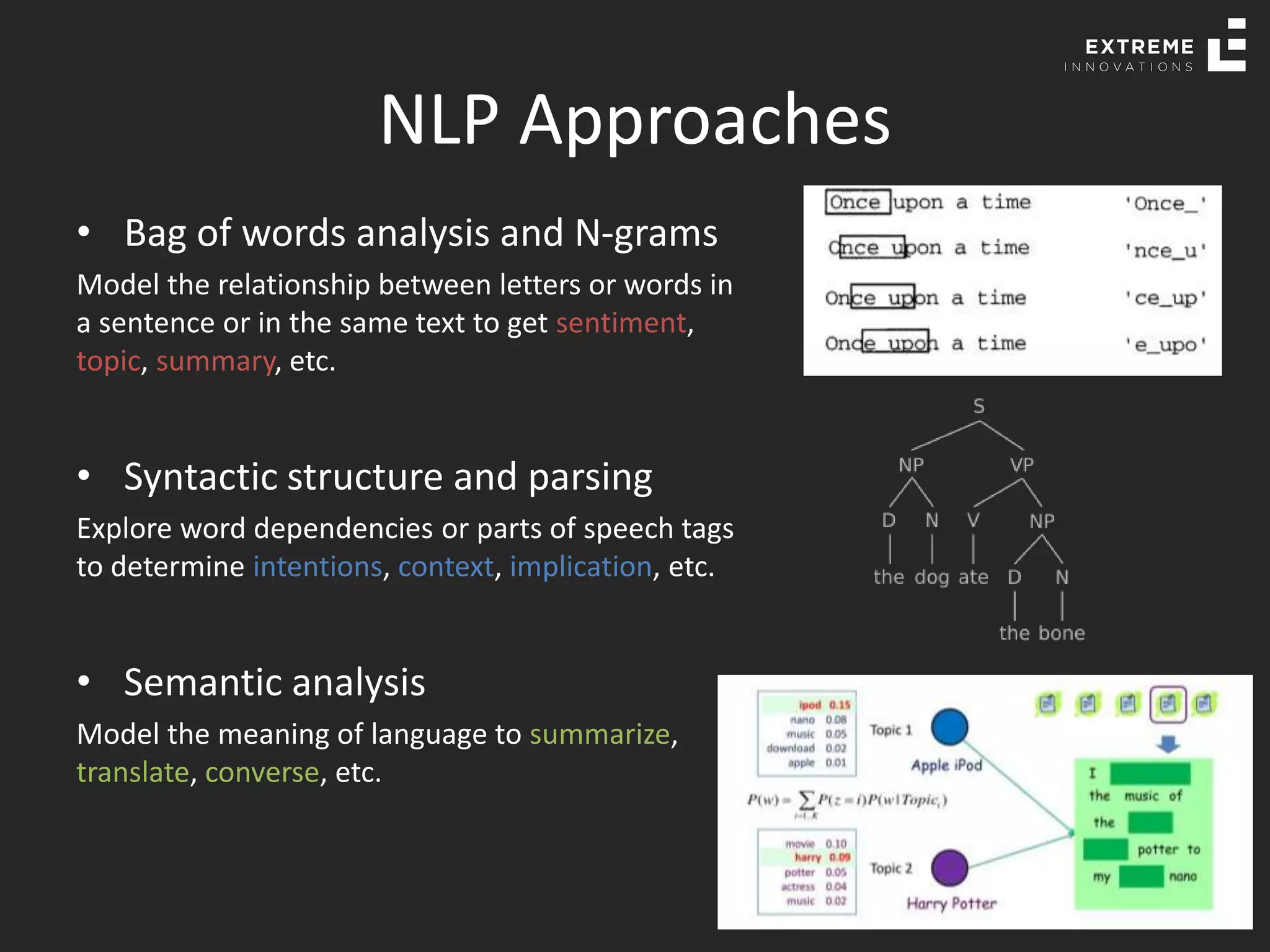
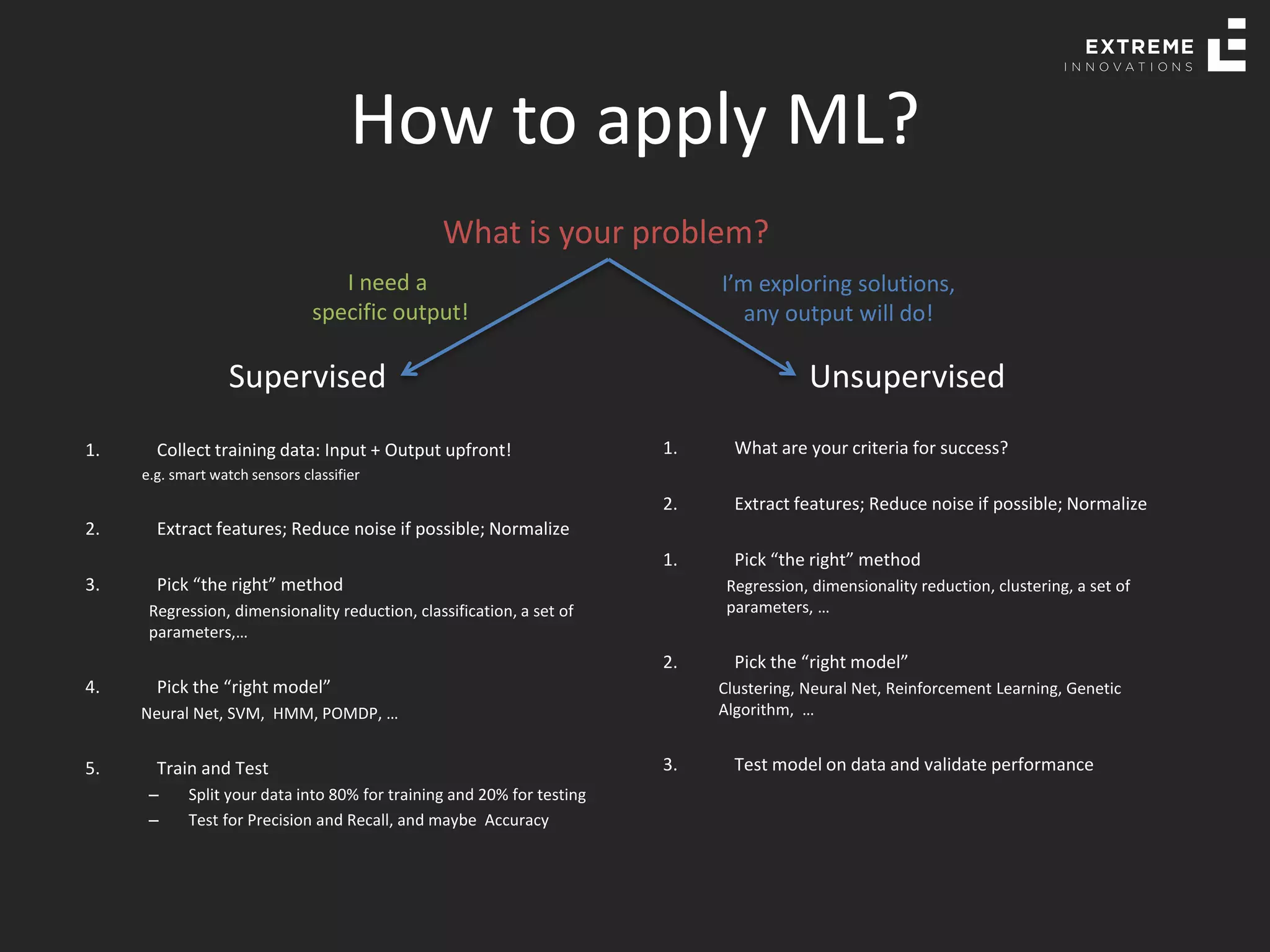
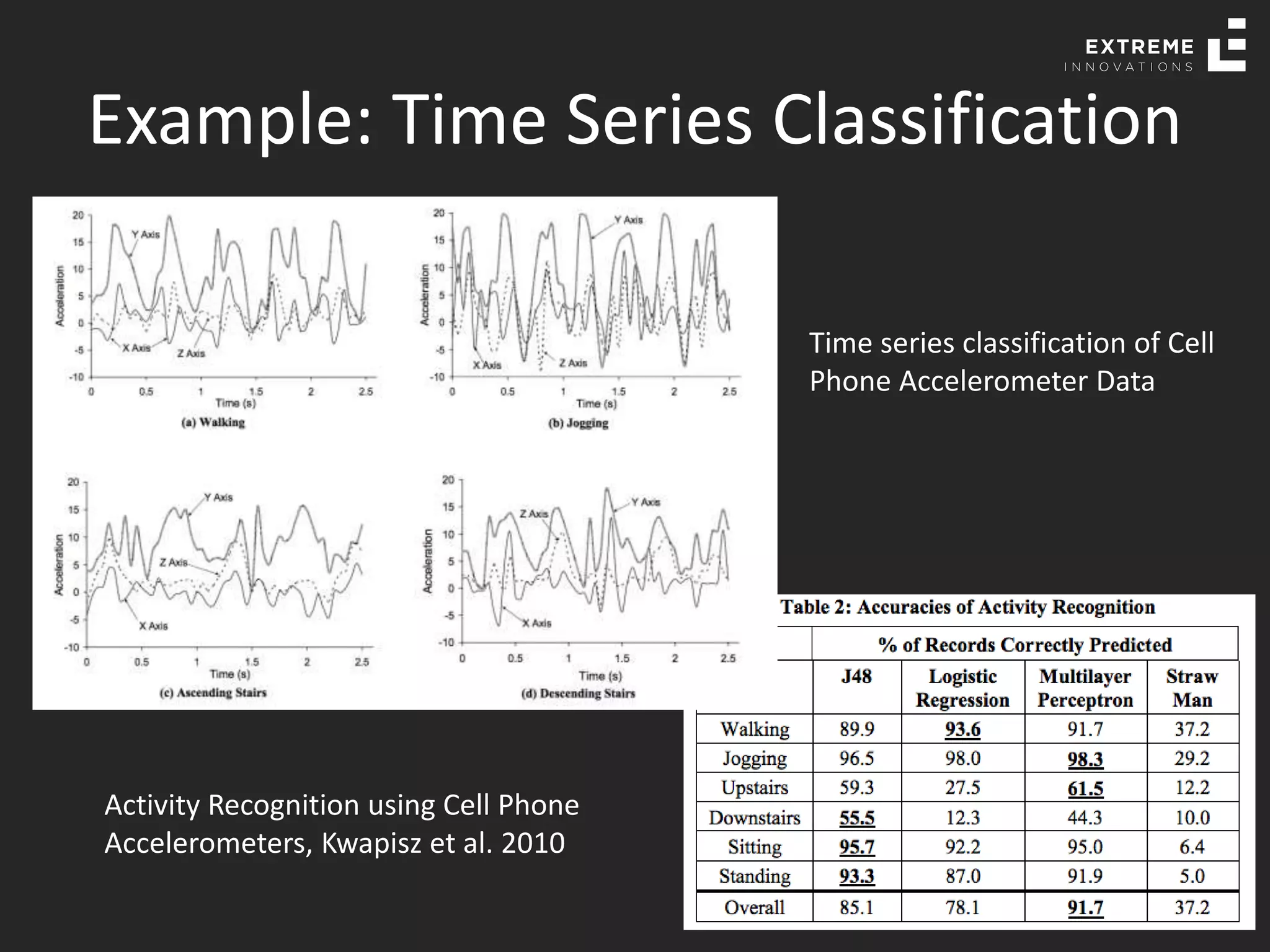
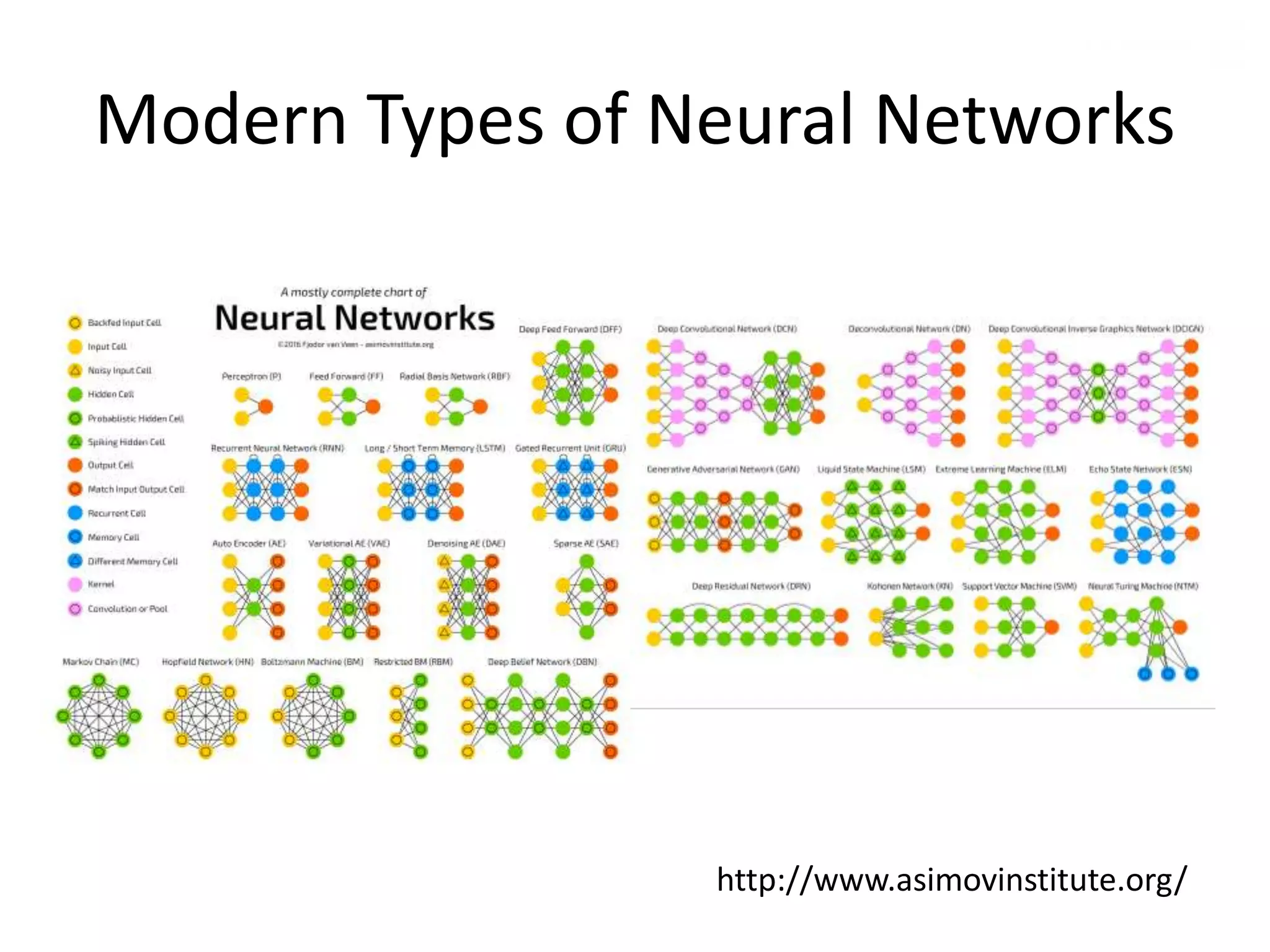
The document outlines the history and evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP), highlighting key developments and notable models from the 1930s to present. It discusses various learning methods, including supervised and unsupervised learning, and explores important AI methods like regression, clustering, and neural networks. Additionally, it touches upon future trends in AI, including generative AI and neuromorphic computing.