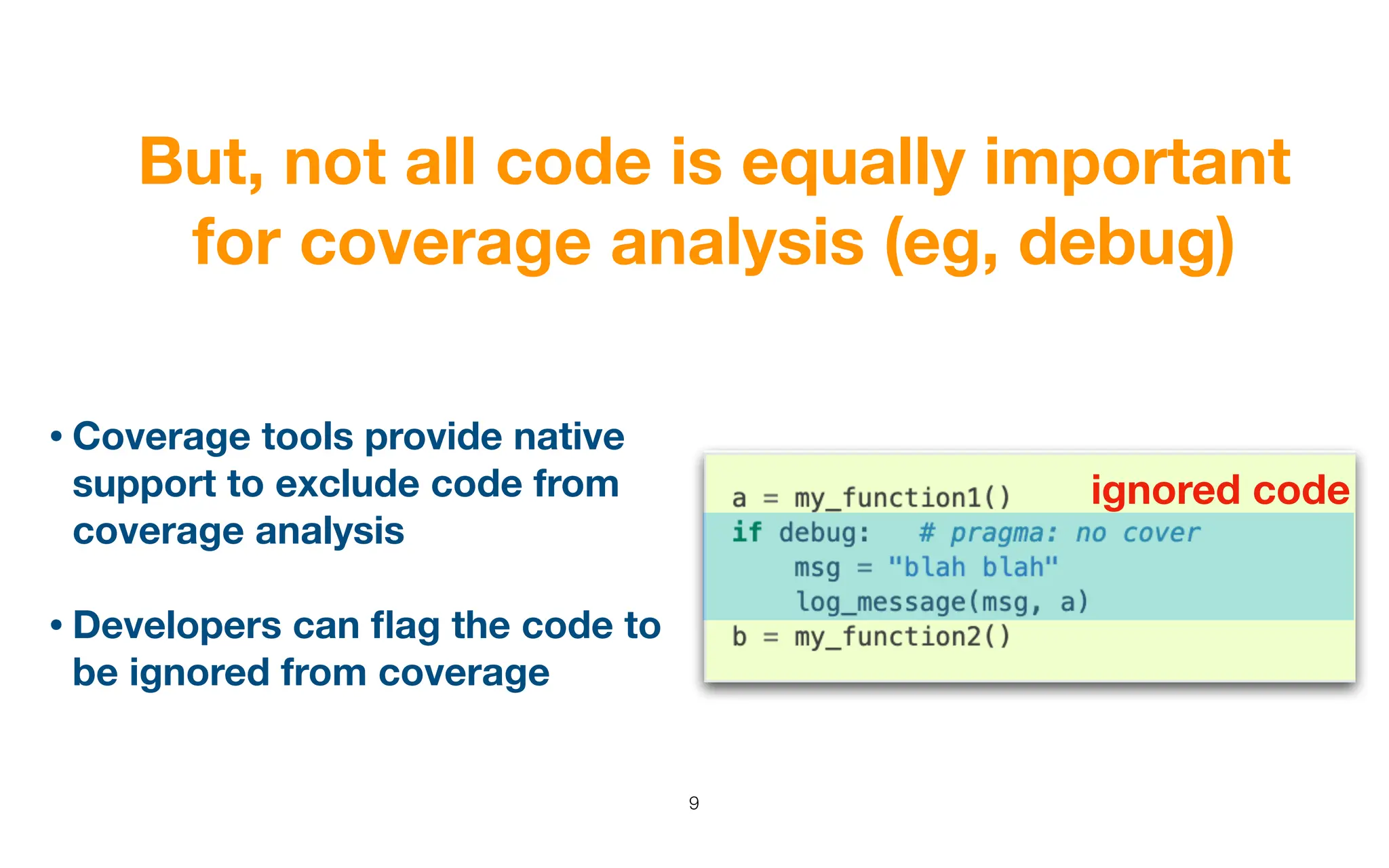
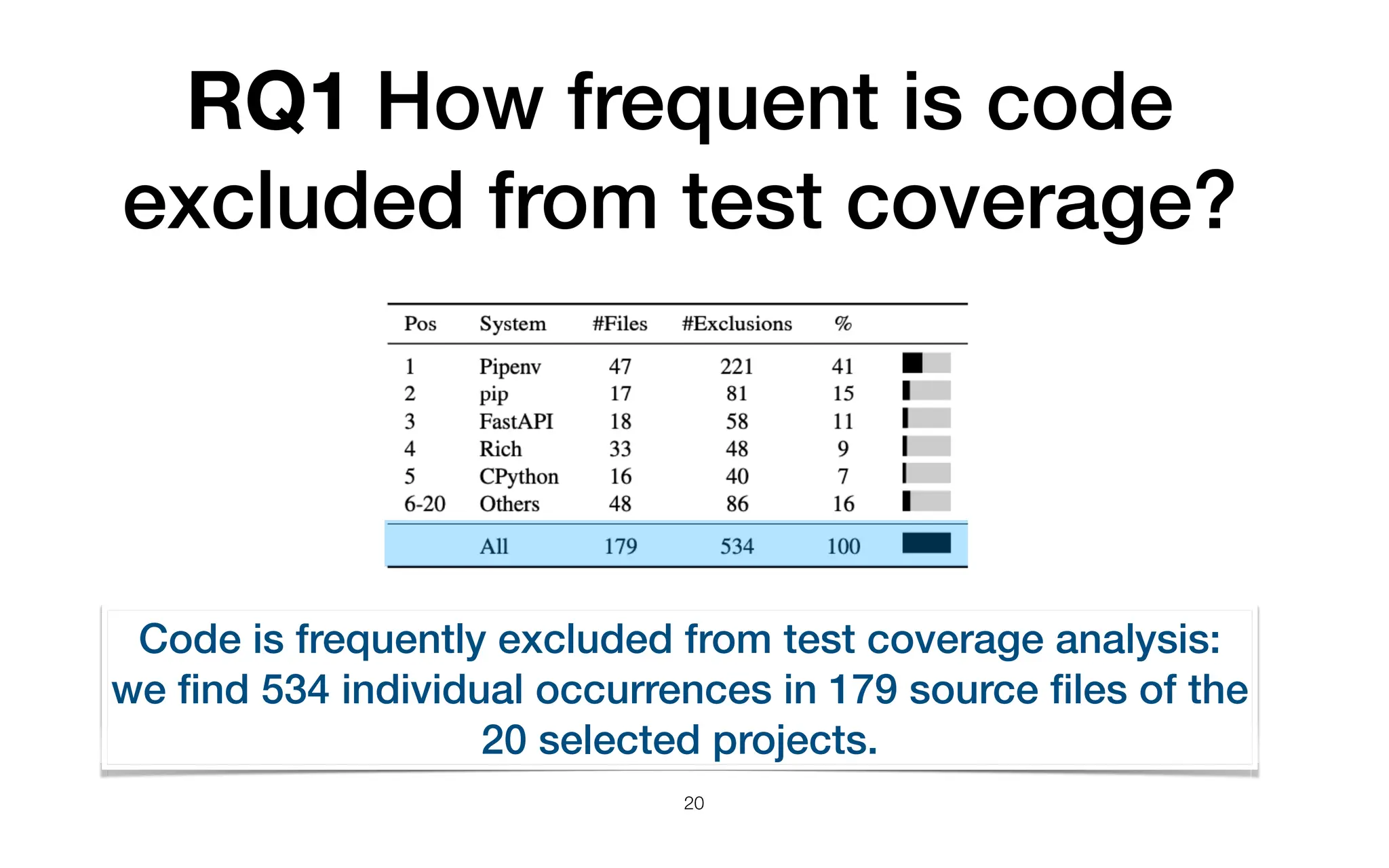
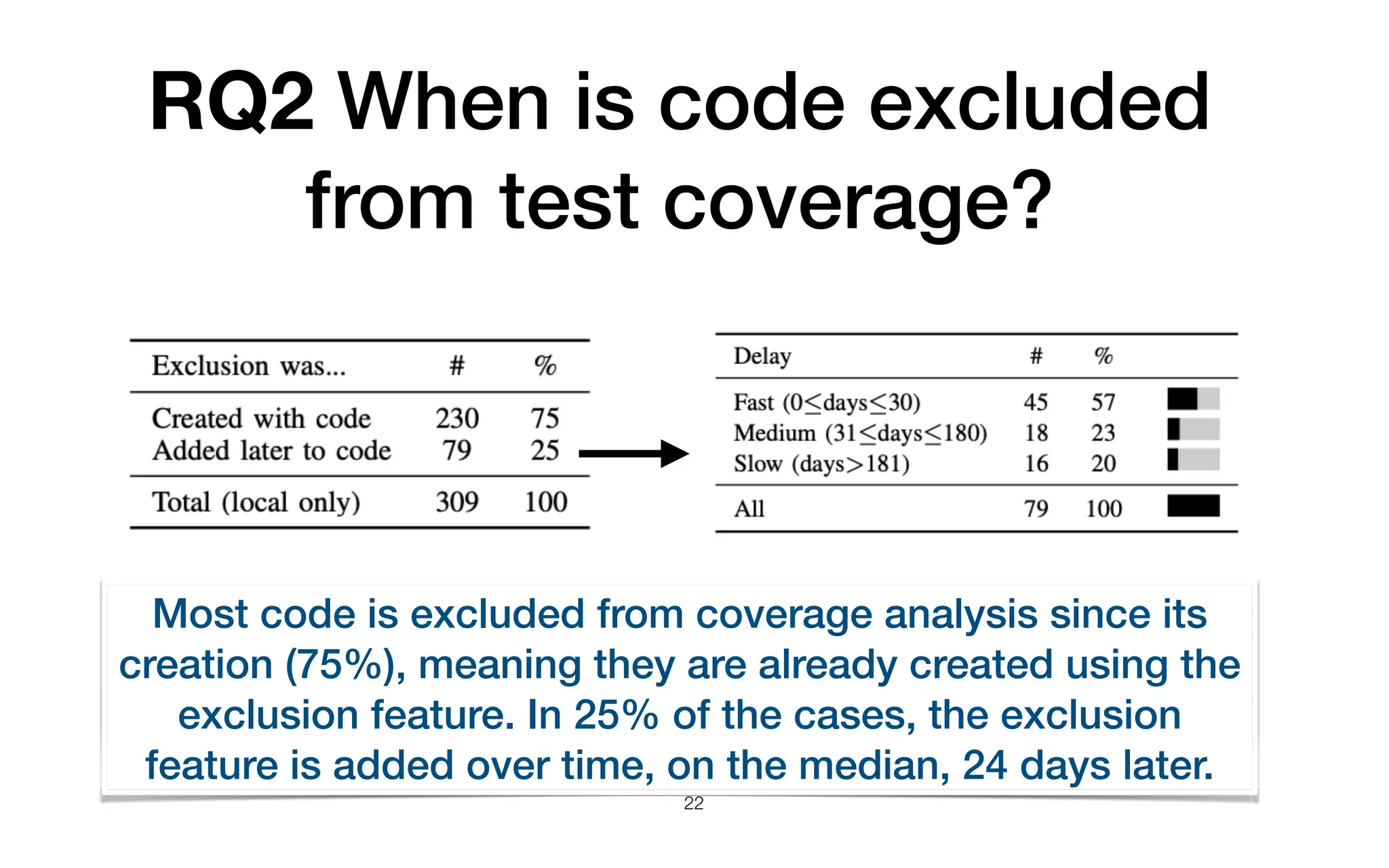
The document analyzes code exclusion from test coverage, revealing that code is frequently omitted for reasons including complexity, debugging, or being non-runnable. A study of 68 popular Python projects found that 36% involved coverage exclusion, mainly in conditional and exception handling code. The findings suggest a need for better practices and guidelines regarding coverage exclusion to ensure accurate test assessments.
























![RQ4 Why is code excluded
from test coverage?
28
Untested code: “Bring coverage up to
100%: Just adds a couple ‘# pragma no-
cover’ comments to skip coverage on
lines that already weren’t covered.”
Complexity: “Adds pragma: no
cover to the recursive functions”.
Deprecated code: “Add pragma no
cover to deprecated flags check”
Parallelism: “very rare multi-thread
only event [...] Disable test cover”
Trivial/Safe Code:“Add some no-cover
pragmas on functions that don’t need tests”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msr2021-test-coverage-240725130610-f971875b/75/What-Code-Is-Deliberately-Excluded-from-Test-Coverage-and-Why-MSR-2021-28-2048.jpg)
![RQ4 Why is code excluded
from test coverage?
29
Mostly because it is already untested (22%), low-level (20%), or
complex (15%). Other rationales are related to deprecated/legacy
code, parallelism, trivial/safe code, and non-determinism.
Untested code: “Bring coverage up to
100%: Just adds a couple ‘# pragma no-
cover’ comments to skip coverage on
lines that already weren’t covered.”
Complexity: “Adds pragma: no
cover to the recursive functions”.
Deprecated code: “Add pragma no
cover to deprecated flags check”
Parallelism: “very rare multi-thread
only event [...] Disable test cover”
Trivial/Safe Code:“Add some no-cover
pragmas on functions that don’t need tests”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msr2021-test-coverage-240725130610-f971875b/75/What-Code-Is-Deliberately-Excluded-from-Test-Coverage-and-Why-MSR-2021-29-2048.jpg)

