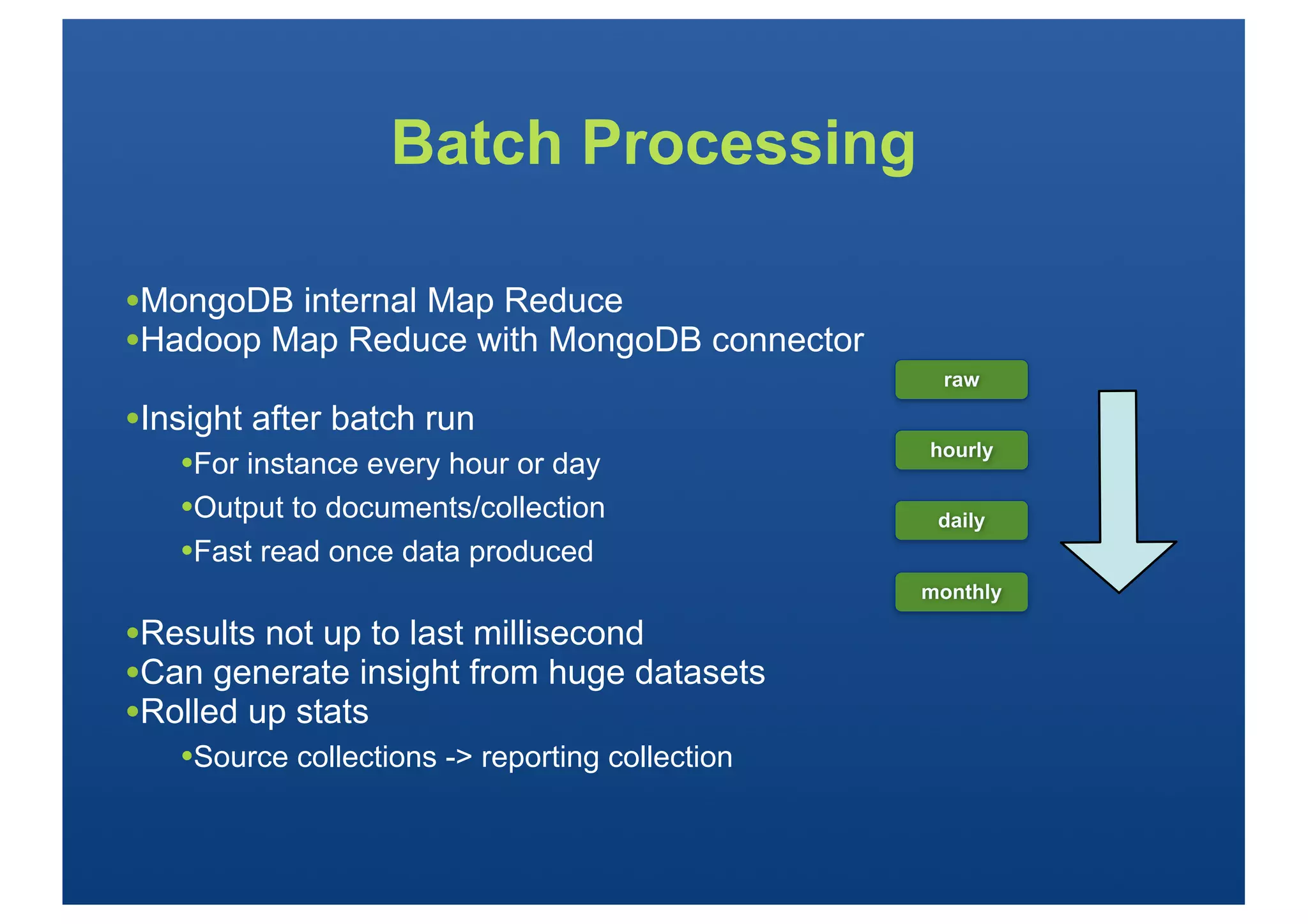
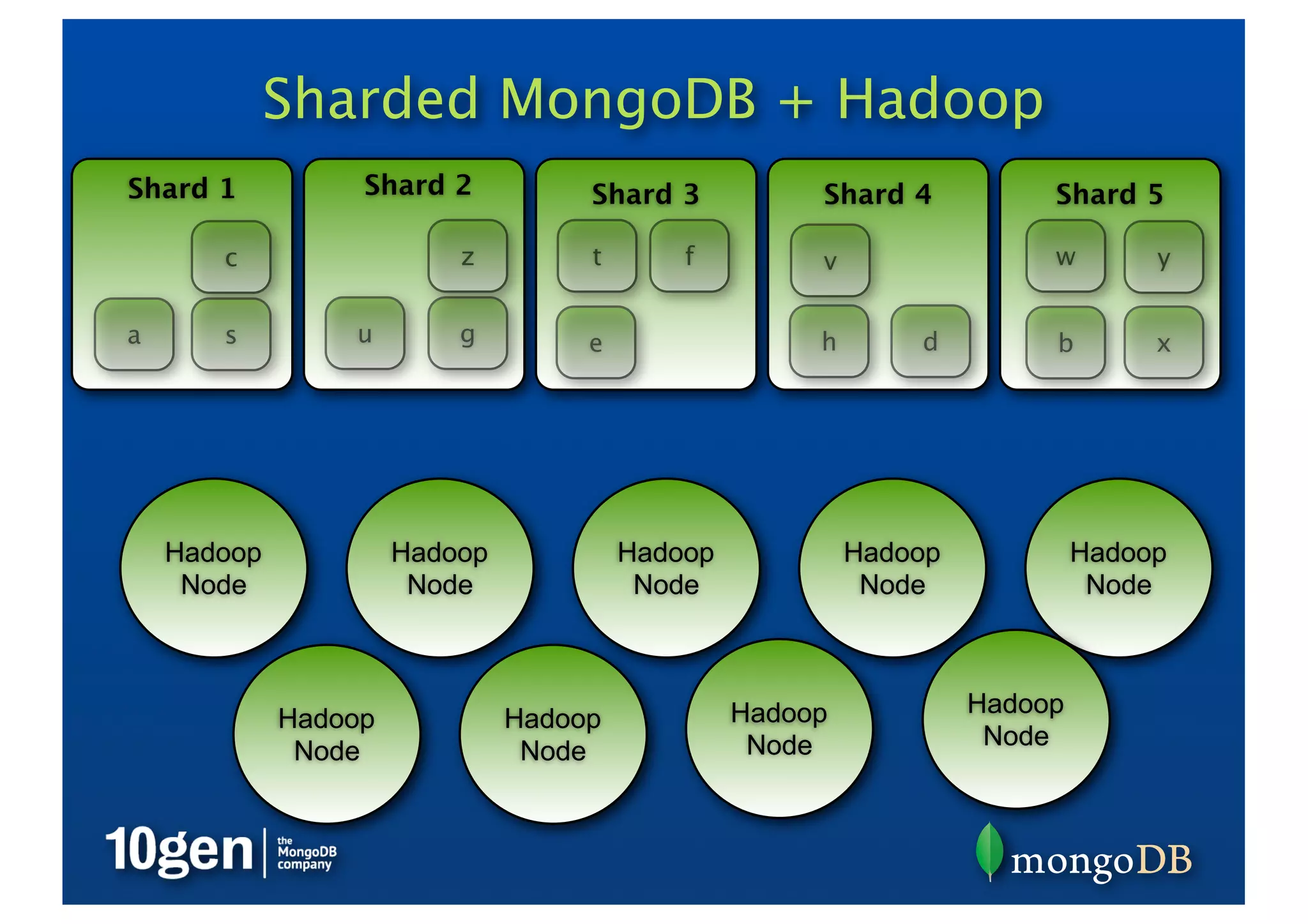
The webinar on managing real-time risk analytics with MongoDB will start at various global times and requires participants to have quality audio equipment and internet. Attendees can engage in a Q&A session, and a recording will be accessible post-event. The document discusses MongoDB's features, use cases for risk analytics, and various methods for data aggregation, including the aggregation framework and Hadoop integration.








![Use Query Language
•Query across documents using MongoDB JSON query language
•Infer results in the application code.
•Dynamic - but what happens when we have 1 billion documents.
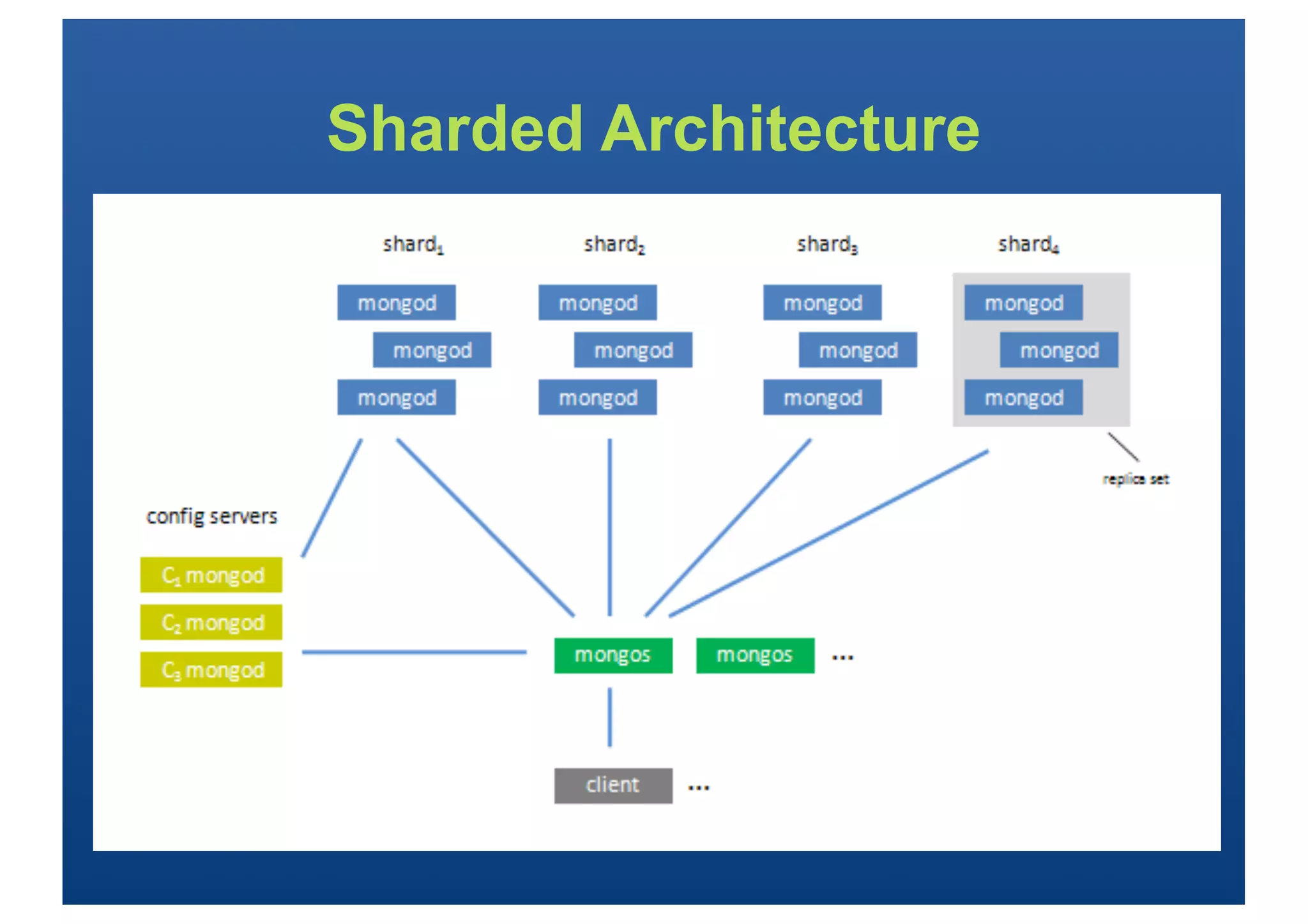
•Indexing strategy key
•var data = db.pl.find({ positionId: 1234 })[0]
{
"_id" : ObjectId("50990a10fd421cb025407cb1"),
"positionId" : 1234,
"security" : "ORCL",
"quantity" : 1000,
"price" : 30.23,
"currency" : "USD"
}
data.price * data.quantity = 30230.00](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1211-fs-managingrealtimeriskanalyticswithmongodb-121106085517-phpapp01/75/Webinar-Managing-Real-Time-Risk-Analytics-with-MongoDB-12-2048.jpg)
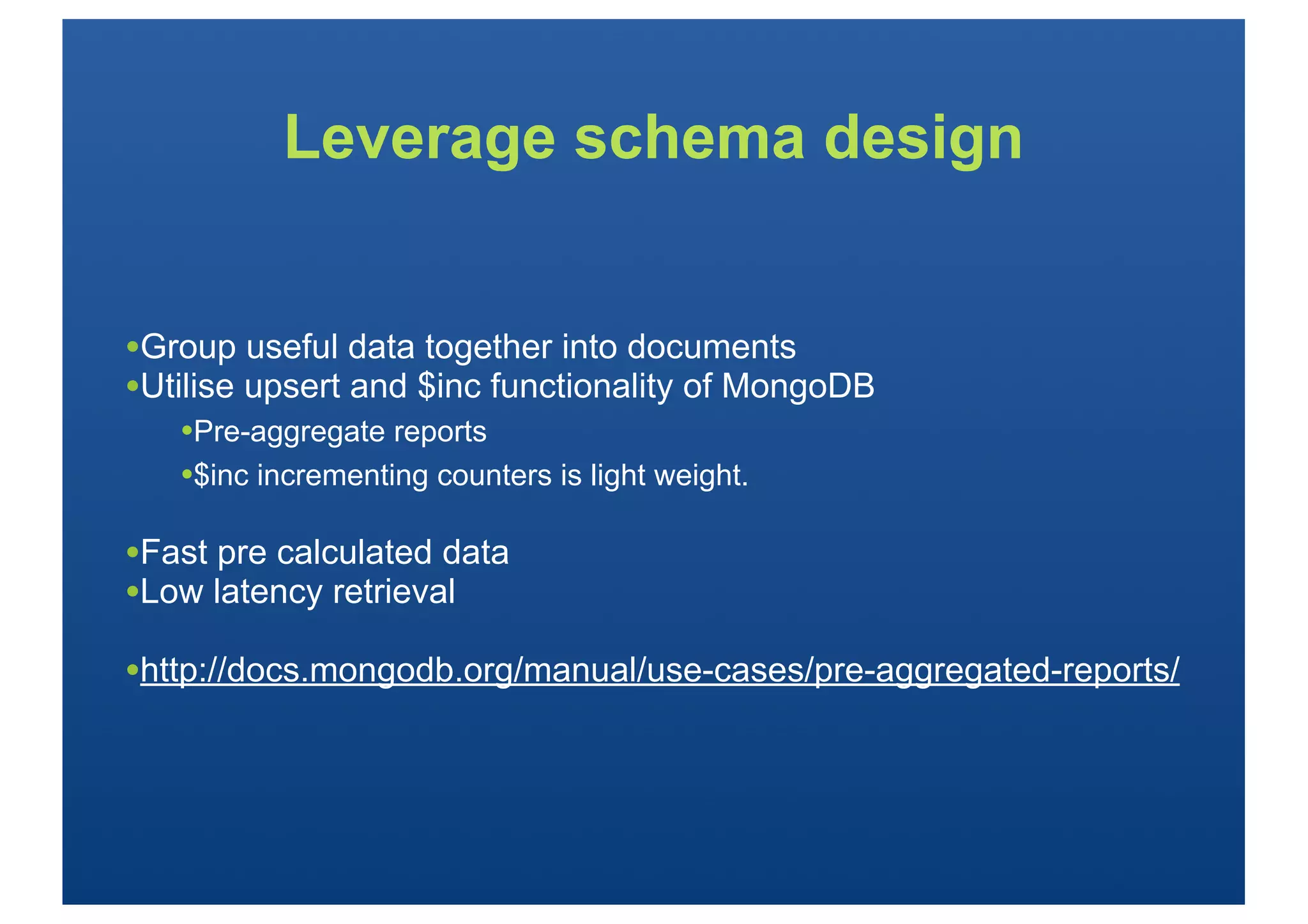
![Aggregation Framework
•Much simpler and faster than MongoDB map reduce
•Replaces common MR use cases in MongoDB
•Native operators in the MongoDB core
db.pl.aggregate([
! {$match:{"clientId" : 4321}},
{ $project :
{ value :
{ $multiply:["$quantity", "$price"] }
}
}
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1211-fs-managingrealtimeriskanalyticswithmongodb-121106085517-phpapp01/75/Webinar-Managing-Real-Time-Risk-Analytics-with-MongoDB-15-2048.jpg)


