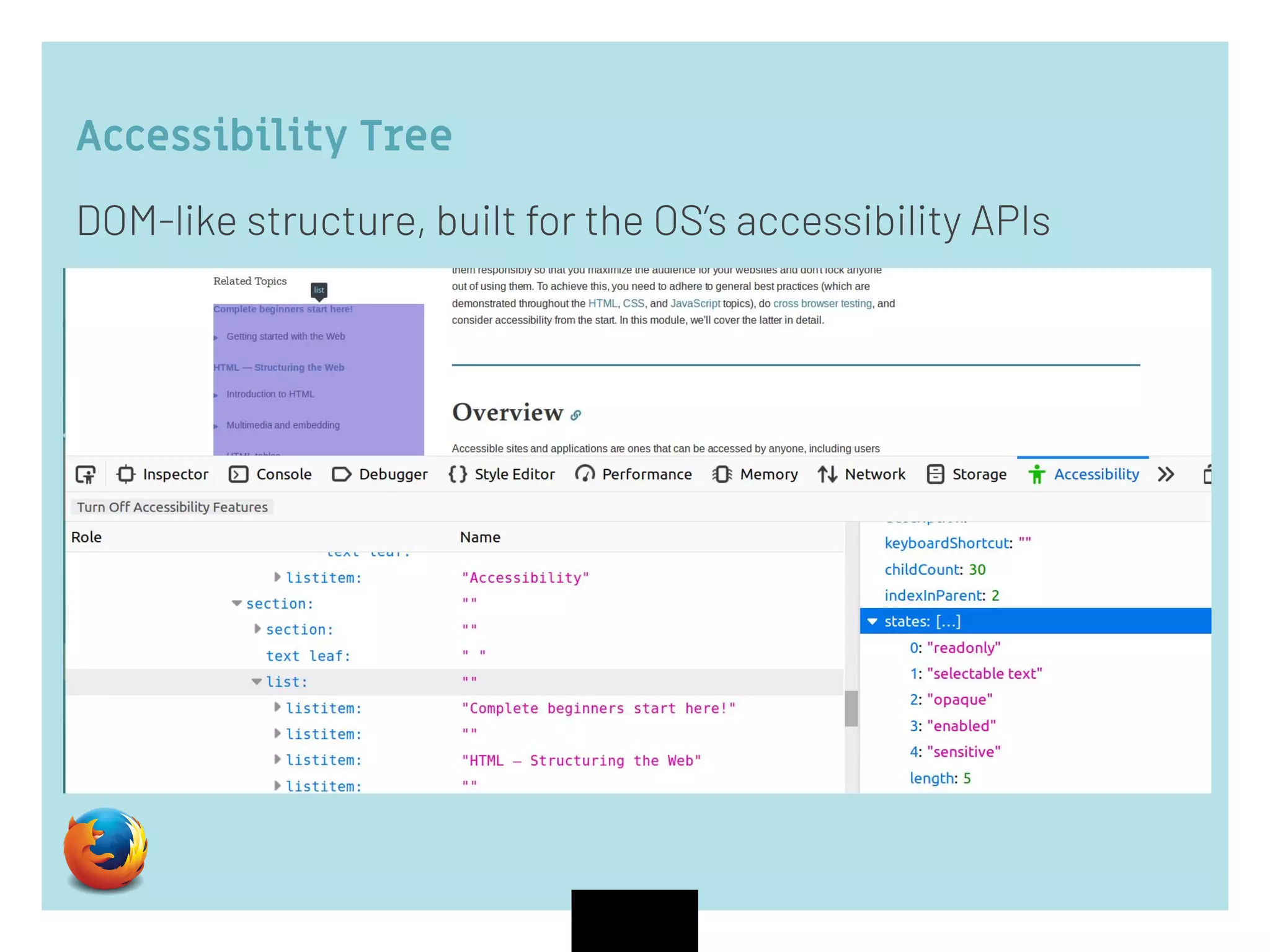
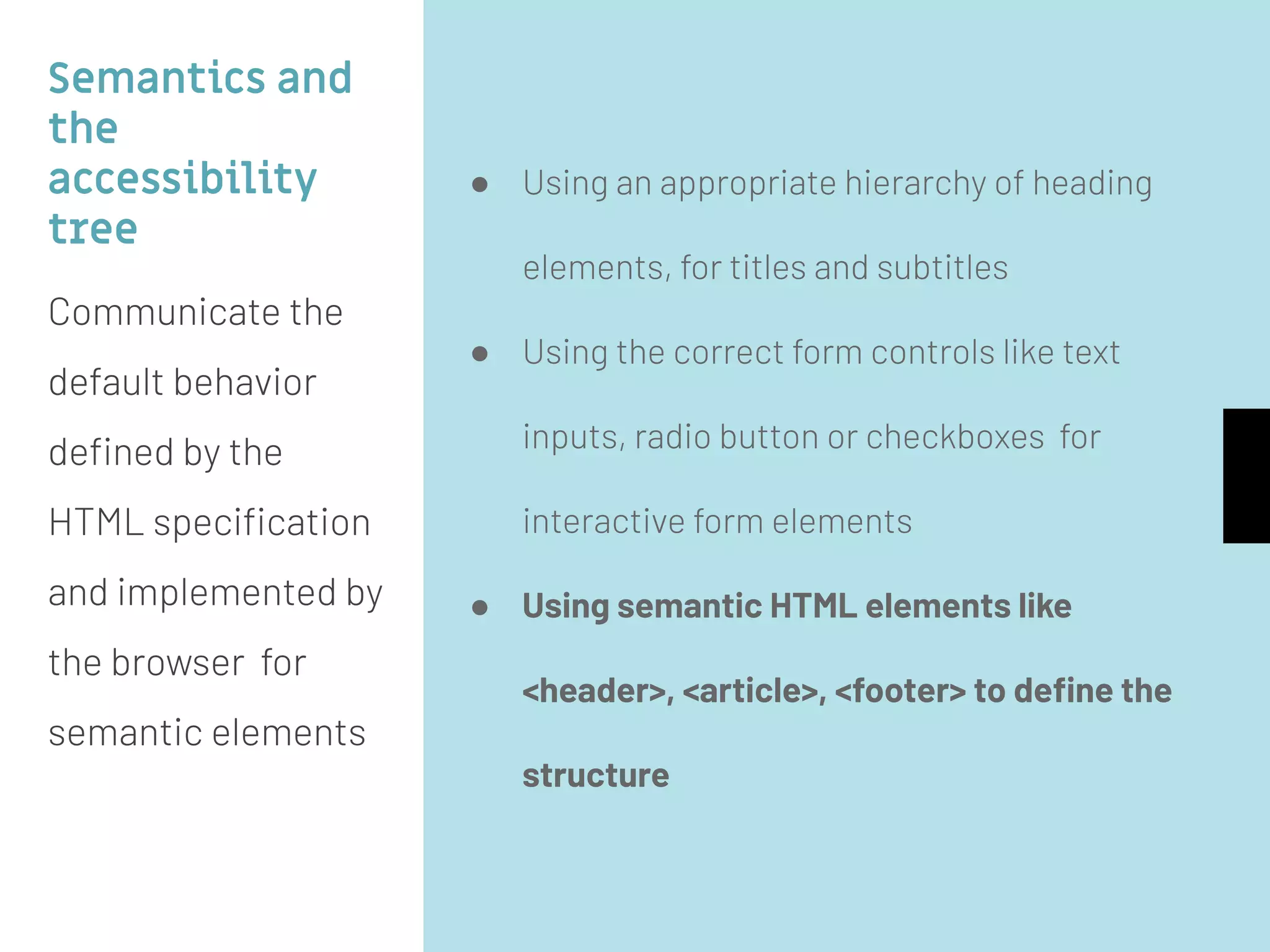
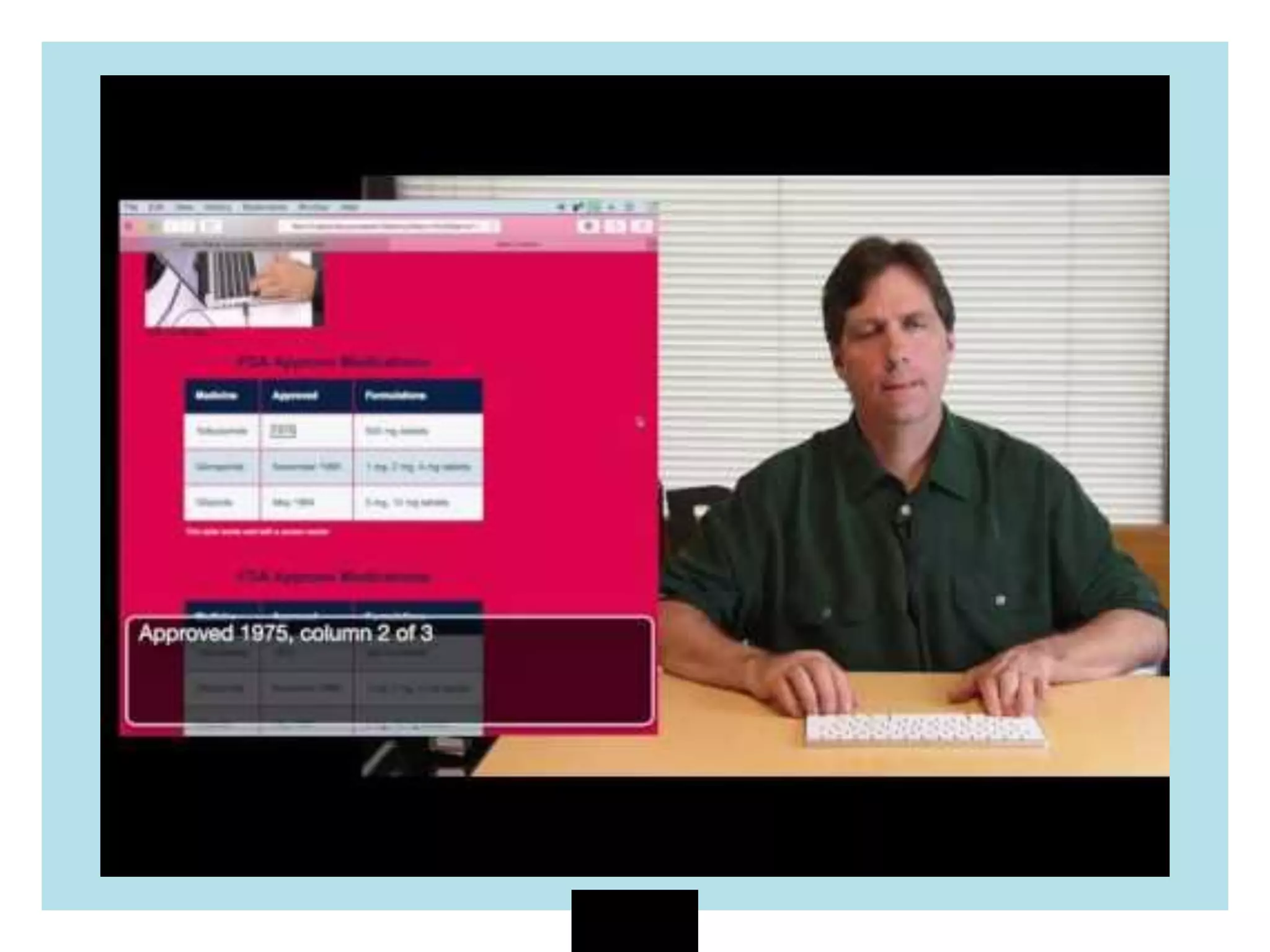
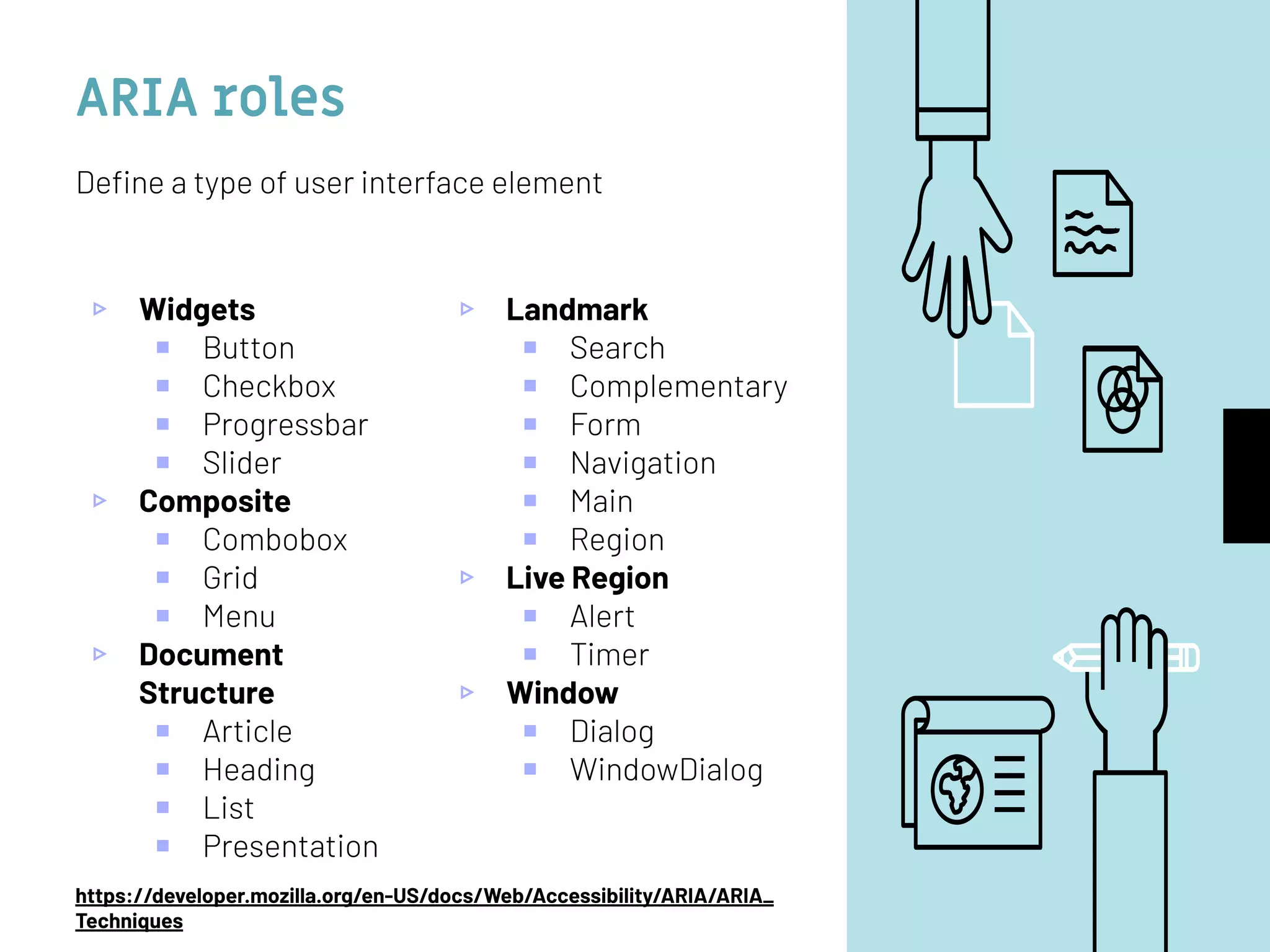
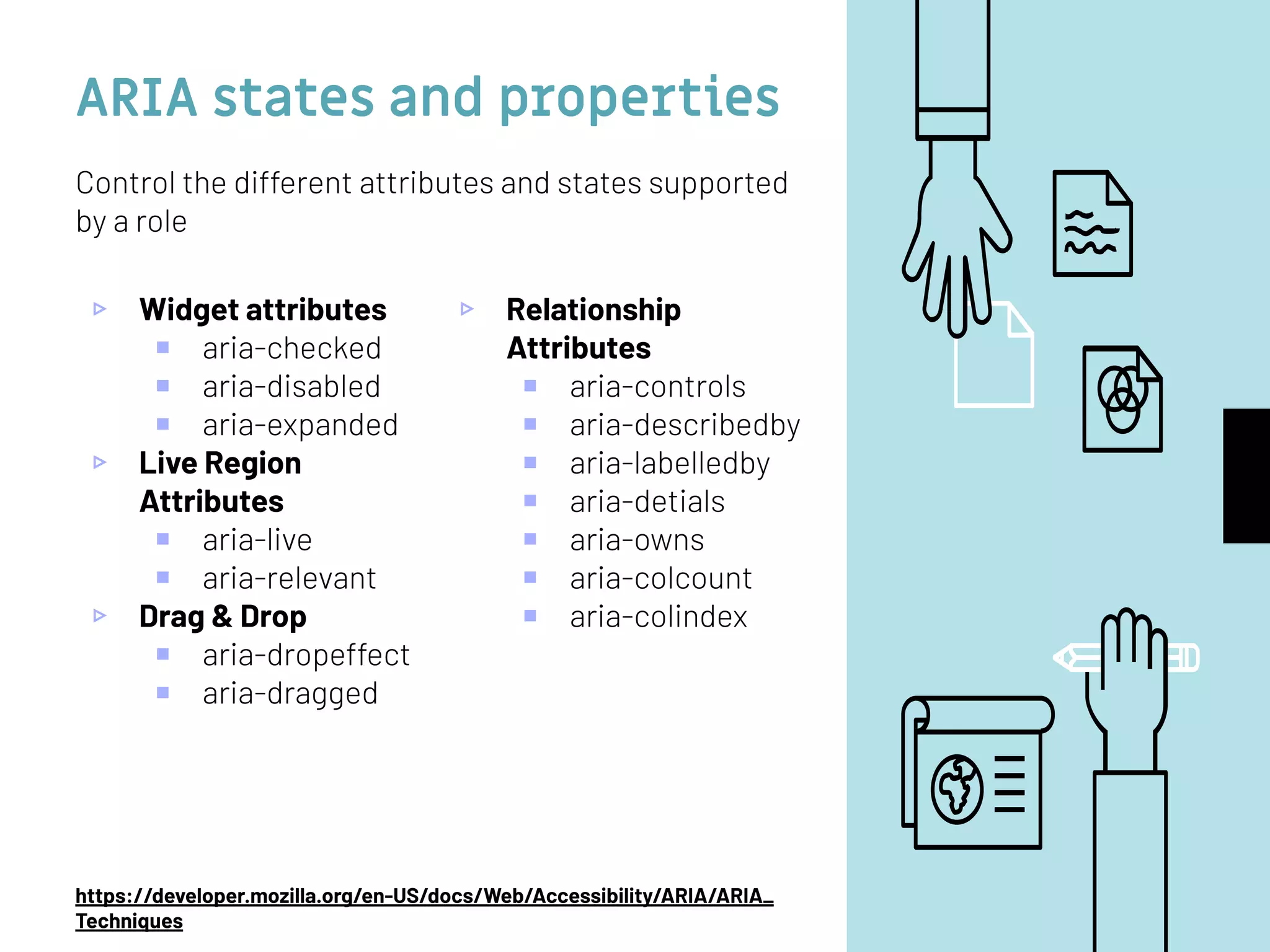
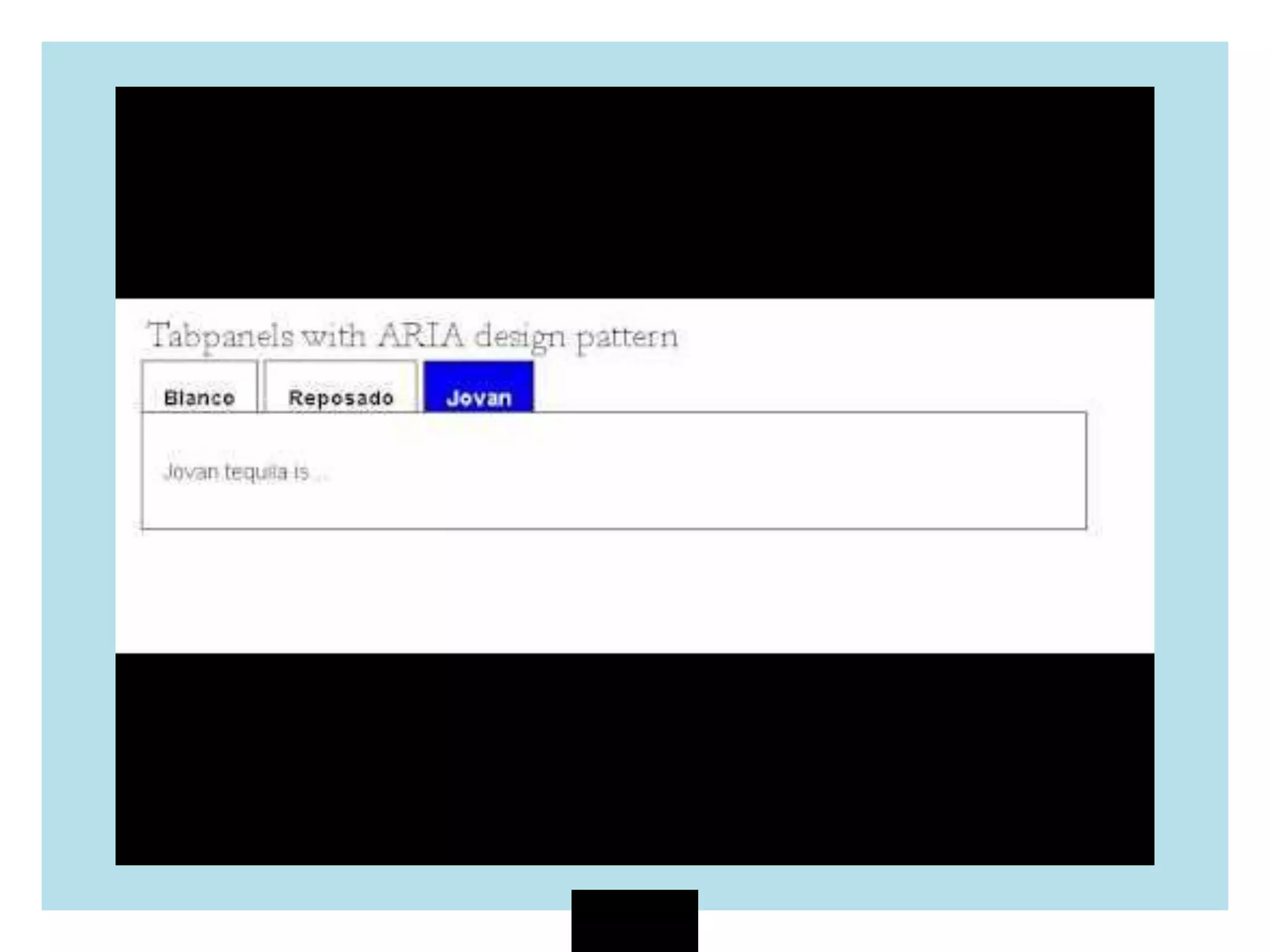
The document discusses web accessibility and the importance of making digital spaces usable for individuals with disabilities, highlighting the World Health Organization's report of 1 billion people affected. It outlines the WCAG 2.1 guidelines, including the foundational POUR principles (Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, Robust), and emphasizes the role of semantic HTML and ARIA in enhancing accessibility. Additionally, it lists testing tools and learning resources for improving web accessibility, advocating for an inclusive digital environment.