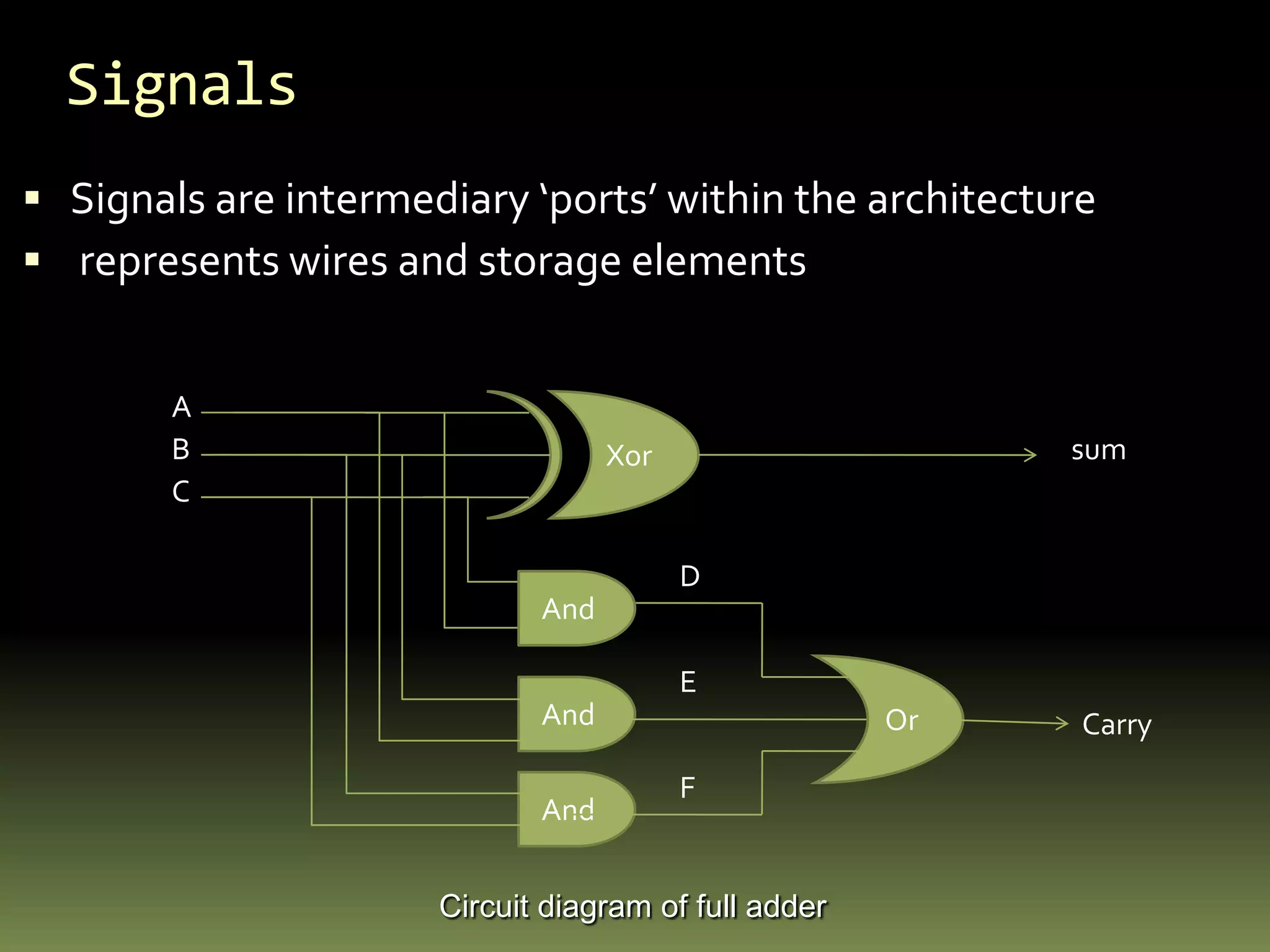
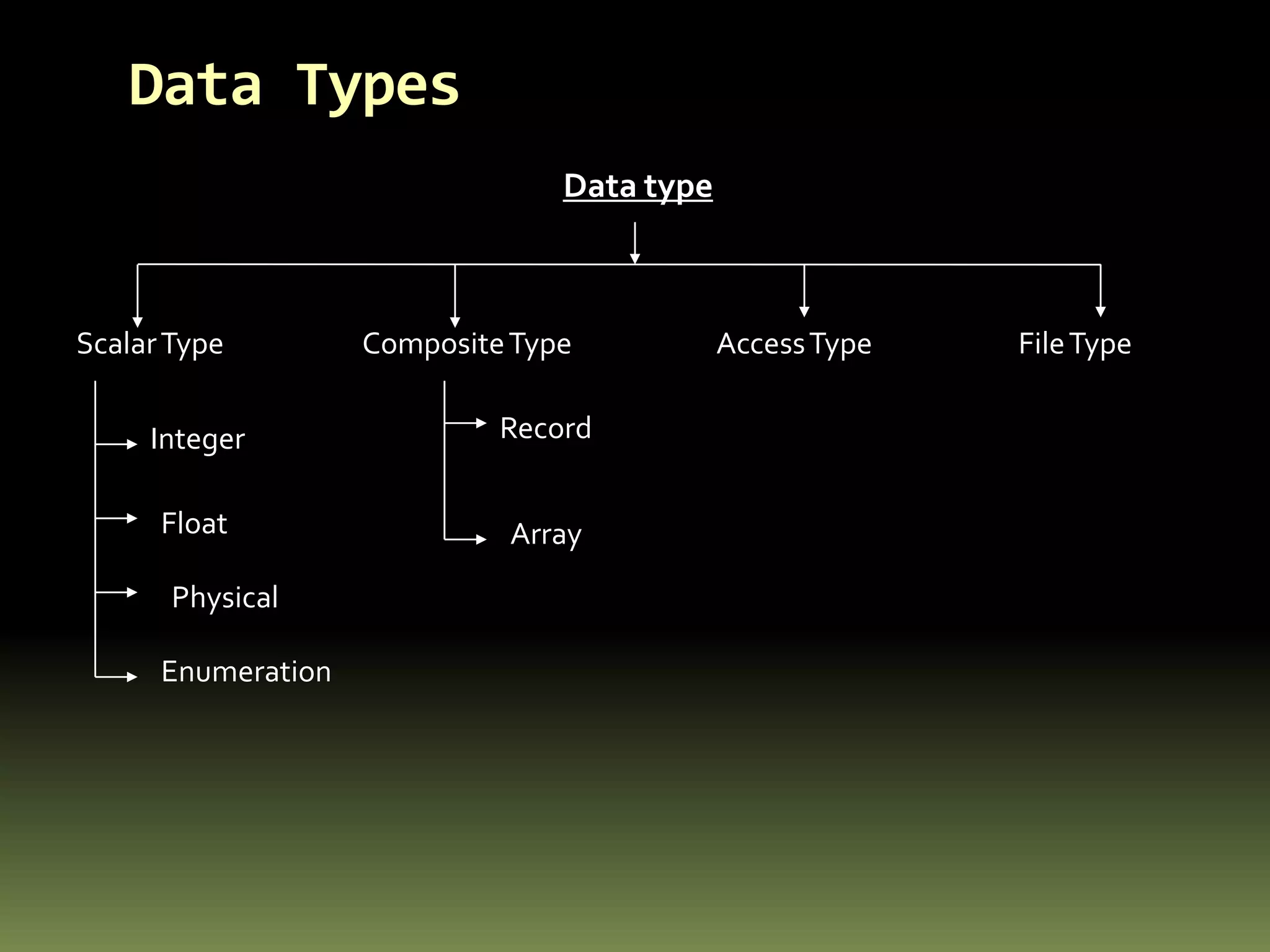
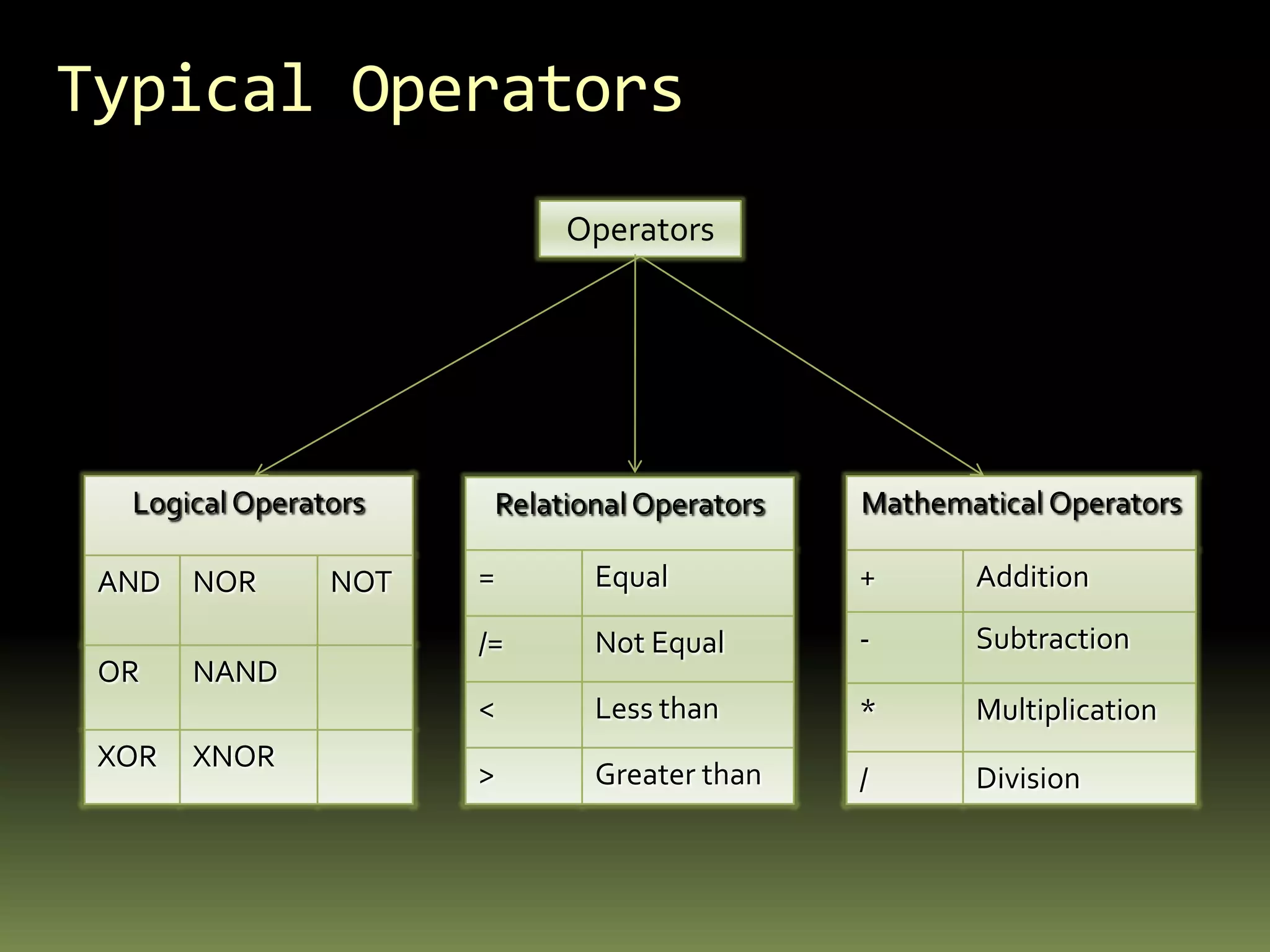
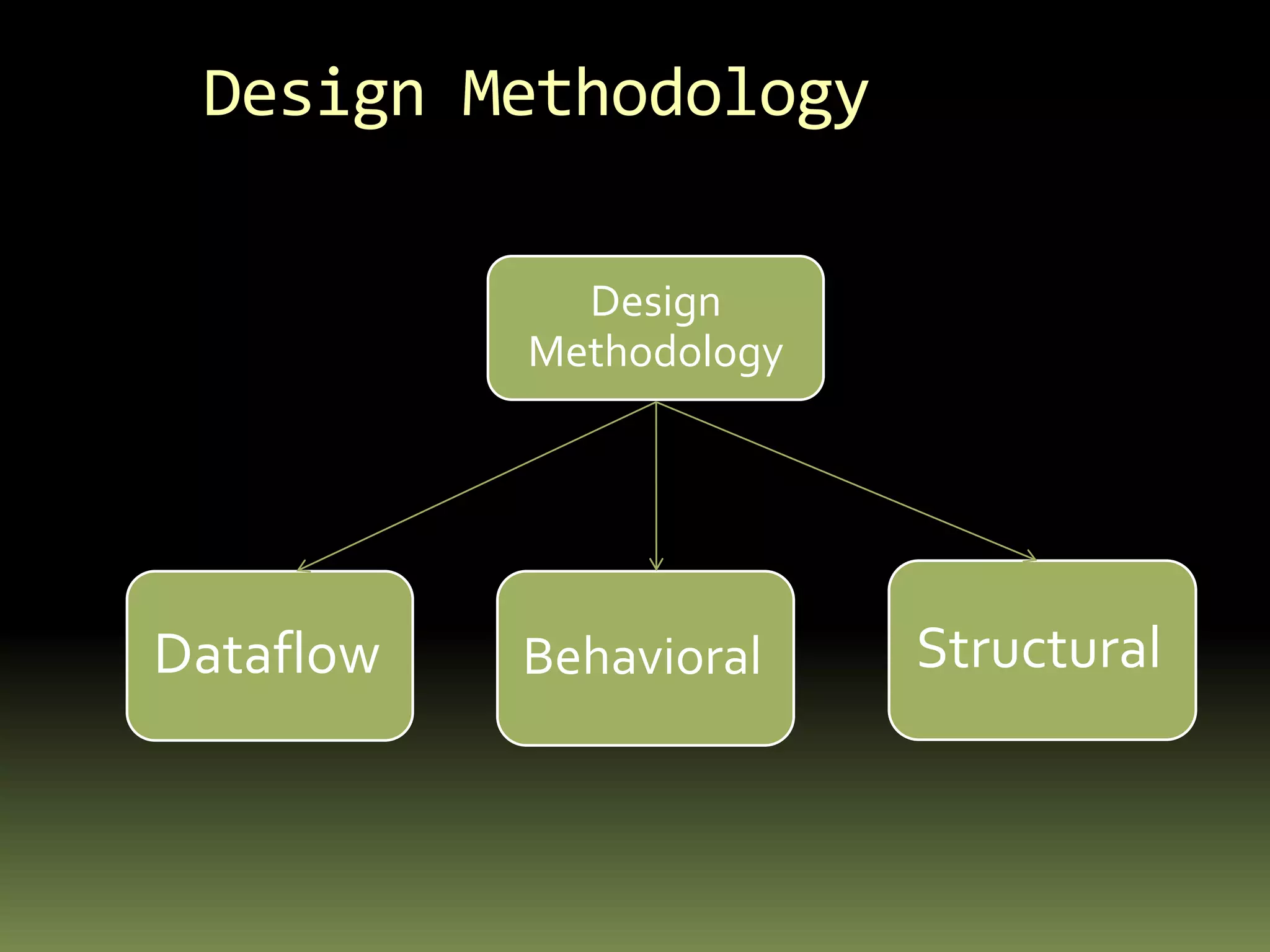
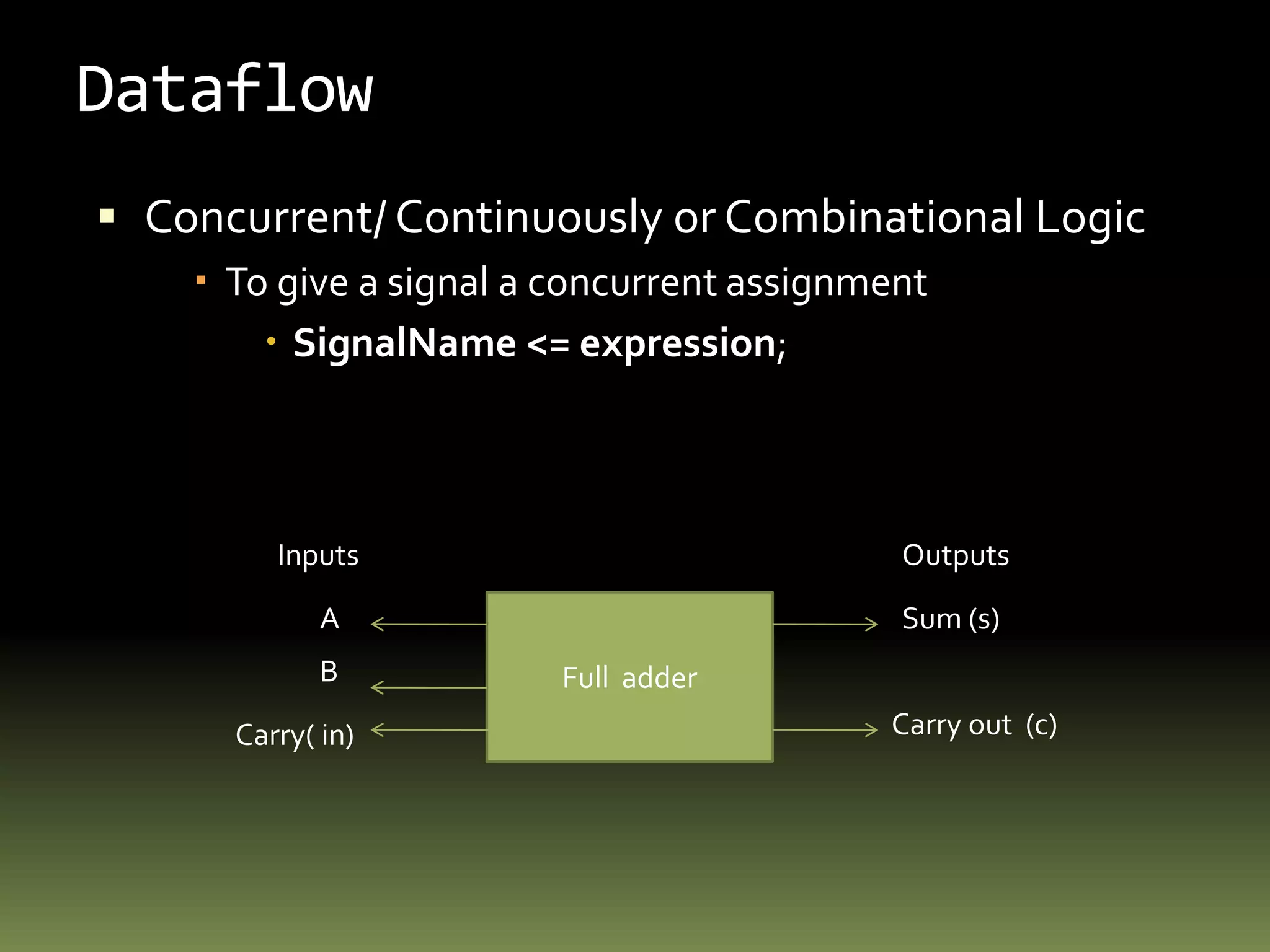
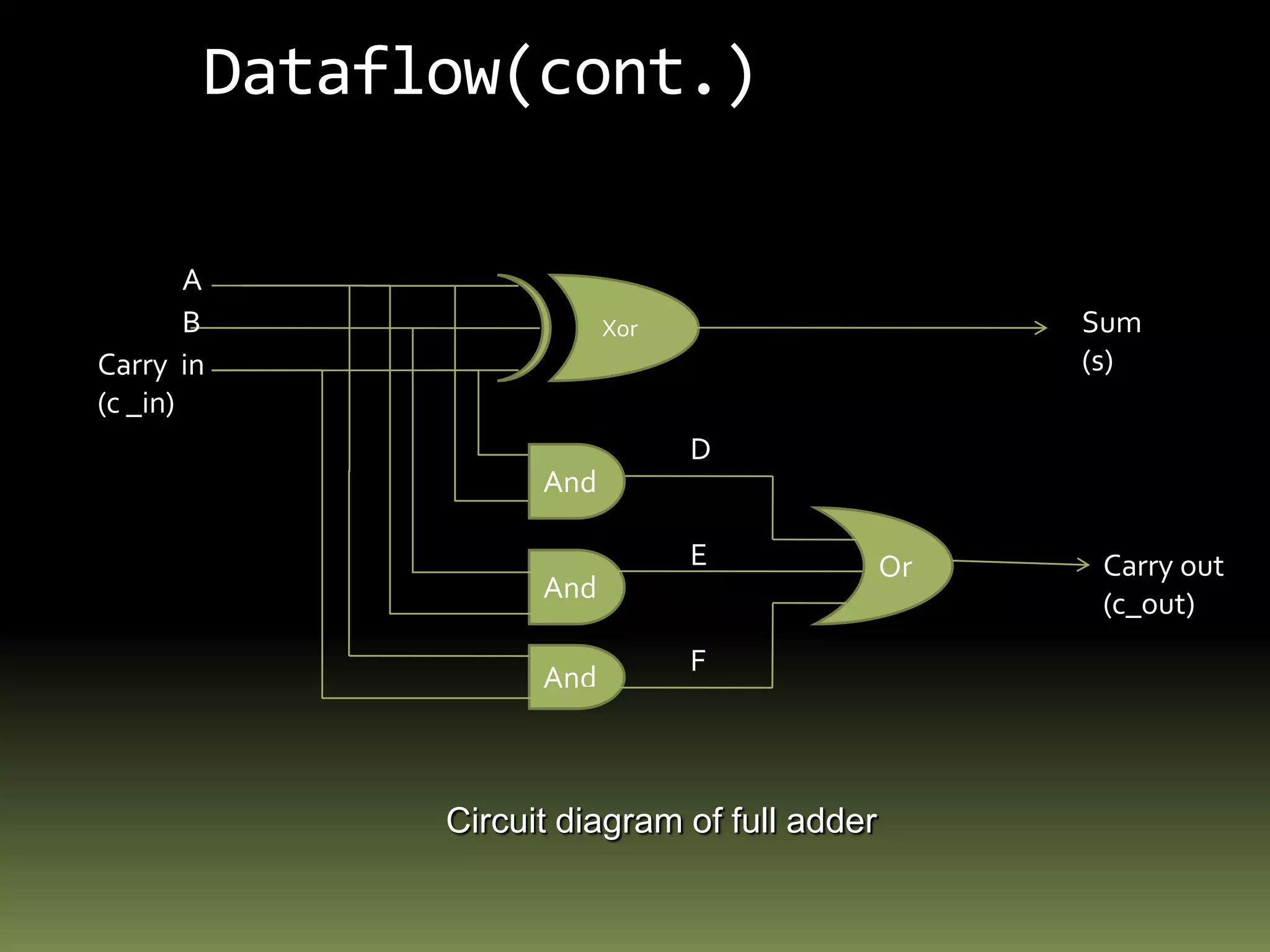
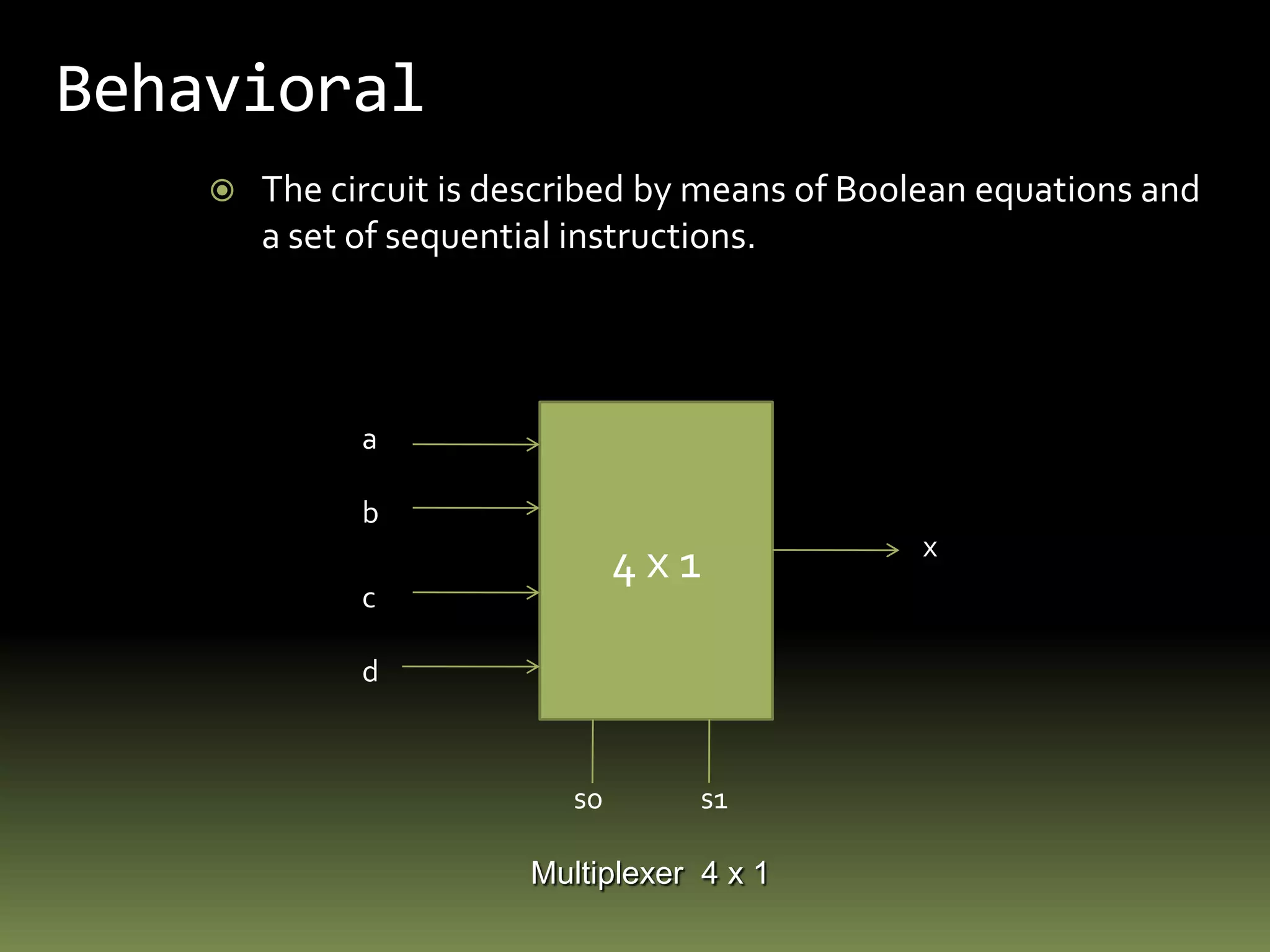
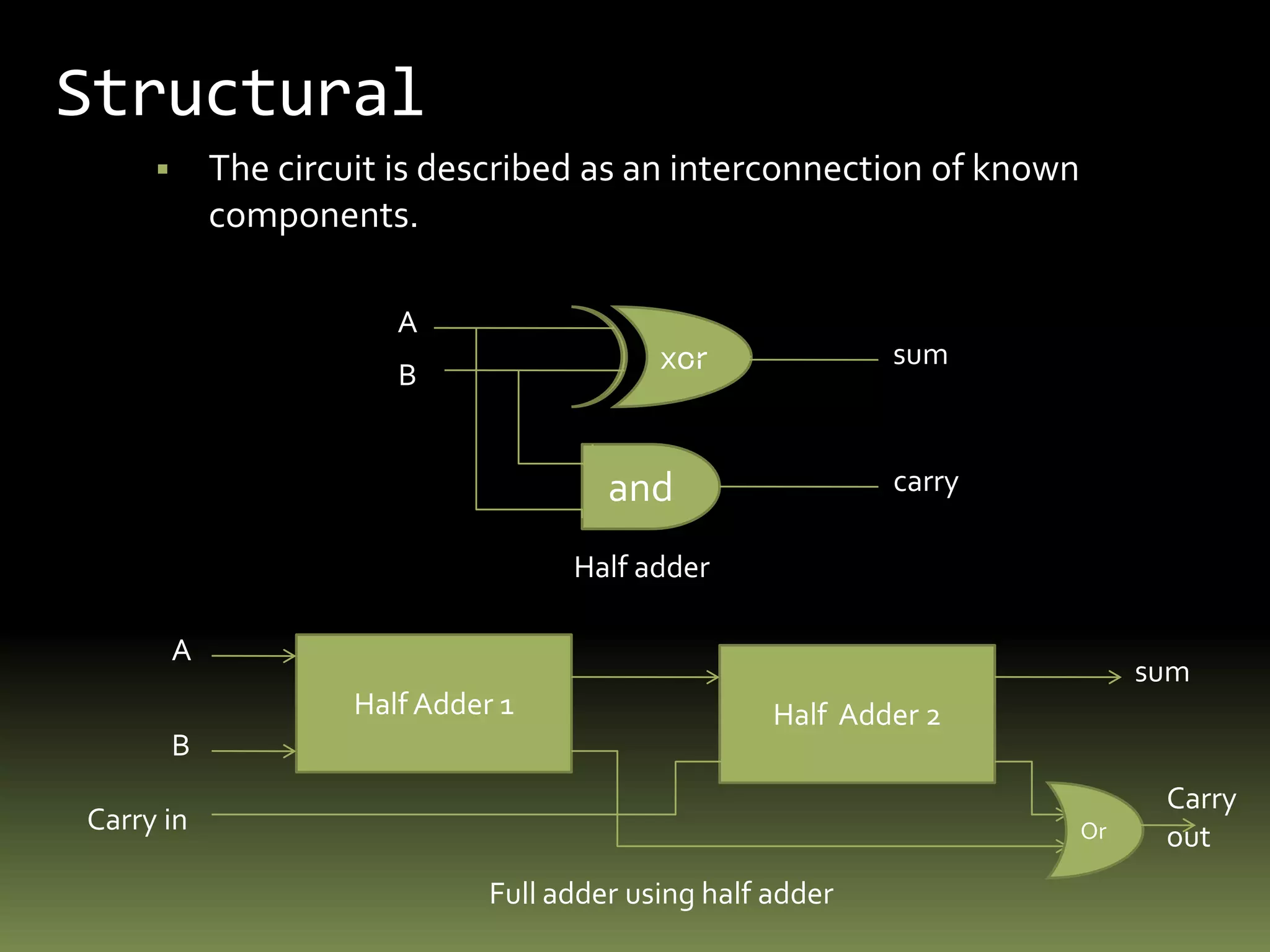
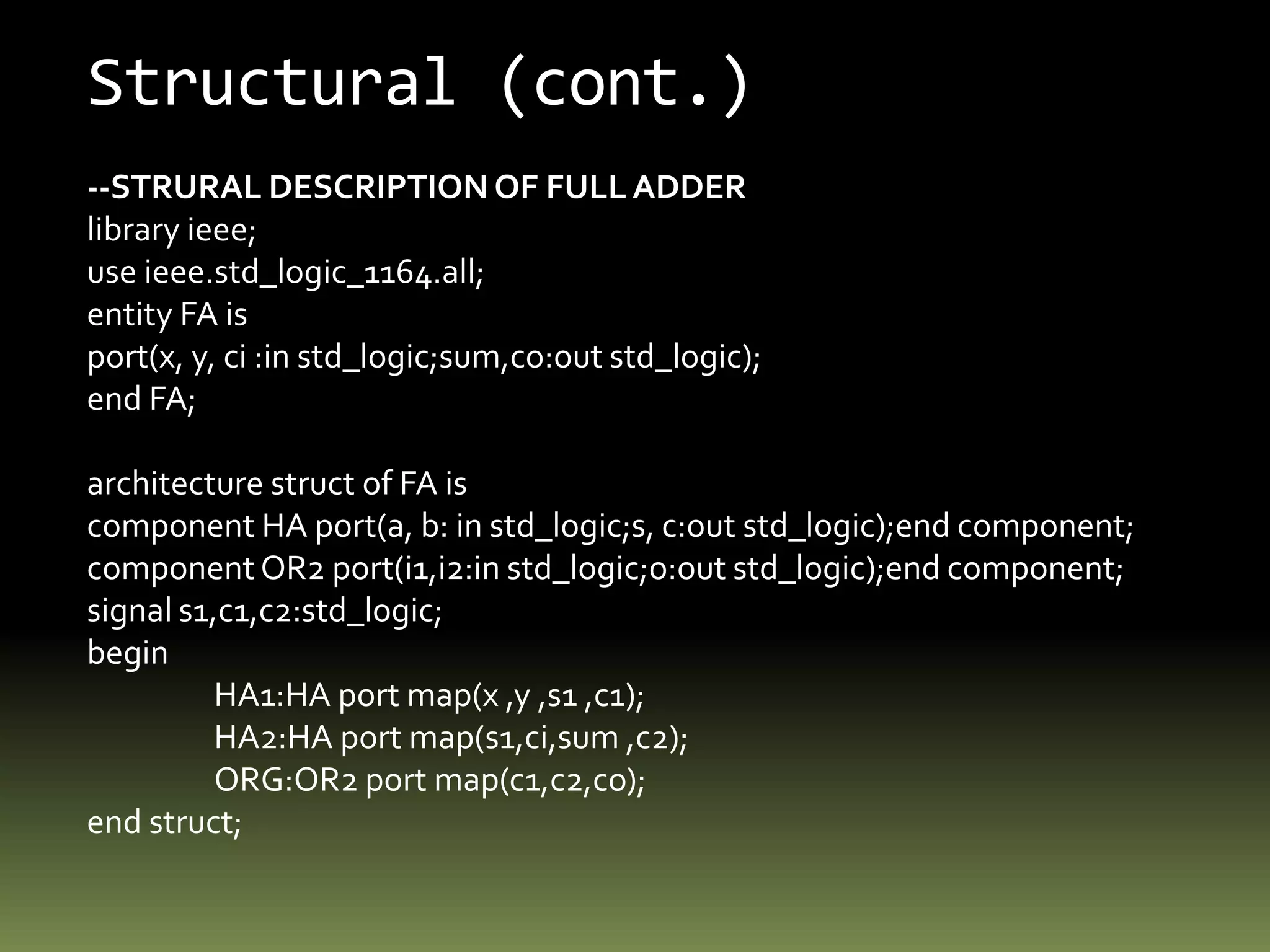
VHDL is a hardware description language used to model electronic systems. The document outlines the key structural elements of VHDL including entities, architectures, signals, and data types. It describes different design methodologies in VHDL like behavioral, dataflow, and structural. Behavioral models use boolean equations, dataflow uses concurrent assignments, and structural connects known components. The document provides examples of modeling half adders, full adders, and multiplexers in VHDL using the different methodologies.


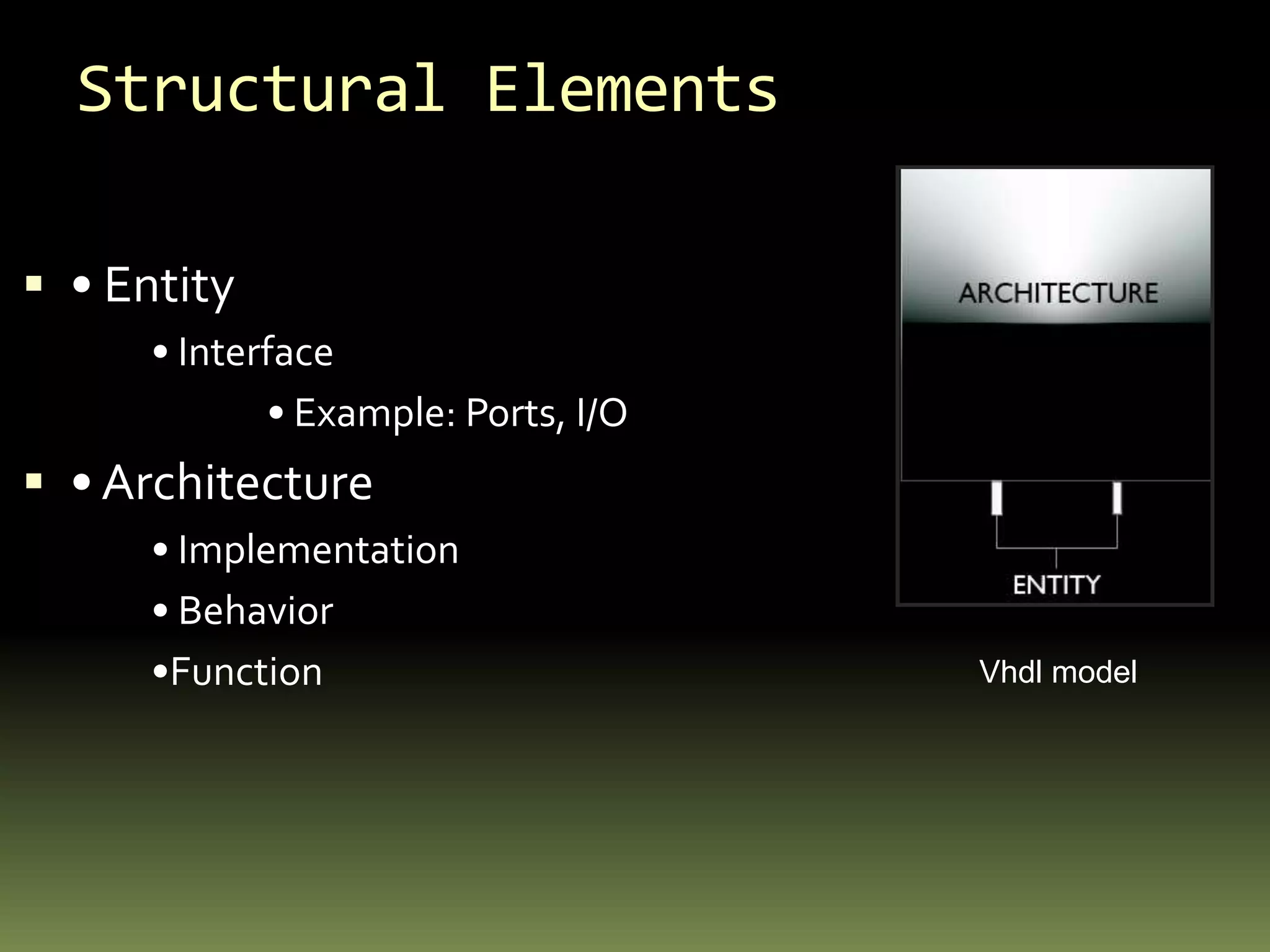

![ENTITYprovides a name to the component contains the port definitions in the interface listcan contain some generic definitions which can be used to override default valuesentity identifier is generic interface_list; port interface_list; declarationsbeginstatementsend [entity] [identifier];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vhdlhigh2003-101010065651-phpapp01/75/Vhd-lhigh2003-6-2048.jpg)

![Architectureencapsulates the behavior and timing informationcontains a number of concurrent statementsthere can be multiple architecture bodies for a given entity architecture identifier of entity_name isdeclarations beginstatements end [architecture] [identifier];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vhdlhigh2003-101010065651-phpapp01/75/Vhd-lhigh2003-8-2048.jpg)






![References[1] Douglas L. Perry, VHDL: “programming by example”, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002, Fourth Edition.[2] Wai-Kai Chen,” The VLSI Handbook “, CRC Press, USA, Second Edition. [3] Dr. Cecil alford tsai chi huang, “Digital design vhdl laboratory notes”, 1996, version 1.01, [4] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Very-large-scale_integration [5] 1076 IEEE Standard VHDL Language Reference Manual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vhdlhigh2003-101010065651-phpapp01/75/Vhd-lhigh2003-24-2048.jpg)