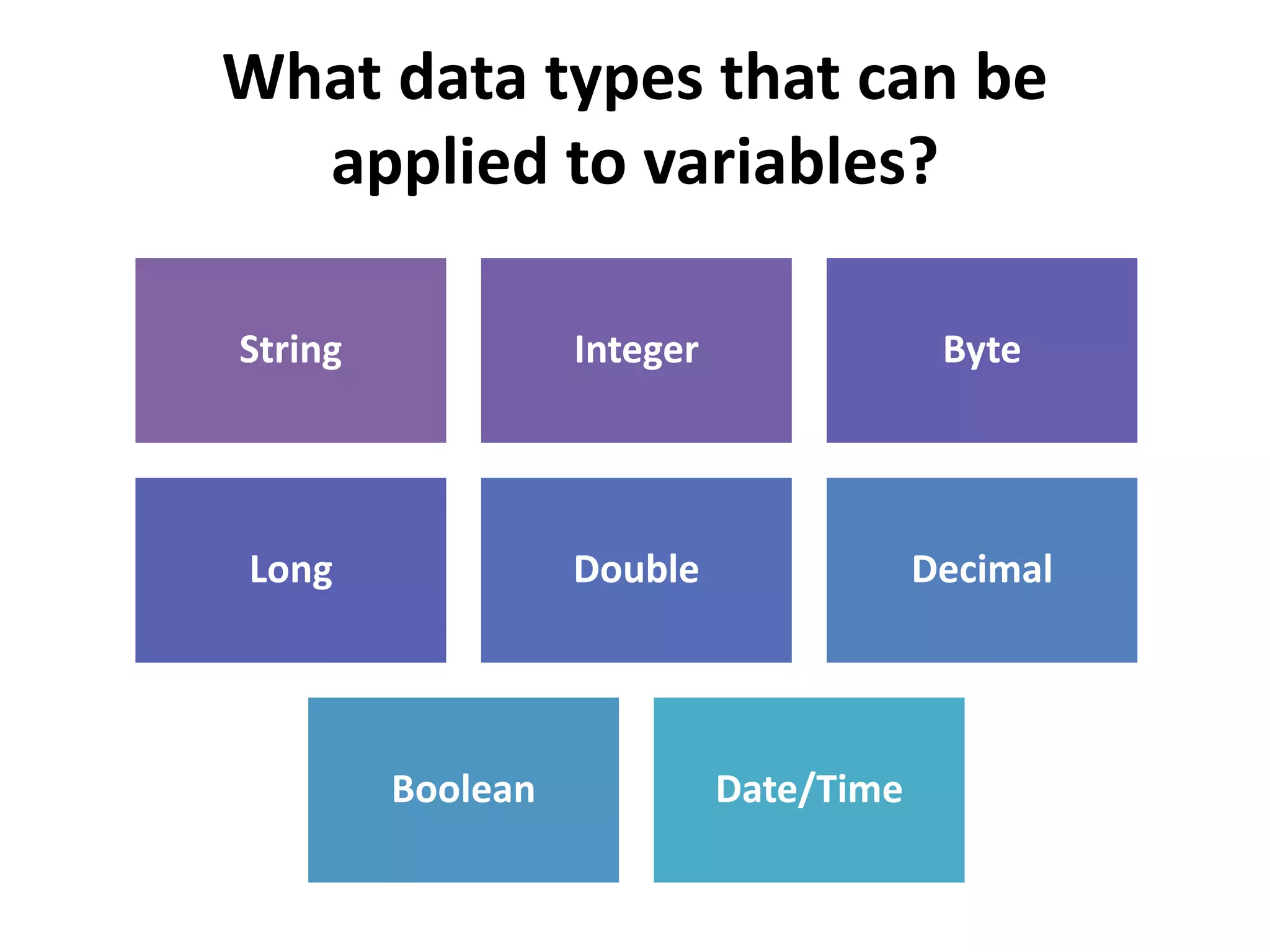
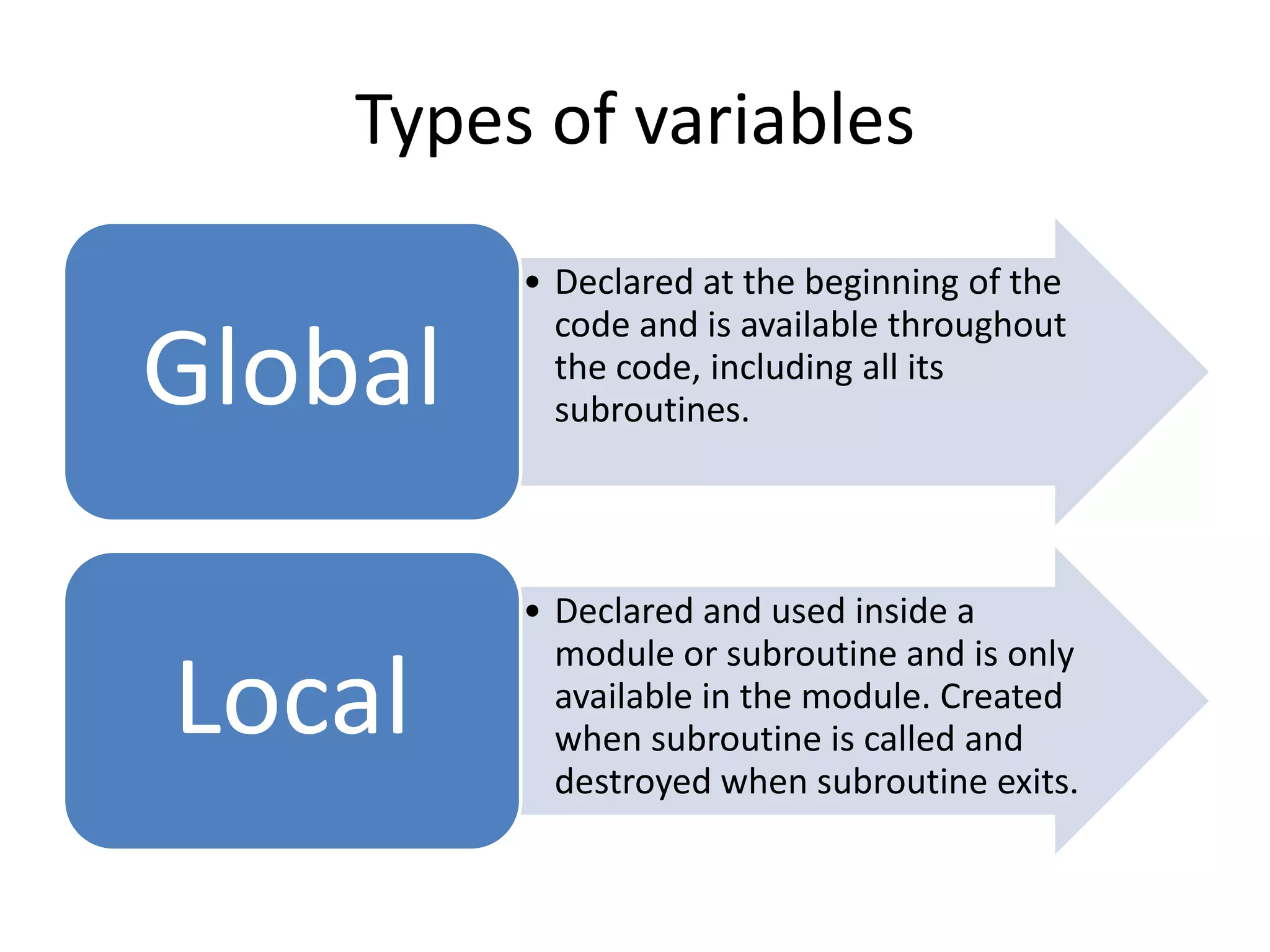
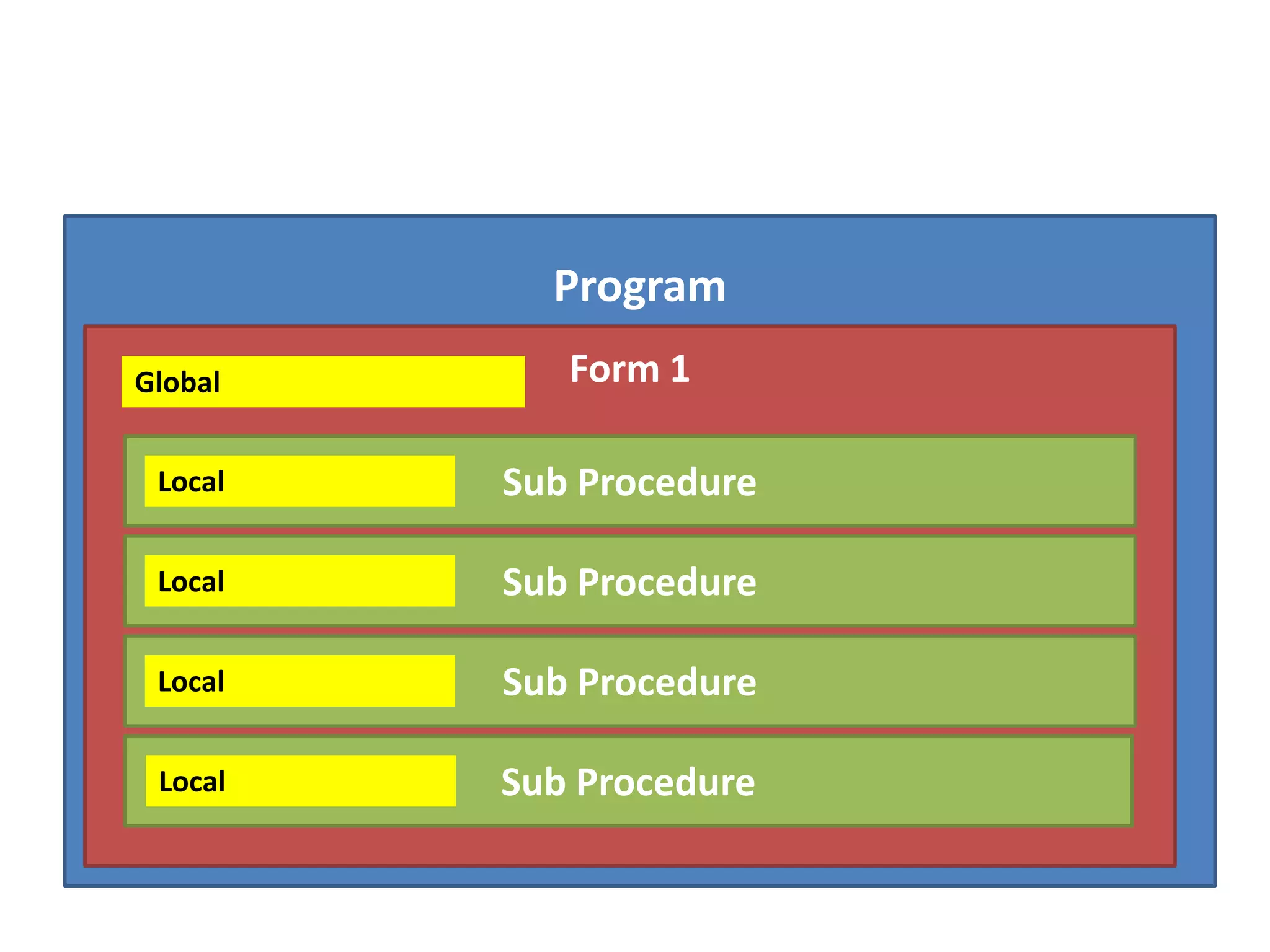
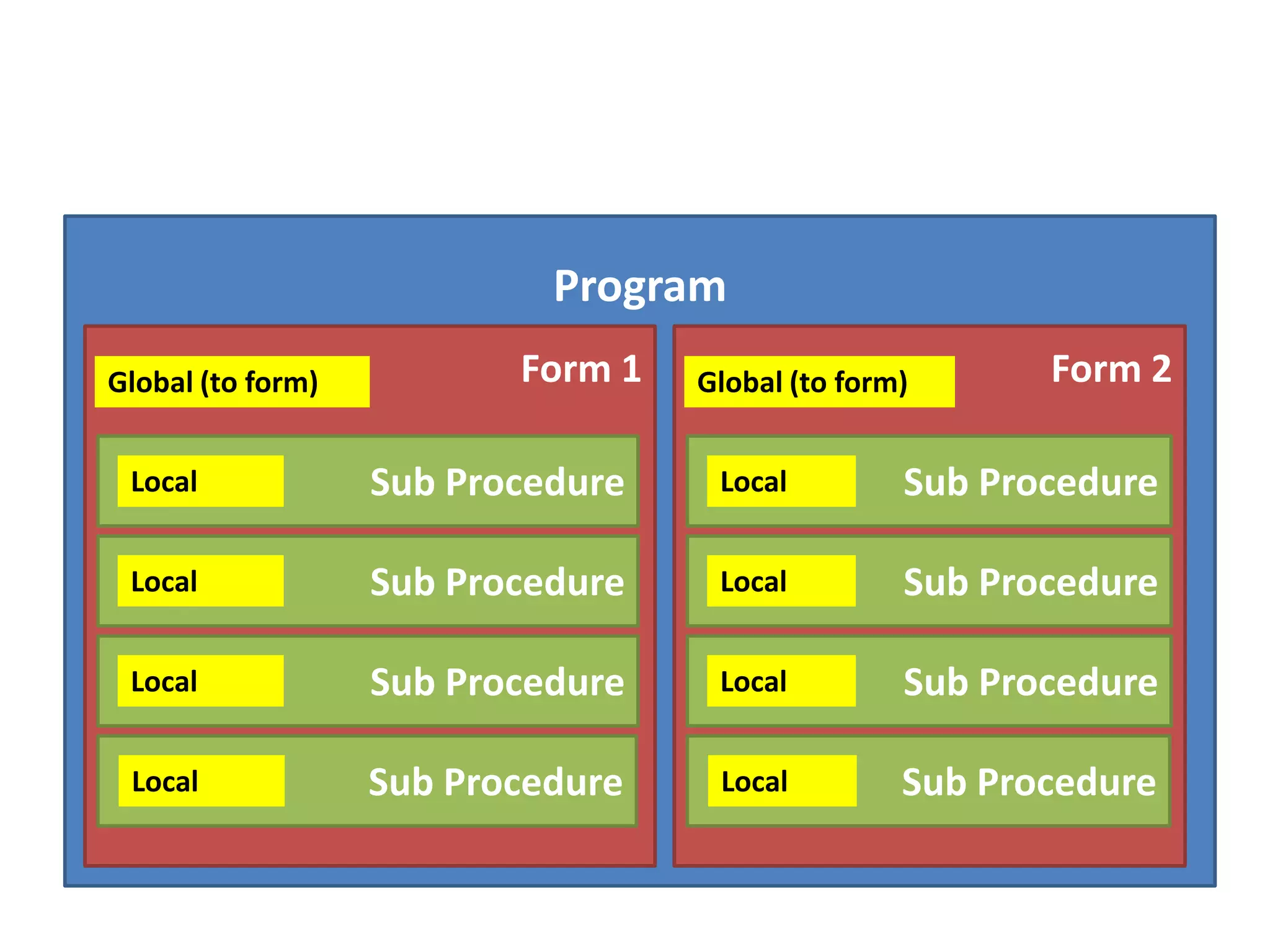
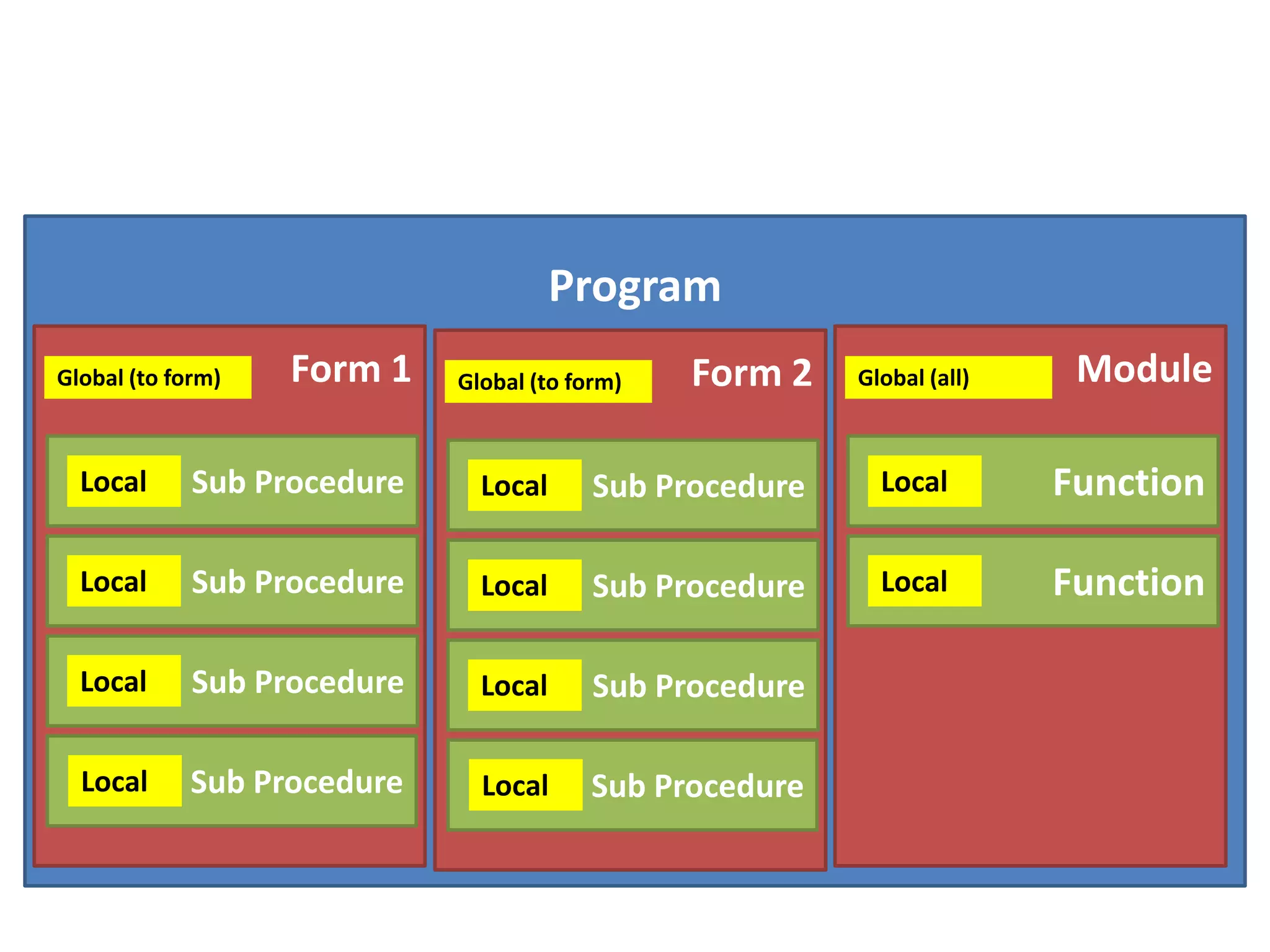
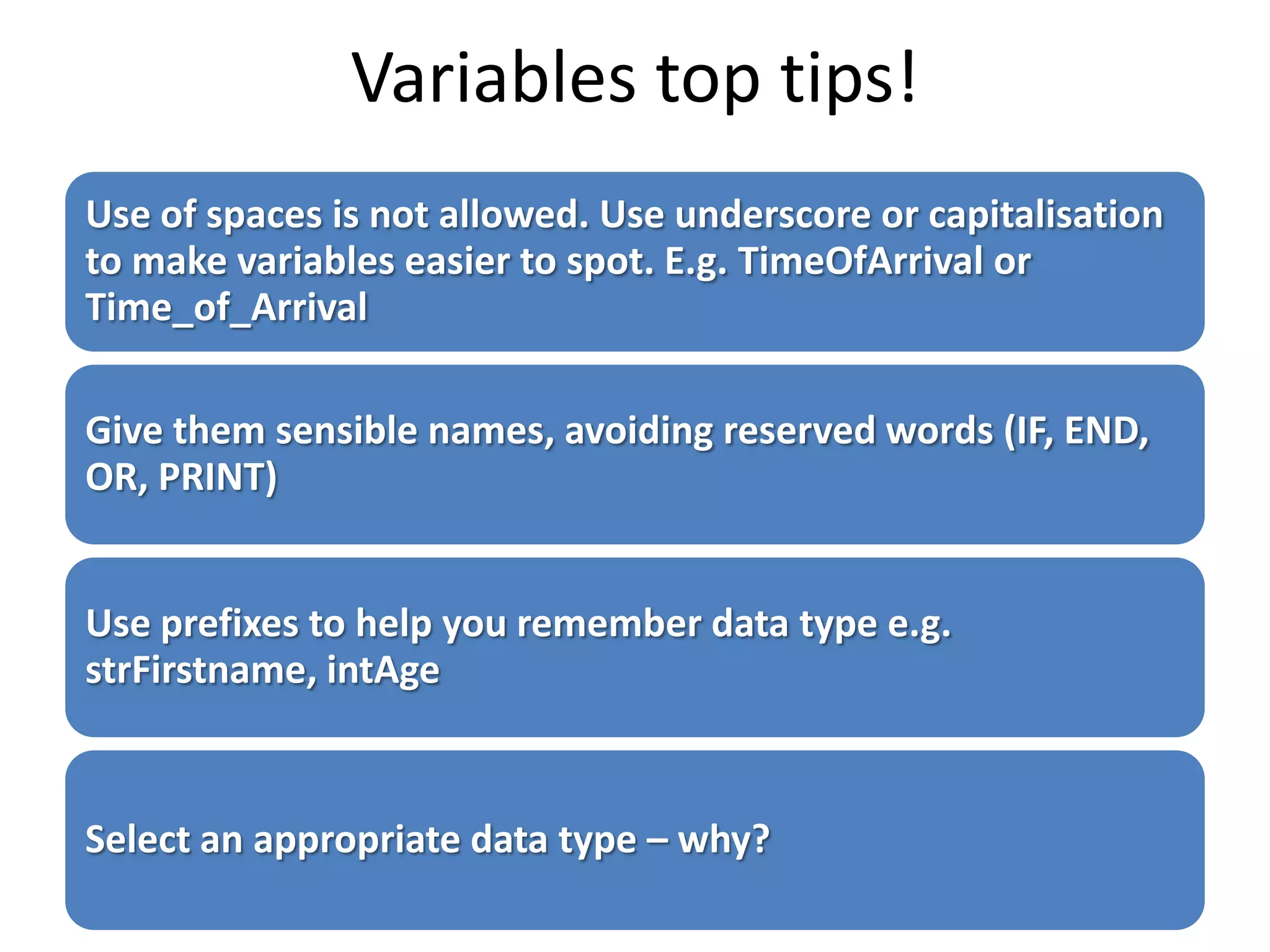
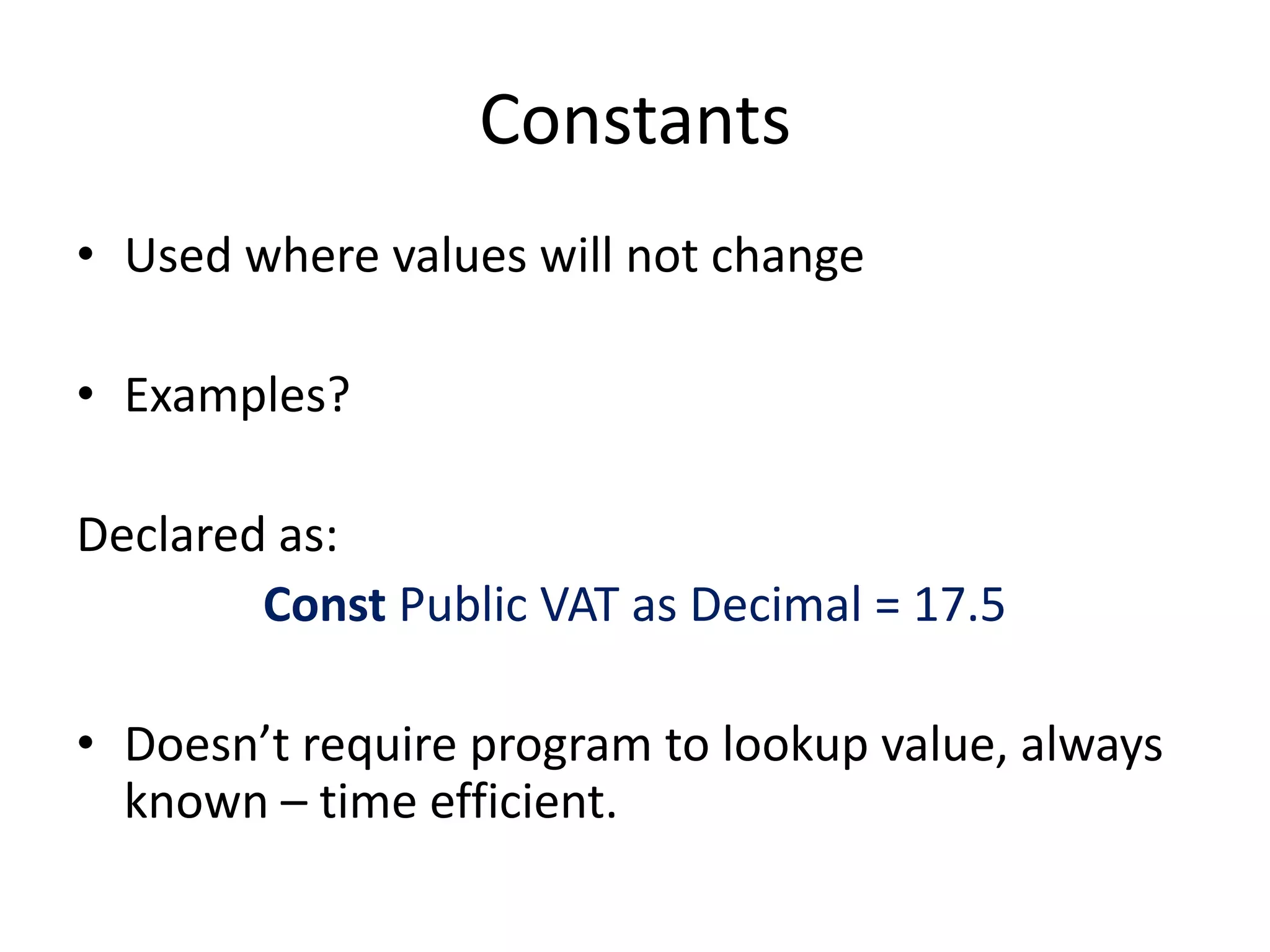
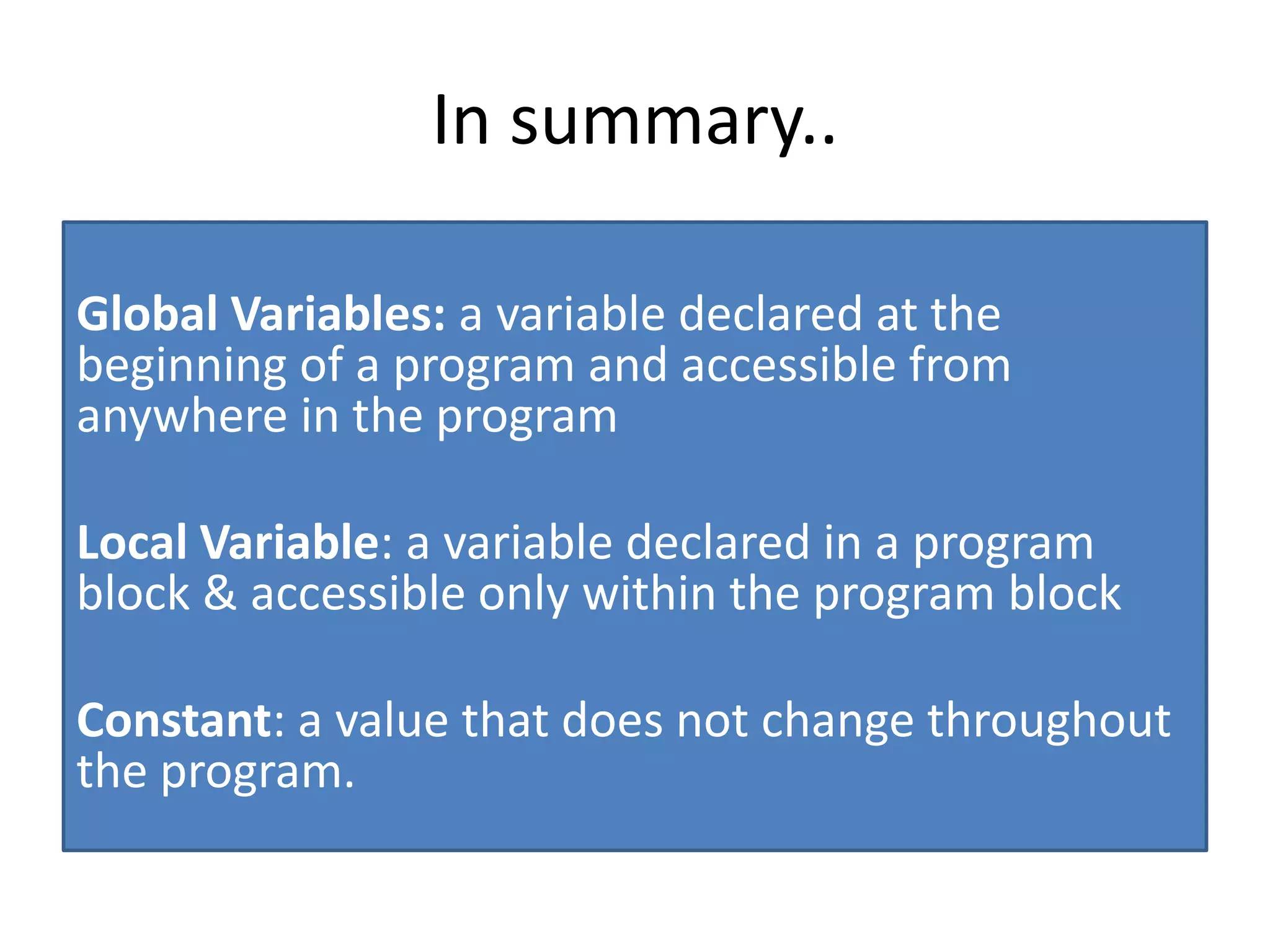
The document discusses variables in VB programming, including global variables which are declared at the beginning and accessible throughout a program, local variables which are declared within a program block and only accessible within that block, and constants which represent values that do not change throughout a program. It provides examples of different variable data types and best practices for naming variables.