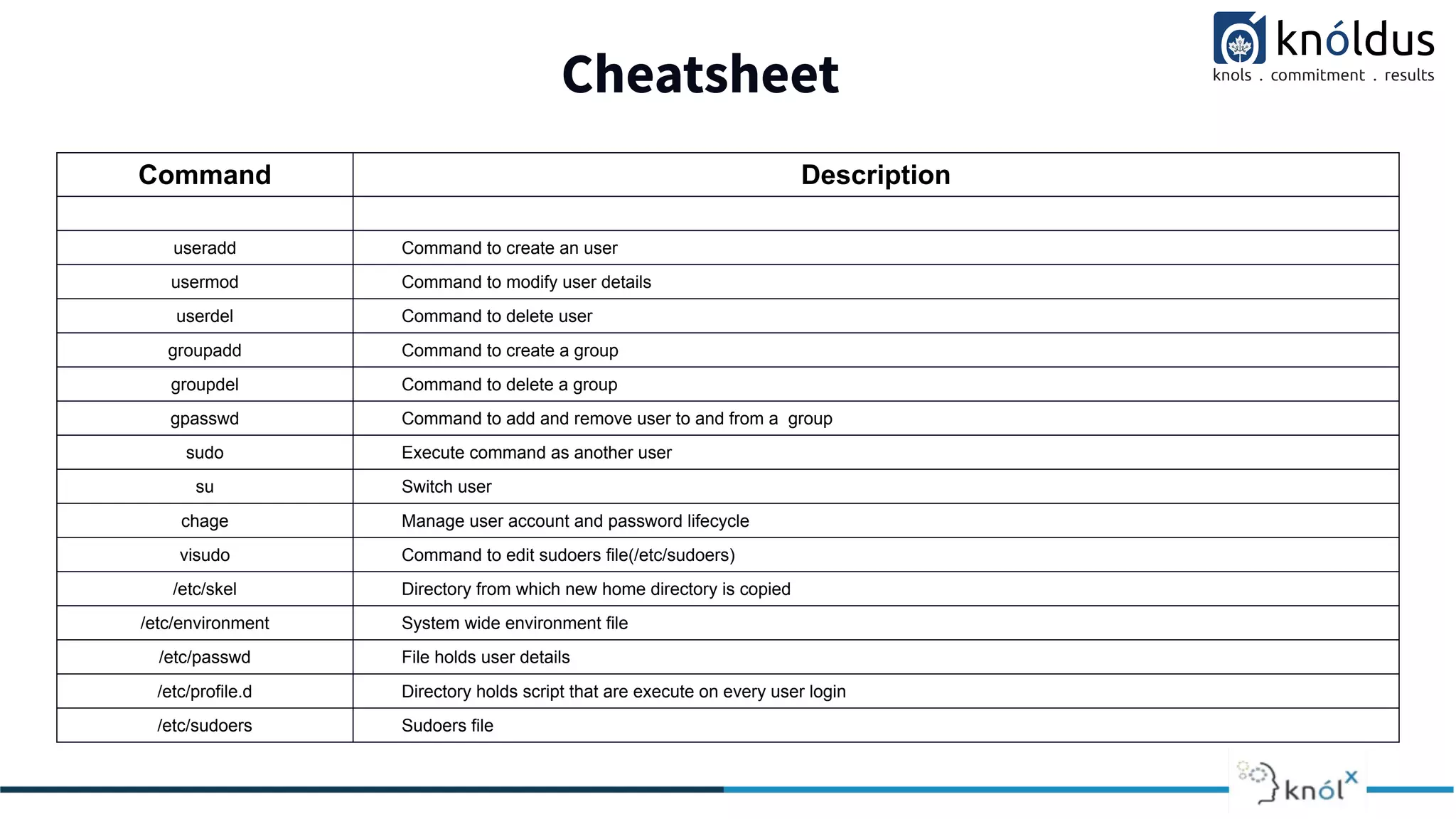
The document outlines essential etiquette and guidelines for users attending Linux sessions, including punctuality, feedback submission, and maintaining silence during presentations. It provides a comprehensive overview of user and group management in Linux, detailing commands for creating, modifying, and managing users and groups, as well as the use of the sudo command. Additionally, it covers system-wide environment settings and best practices for maintaining user privileges and accounts.