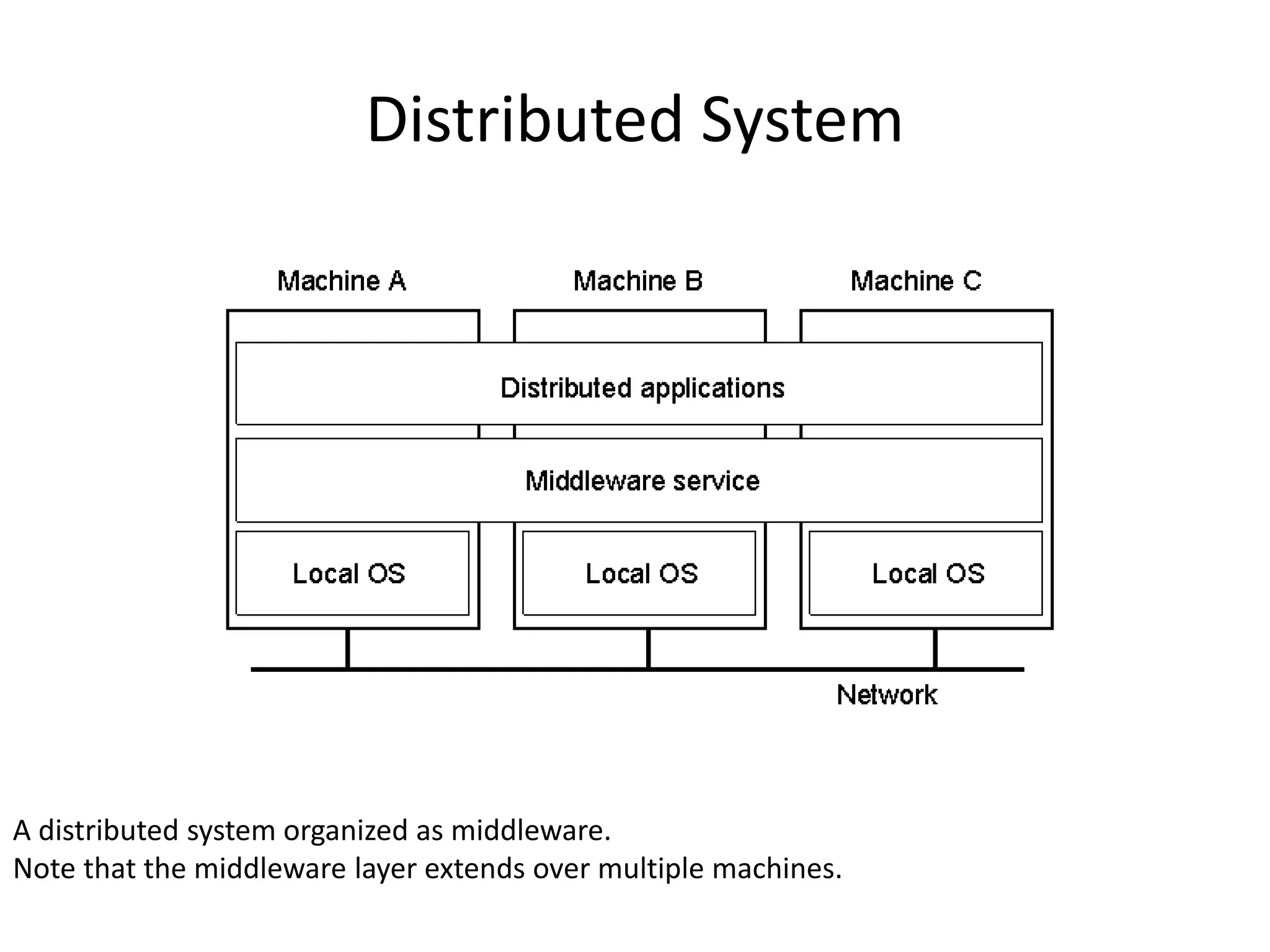
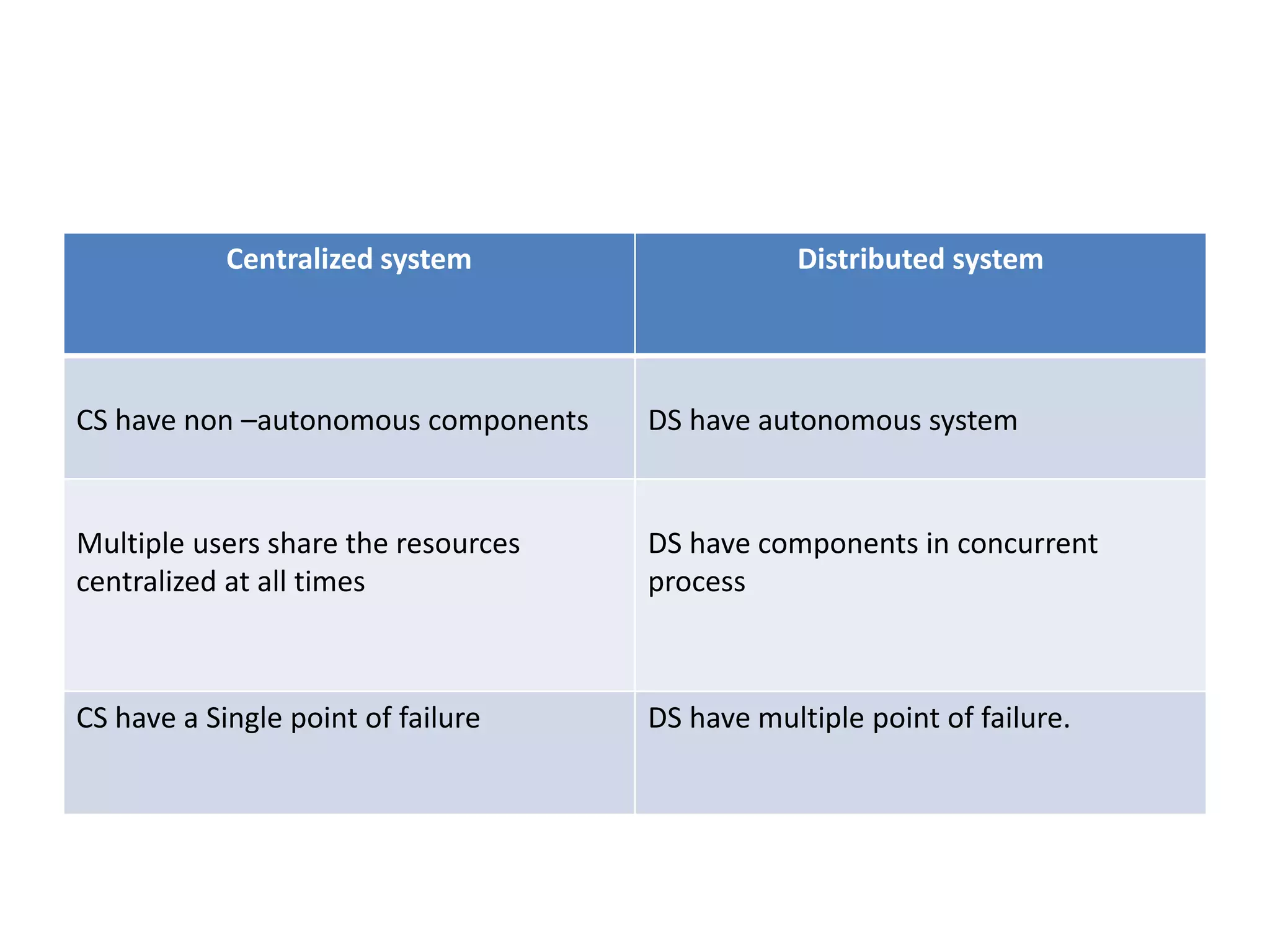
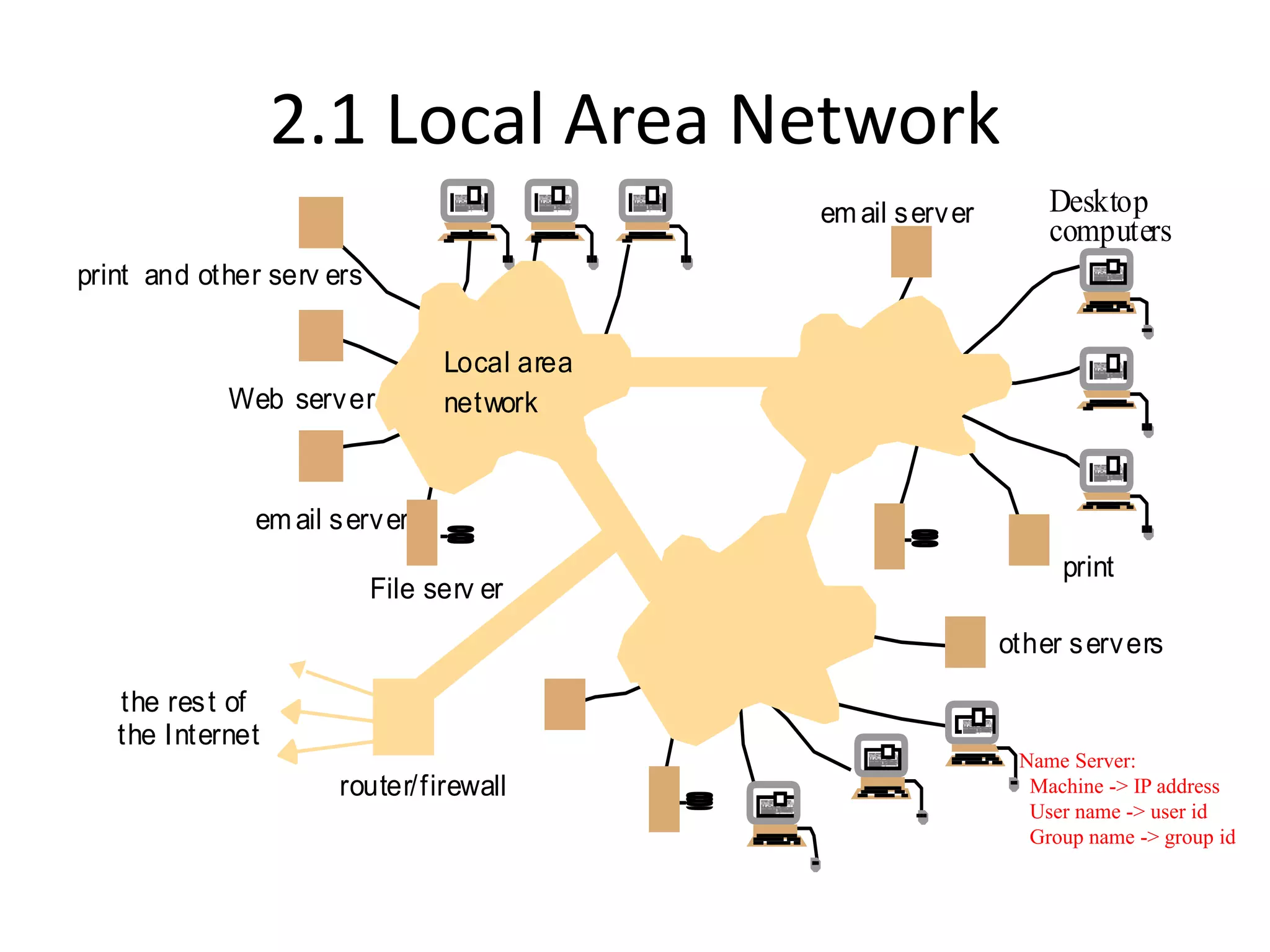
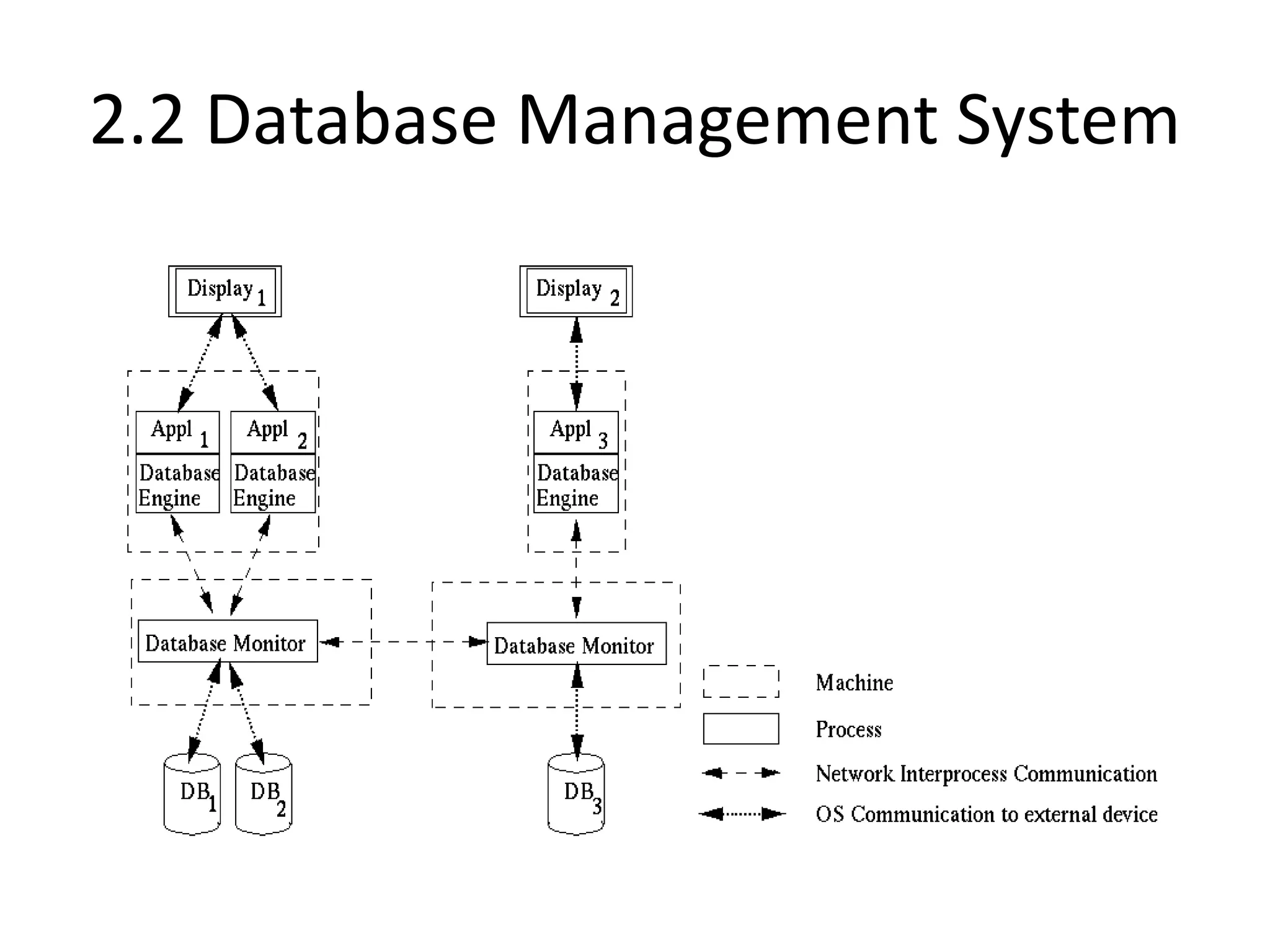
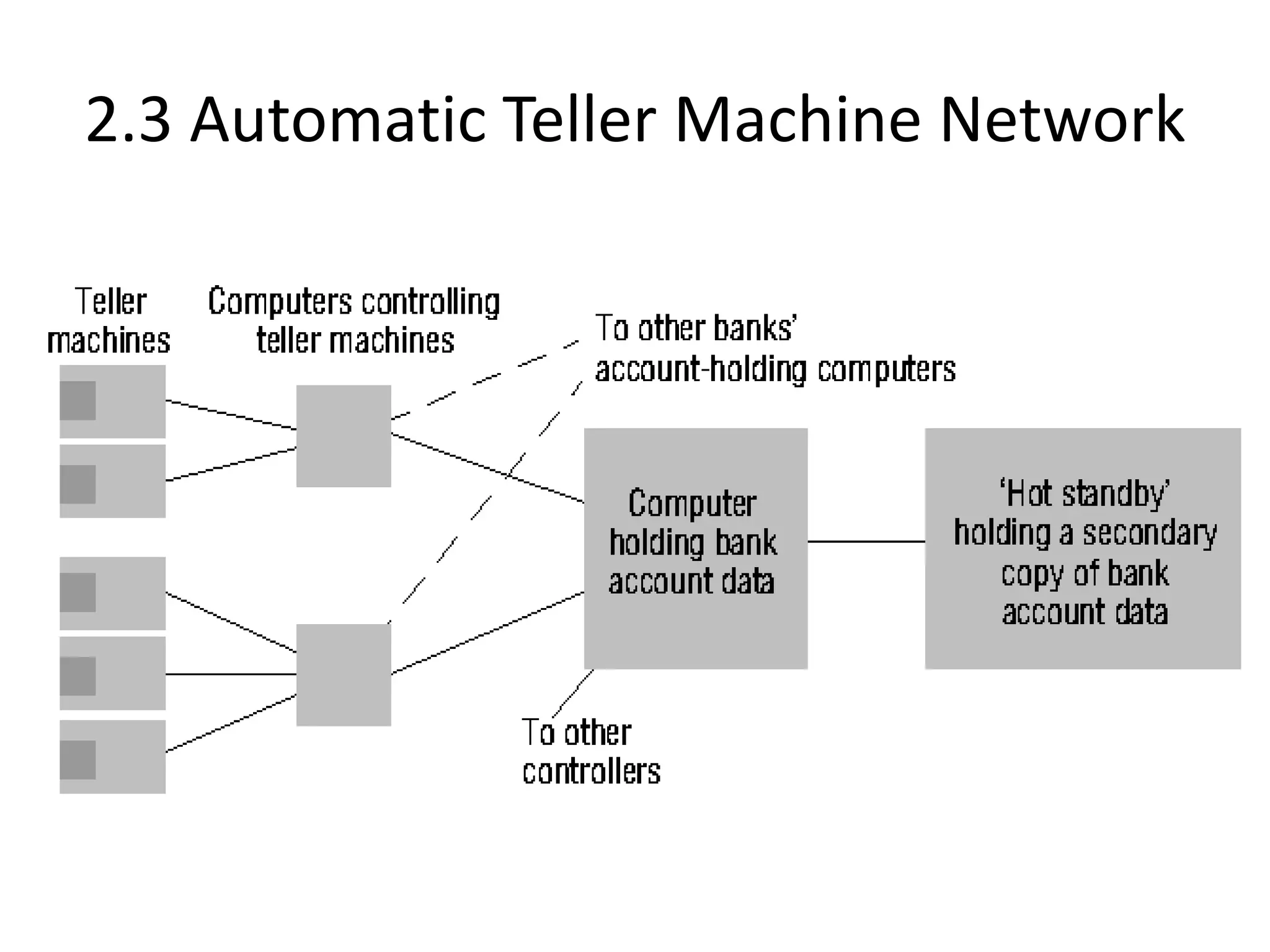
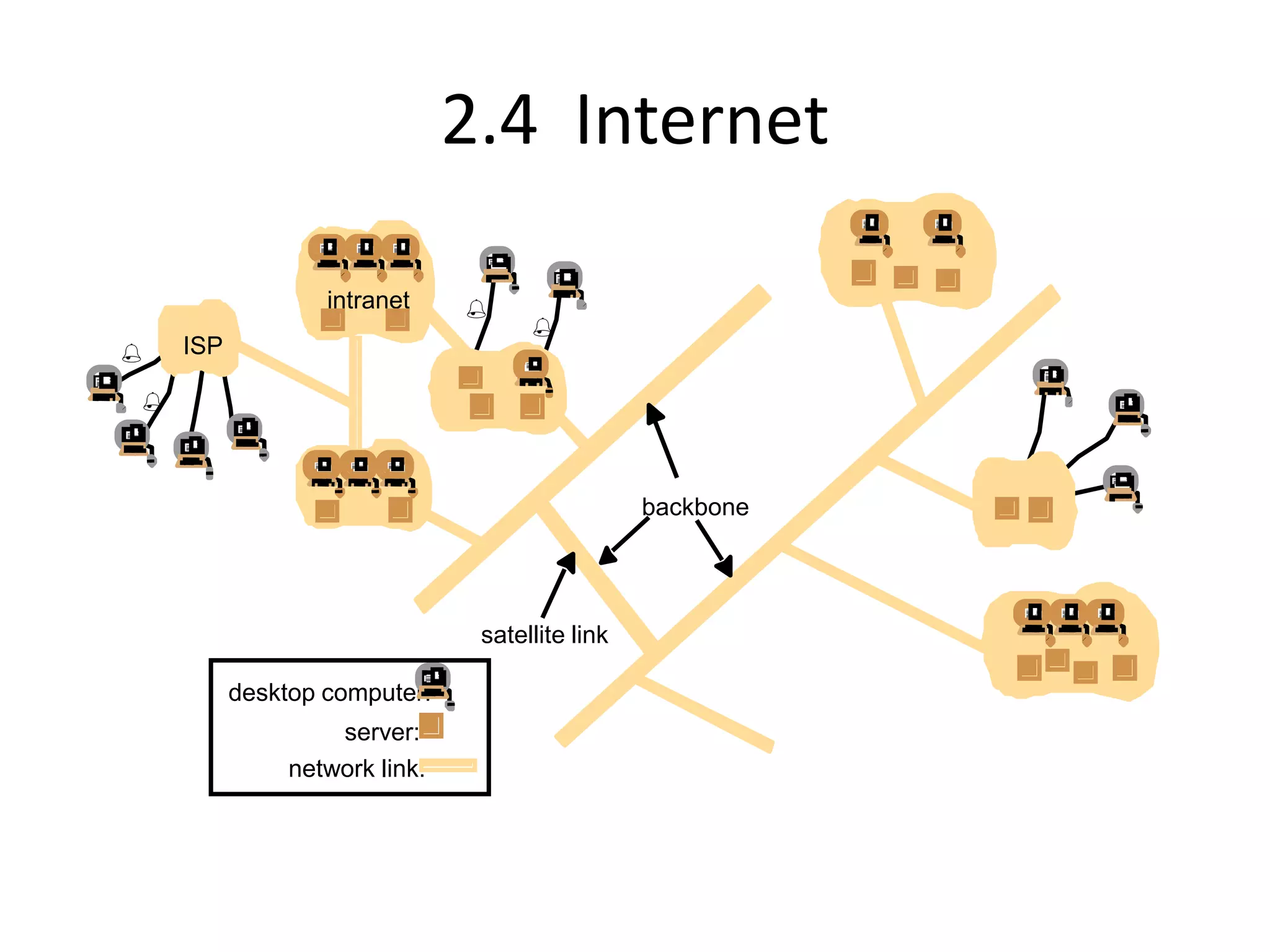
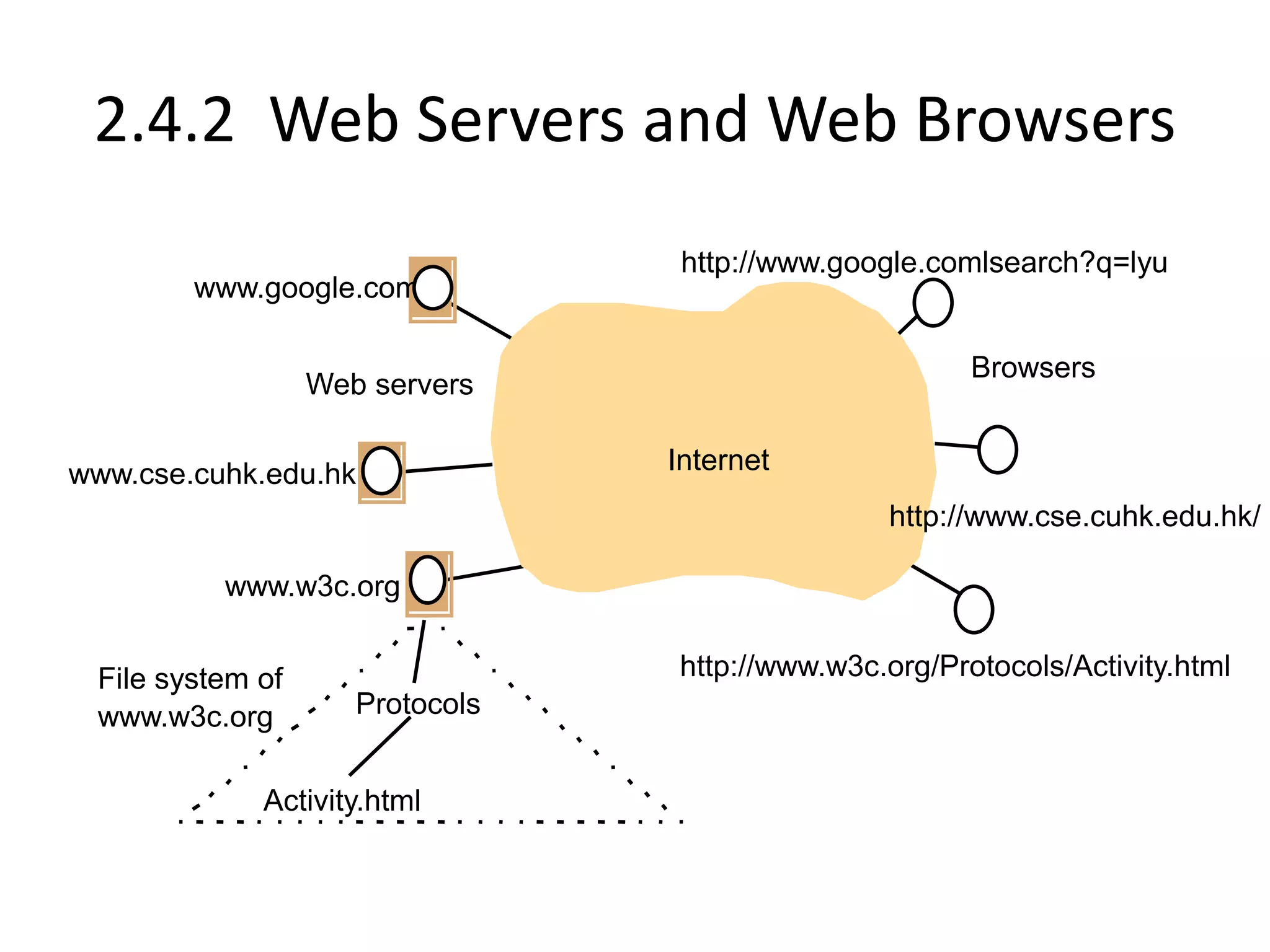
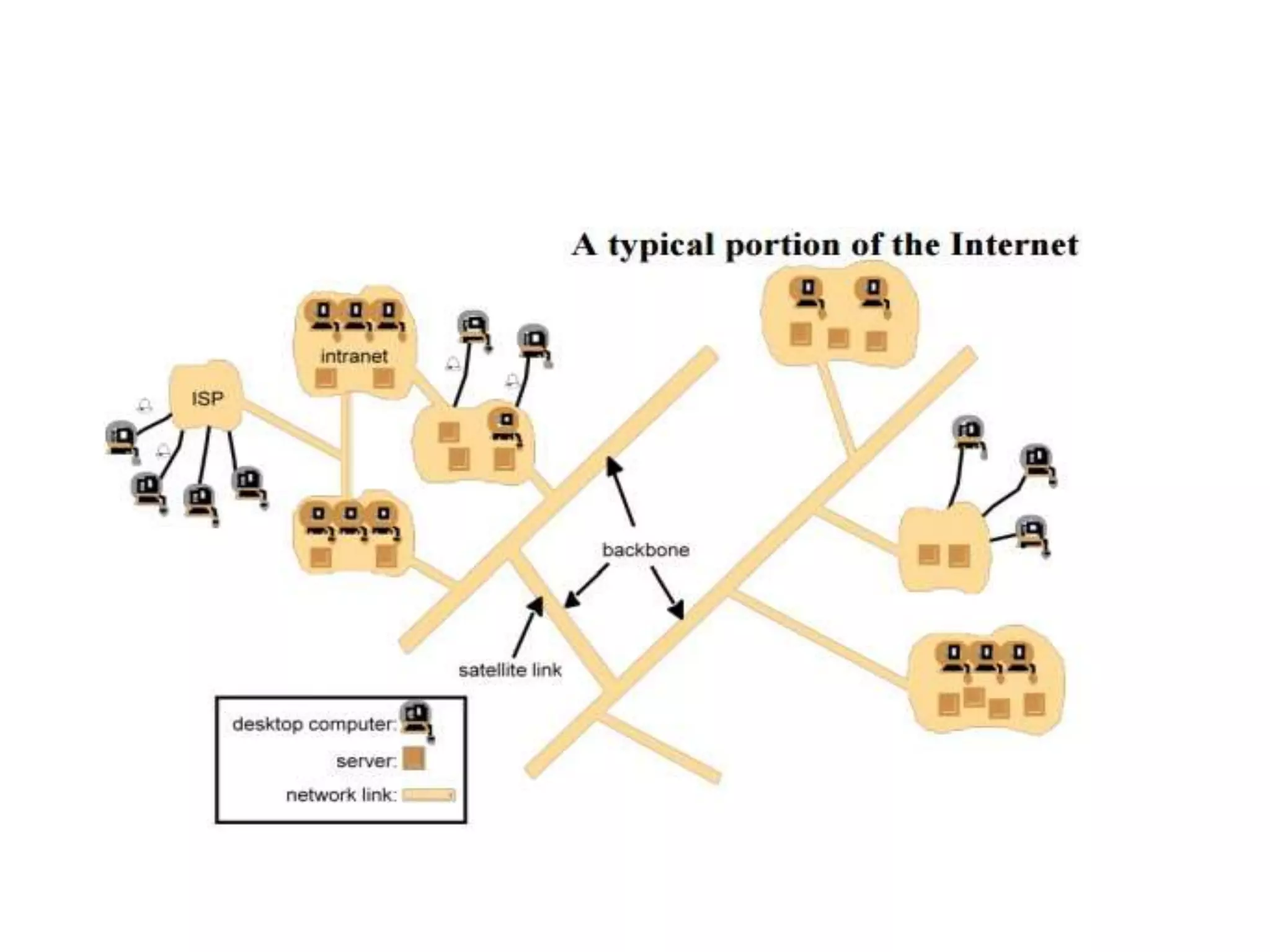
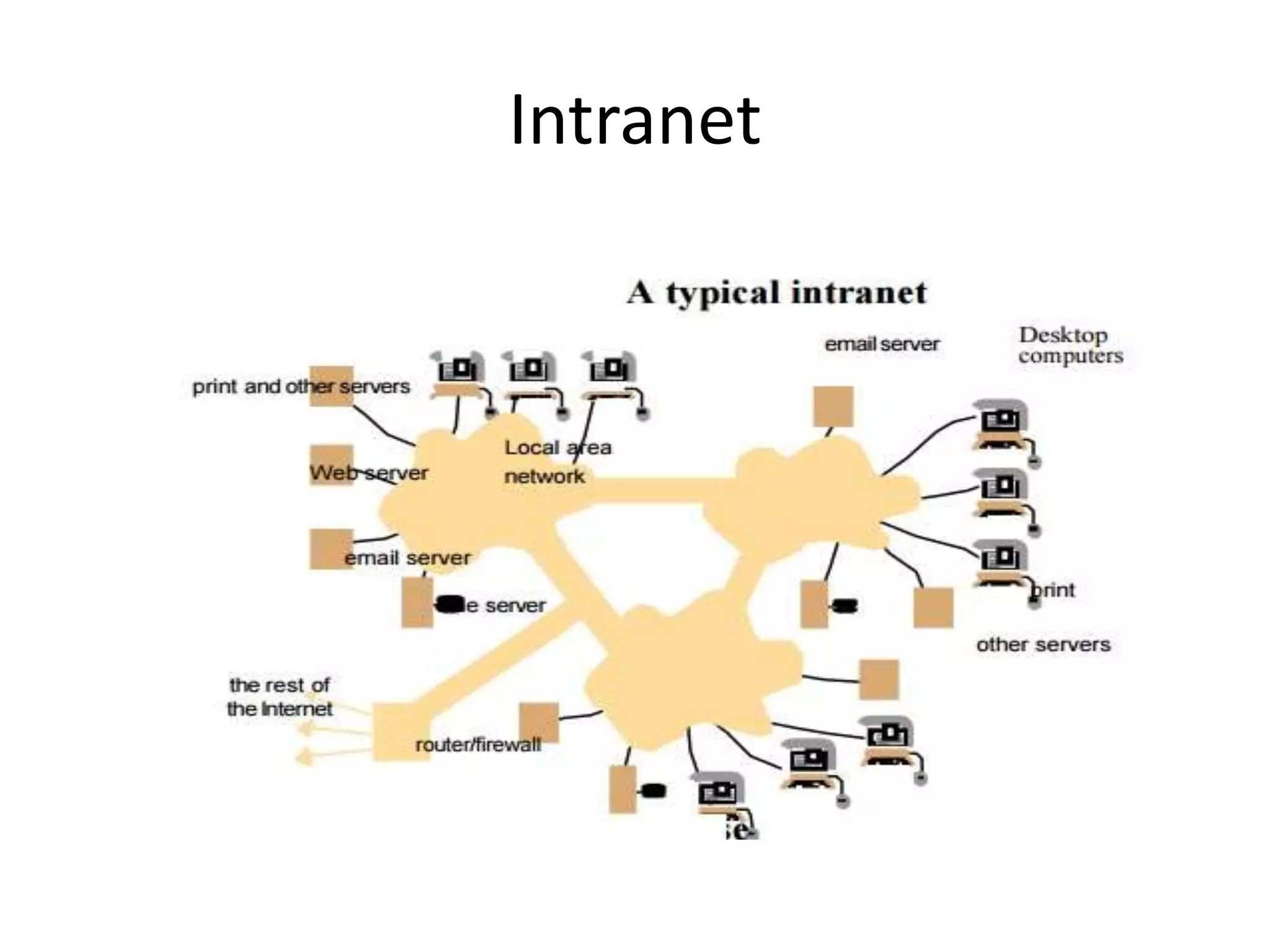
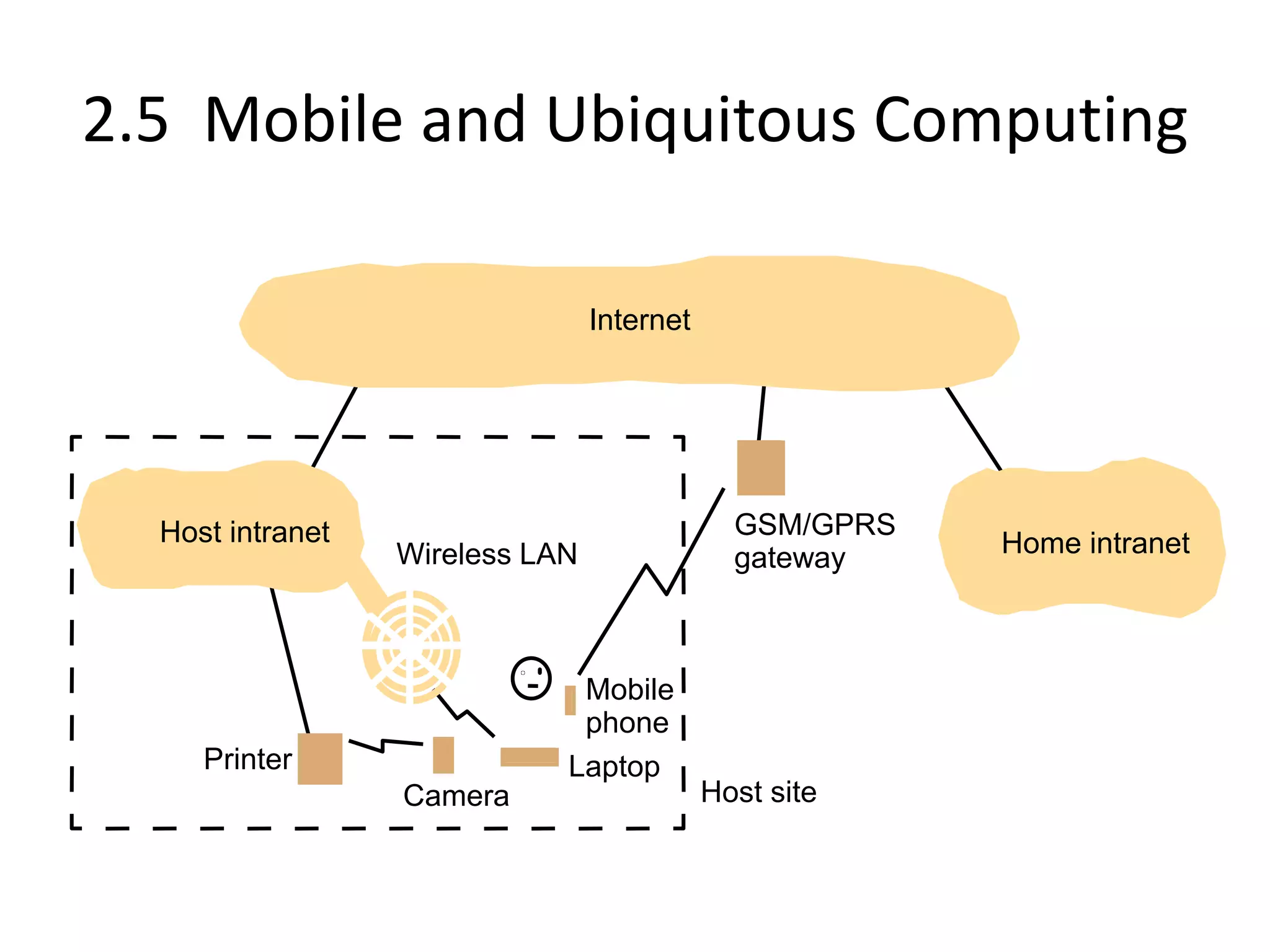
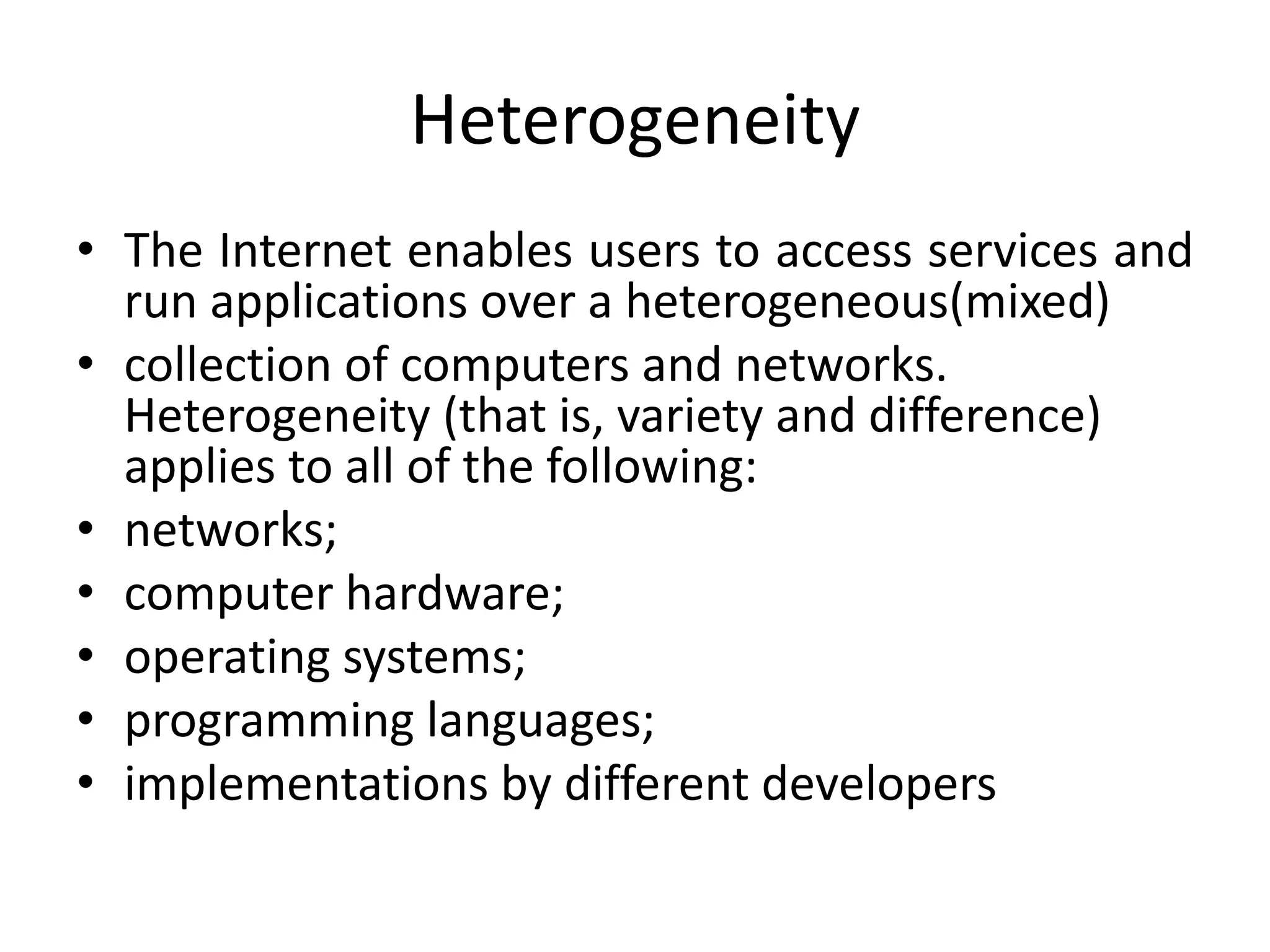
A distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears as a single coherent system to its users. It allows sharing of resources and workload across networked computers. Key characteristics include multiple autonomous components, lack of shared memory, and message-based communication. The World Wide Web is a large-scale distributed system that allows sharing of documents, files, and other resources across the internet through web servers and browsers. It faces challenges like heterogeneity, security, scalability, and fault tolerance.