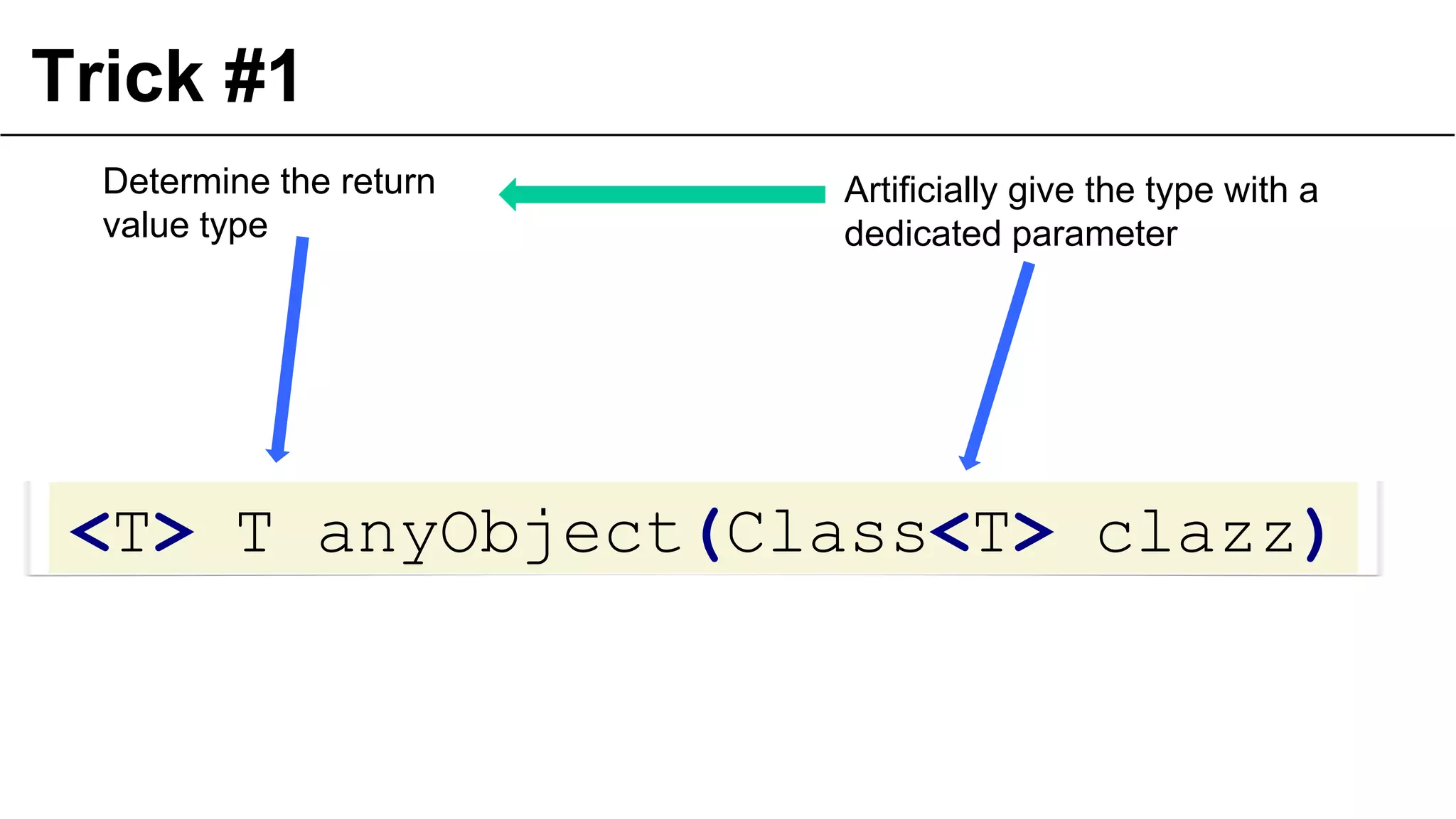
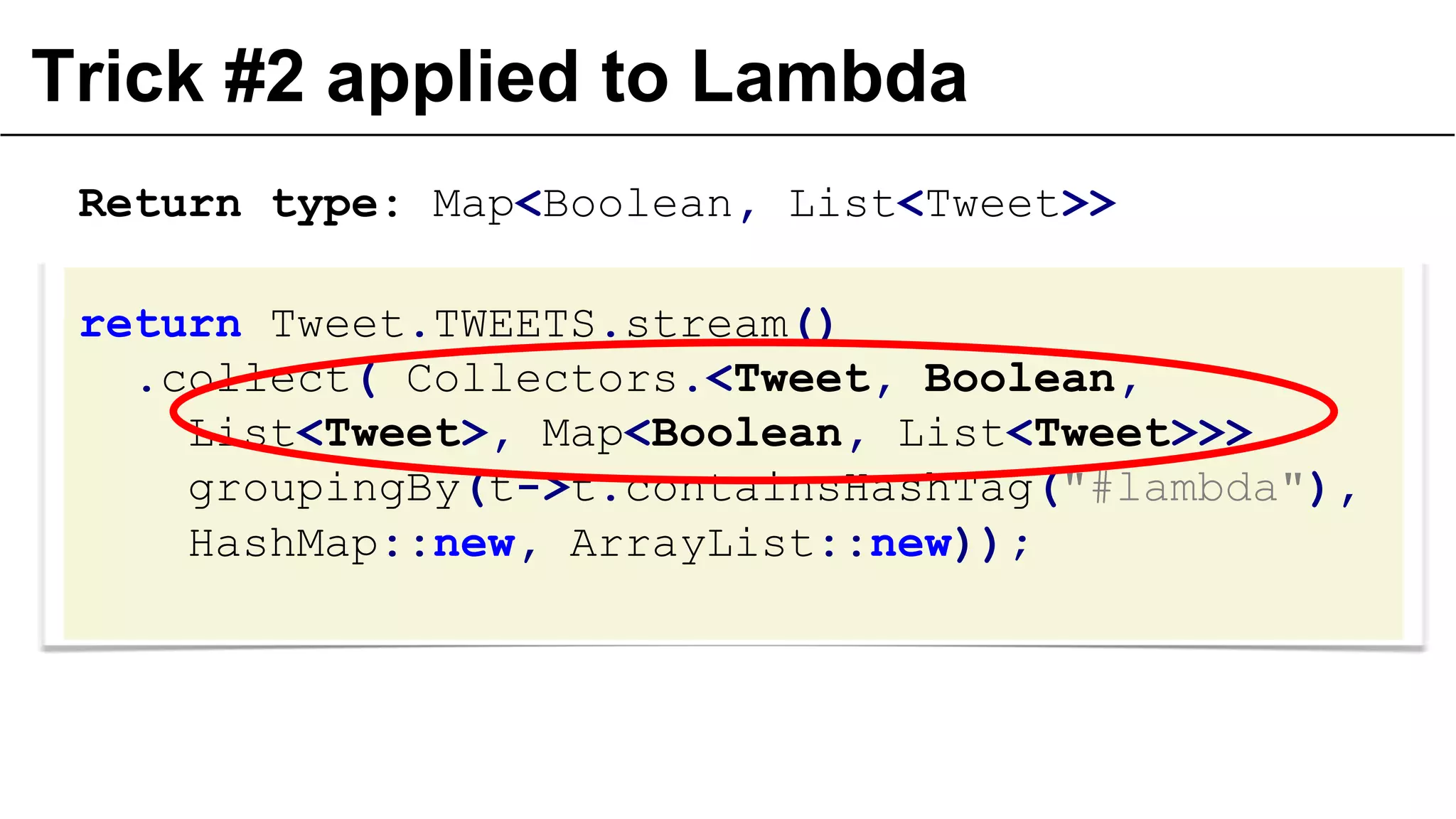
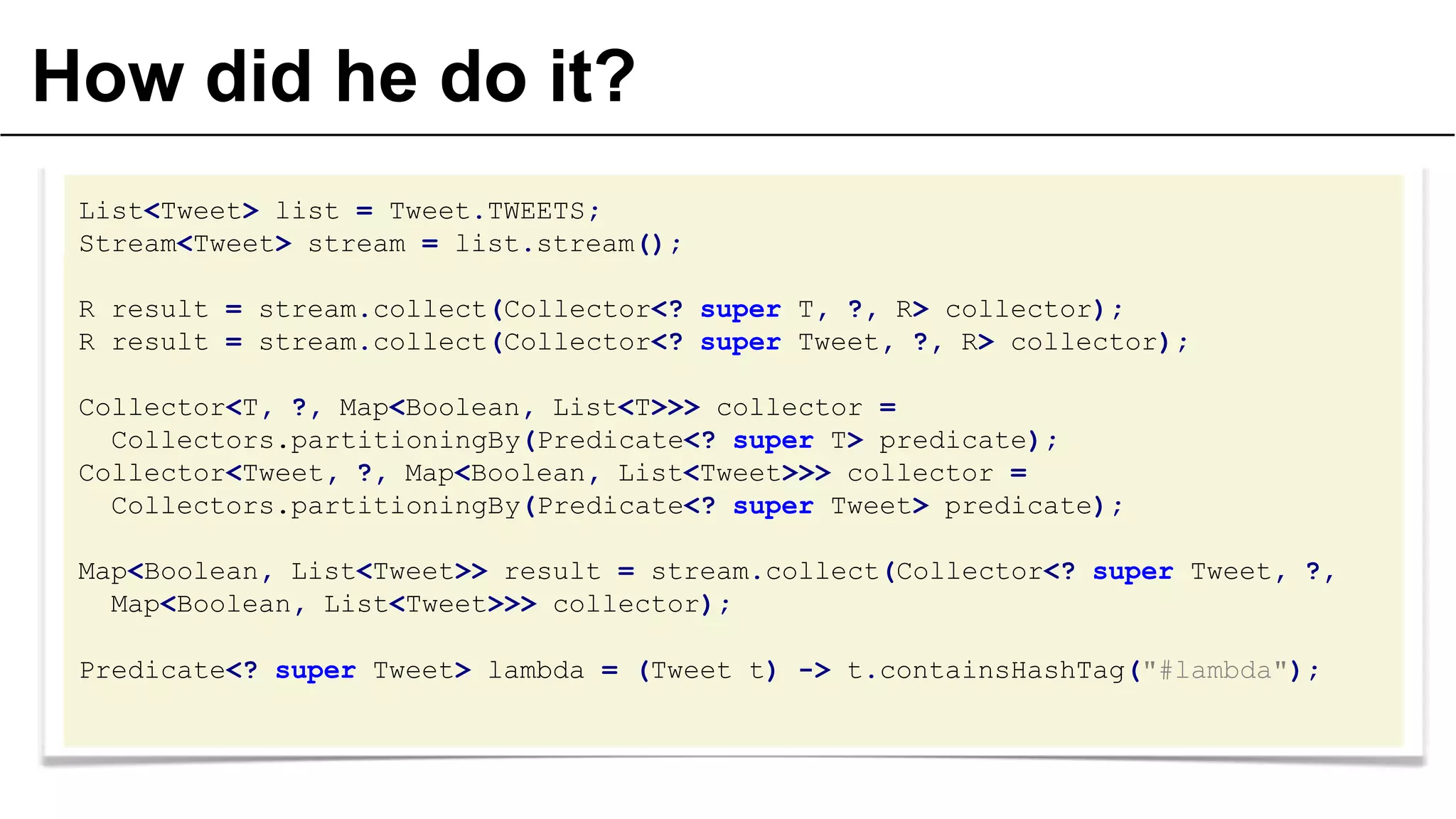
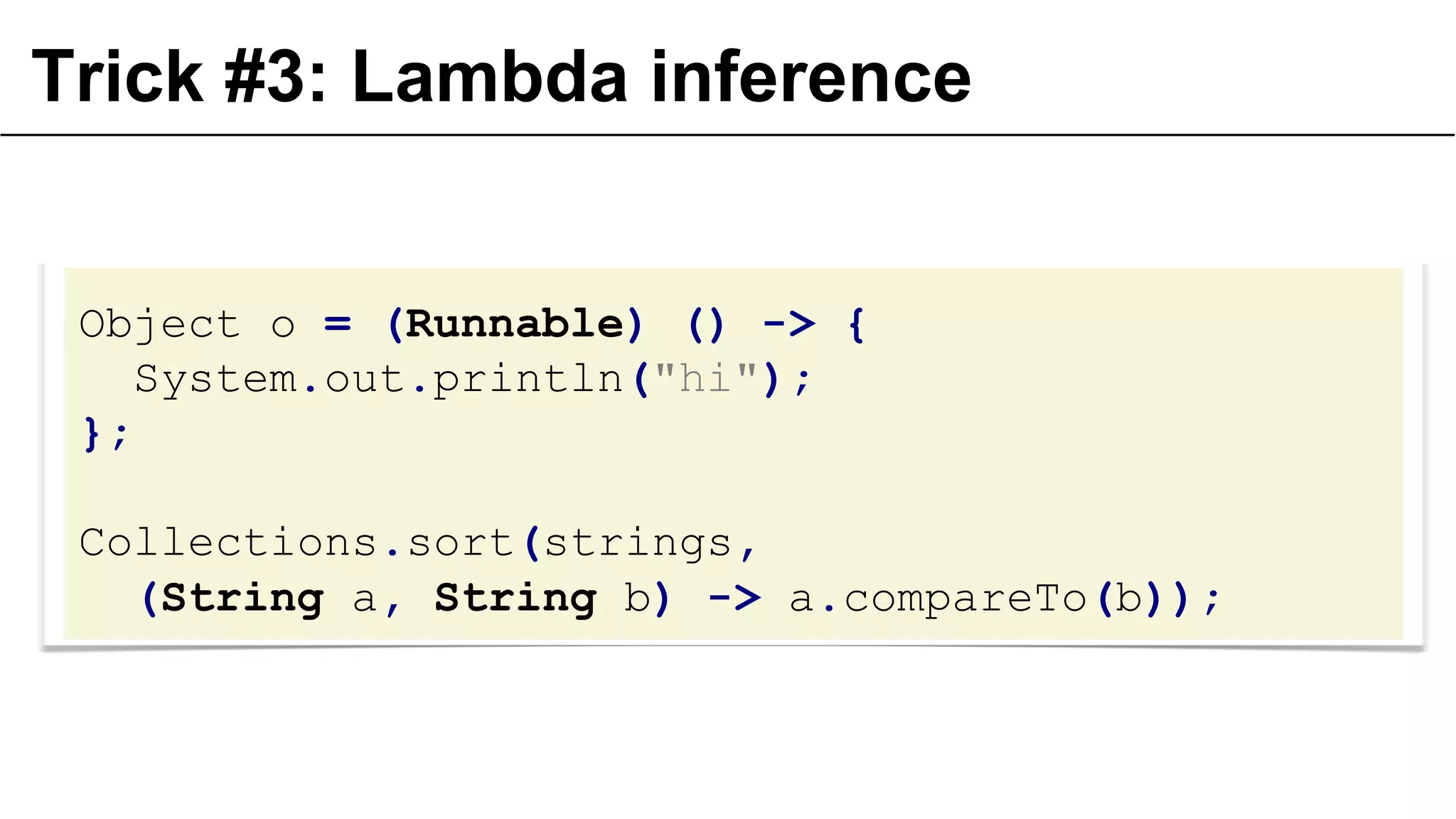
The document presents a detailed exploration of lambda expressions and generics in programming, particularly emphasizing their nuances and potential pitfalls. It discusses various coding techniques, type safety, and the consequences of improper use of generics. Additionally, it includes practical examples and references to further resources for understanding these concepts.


















![Arrays
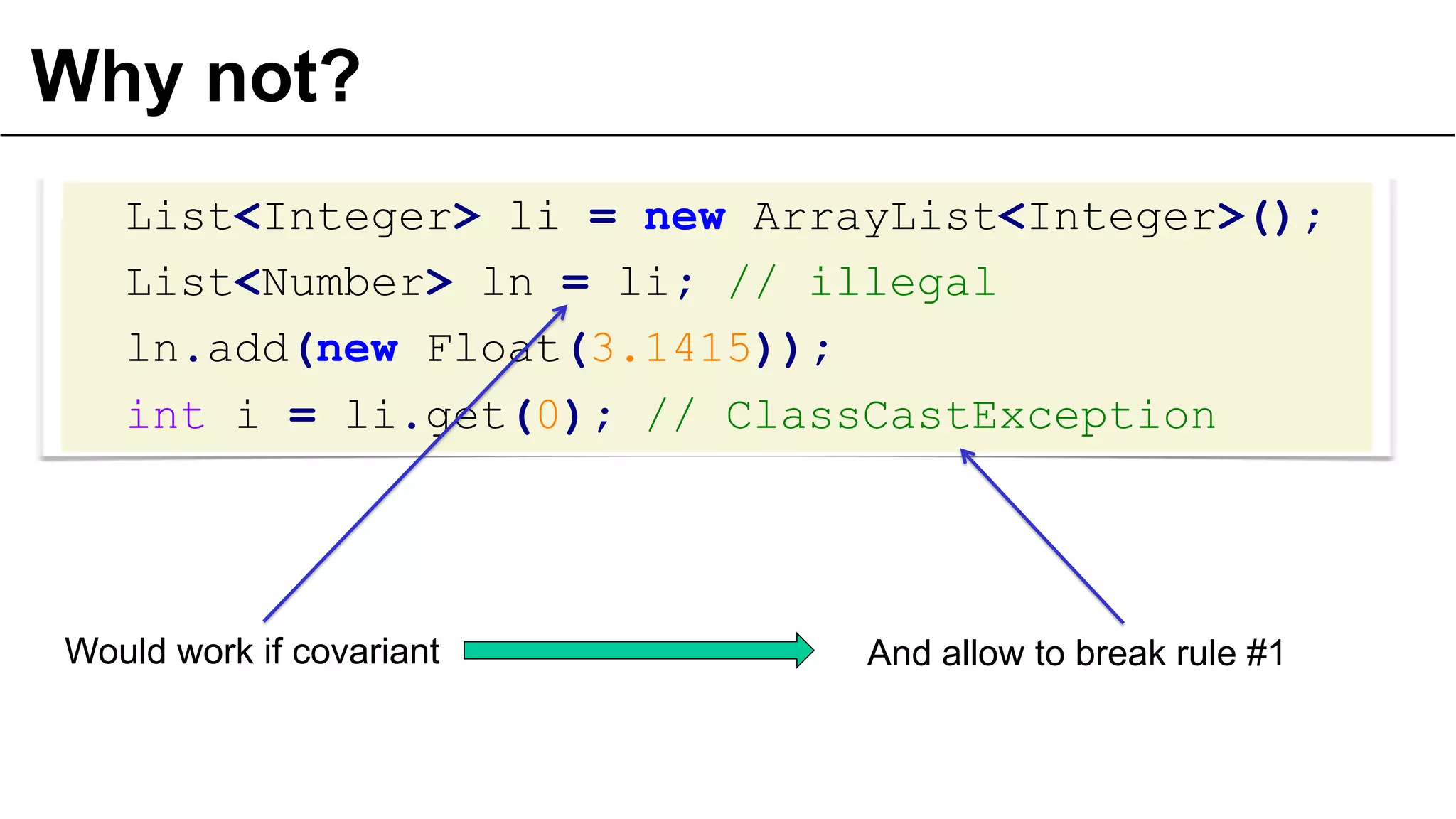
Arrays are covariant:
Number n = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Number[] list = new Integer[0];
Generics are not:
List<Number> l =
new ArrayList<Integer>(); // Illegal
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-24-2048.jpg)
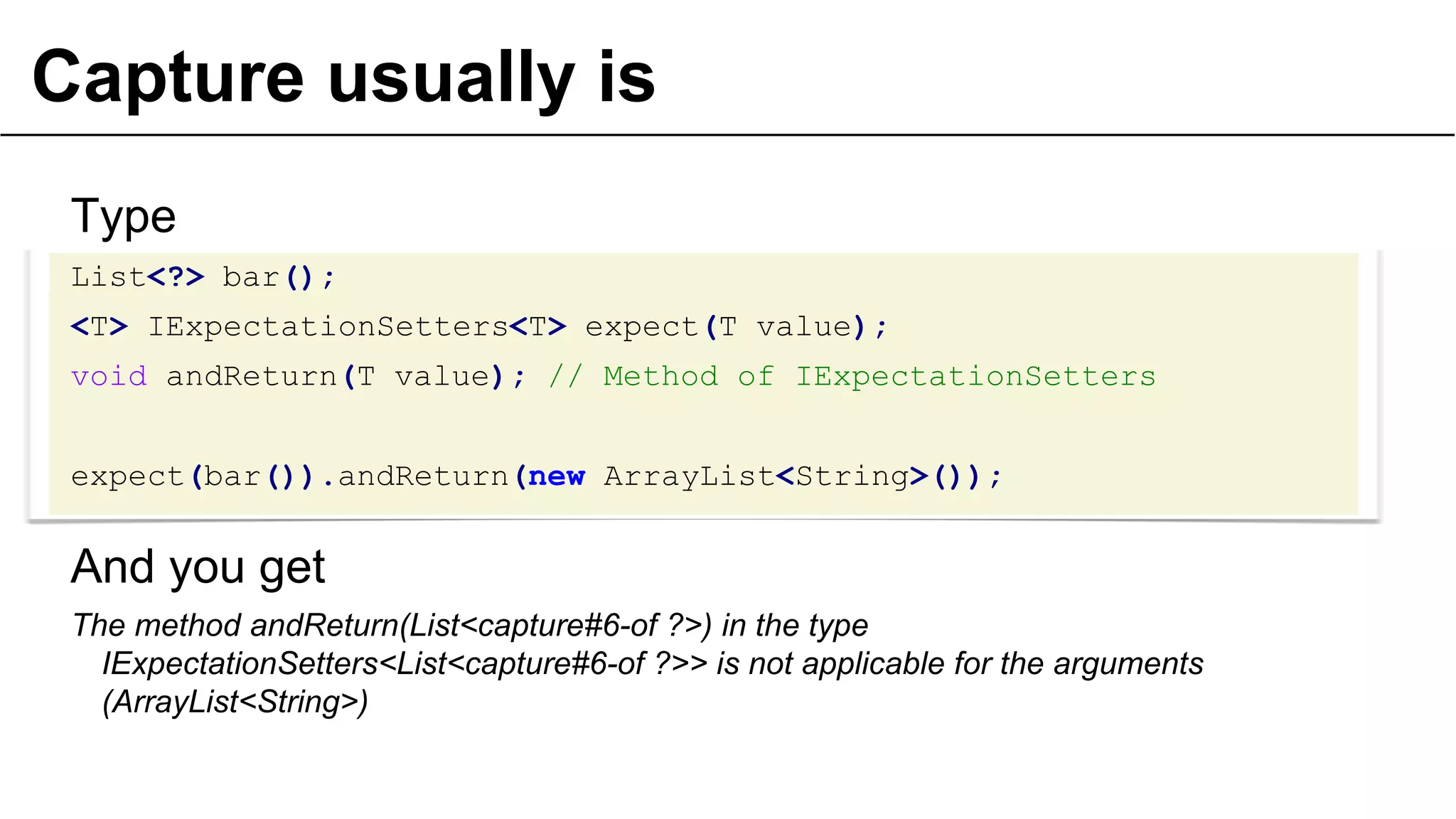
![Why for array?
Integer[] list = // ...
foo(list);
public void foo(Object[] o) {
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-26-2048.jpg)
![Arrays and generics don’t mix well
Can’t have an array of generics
List<String>[] lsa = new List<String>[10];// illegal
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-27-2048.jpg)
![Because
If it was allowed
List<String>[] lsa = new List<String>[10]; // illegal
Object[] oa = lsa; // OK (covariant)
oa[0] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // OK
String s = lsa[0].get(0); // bad
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-28-2048.jpg)
![Exception
List<?>[] l = new ArrayList<?>[3];
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-29-2048.jpg)

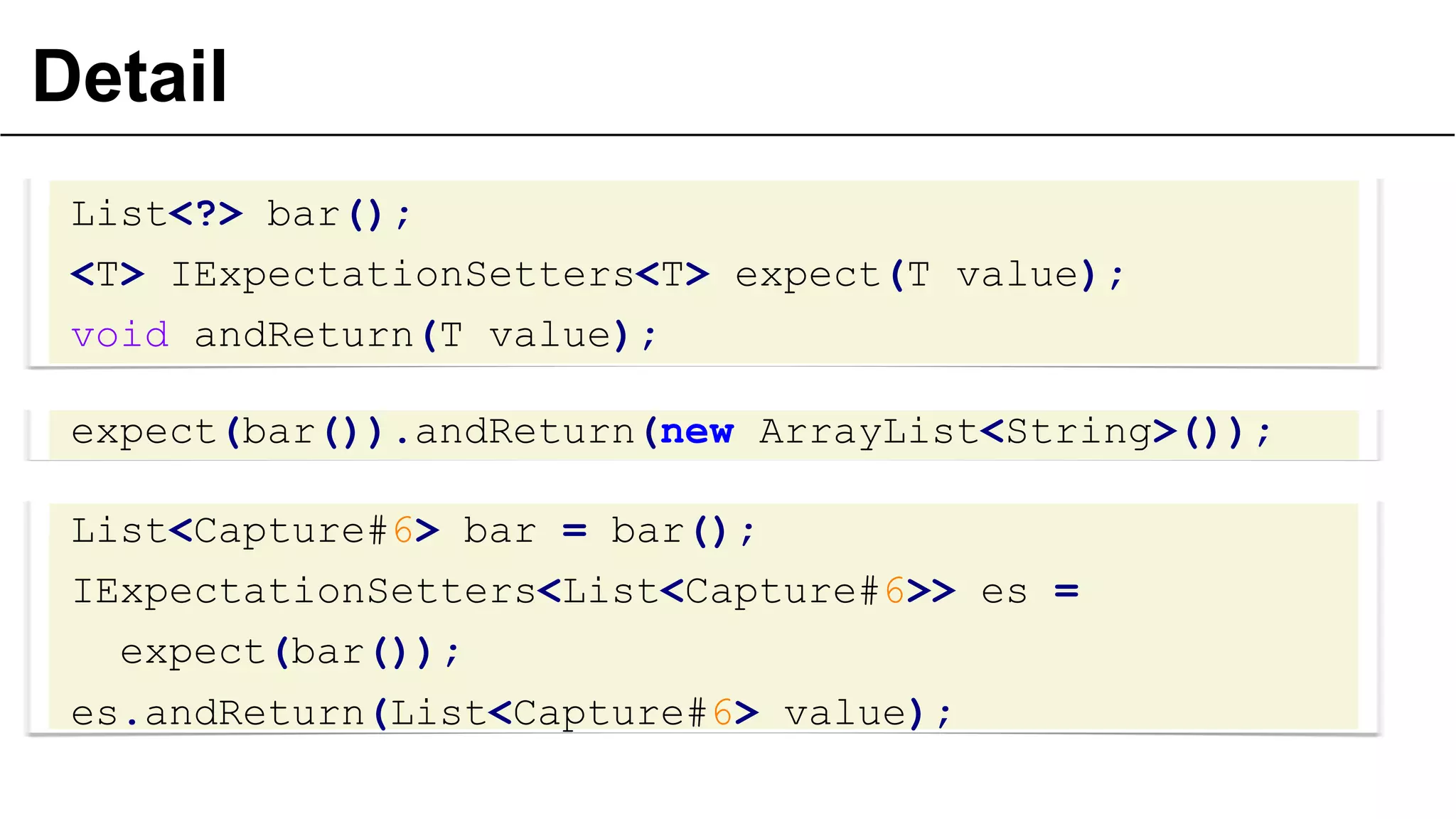


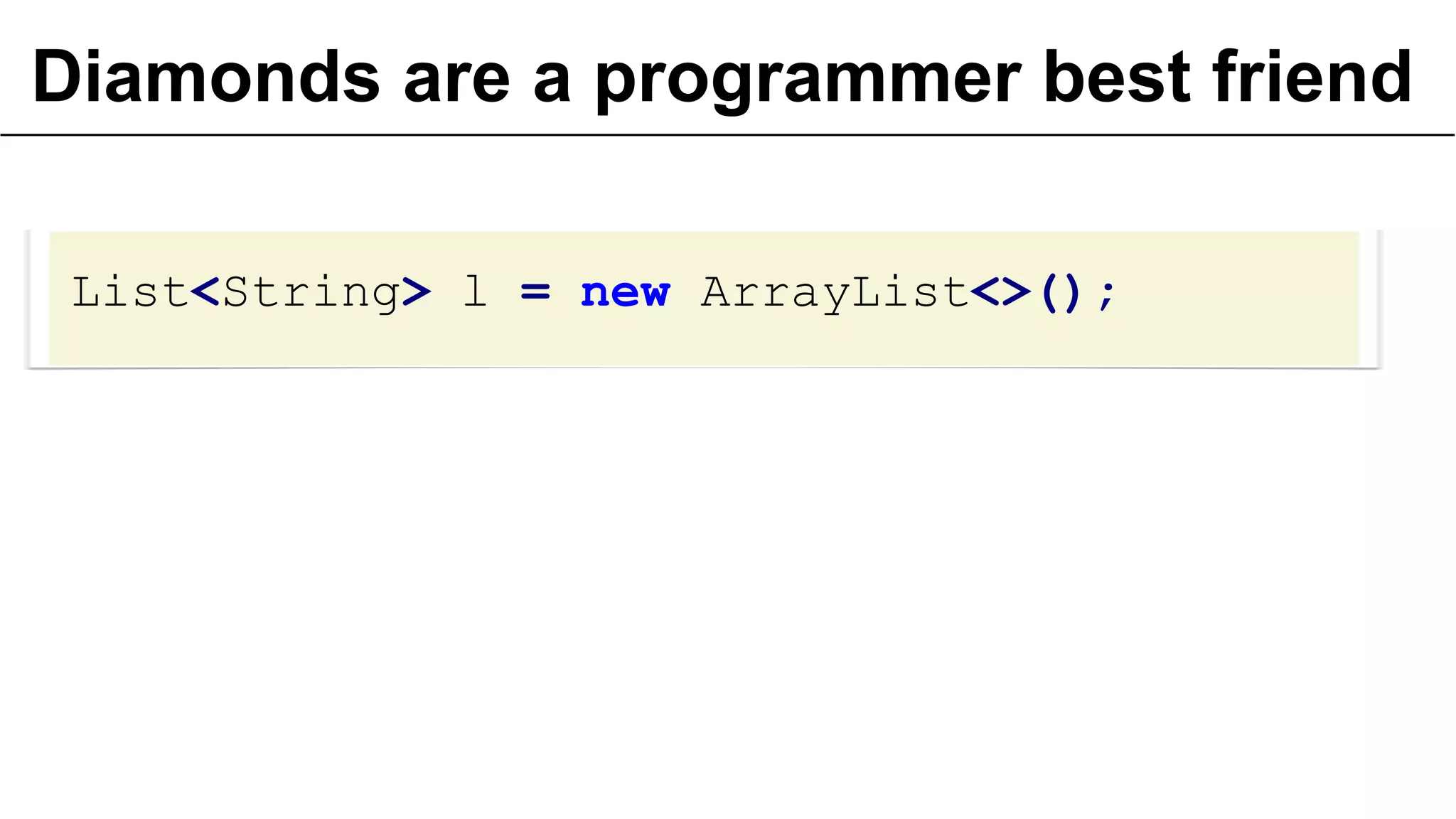
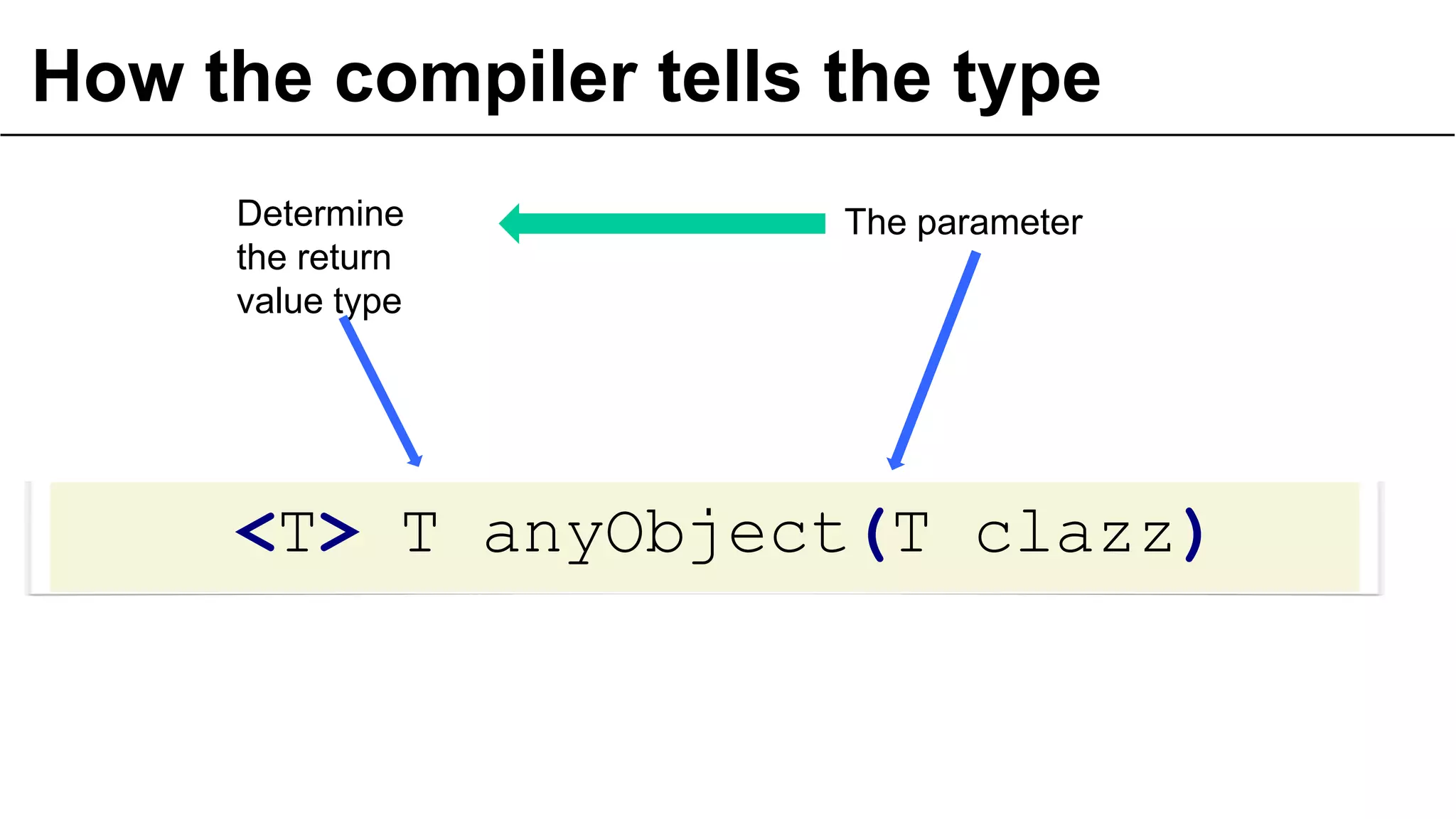
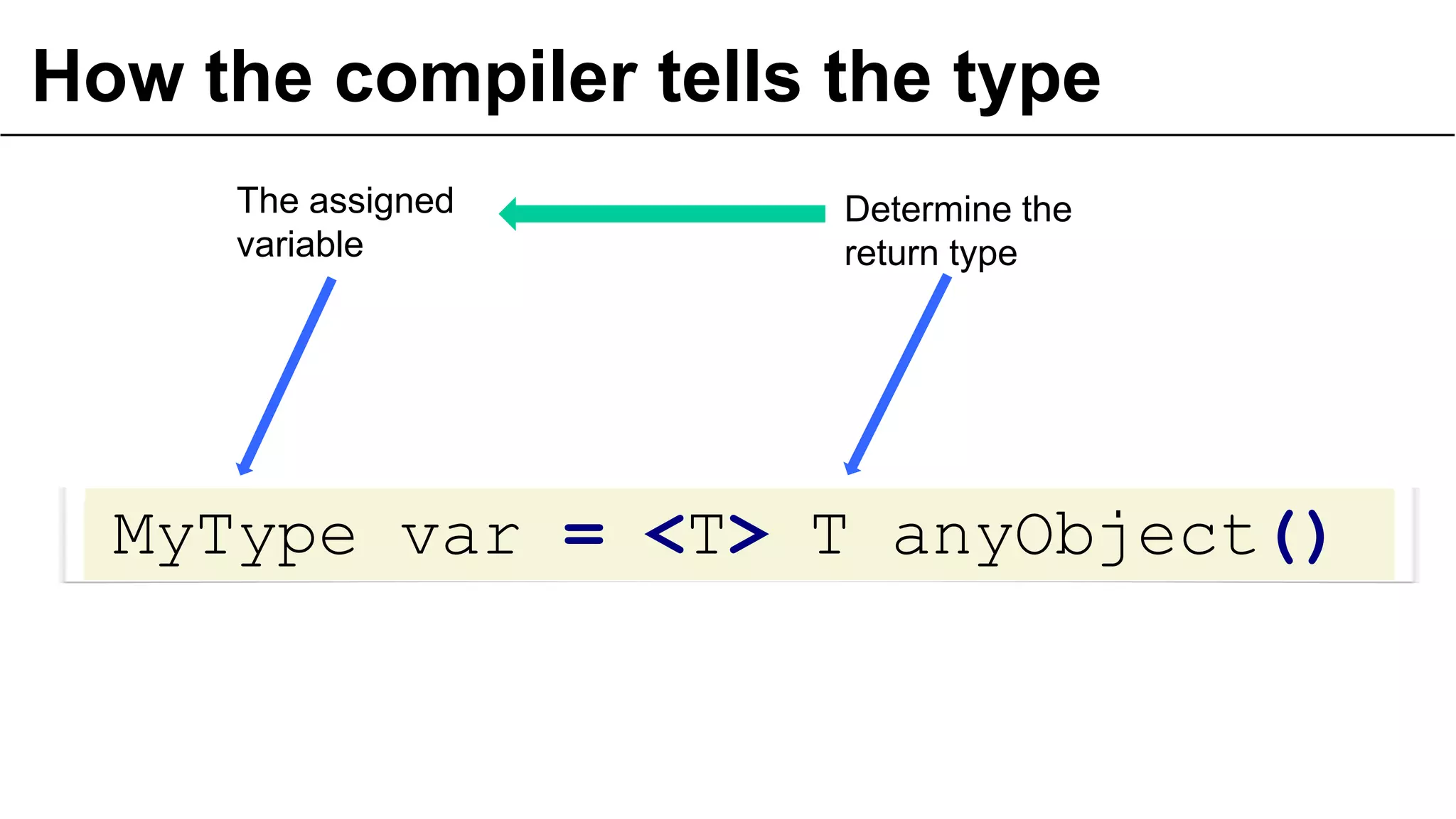






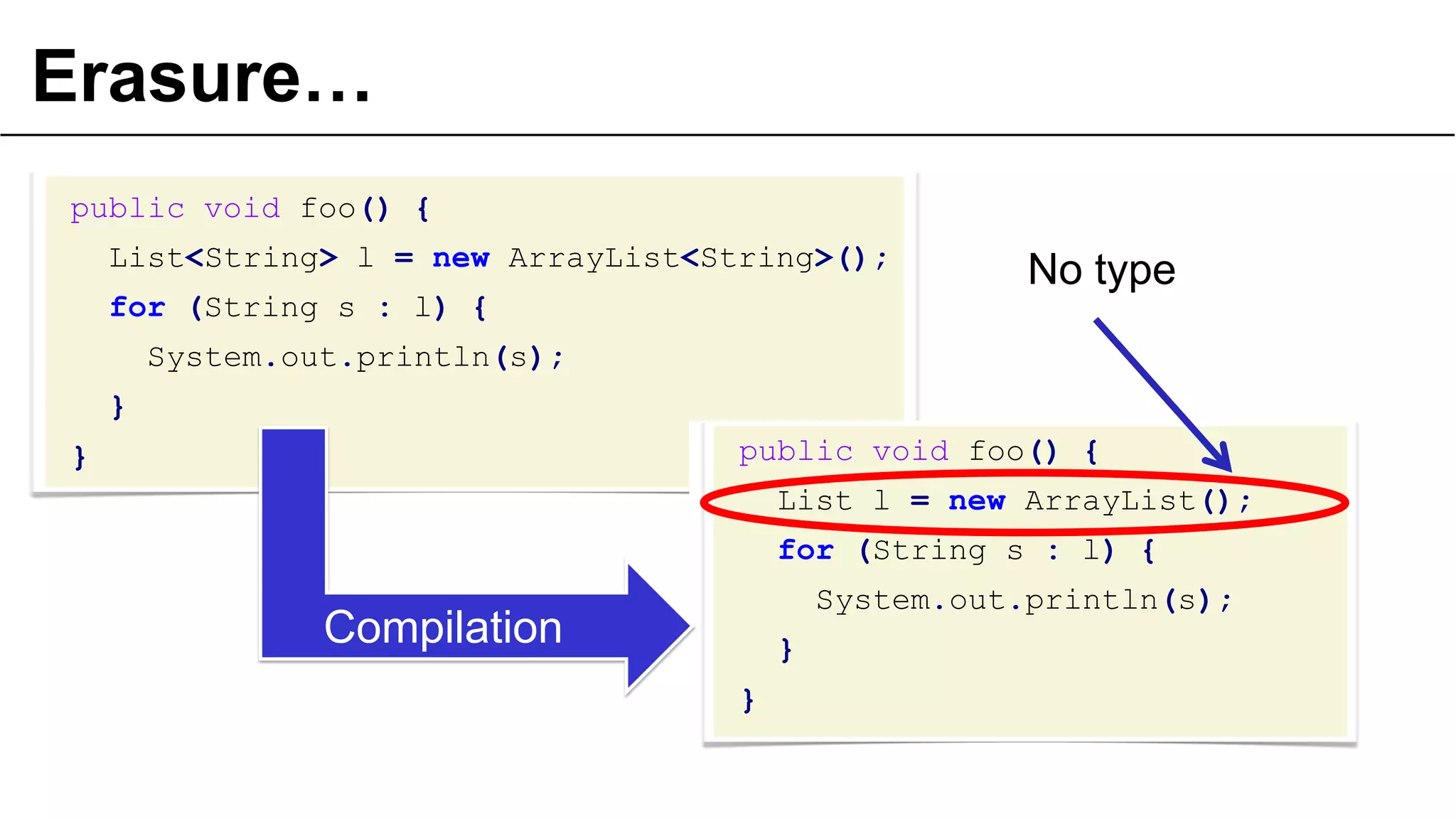
![… or not erasure
public class A extends ArrayList<String> {}
public static void main(final String[] args) {
ParameterizedType type = (ParameterizedType)
A.class.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(
type.getActualTypeArguments()[0]);
}
prints class java.lang.String
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-49-2048.jpg)
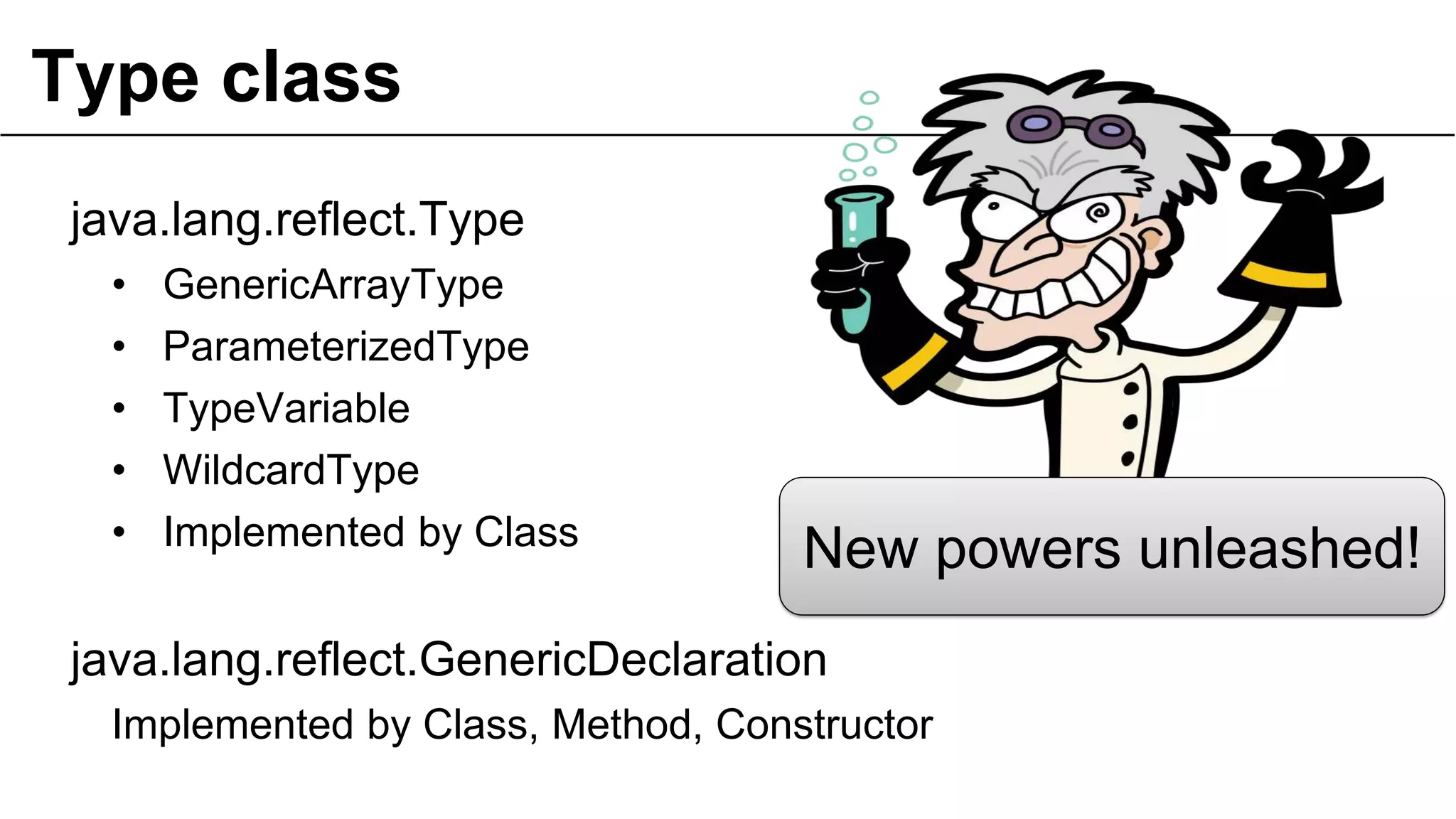

![Useful!
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T load(final long id) {
ParameterizedType type =
(ParameterizedType) getClass()
.getGenericSuperclass();
ADao
BaseDao<A>
A
Type actualType = type.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
return em.find((Class<T>) actualType, (Long) id);
}
Unsafe cast](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-52-2048.jpg)



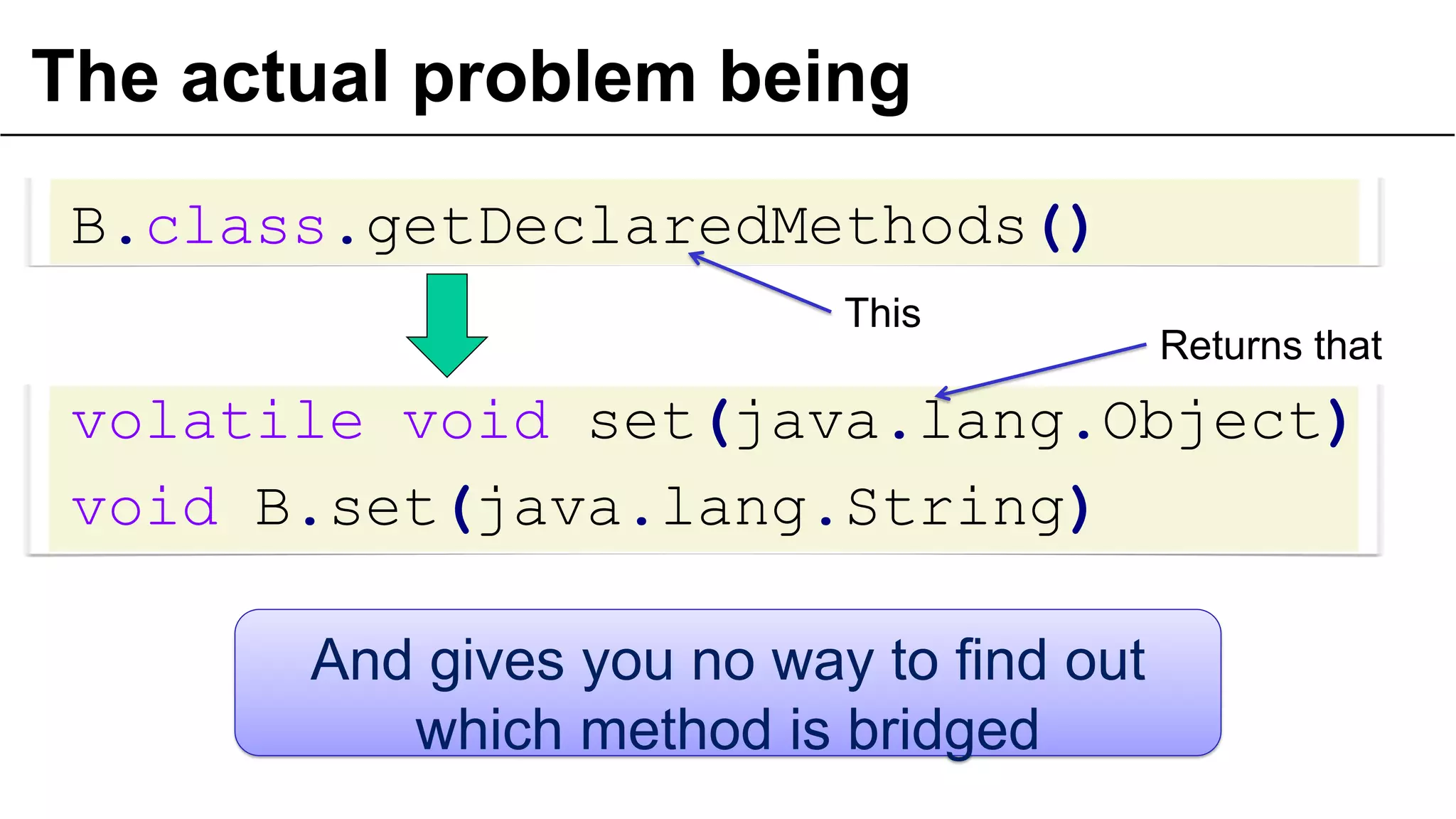
![What about lambdas?
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Method[] methods = A.class.getDeclaredMethods();
Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(m ->
System.out.println(m + " "
+ m.isBridge() + " " + m.isSynthetic()));
}
}
Prints this
public static void A.main(java.lang.String[]) false false
private static void A.lambda$0(java.lang.reflect.Method) false true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underthehoodofgenerics-20131017bordeauxjug-131019174010-phpapp02/75/Lambdas-and-Generics-long-version-Bordeaux-Toulouse-JUG-58-2048.jpg)