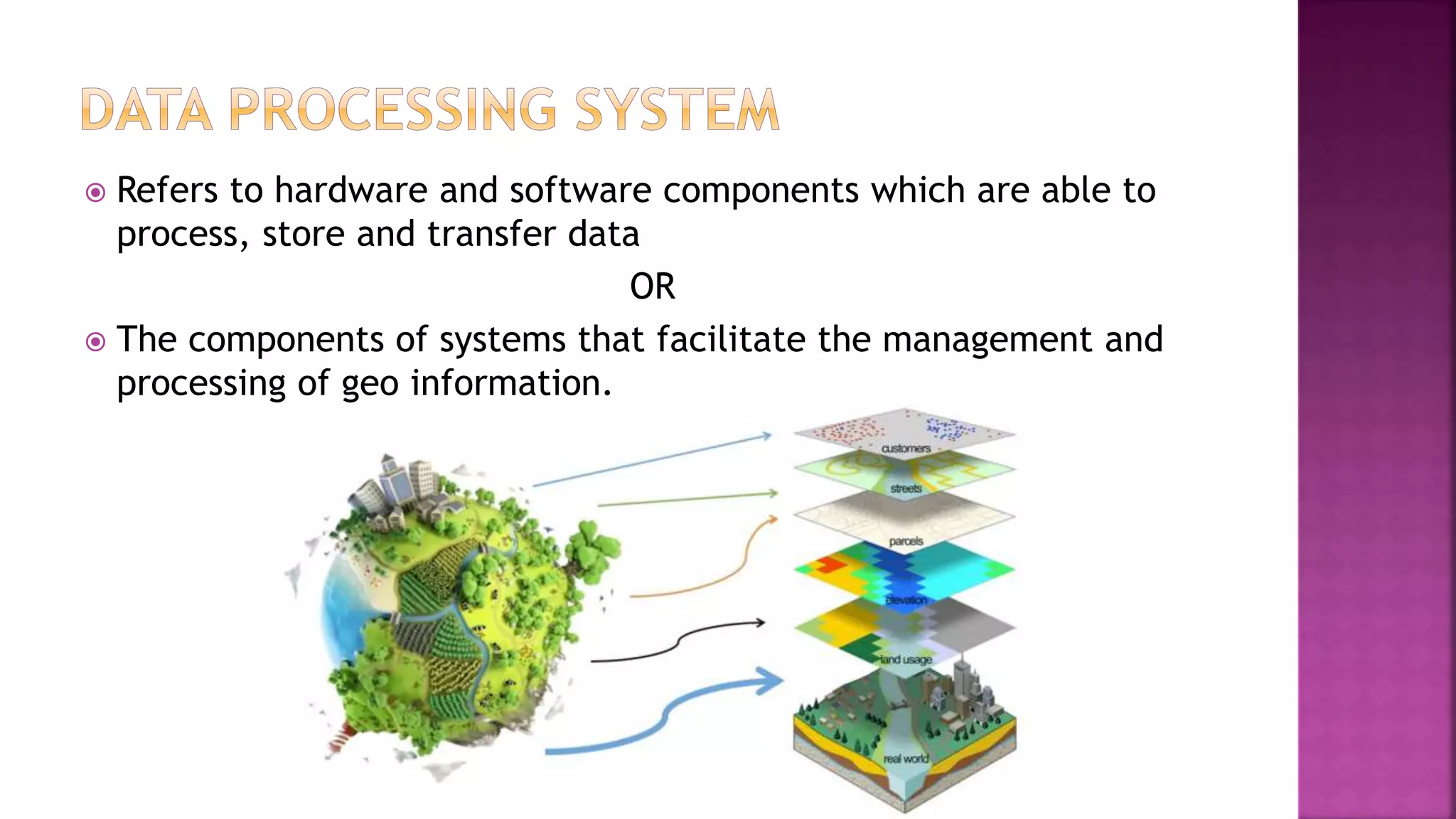
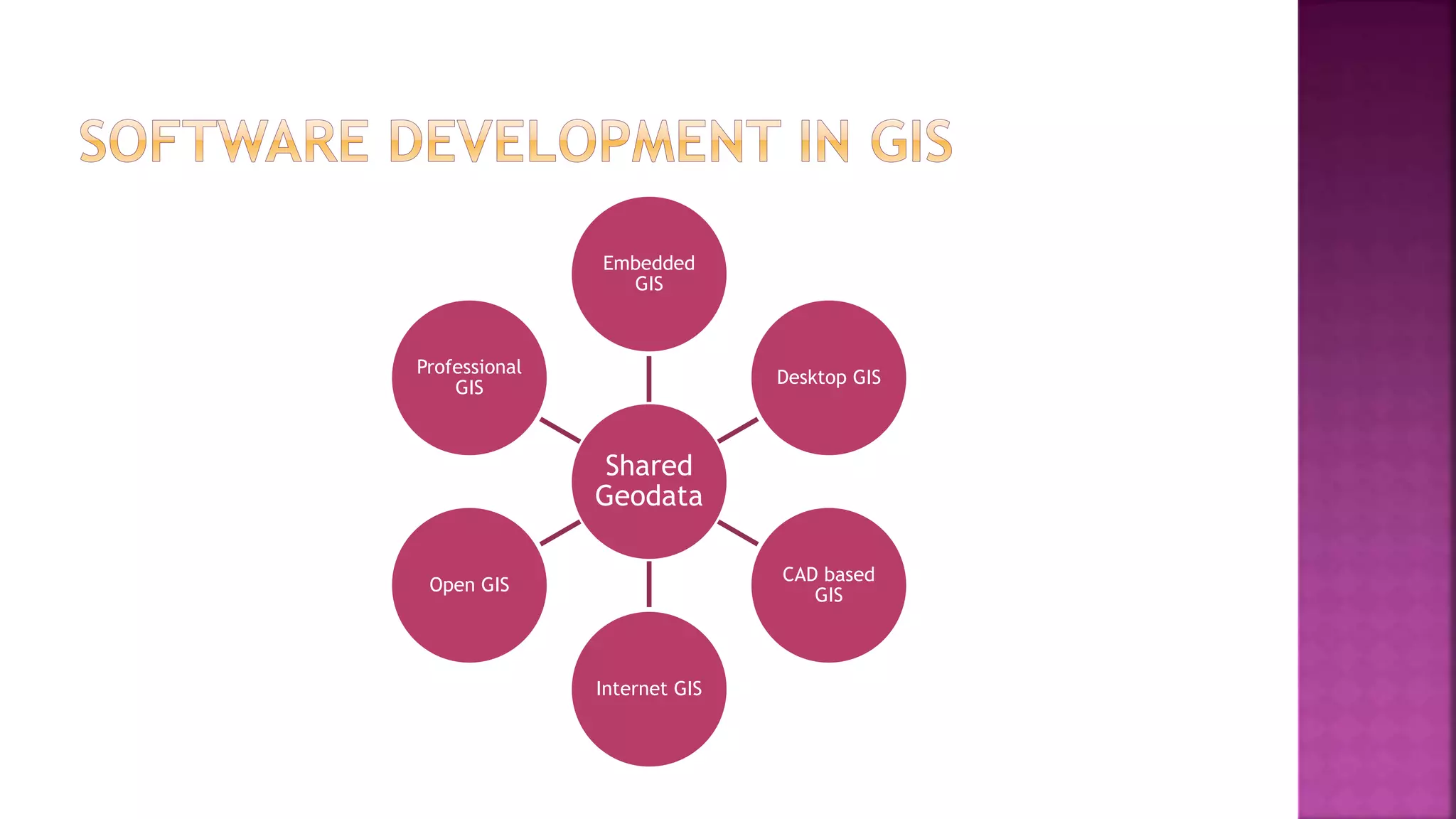
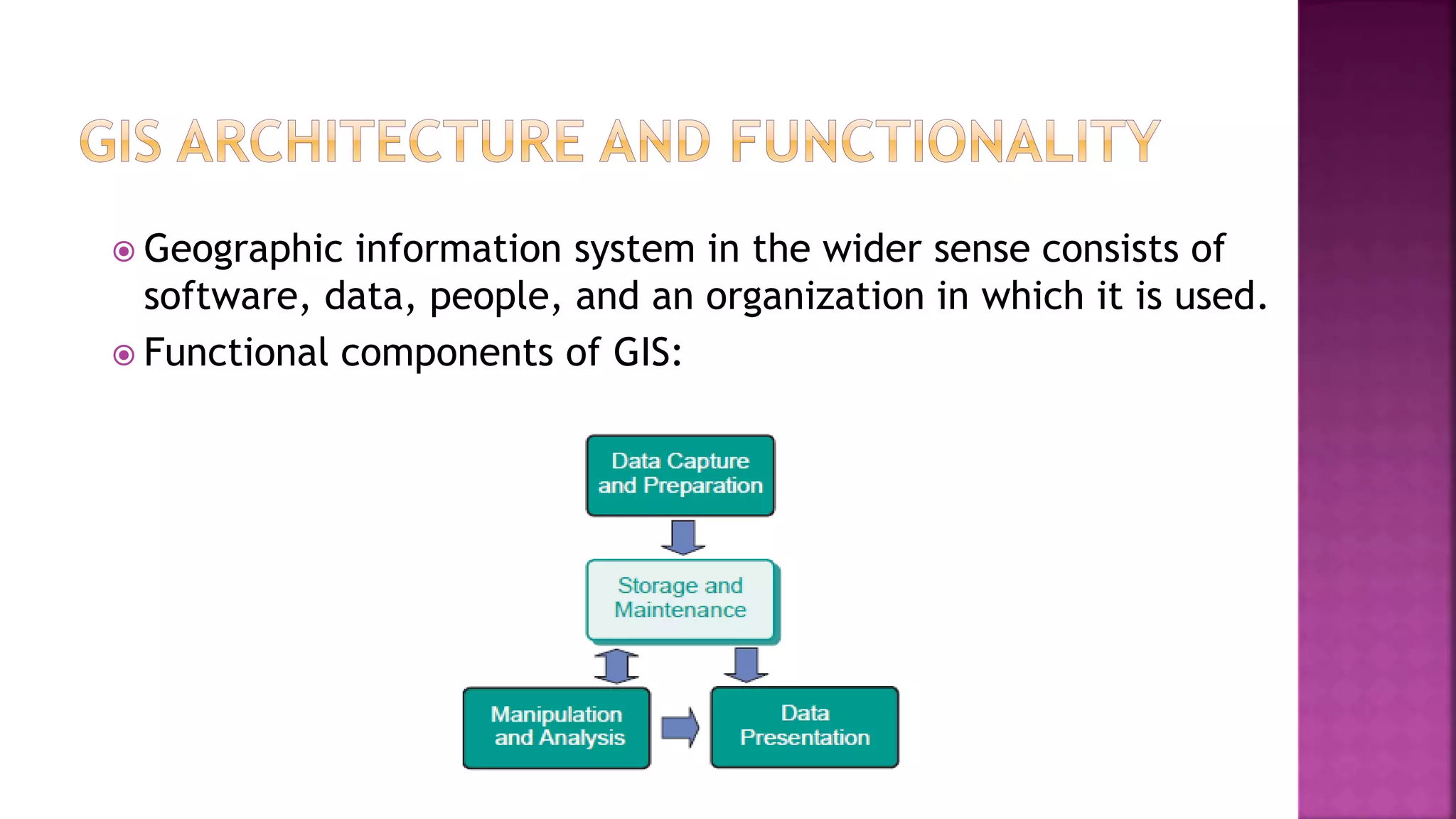
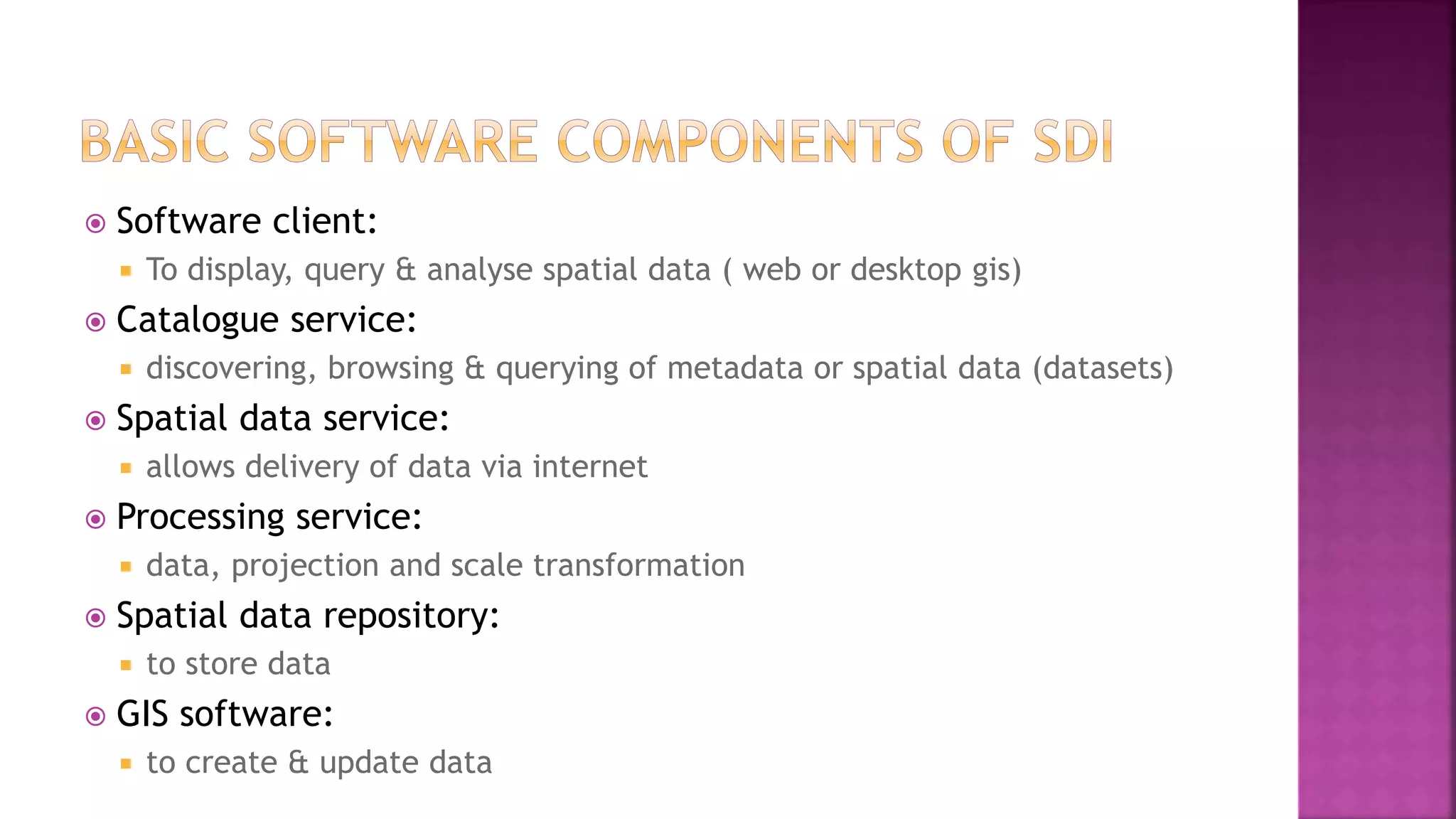
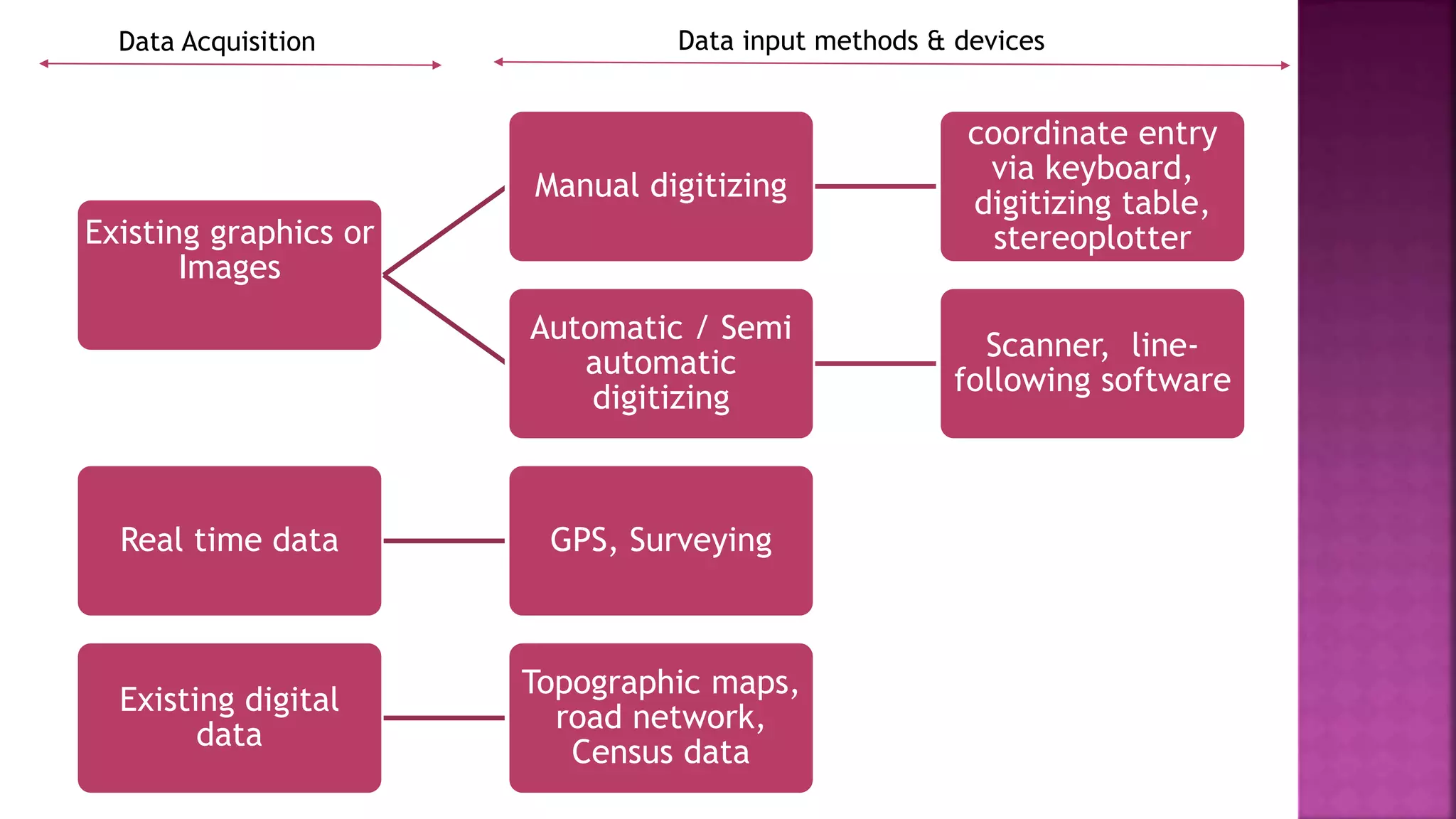
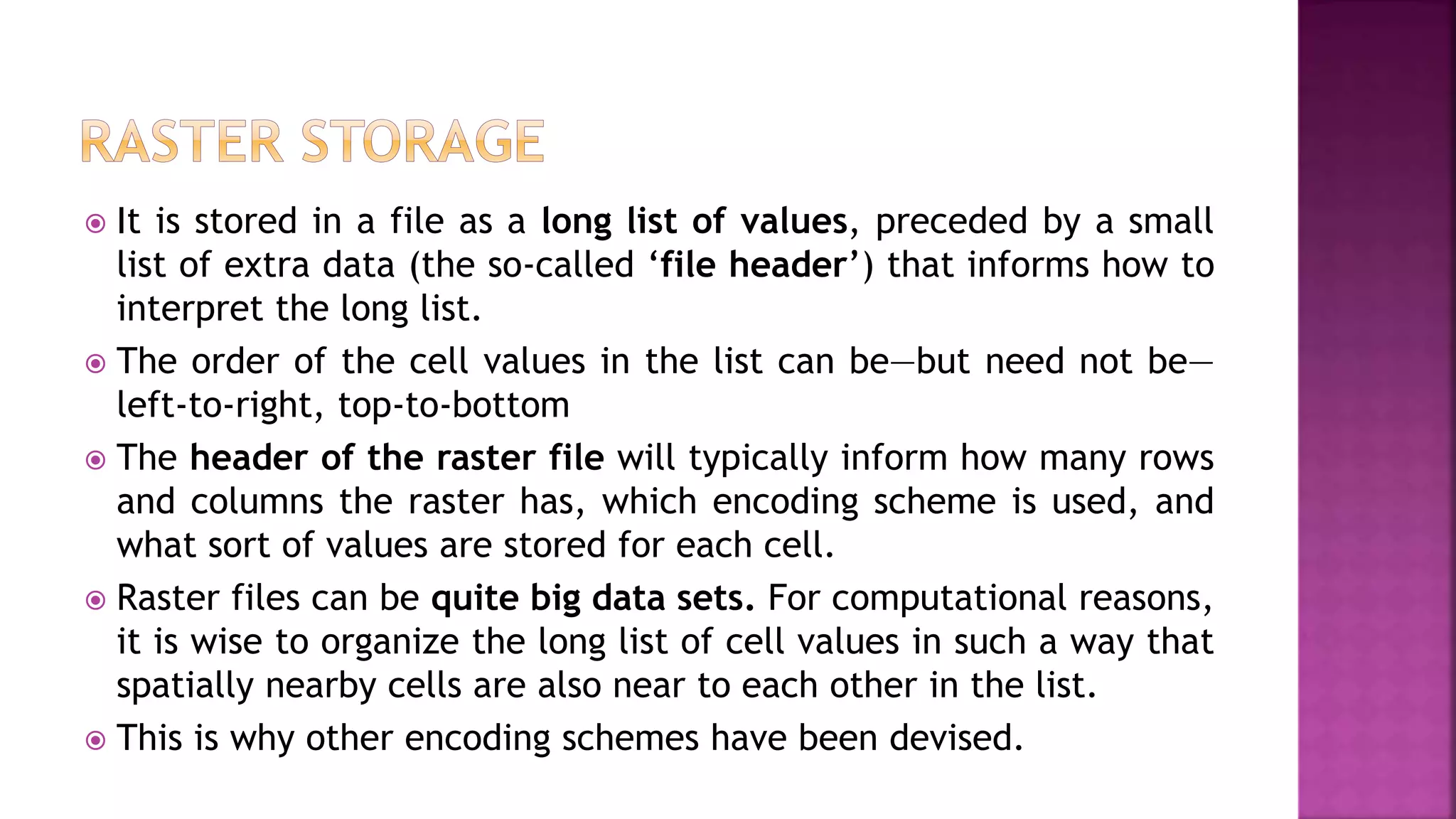
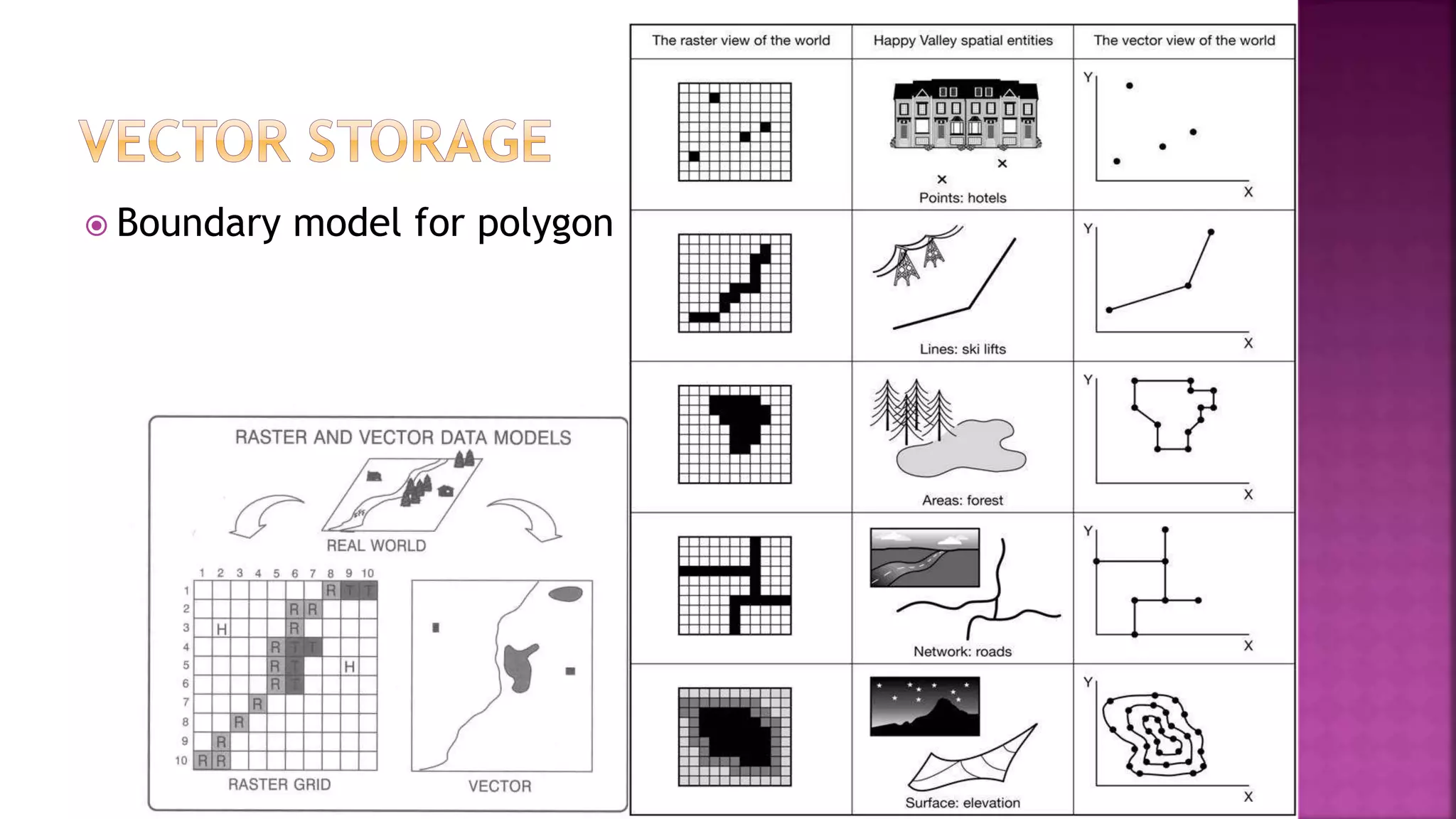
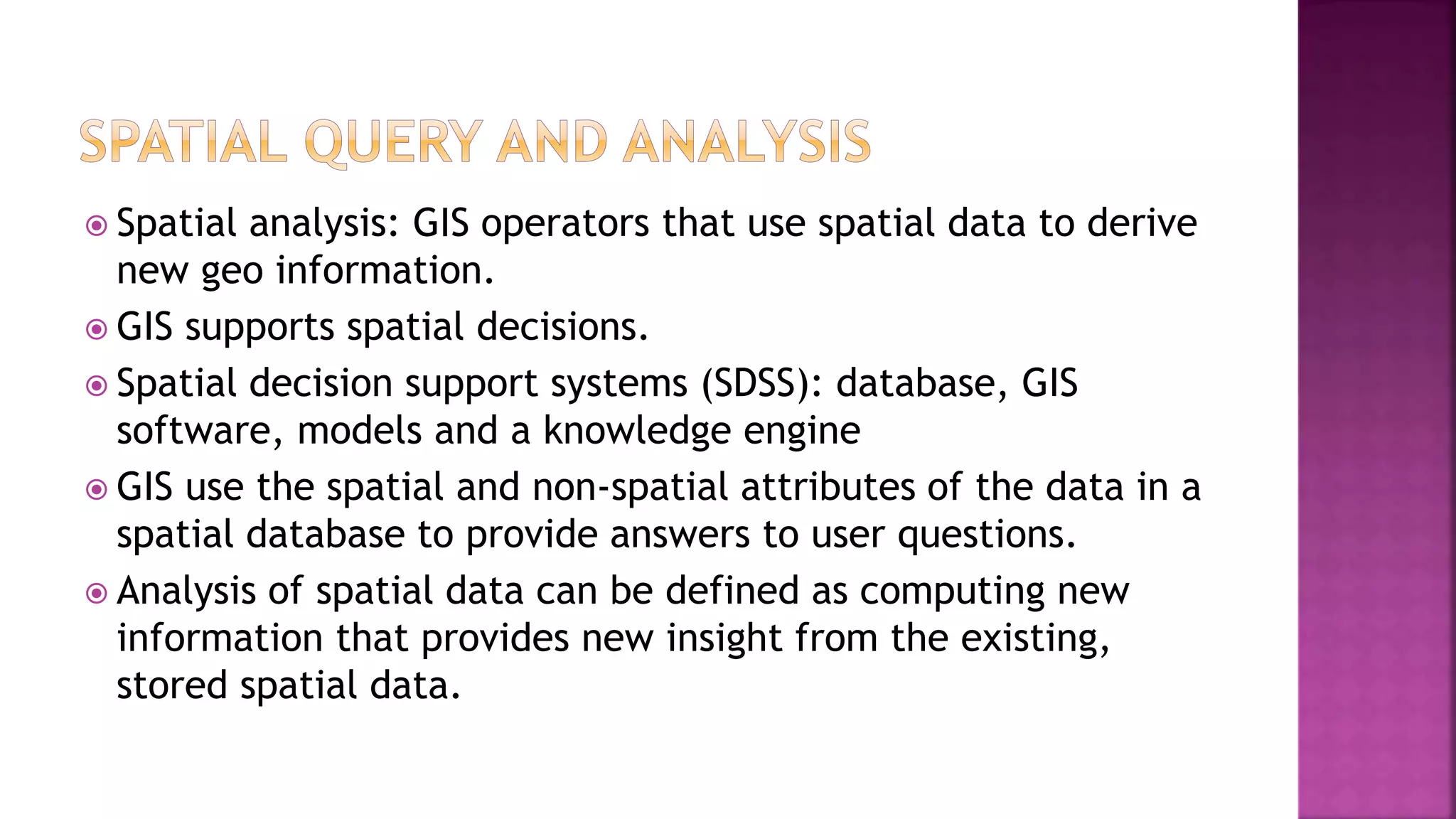
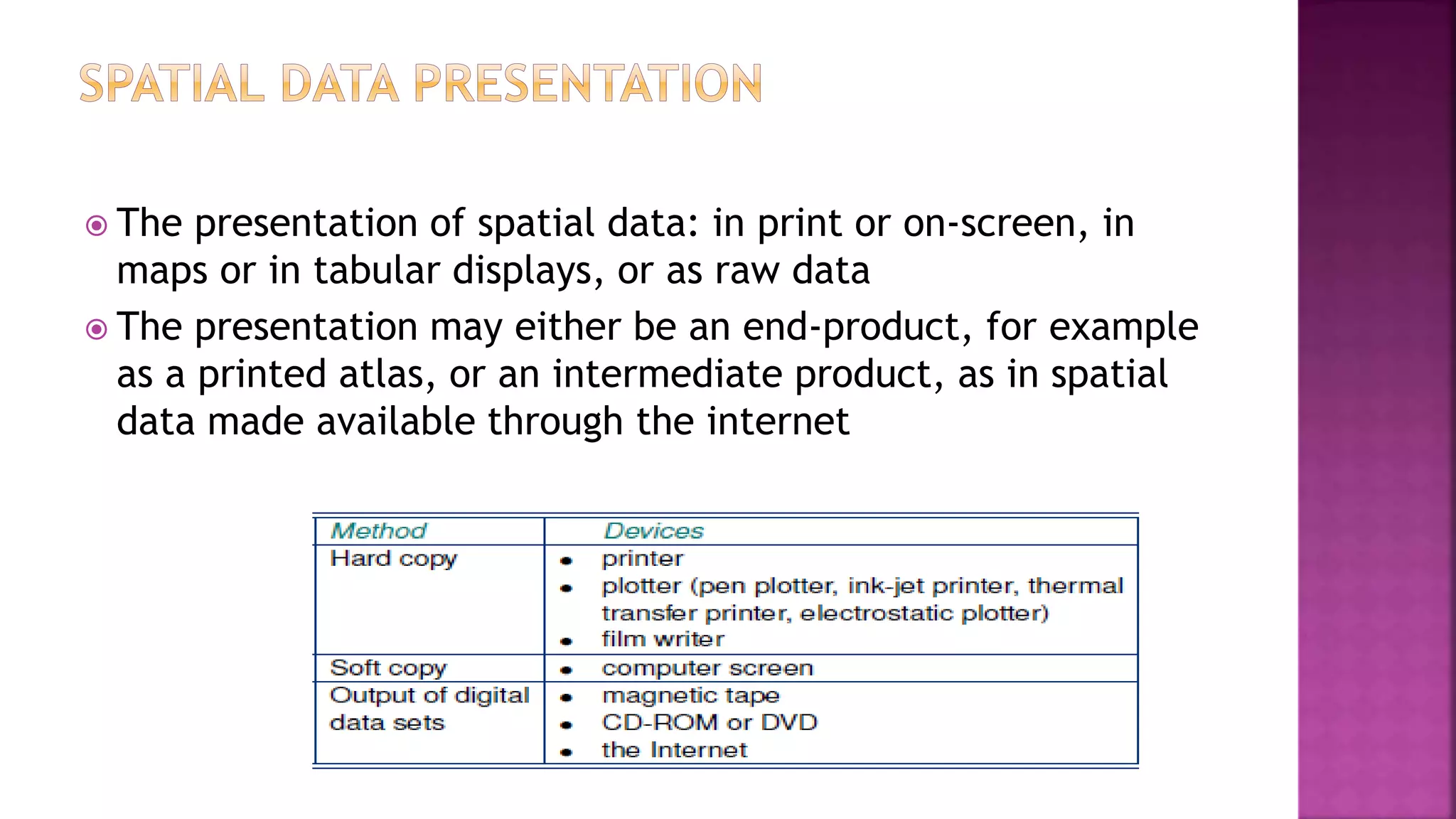
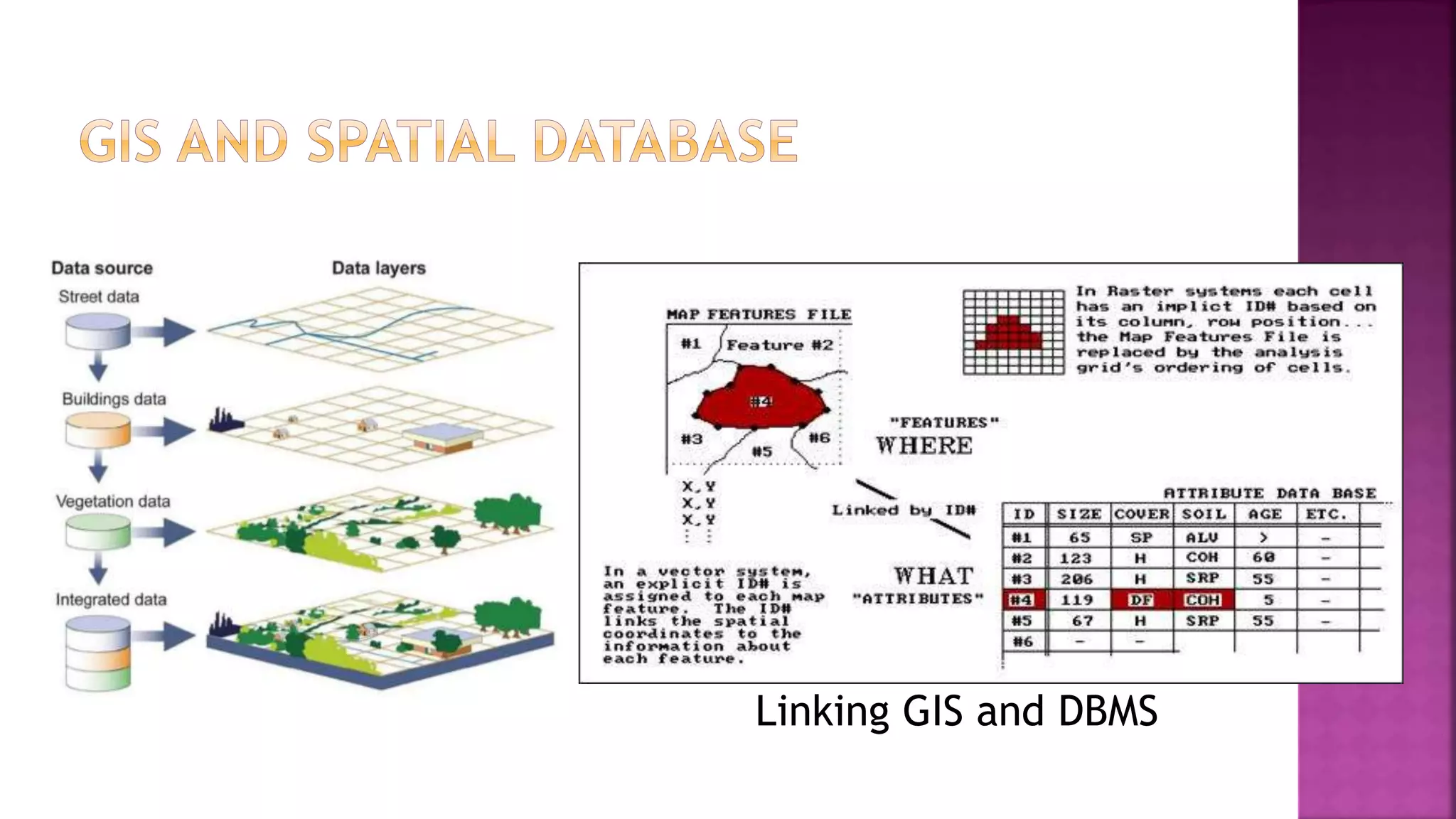
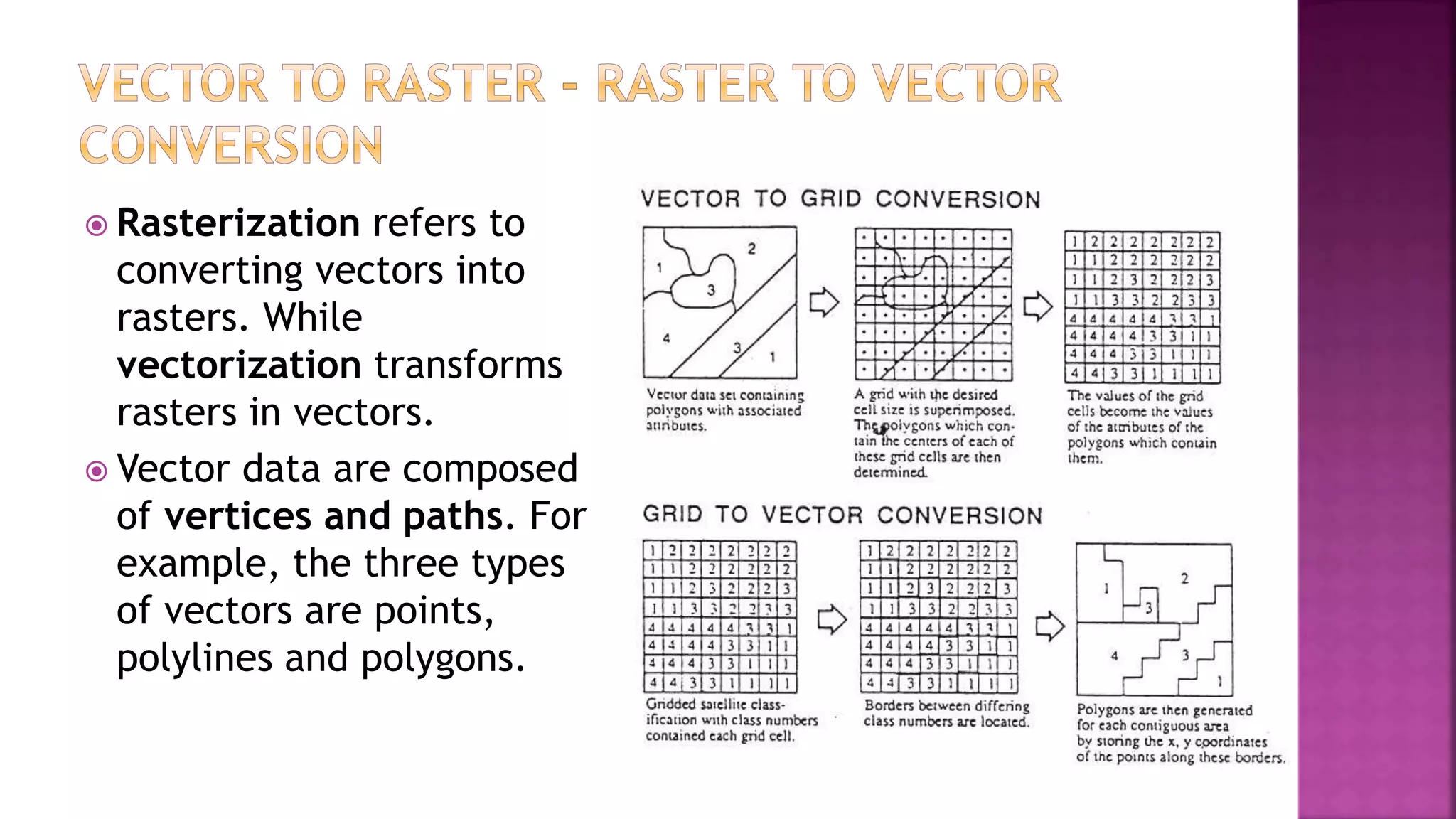
This document discusses geographic information systems (GIS). It defines GIS as hardware and software used to process, store, and transfer geographic data. It describes how GIS has evolved from using analog data and manual processing to increased use of digital data, computers, and software. It also discusses key GIS concepts like spatial data capture and analysis, data storage and management, and data presentation.