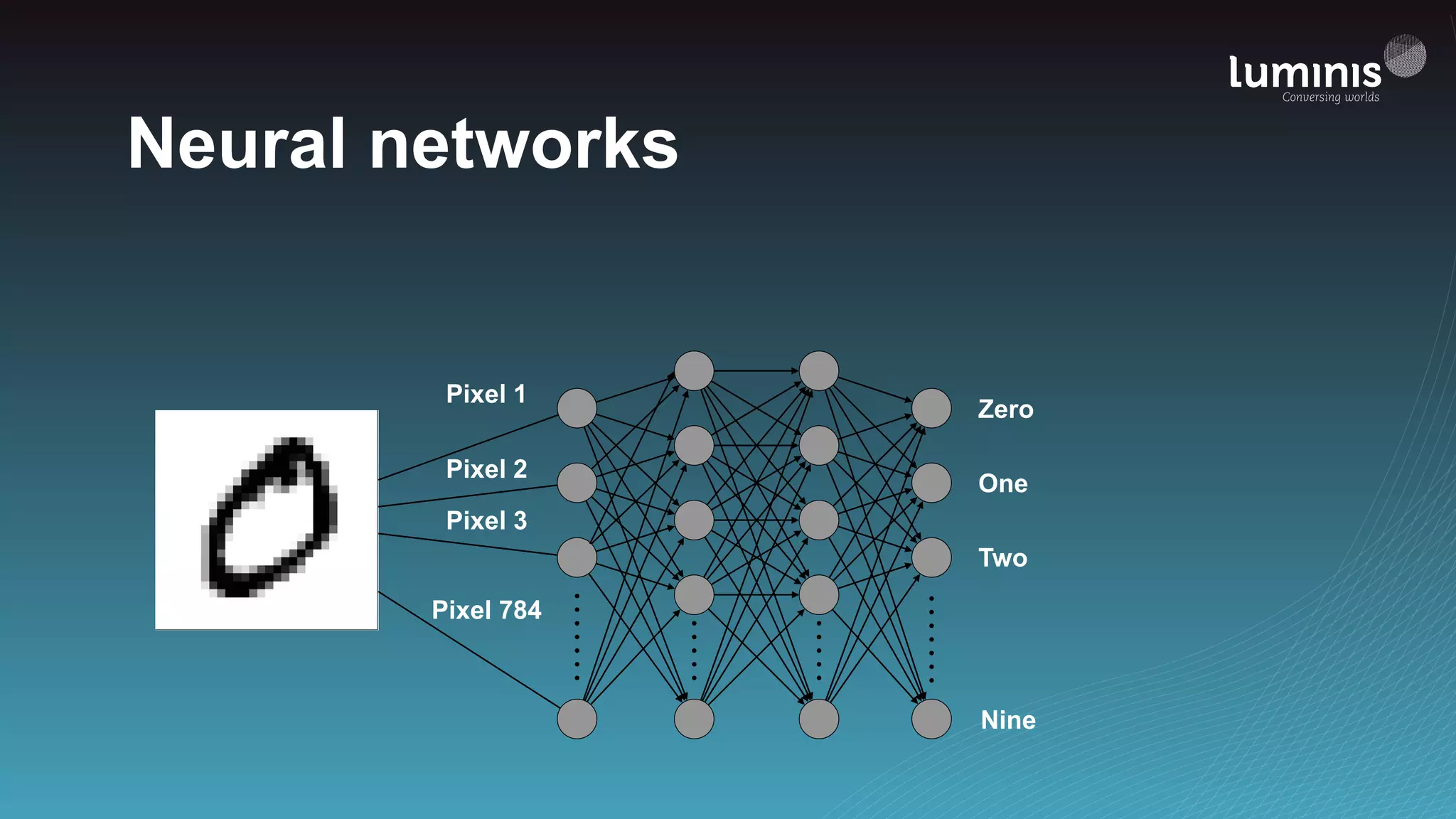
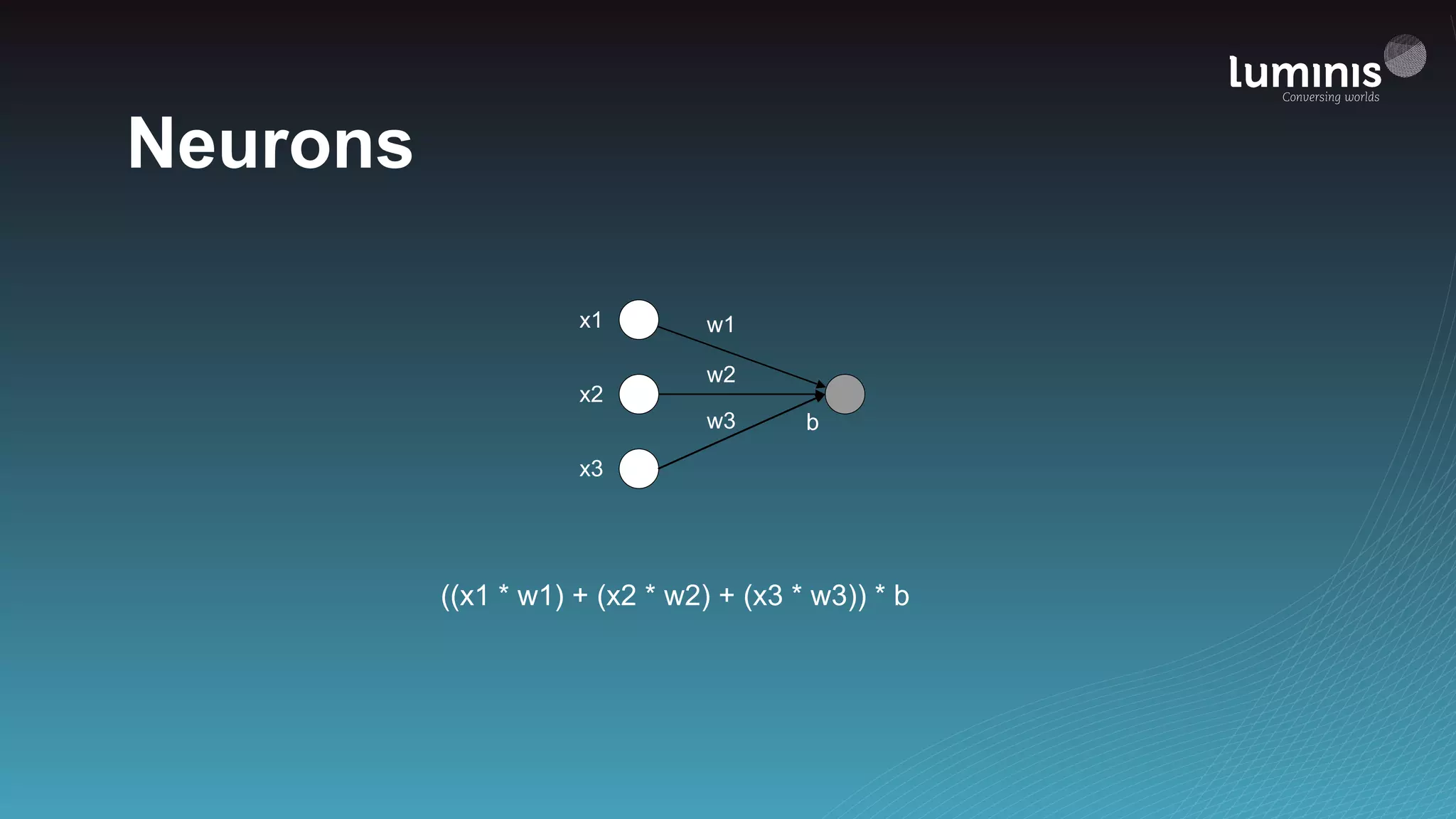
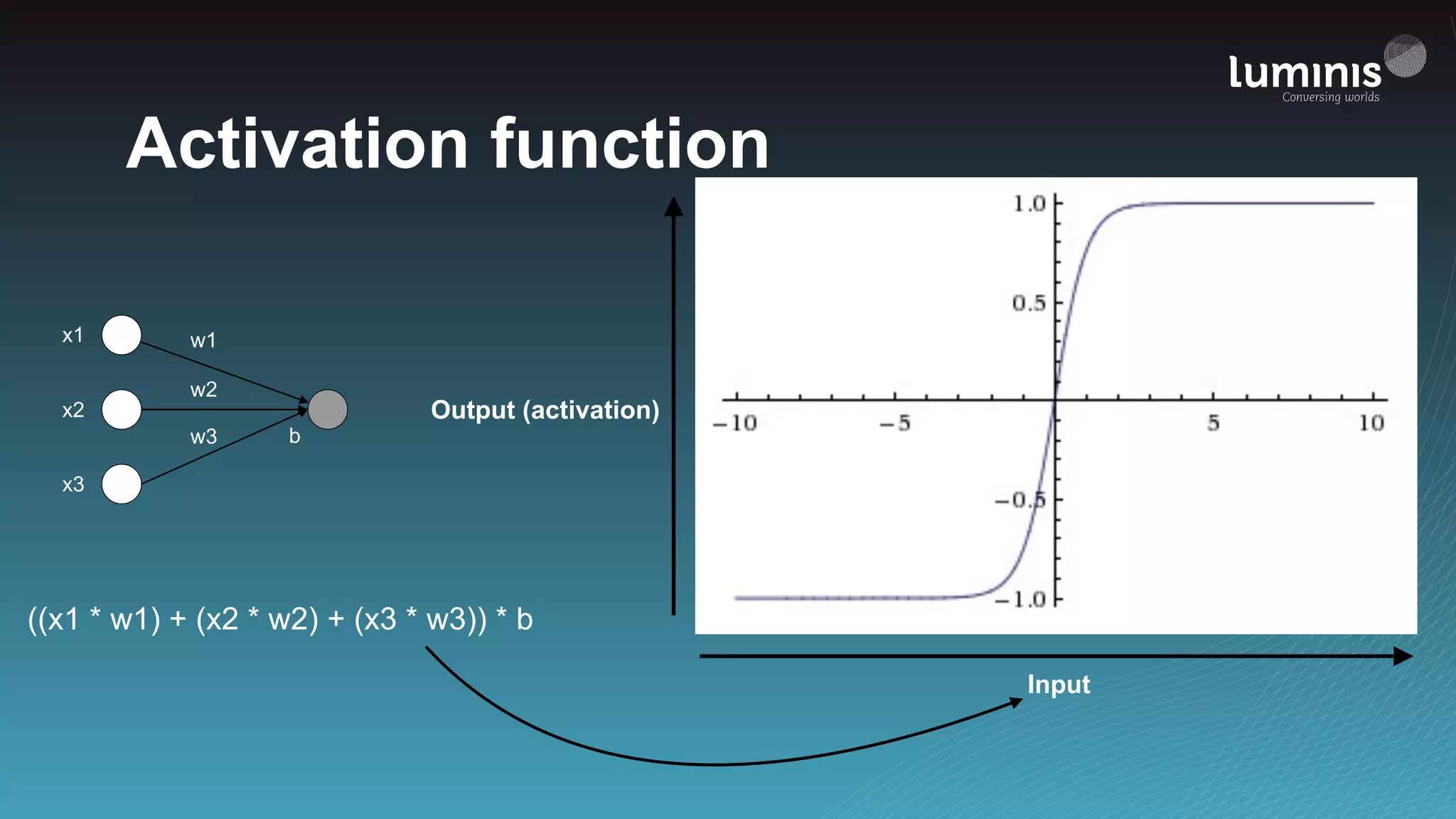
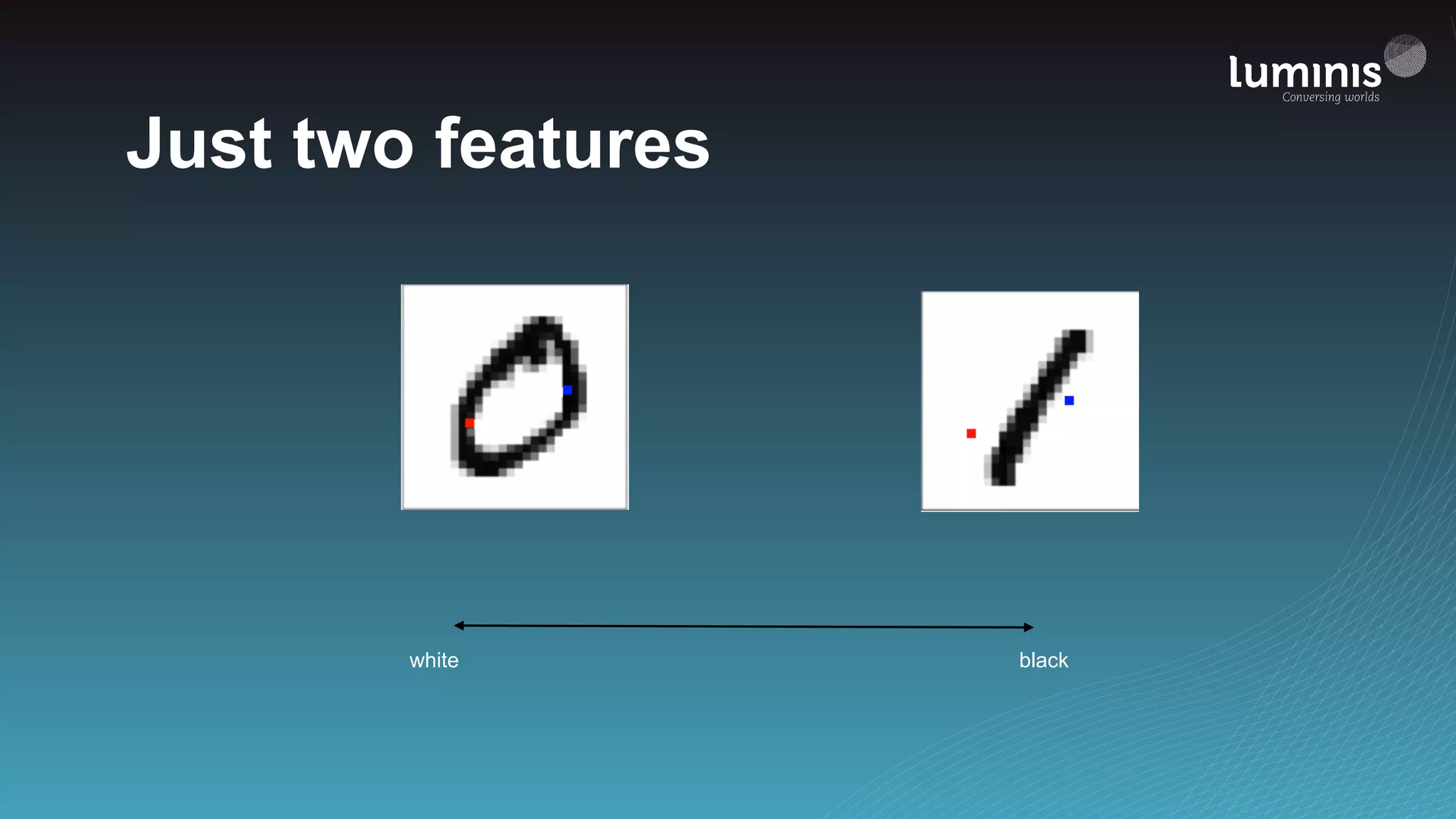
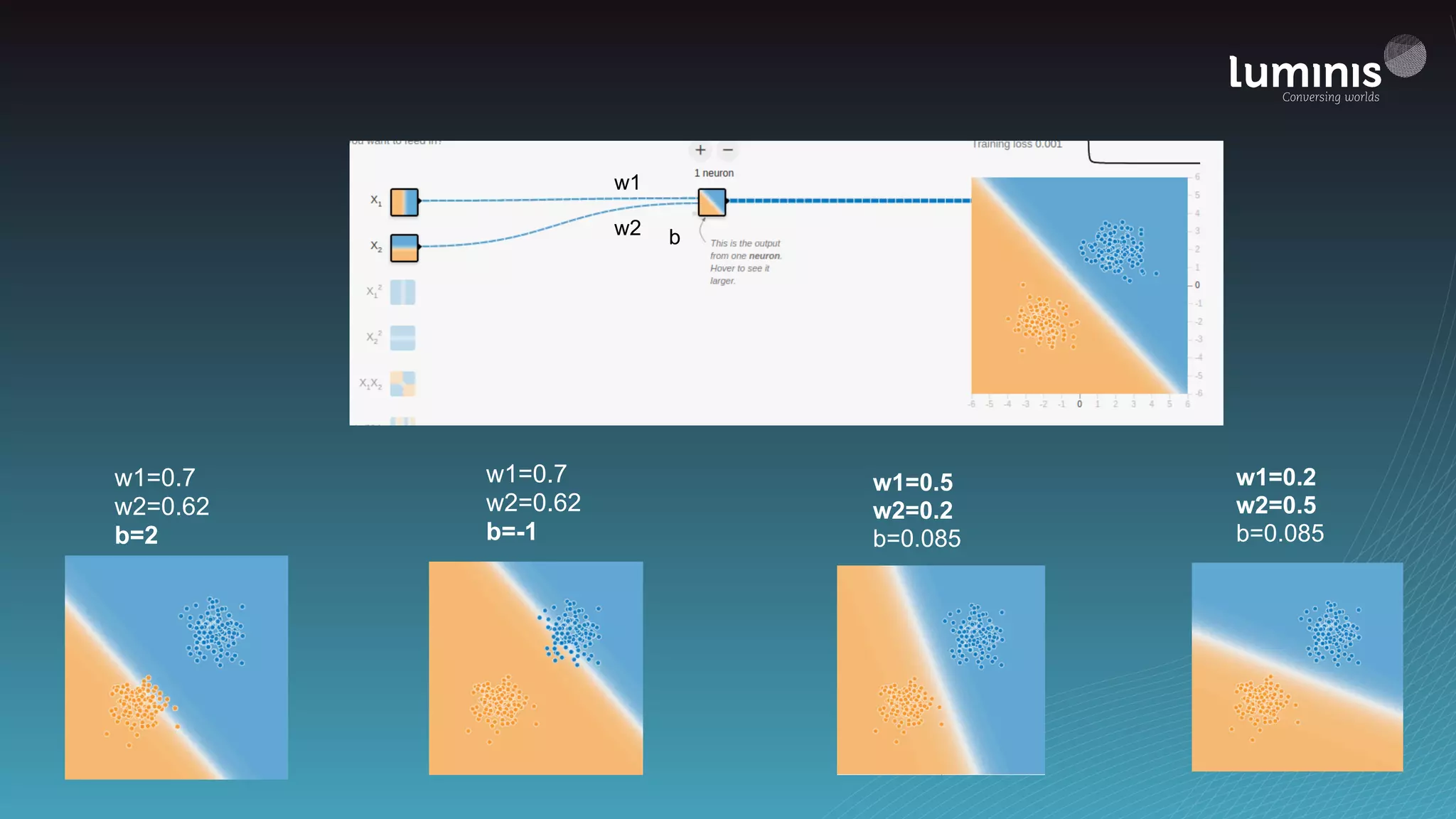
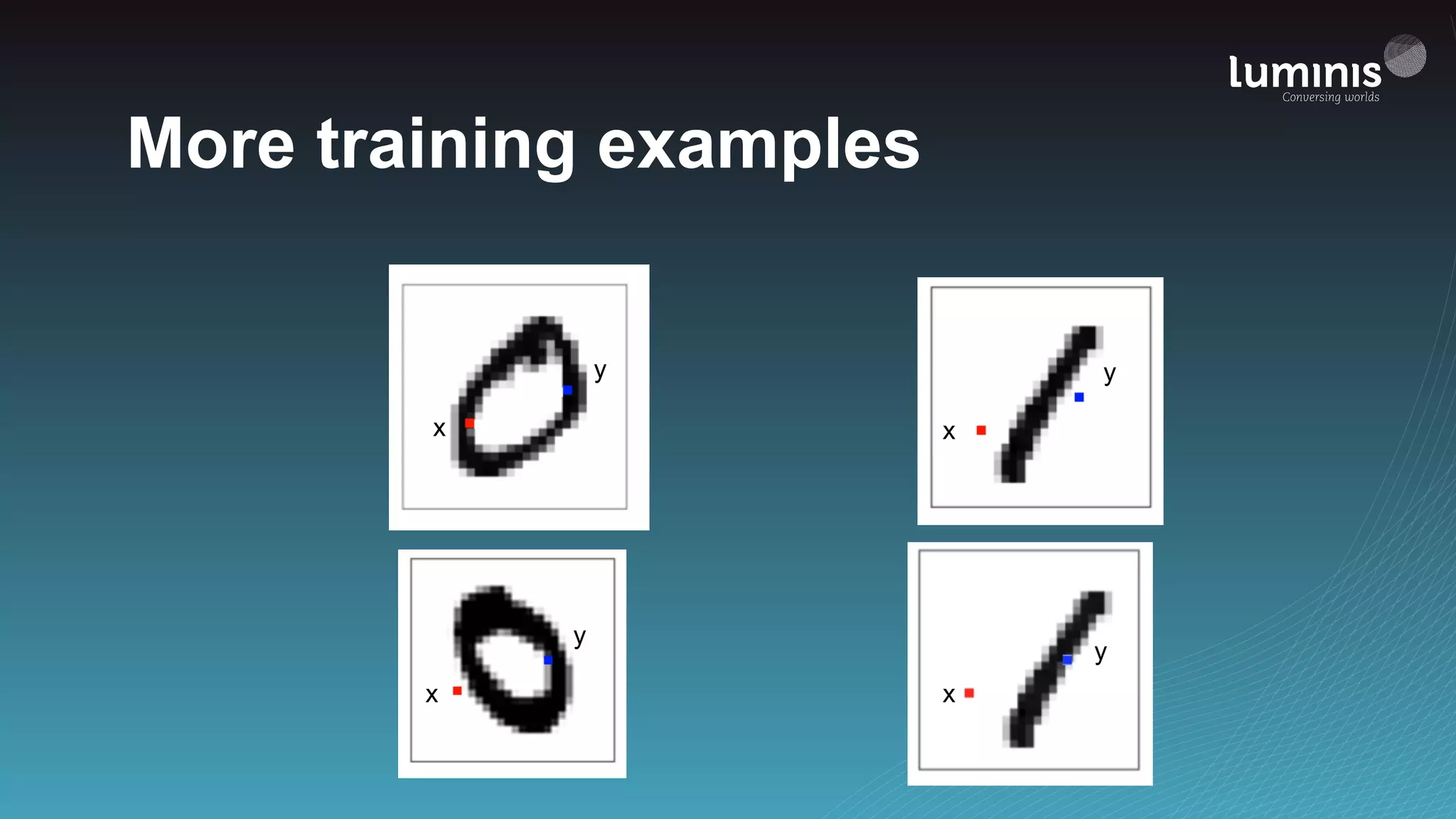
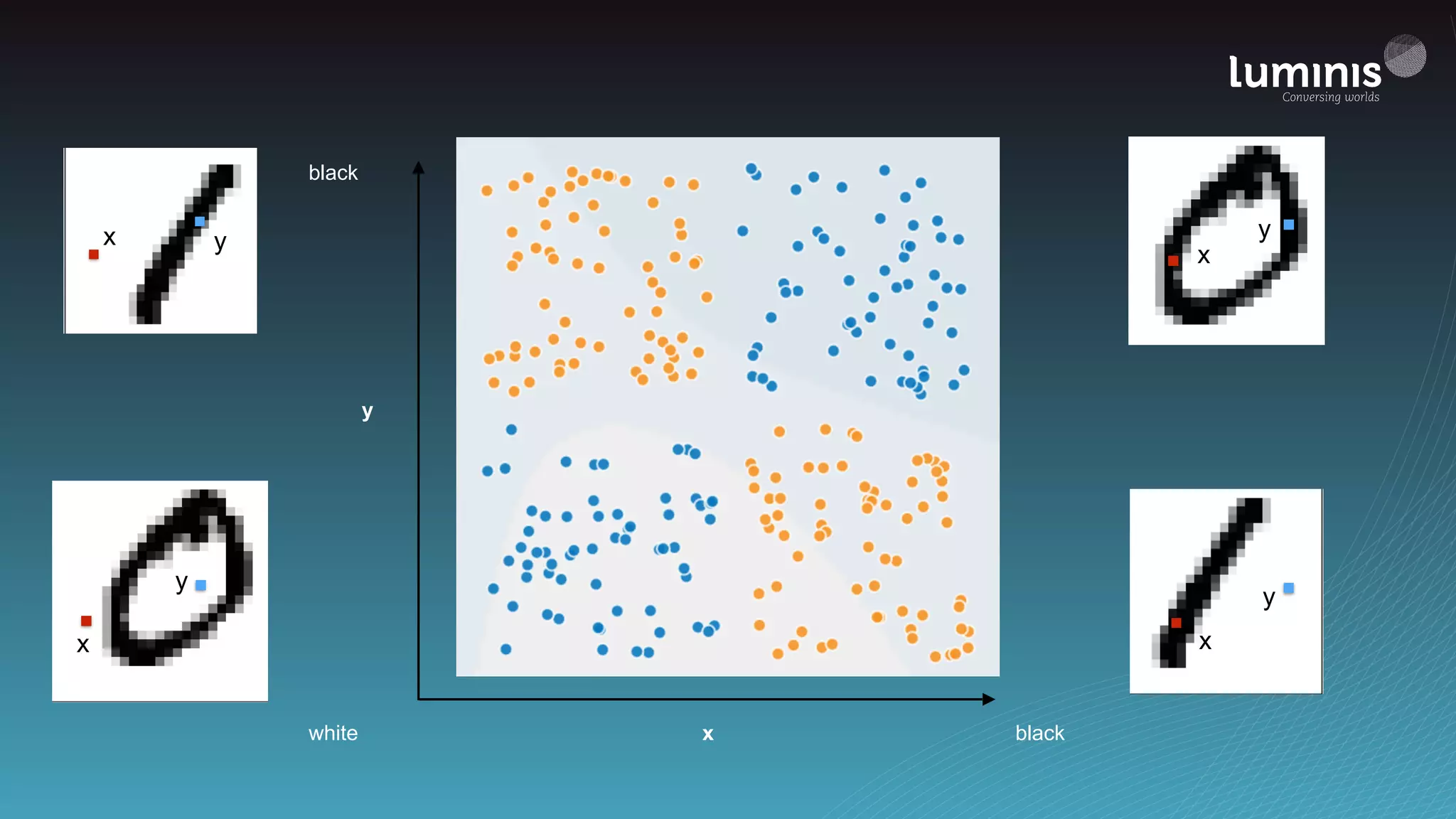
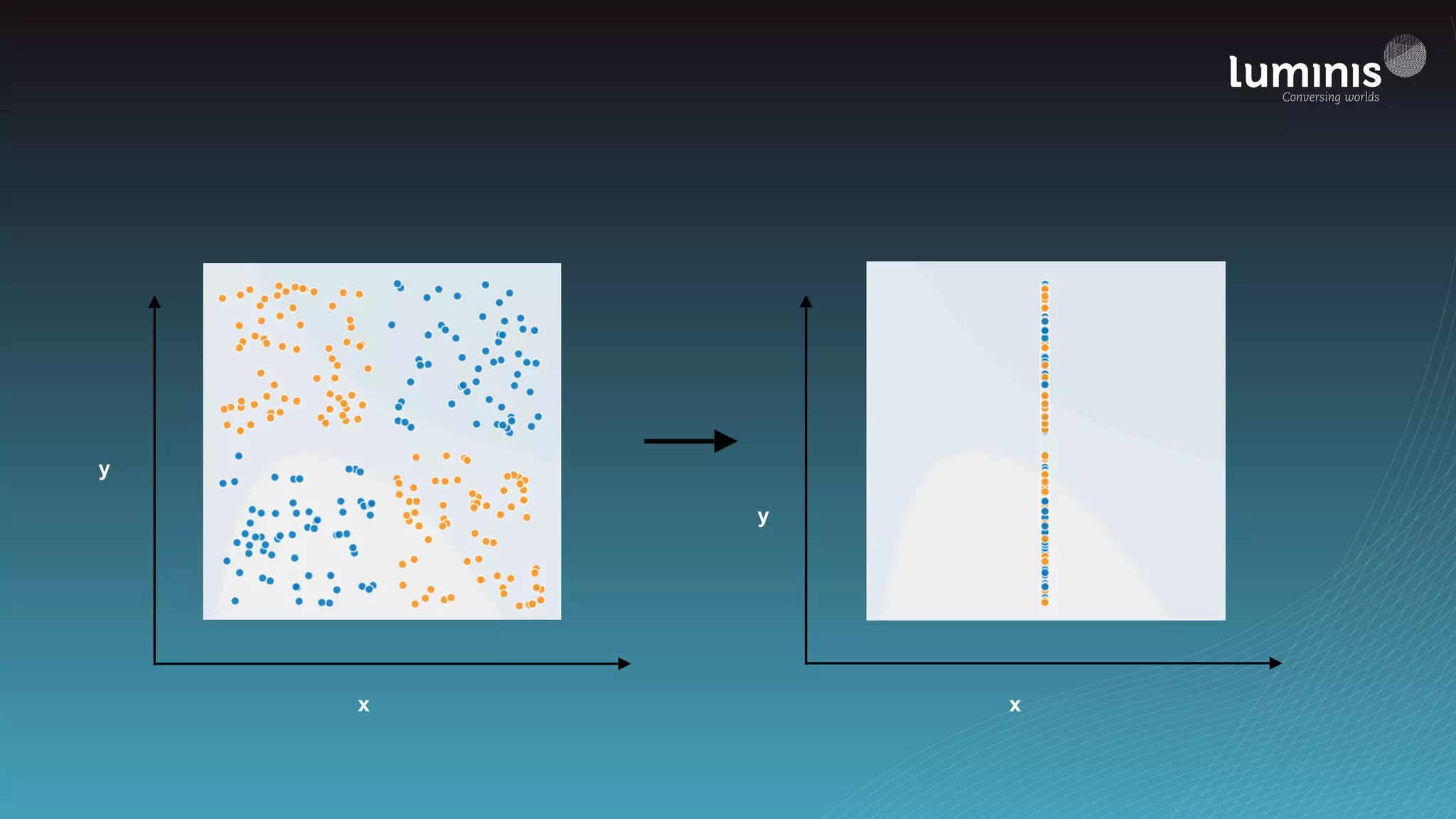
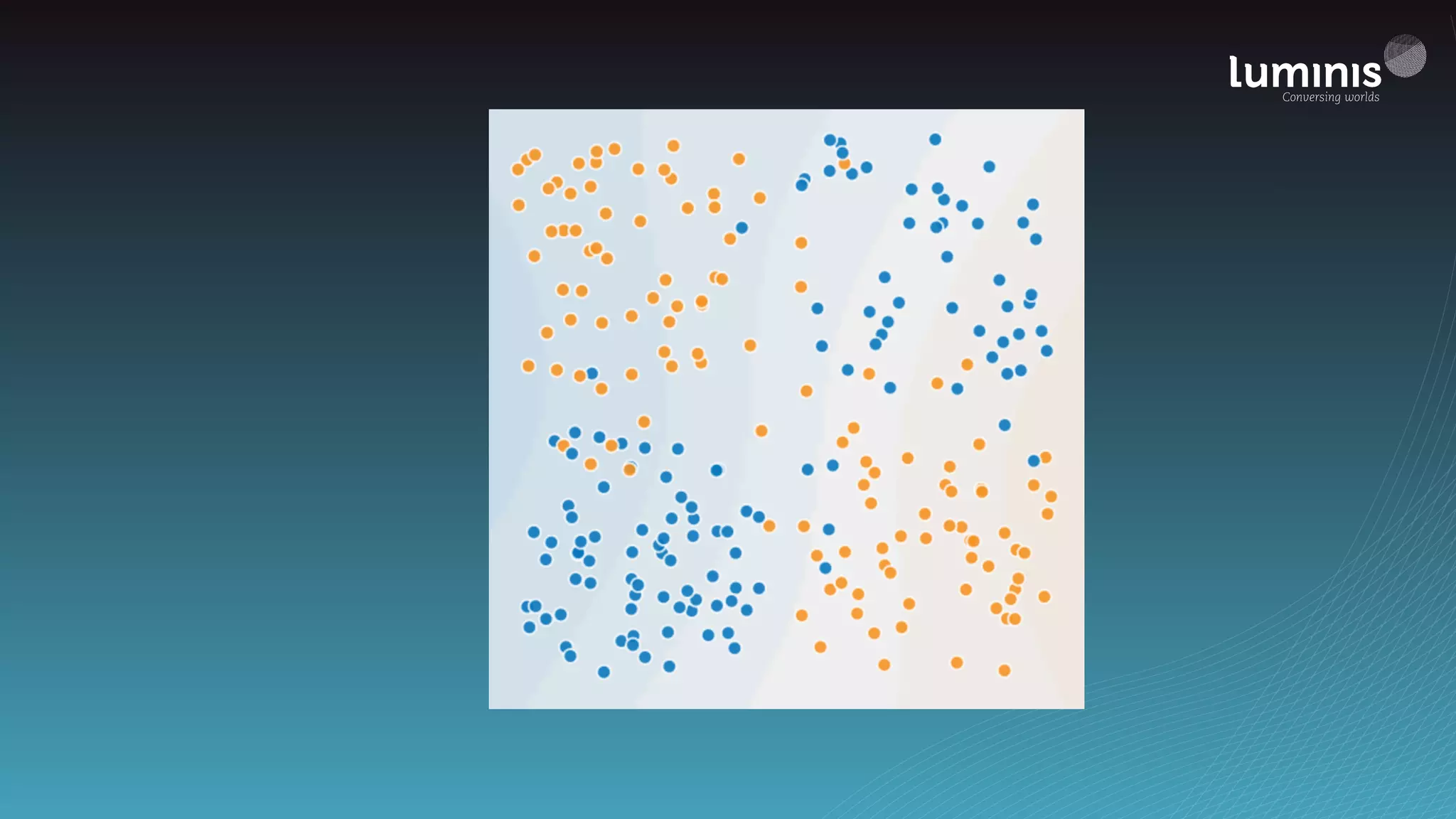
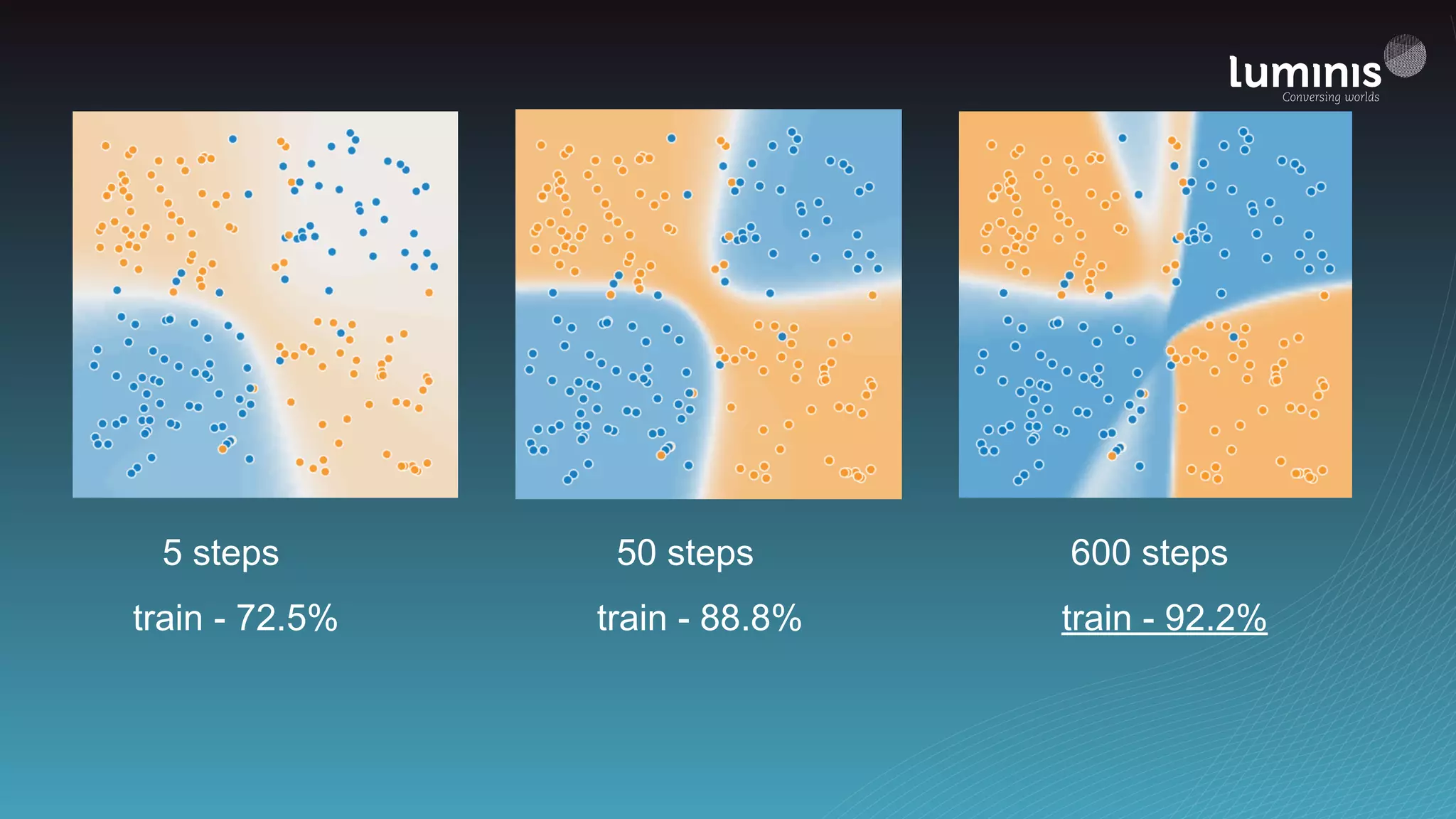
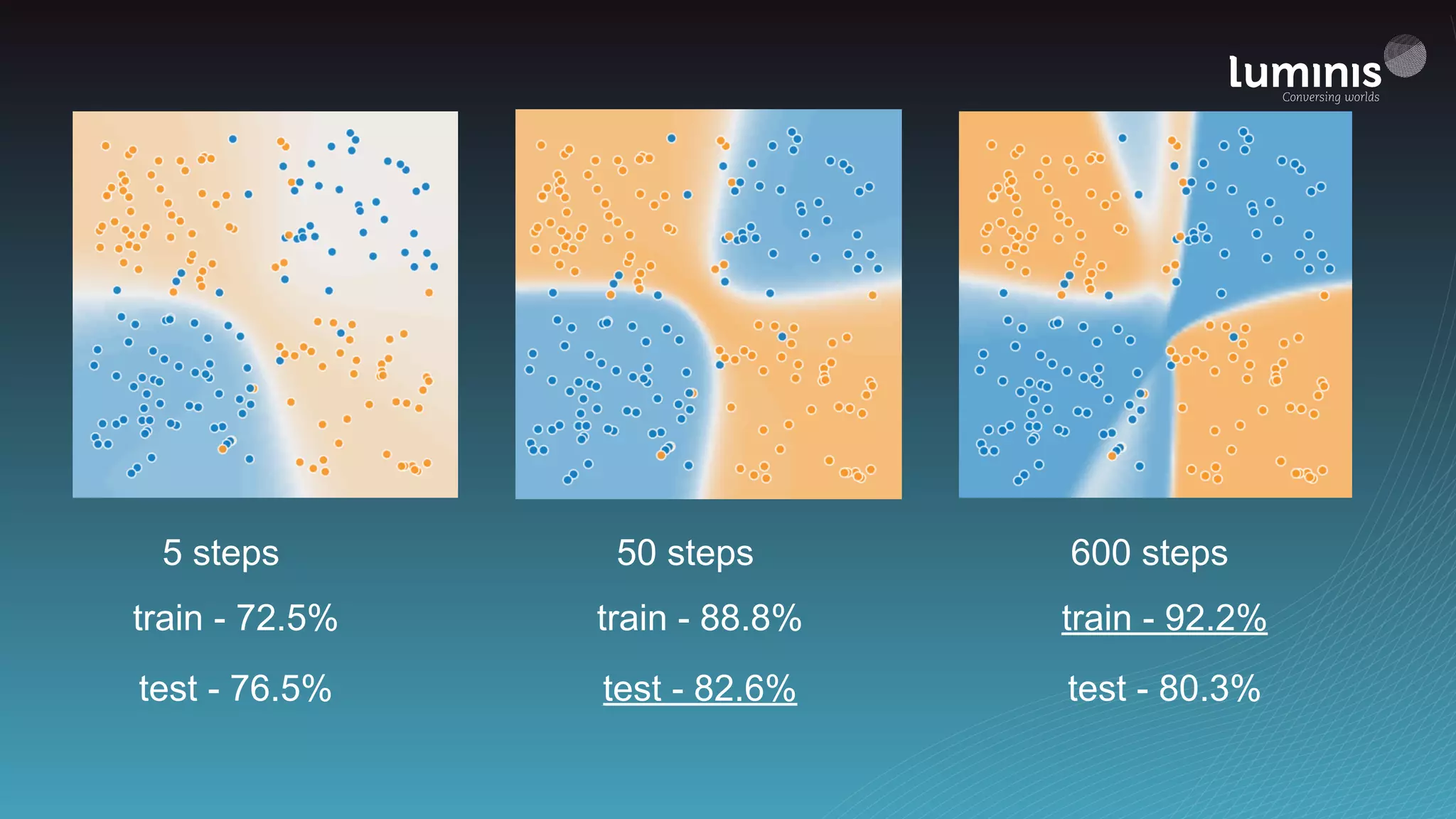
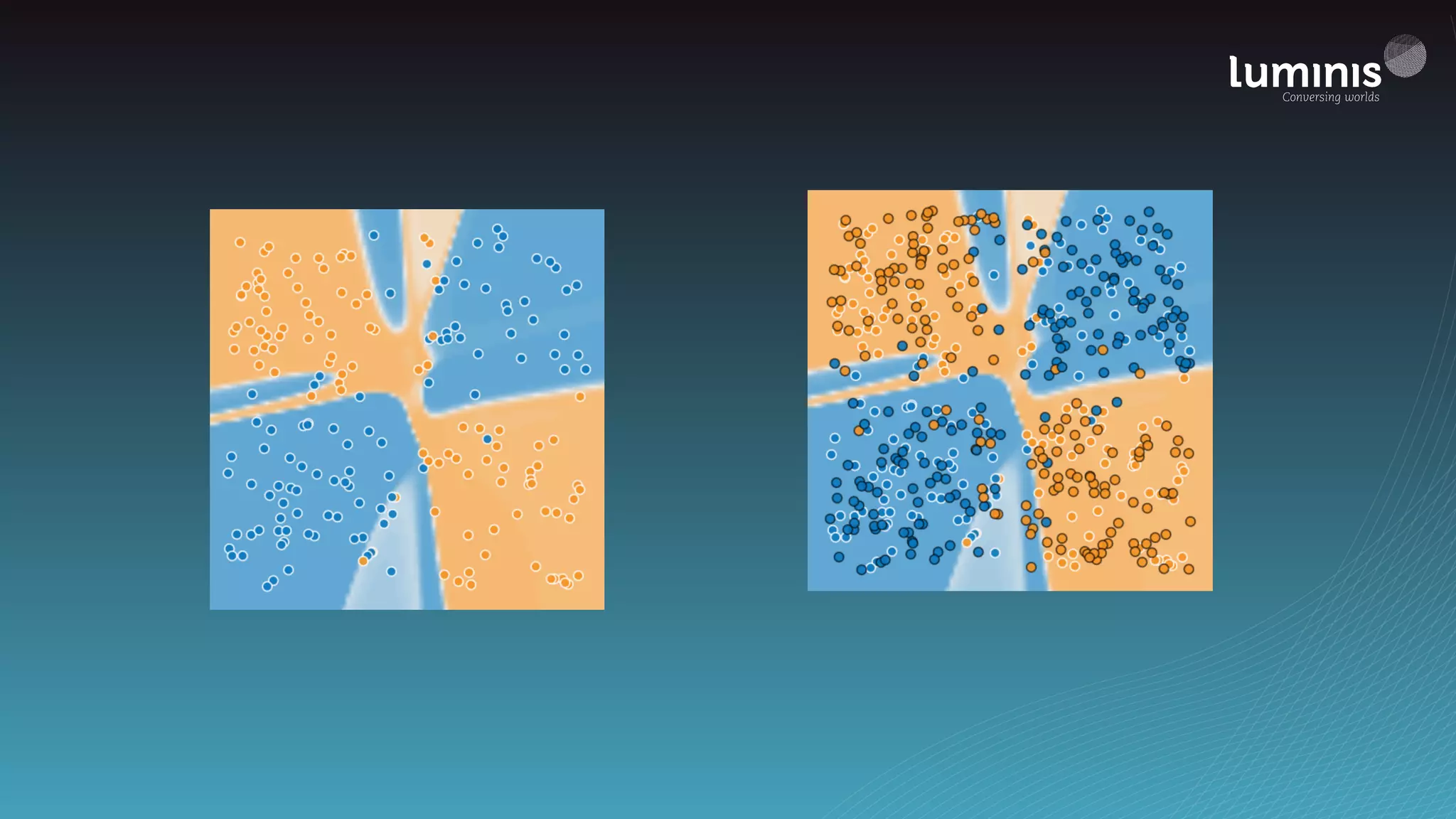
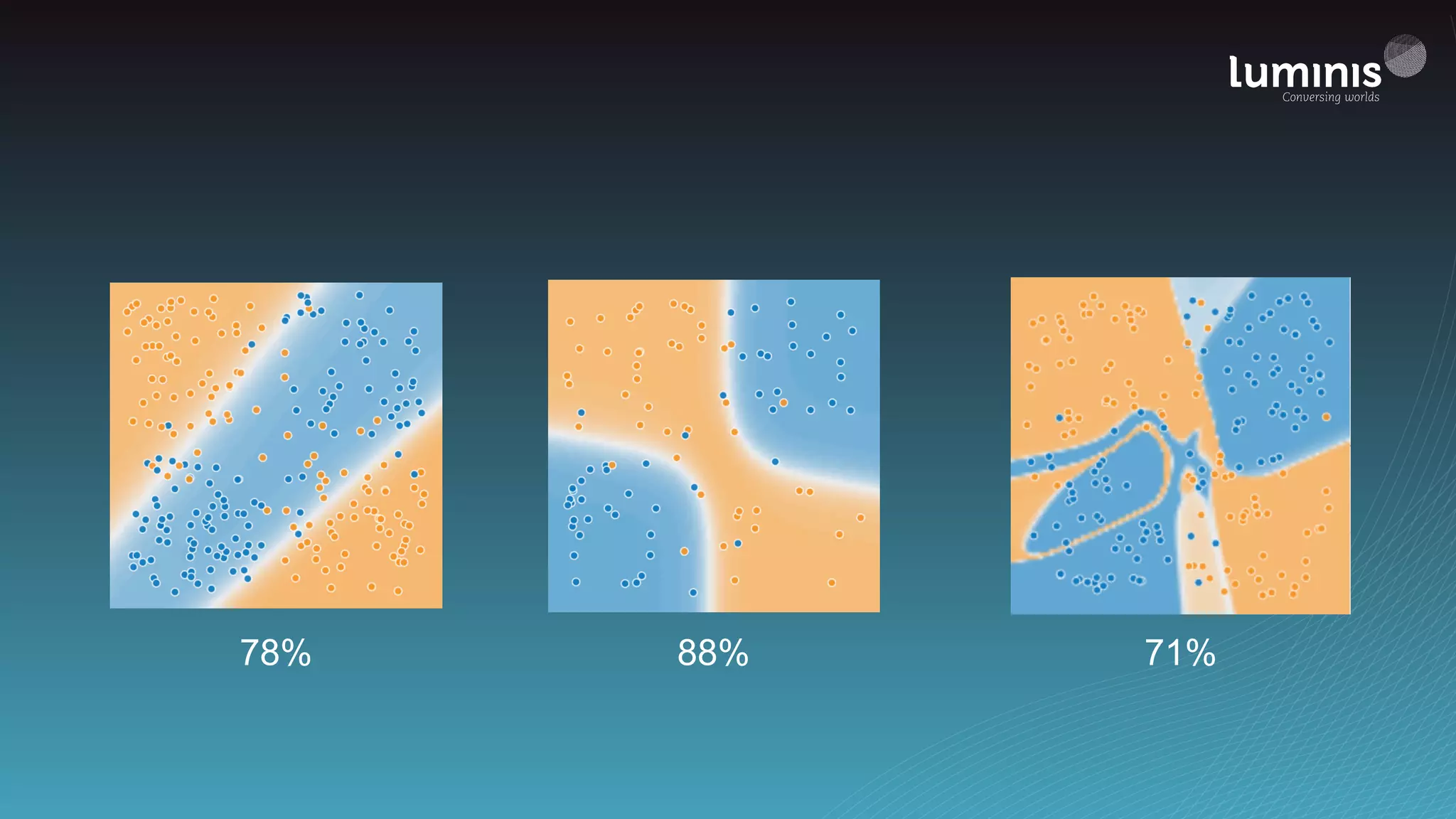
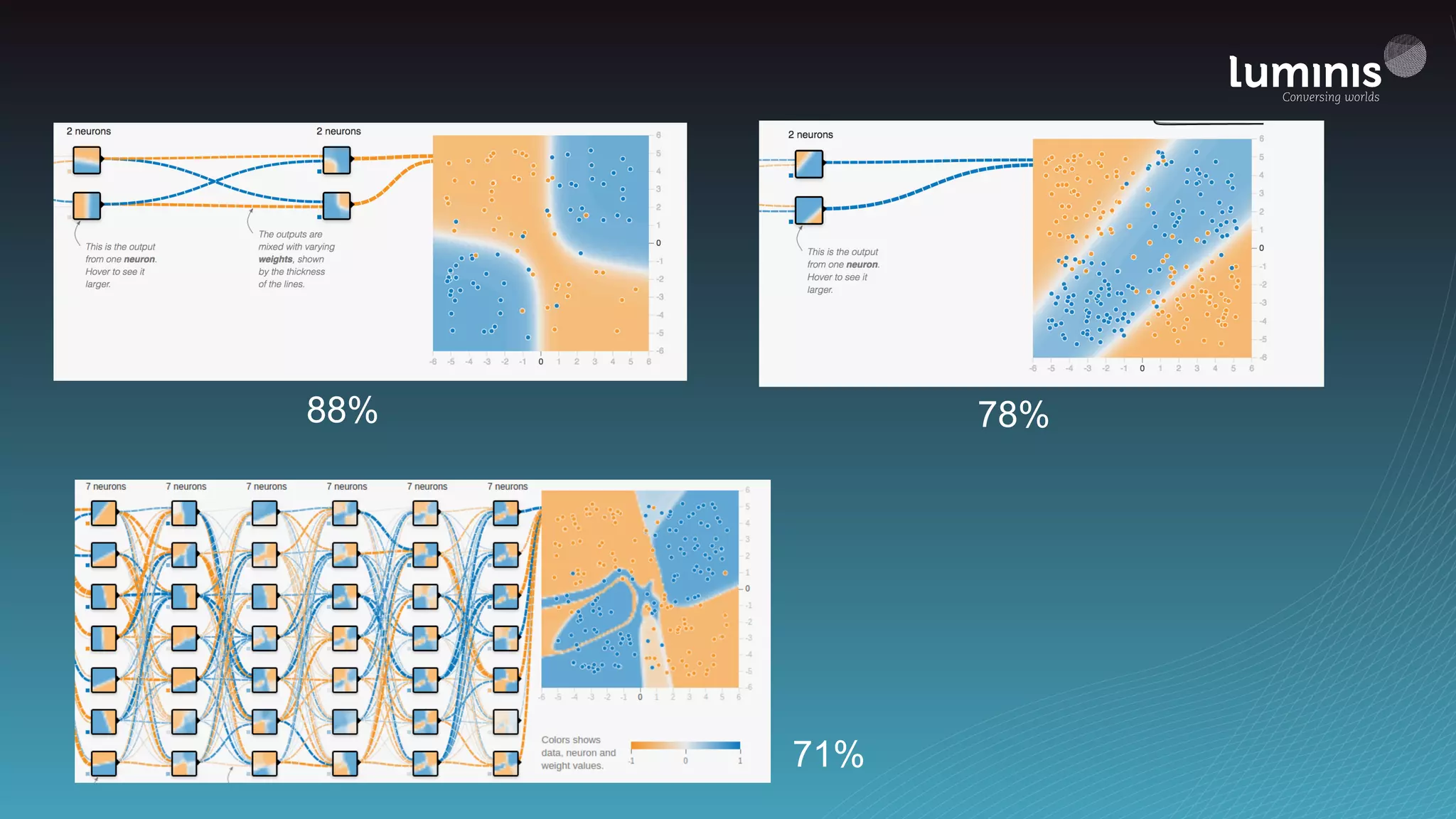
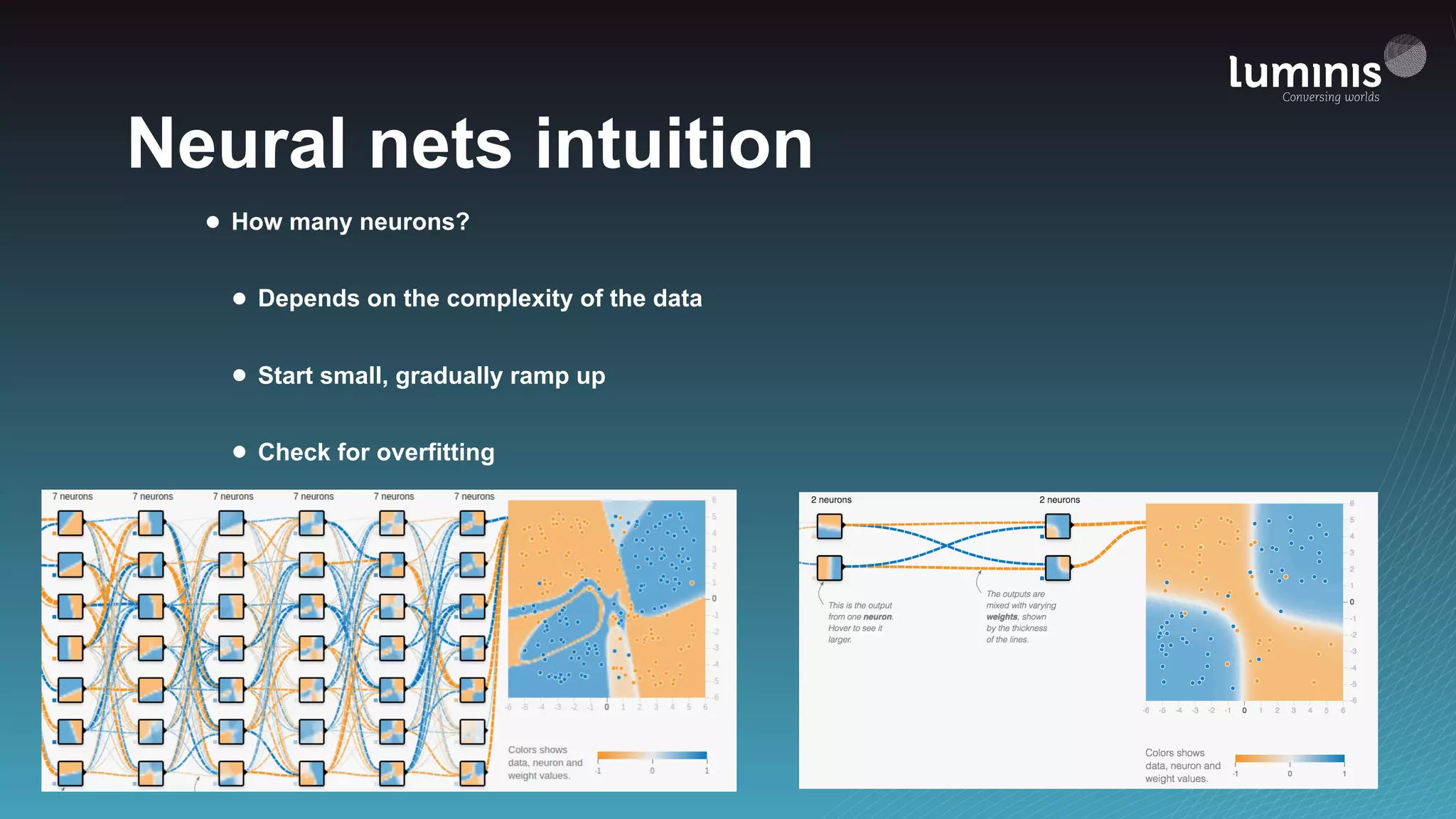
The document provides an overview of machine learning from a software engineer's perspective. It discusses how machine learning can solve various problems, introduces TensorFlow as an open-source machine learning library, and provides an example of using TensorFlow to build a neural network model for handwritten digit classification that achieves 97.5% accuracy on MNIST data. The document emphasizes that machine learning requires examples to learn from and recommends starting simply before gradually increasing complexity when experimenting with neural networks.













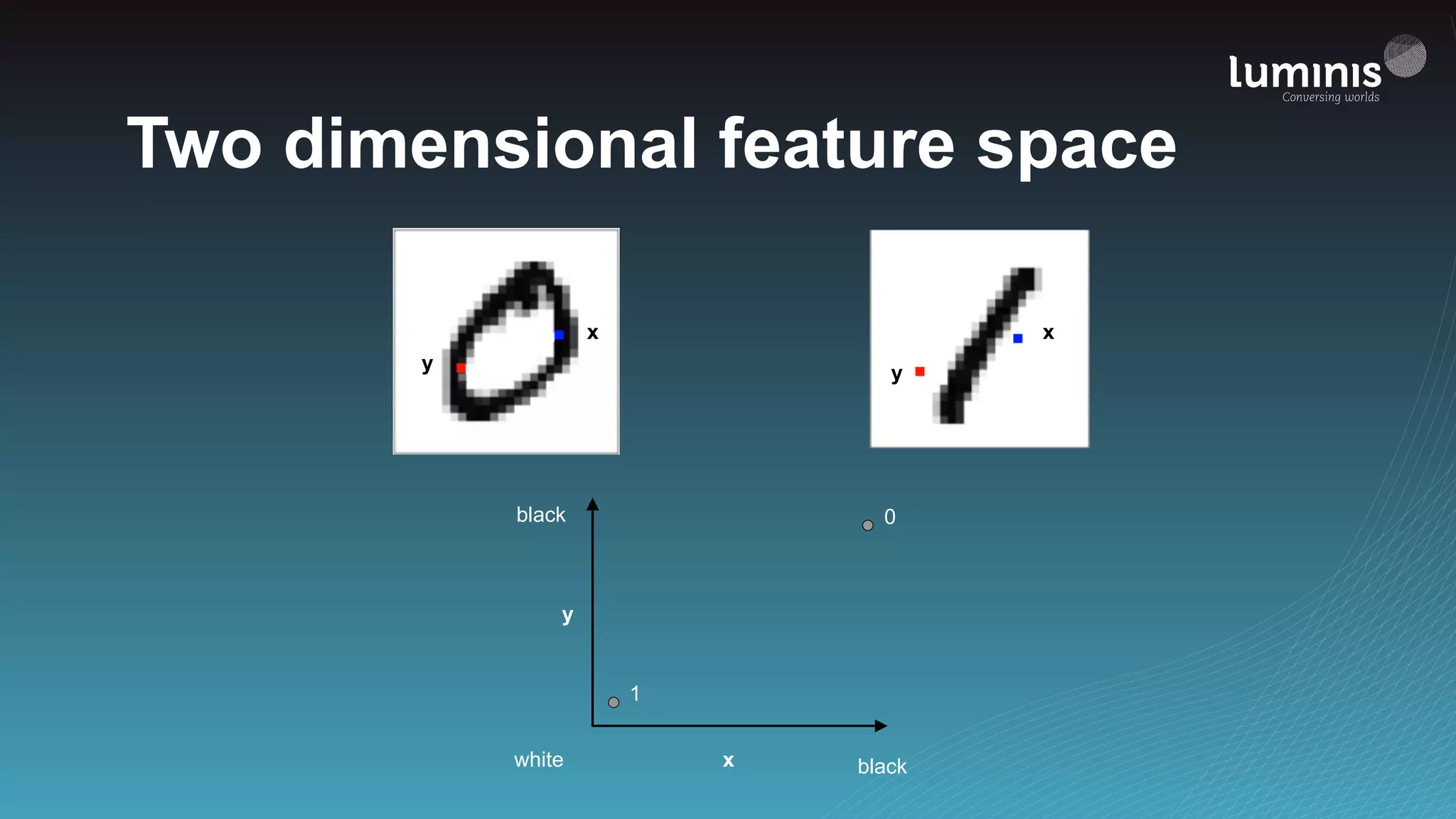
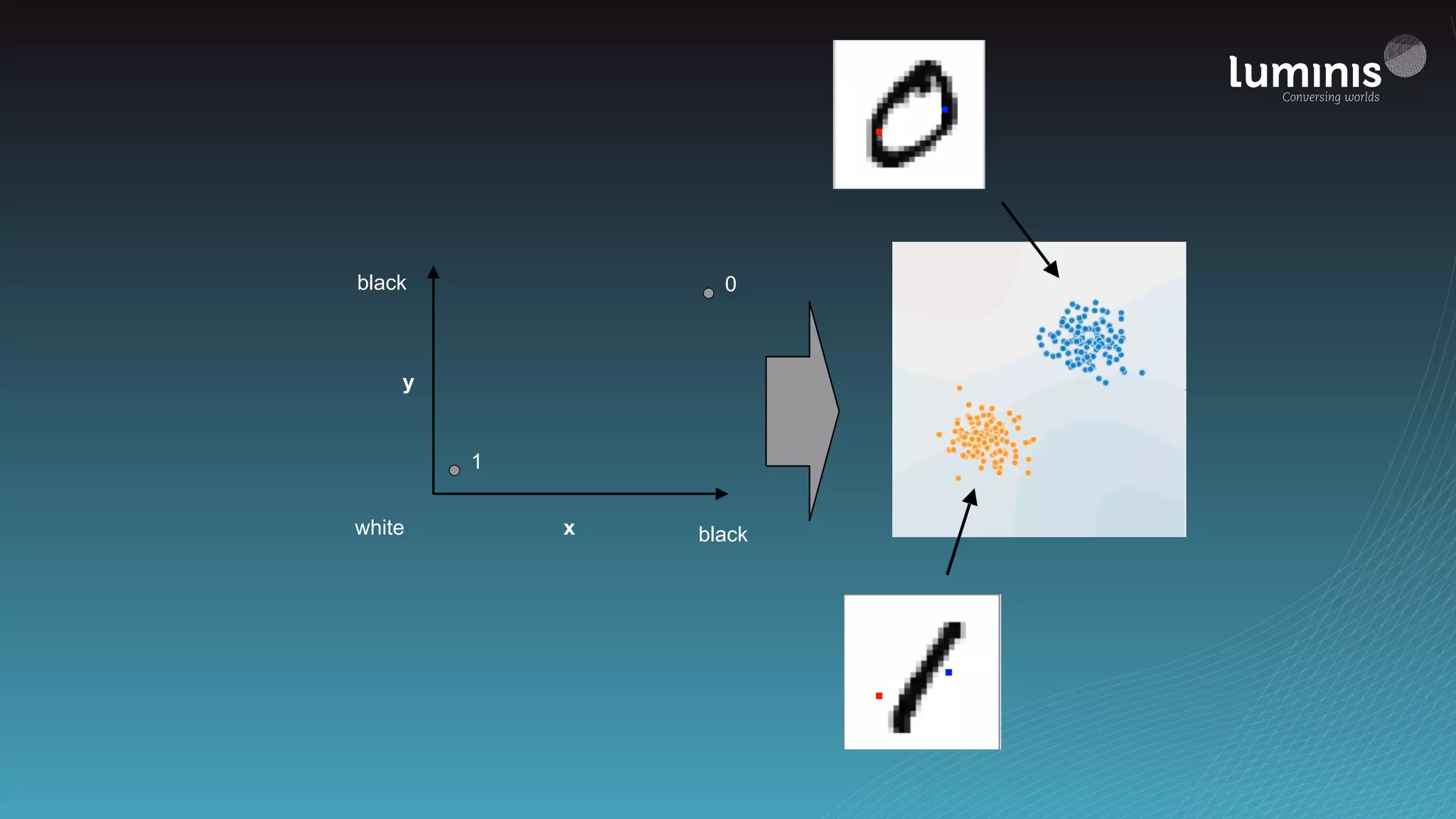

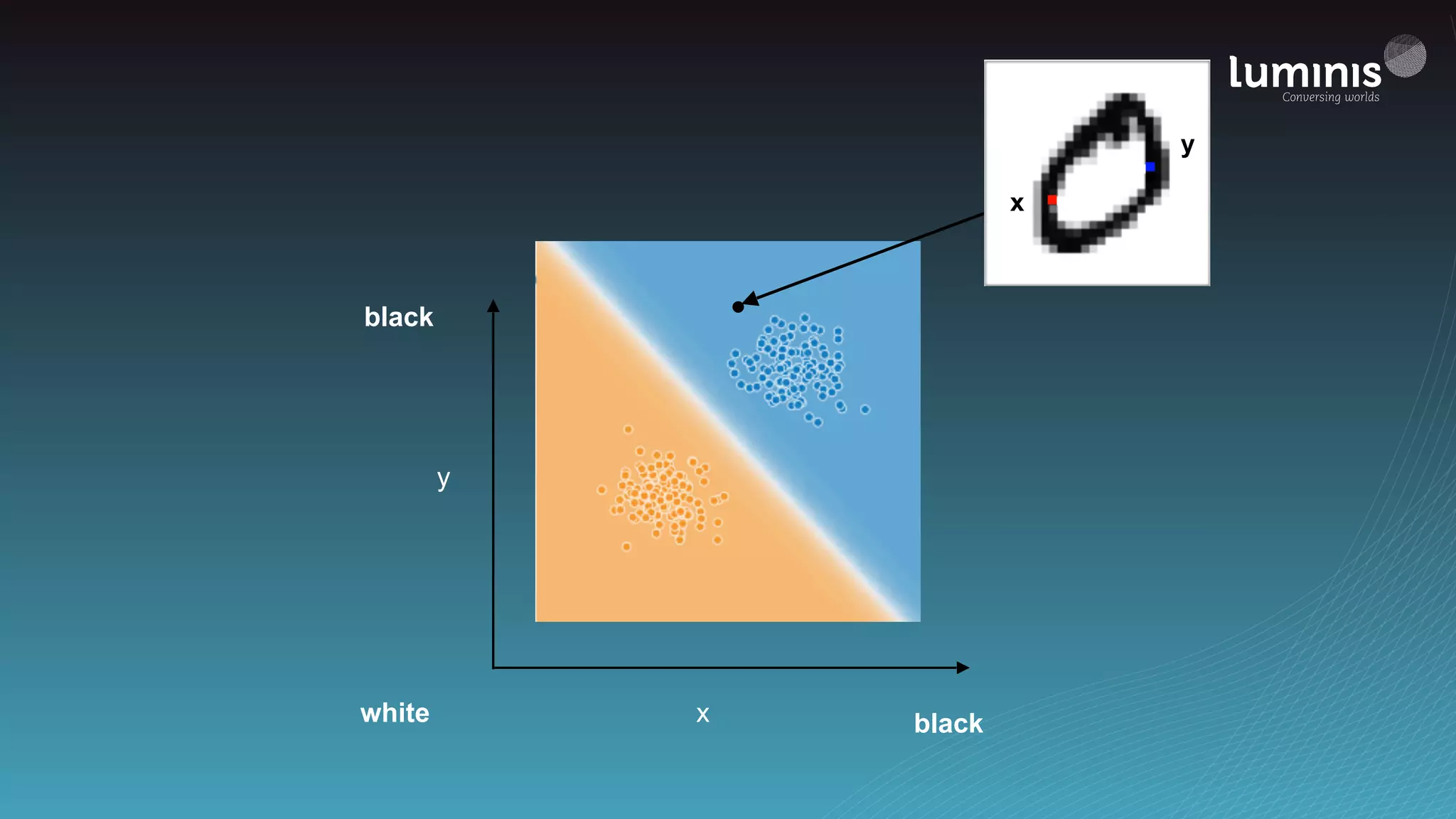
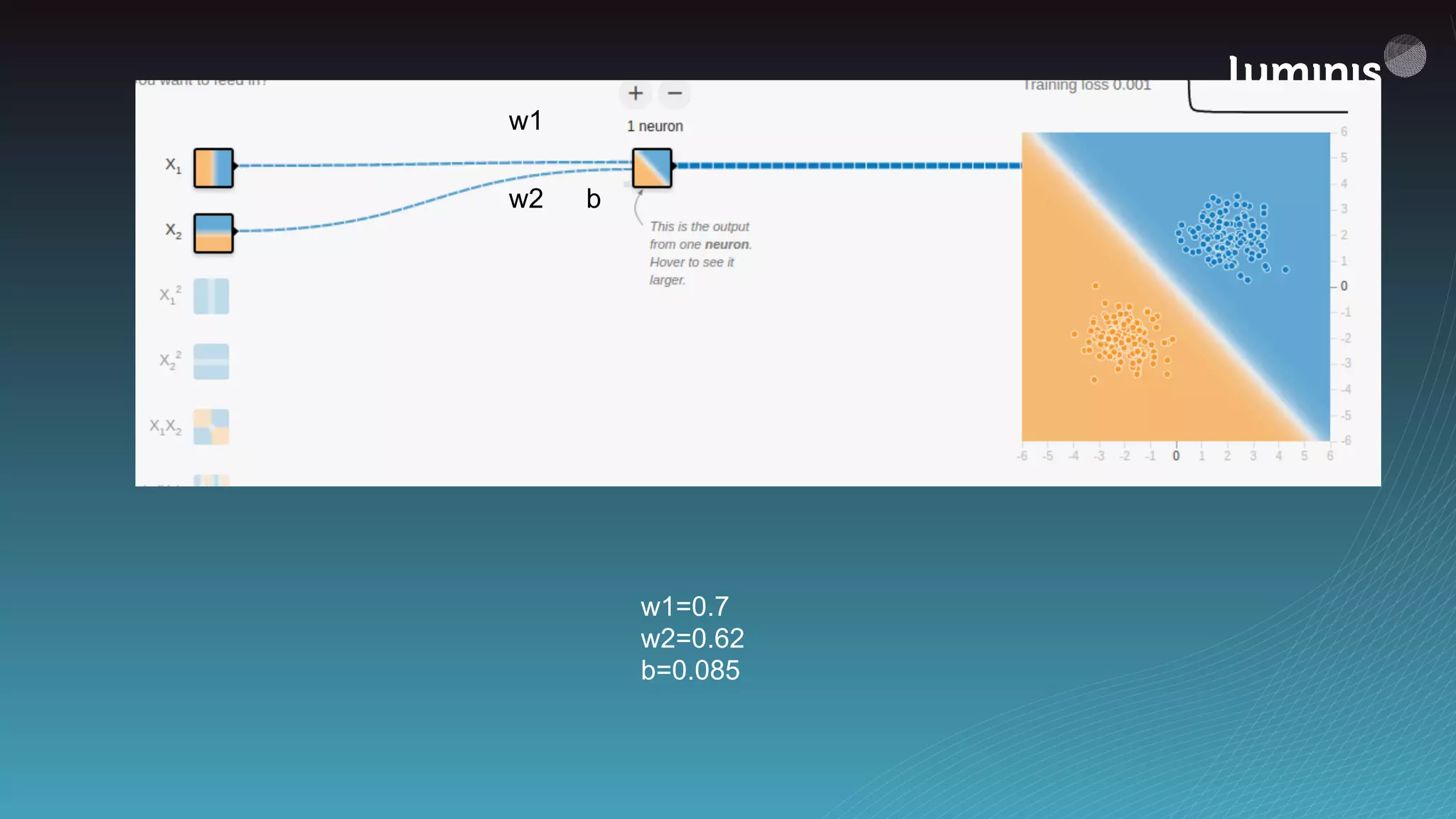







![from tensorflow.contrib.learn import infer_real_valued_columns_from_input, DNNClassifier
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials import mnist
mnist_data = mnist.input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/")
train_data, test_data = mnist_data.train.images, mnist_data.test.images
train_labels, test_labels = mnist_data.train.labels.astype('int32'),
mnist_data.test.labels.astype('int32')
estimator = DNNClassifier(
feature_columns=infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(mnist_data.train.images),
hidden_units = [2500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 500],
n_classes = 10)
estimator.fit(x = train_data, y = train_labels, steps = 1000)
print(estimator.evaluate(x = test_data, y = test_labels)['accuracy'])
# 97.5% accuracy in ~15min
Handwritten digit classifier in TensorFlow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tr5vi0dwt9qtt25pv36d-signature-564dbe09c3073c373a17b41a3283b35f54ad8b43cddac524b095f4aac841bba3-poli-190206092658/75/Machine-Learning-from-a-Software-Engineer-s-perspective-41-2048.jpg)


