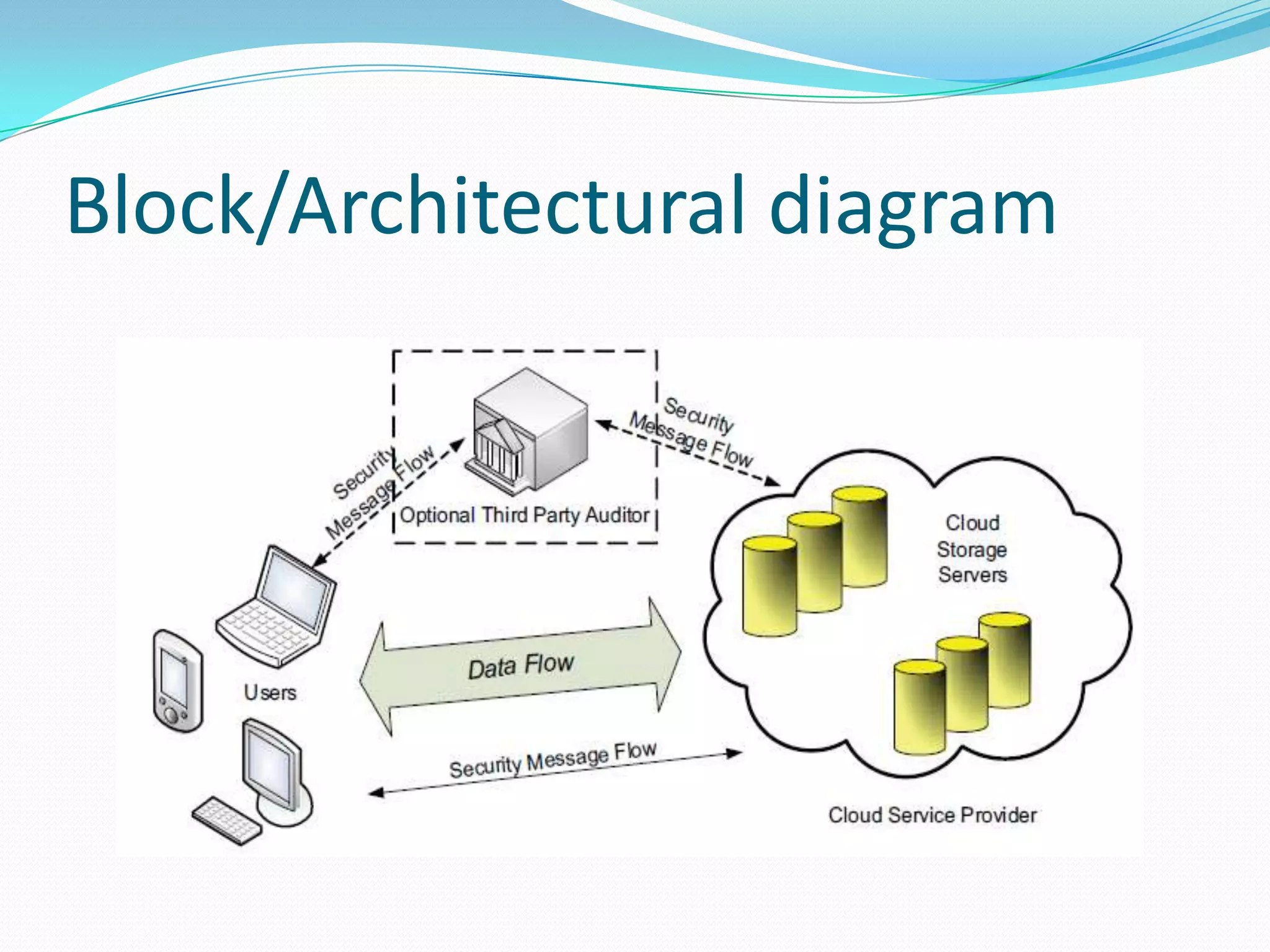
Cloud storage allows users to store data in the cloud without managing local hardware. It provides on-demand access to cloud applications and pay-per-use services. The document discusses different cloud service models including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It proposes a system to ensure correctness of user data in the cloud with dynamic data support and distributed storage. The system features include auditing by a third party, file retrieval and error recovery, and cloud operations like update, delete, and append.