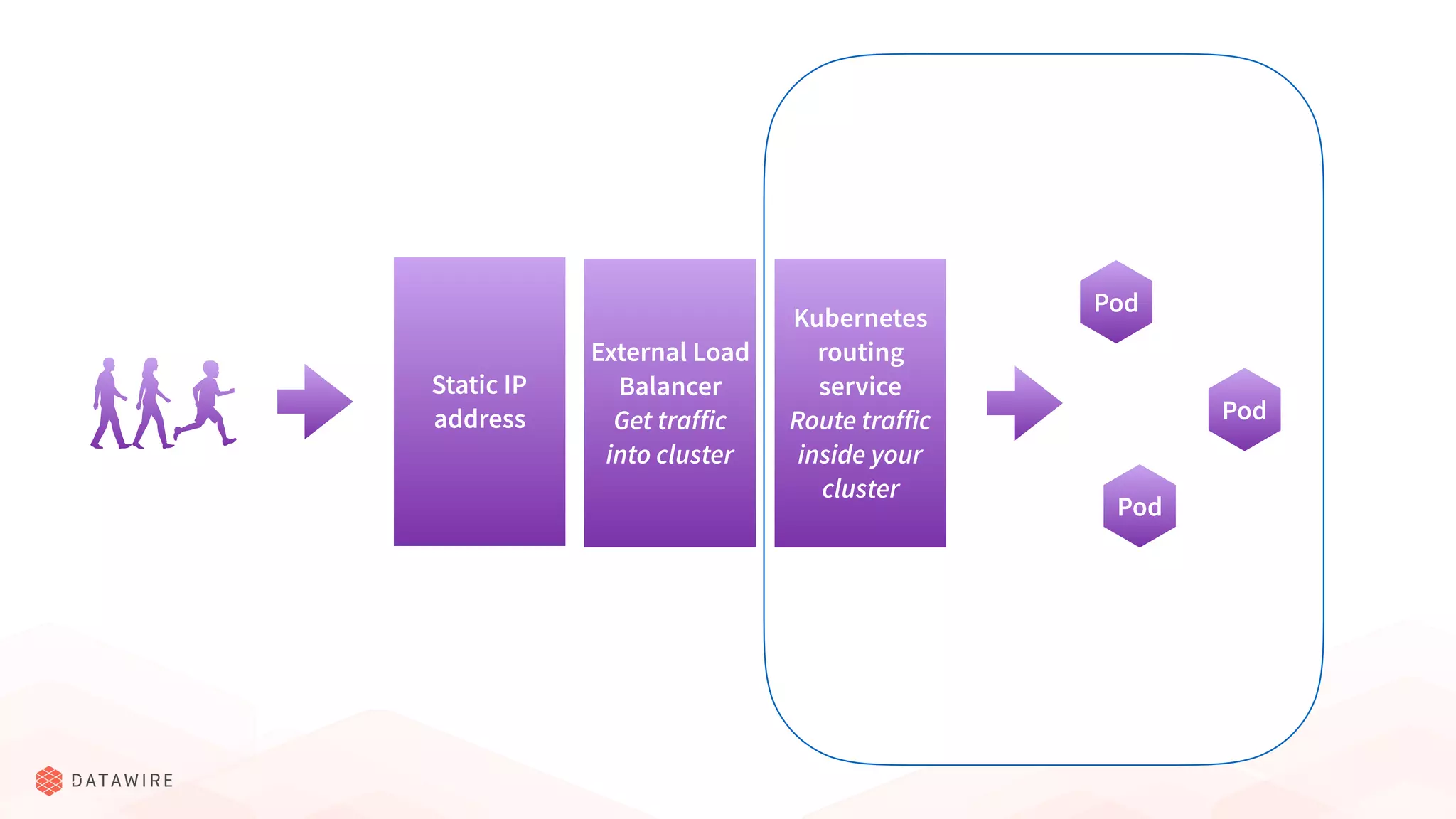
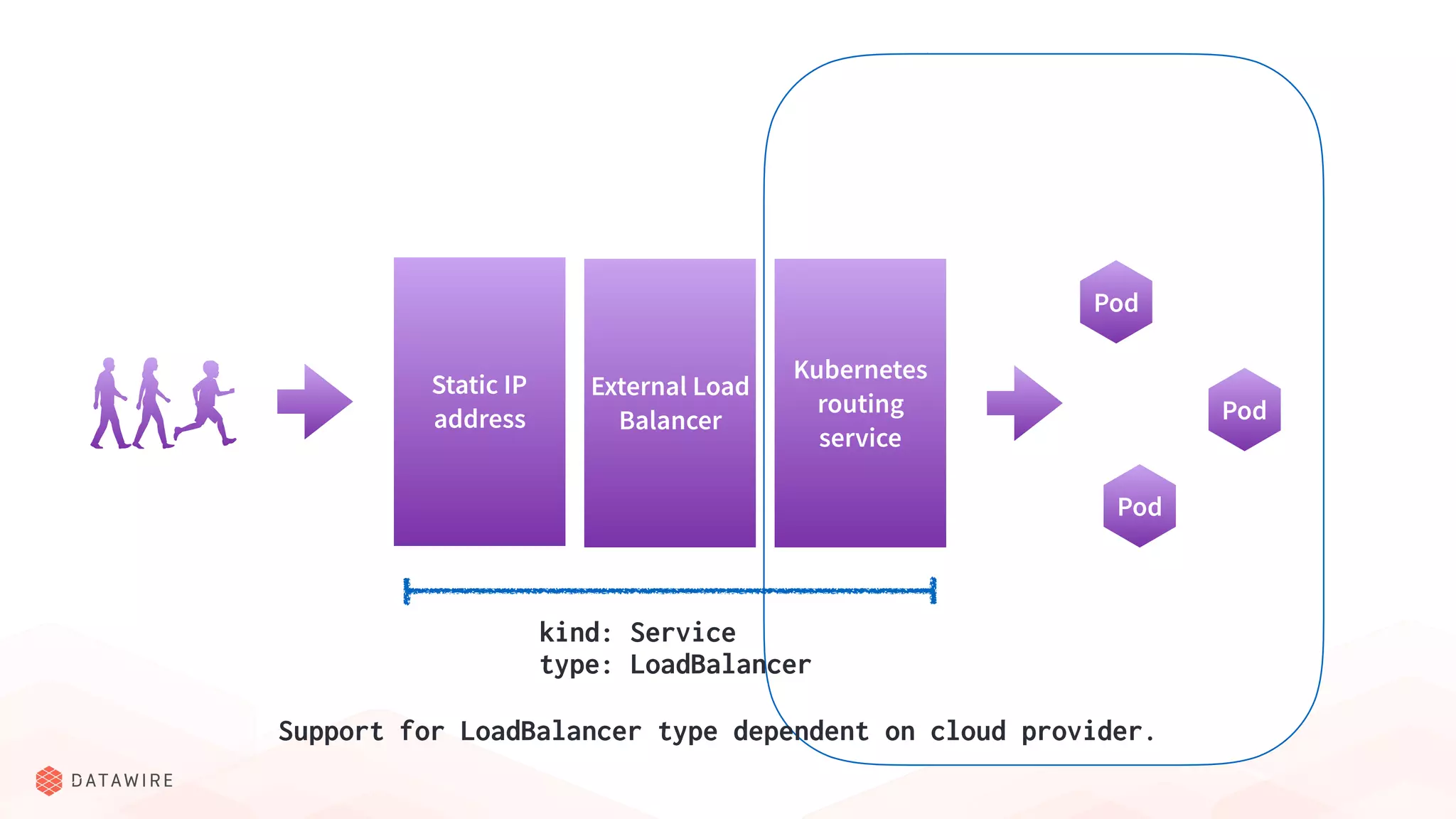
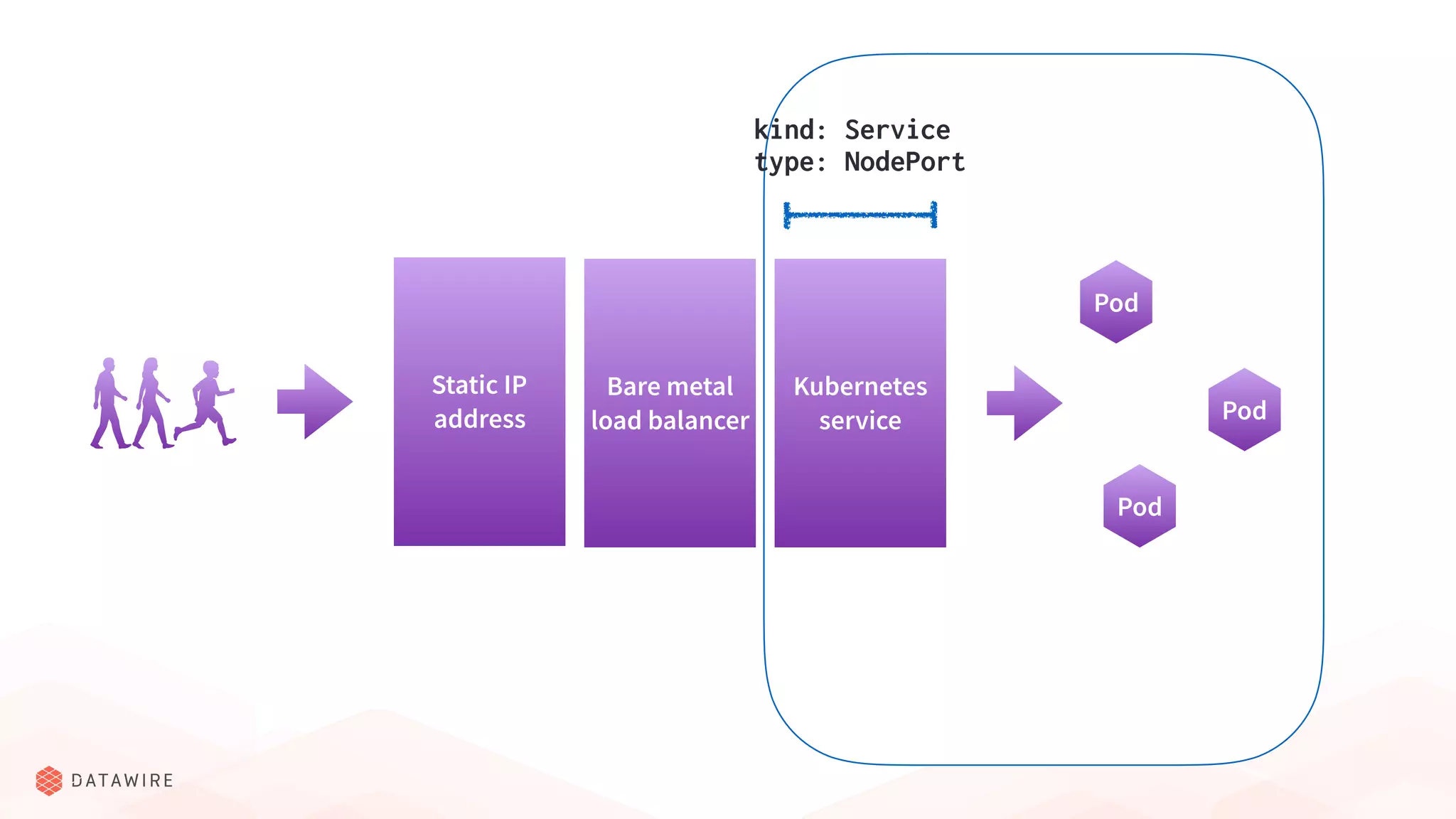
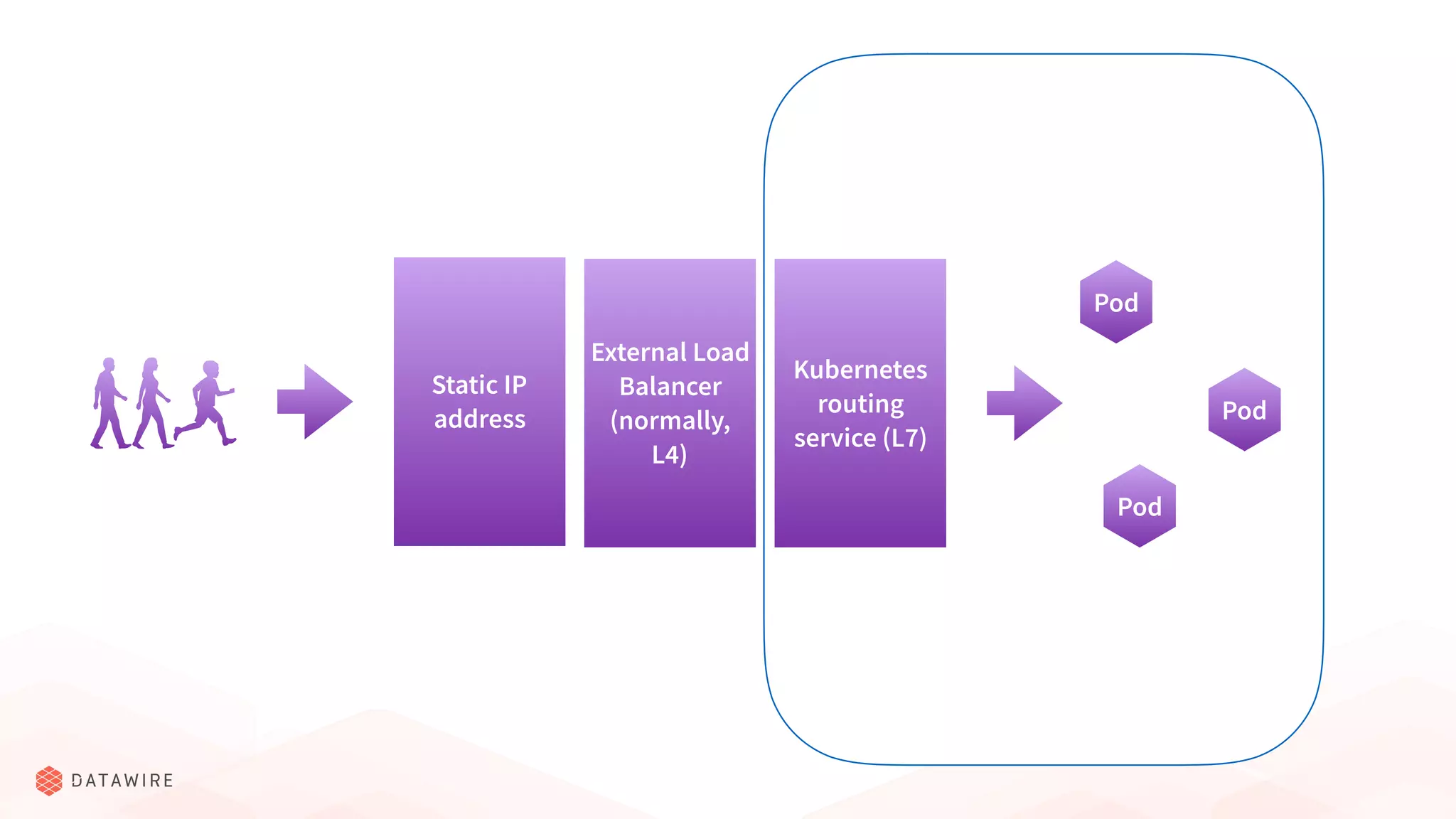
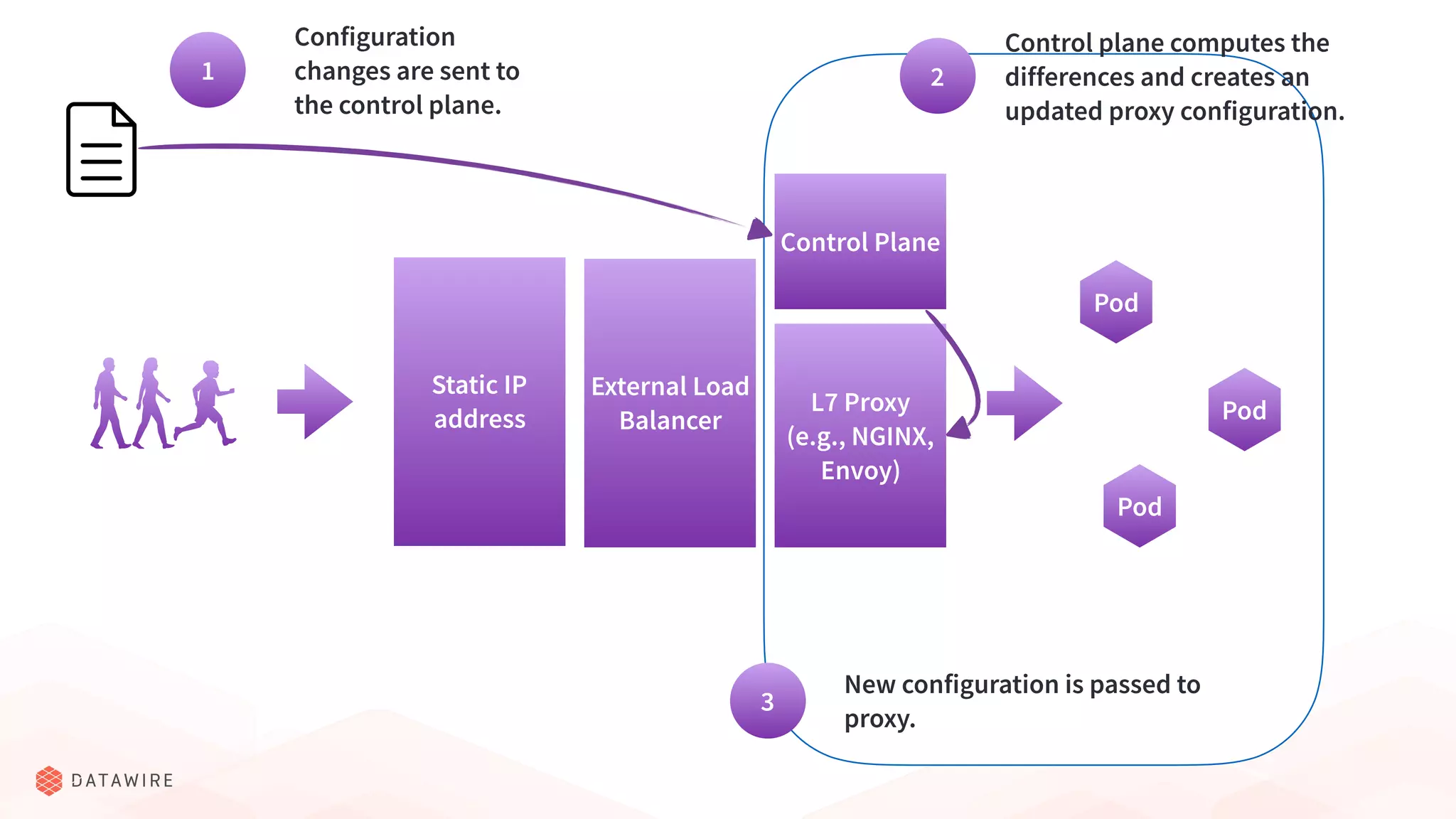
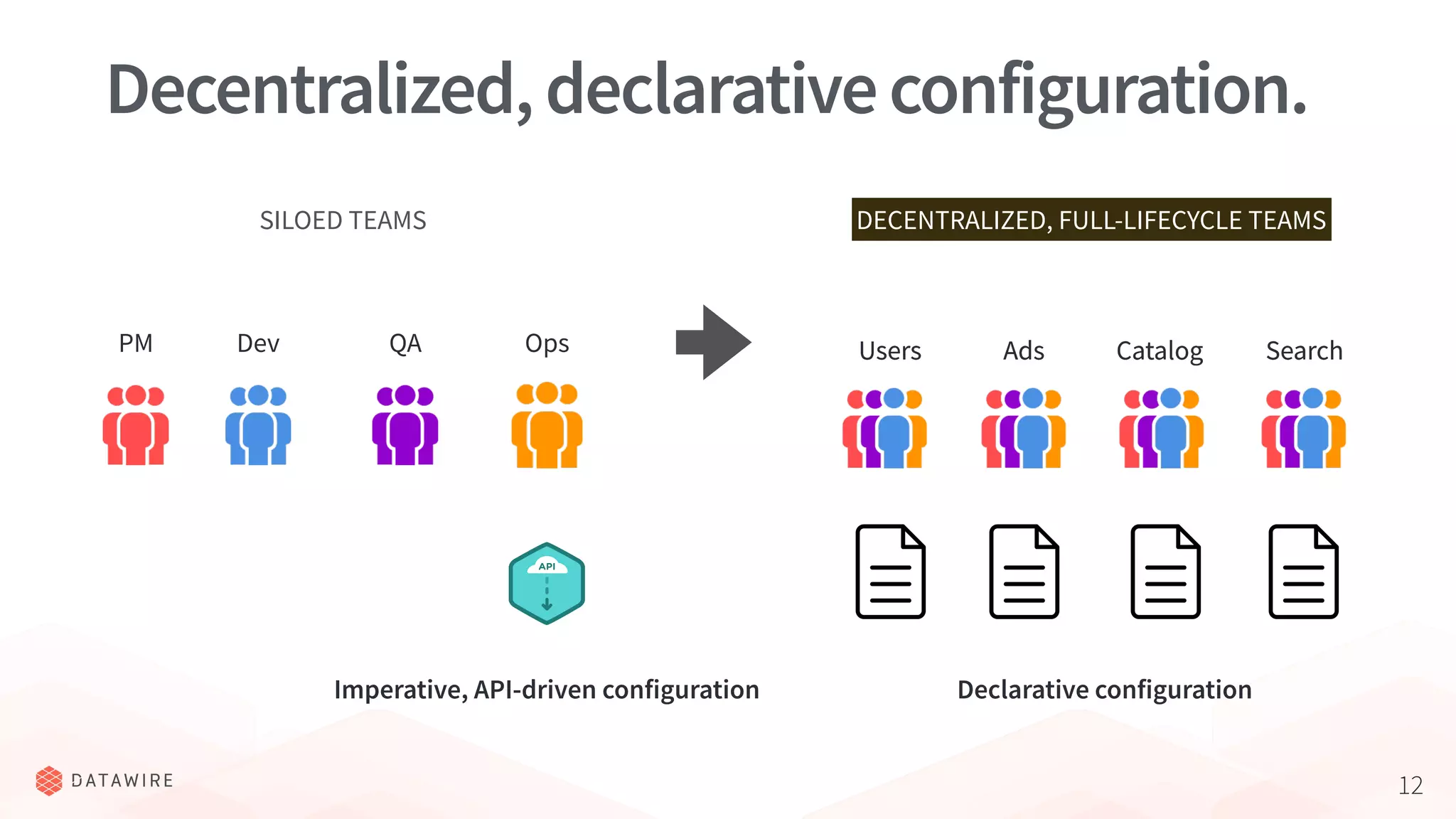
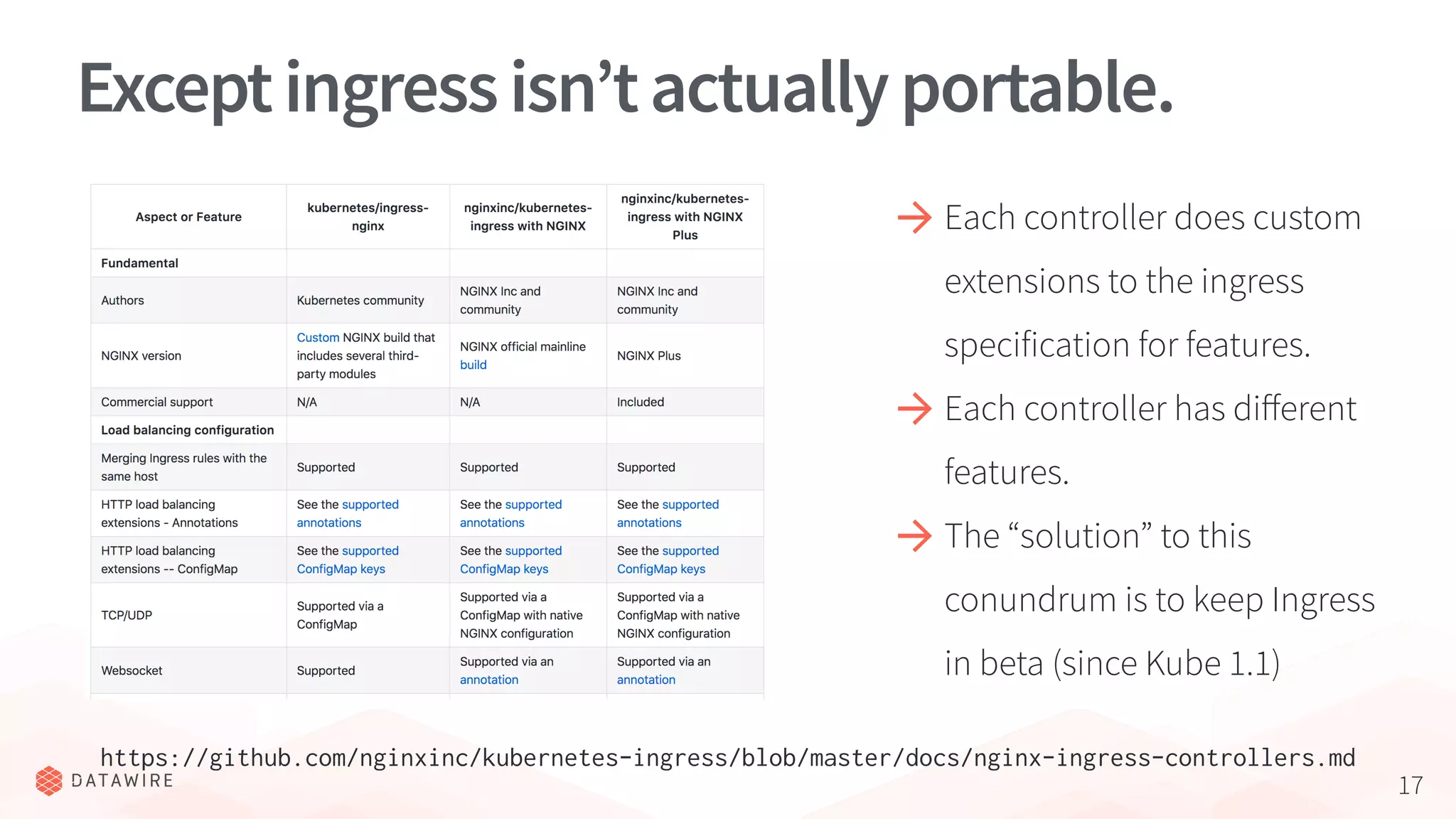
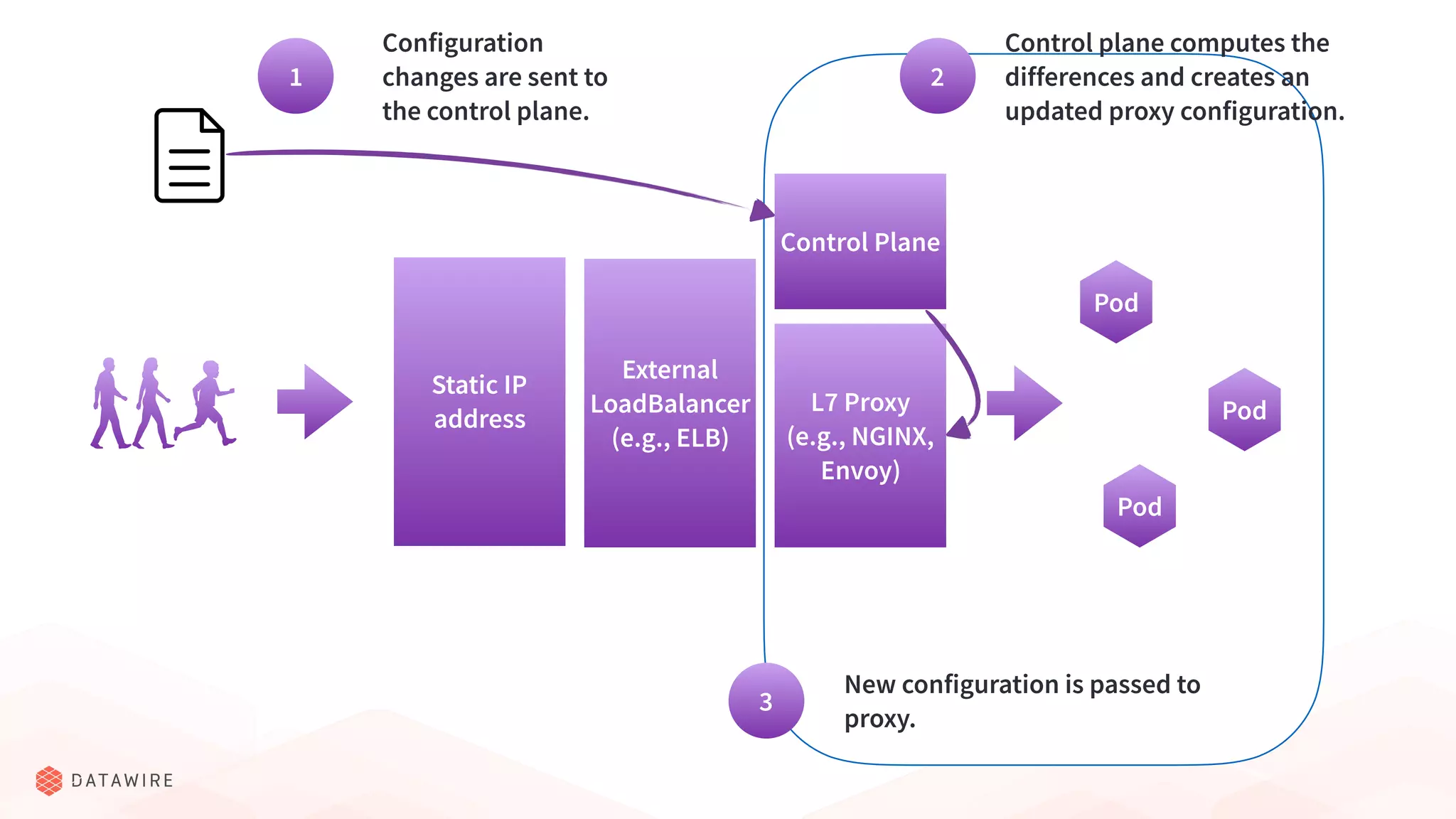
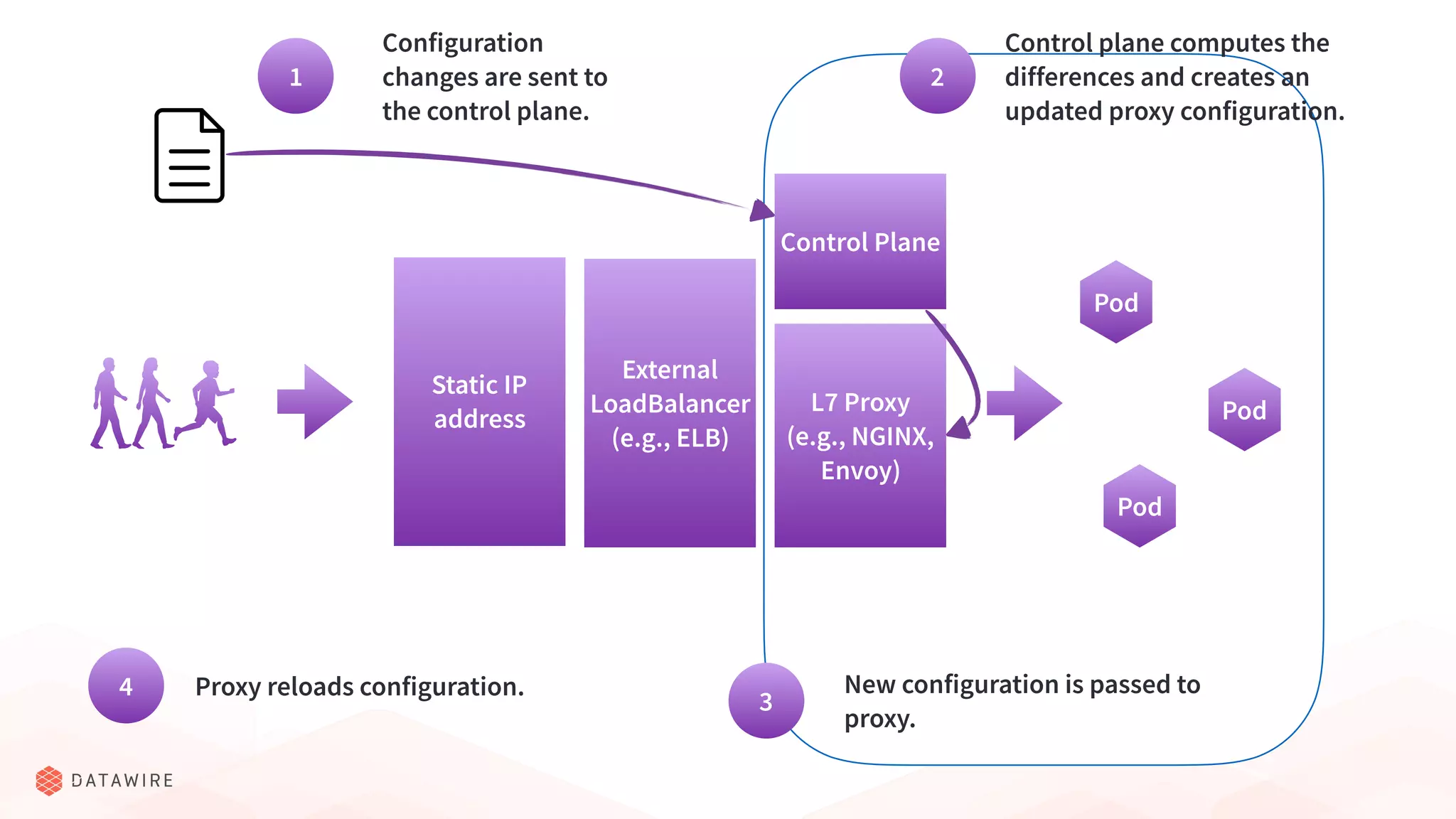
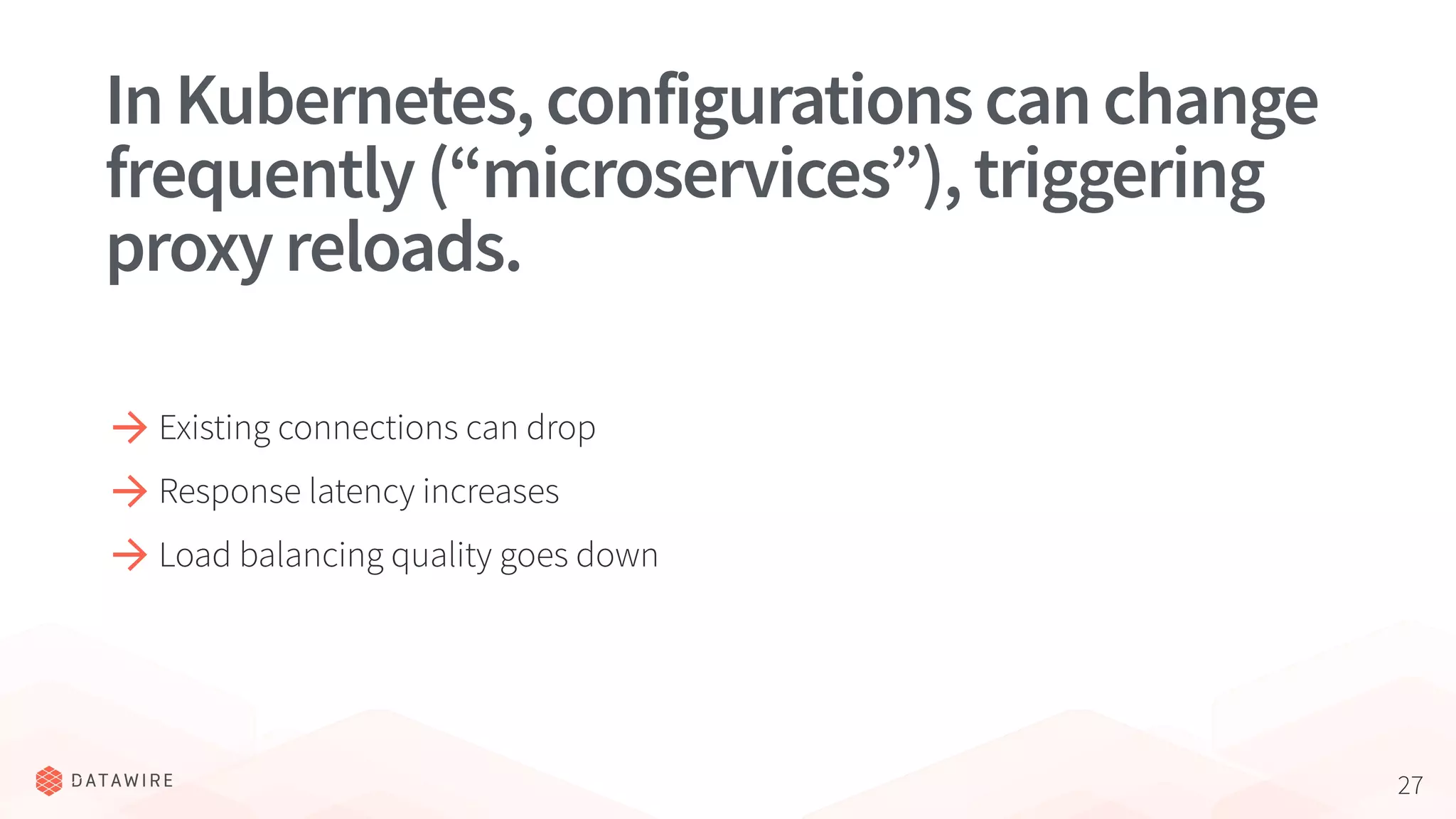
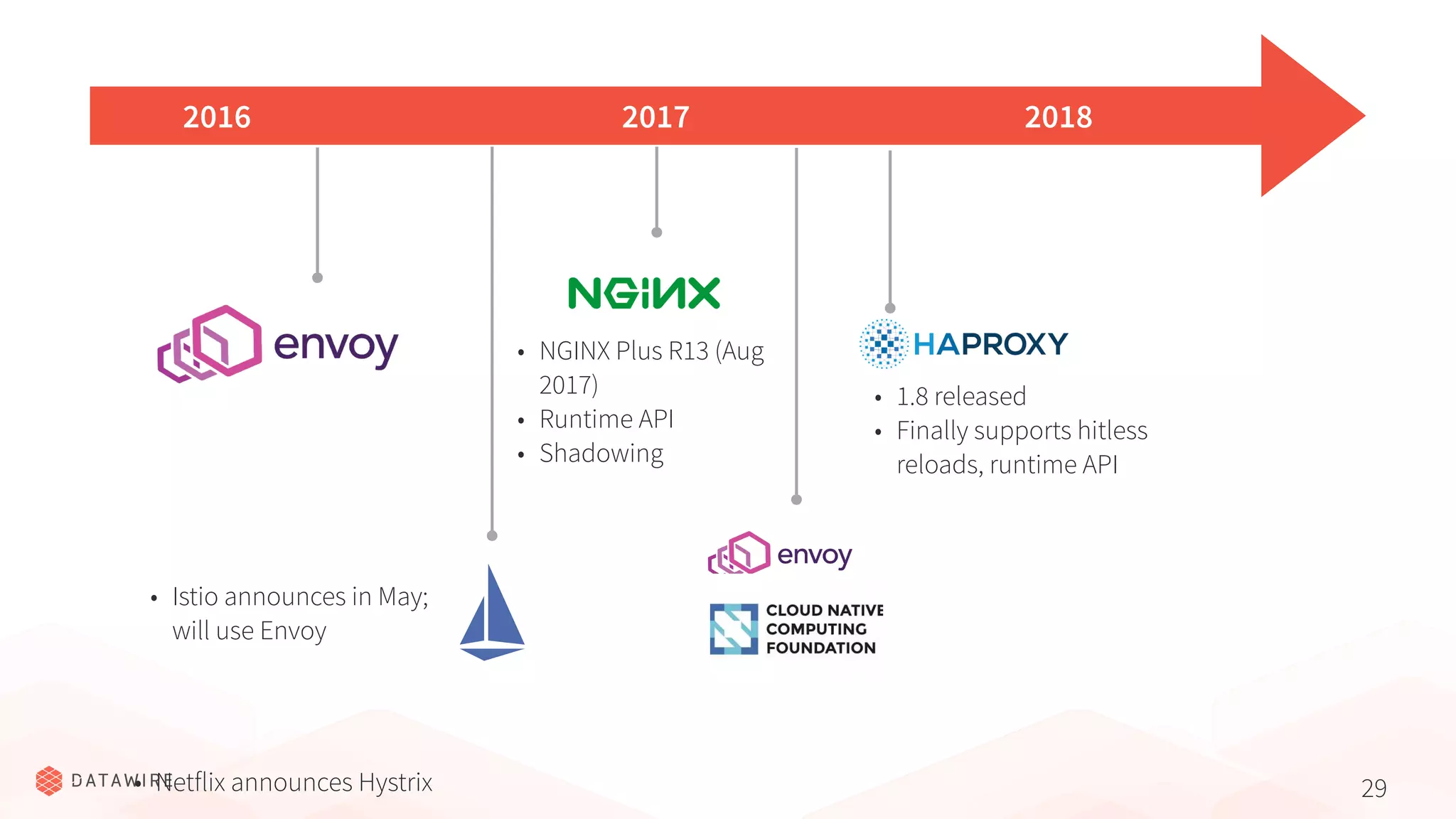
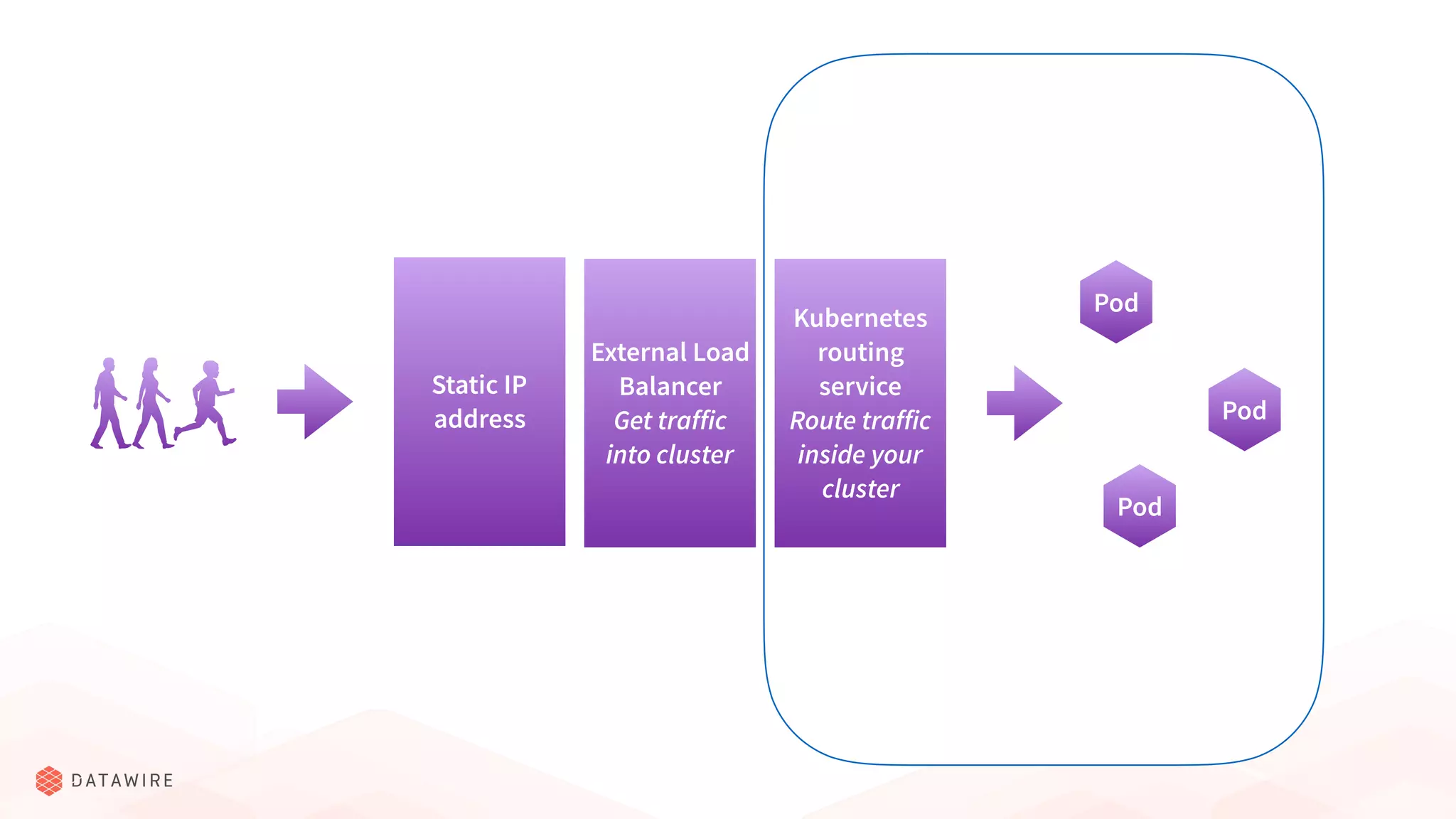
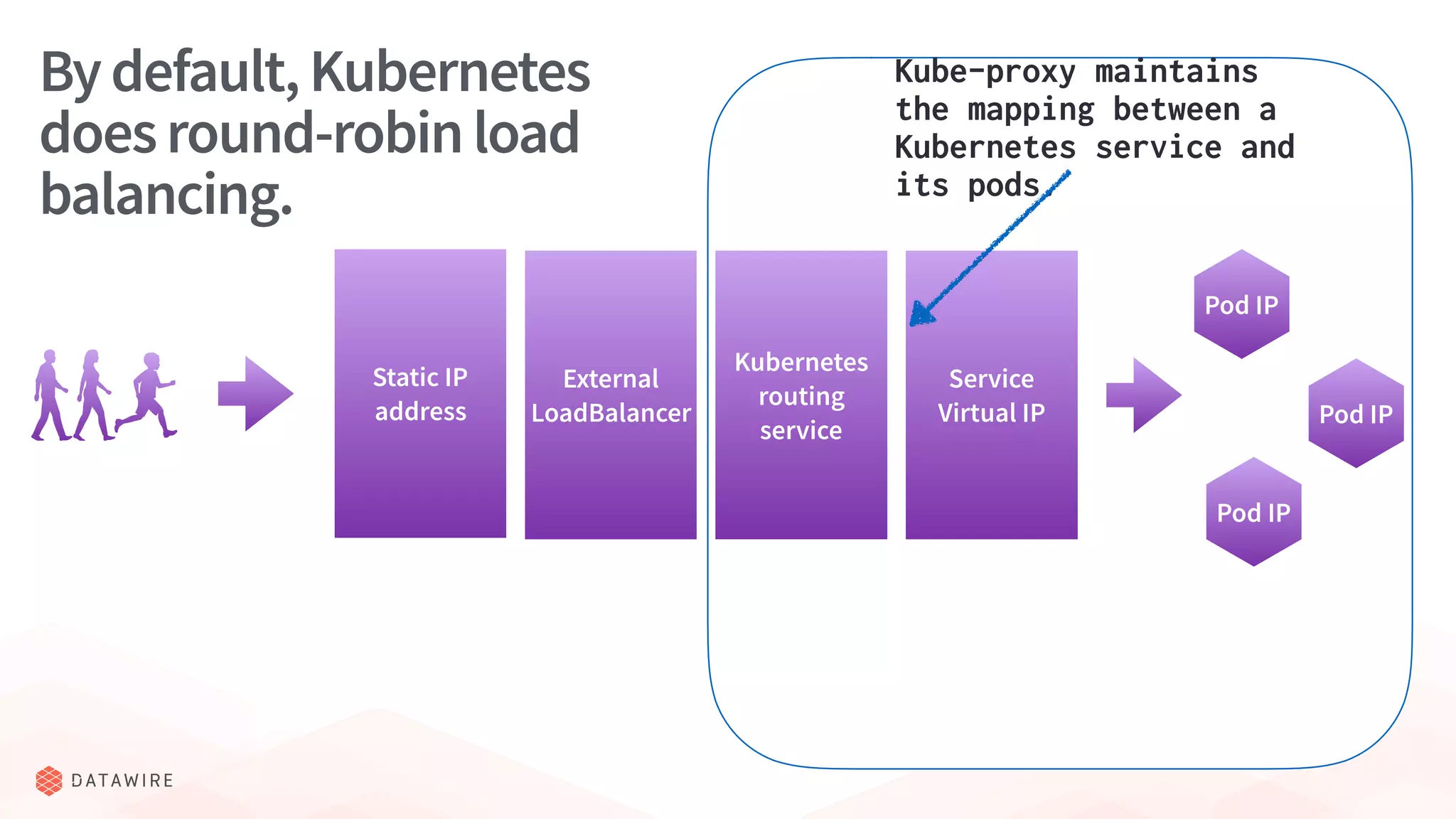
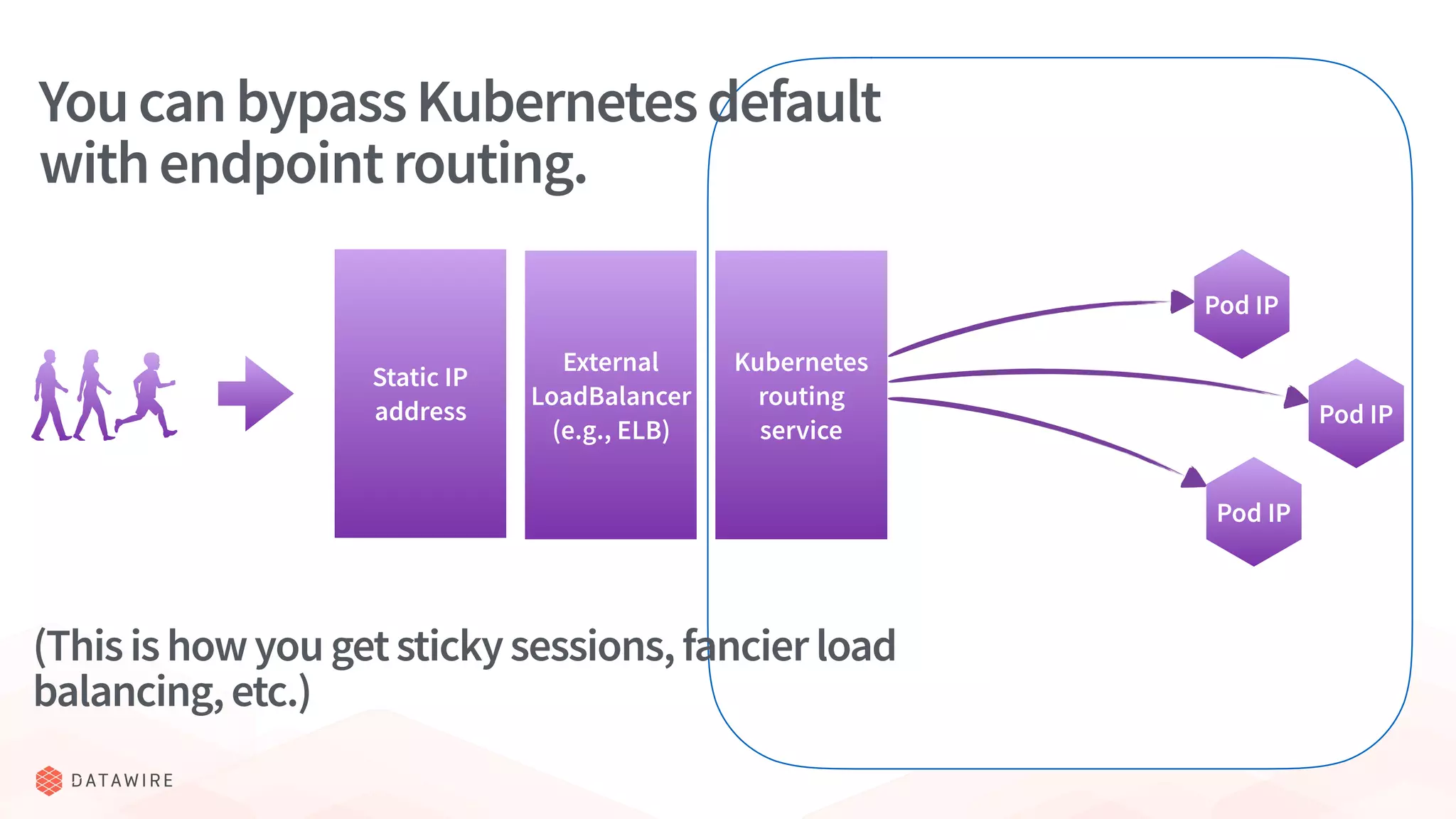
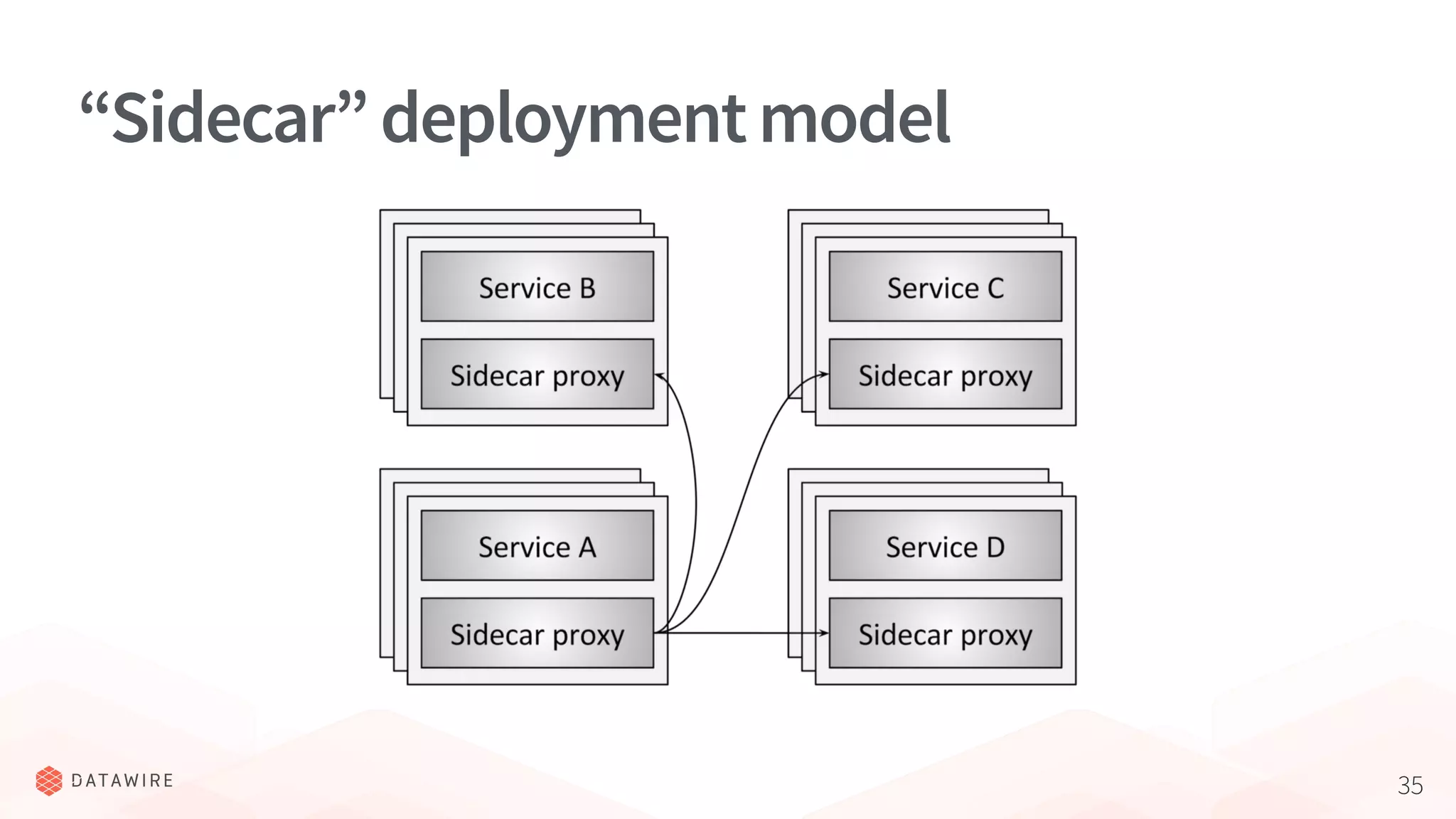
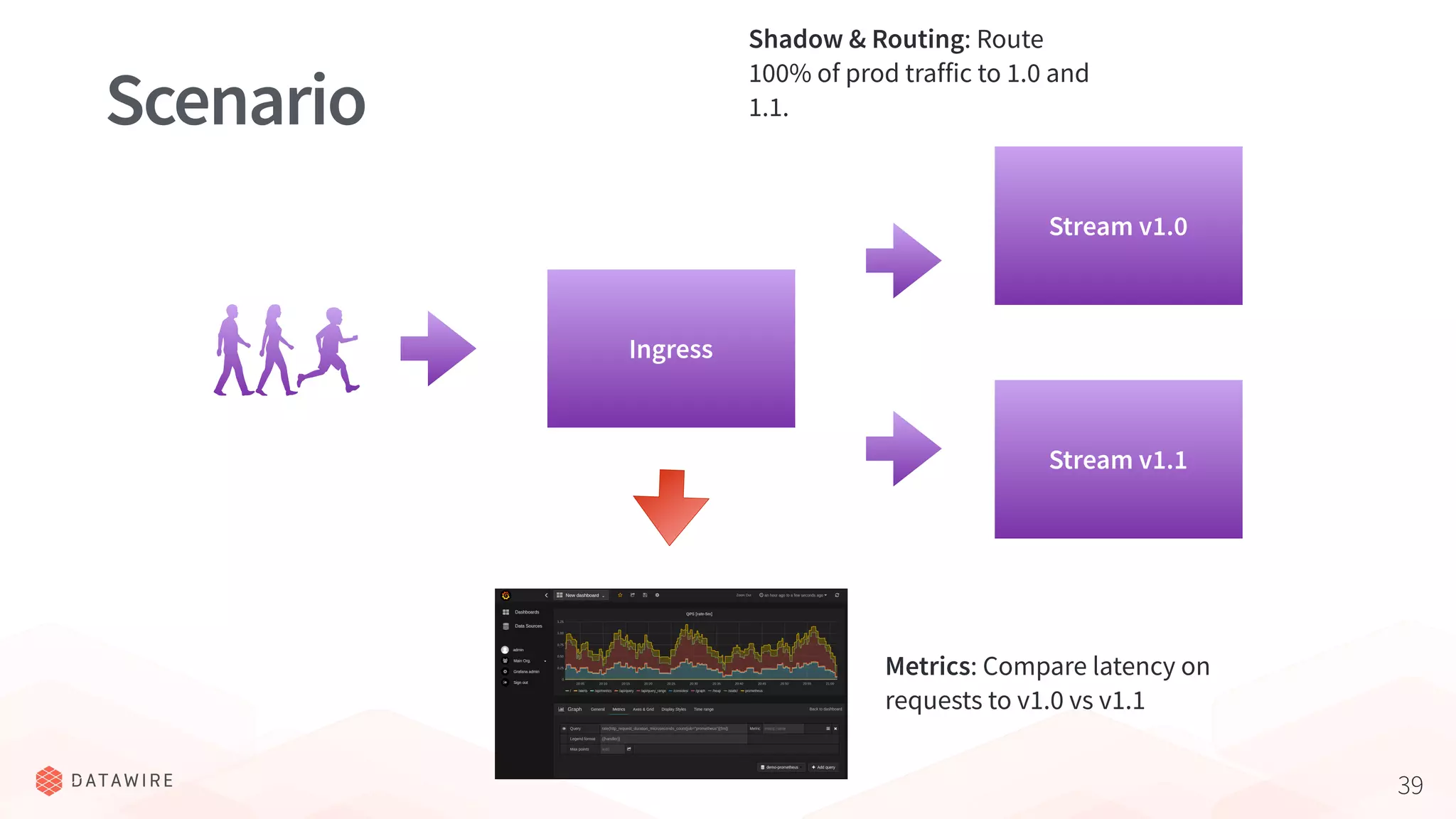
The document discusses Kubernetes ingress, focusing on its role in routing traffic within a cluster using services like LoadBalancer and NodePort. It highlights differences in configurations, including L4 and L7 routing, and mentions various controllers that implement ingress with unique extensions. Key considerations for implementing ingress include protocol support, resilience, observability, and operational aspects such as configuration management and upgrades.