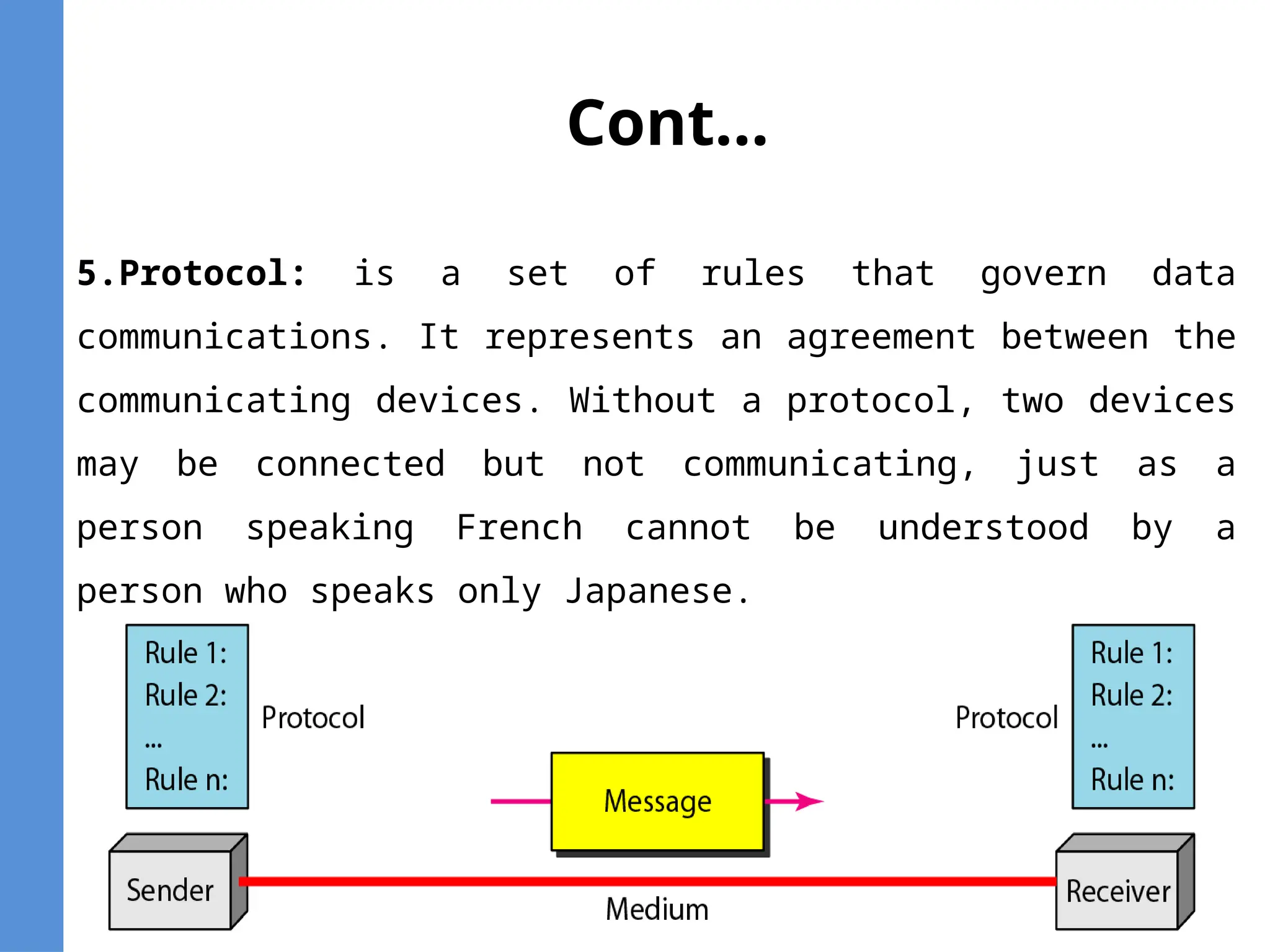
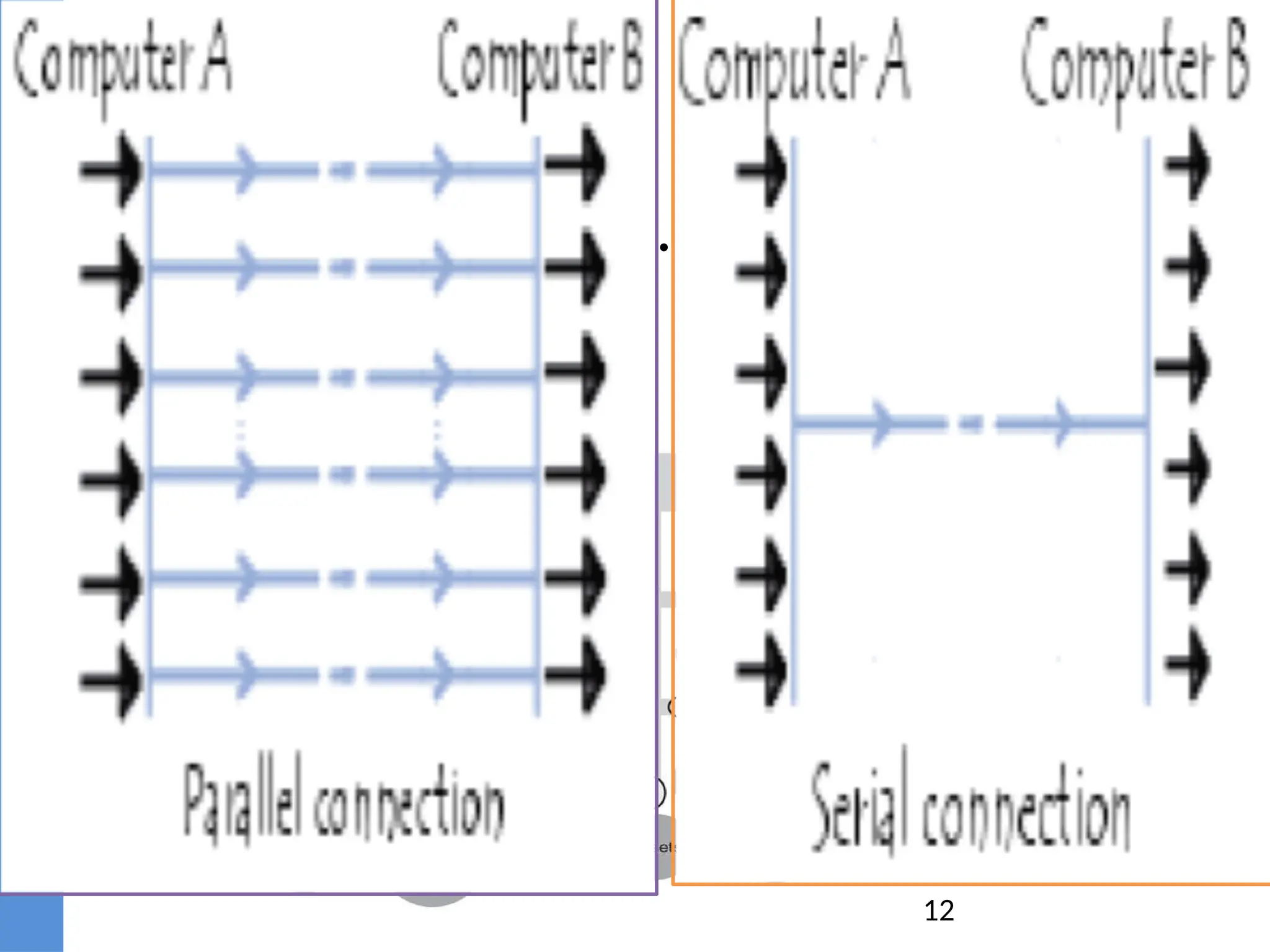
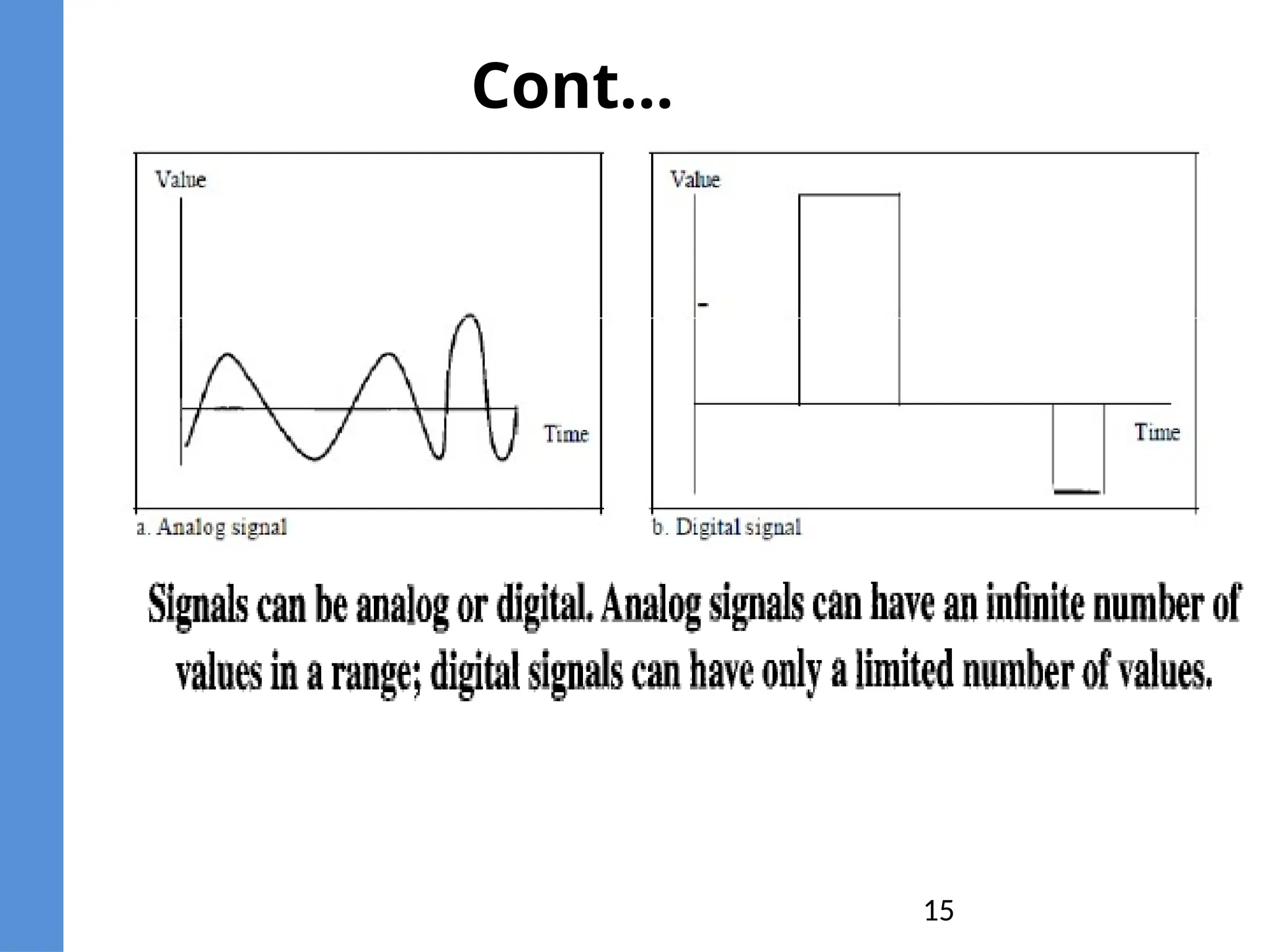
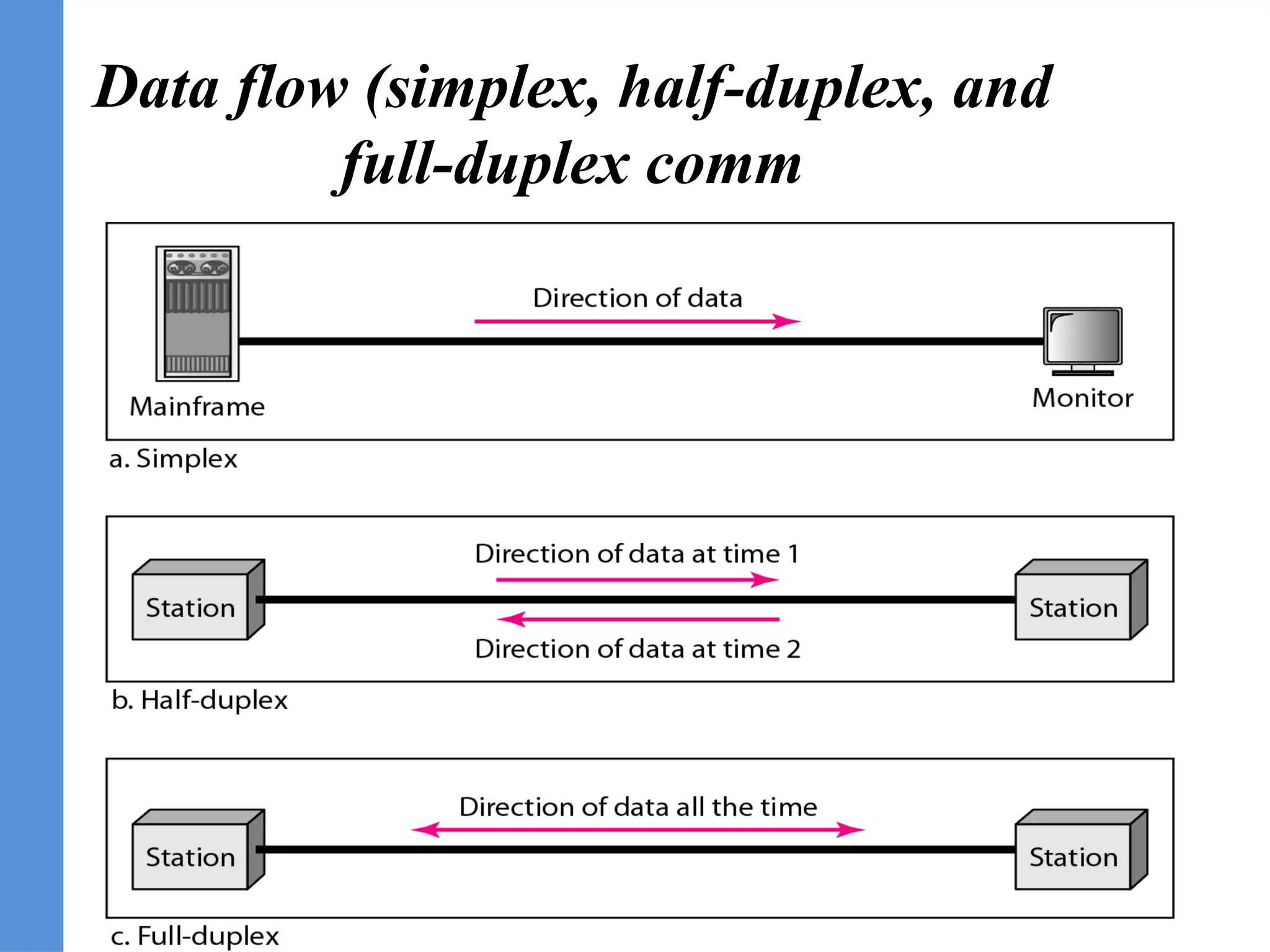
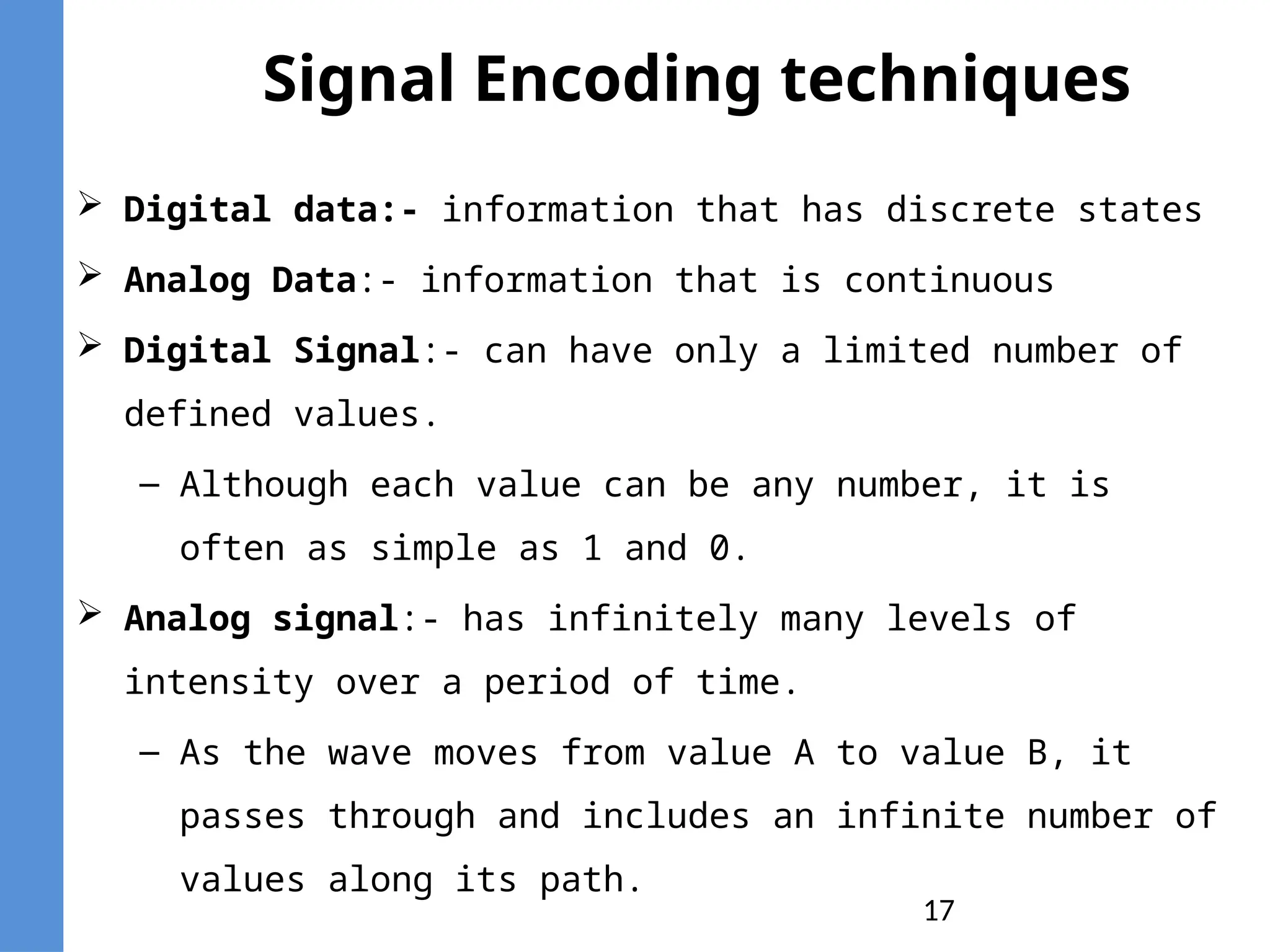
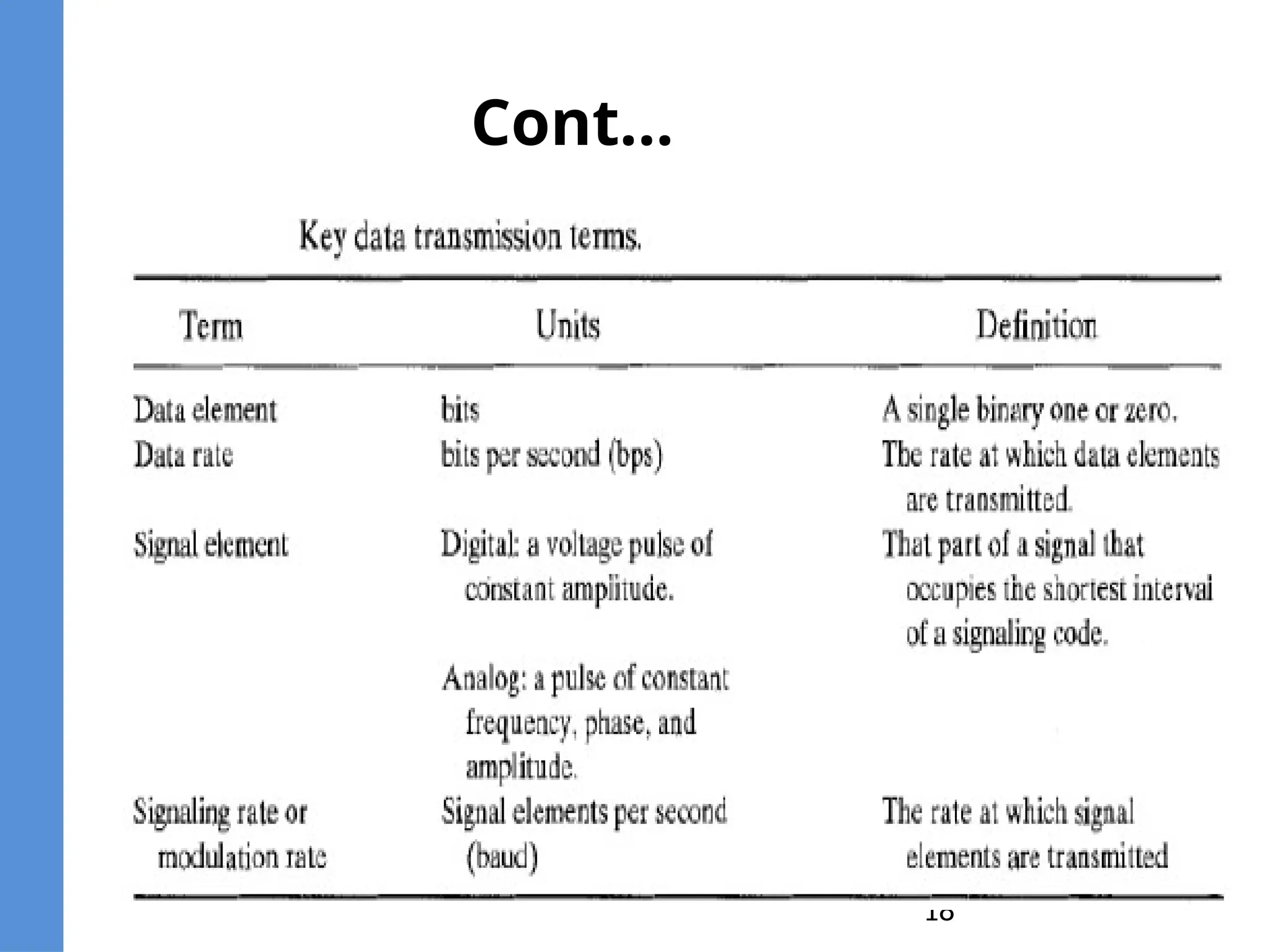
The document provides an overview of telecommunication, defining it as communication at a distance via various technologies. It discusses the components of data communication, the evolution of telecom services, and the participants involved, including public telecom operators and users. Additionally, it outlines the types of communication channels and the differences between analog and digital data.