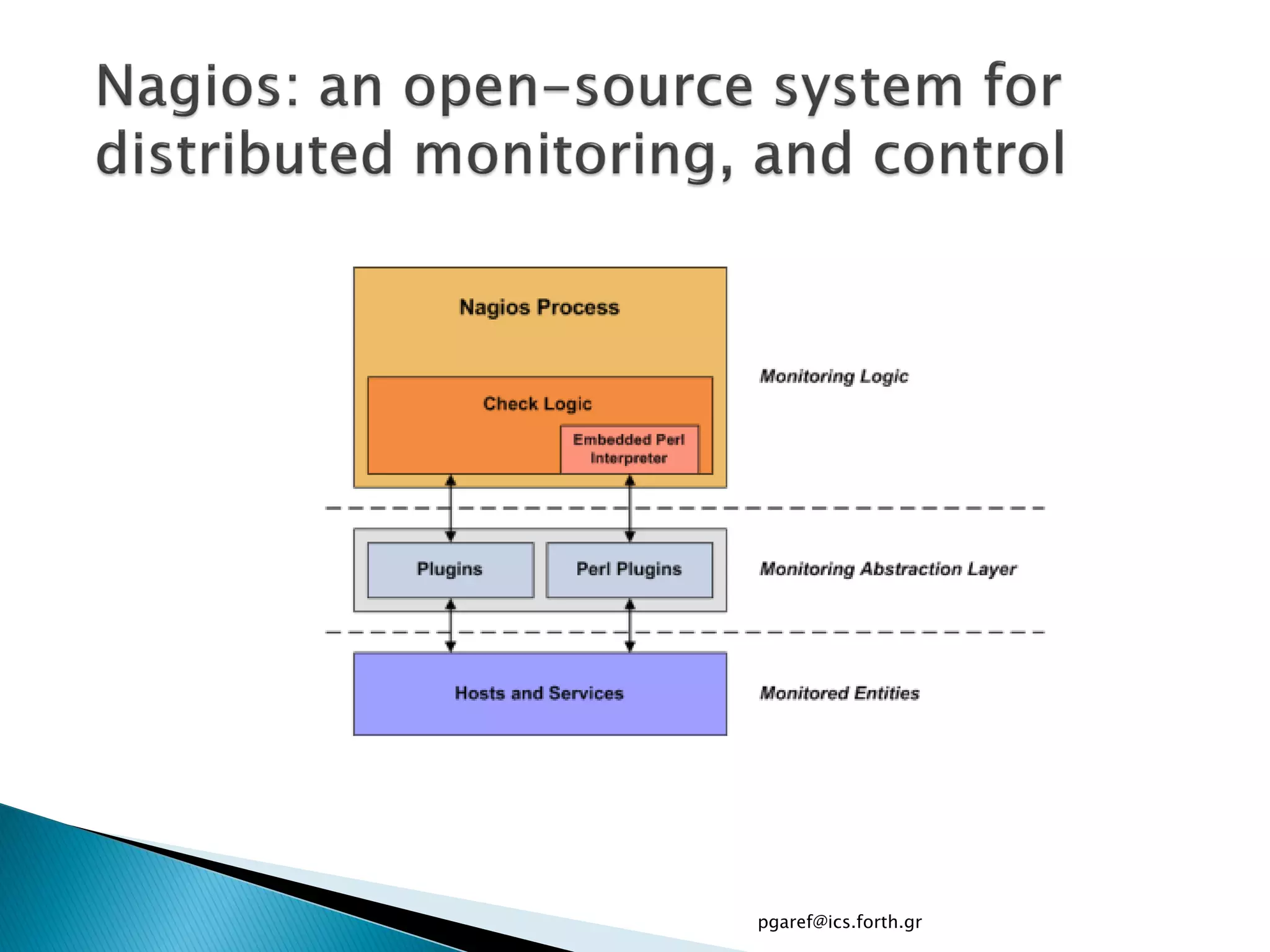
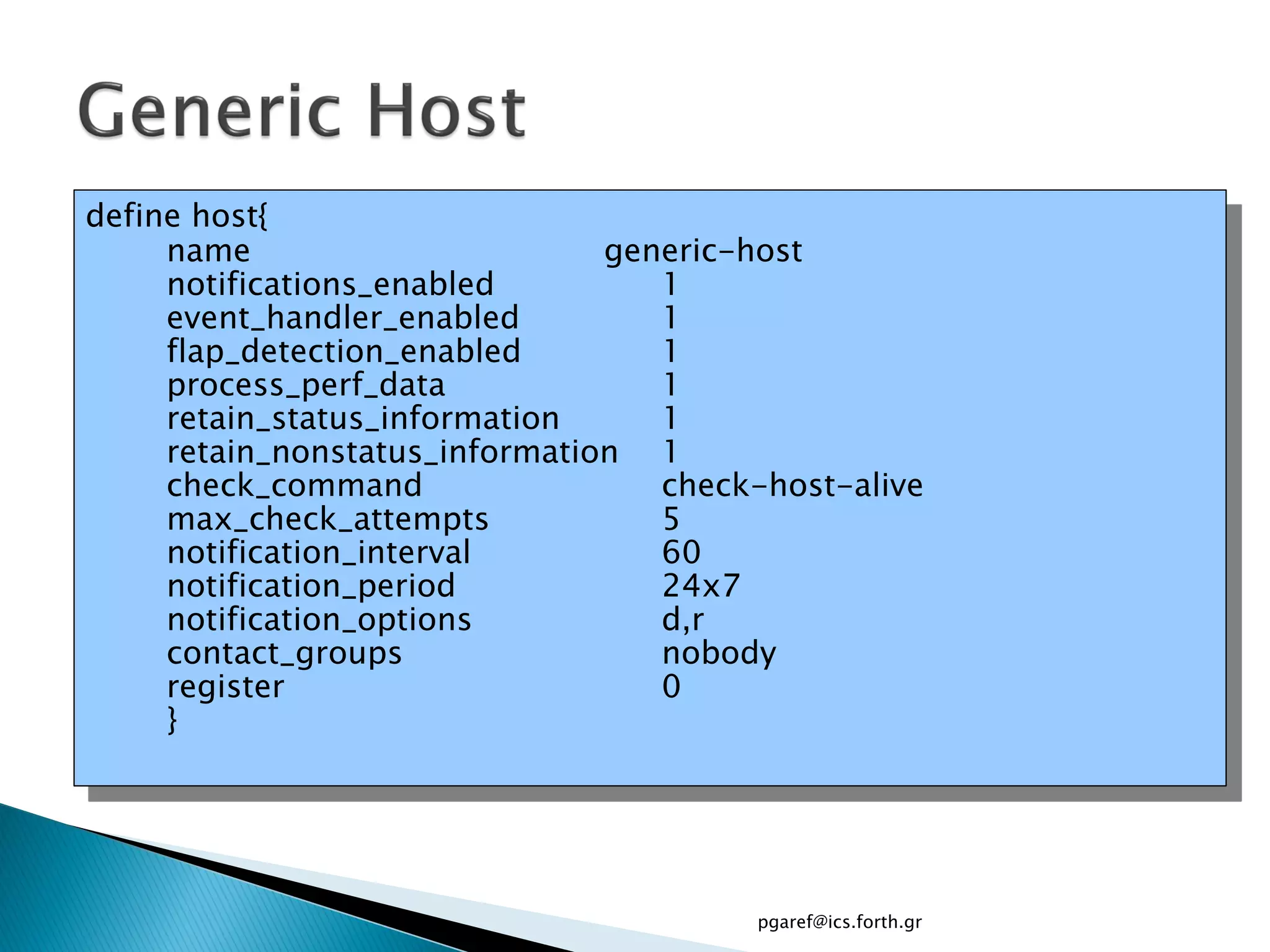
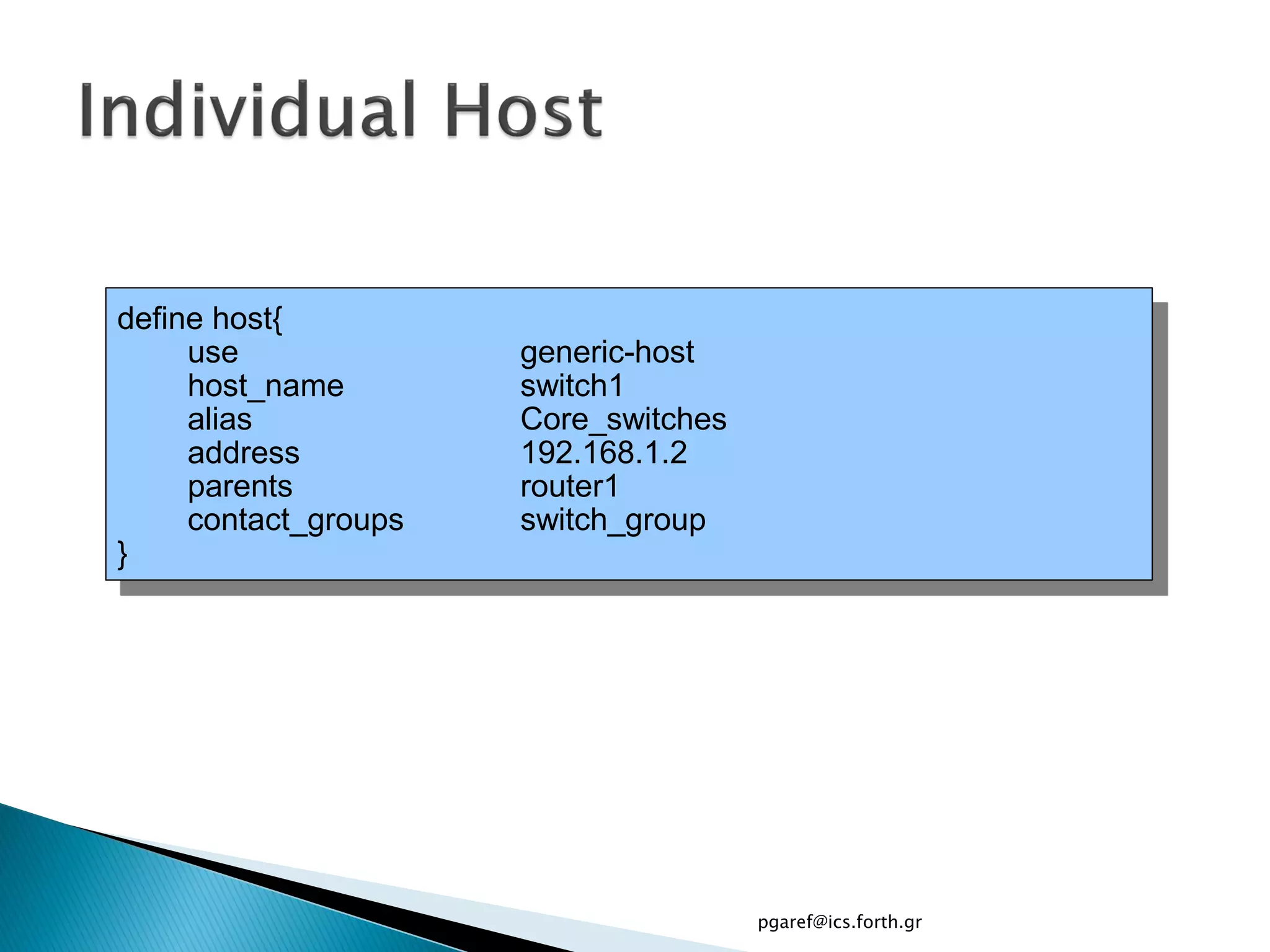
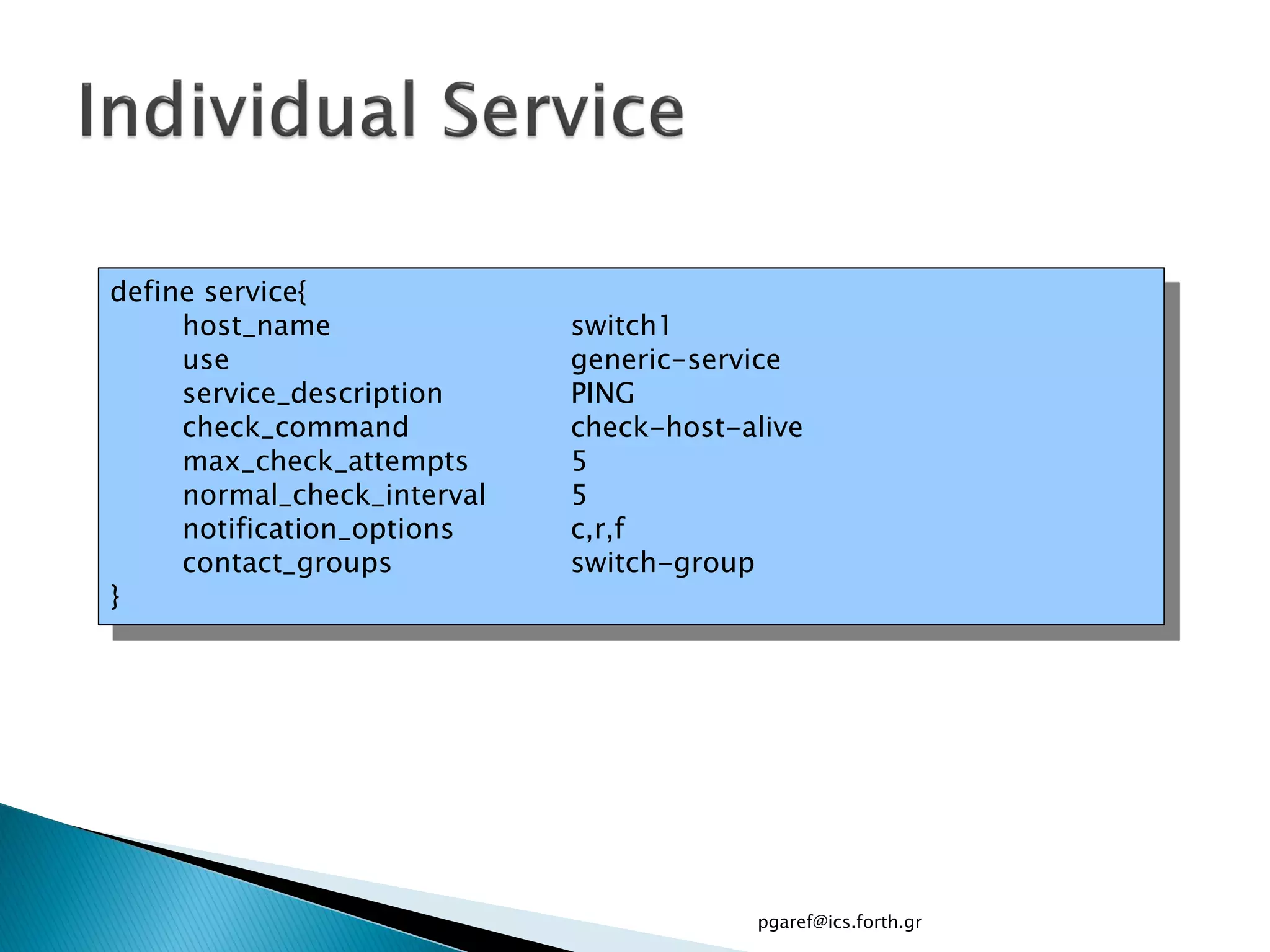
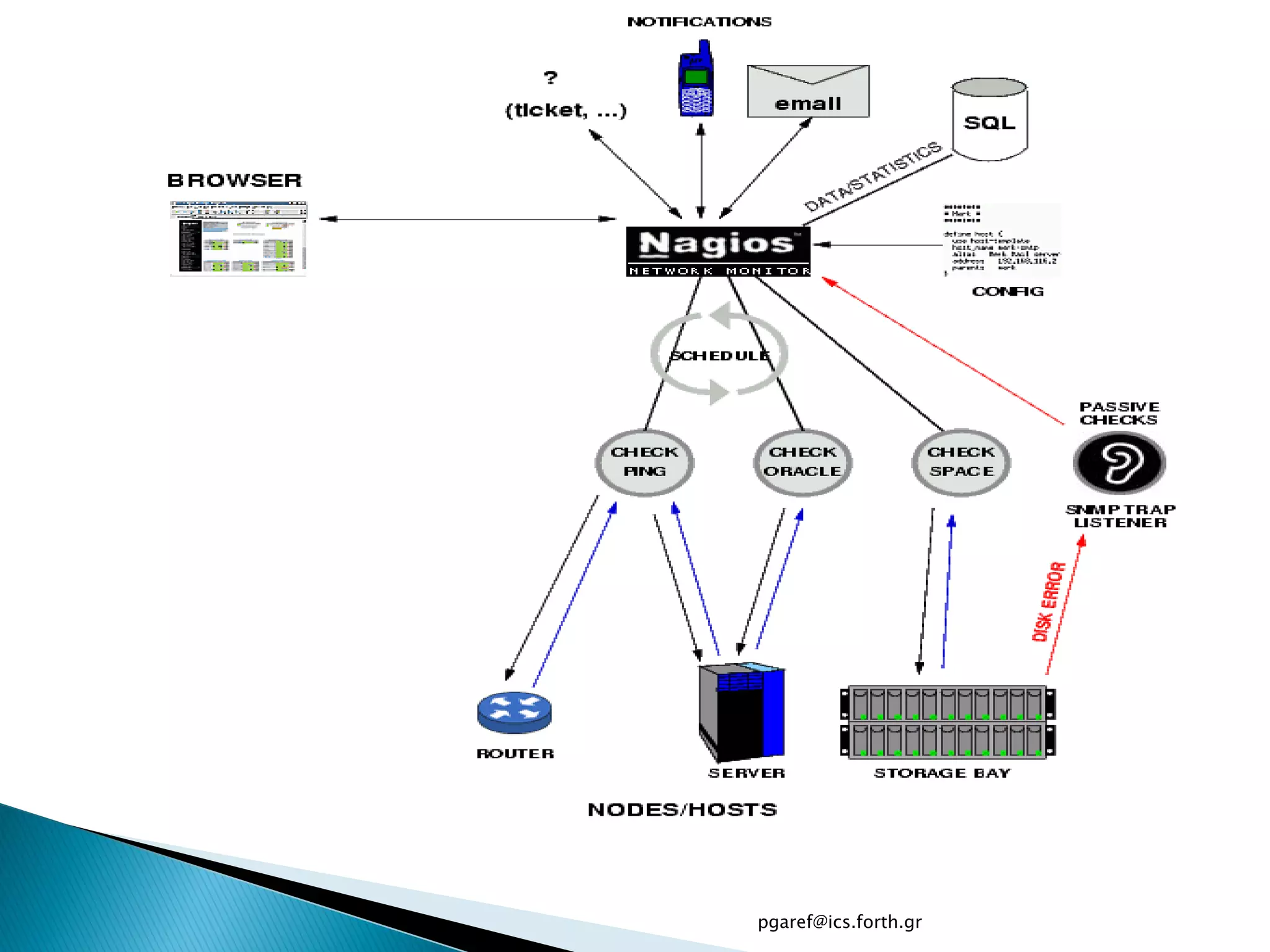
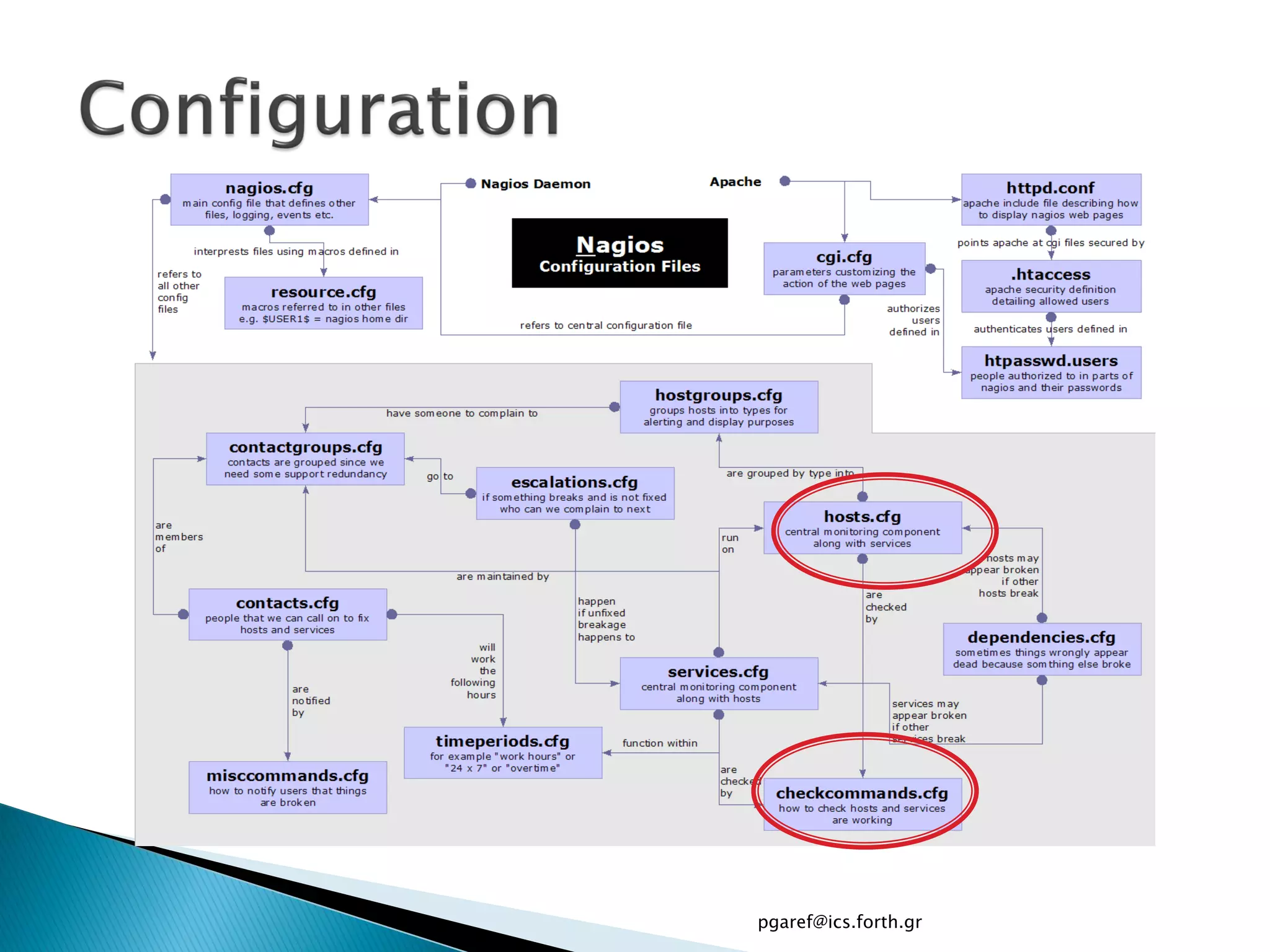
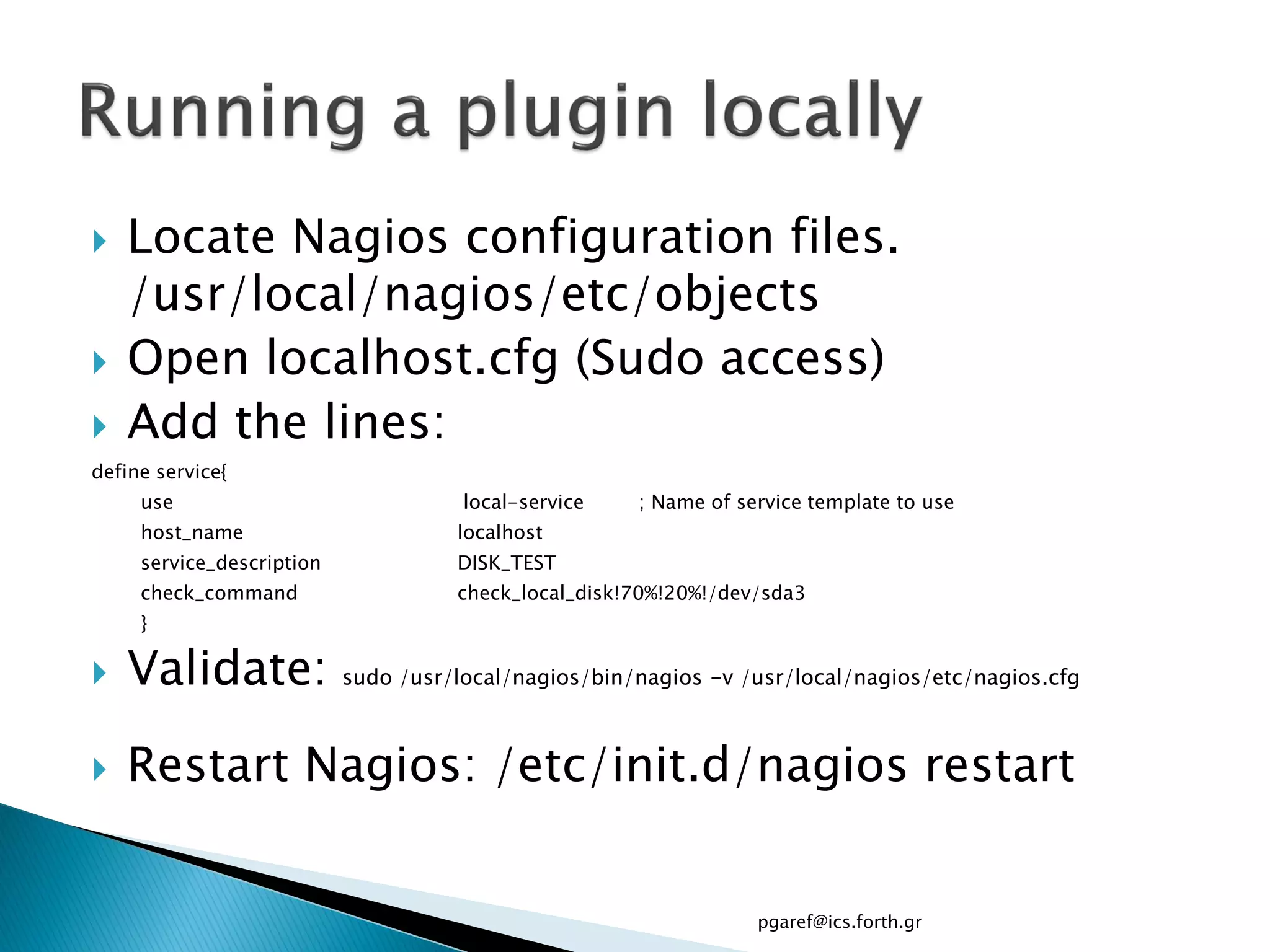
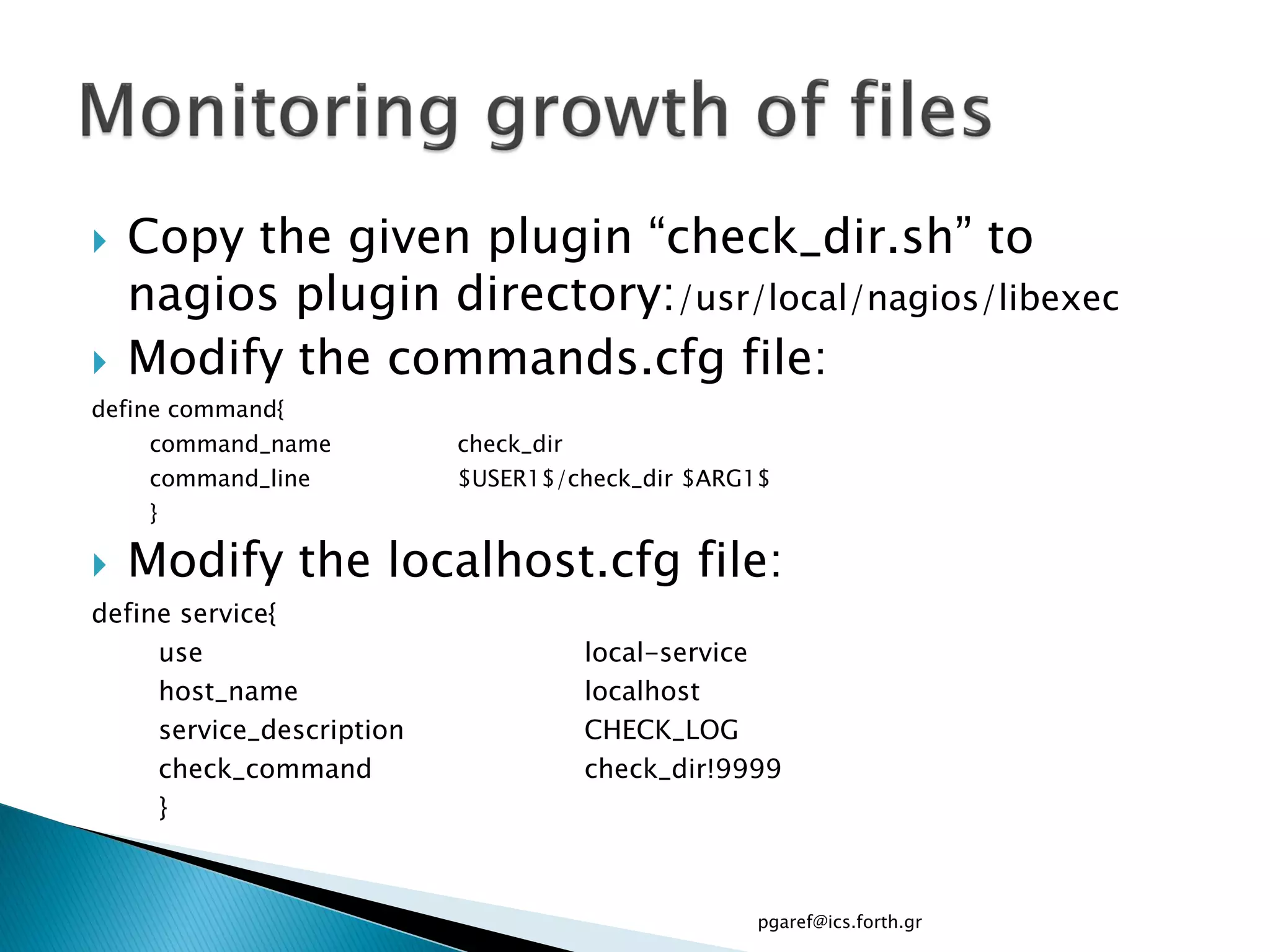
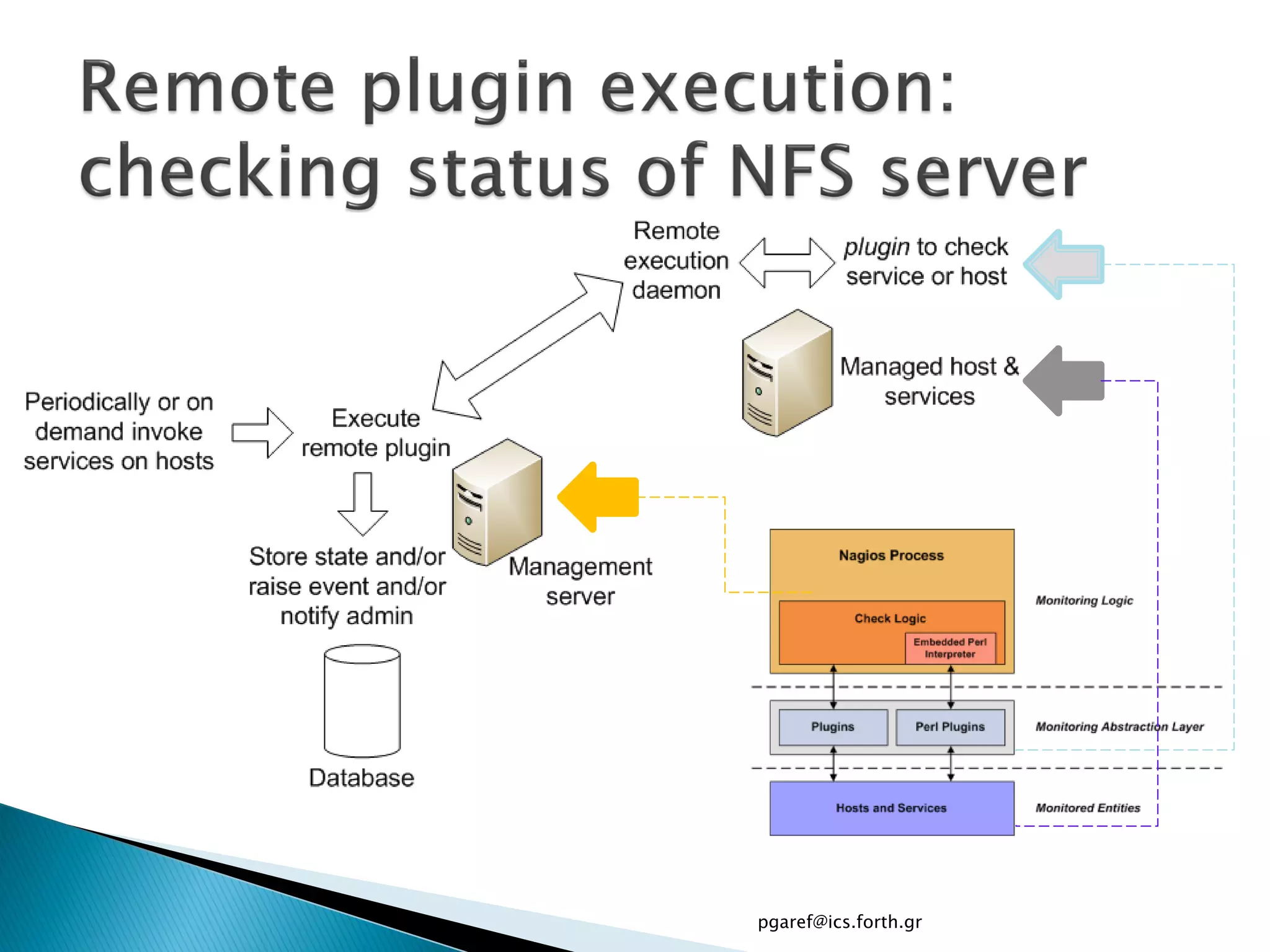
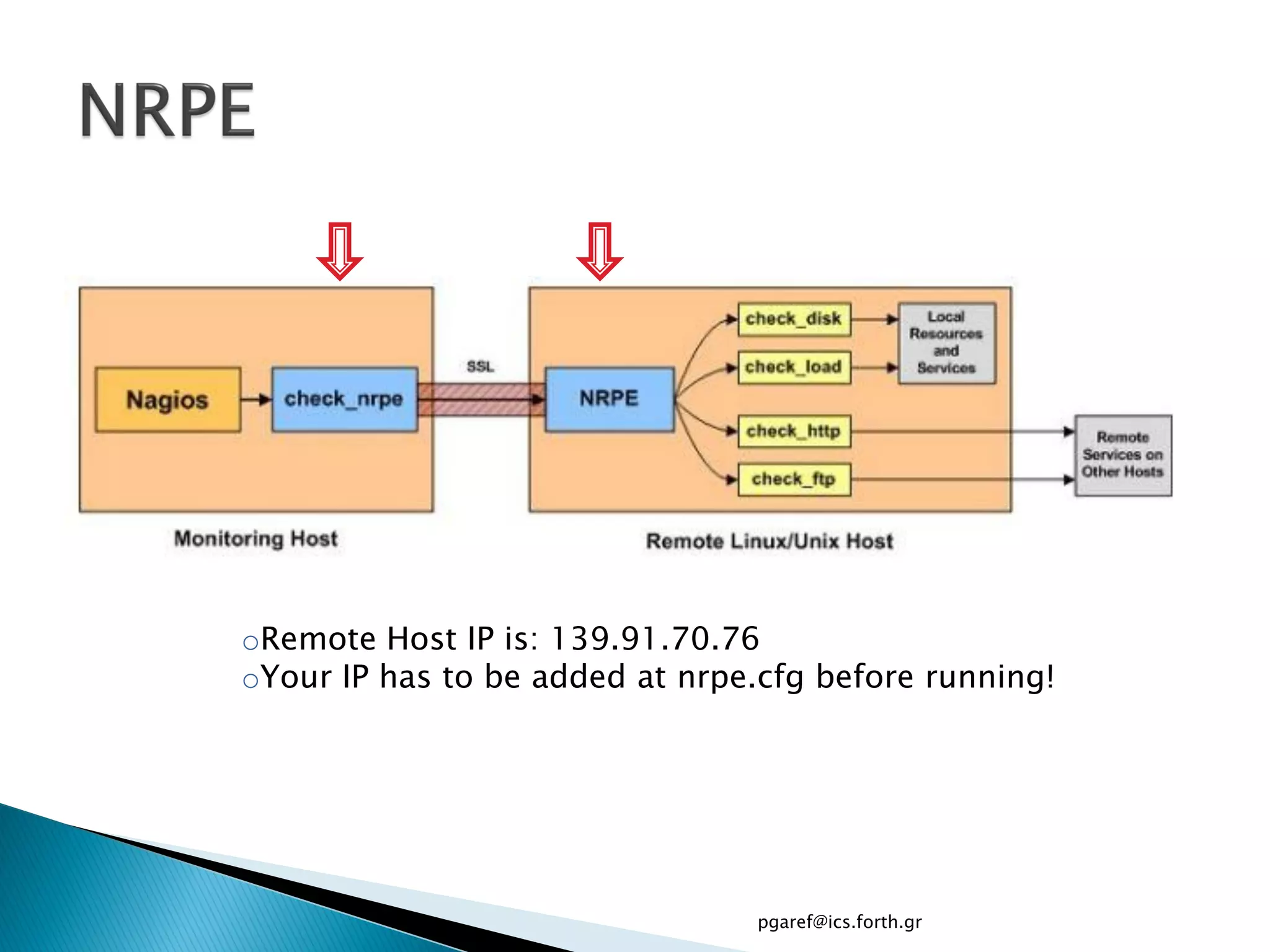
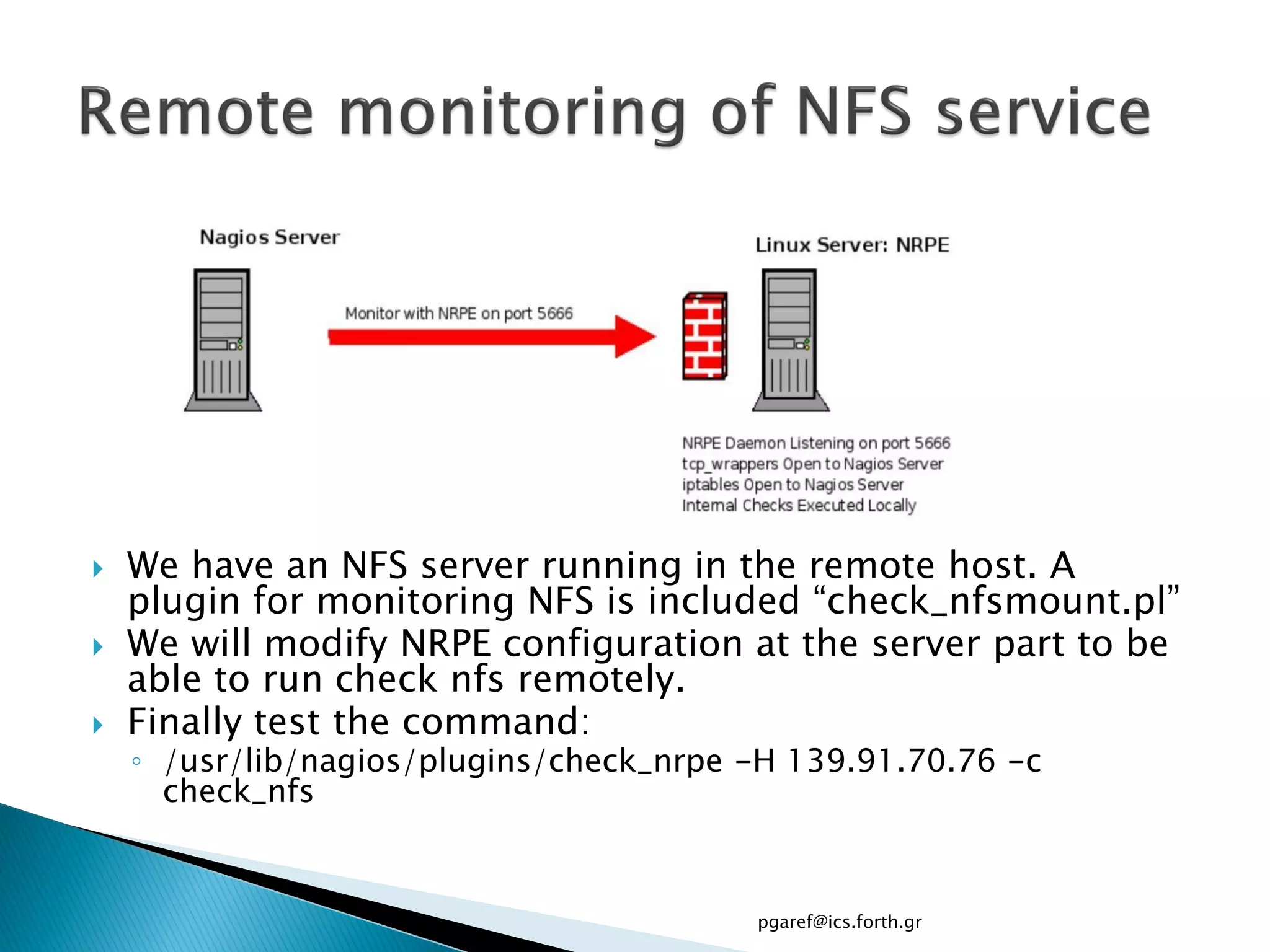
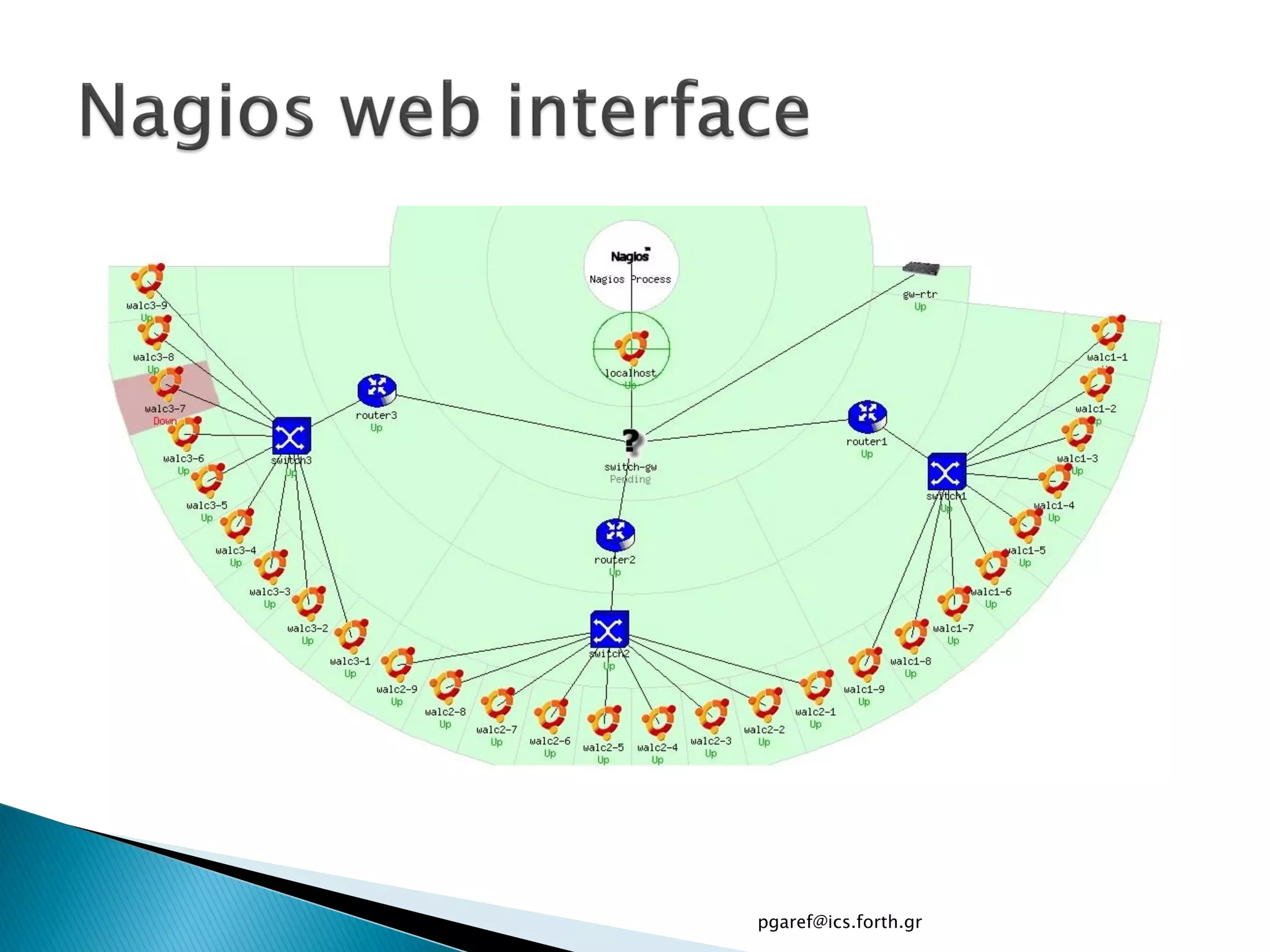
The document provides an overview of Nagios, an open source network monitoring software. It discusses storage management challenges, what Nagios is, and provides tutorial topics on how to start a Nagios server, write storage service monitoring code, monitor local and remote storage, and handle events. The tutorial covers installing and configuring Nagios, defining hosts and services, writing check commands, installing NRPE for remote monitoring, and using event handlers to automate responses. Additional Nagios resources are also listed.