Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times

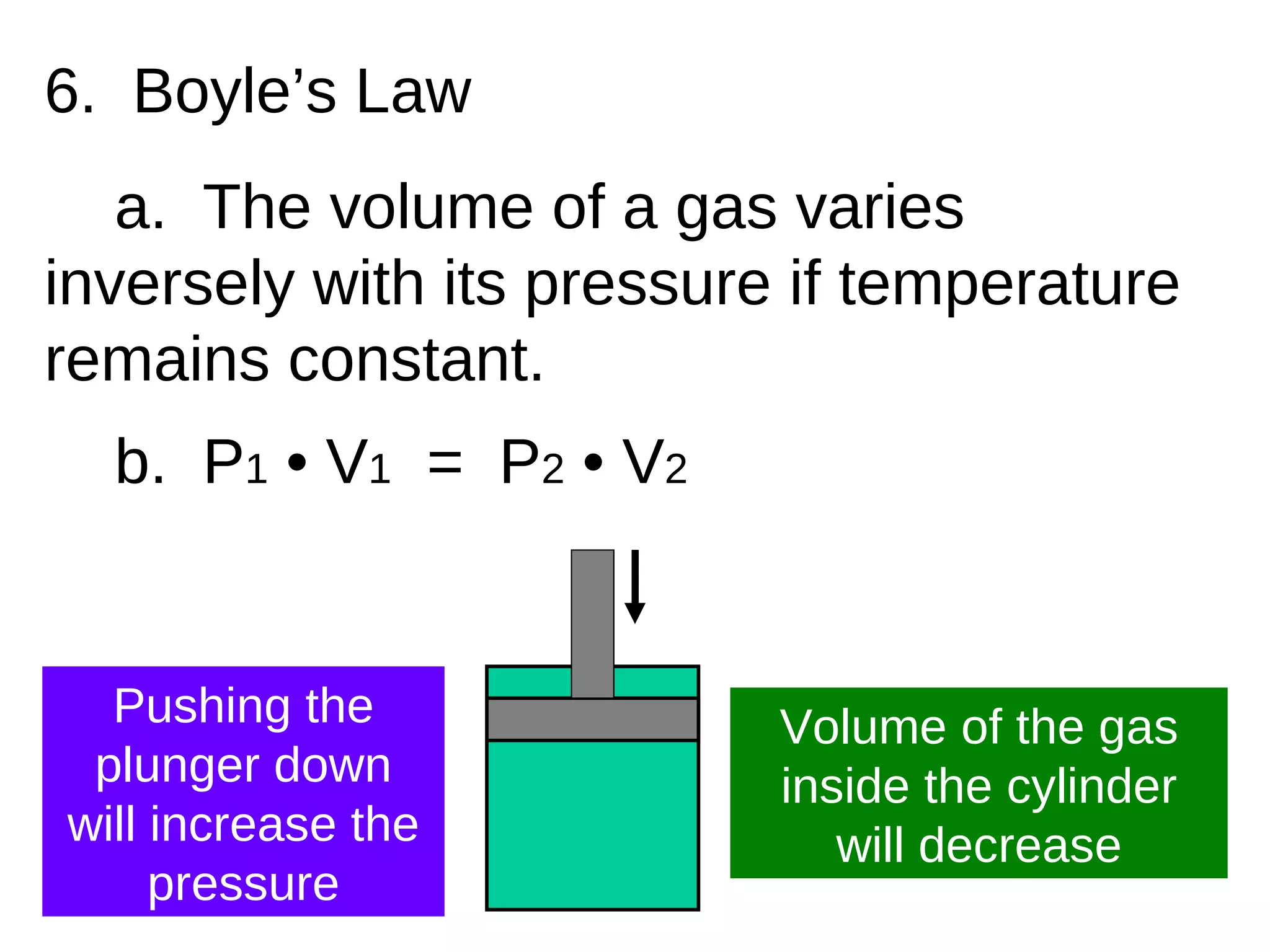



Gas pressure is caused by collisions of gas particles with surfaces. Boyle's Law states that the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure if temperature remains constant. Charles's Law specifies that gas volume varies directly with temperature if pressure remains constant. Gay-Lussac's Law describes pressure varying directly with temperature when volume is kept constant.



