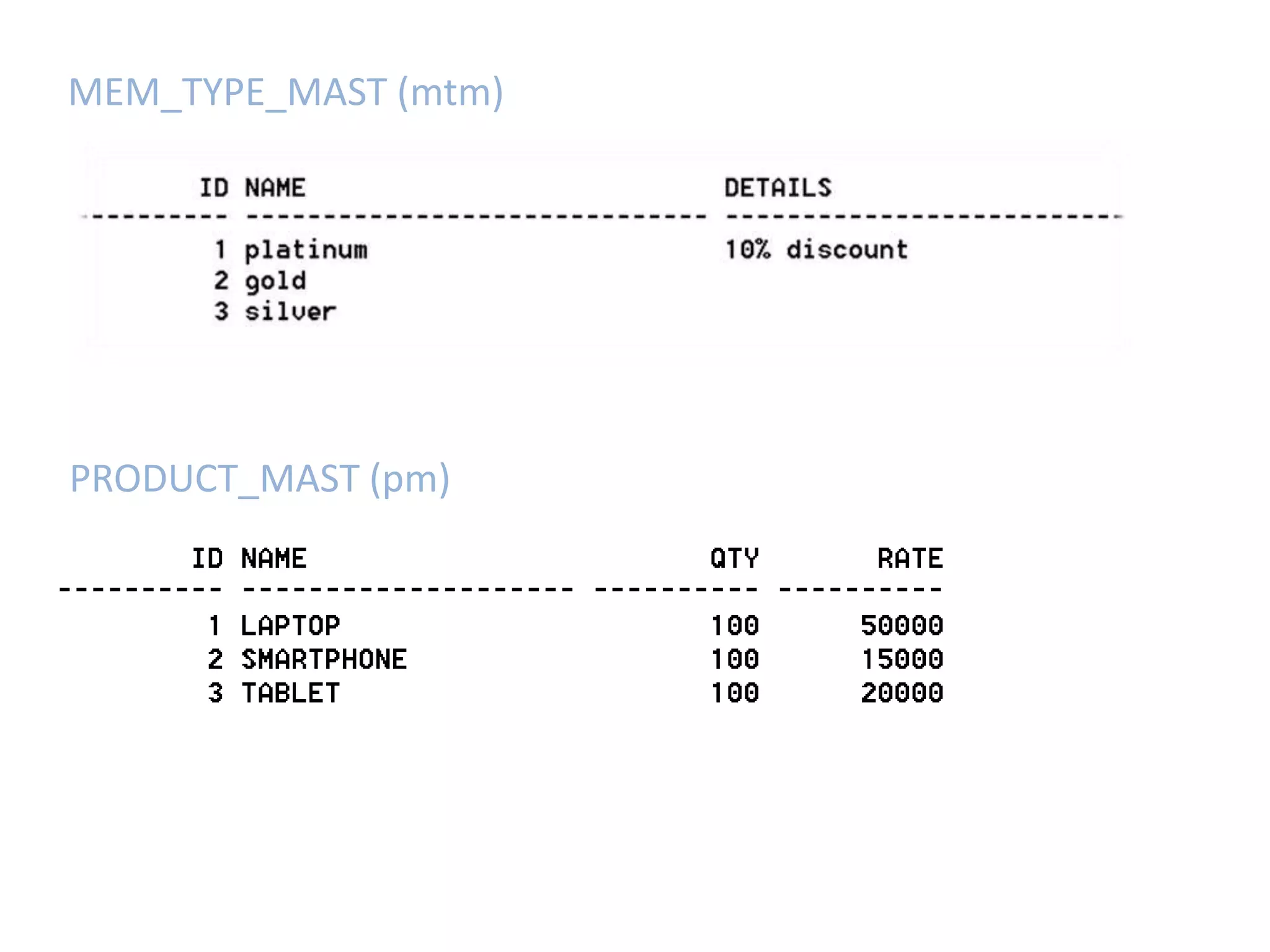
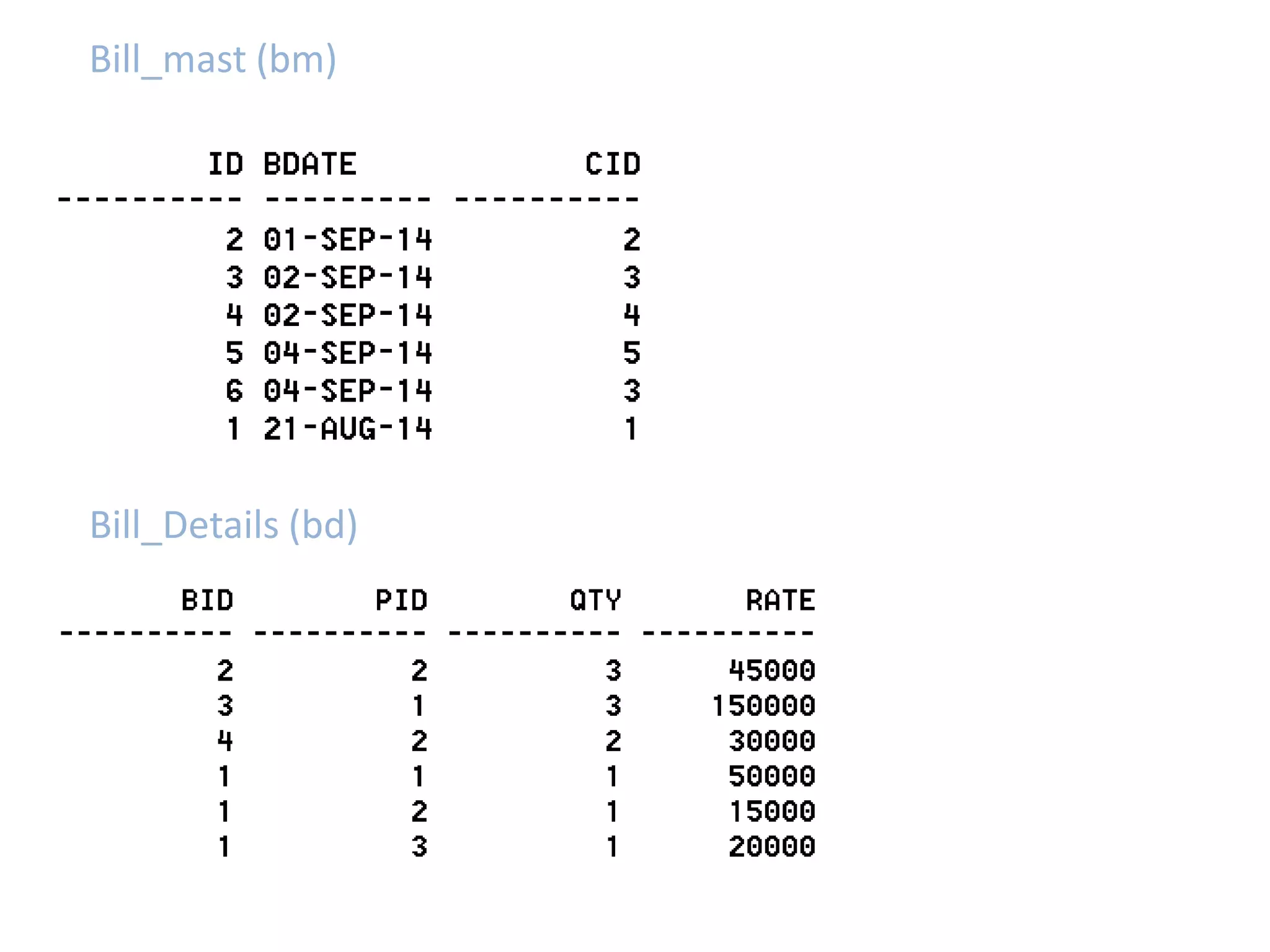
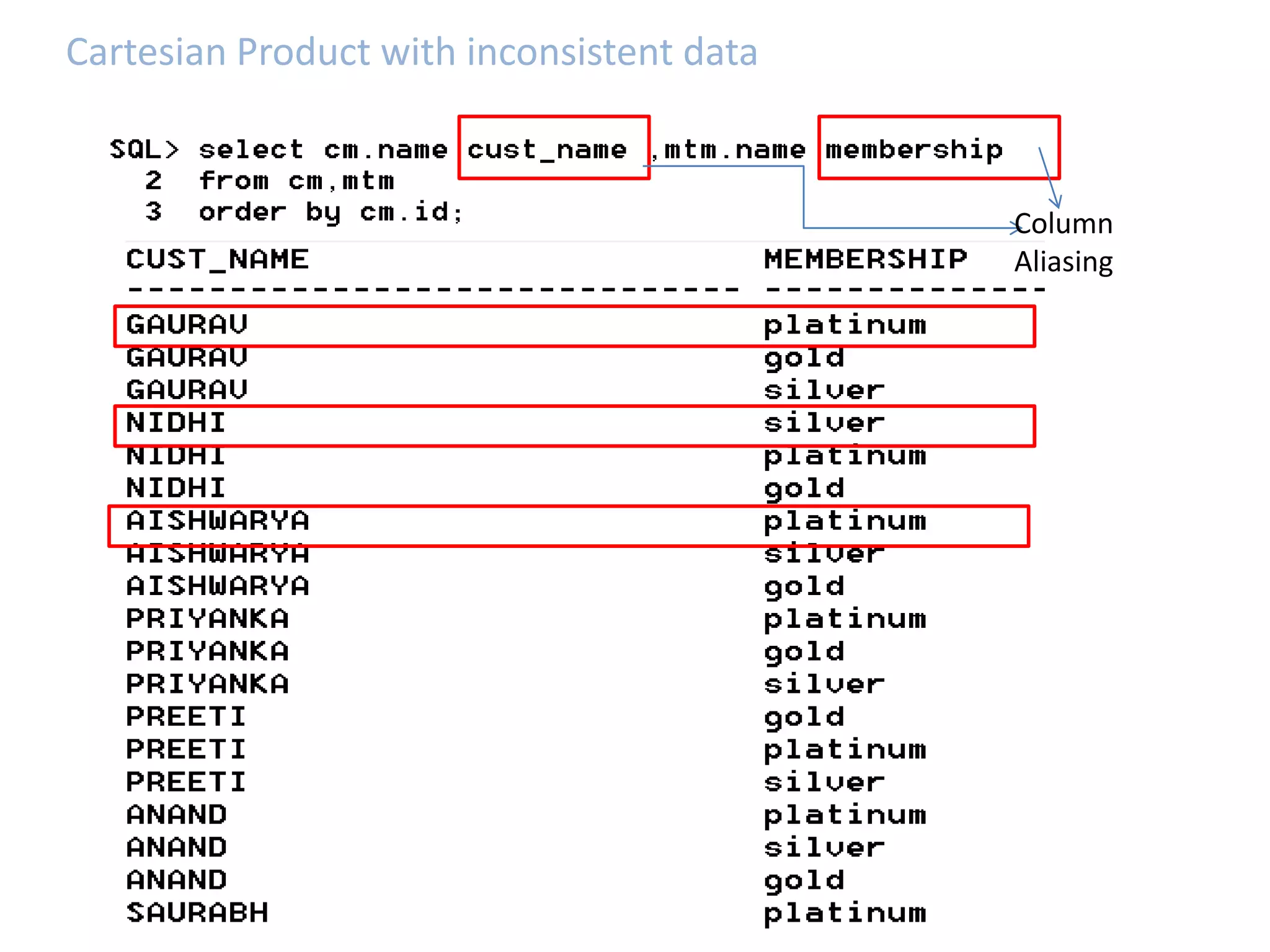
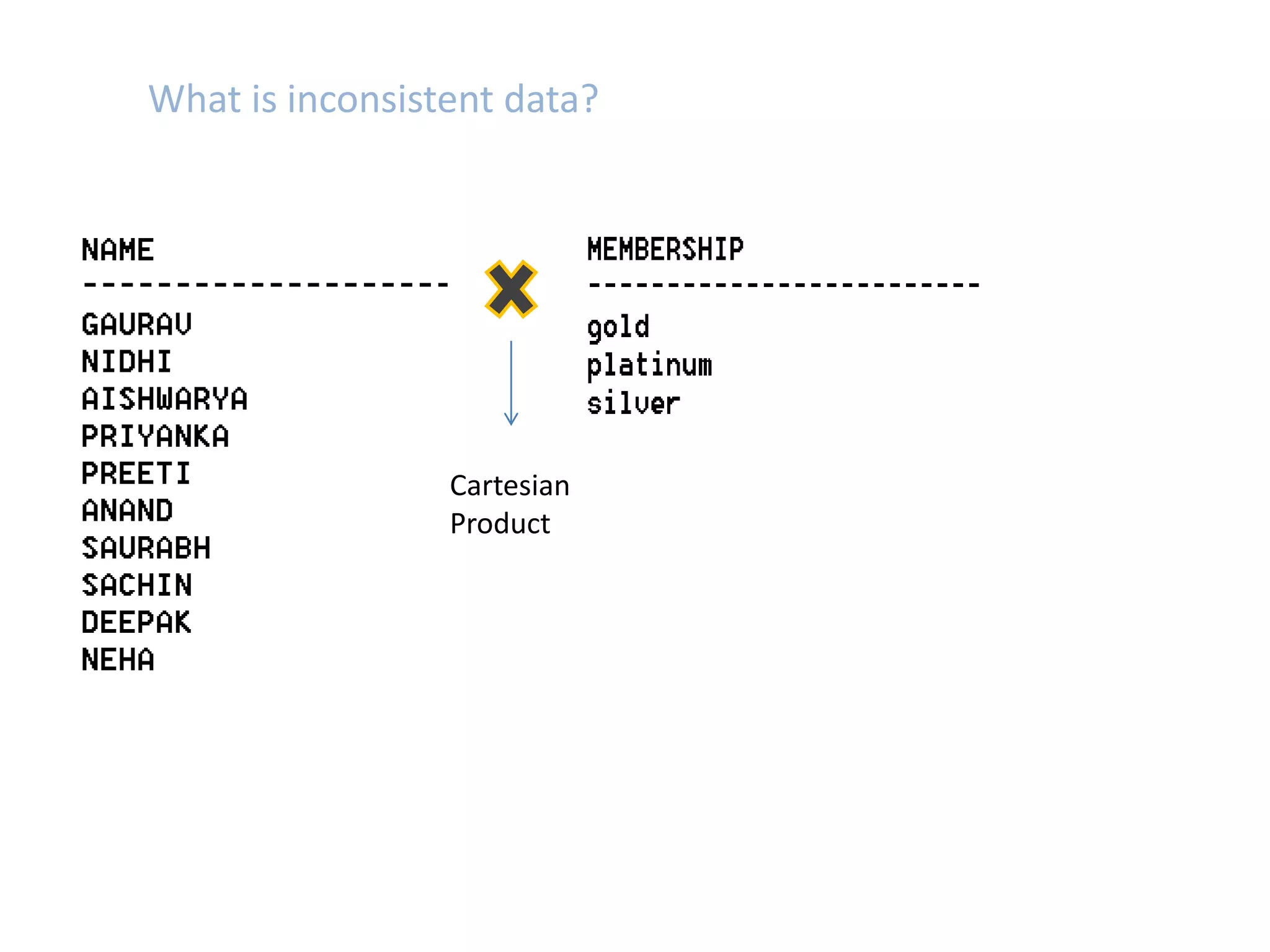
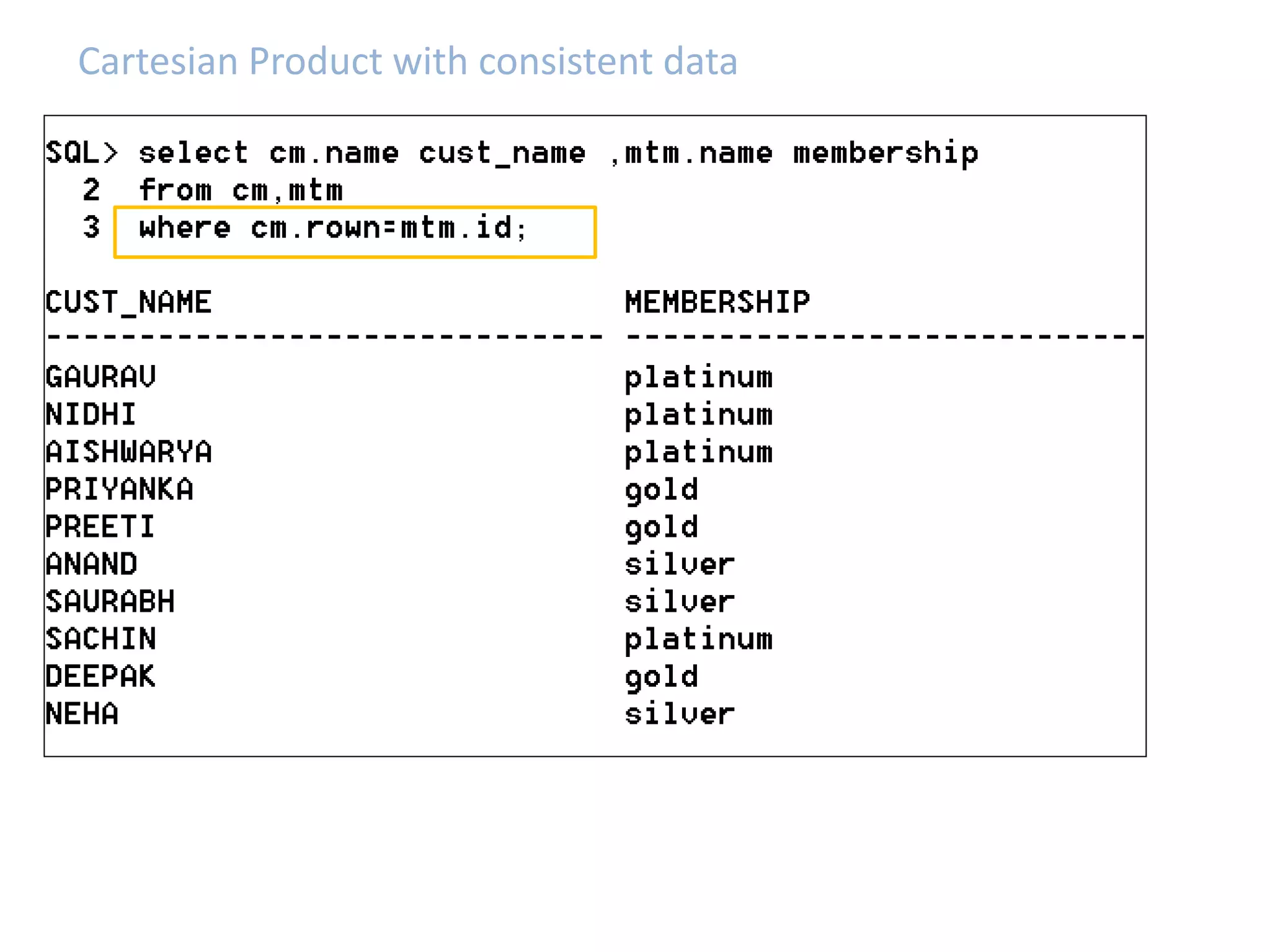
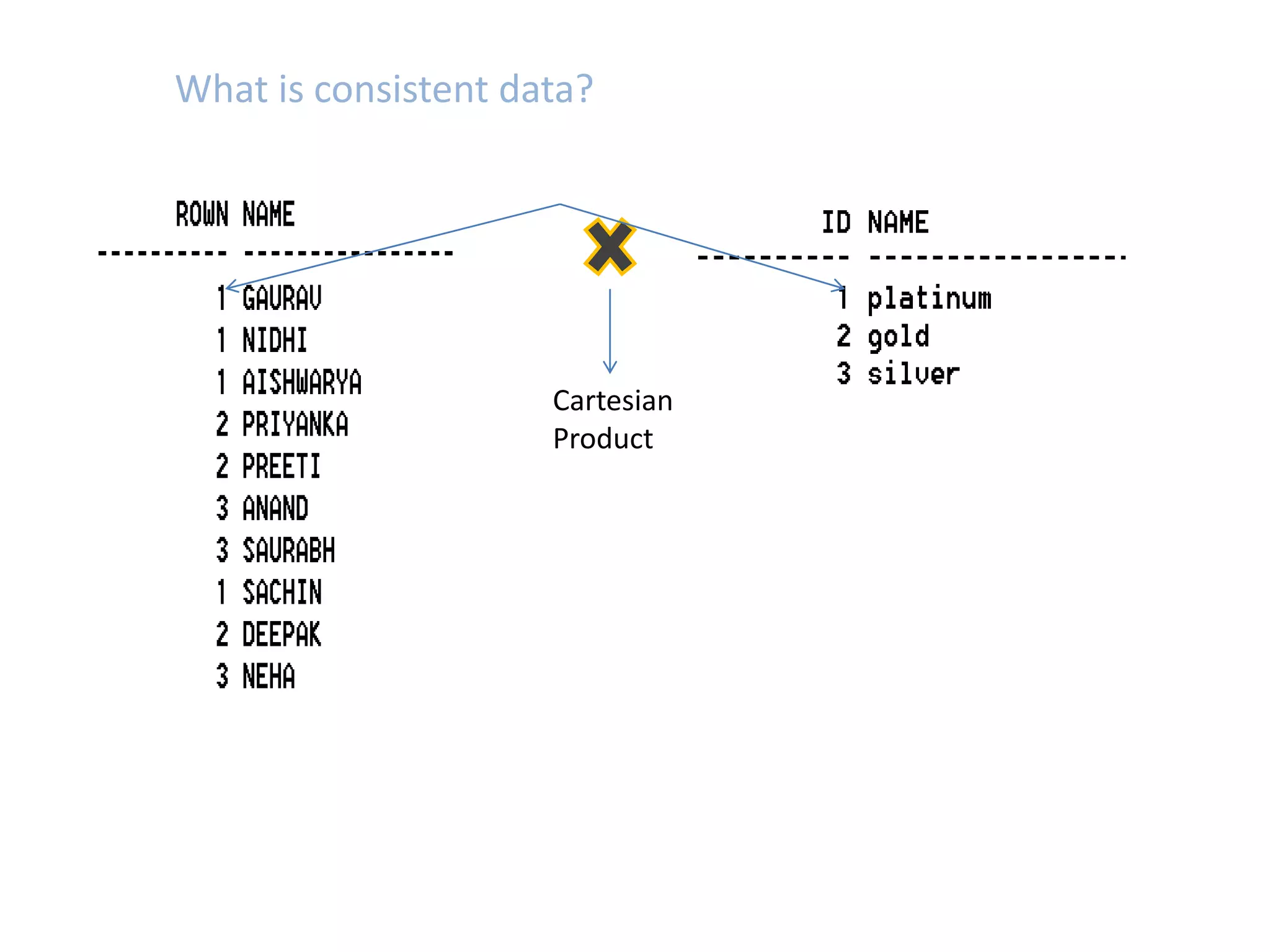
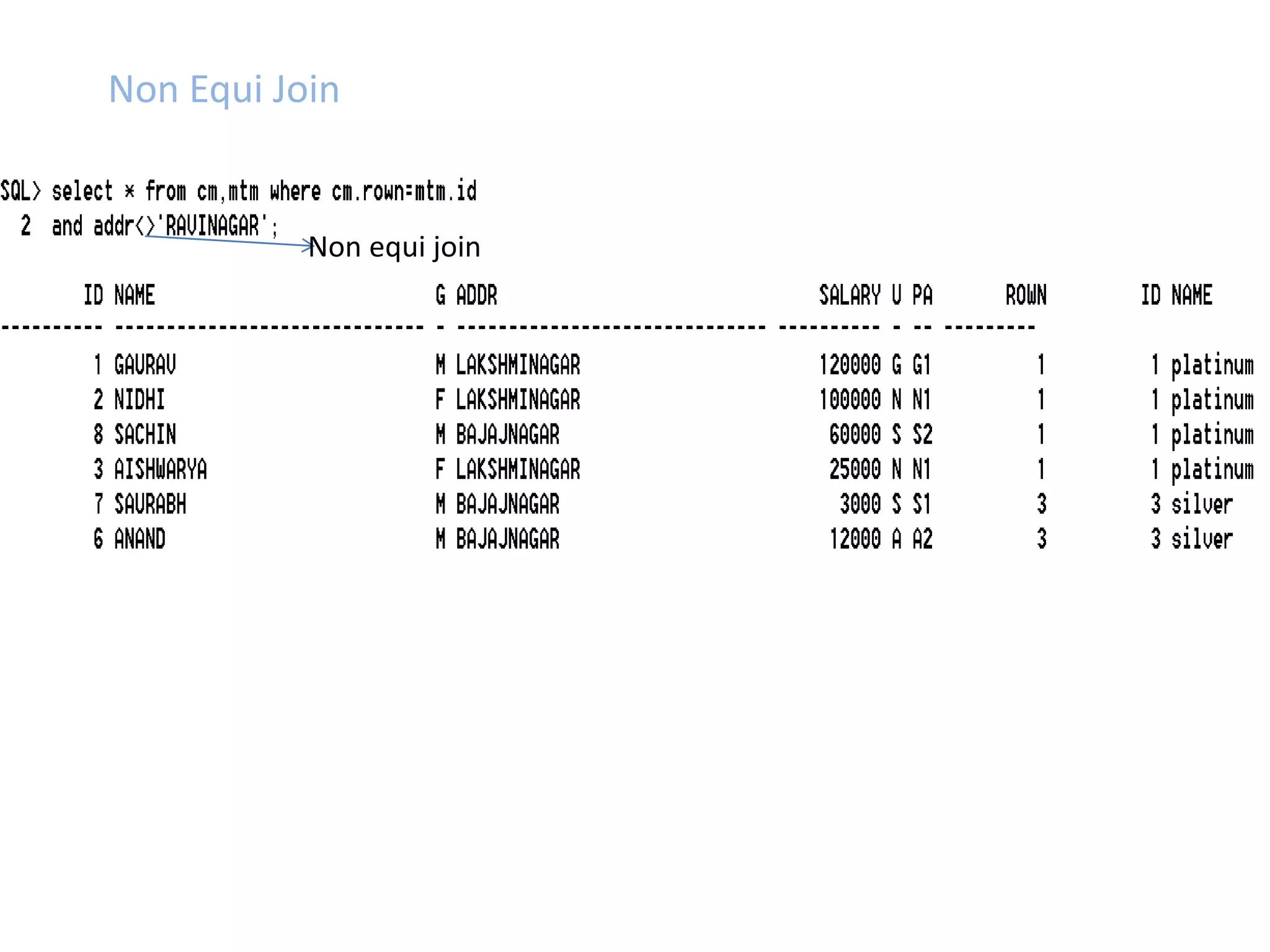
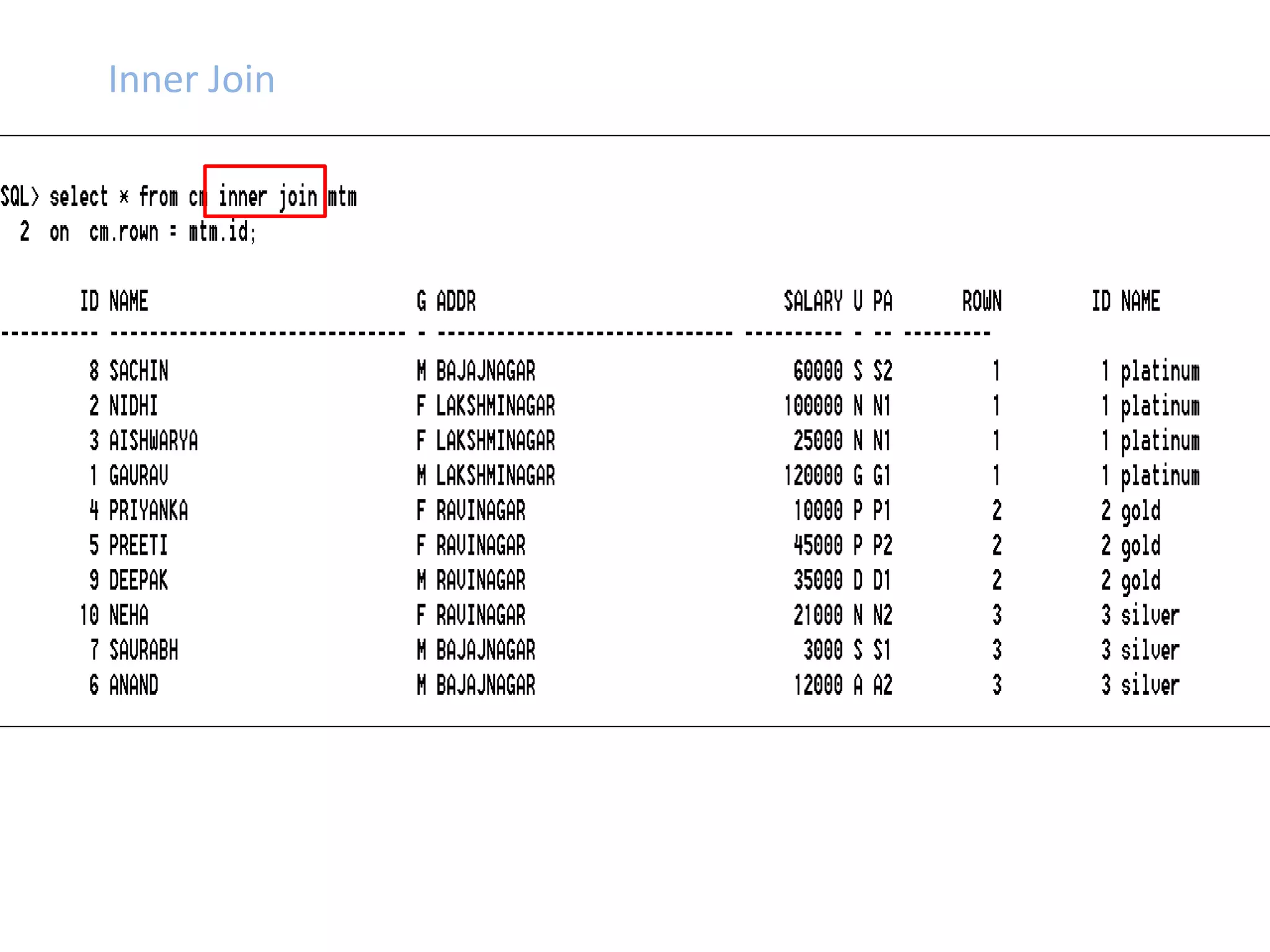
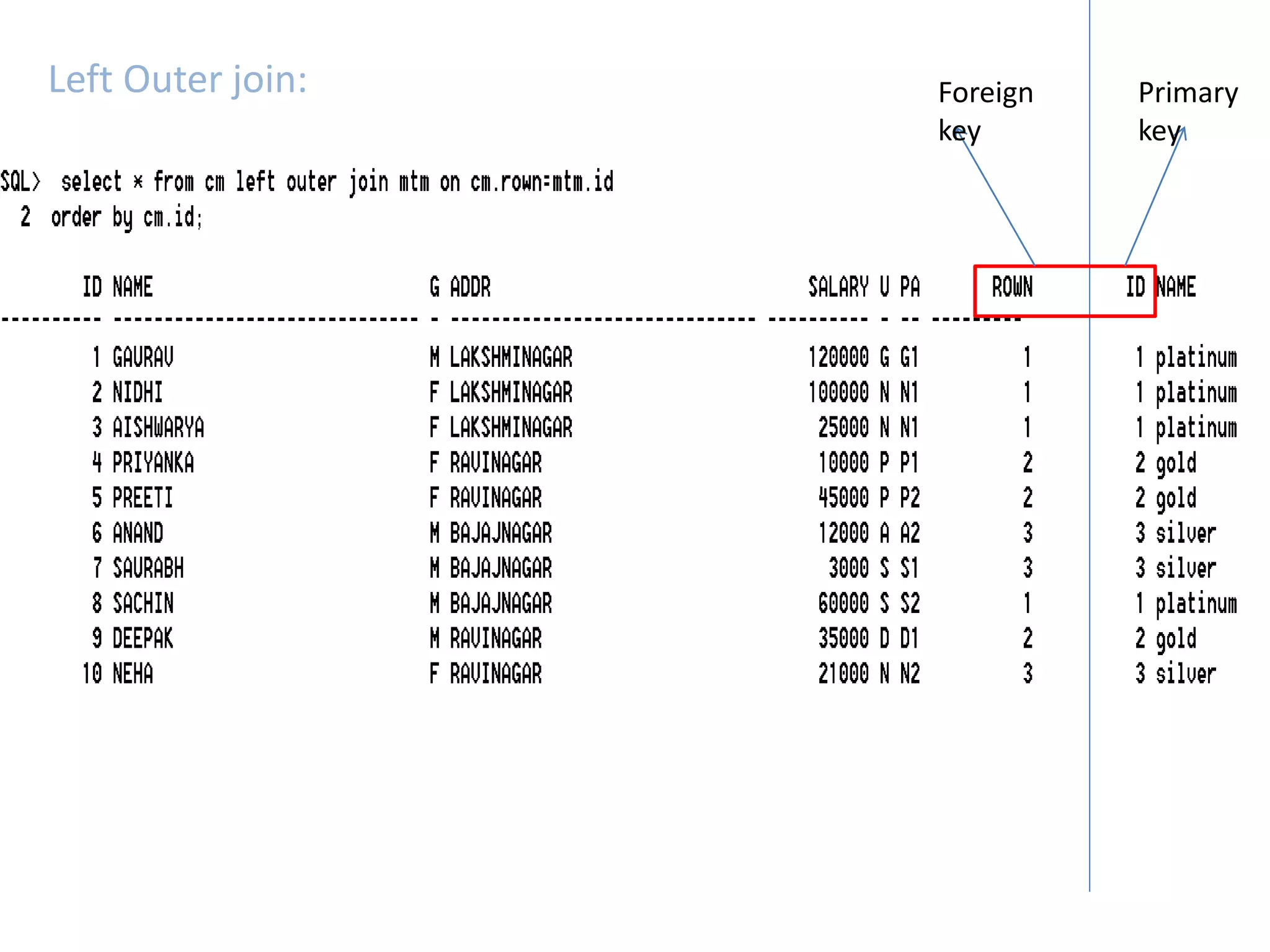
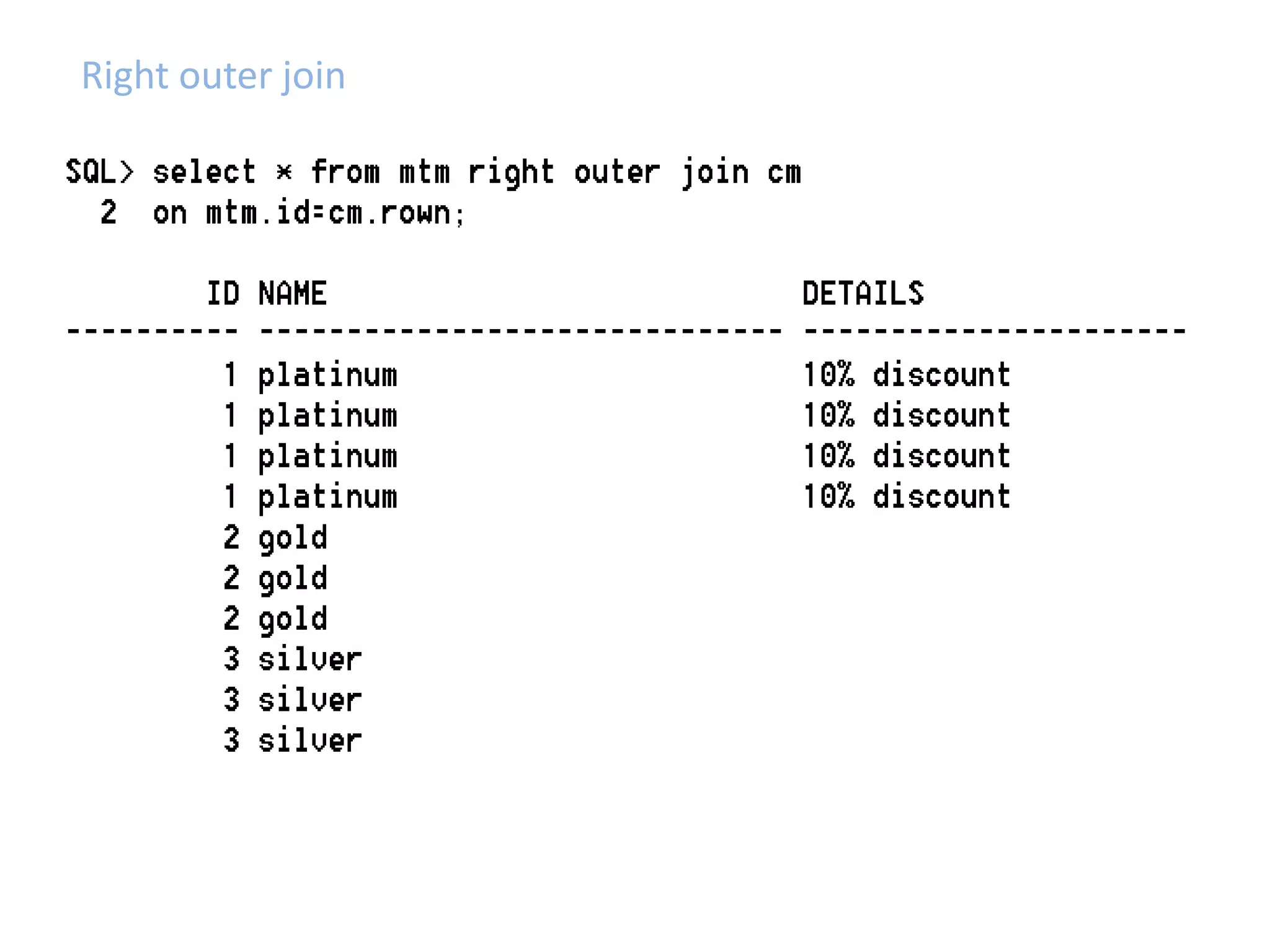
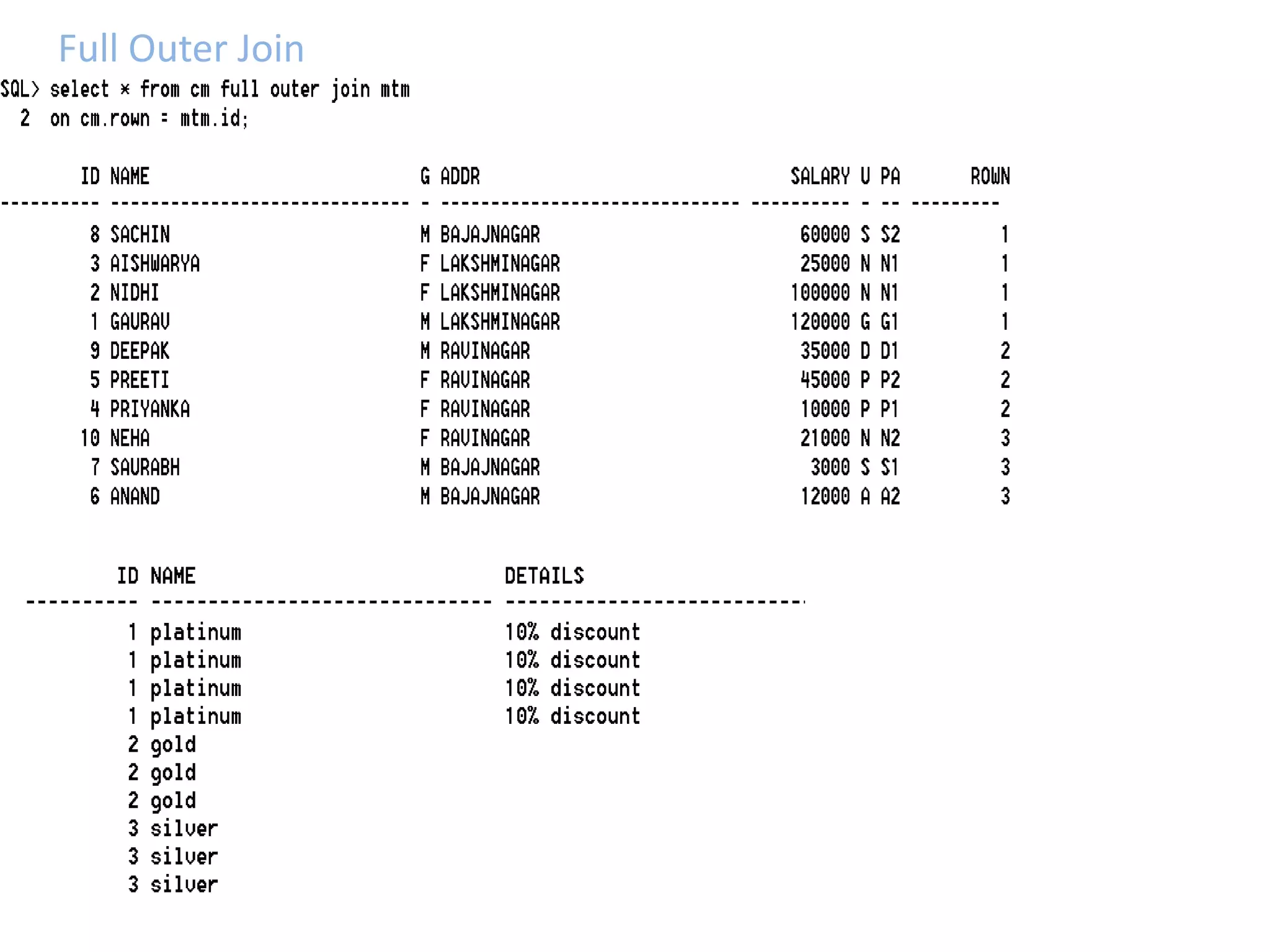
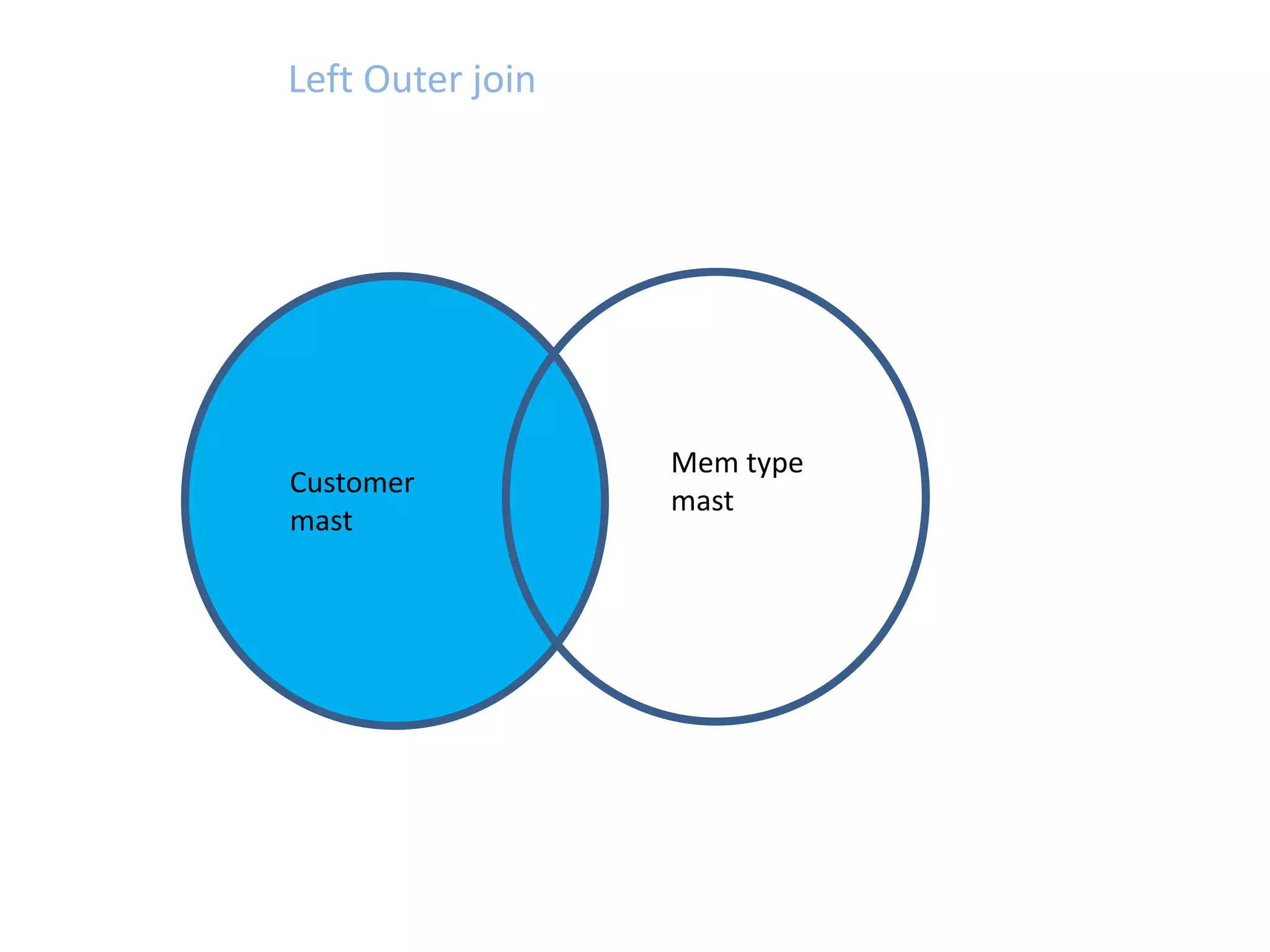
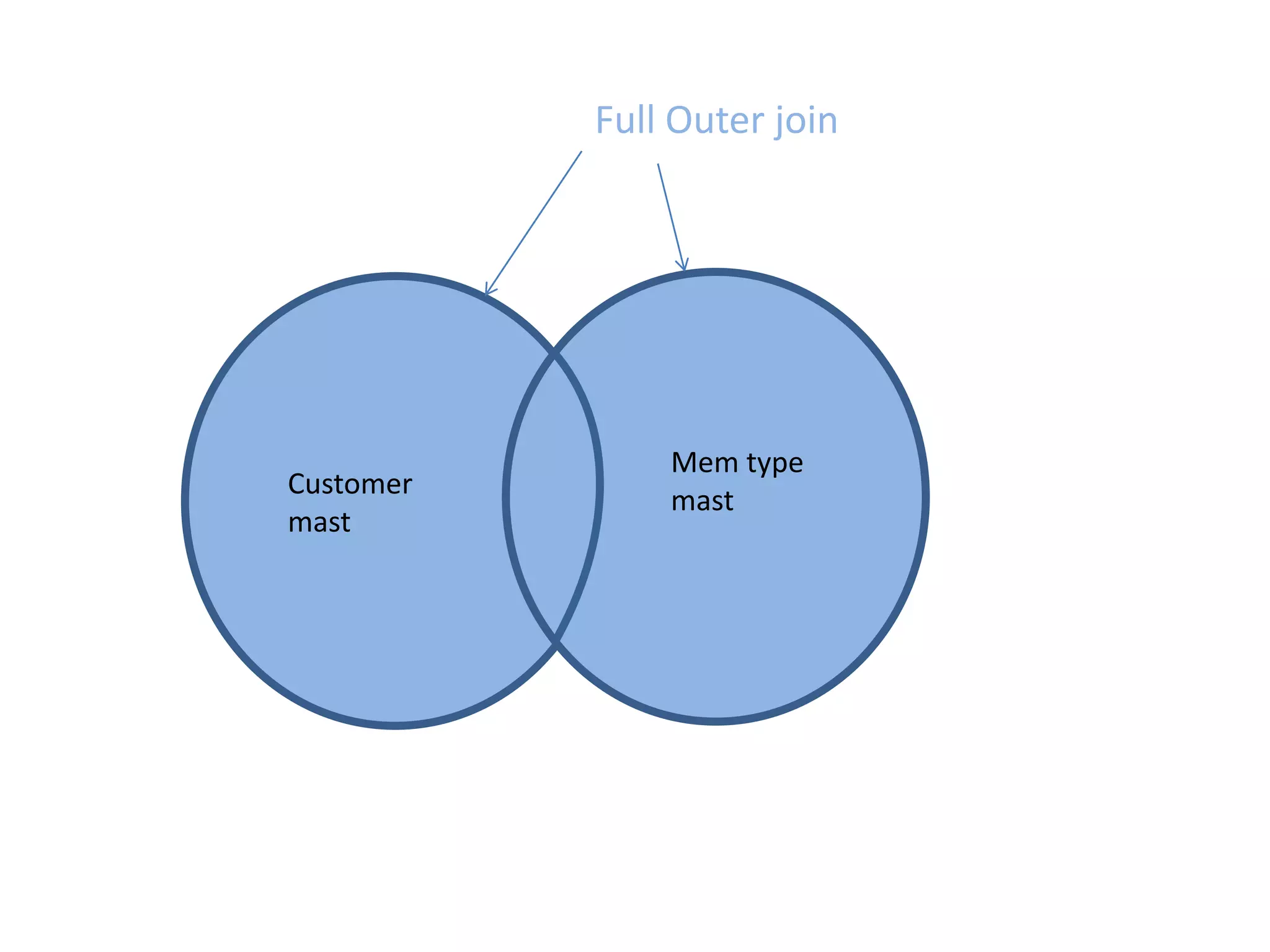
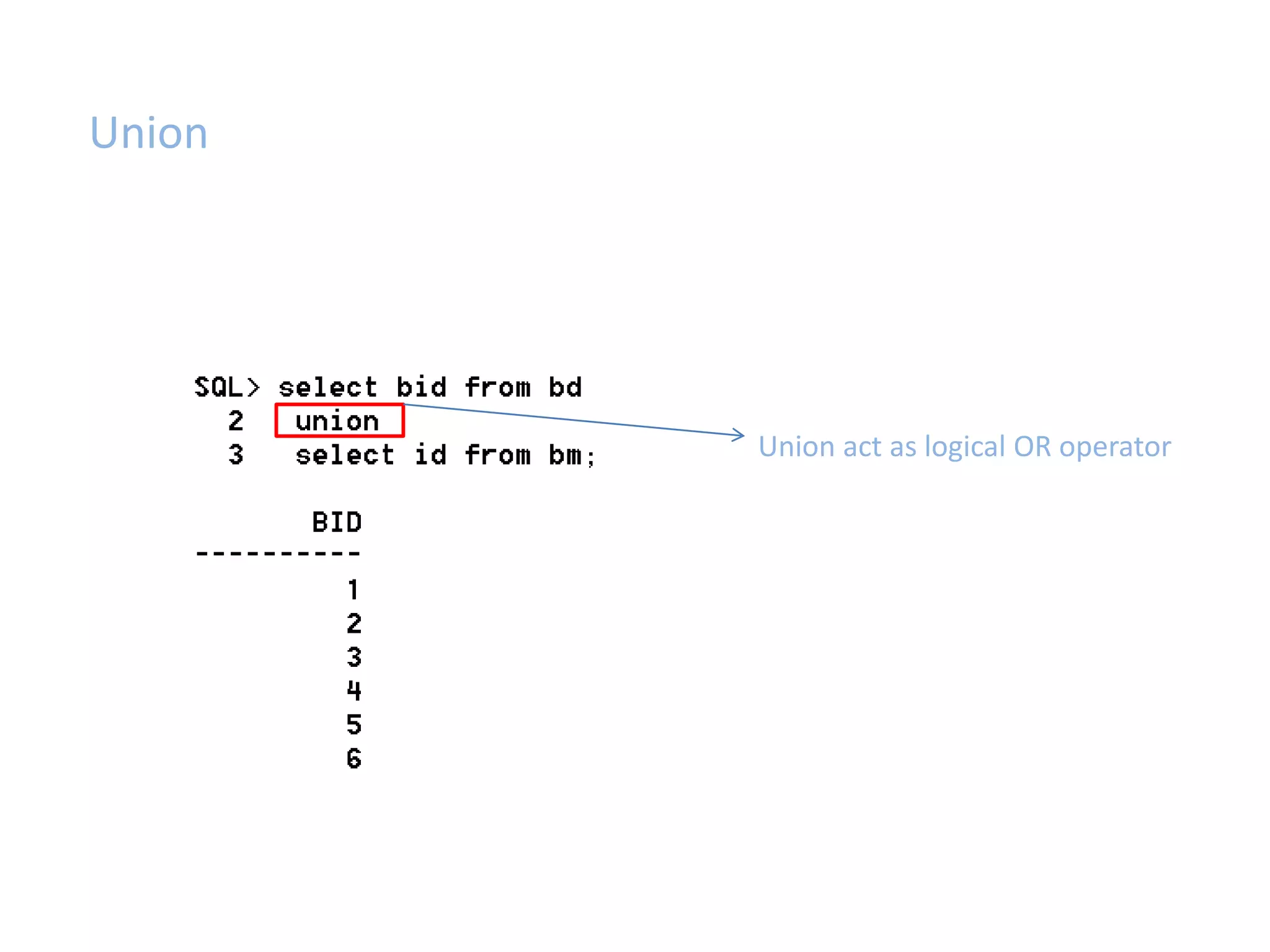
SQL JOINS allow data to be combined from multiple tables by performing joins between columns that share common values. There are five main types of joins: equi joins which combine rows where joined columns are equal, inner joins which return rows where there is a match in both tables, outer joins which return all rows of the left or right table even if there is no match, self joins which join a table to itself, and non-equi joins which join on columns that are not equal. Joins are useful for combining related data across tables and are implemented using conditions in the WHERE clause that compare columns from different tables.