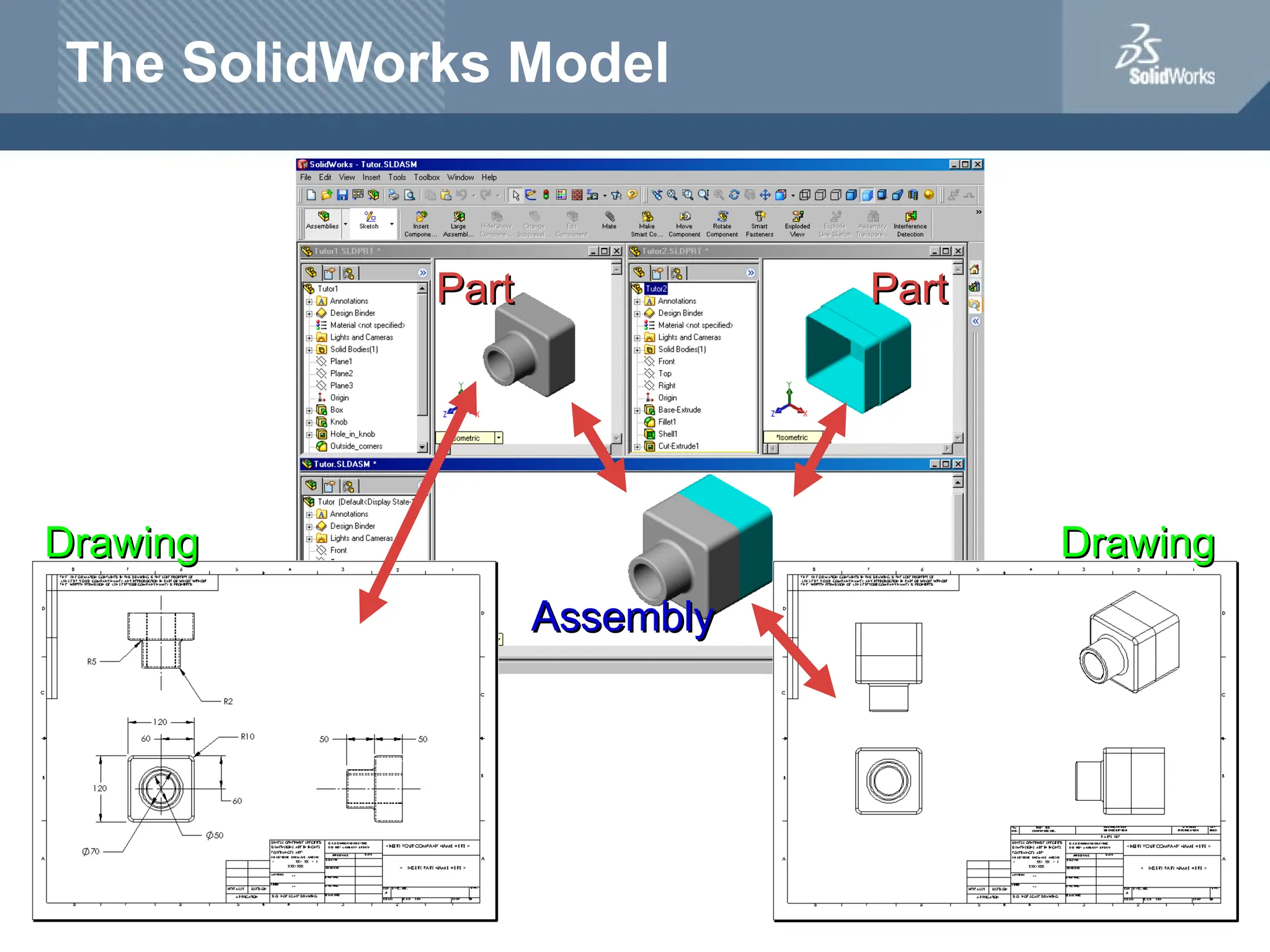
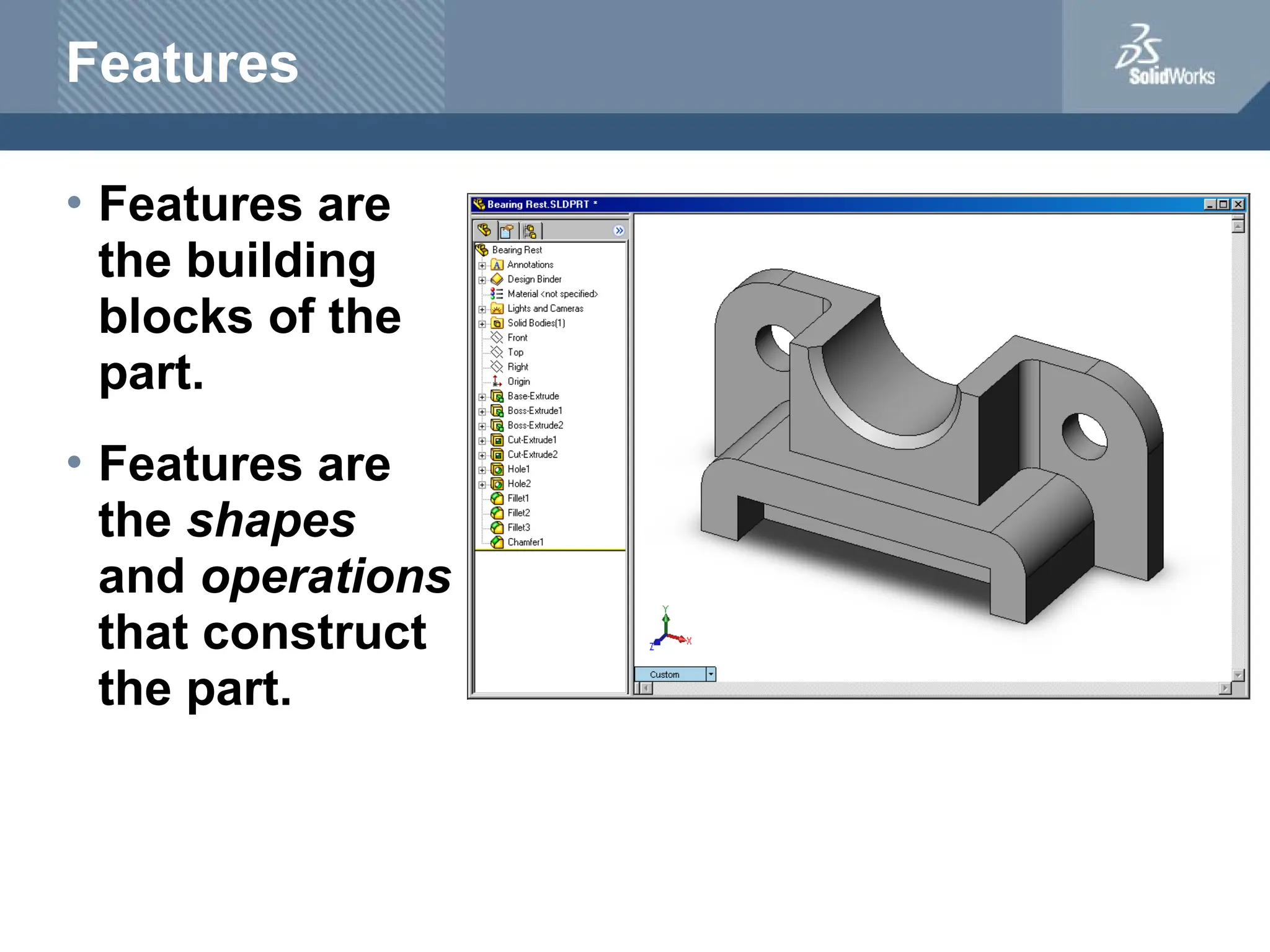
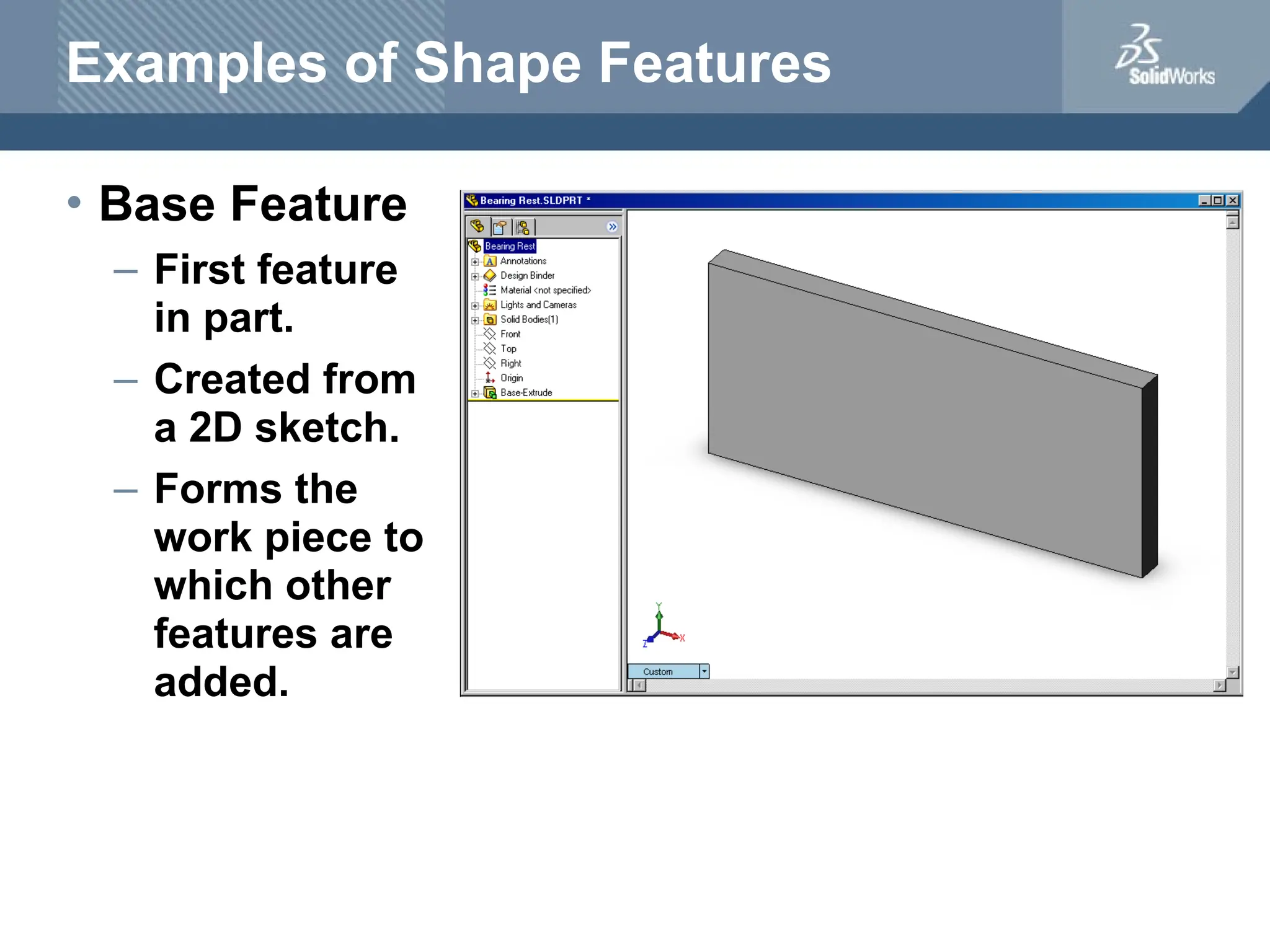
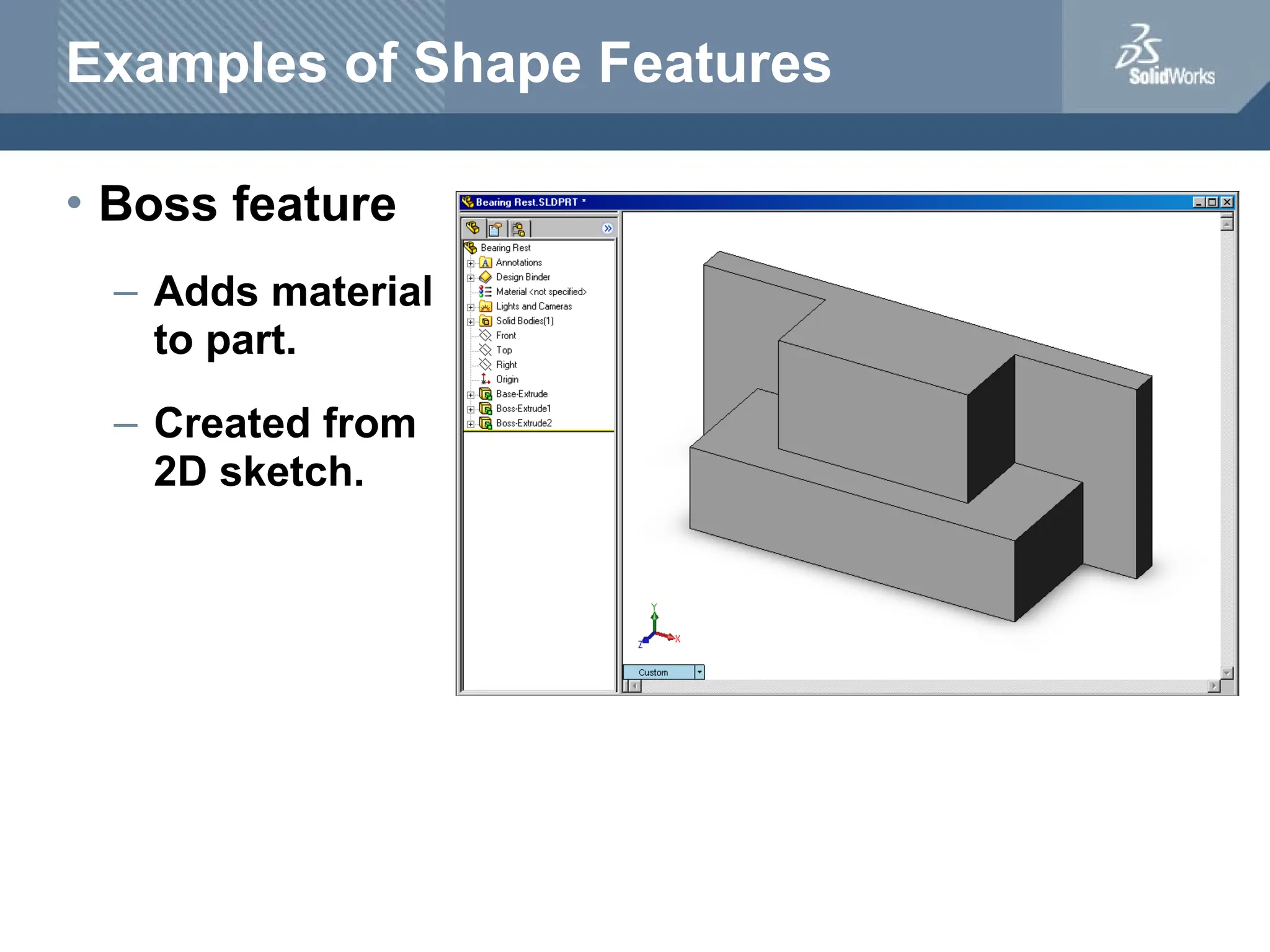
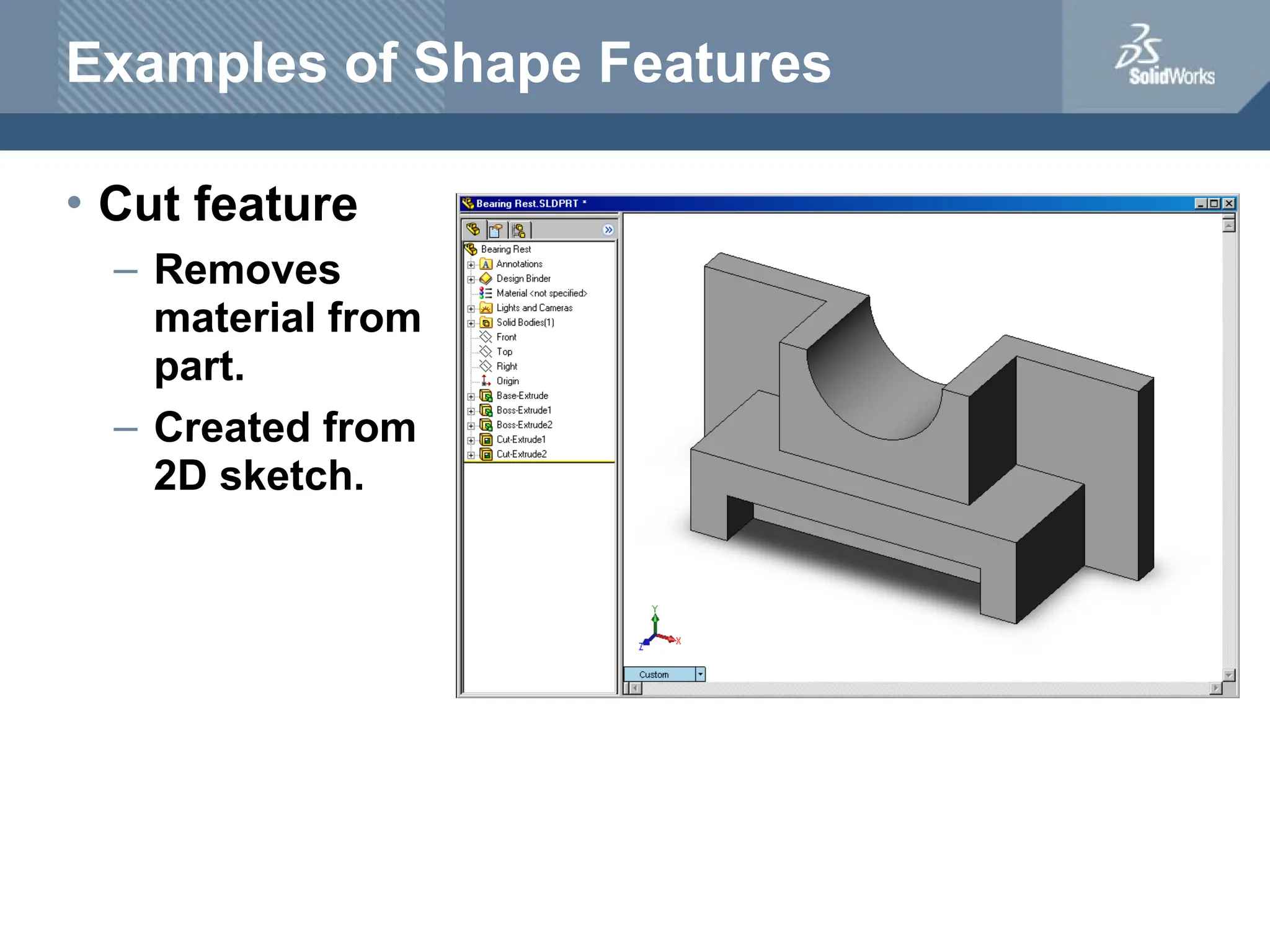
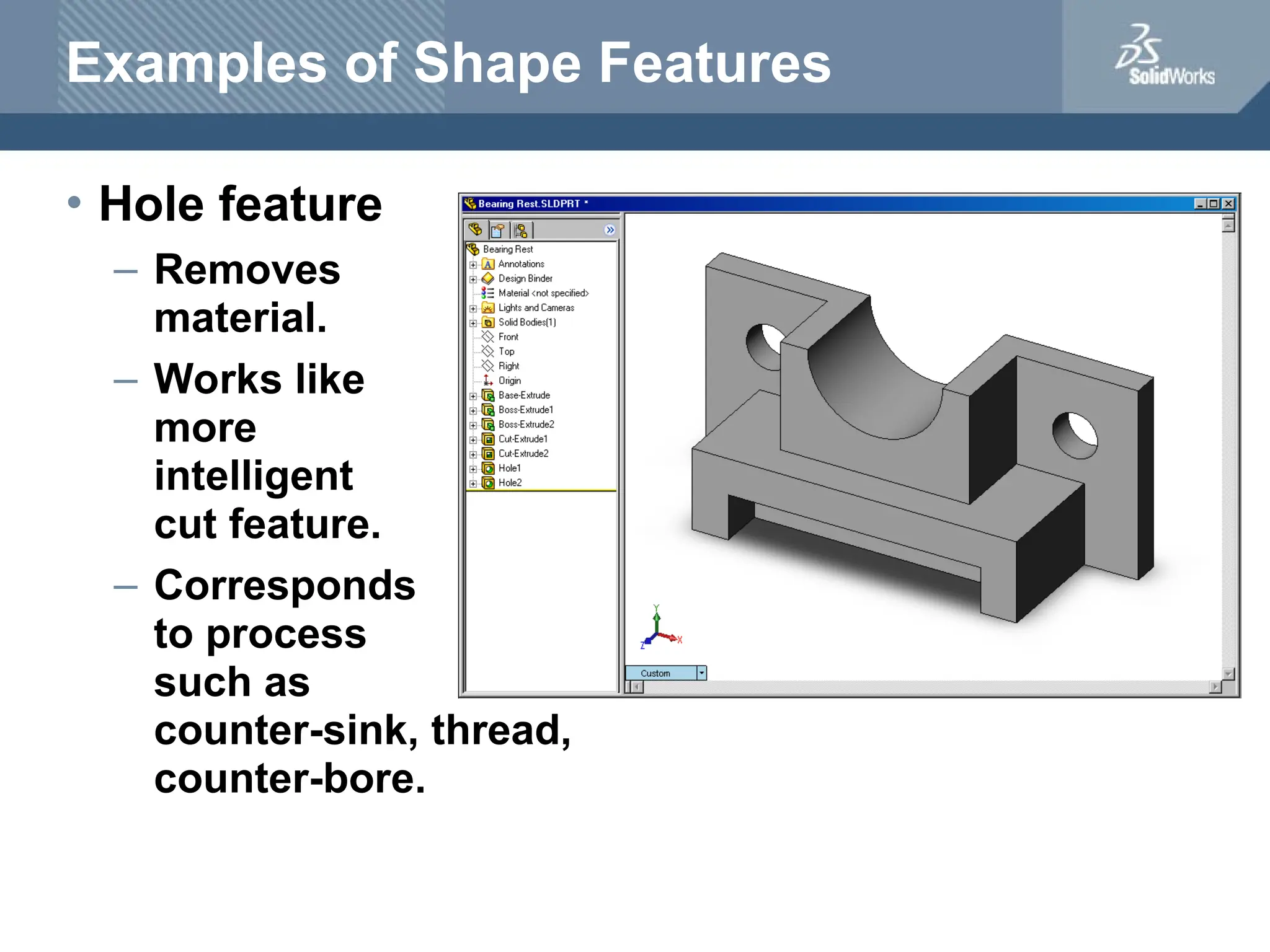
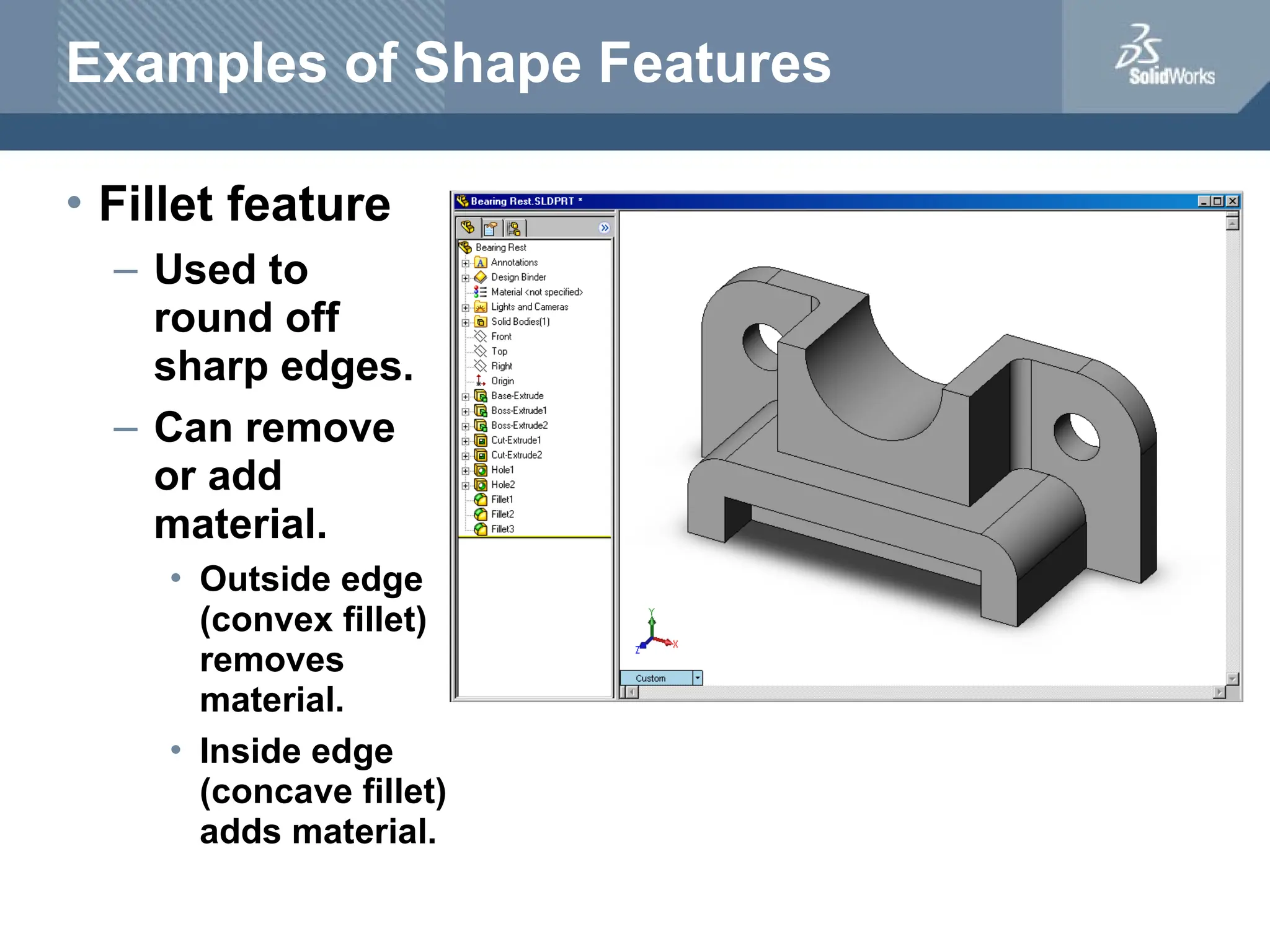
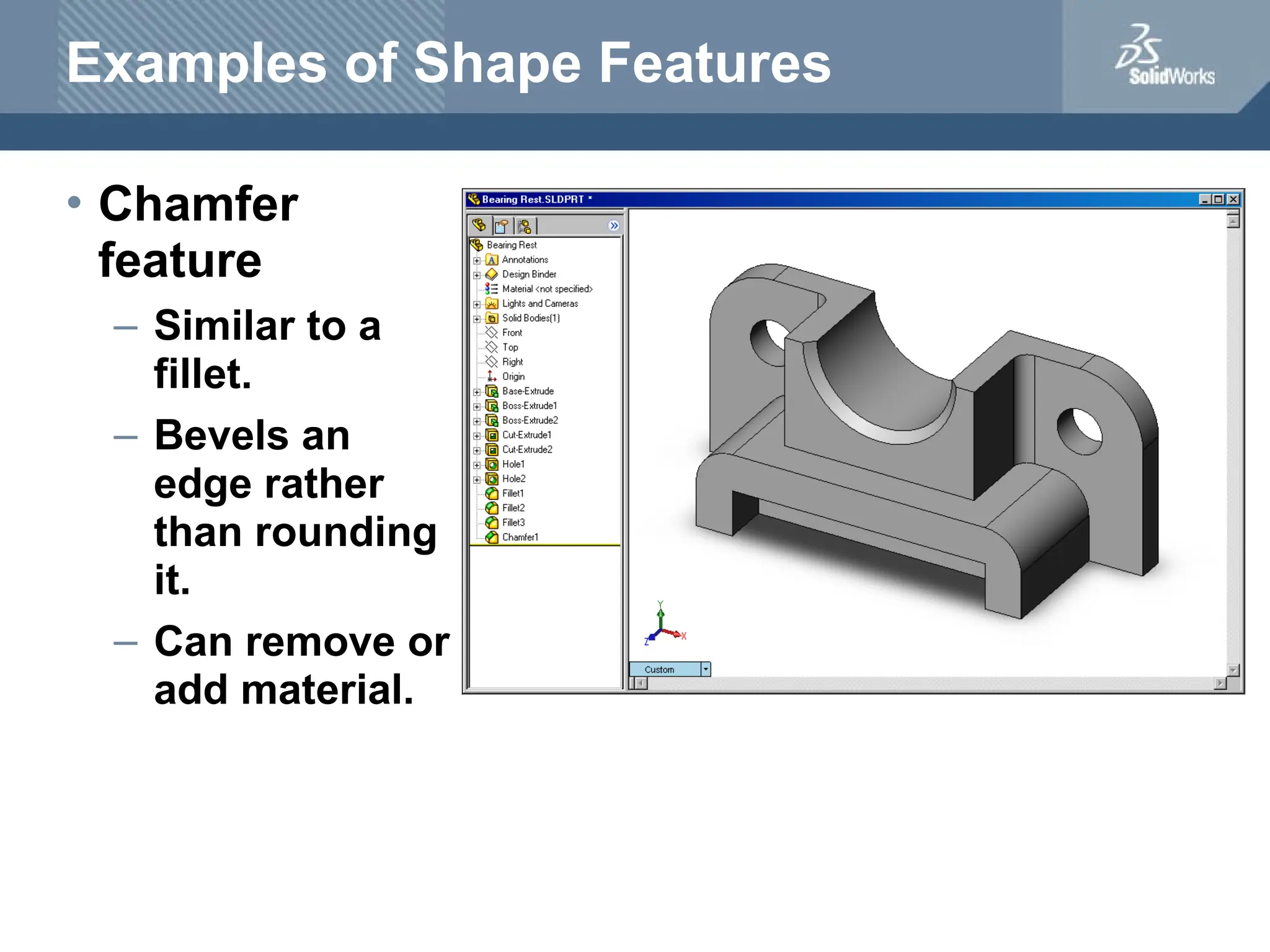
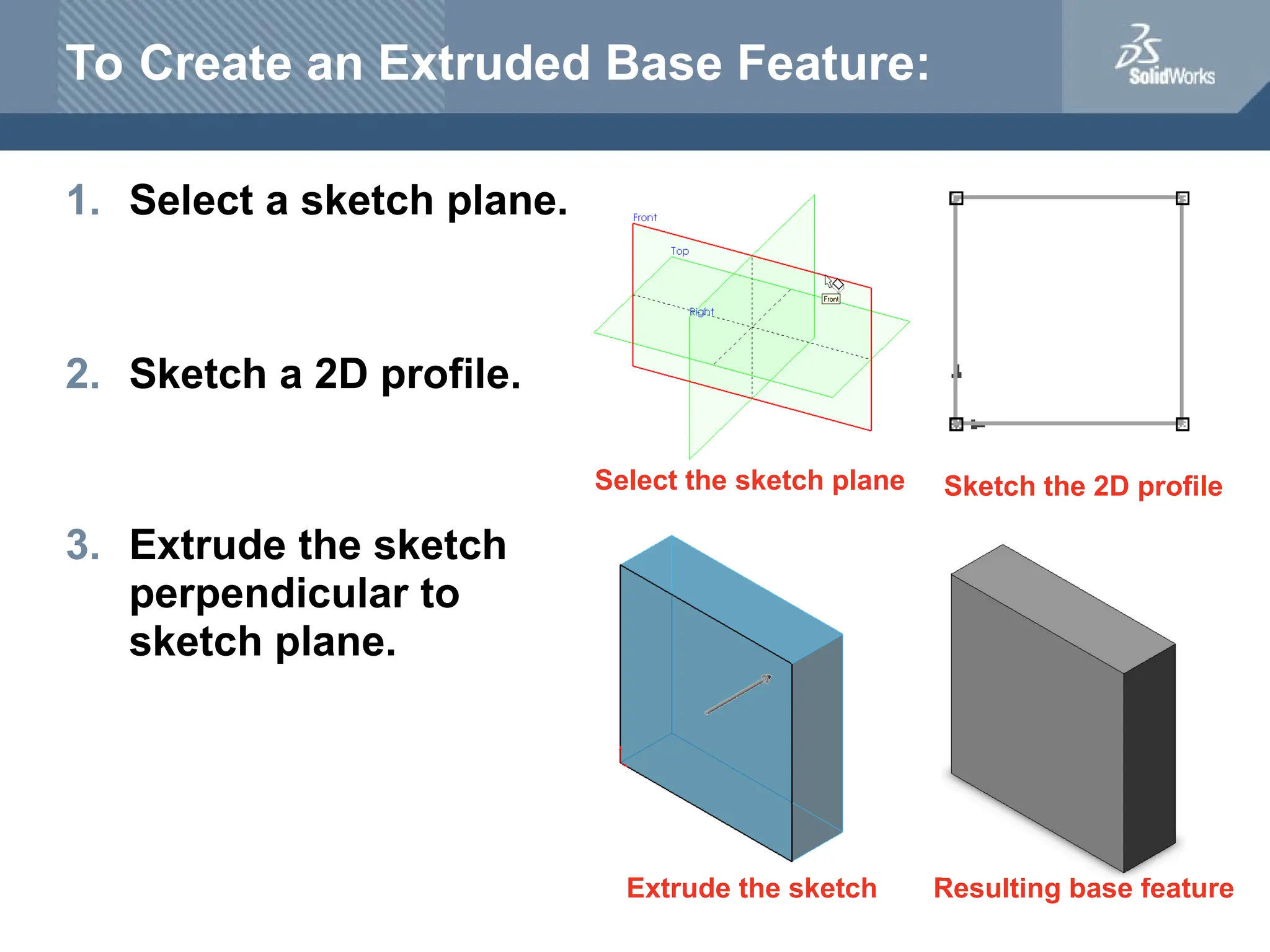
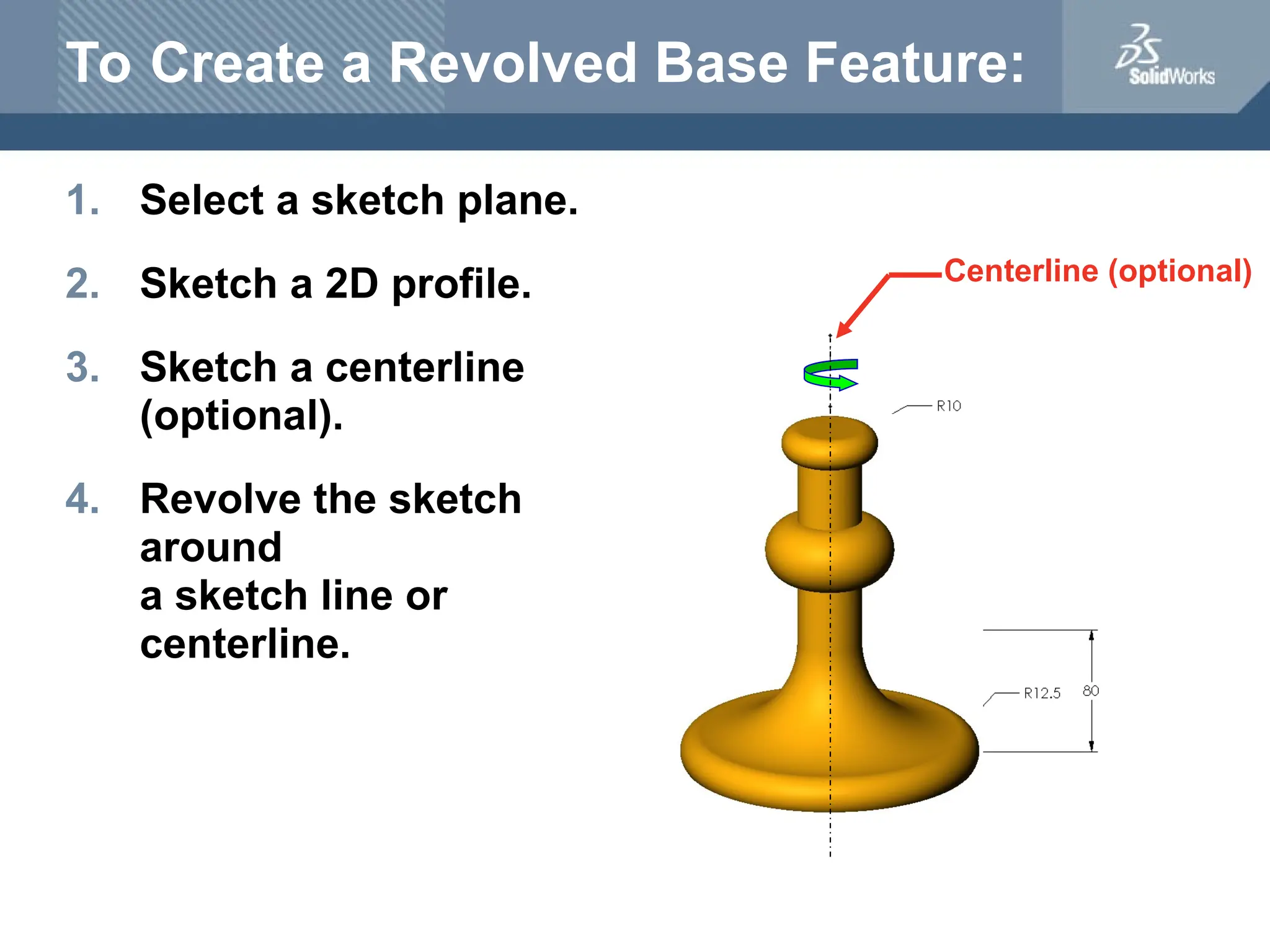
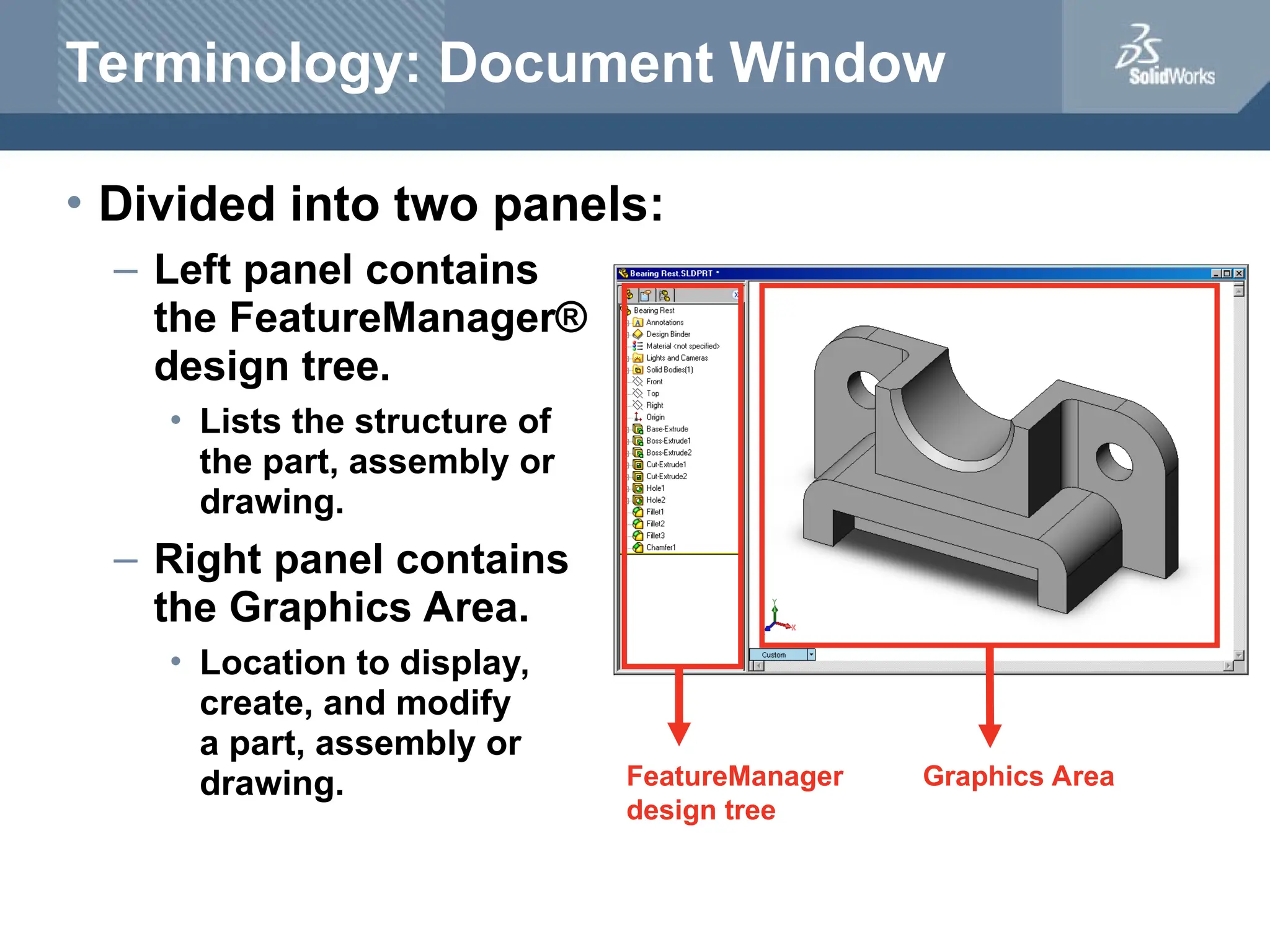
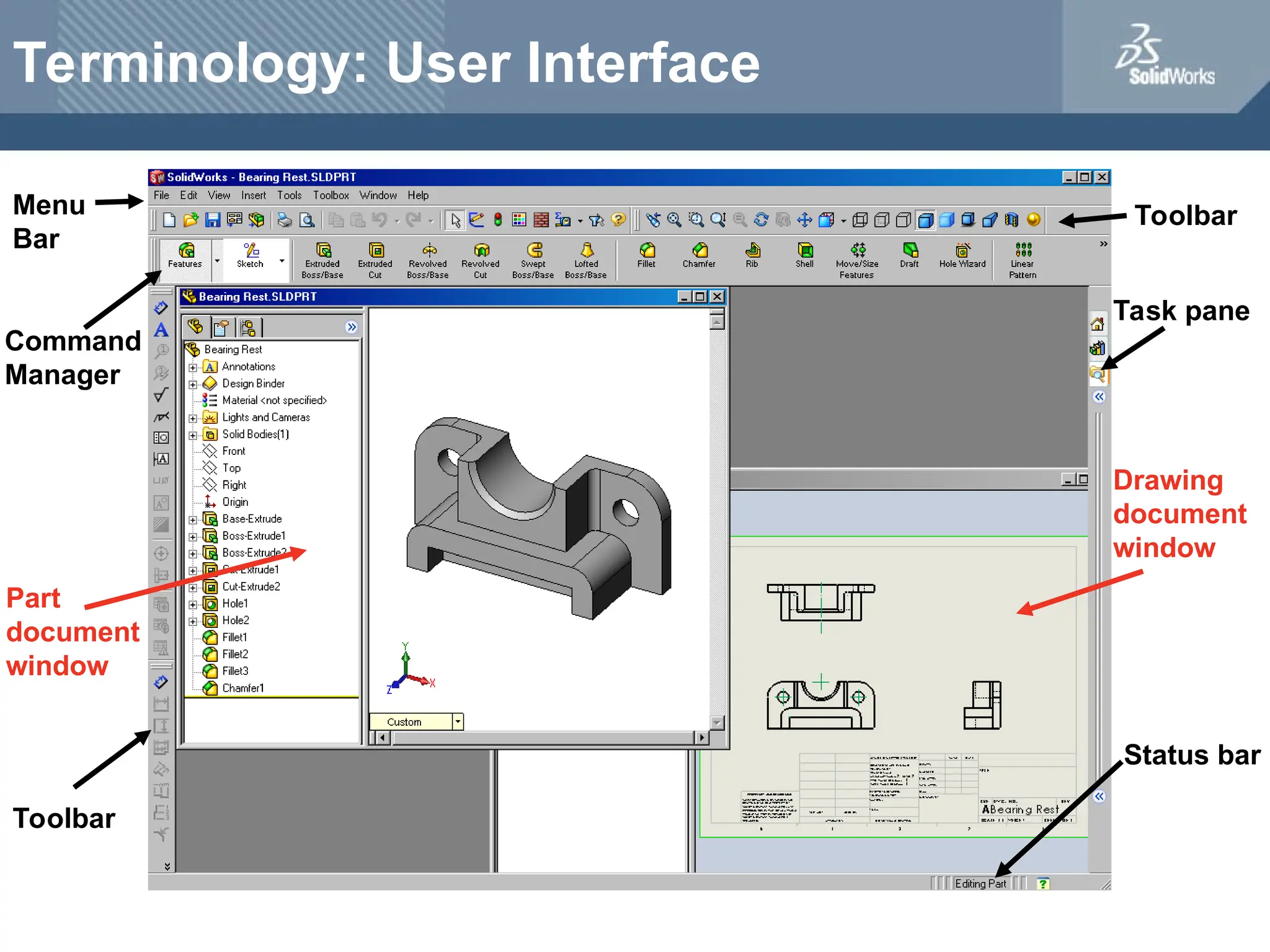
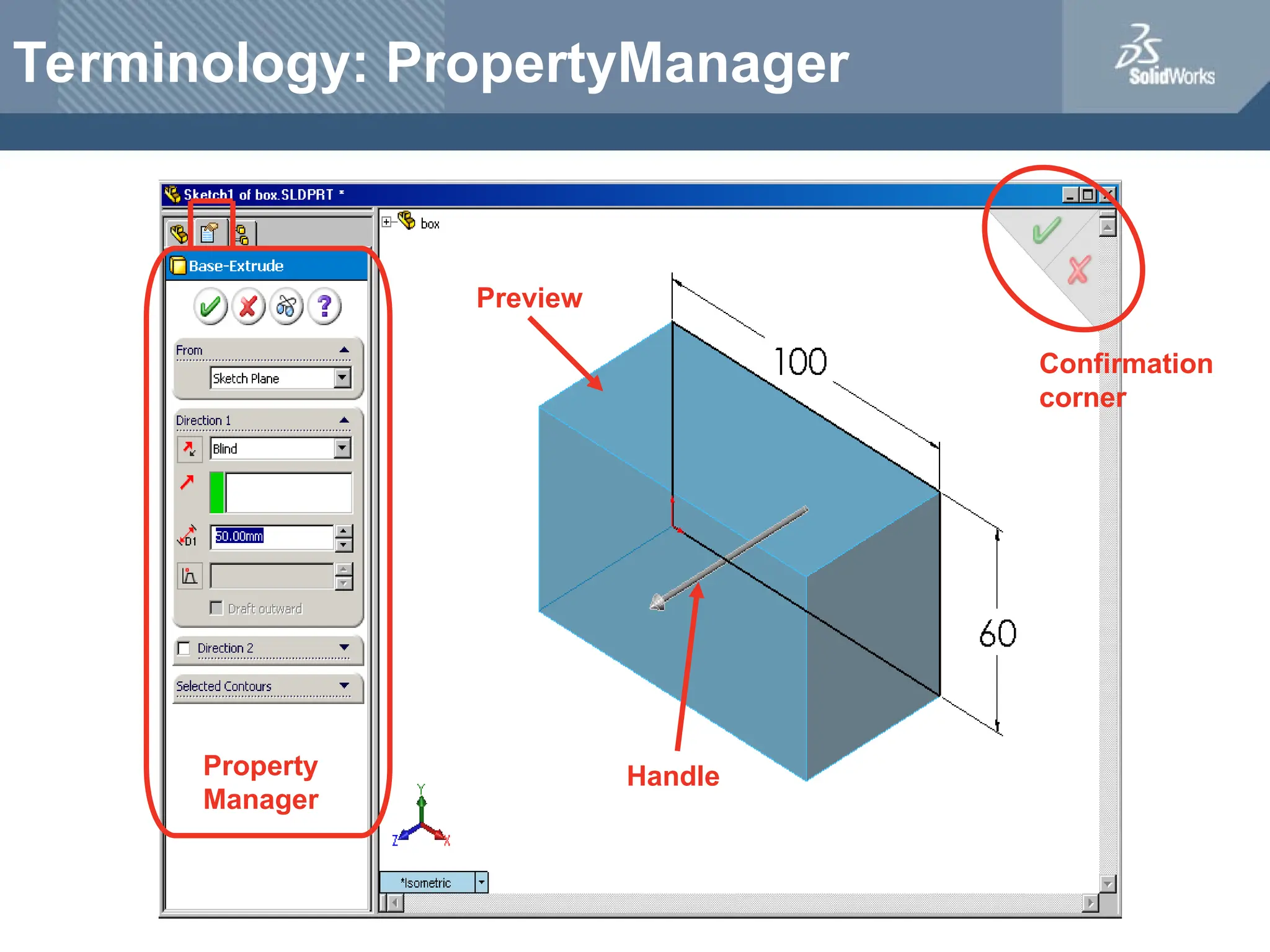
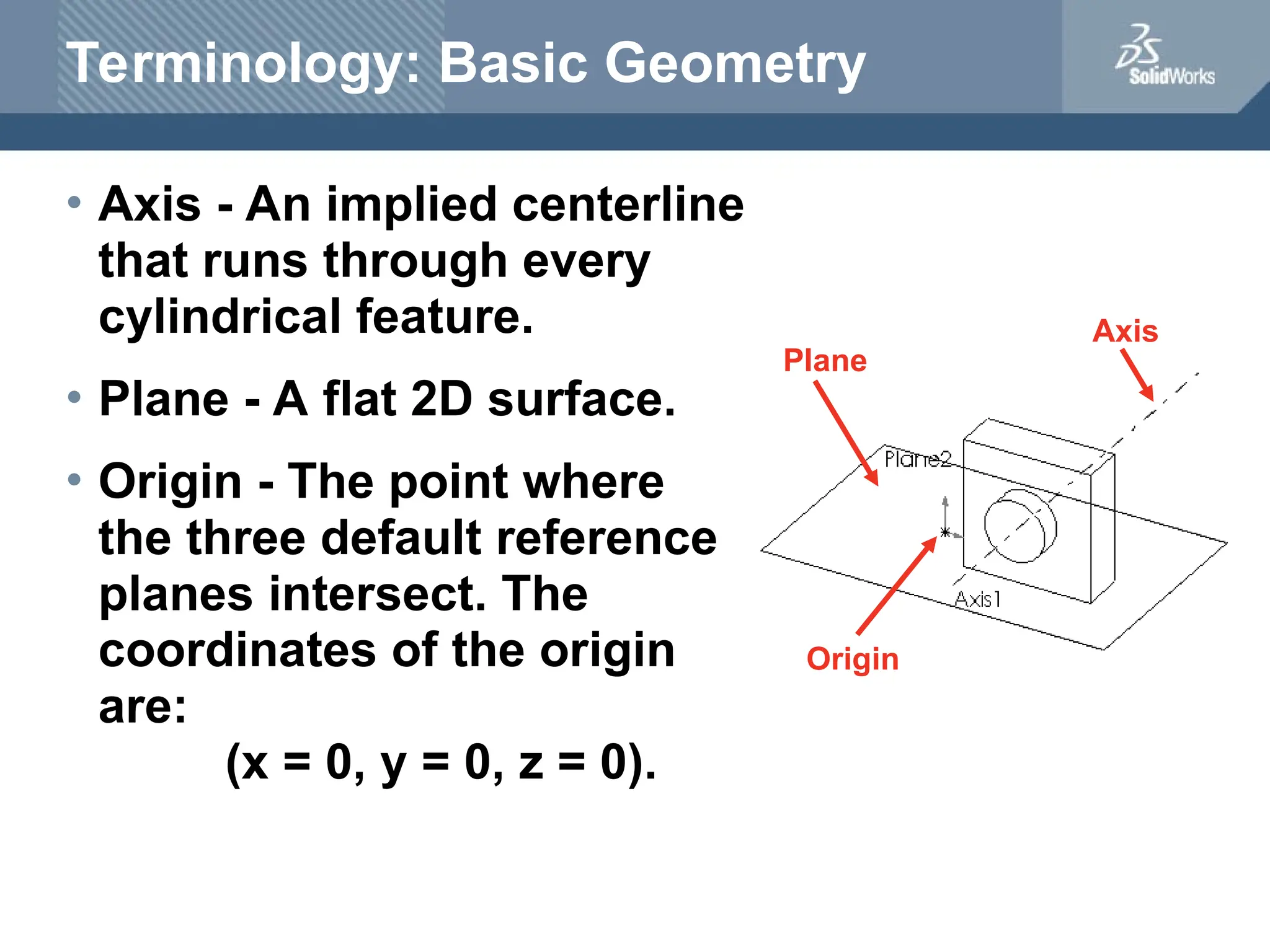
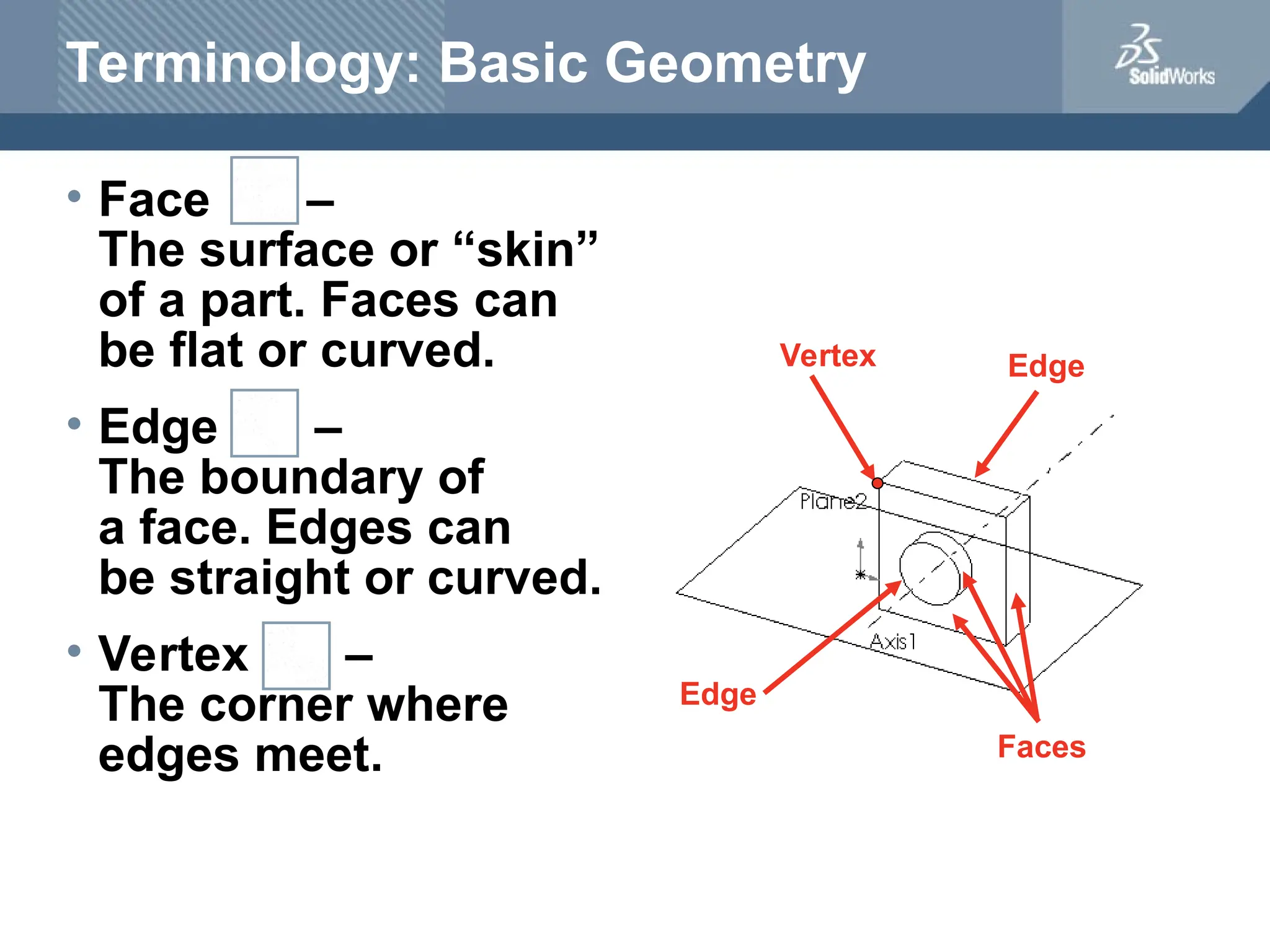
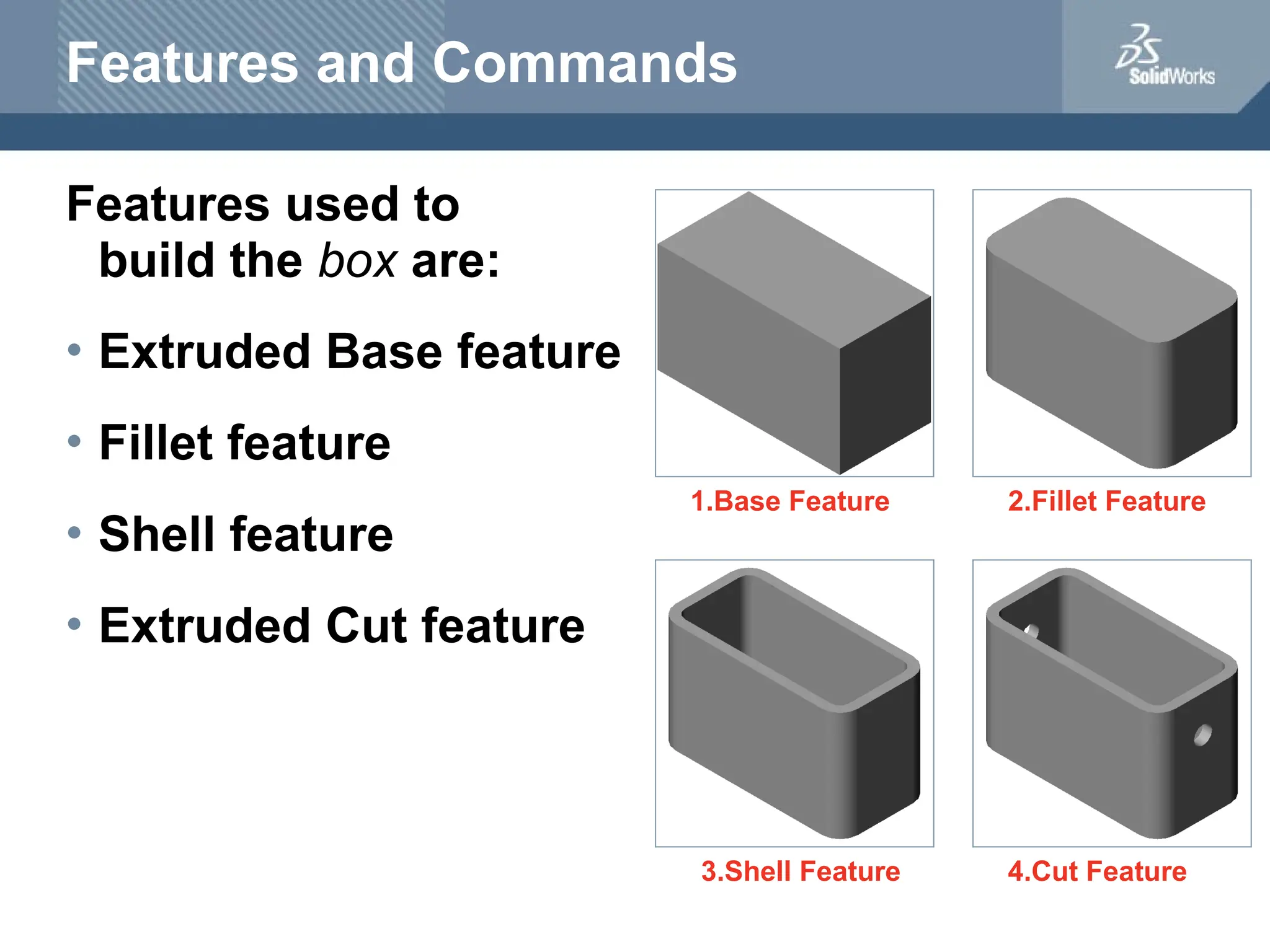
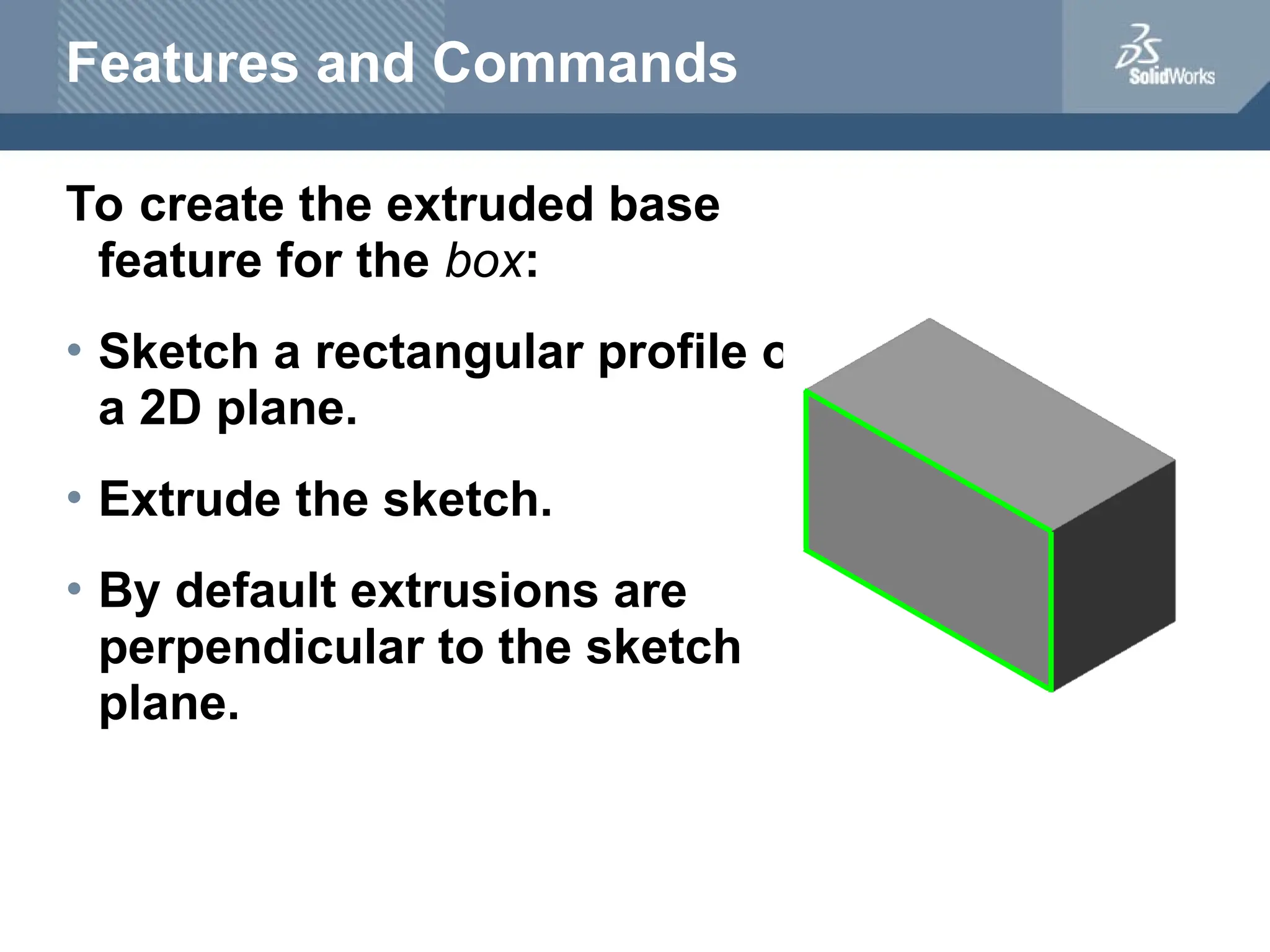
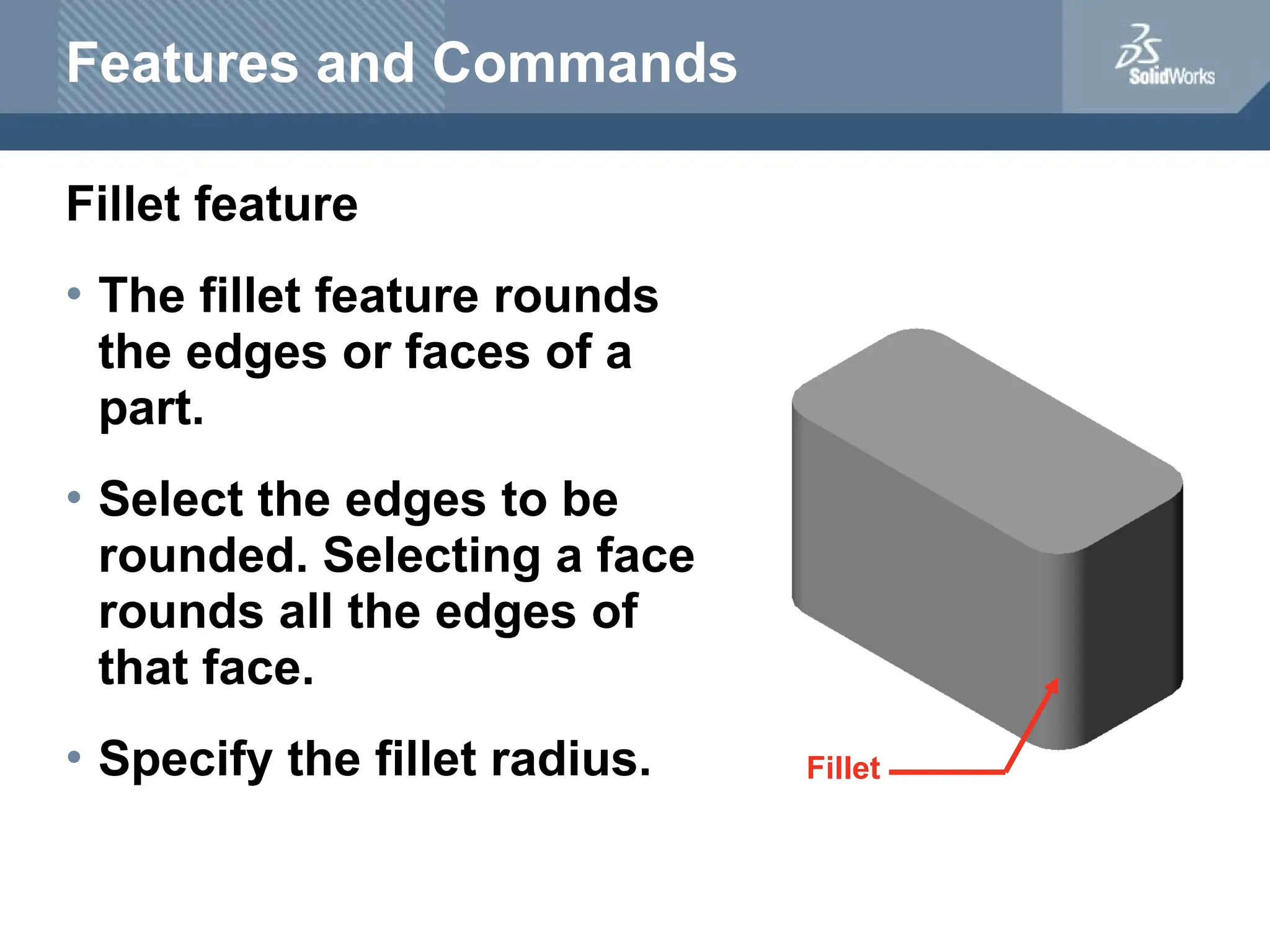
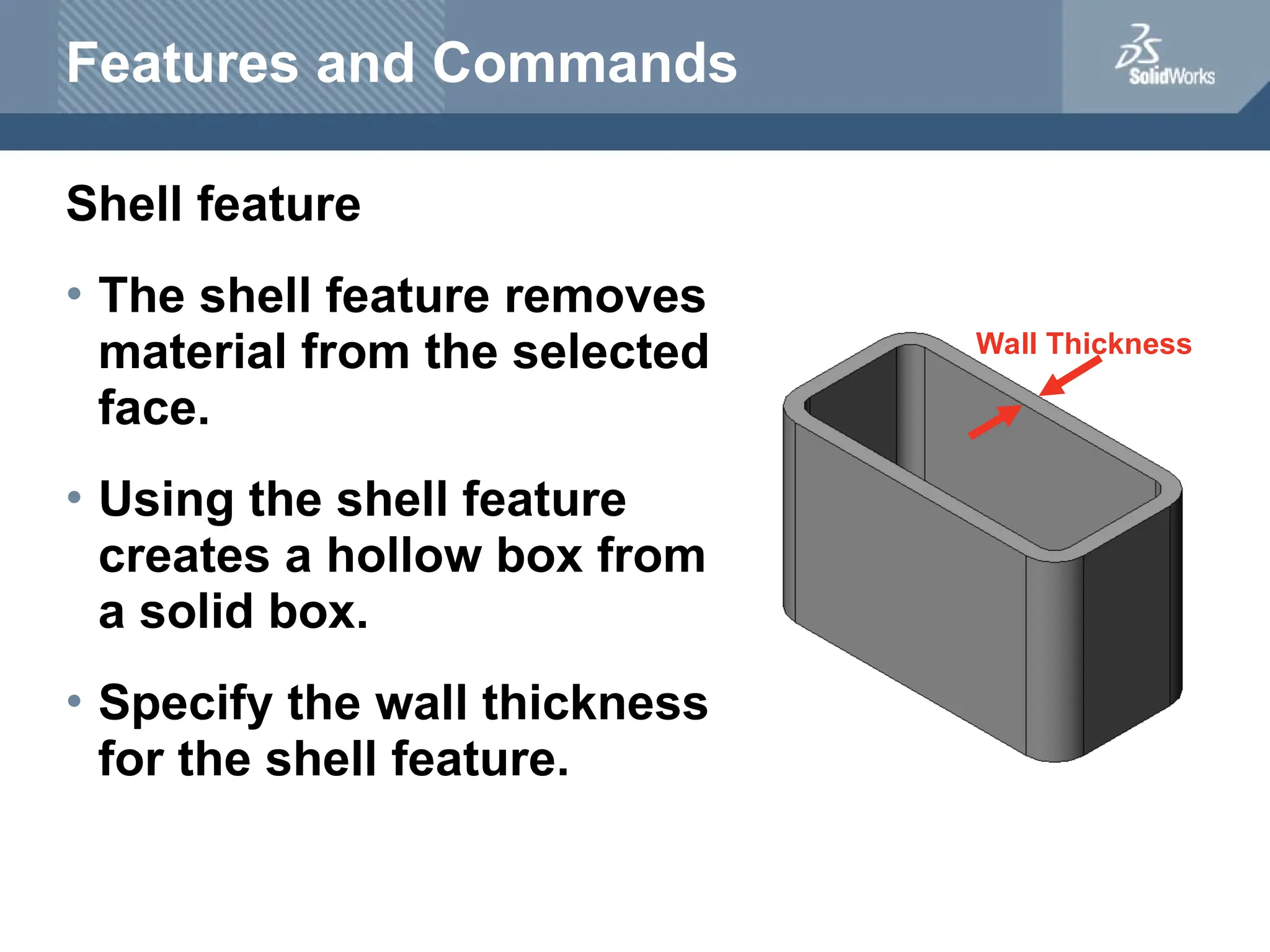
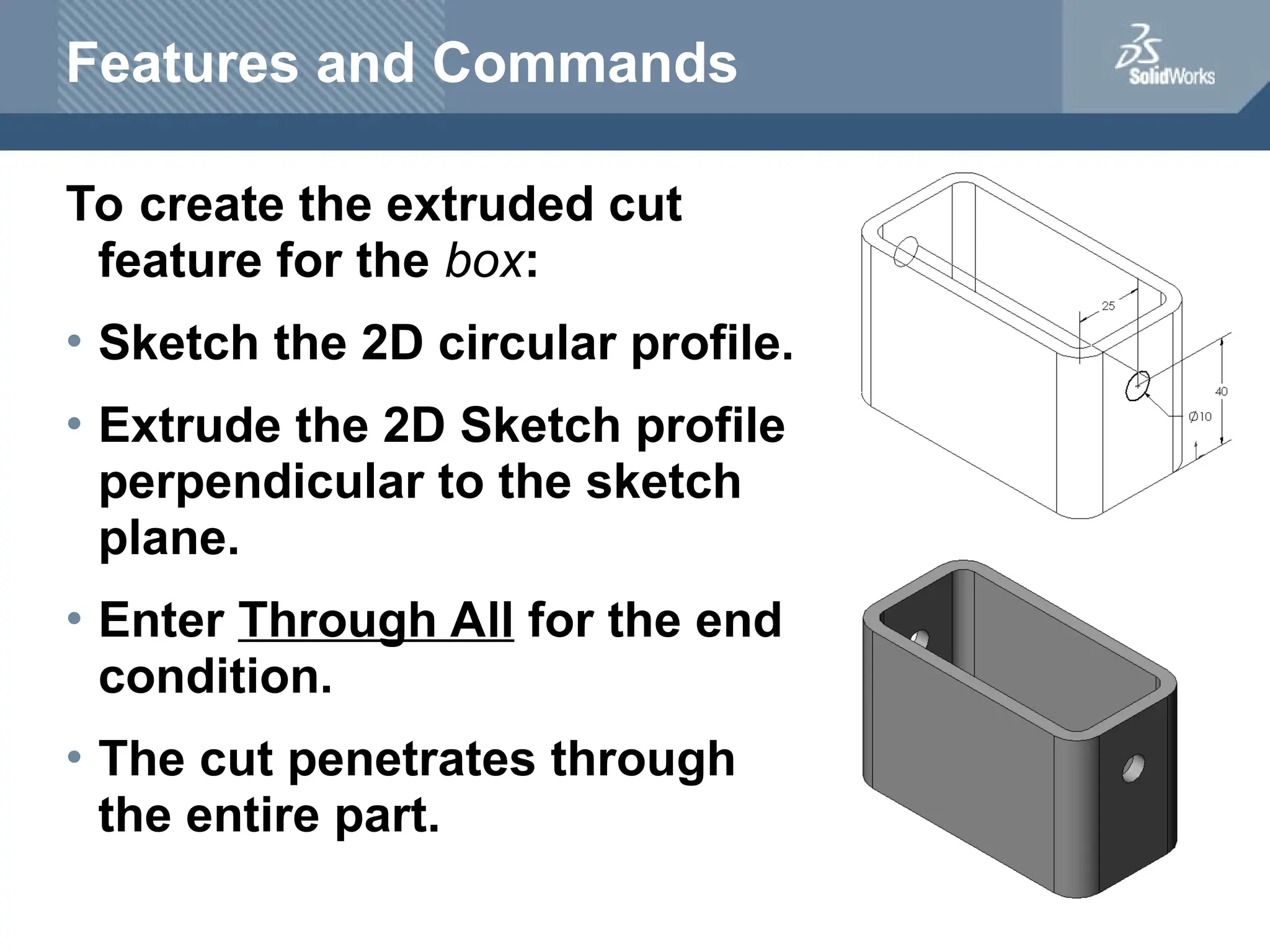
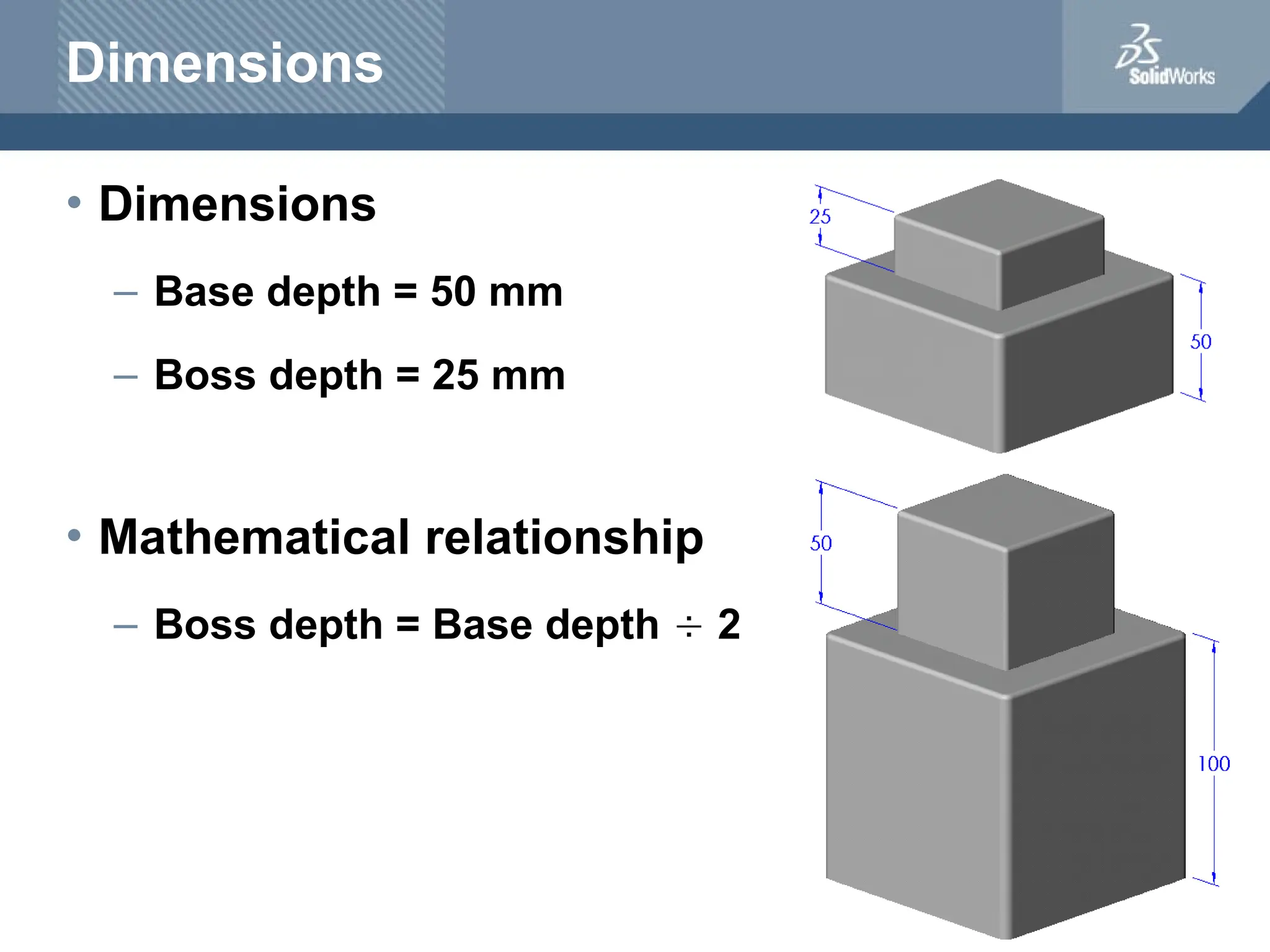
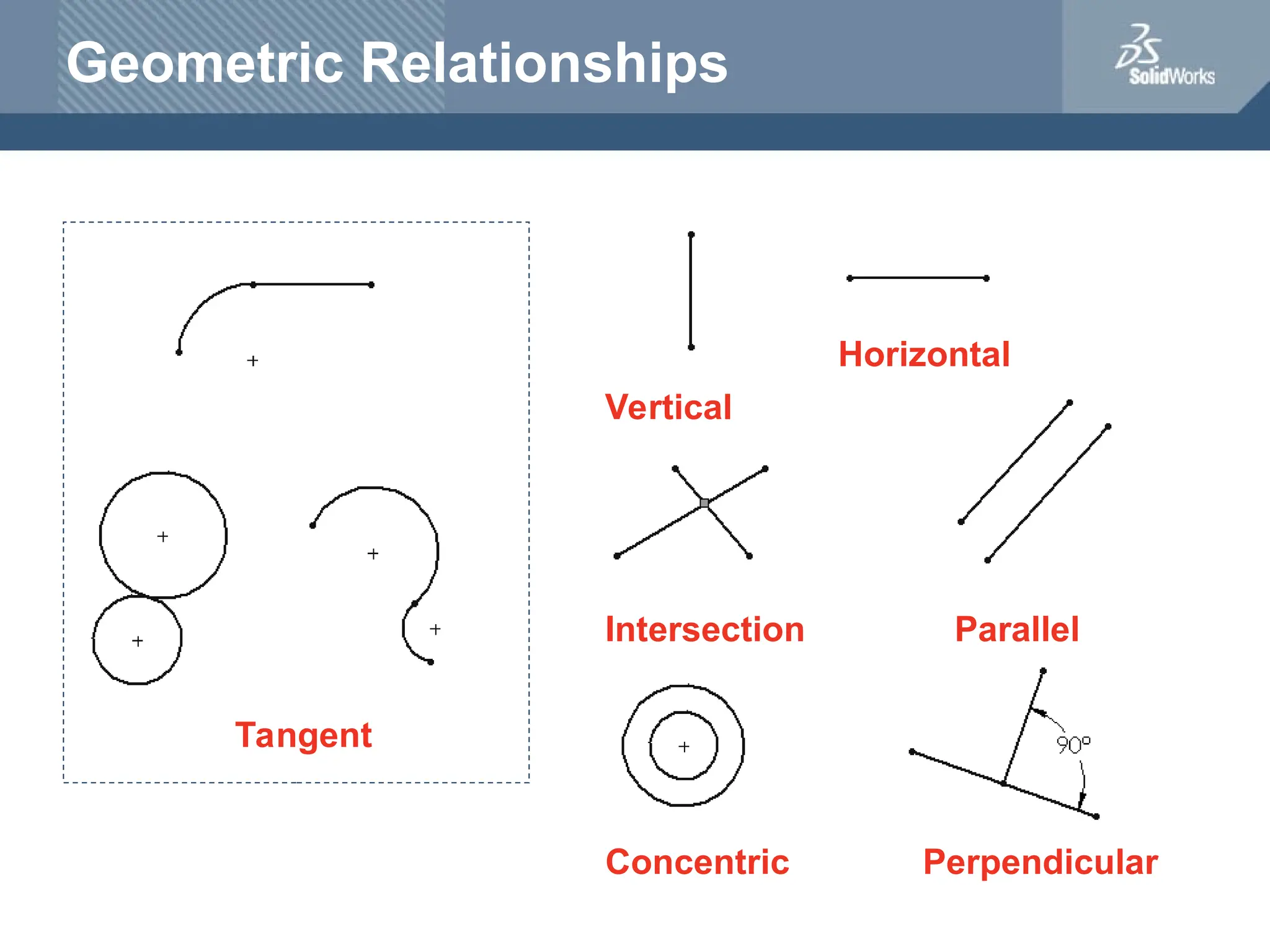
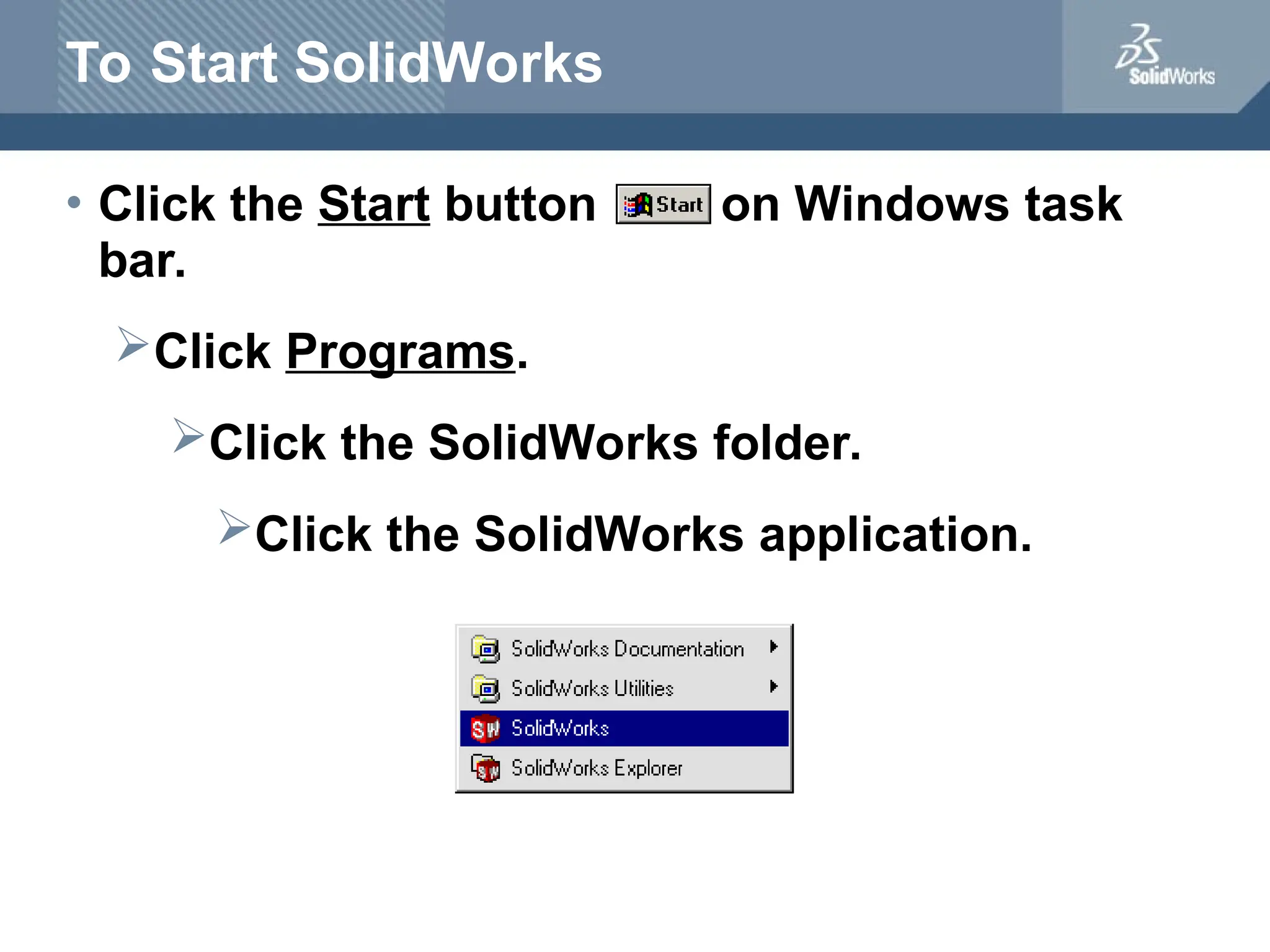
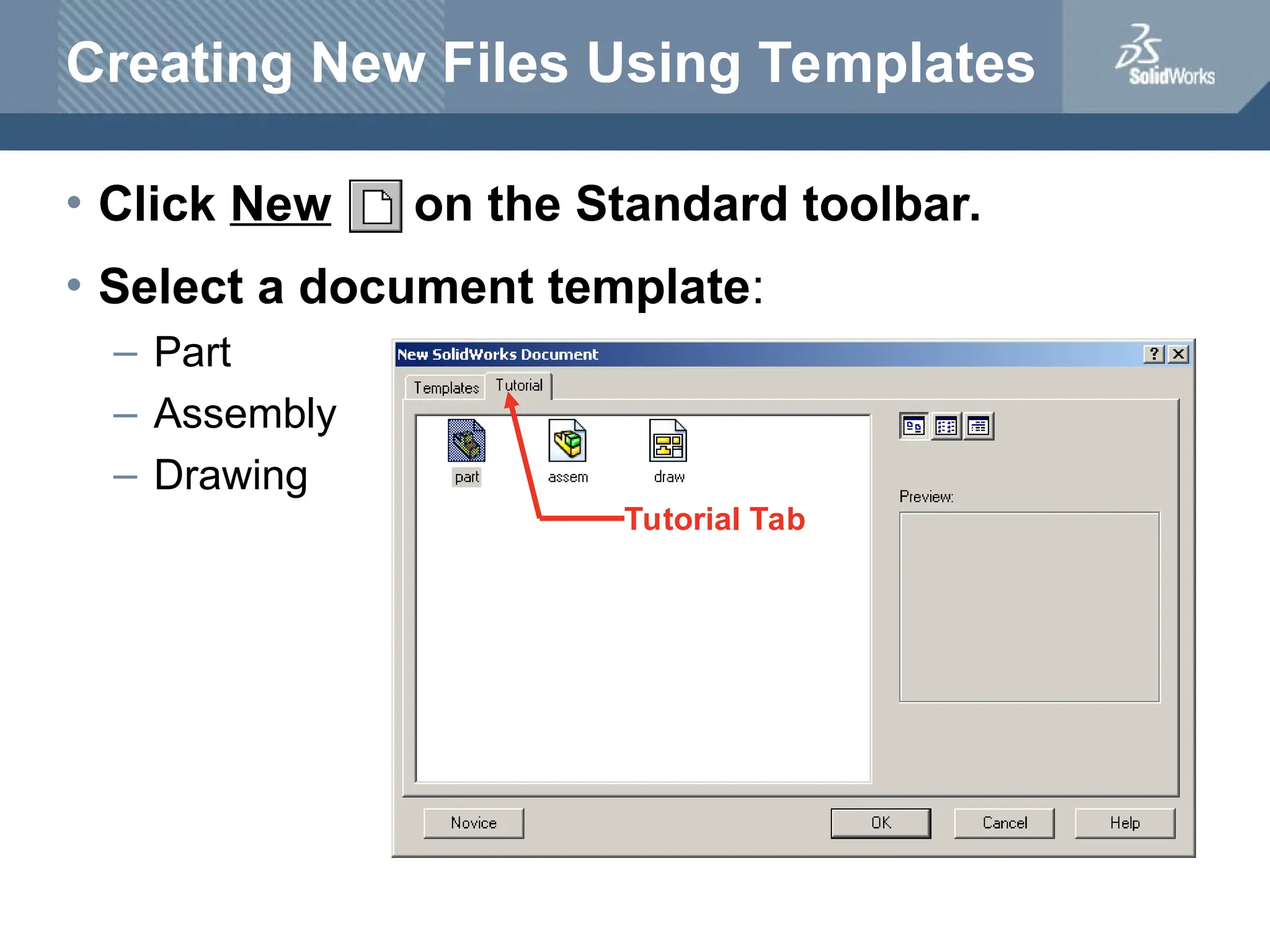
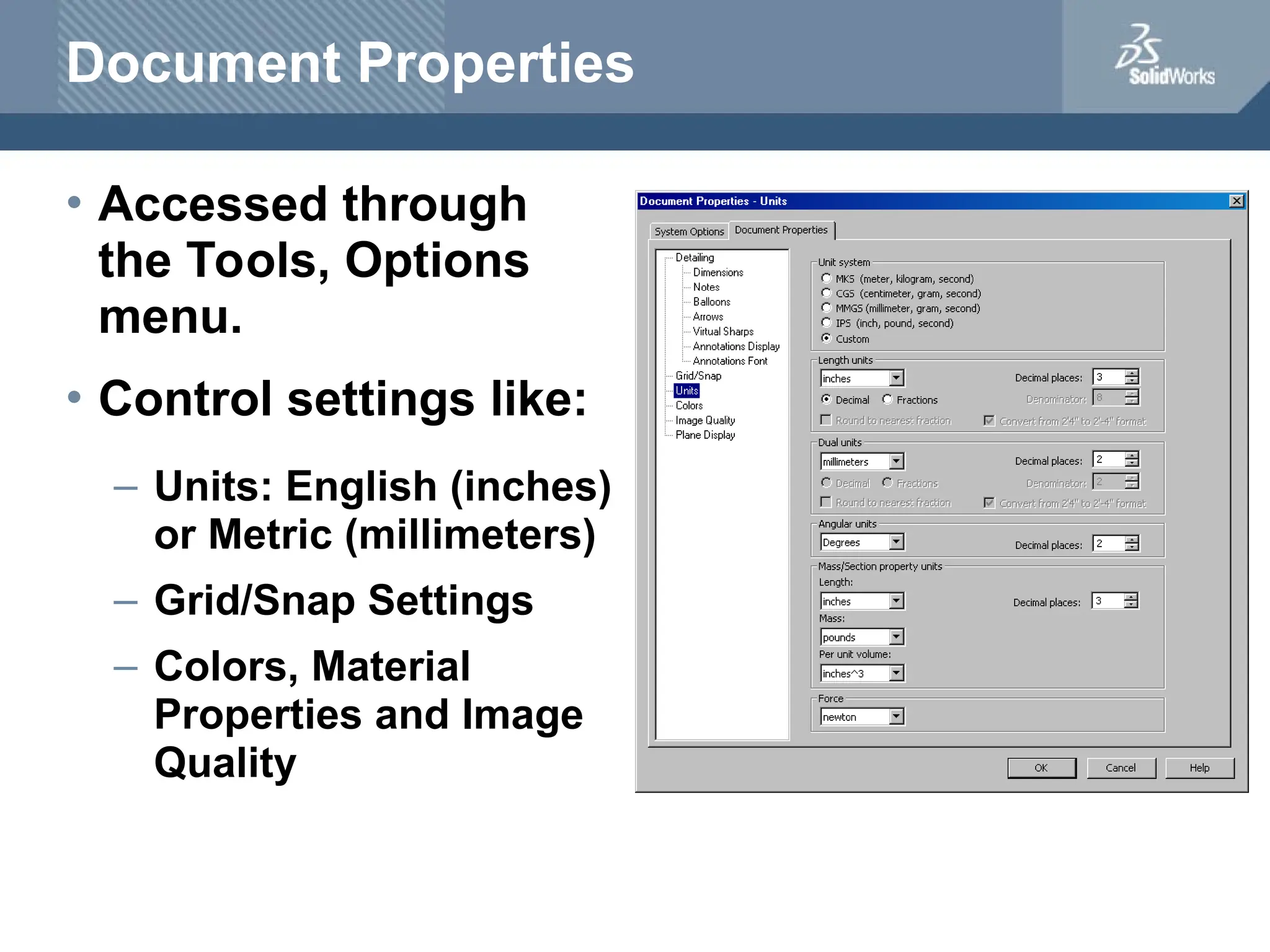
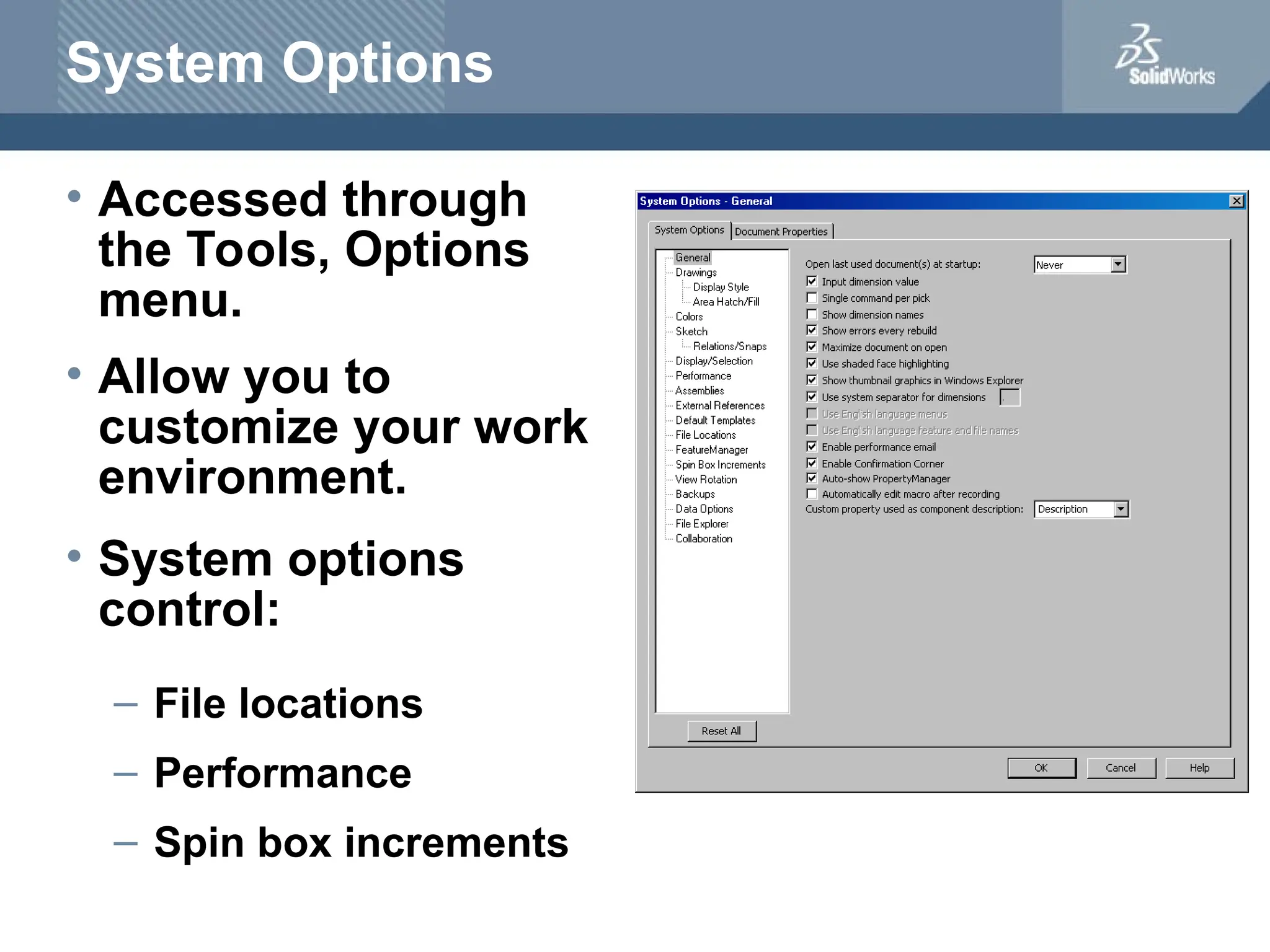
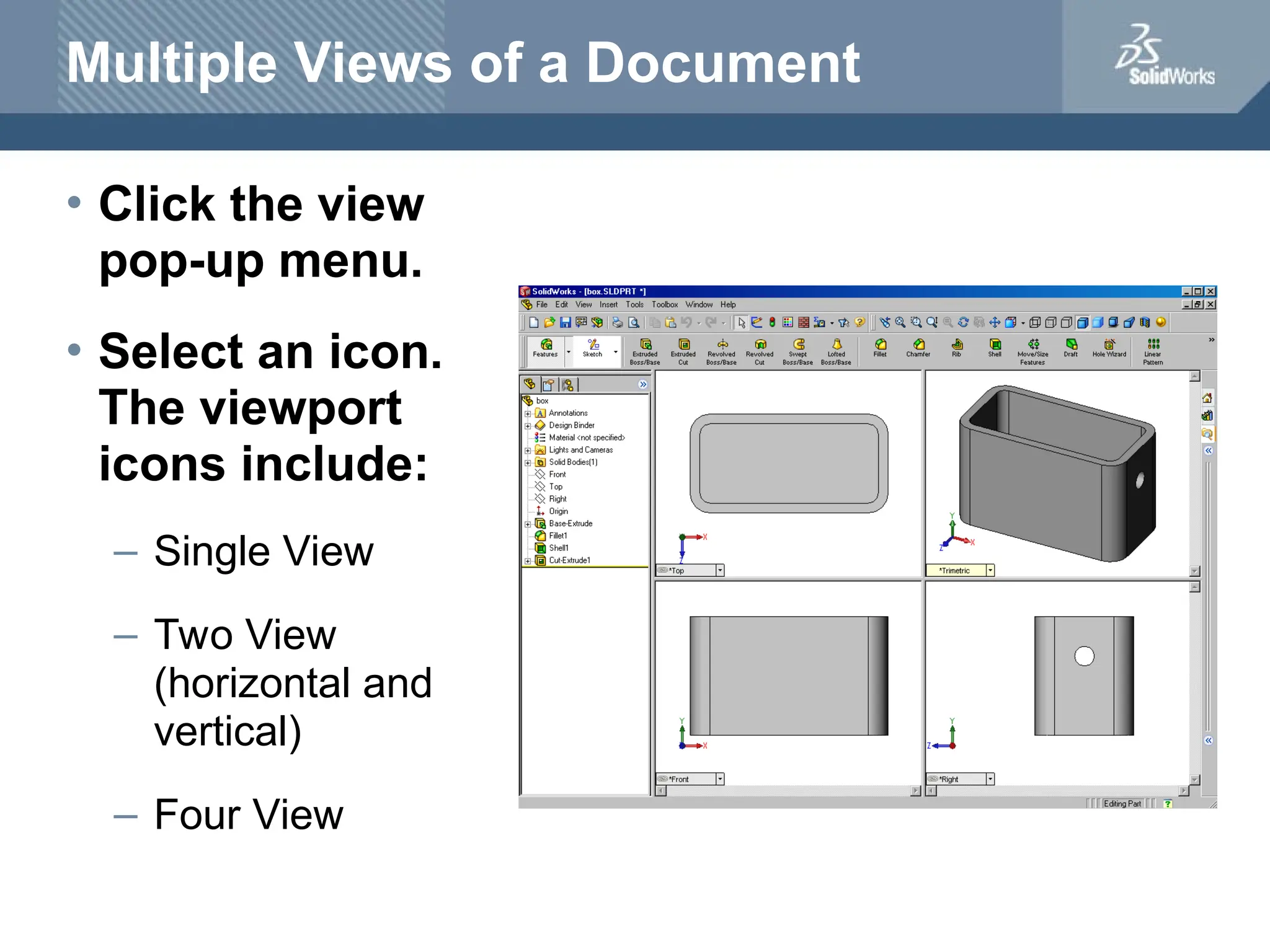
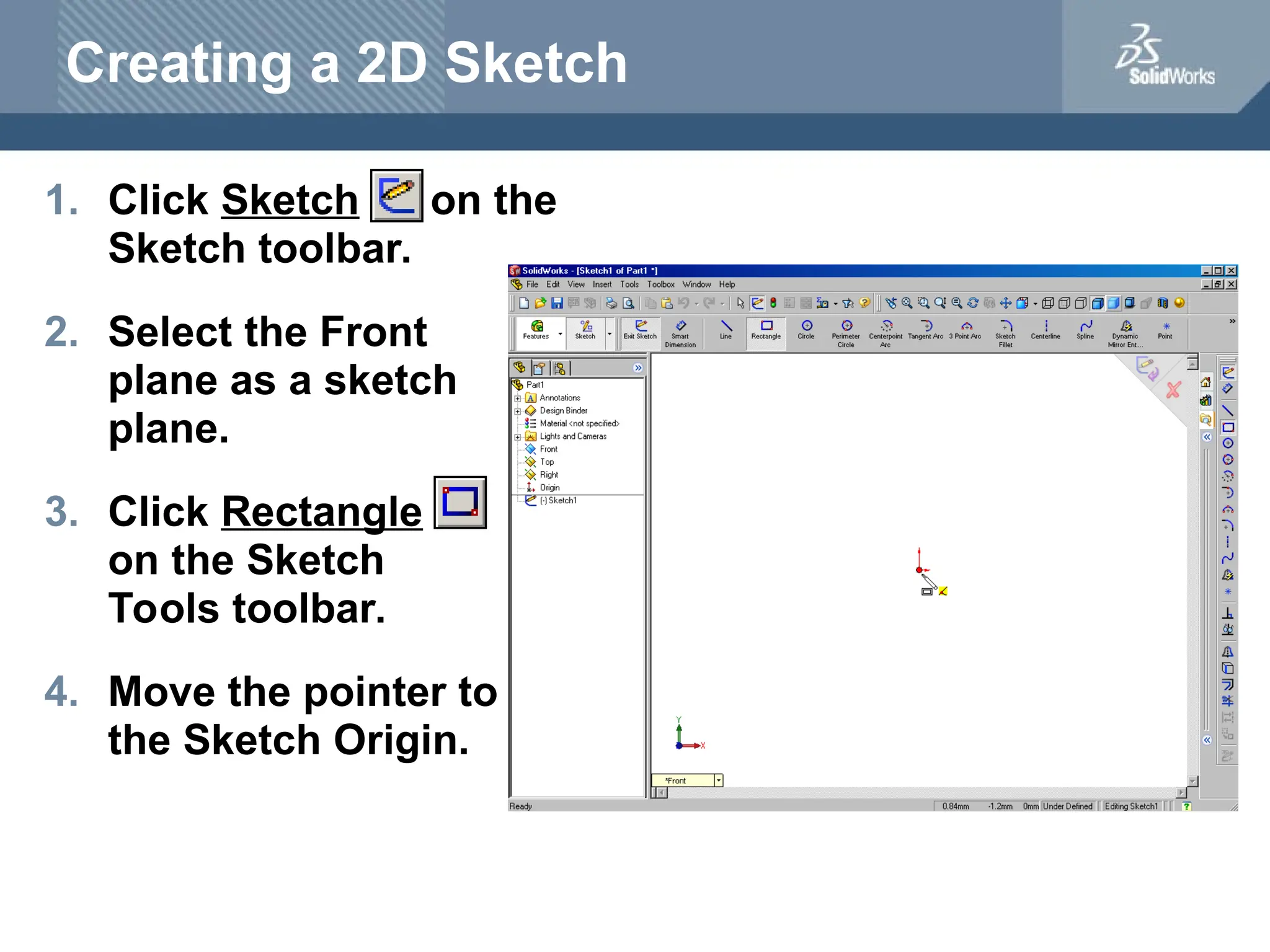
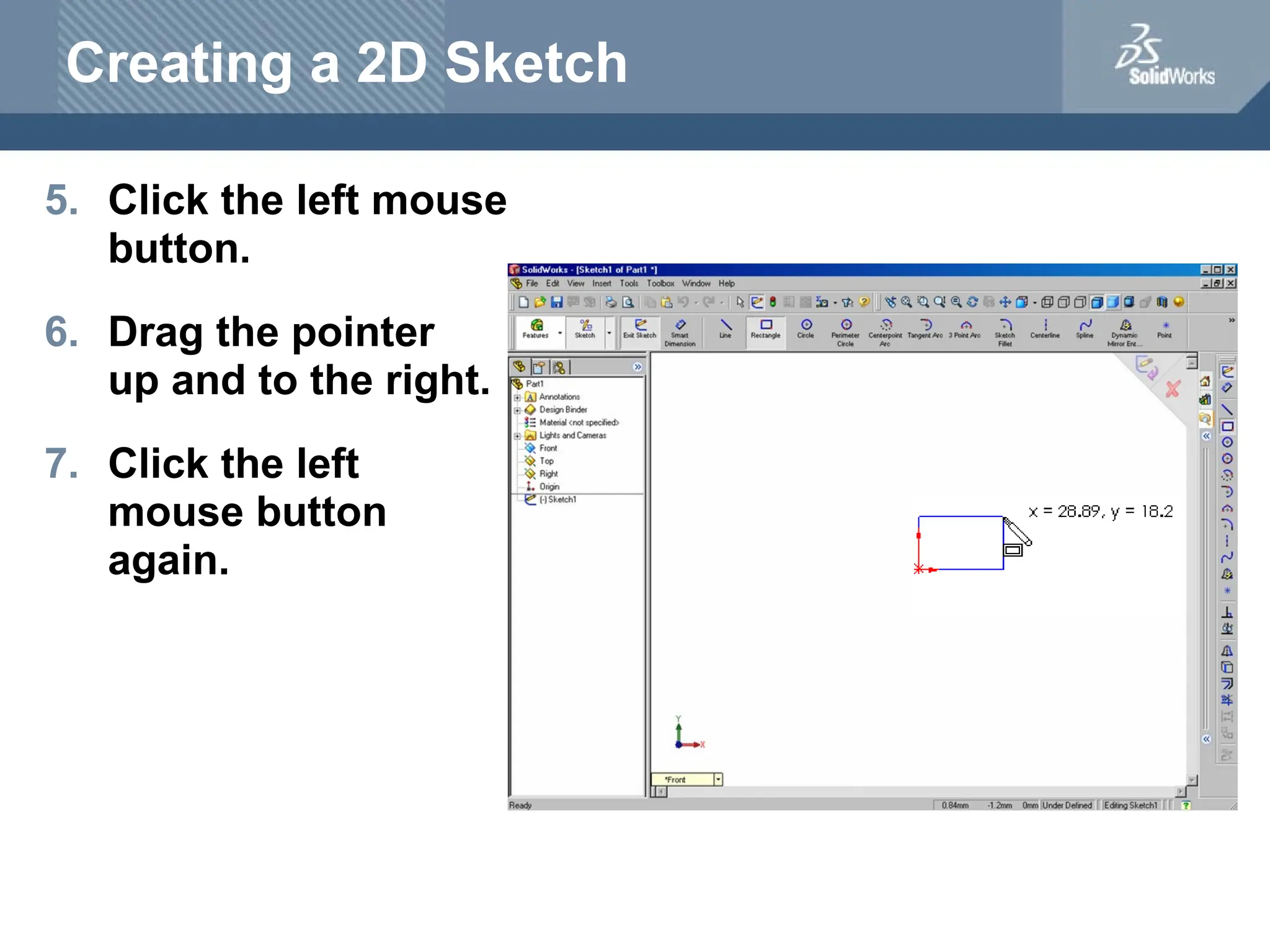
The document serves as a teacher's guide for using SolidWorks, a design automation software that enables users to create 3D models from sketches. It outlines the components of a SolidWorks model, including parts, assemblies, and drawings, and describes various features used in model creation, such as base, boss, and fillet features. Additionally, it covers basic geometry concepts, commands for feature creation, and the fundamentals of setting up and customizing the SolidWorks workspace.