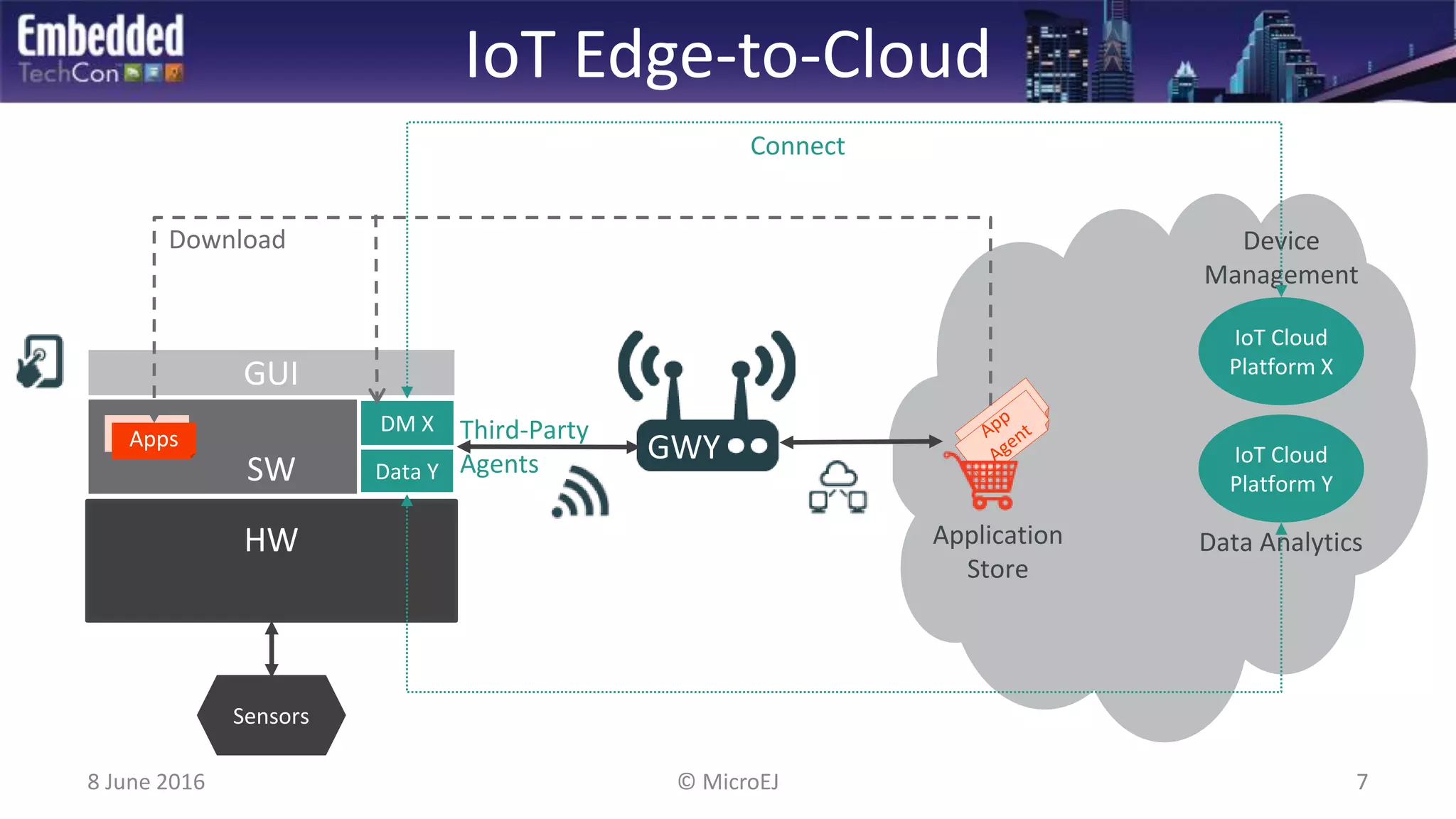
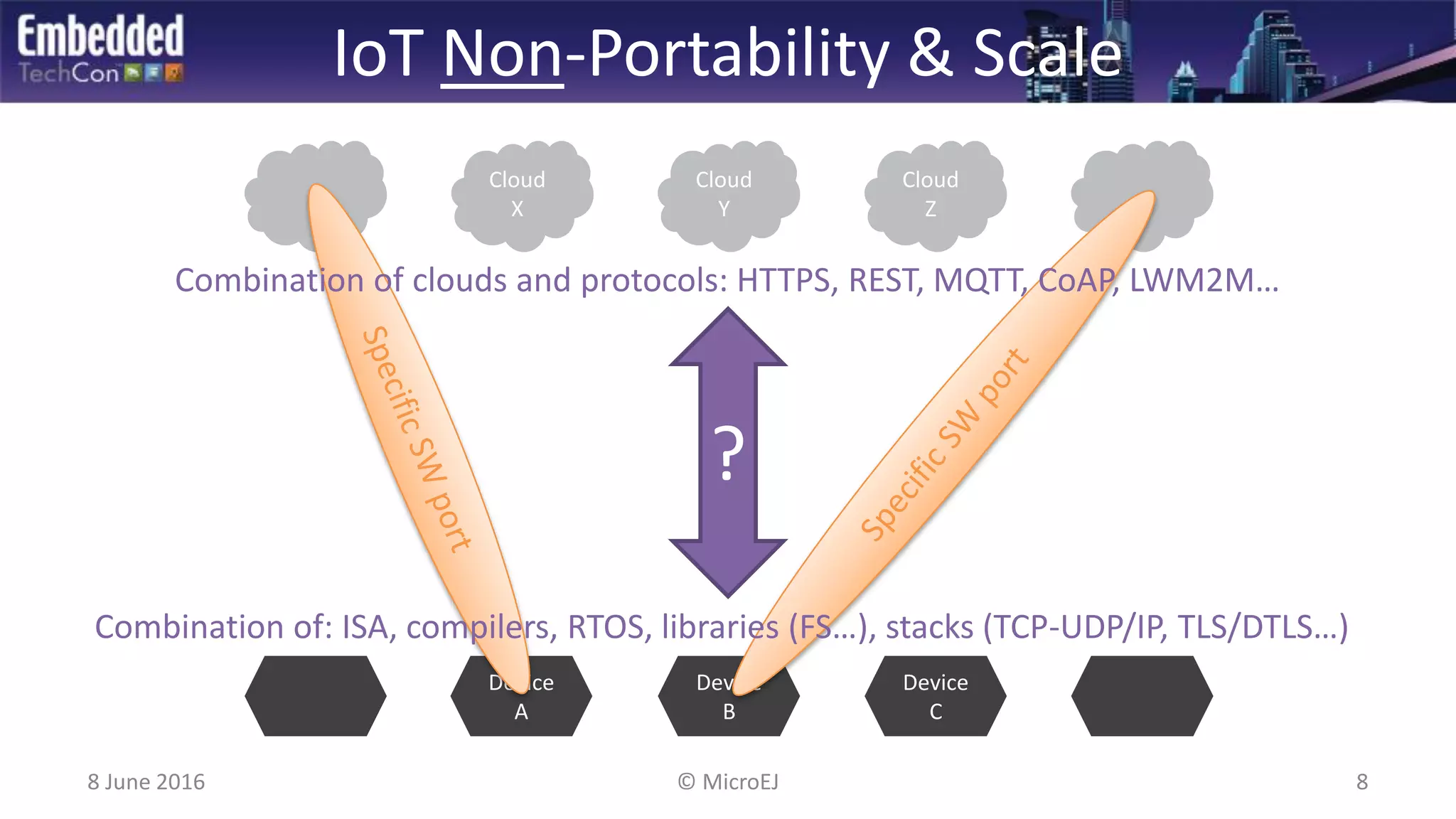
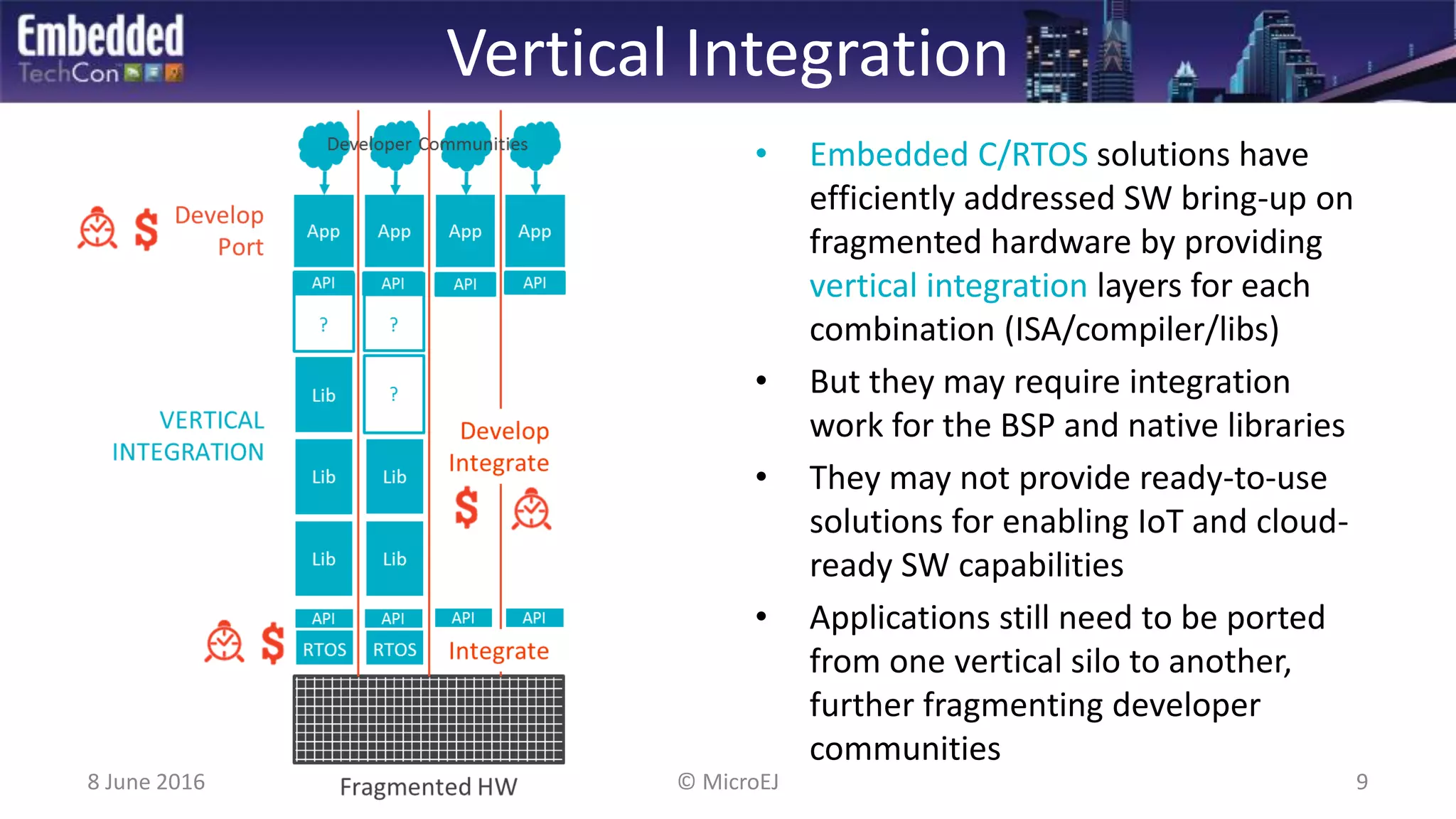
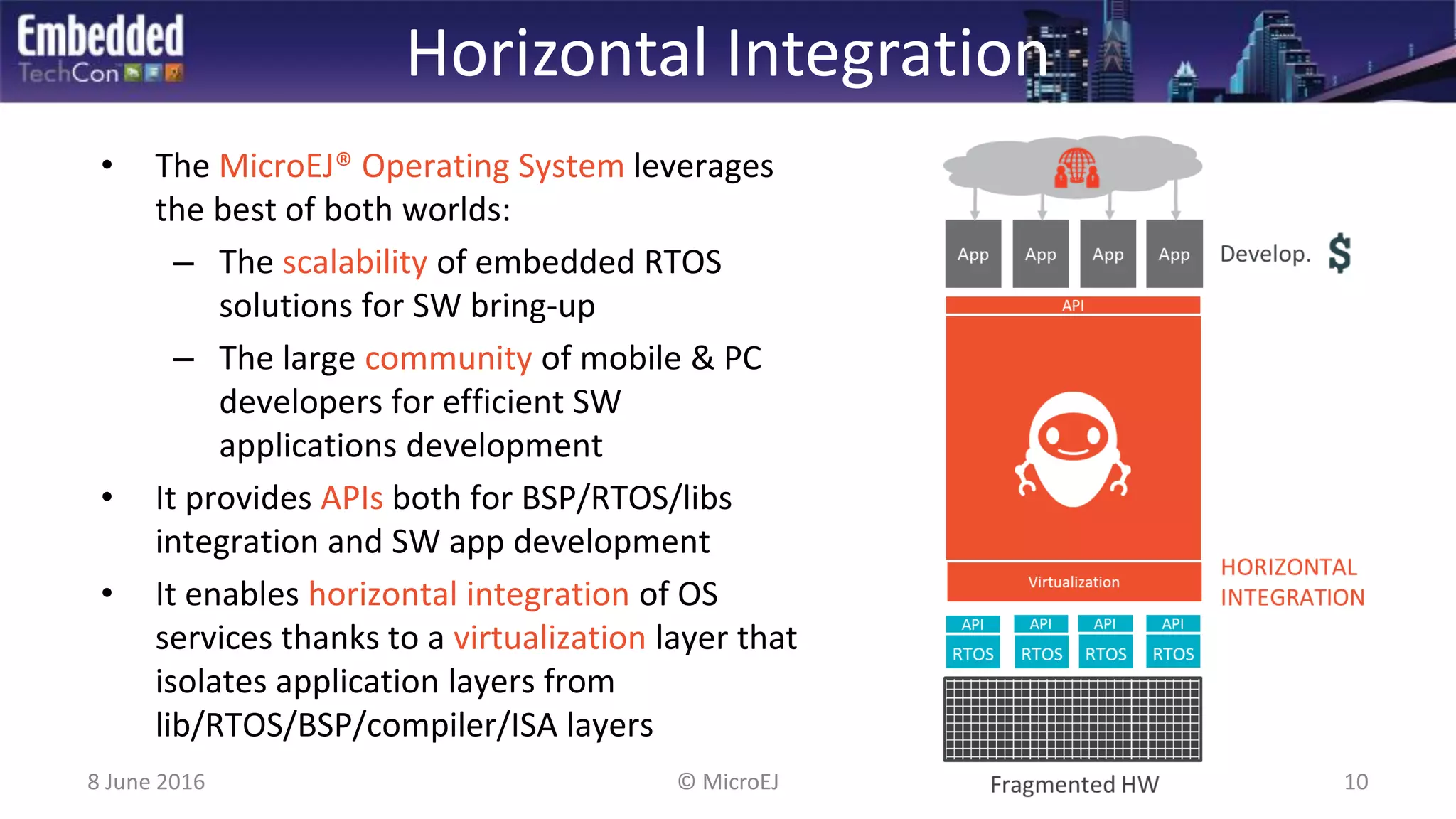
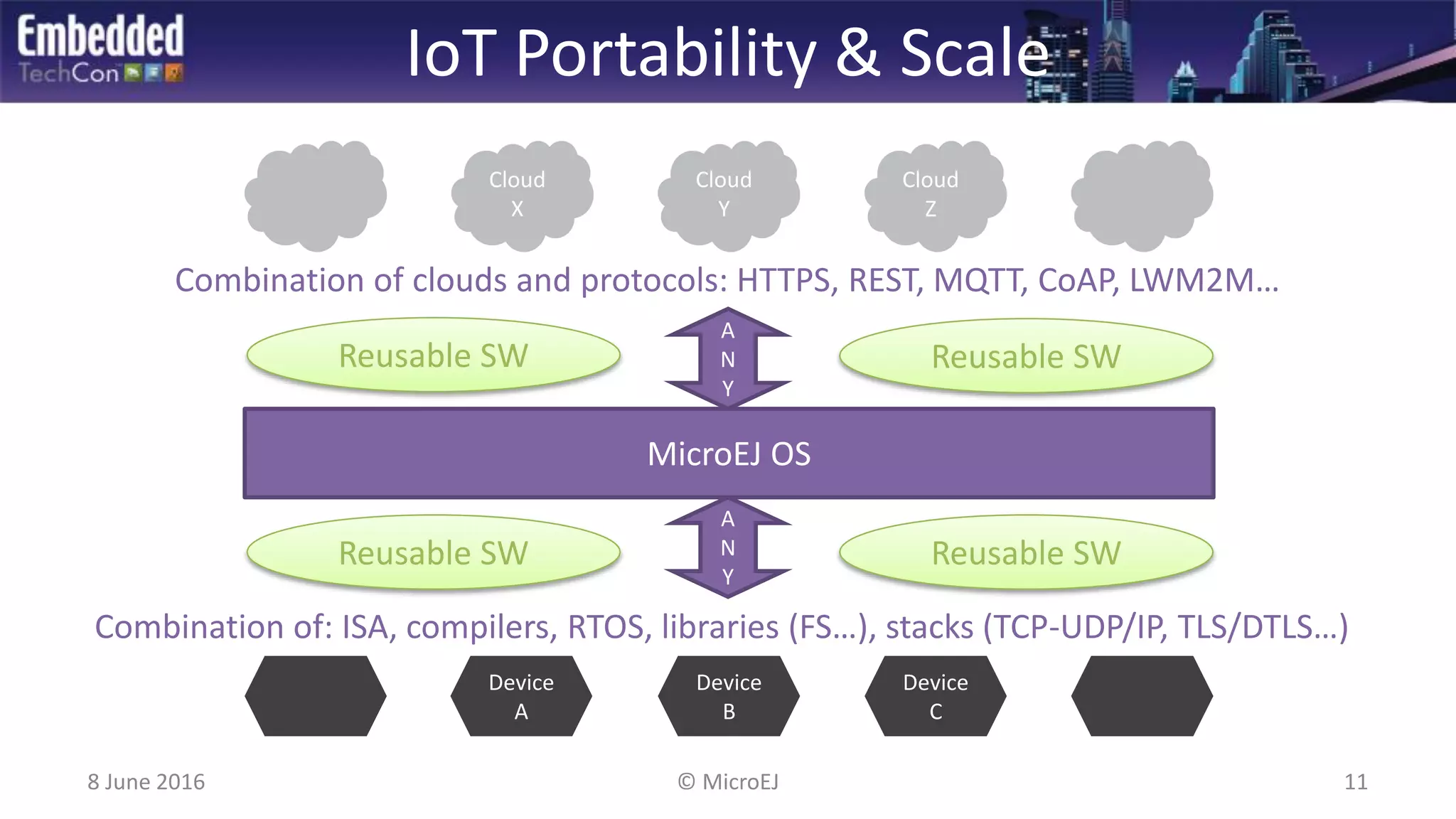
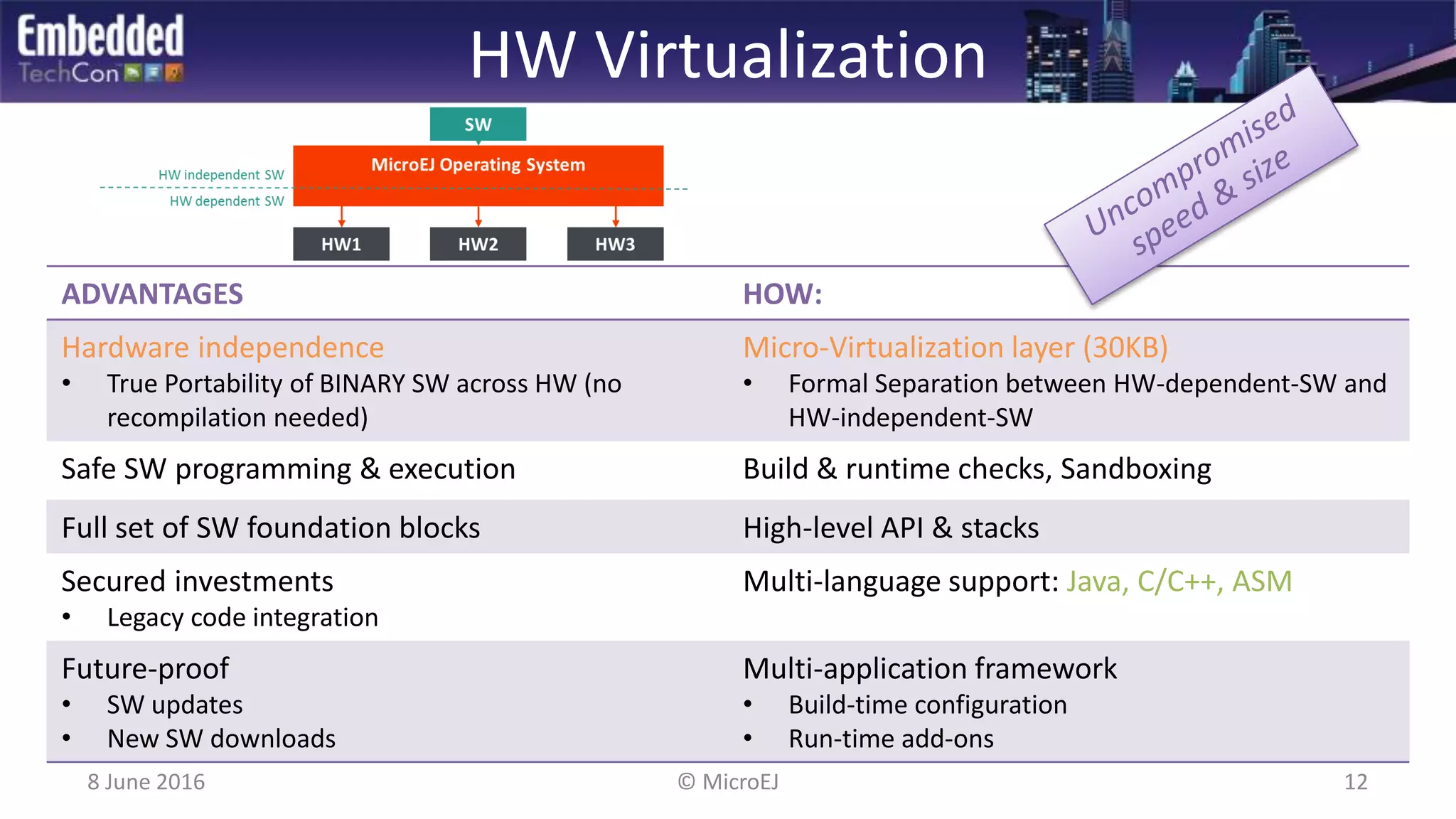
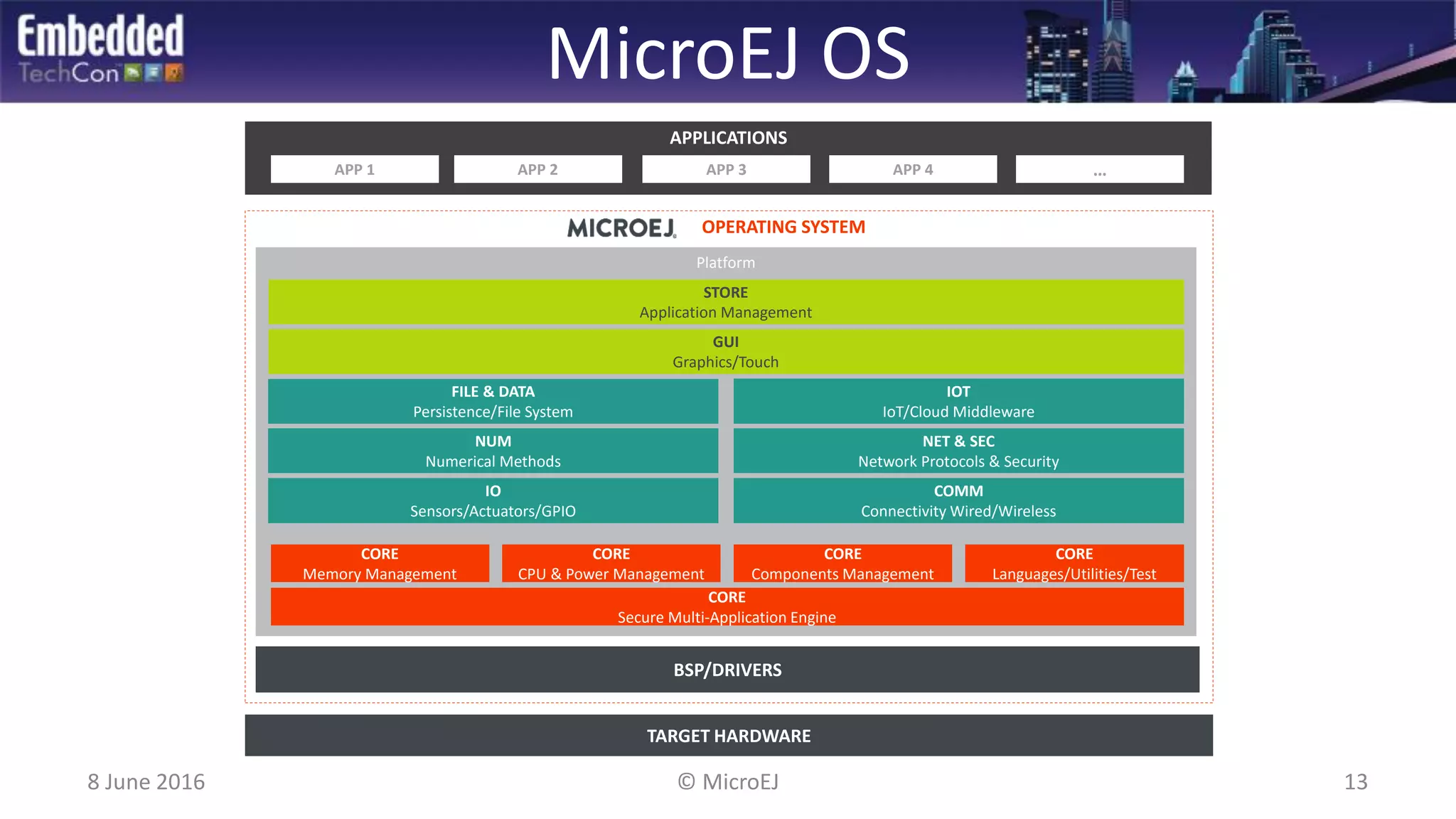
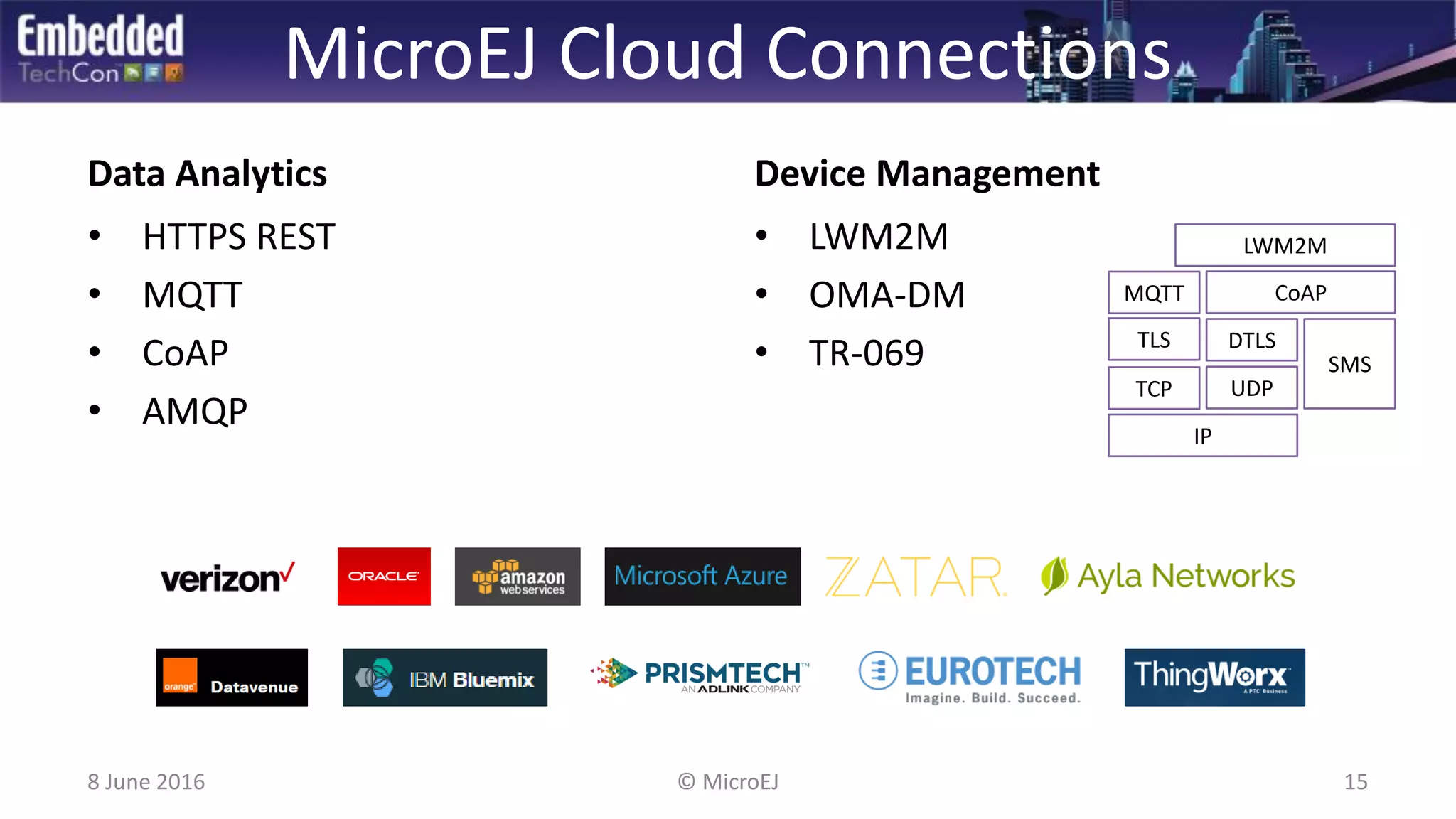
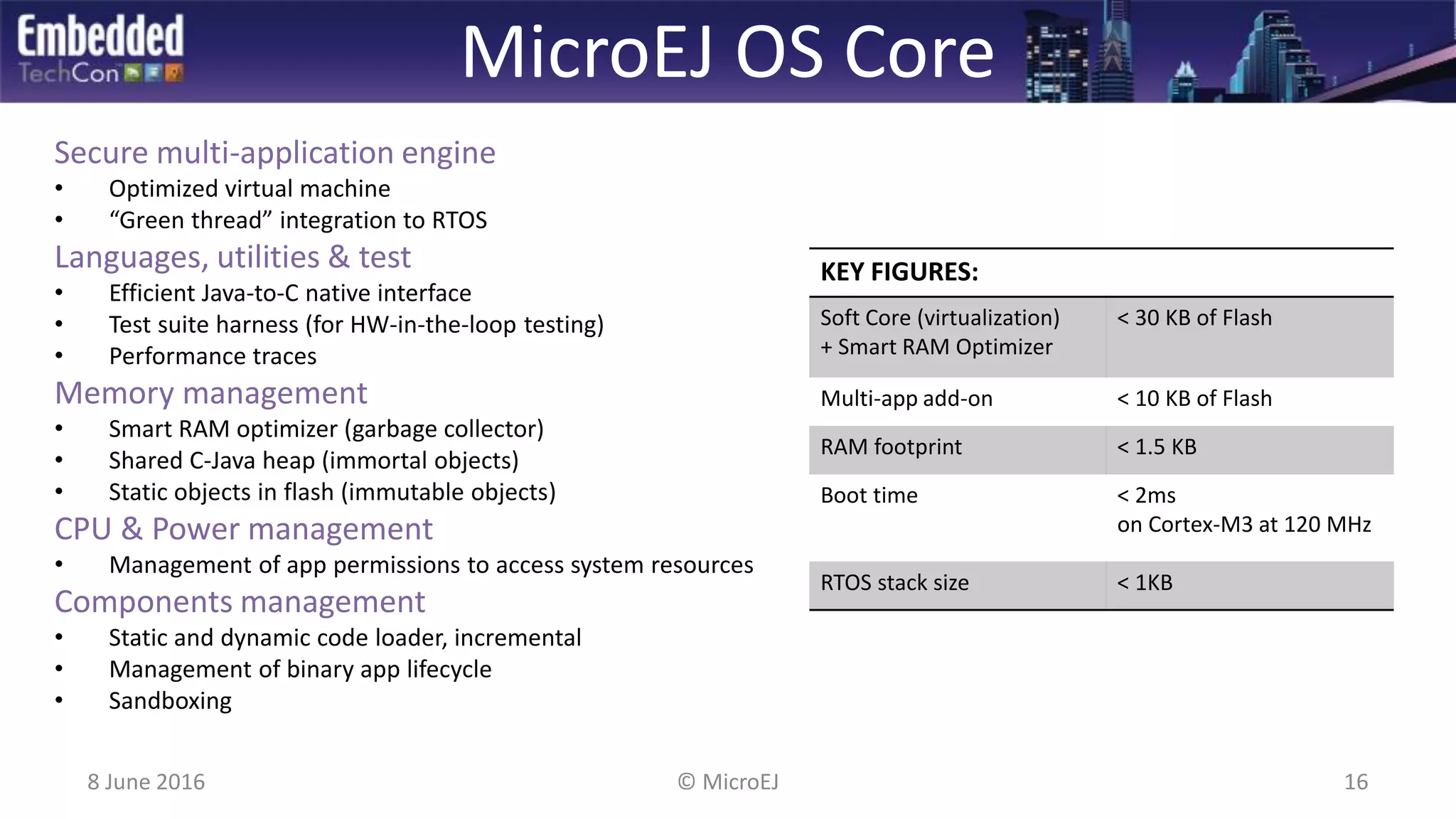
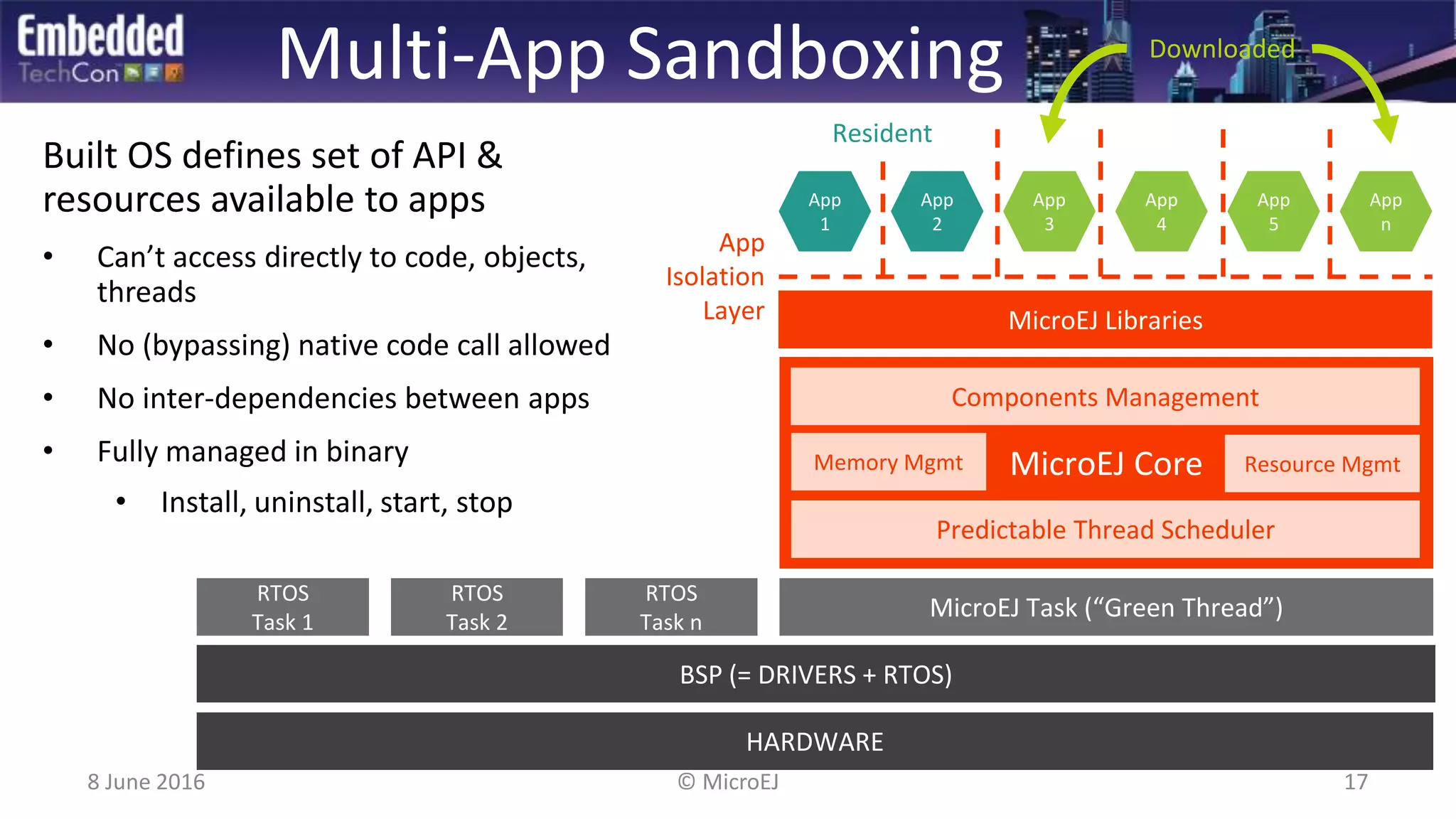
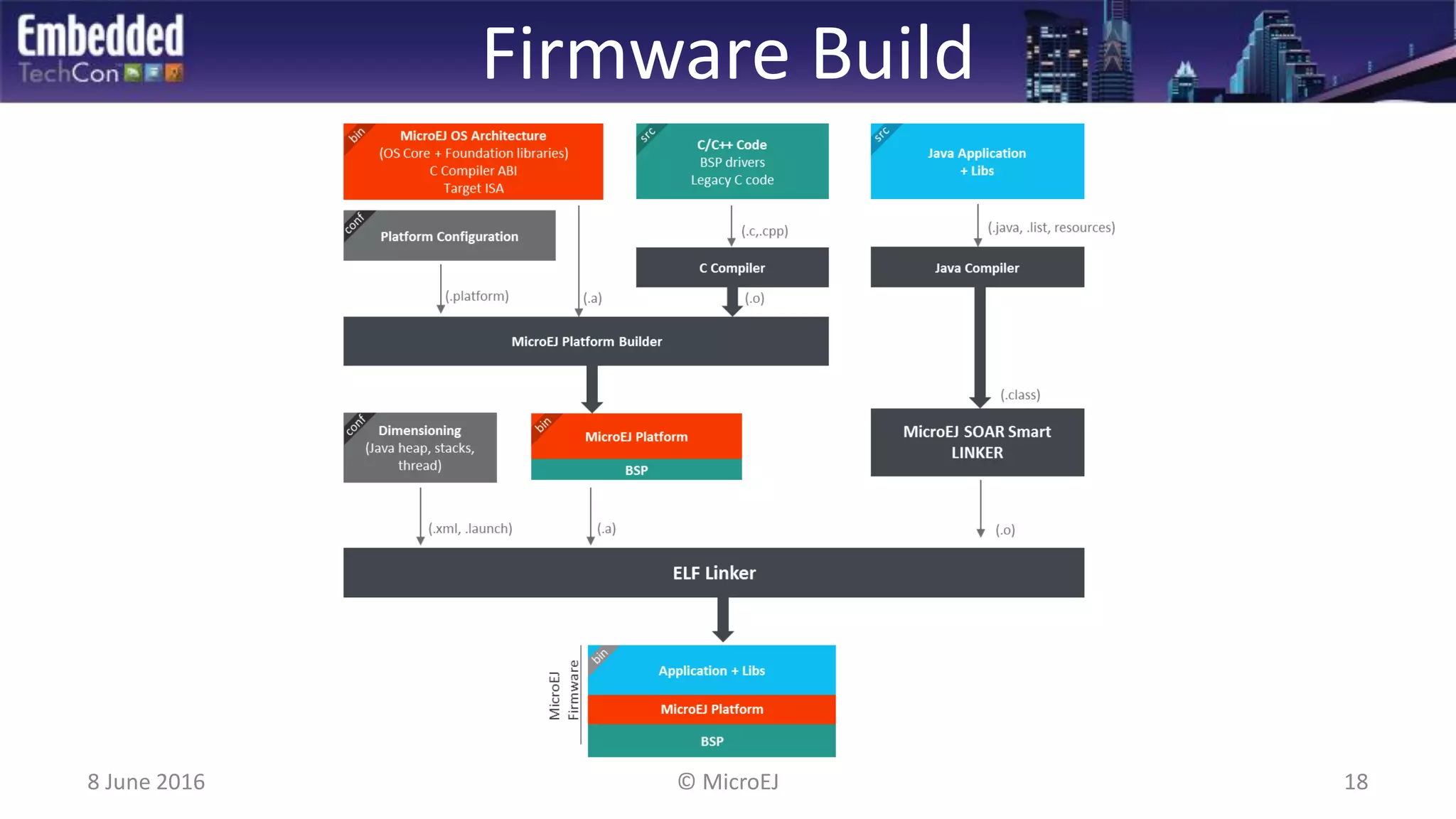
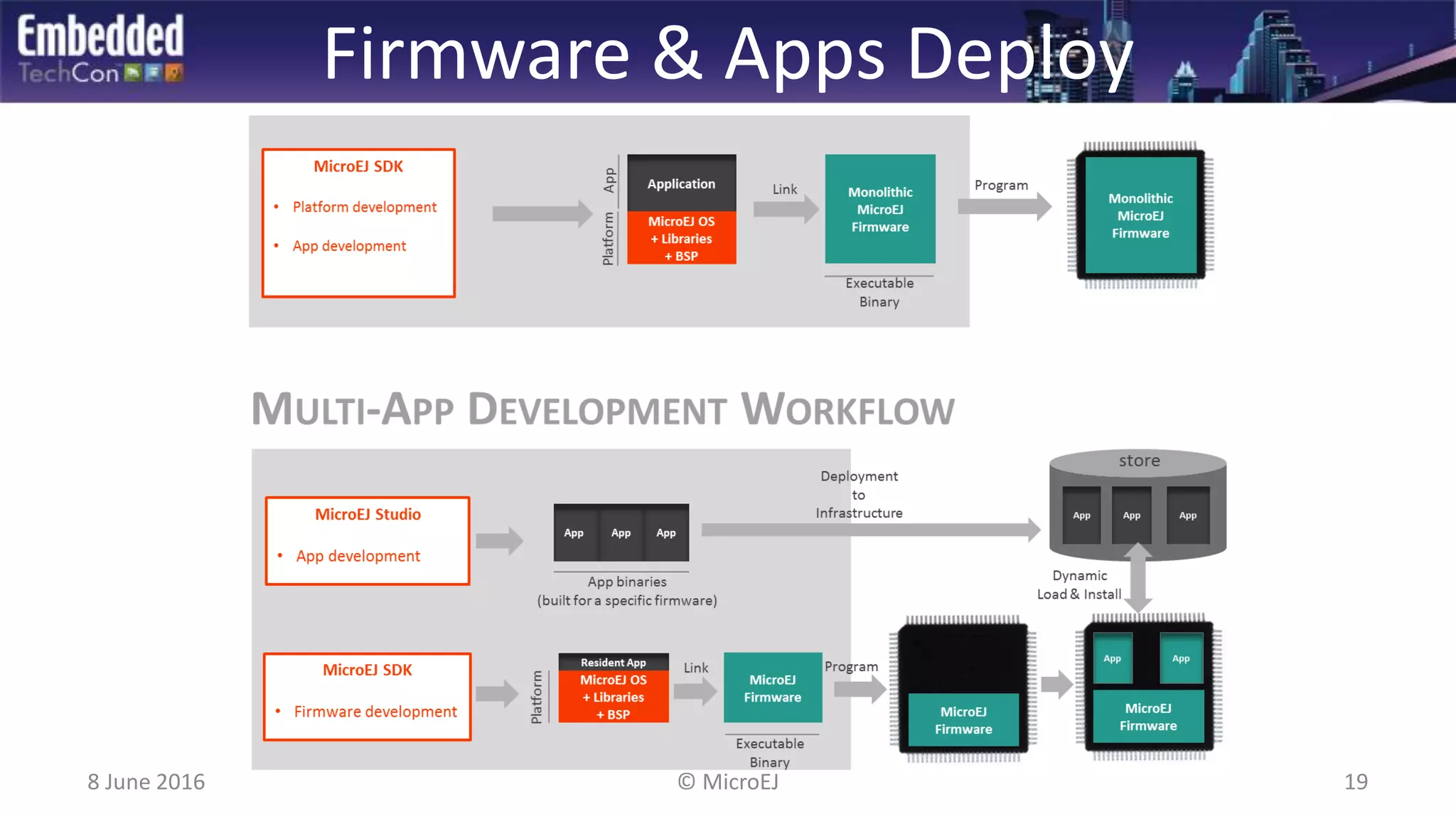
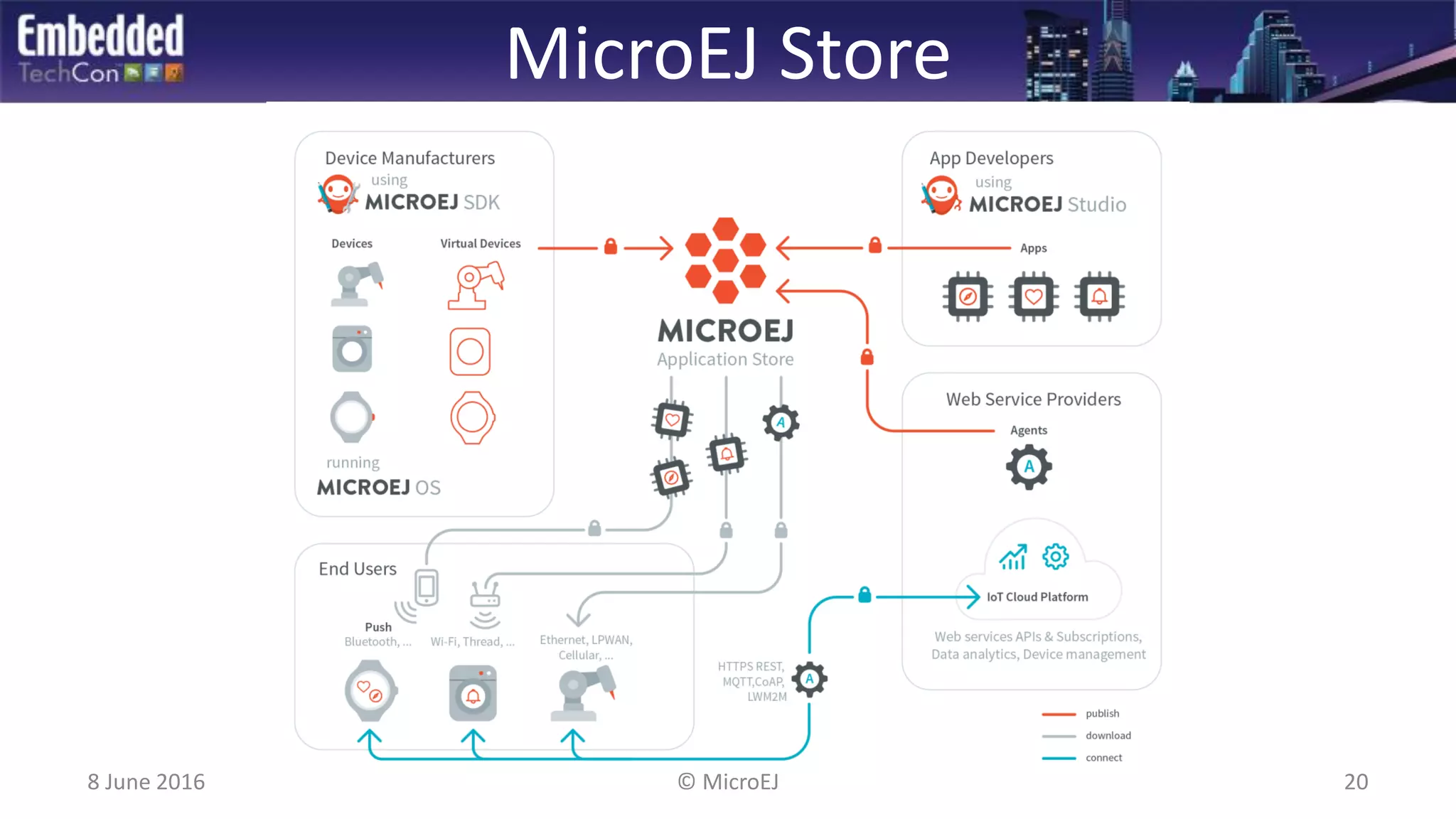
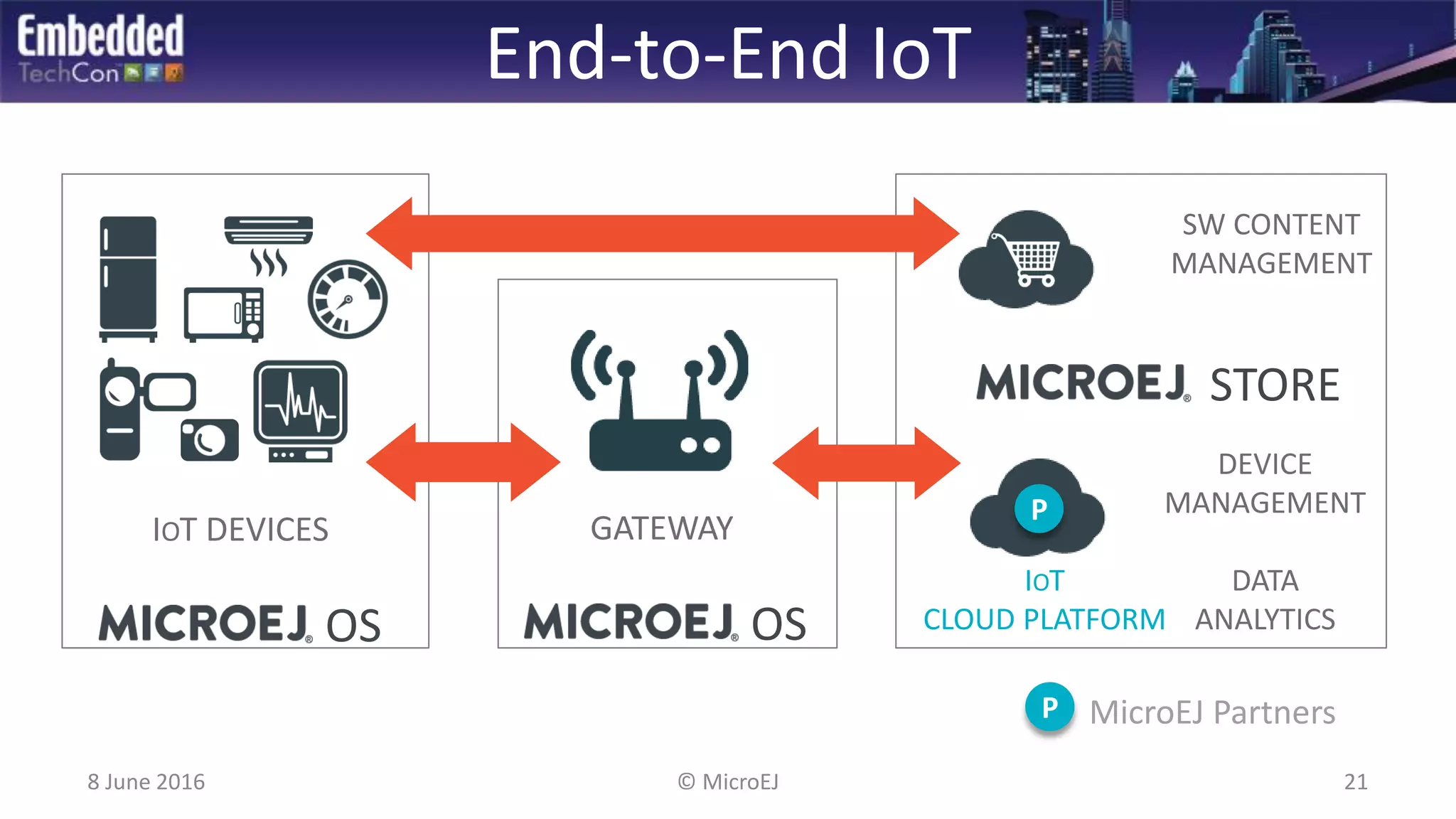
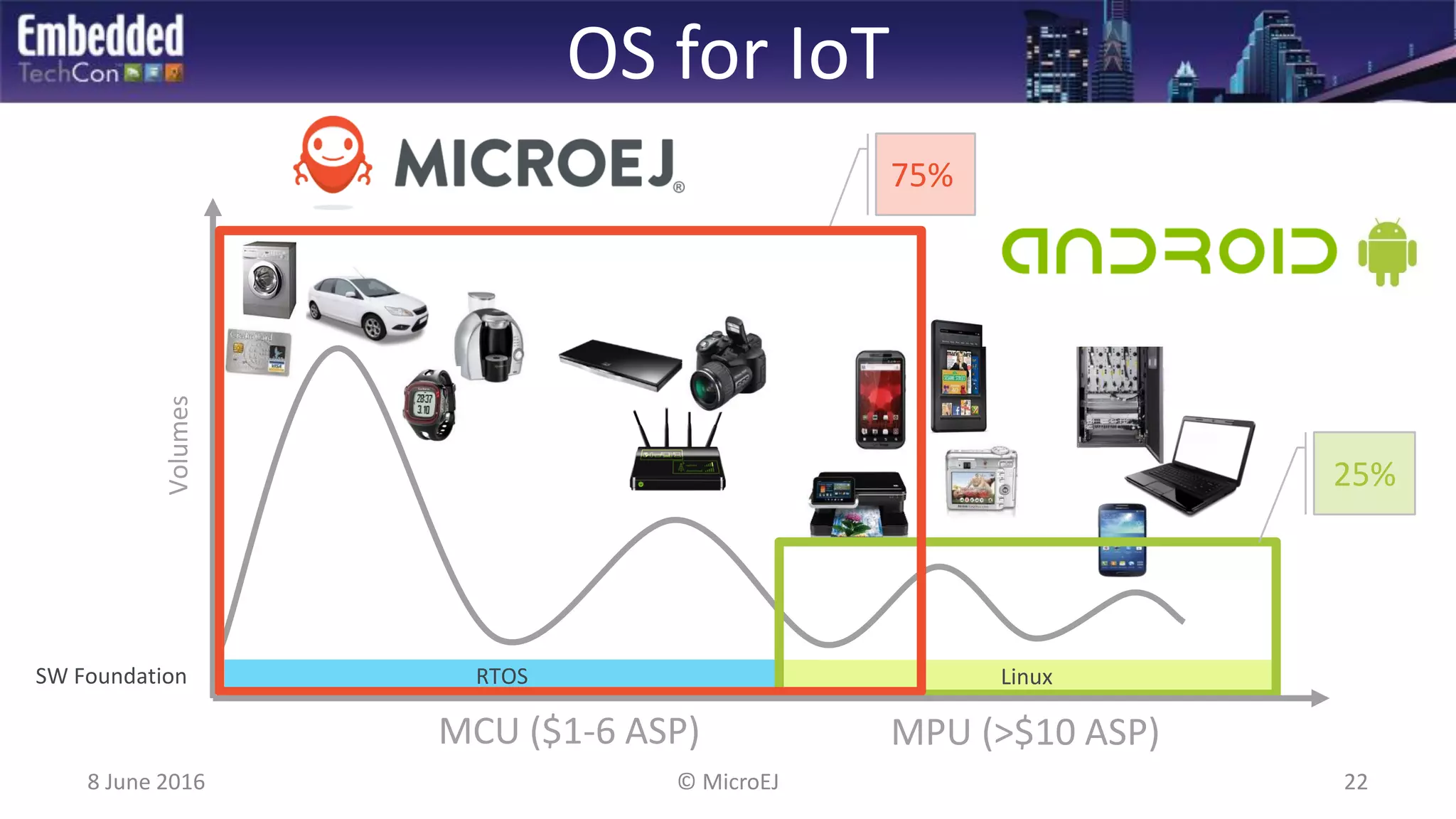
The document discusses the challenges and solutions related to software virtualization for IoT devices, emphasizing the need for portability, scalability, and efficient cloud integration. It introduces the MicroEJ operating system, which facilitates hardware independence and dynamic application management through a micro-virtualization layer. The findings suggest a shift towards data-centric business models in the IoT space, requiring robust software frameworks to support multiple connectivity standards and updates.