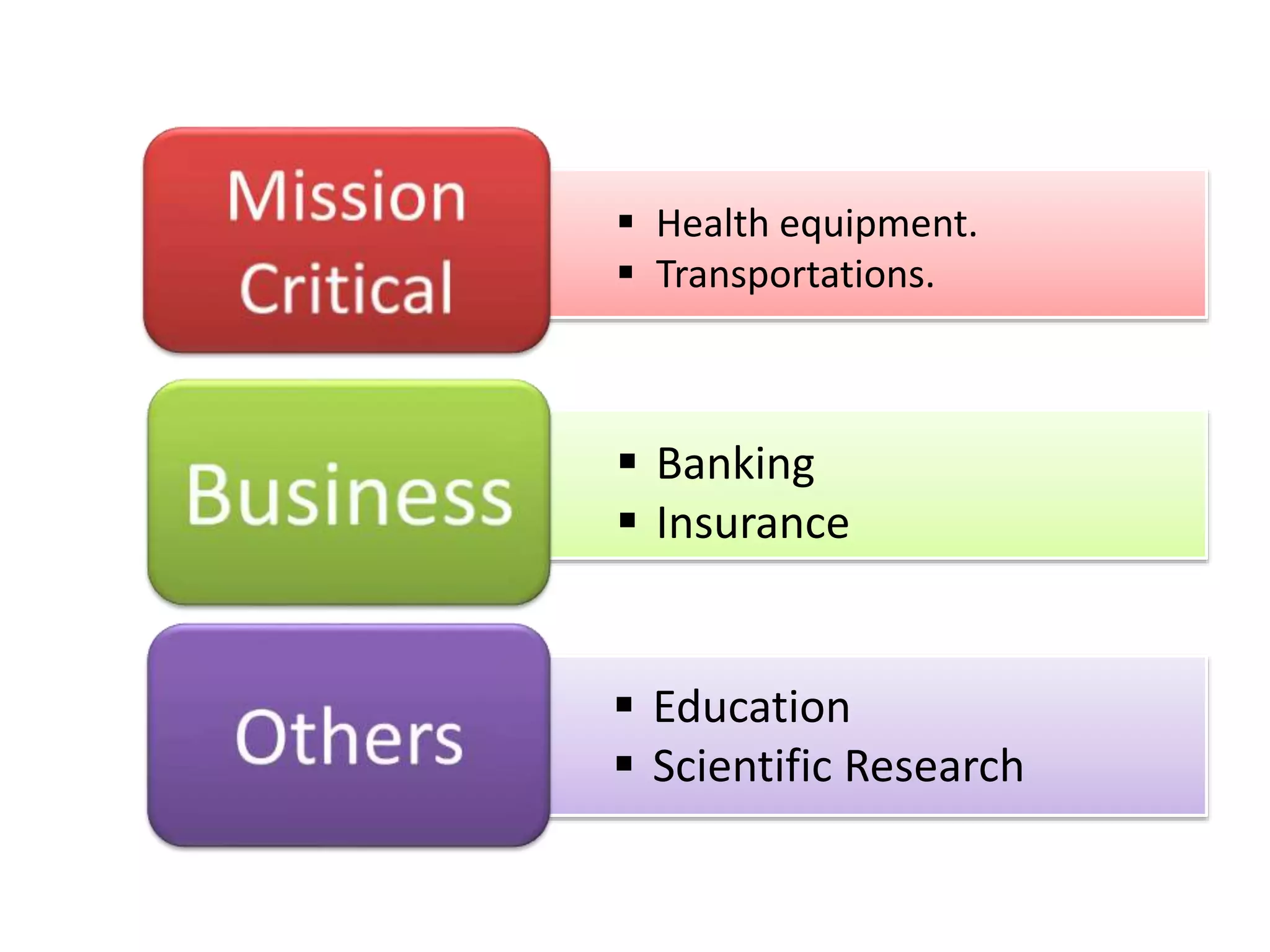
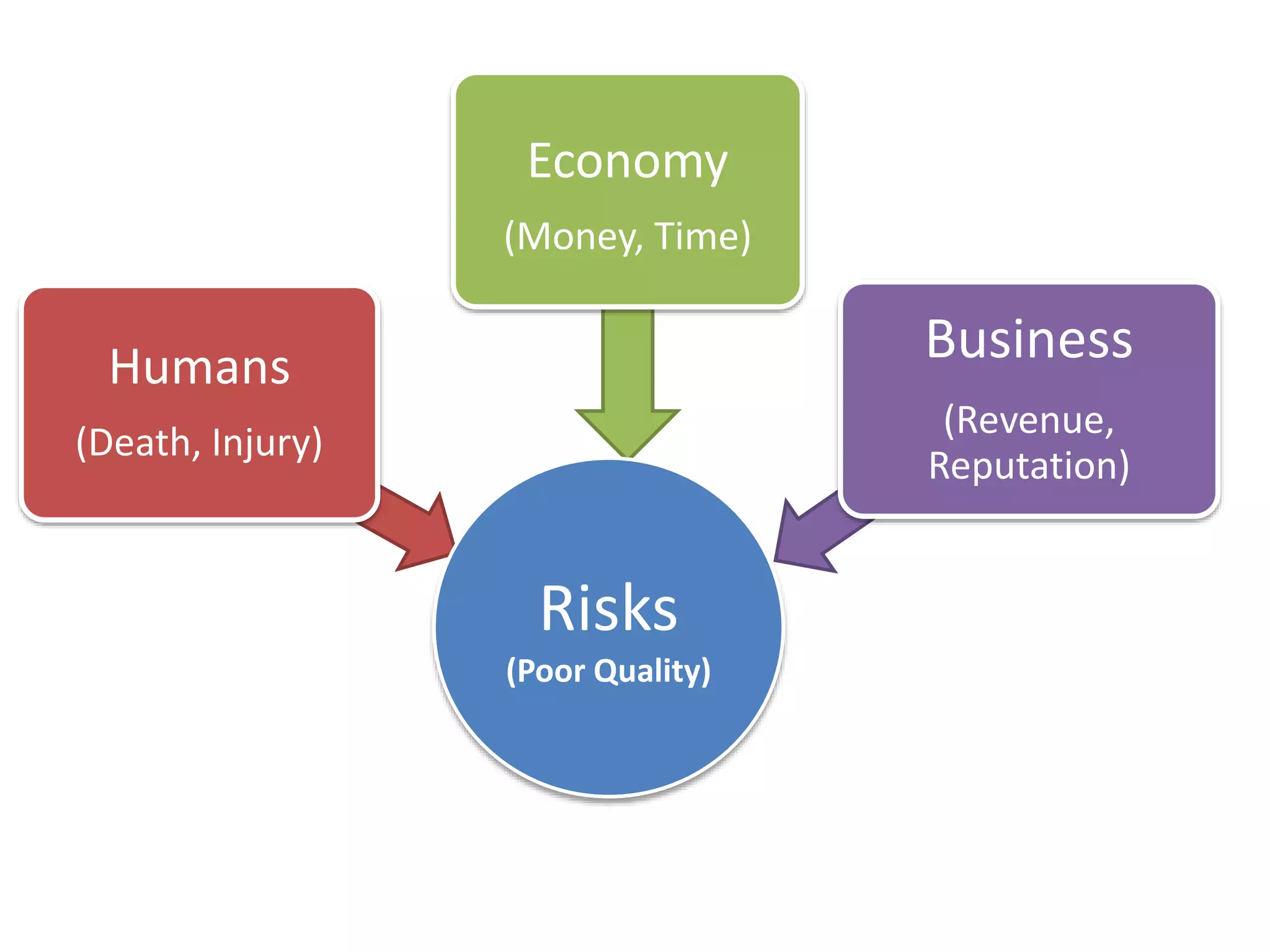
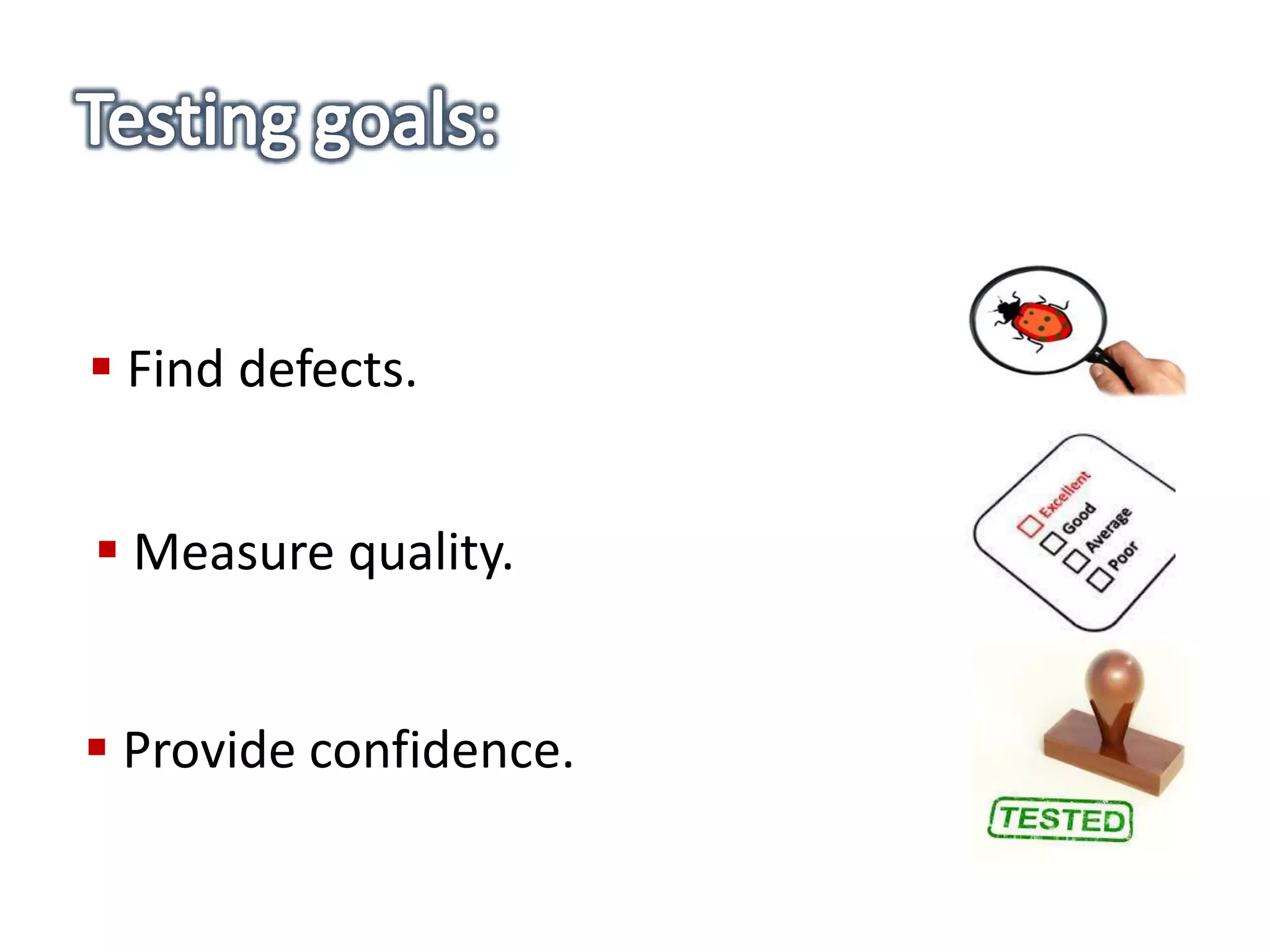
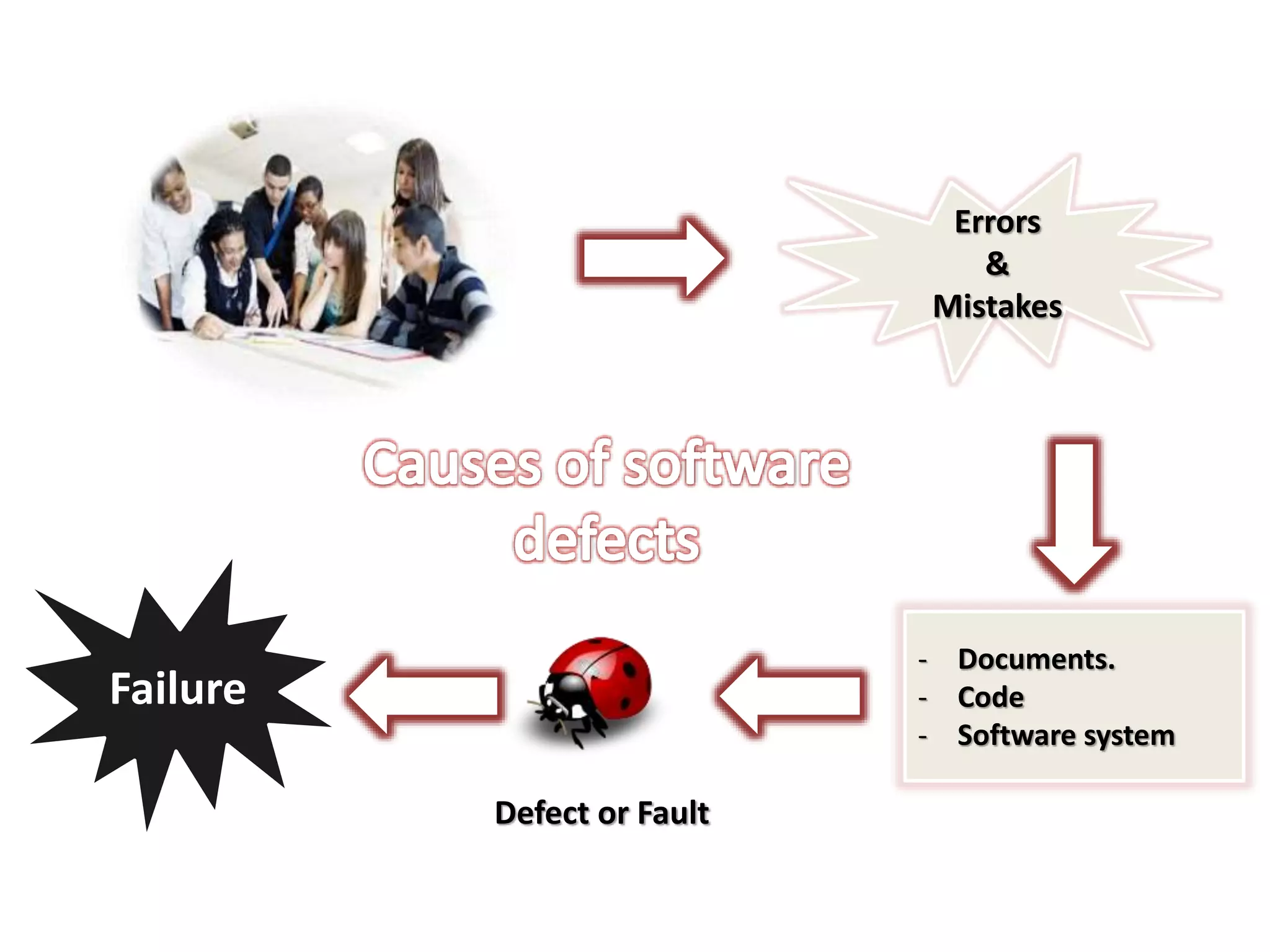
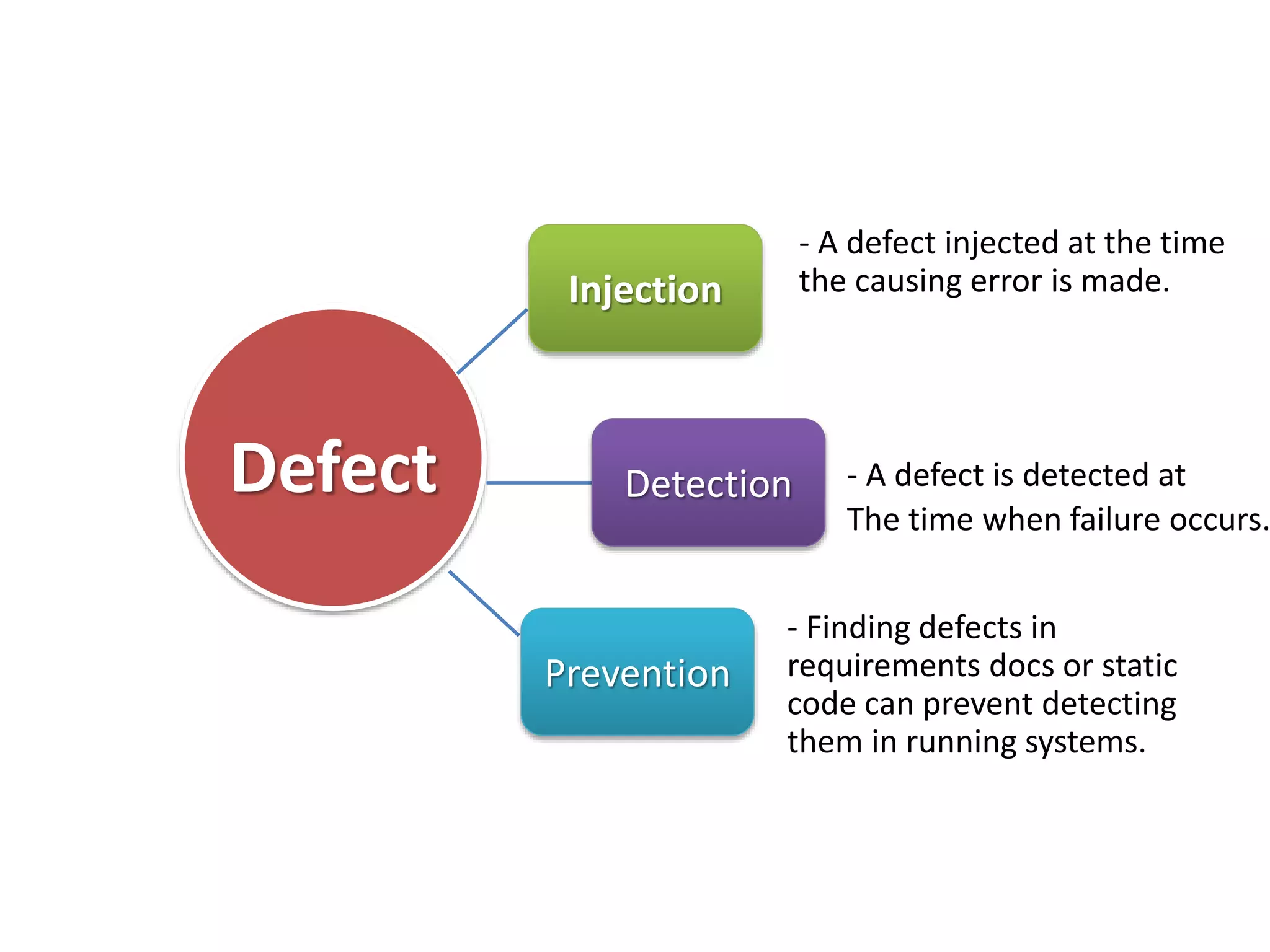
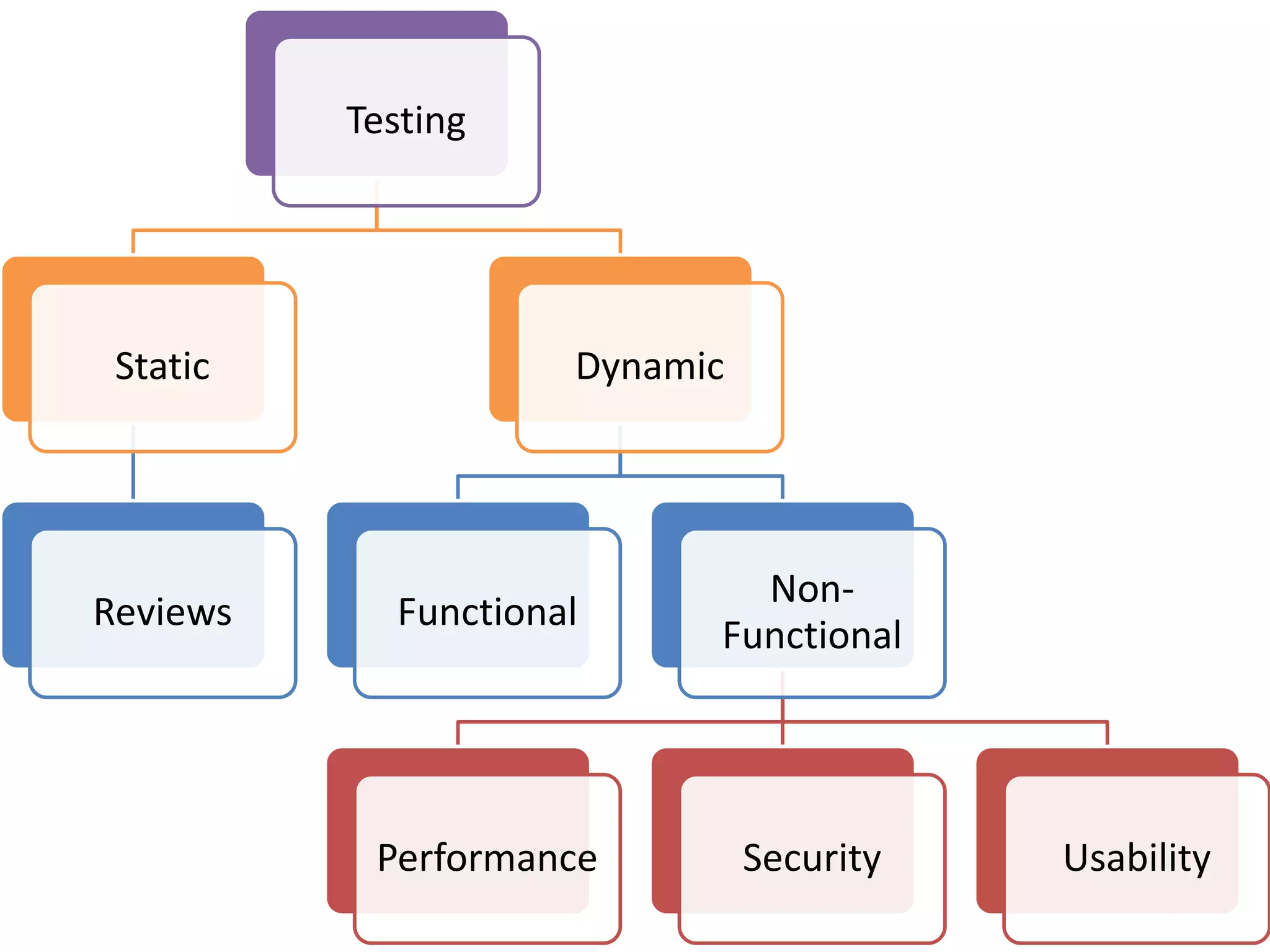
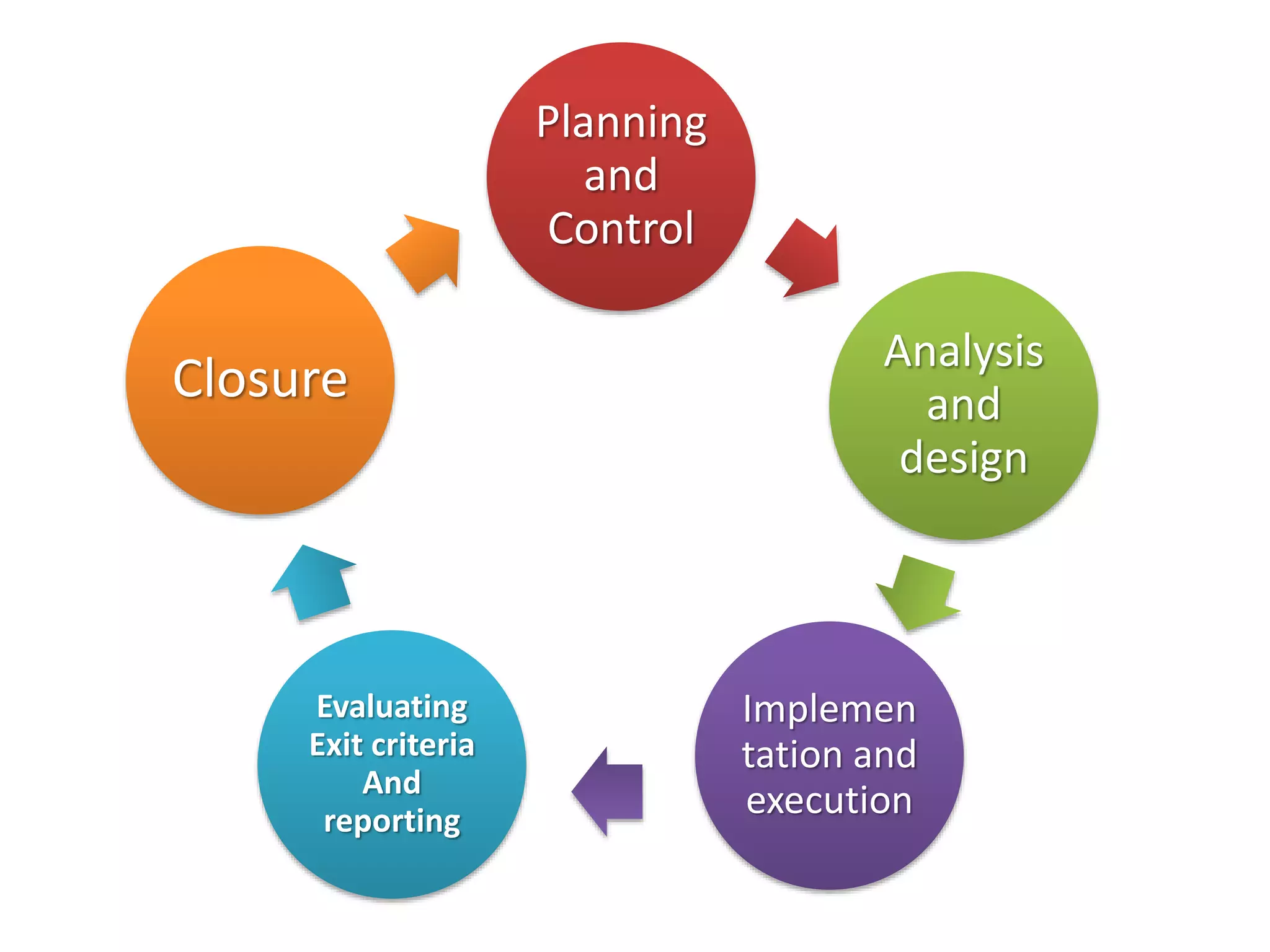
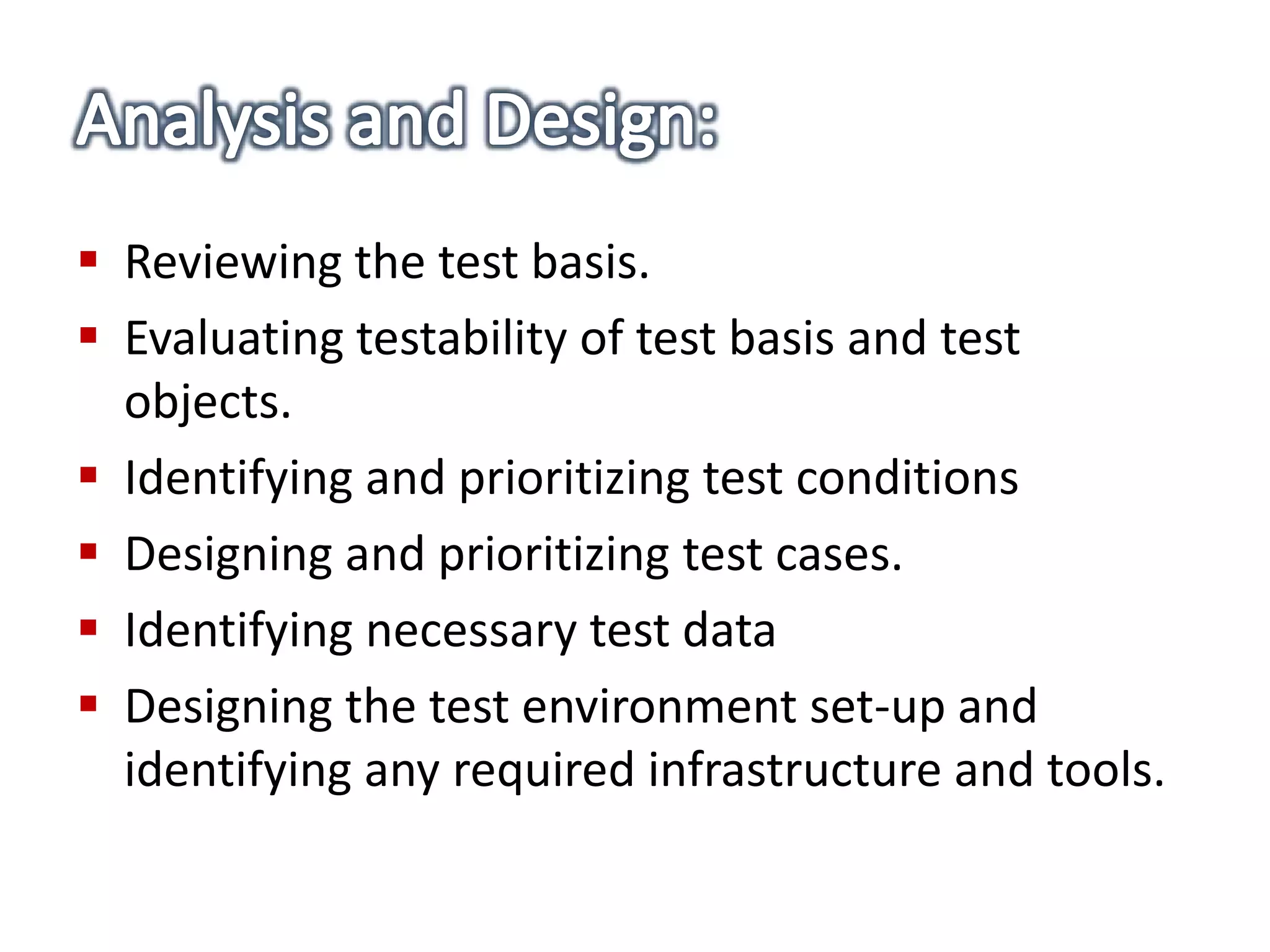
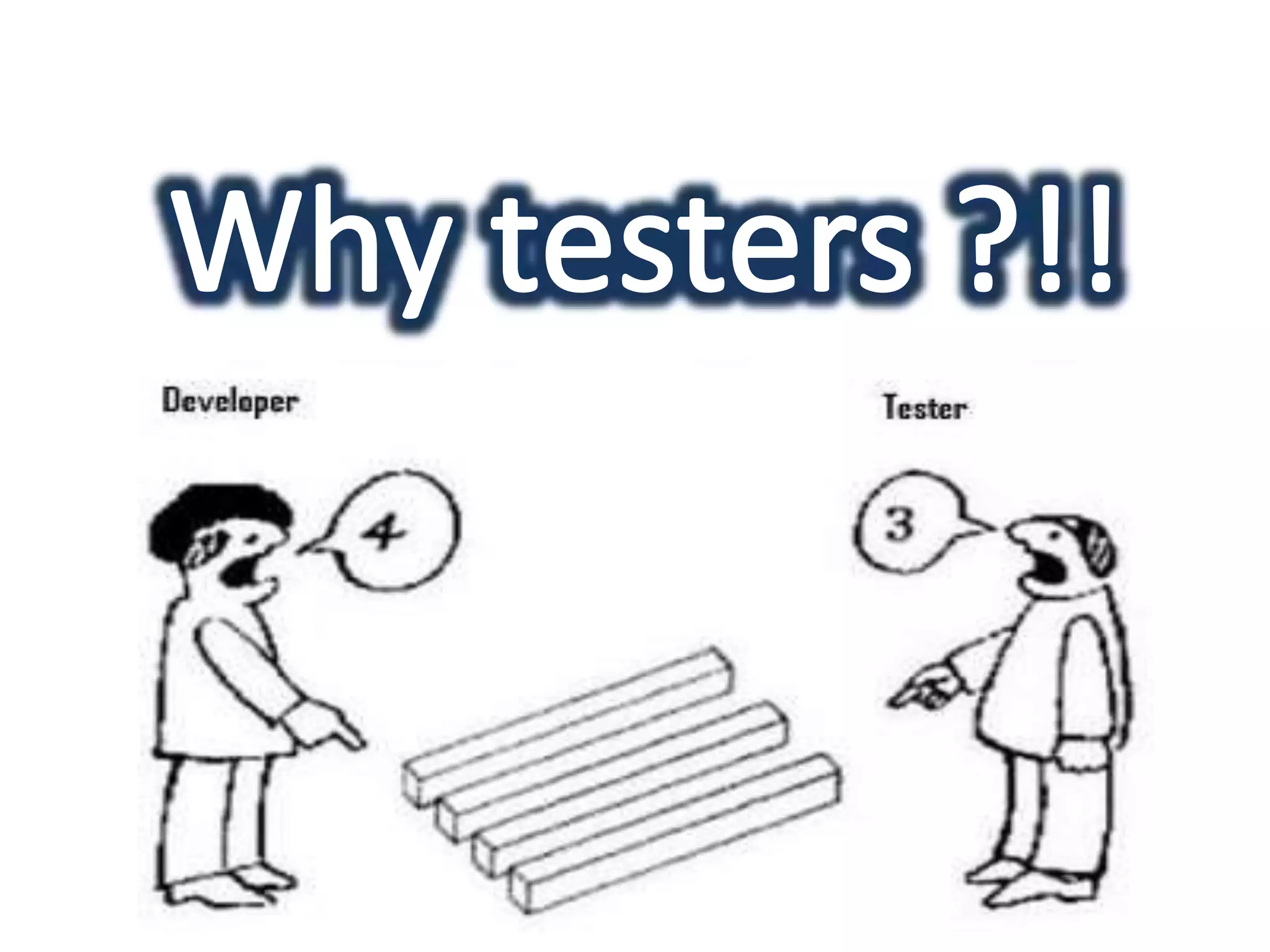
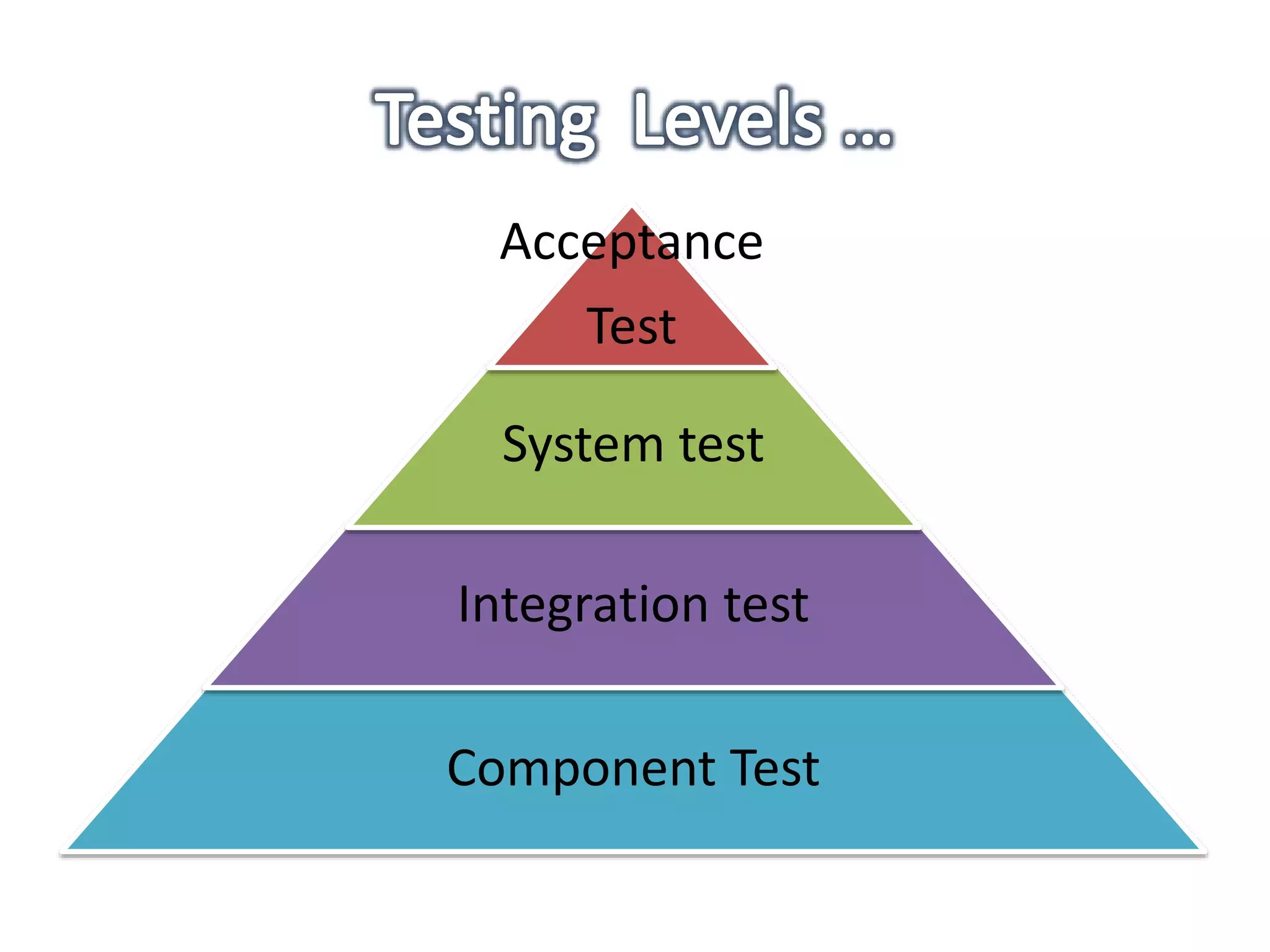
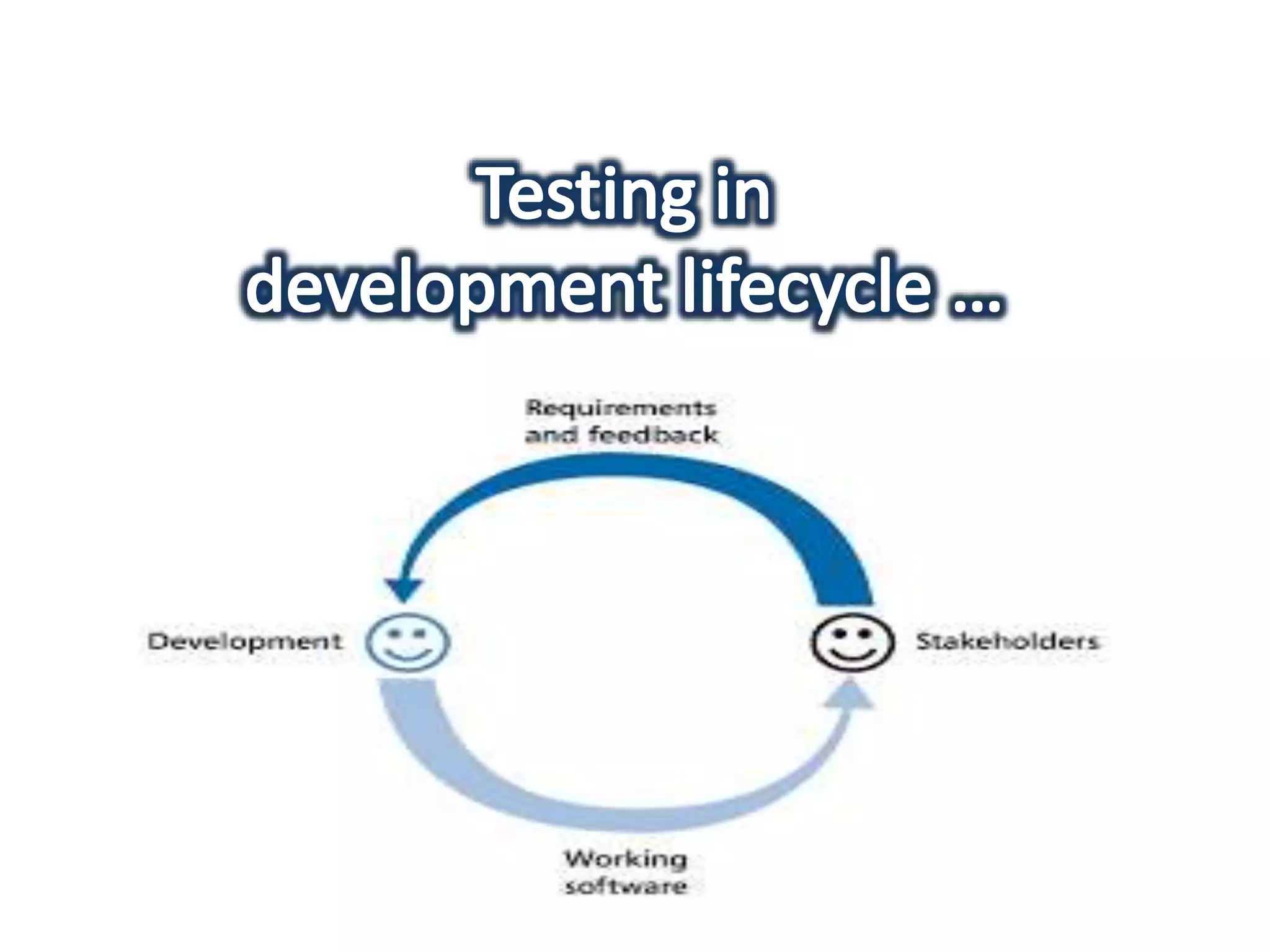
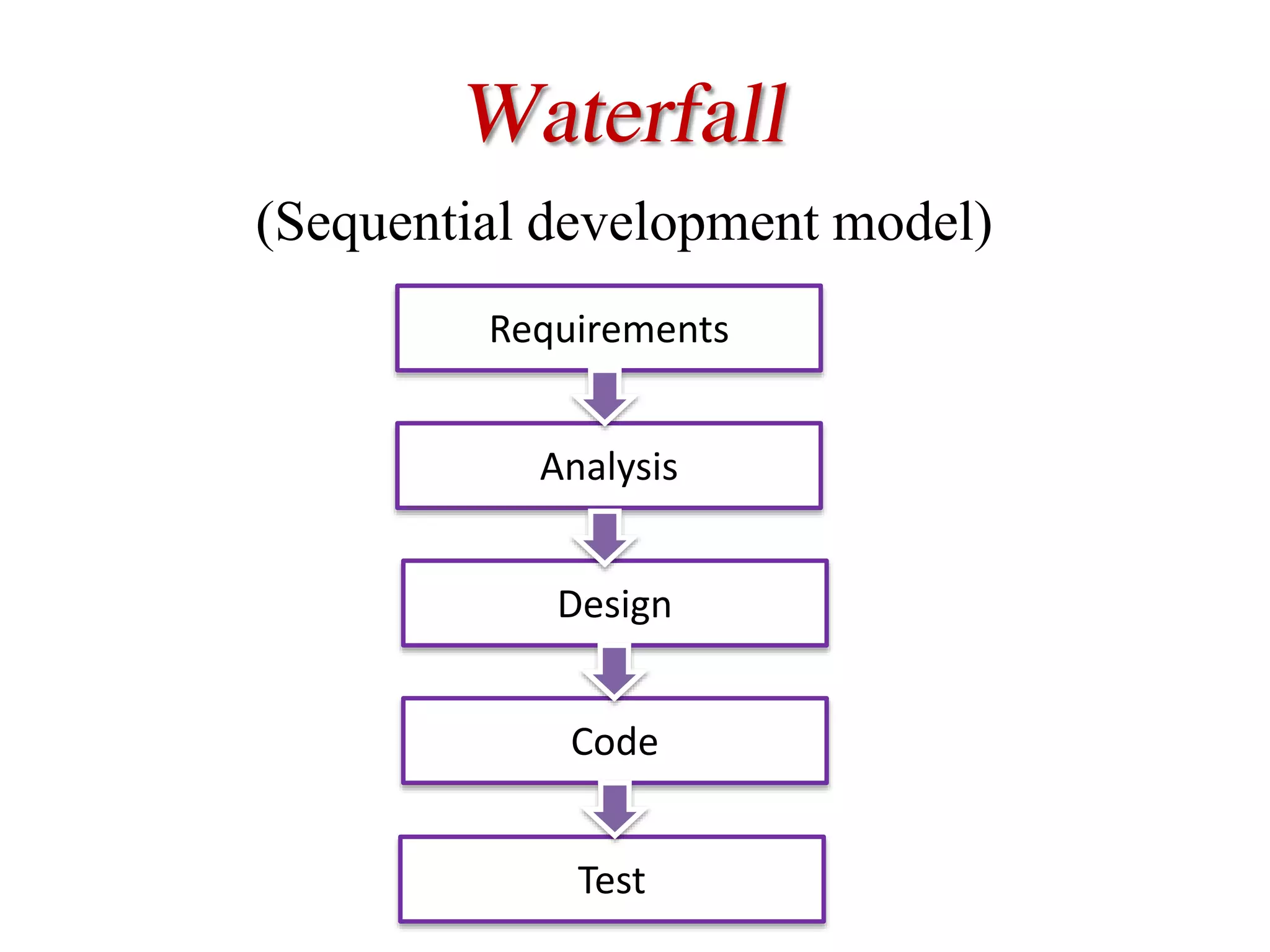
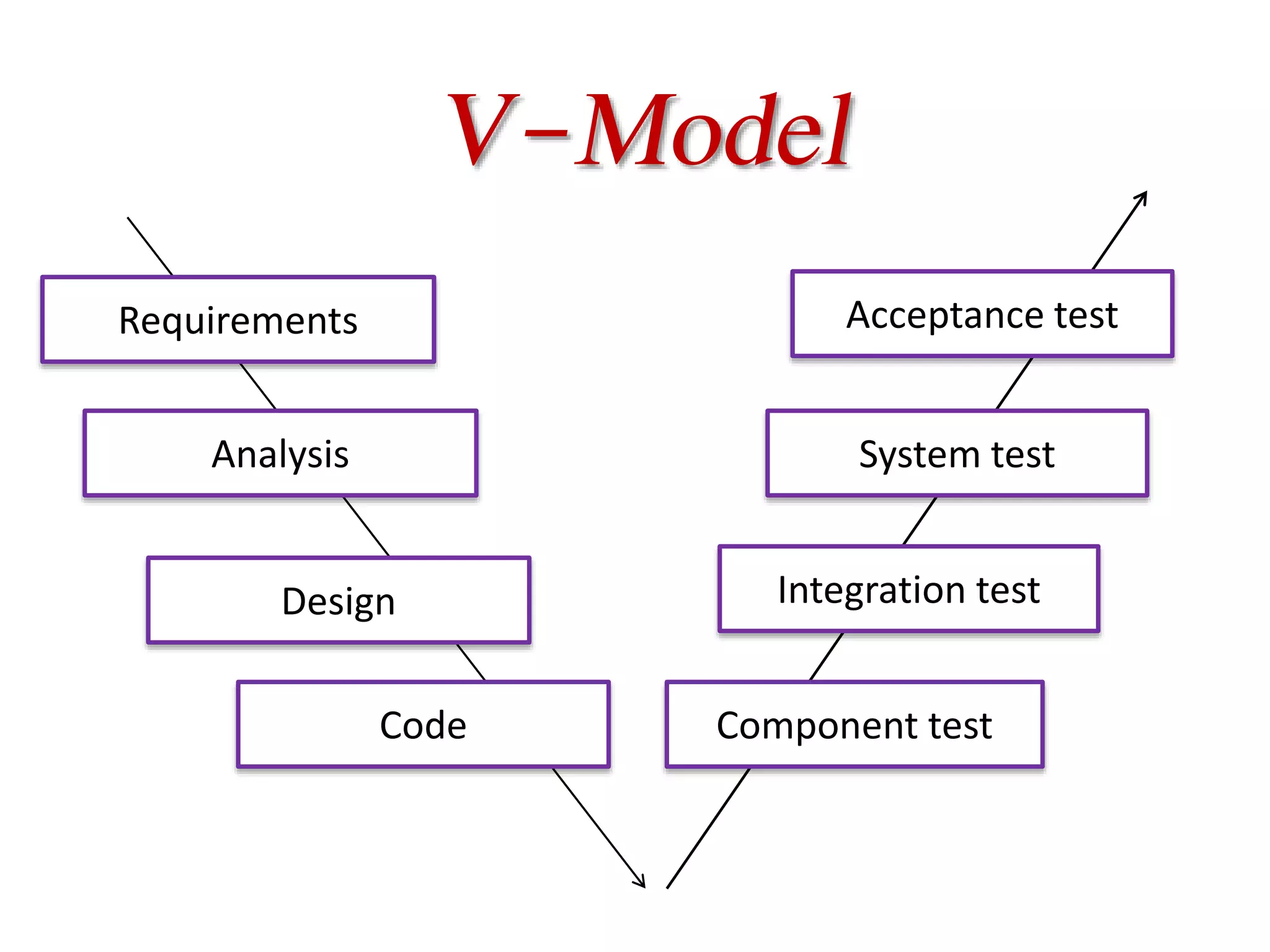
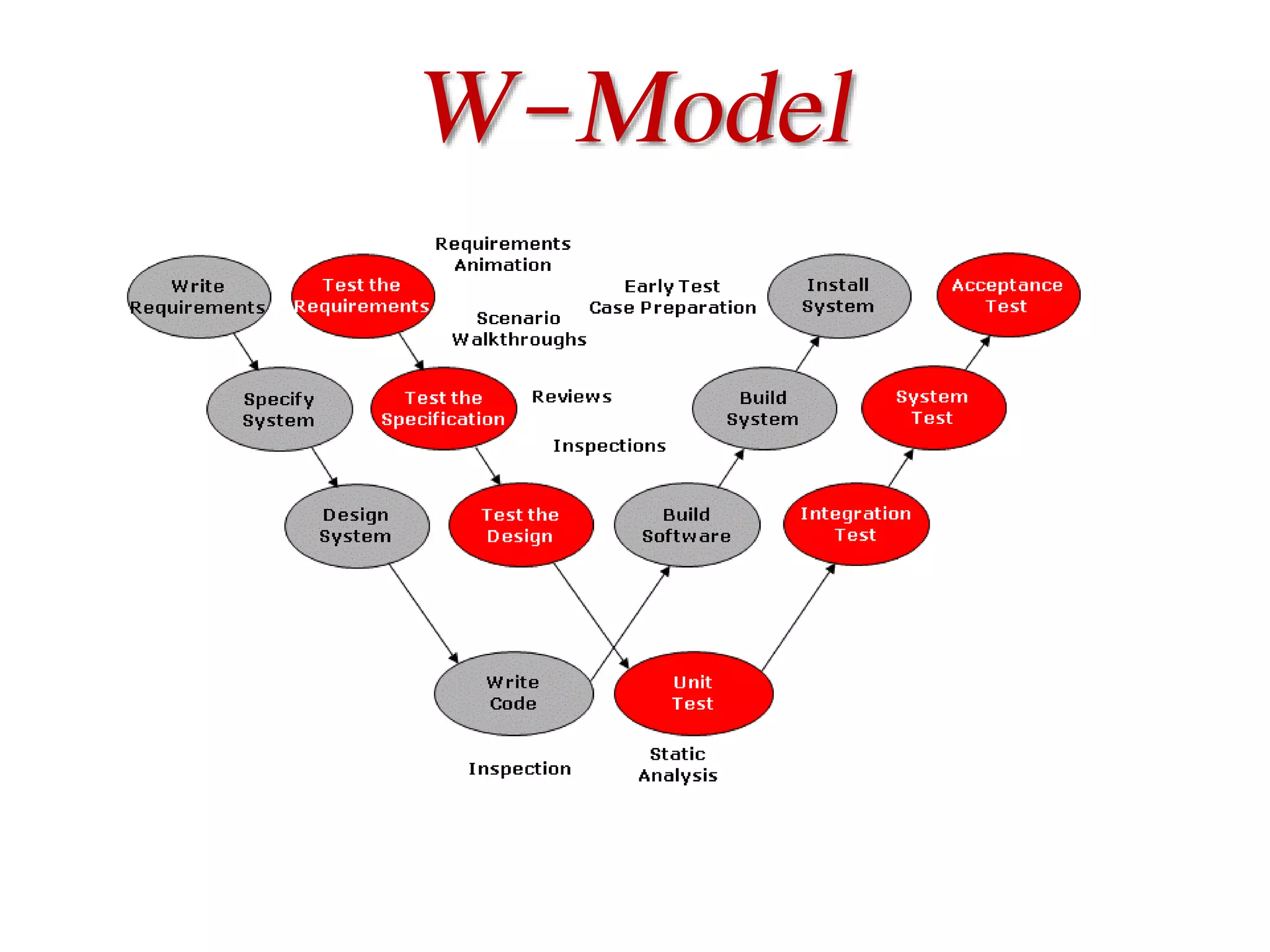
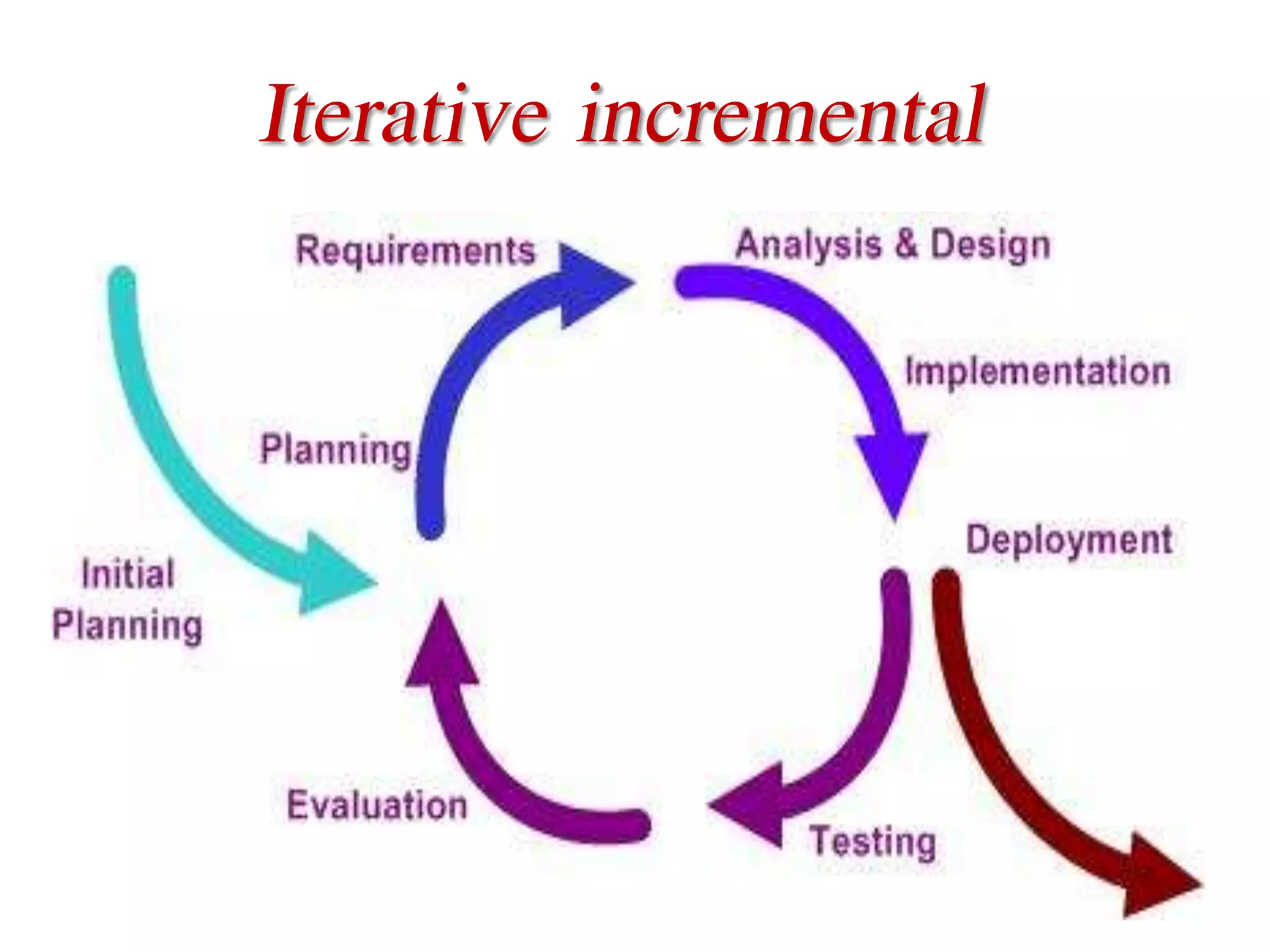
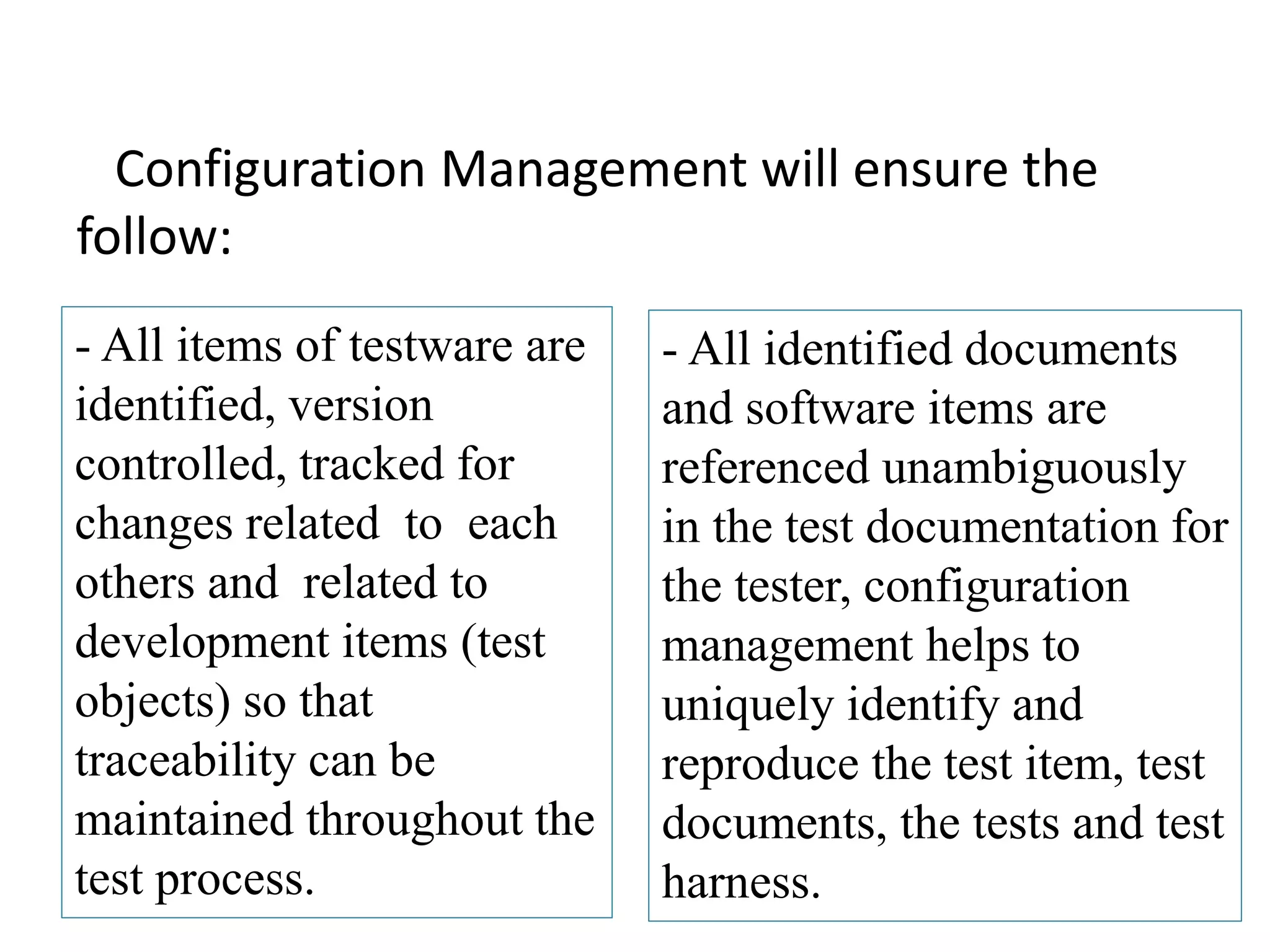
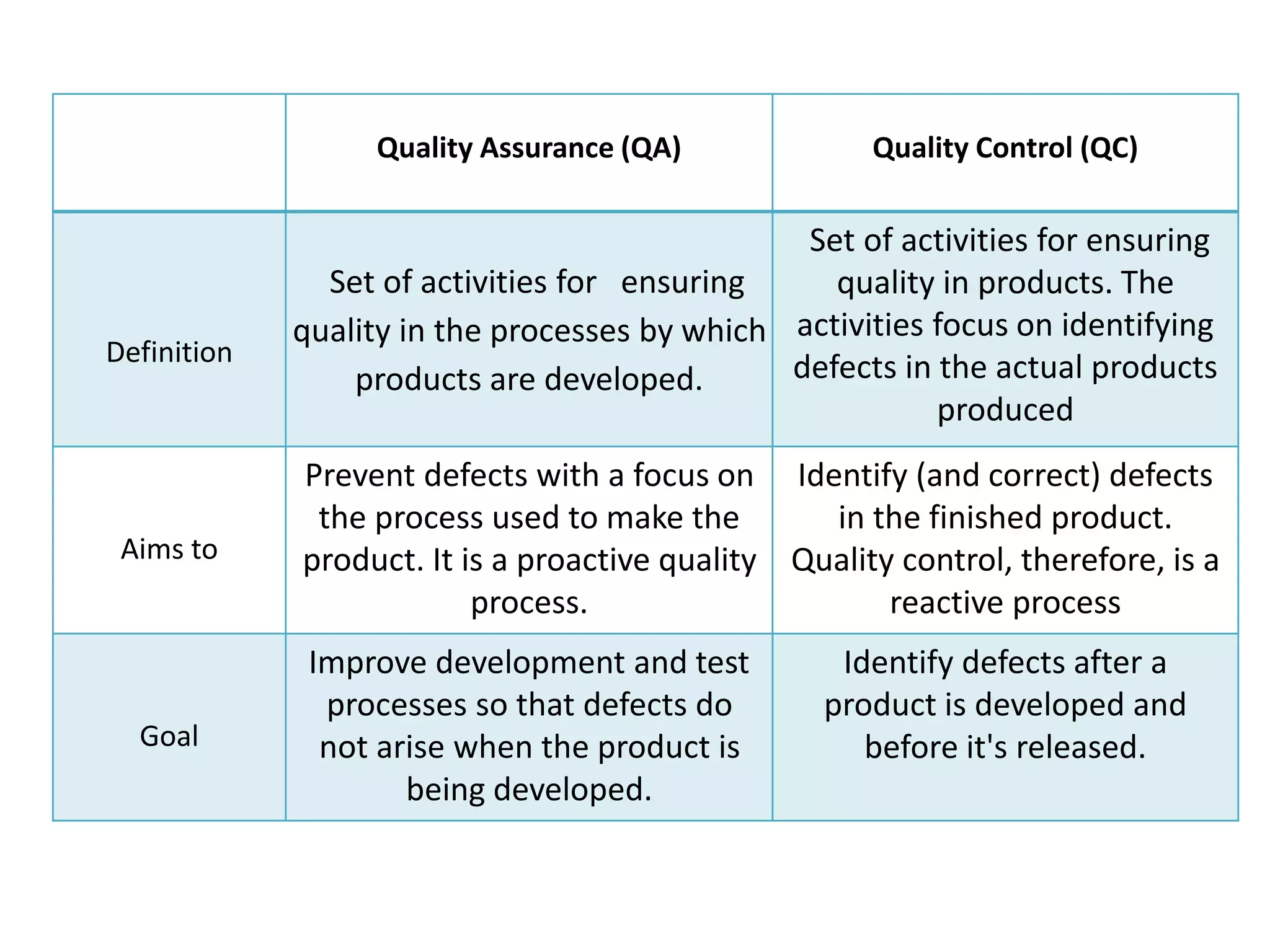
This document provides an overview of software testing concepts and processes. It discusses why testing is important, defines common testing terms, and outlines the typical phases of a testing lifecycle including planning, analysis, implementation, evaluation, and closure. It also describes different testing techniques like static reviews, functional testing, and performance testing. Risks of poor quality like defects, failures, and their impacts on humans, economy, business are highlighted. The roles of testers and differences between quality assurance and quality control are defined. Examples of testing in various industries are provided.