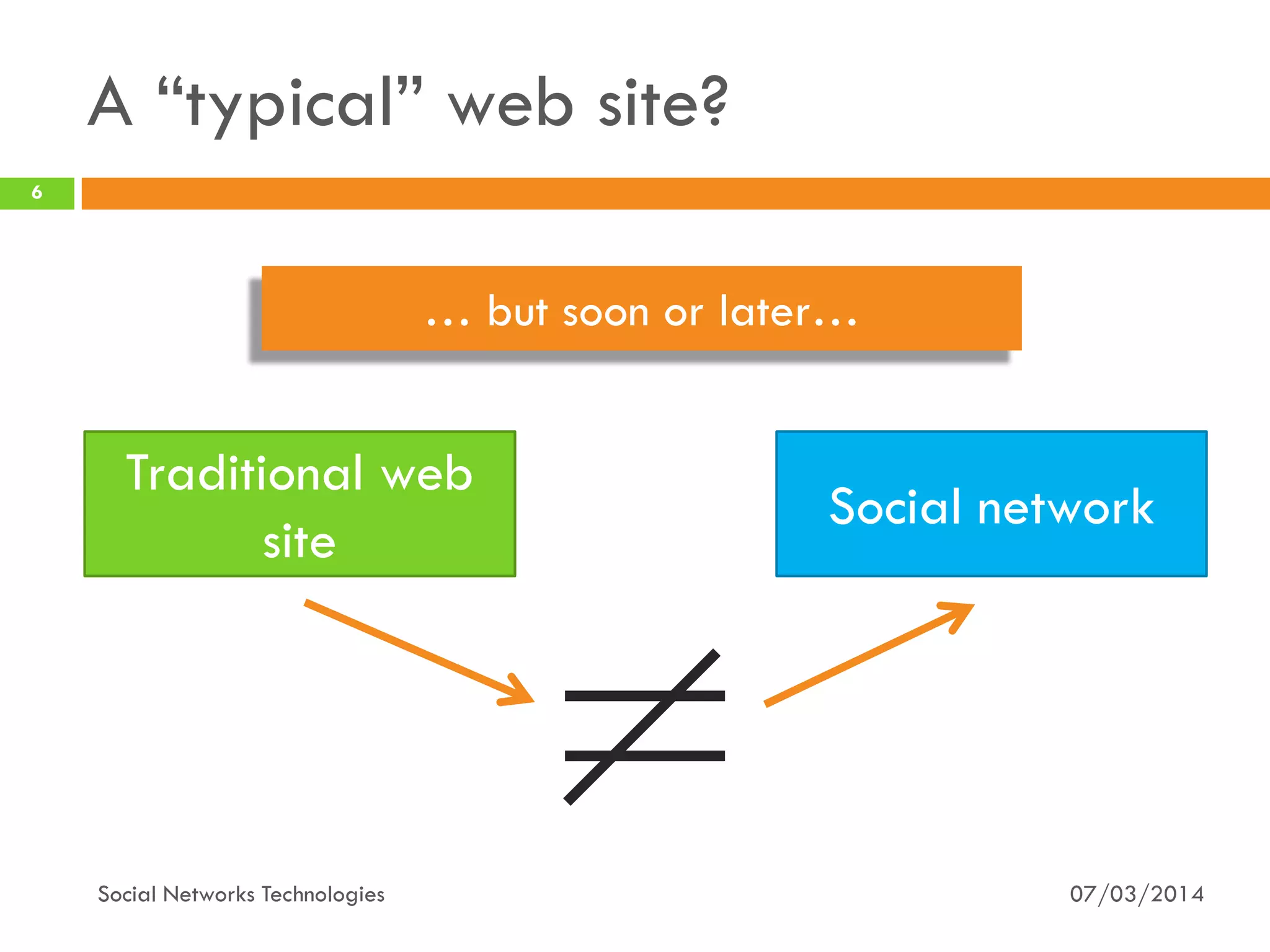
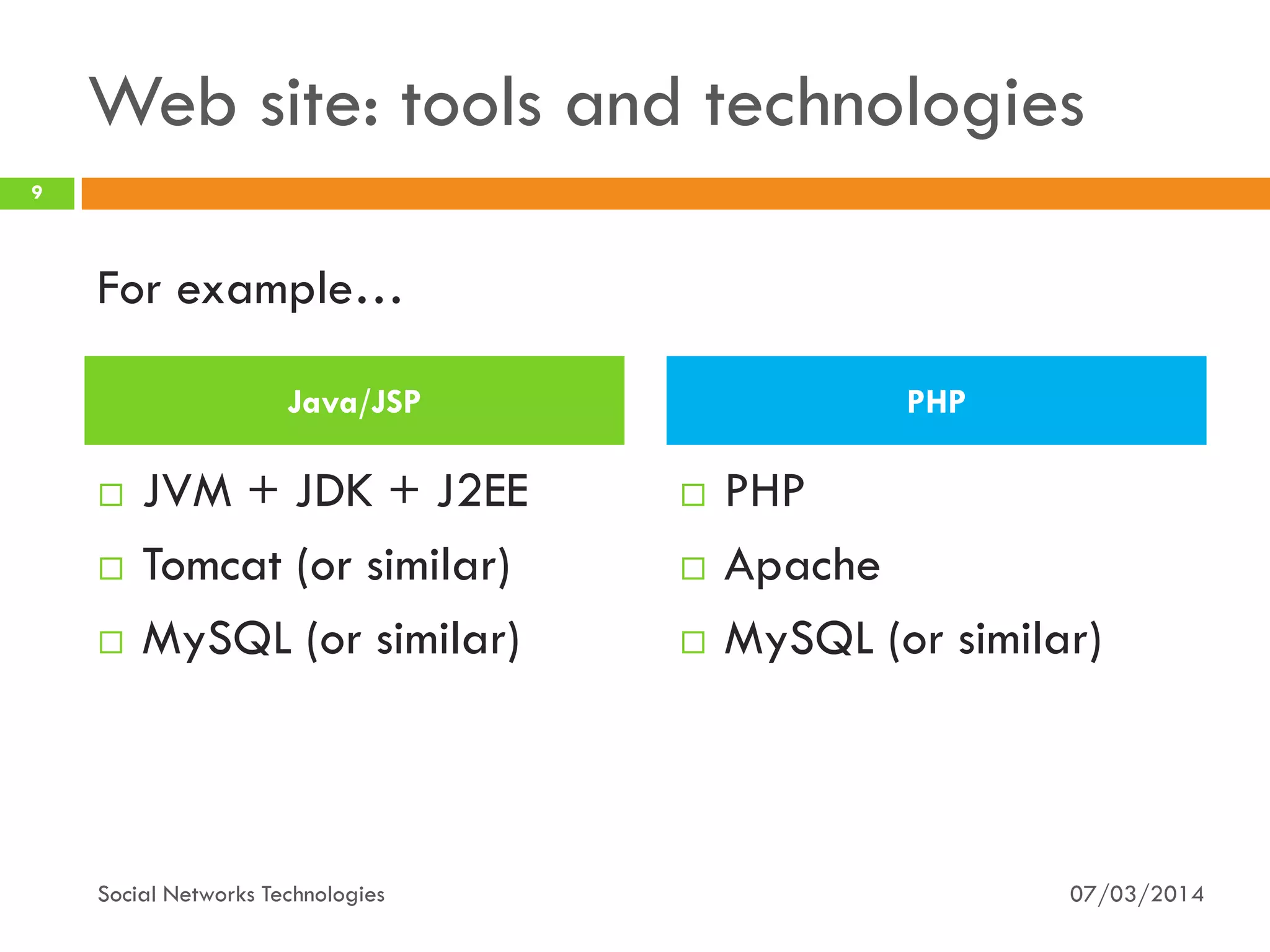
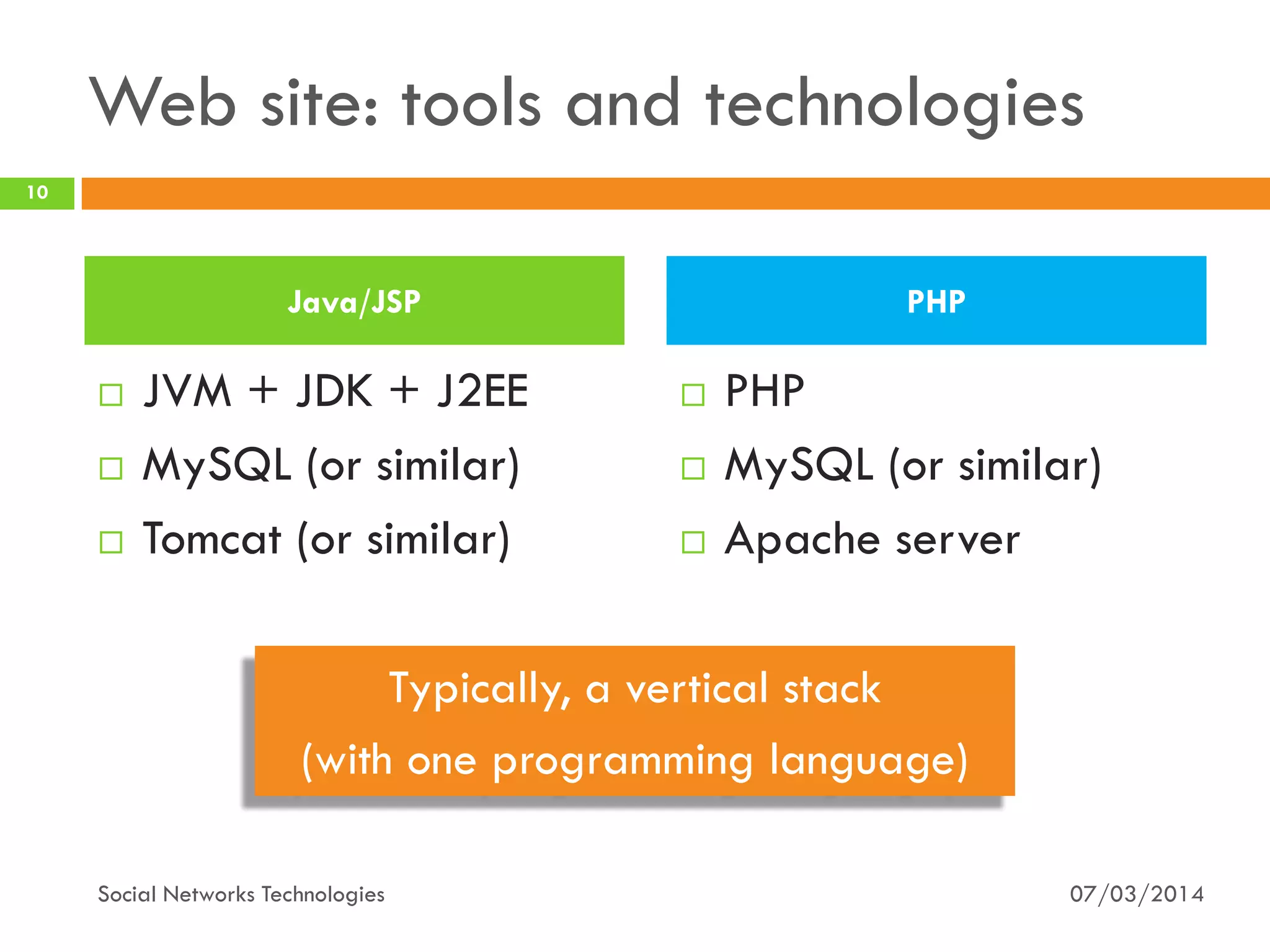
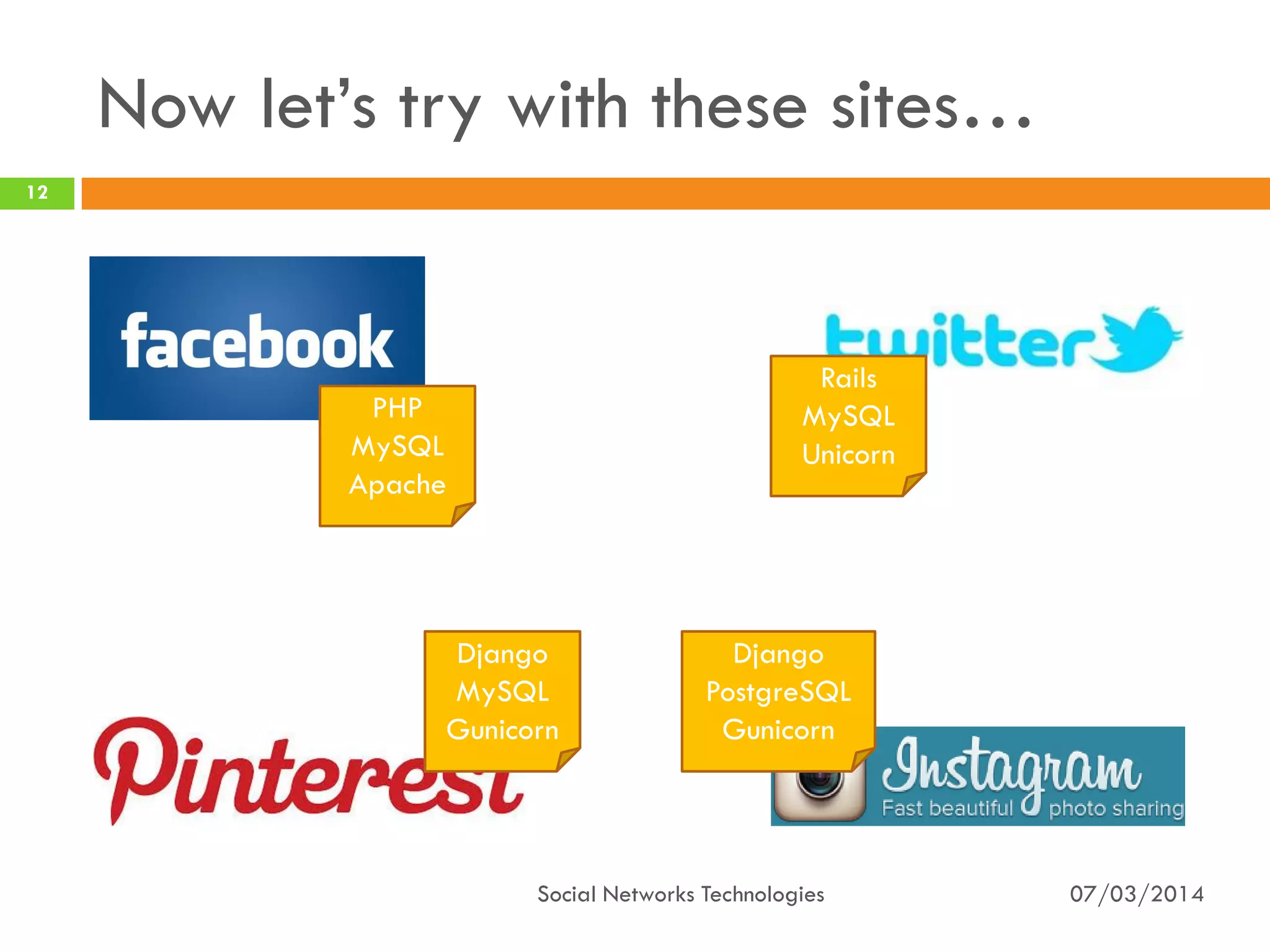
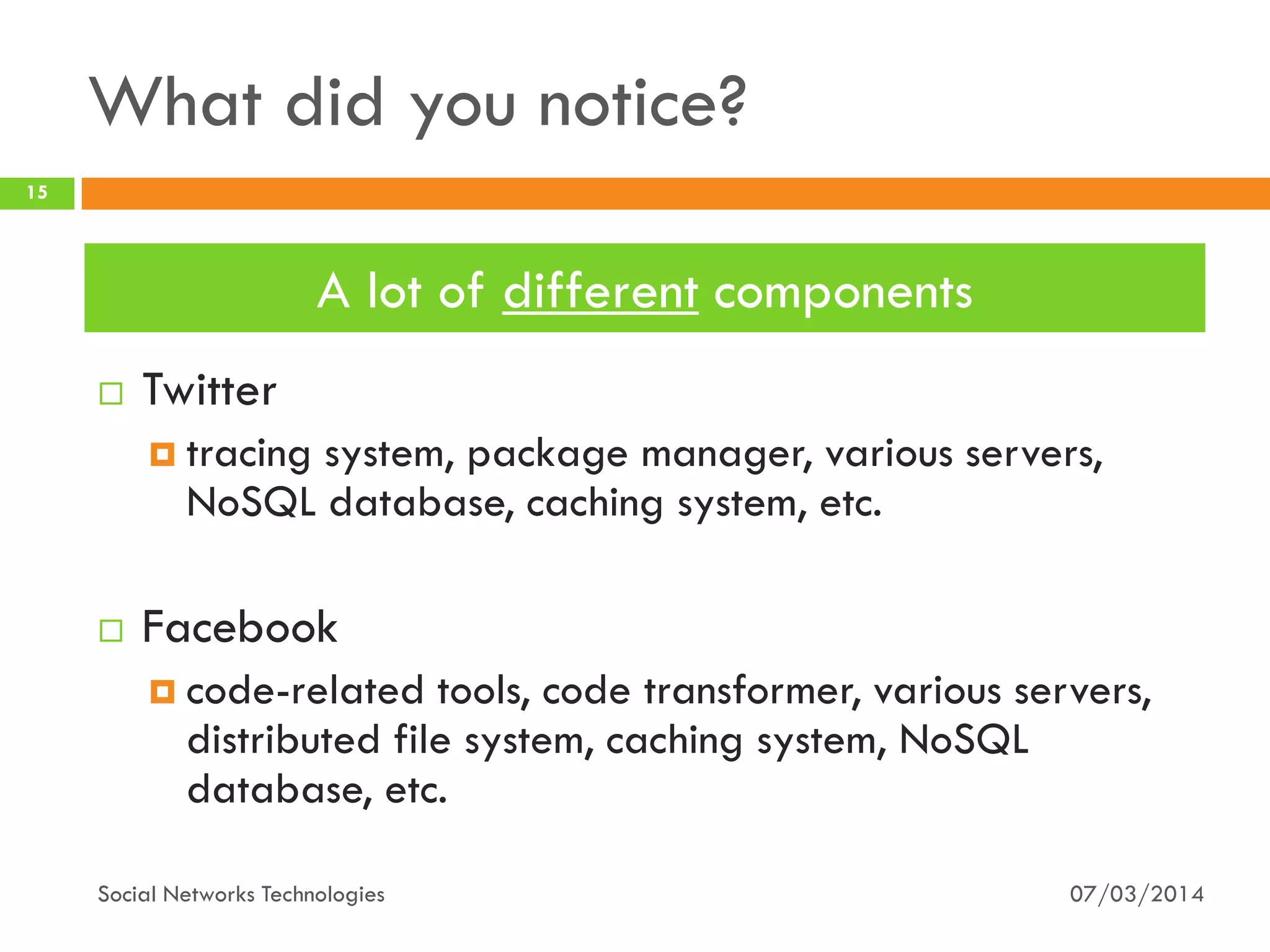
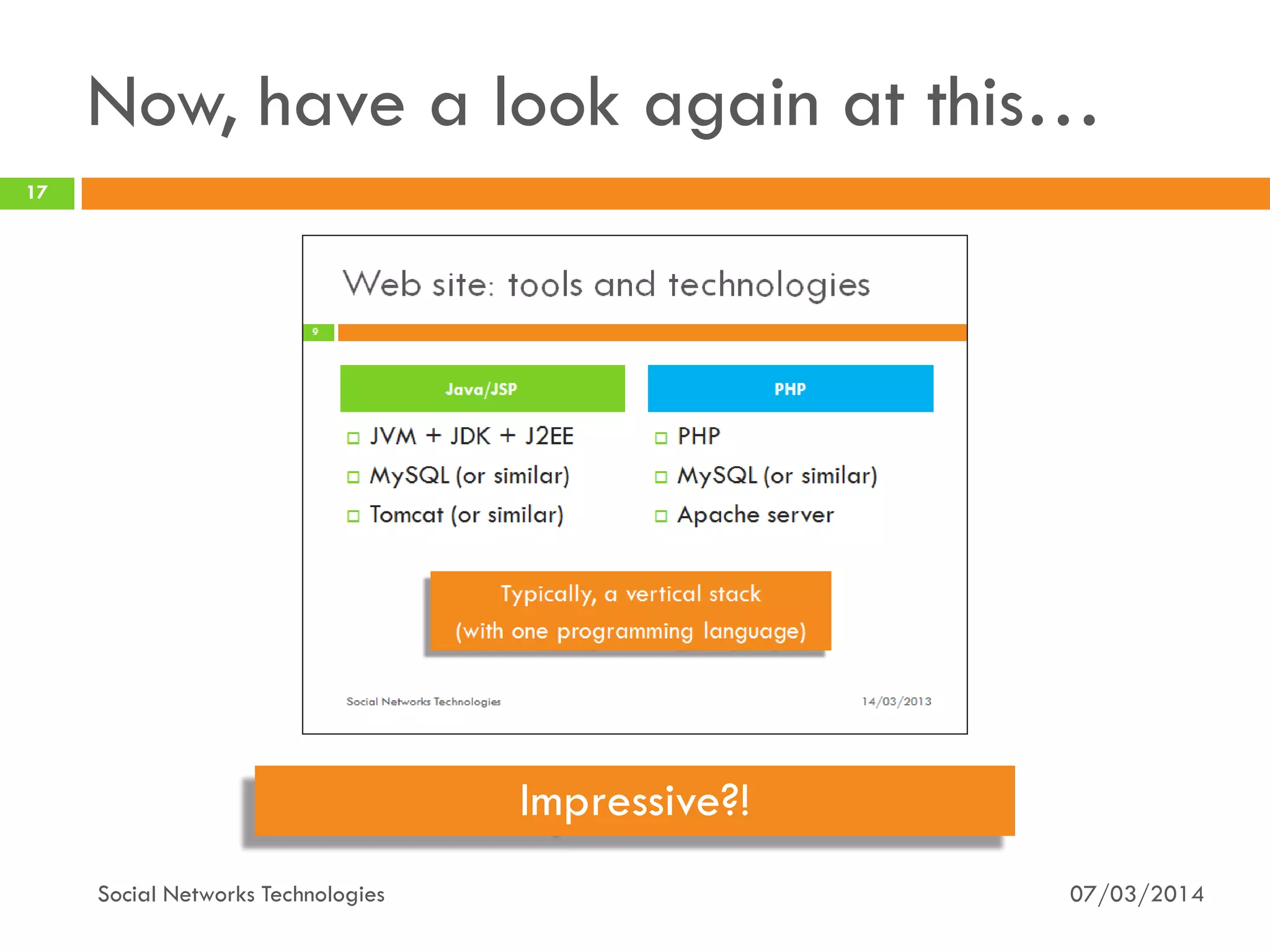
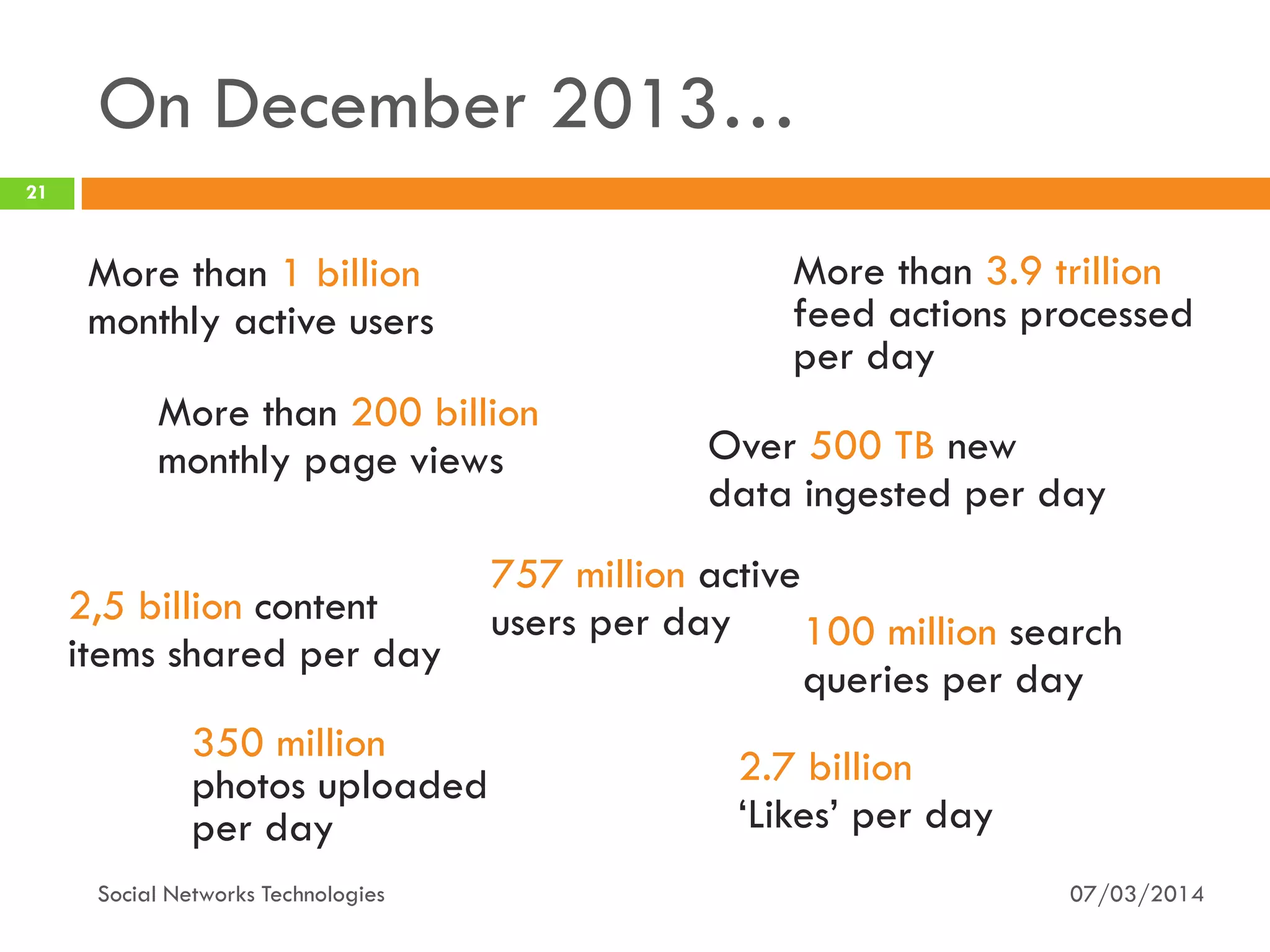
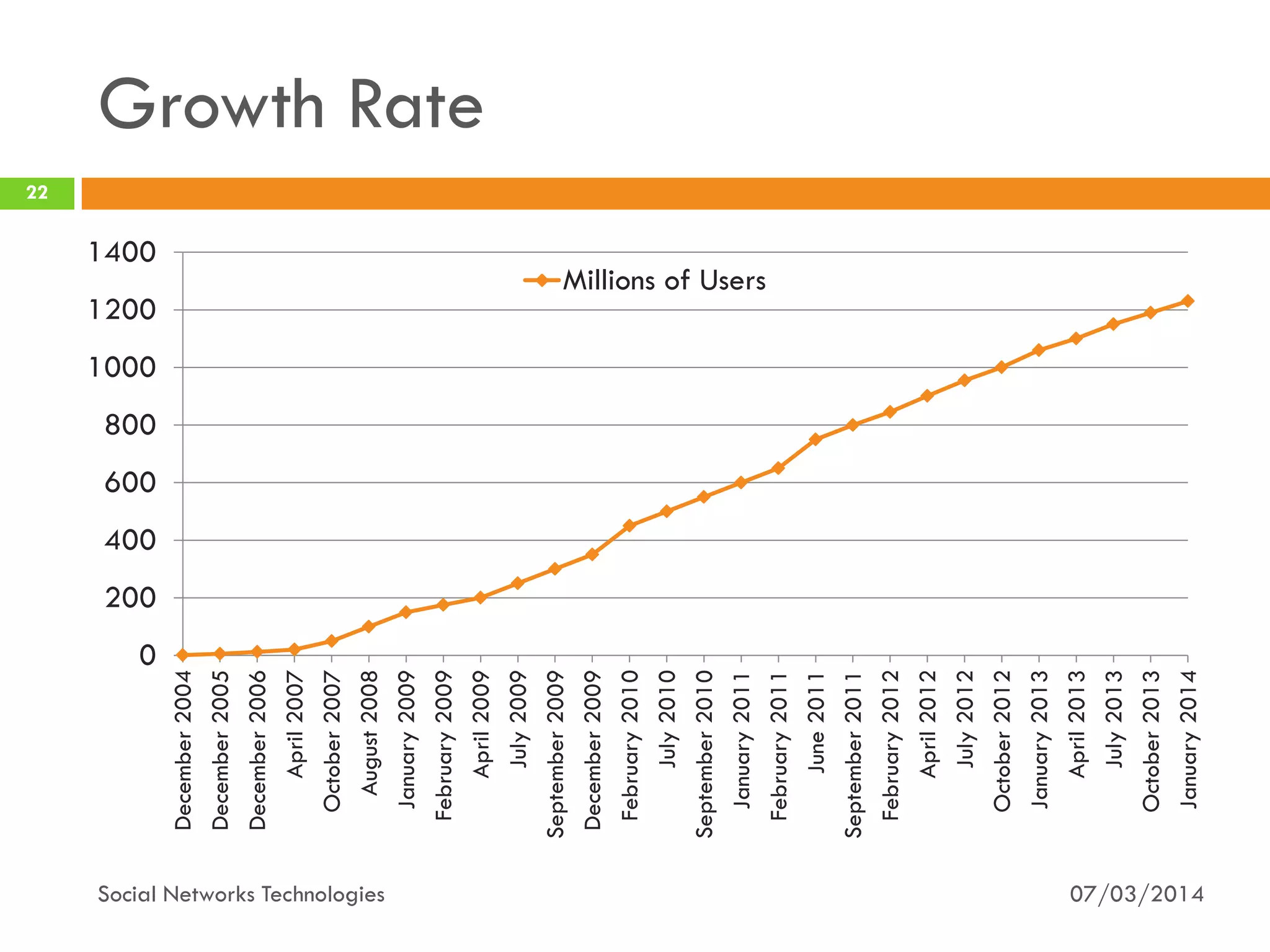
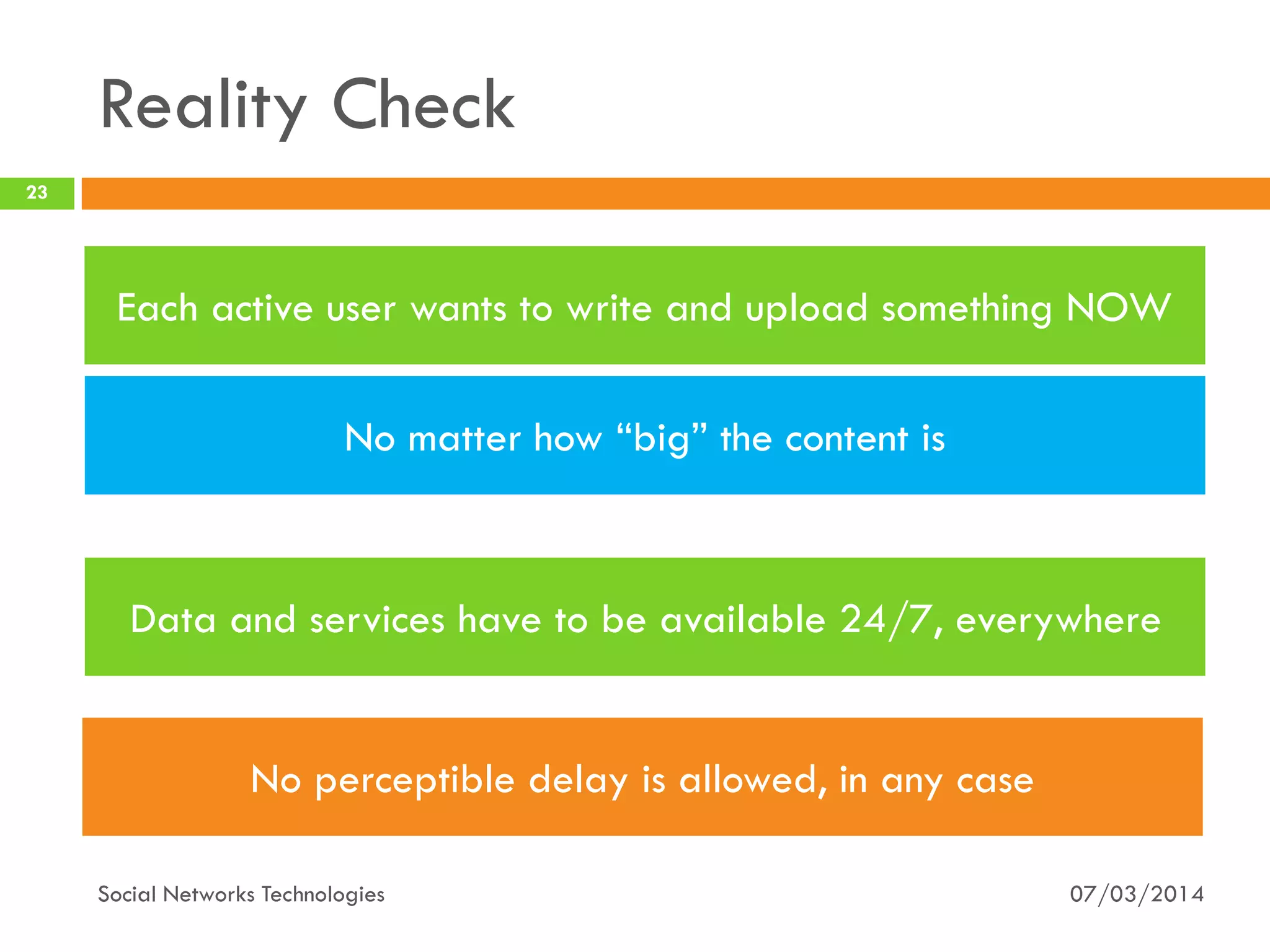
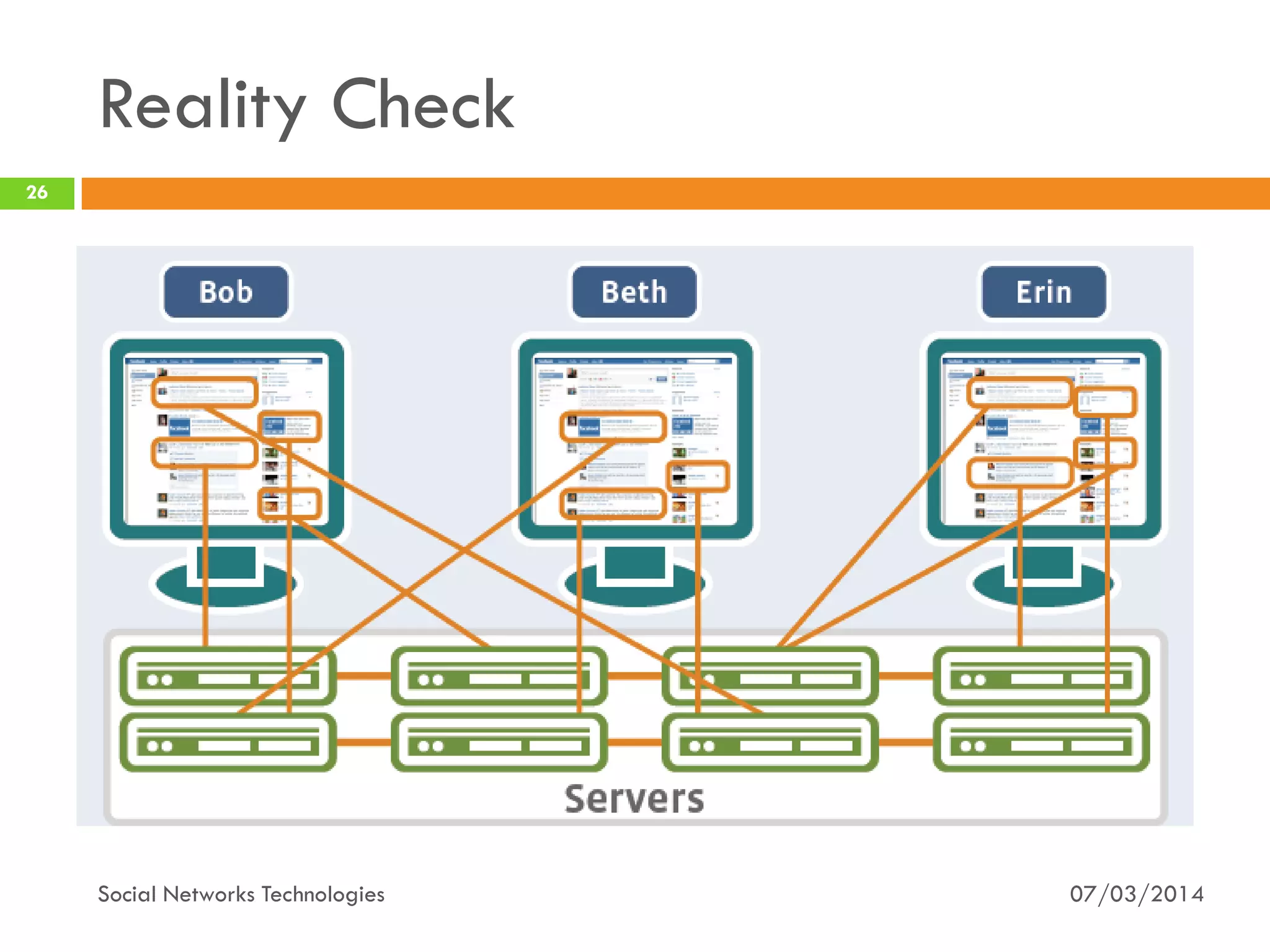
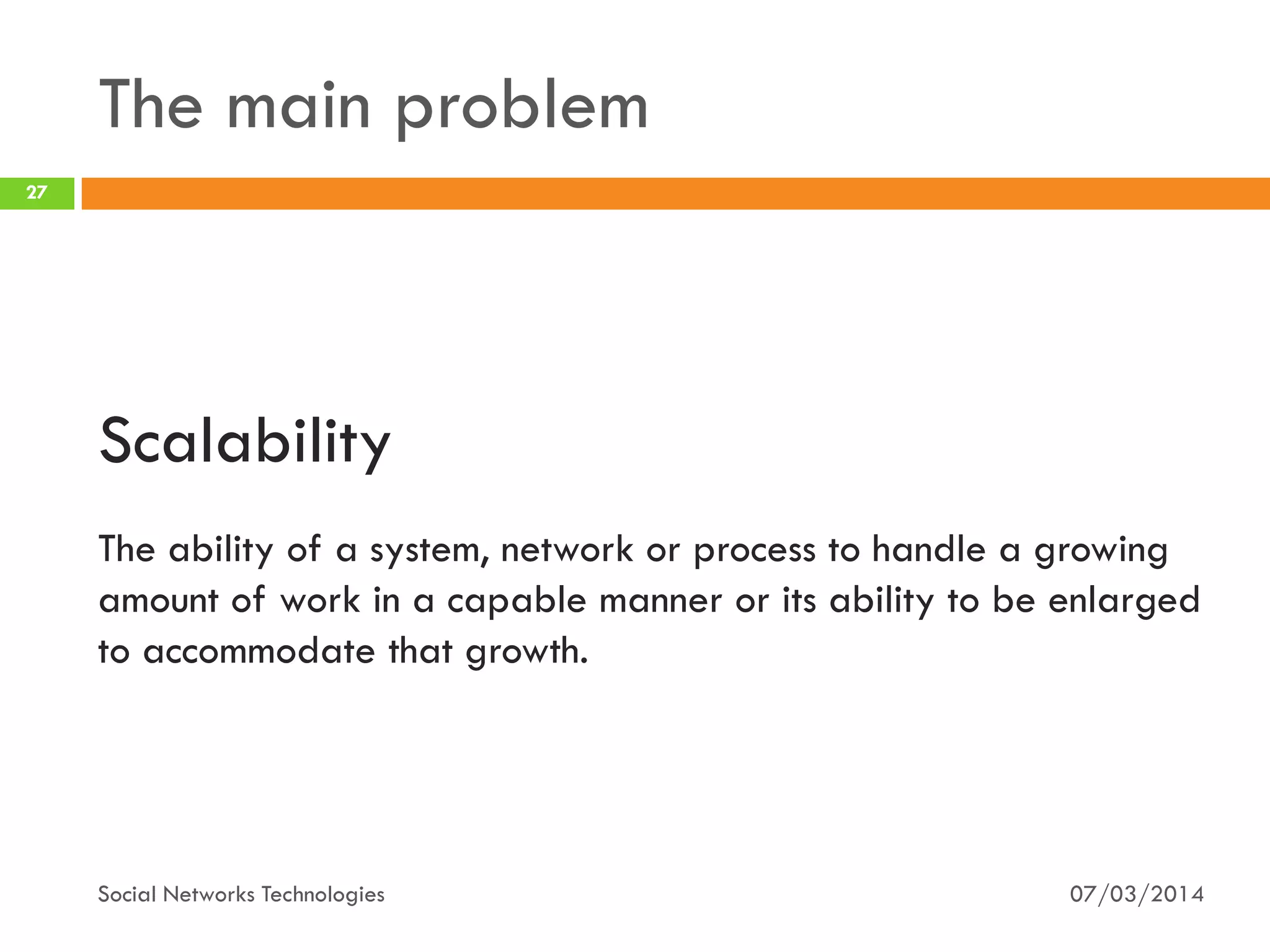
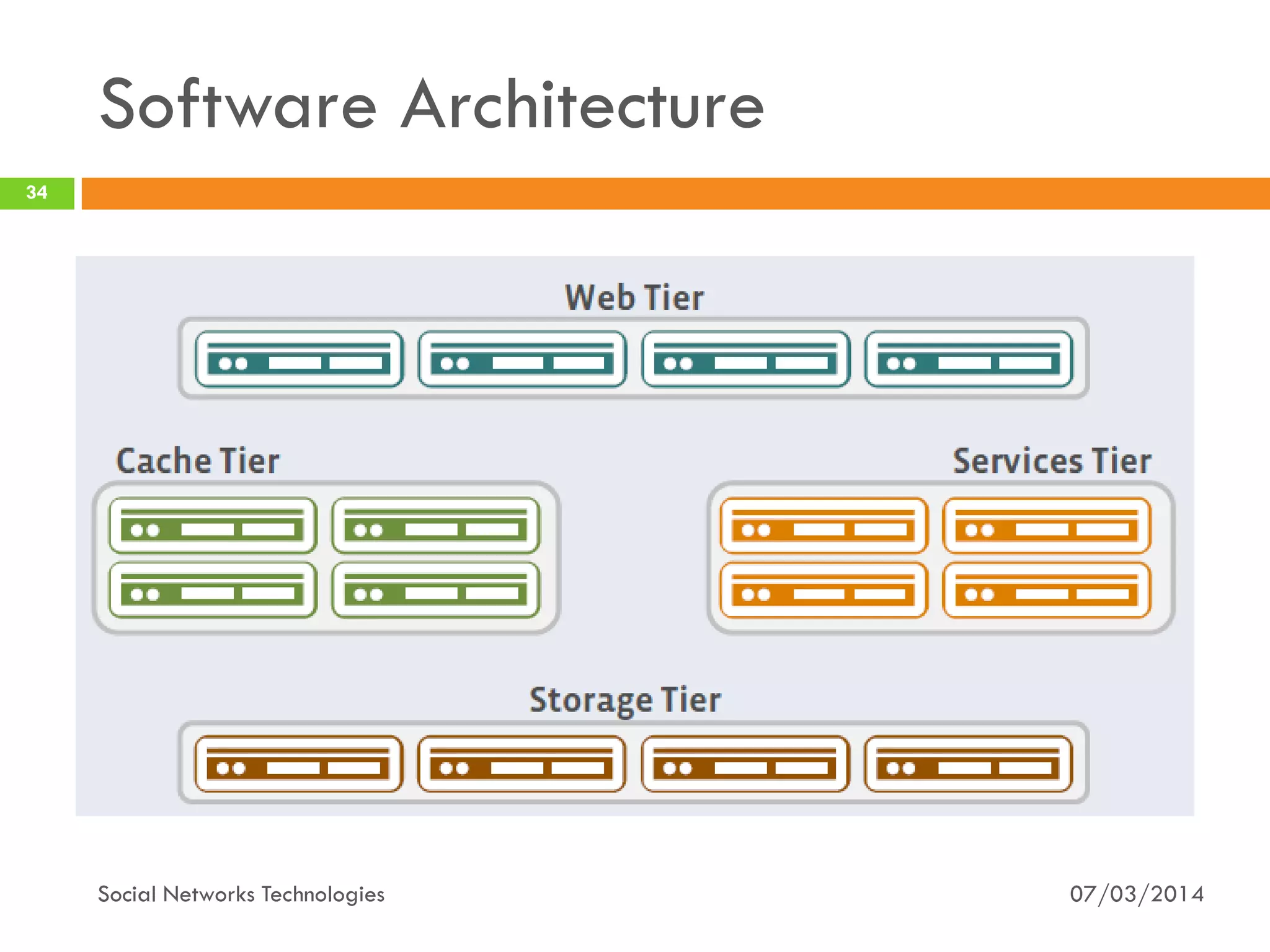
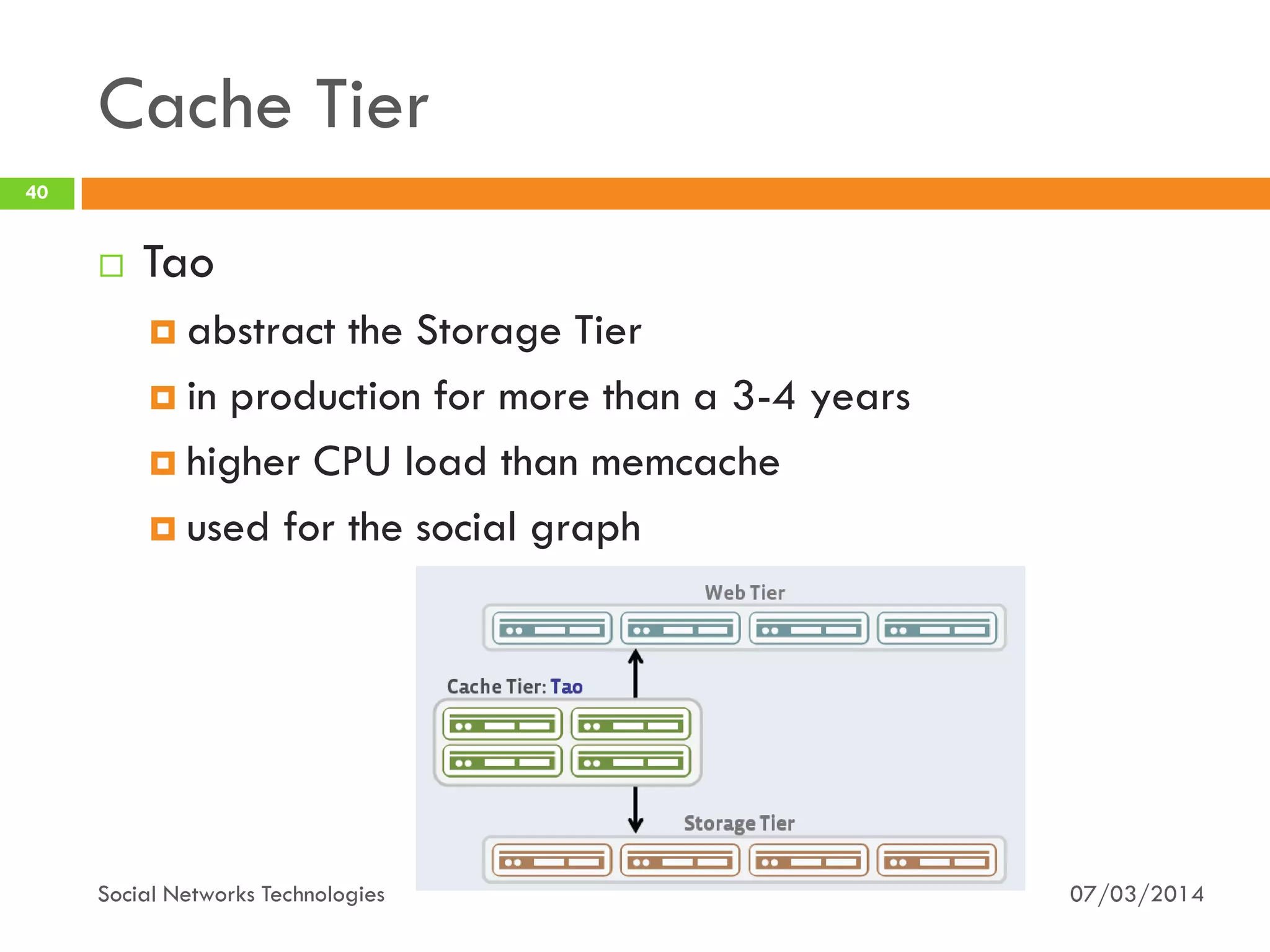
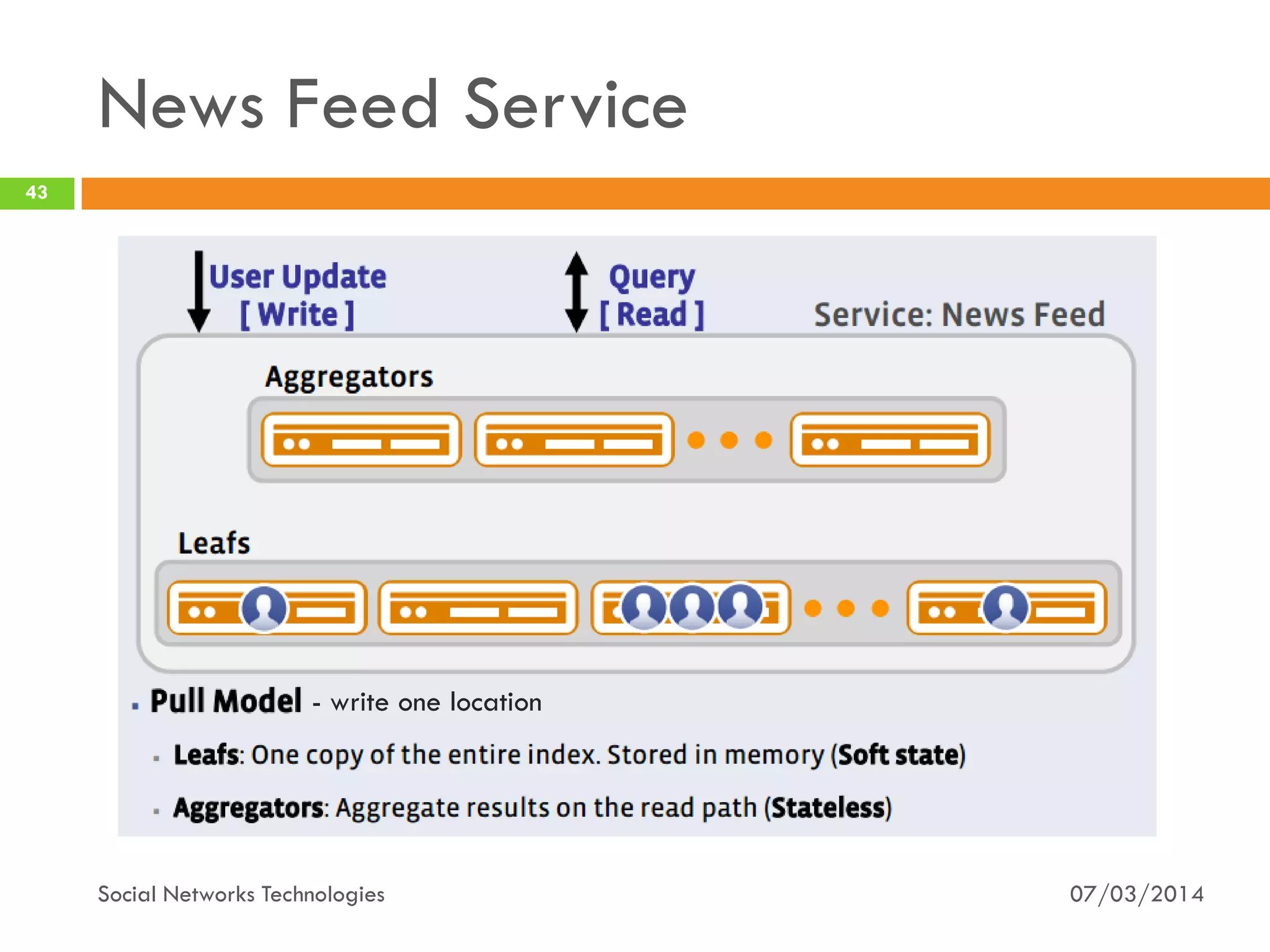
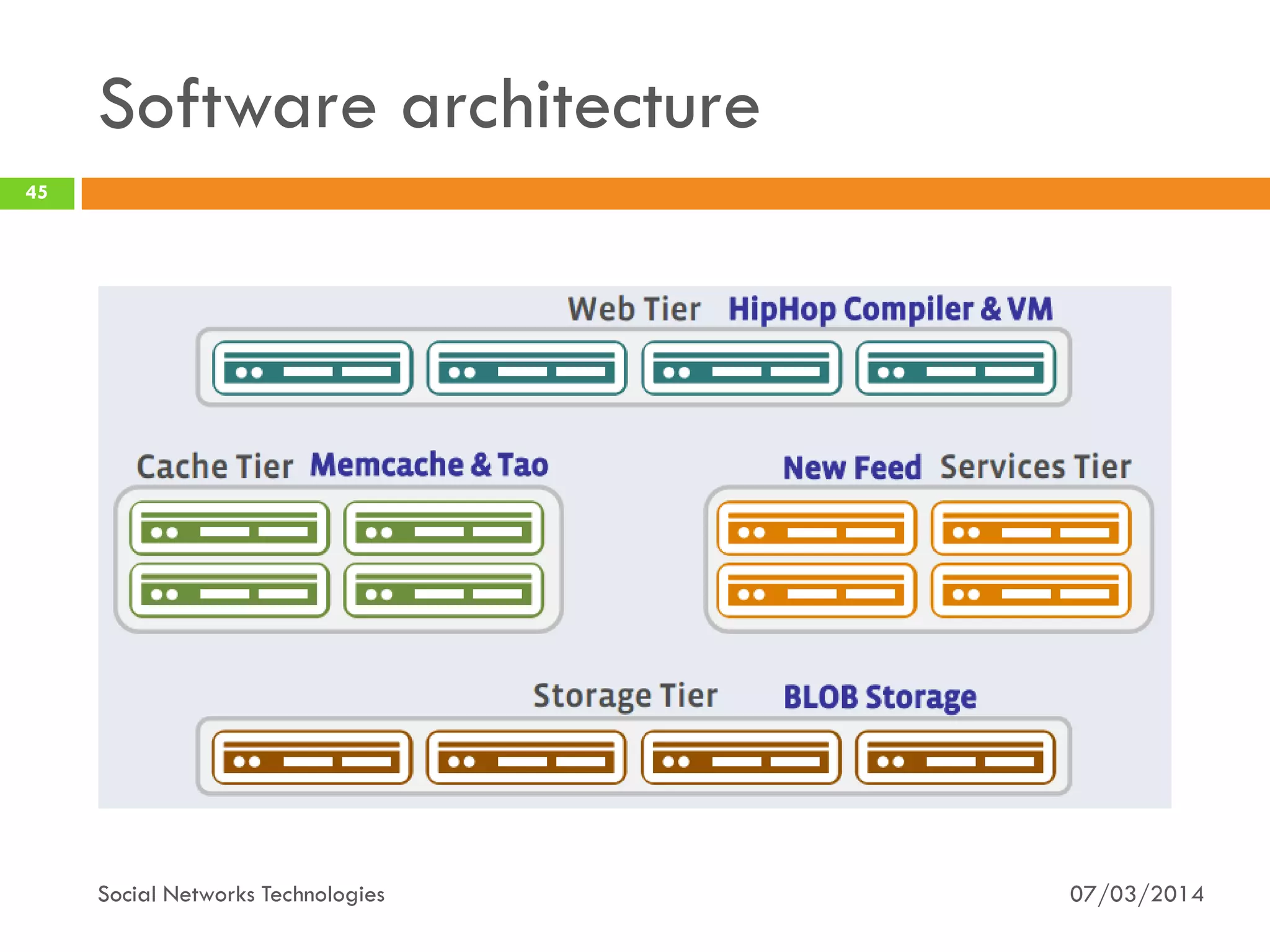
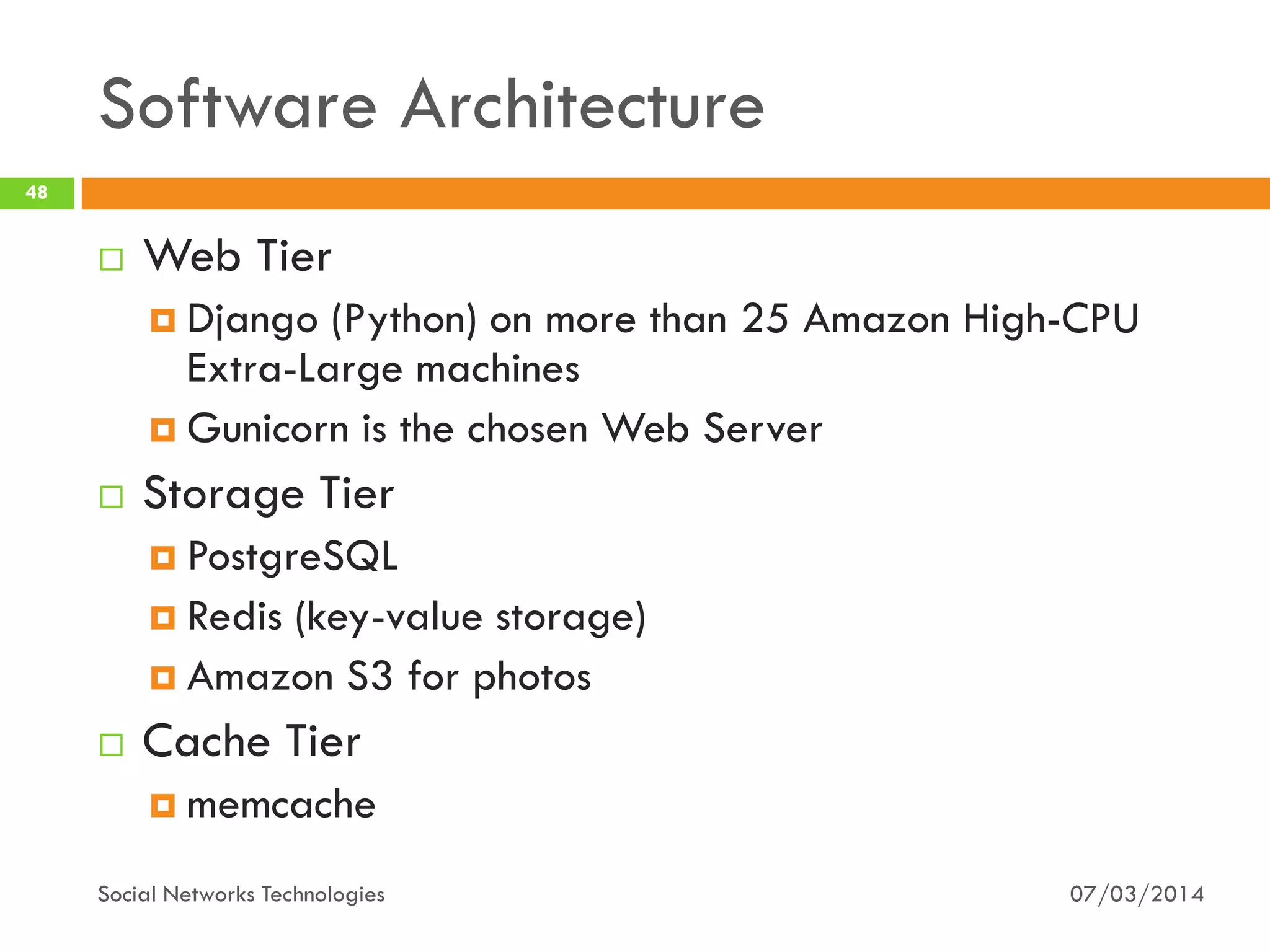
The document provides an overview of social network technologies, focusing on the tools, languages, and architectures used by platforms like Facebook and Instagram. It highlights the challenges of scalability and performance due to the vast user base and content processed daily. The document concludes that social networks evolve from traditional websites while adapting and innovating their infrastructure to handle growth and user demands.