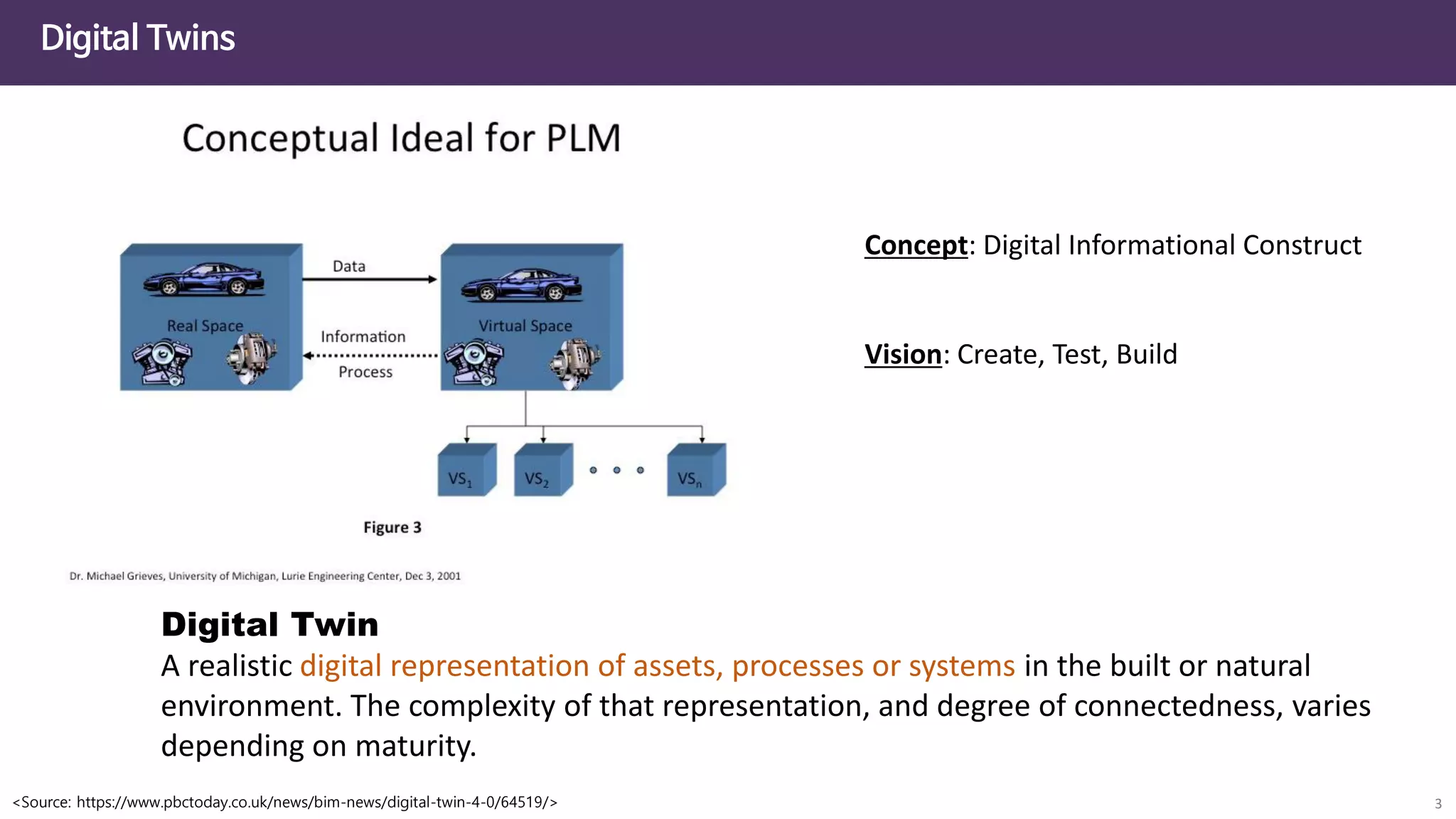
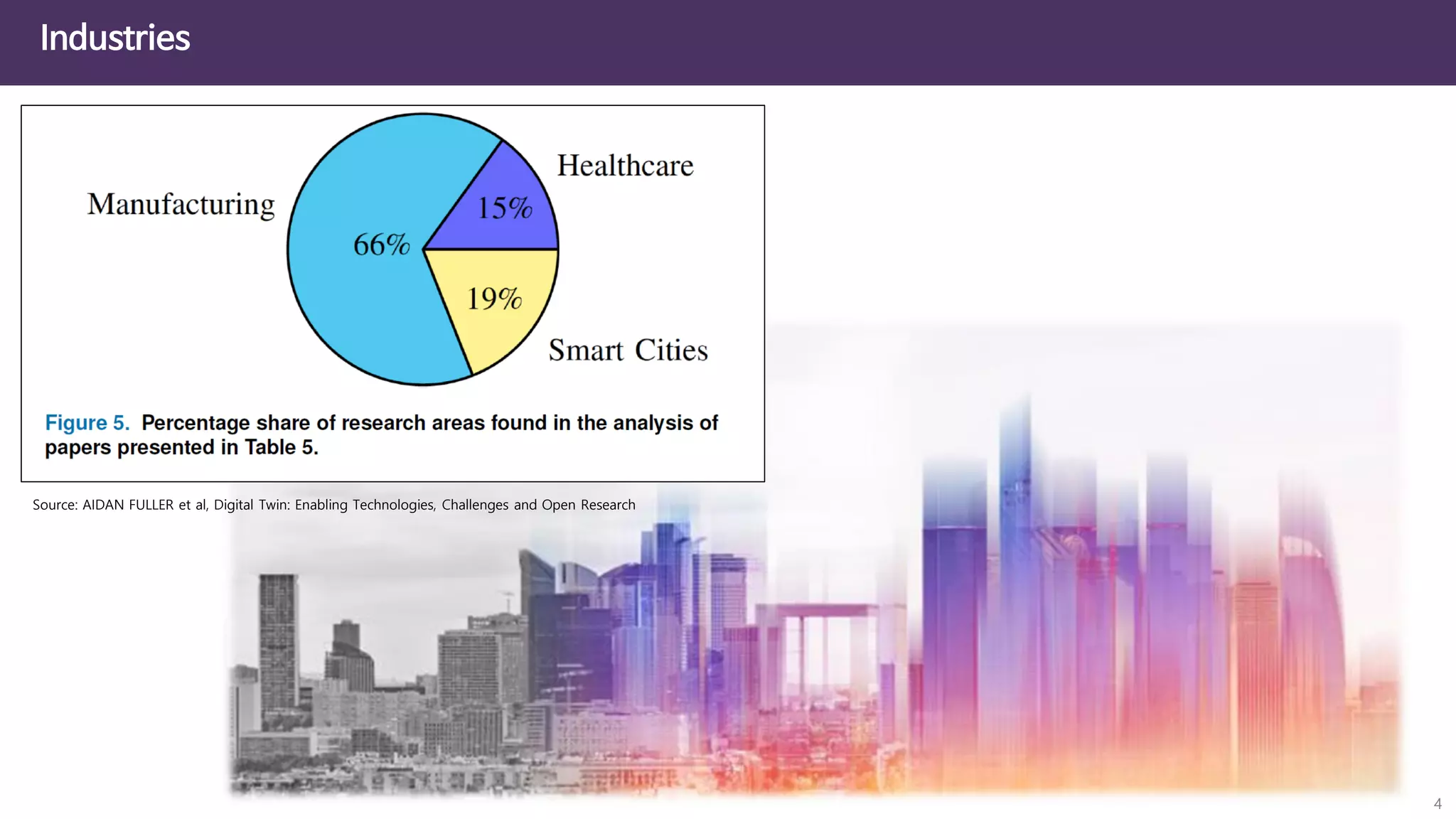
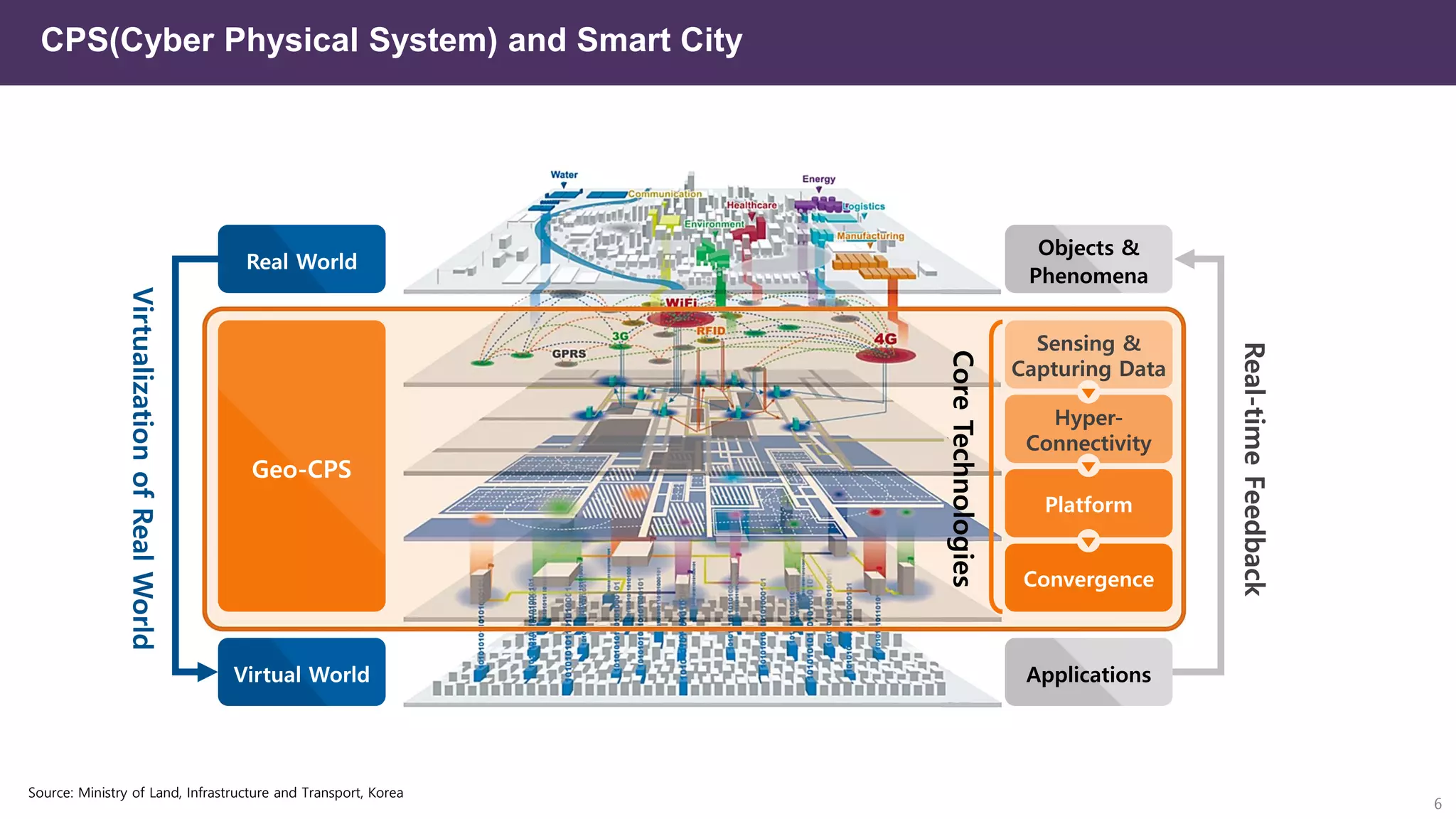
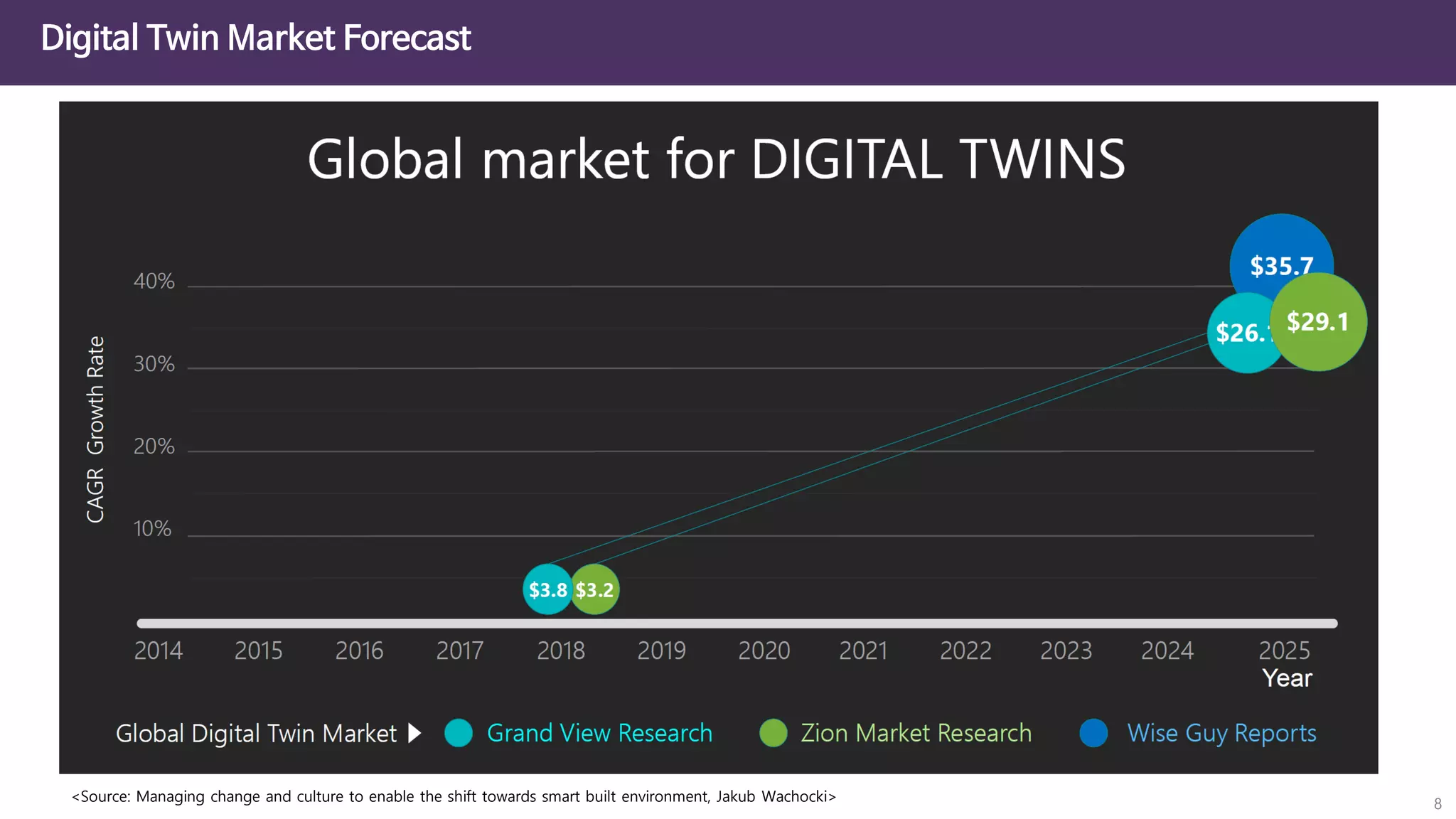
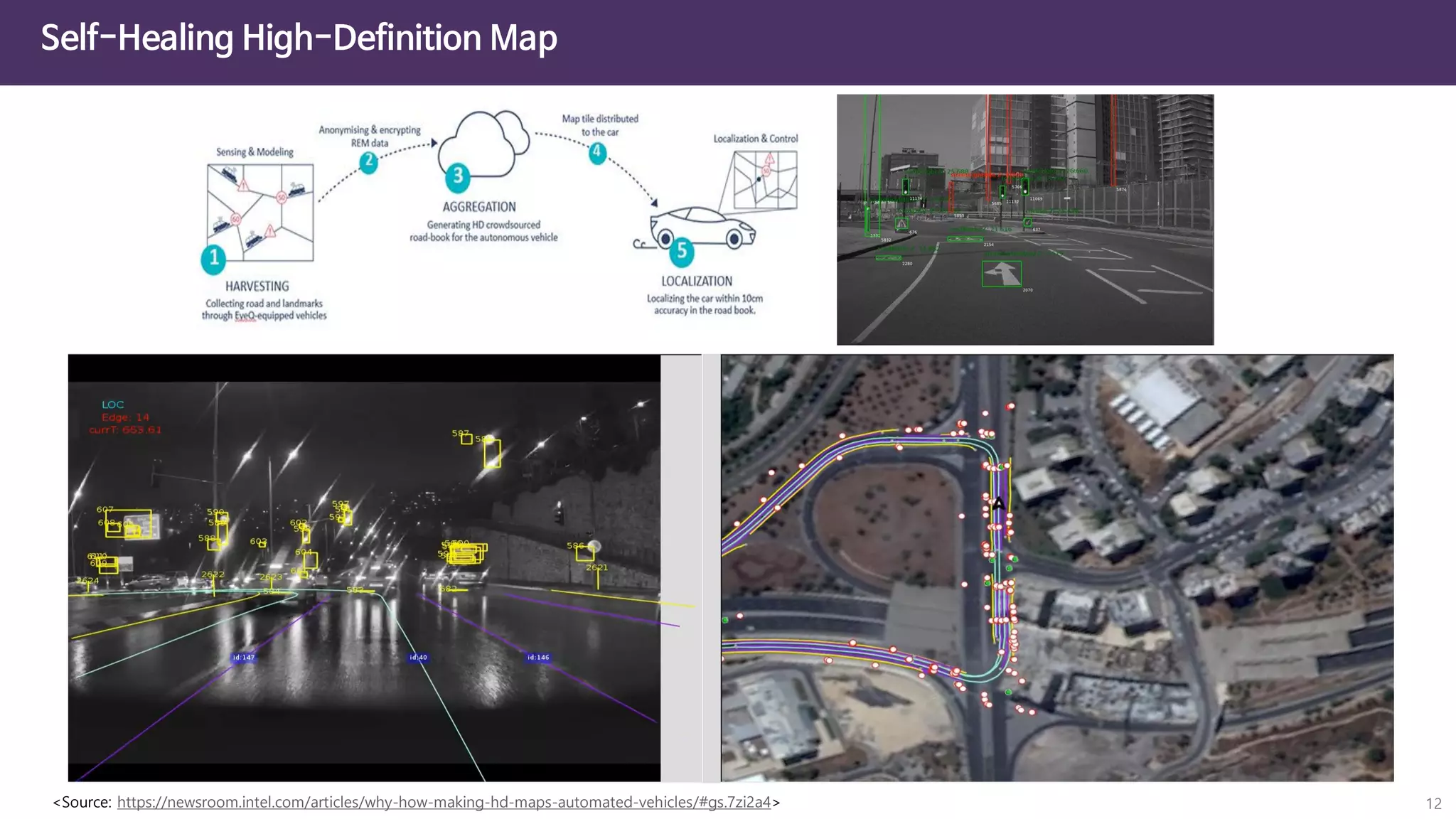
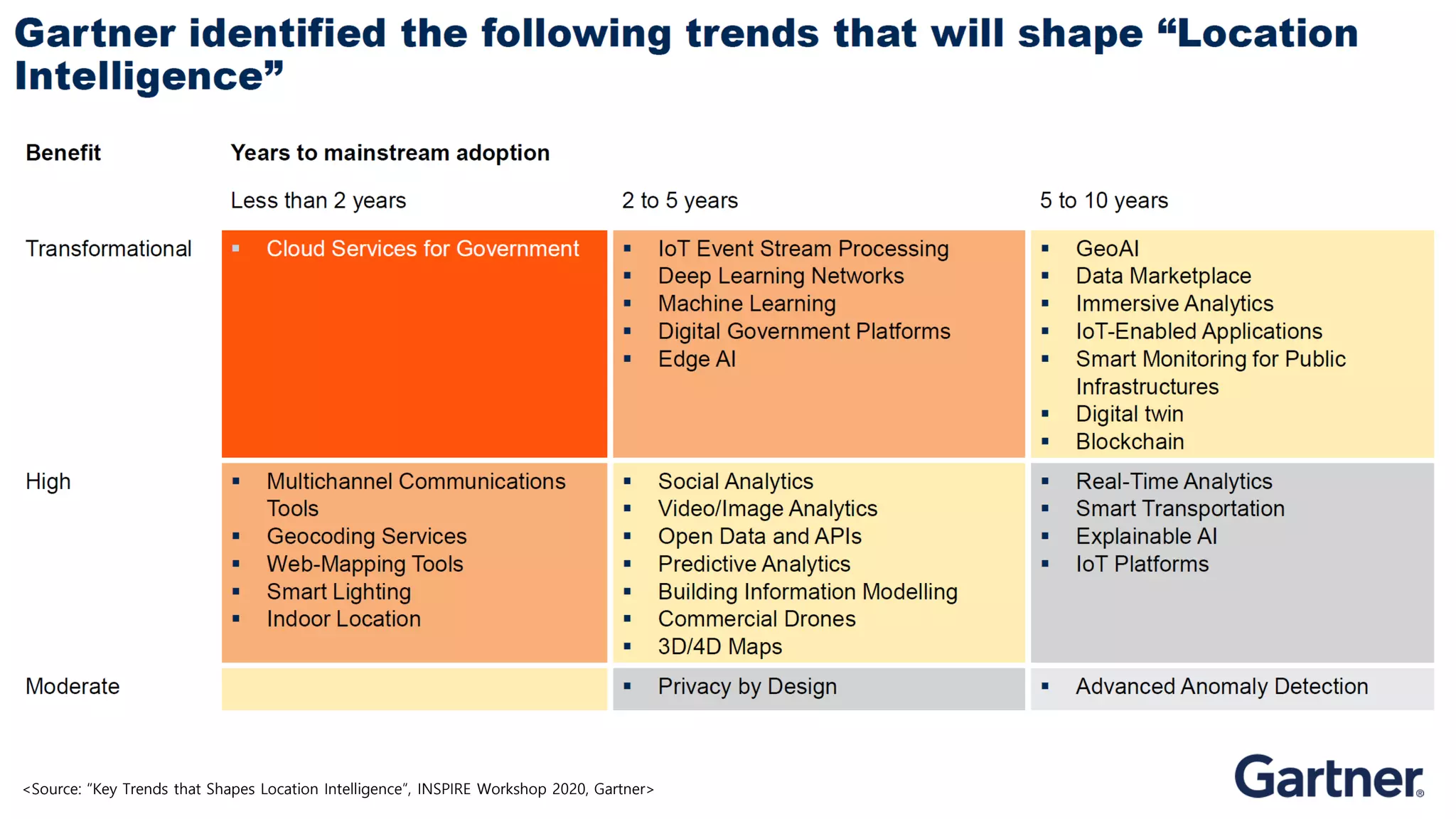
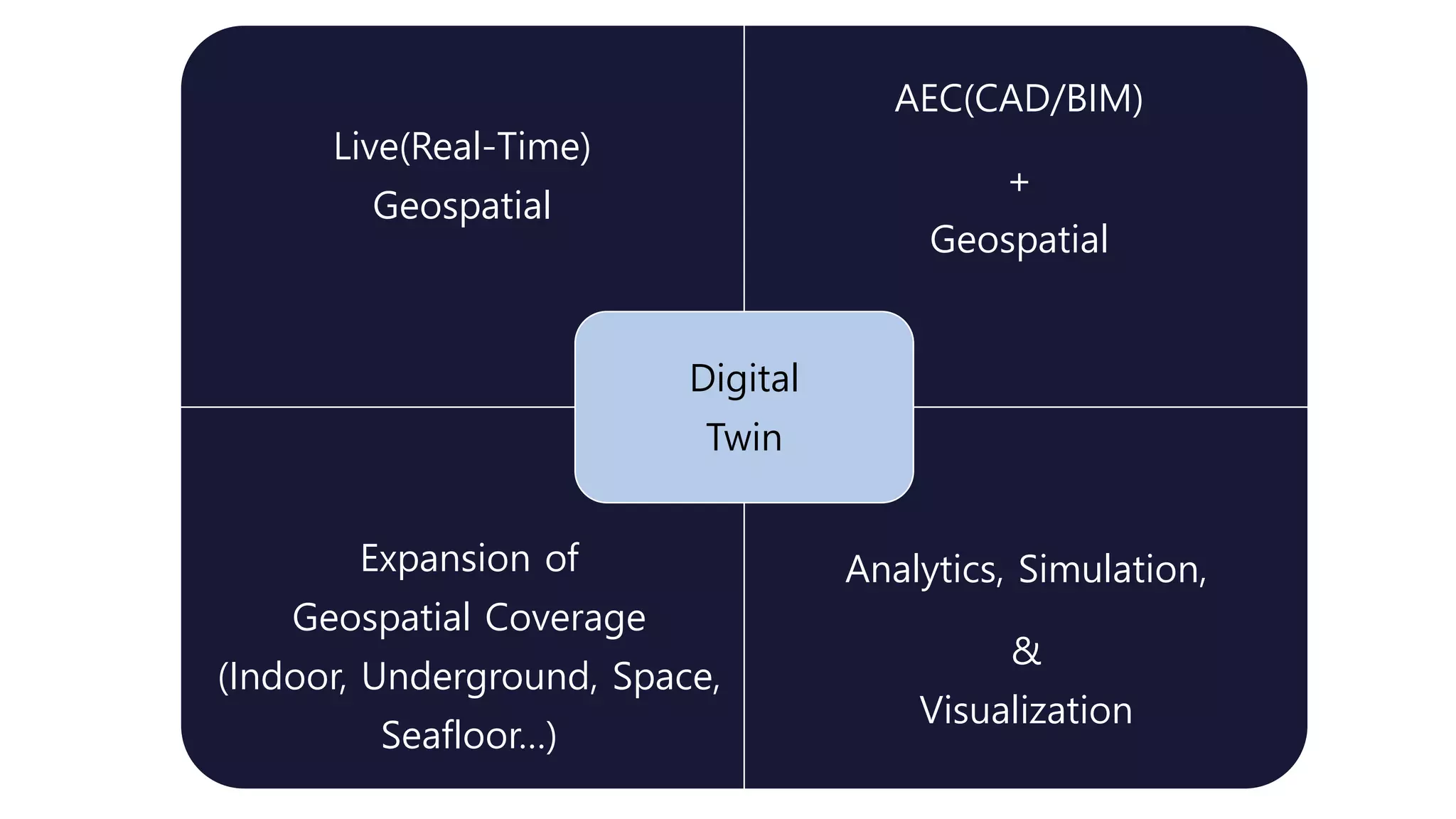
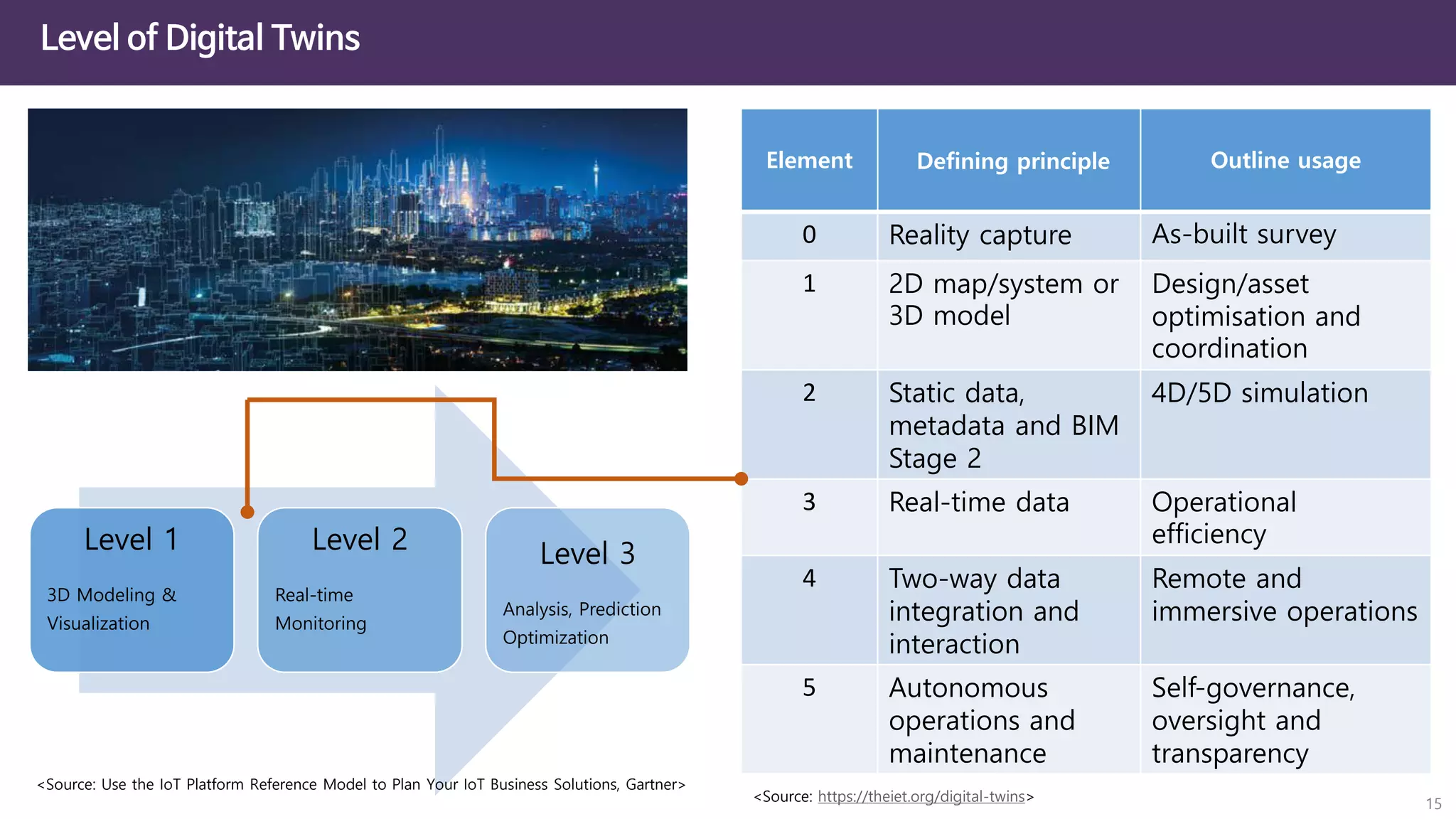
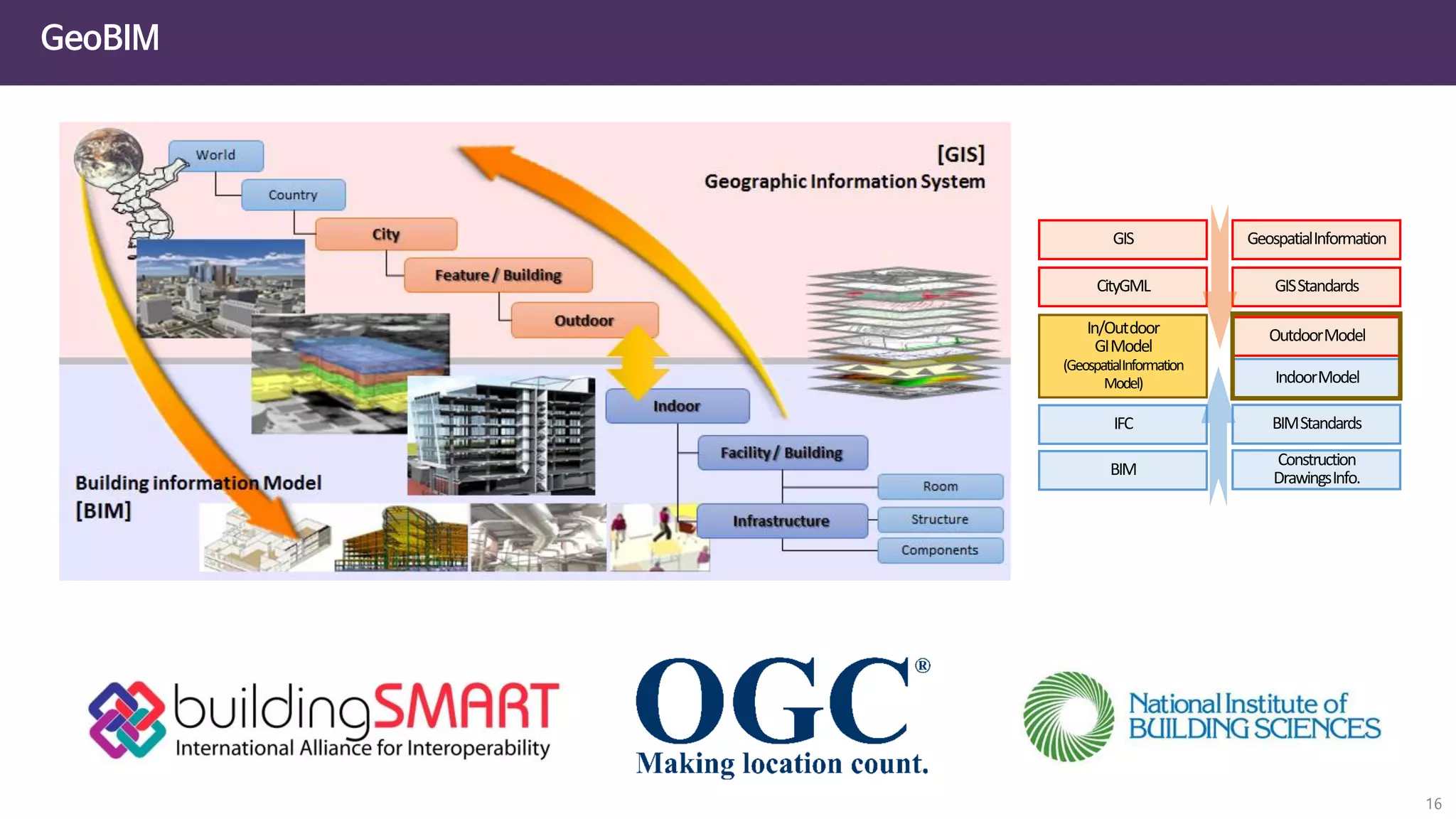
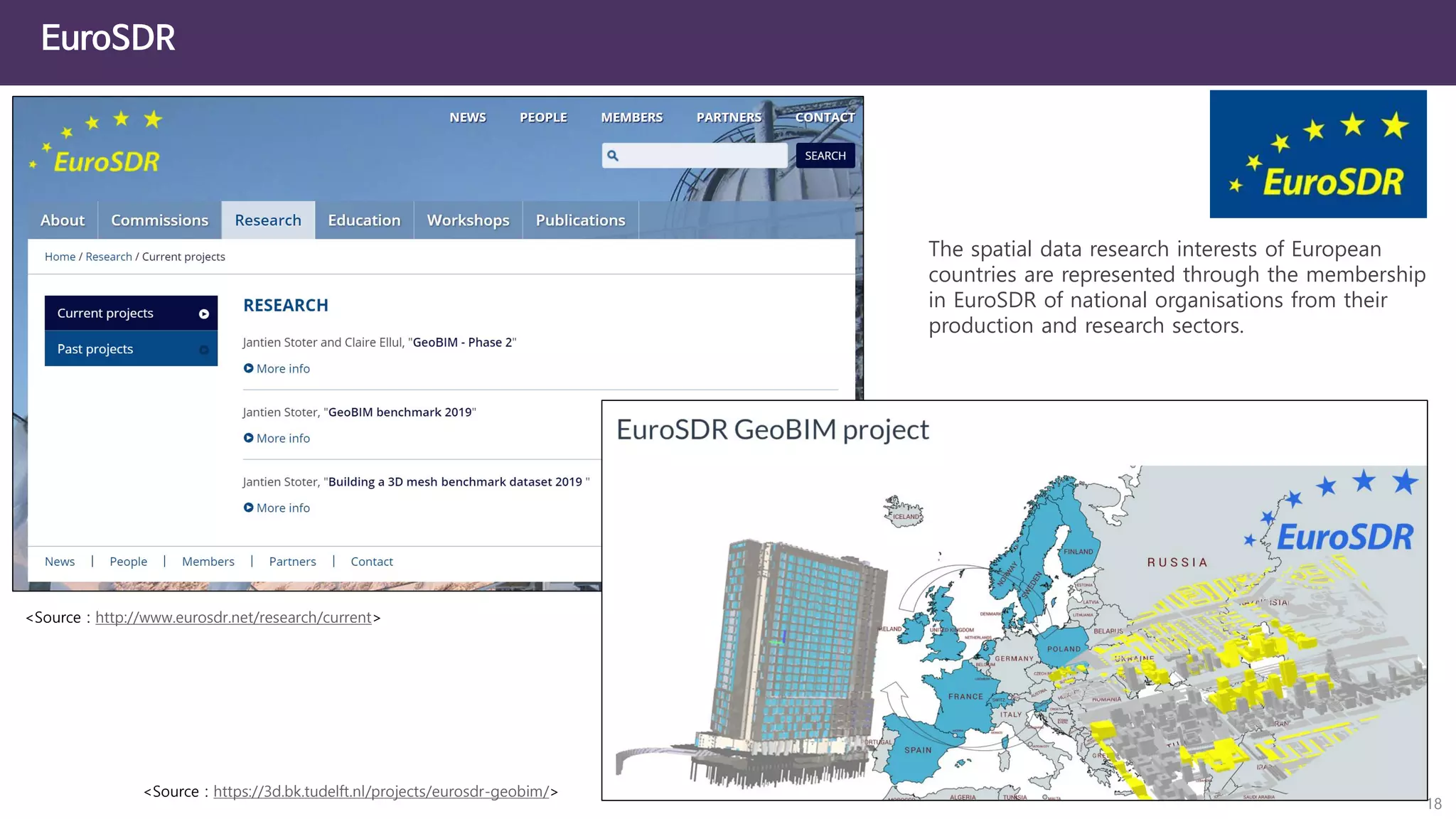
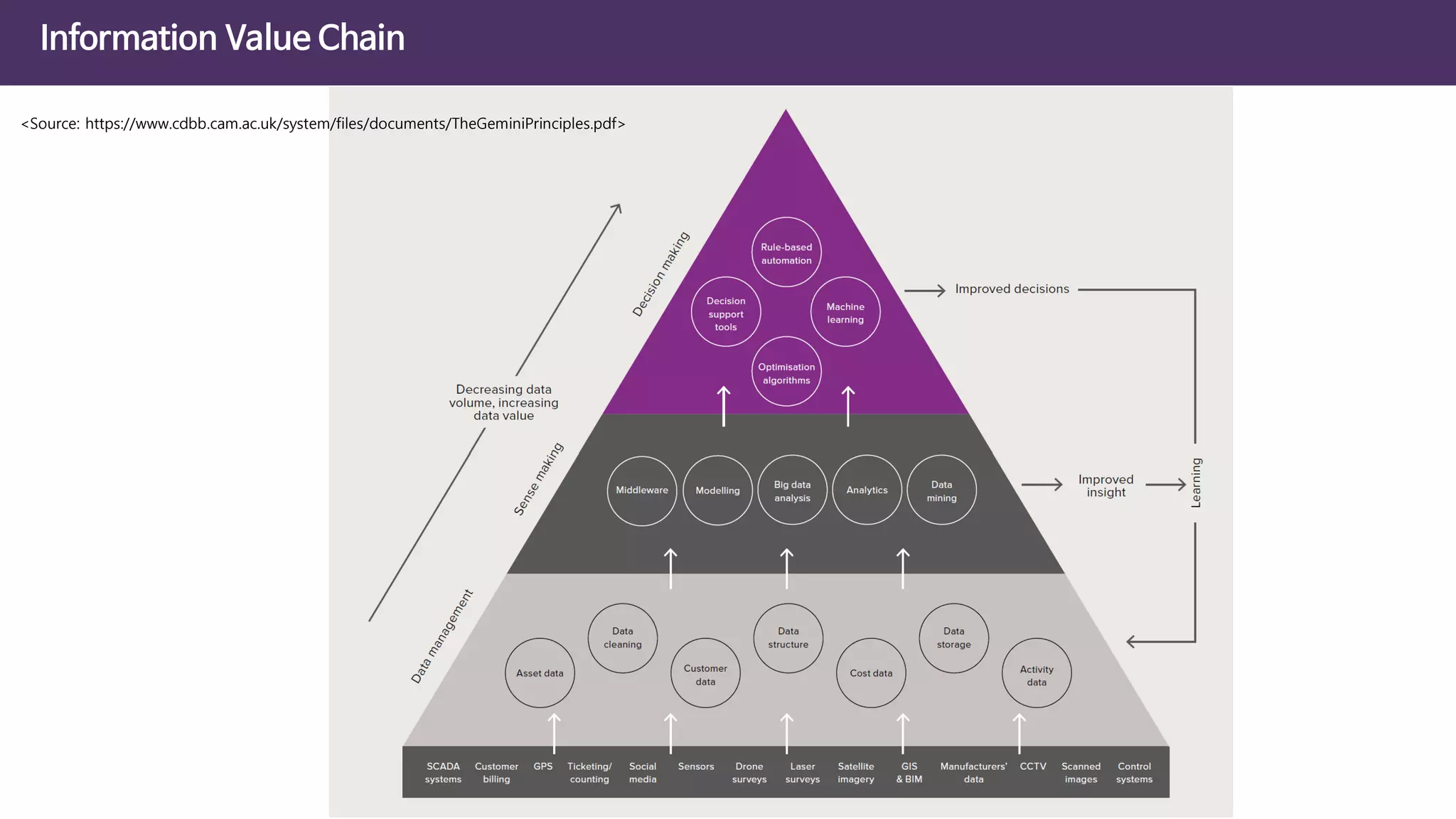
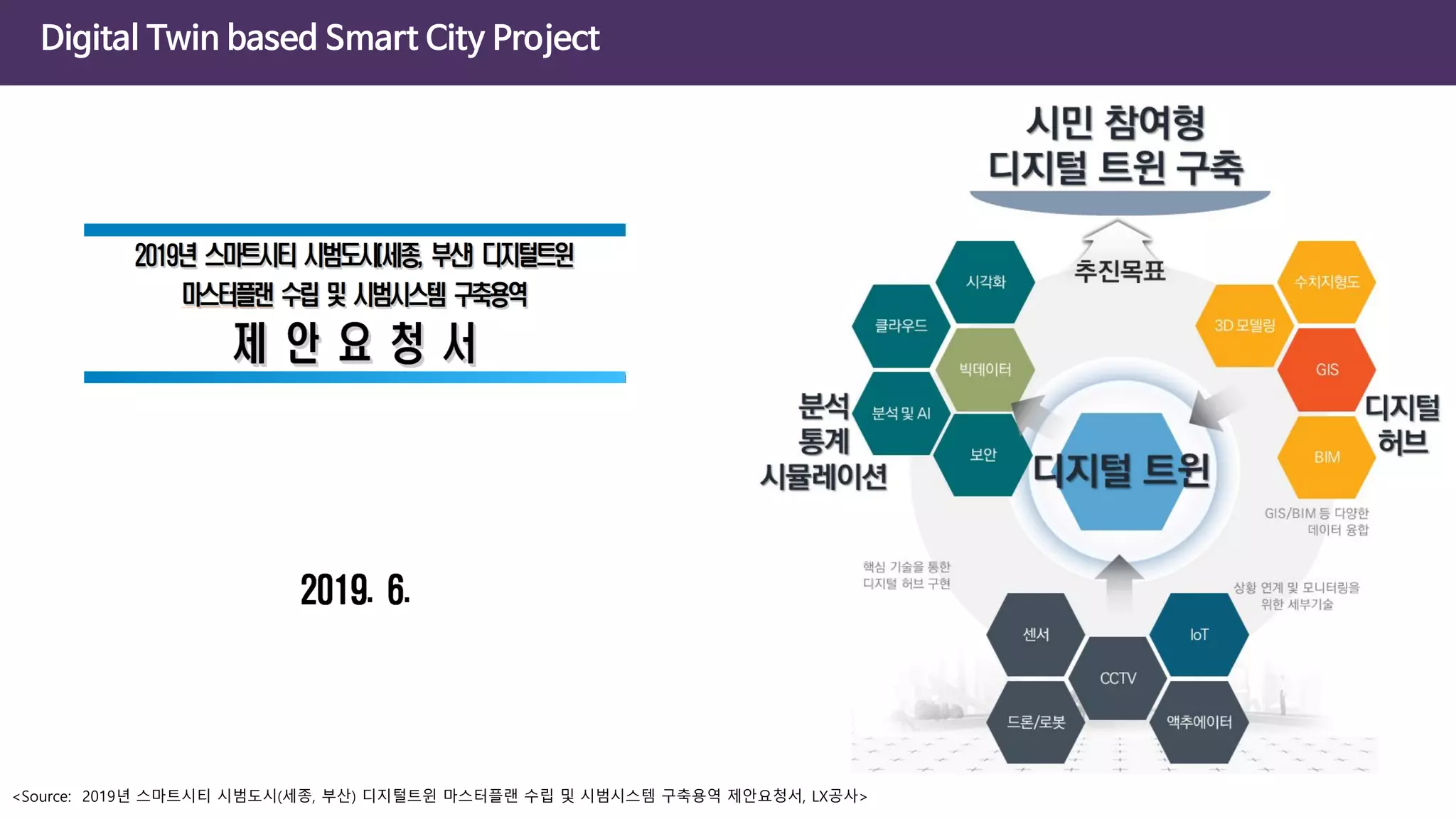
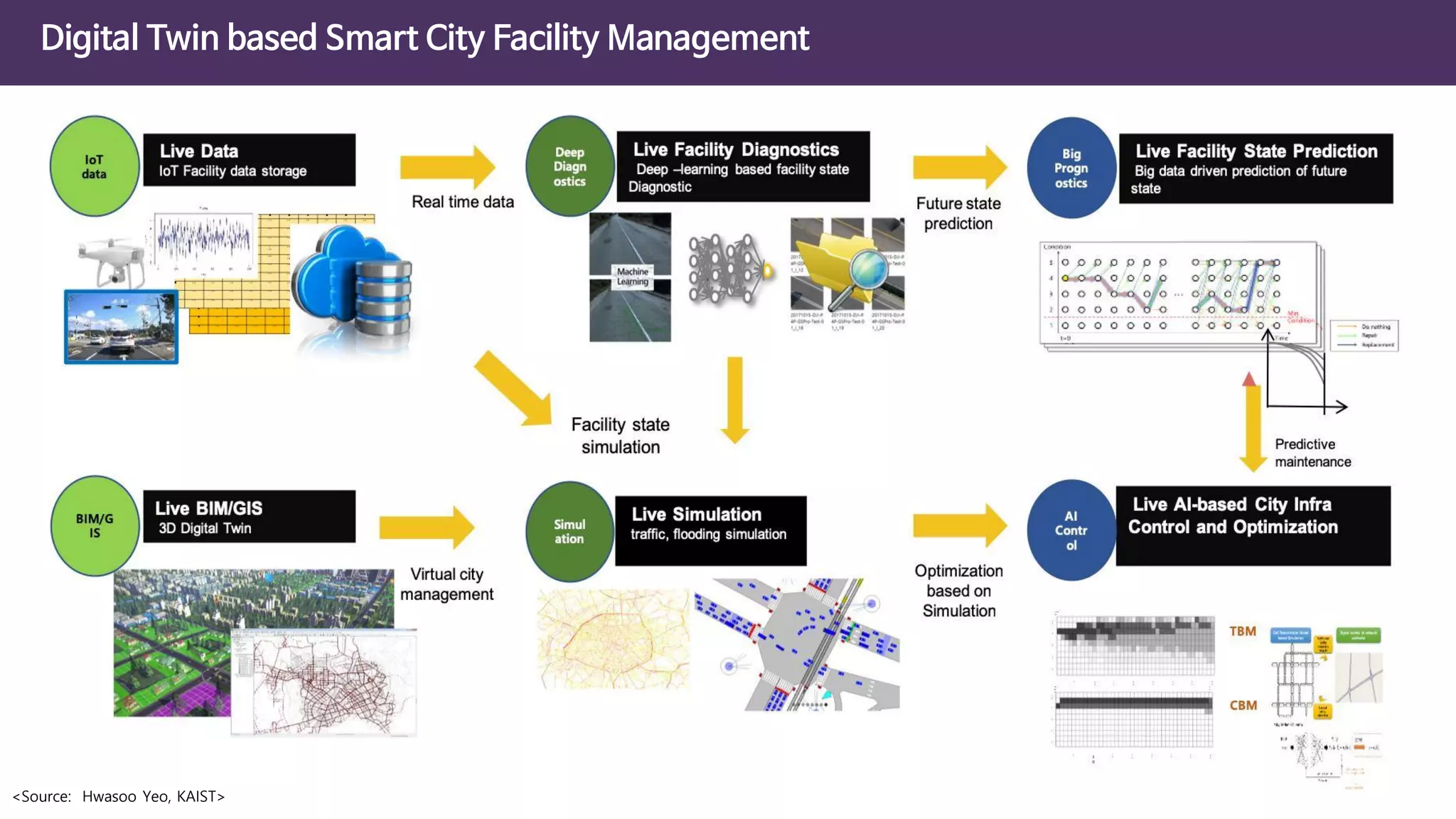
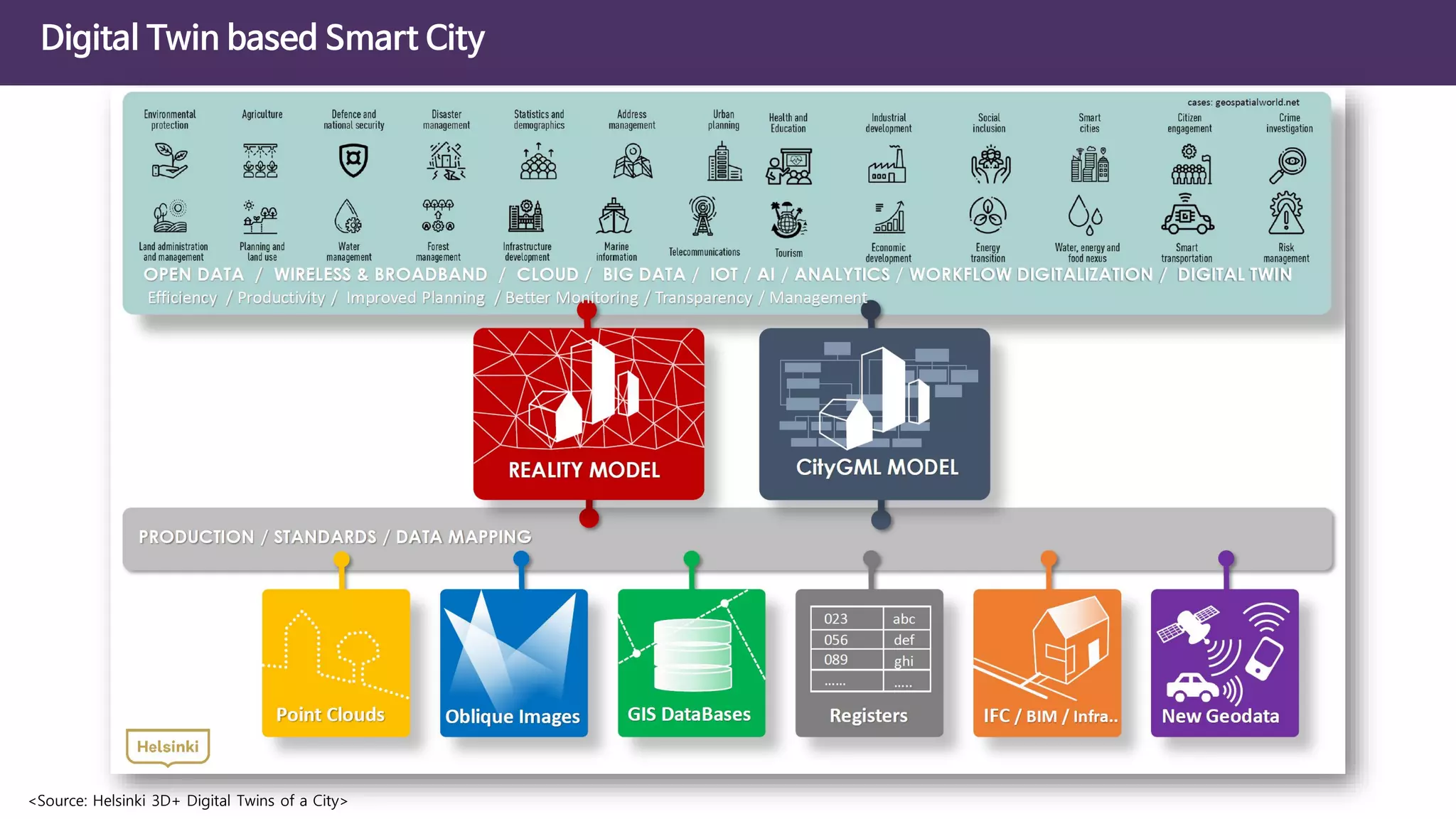
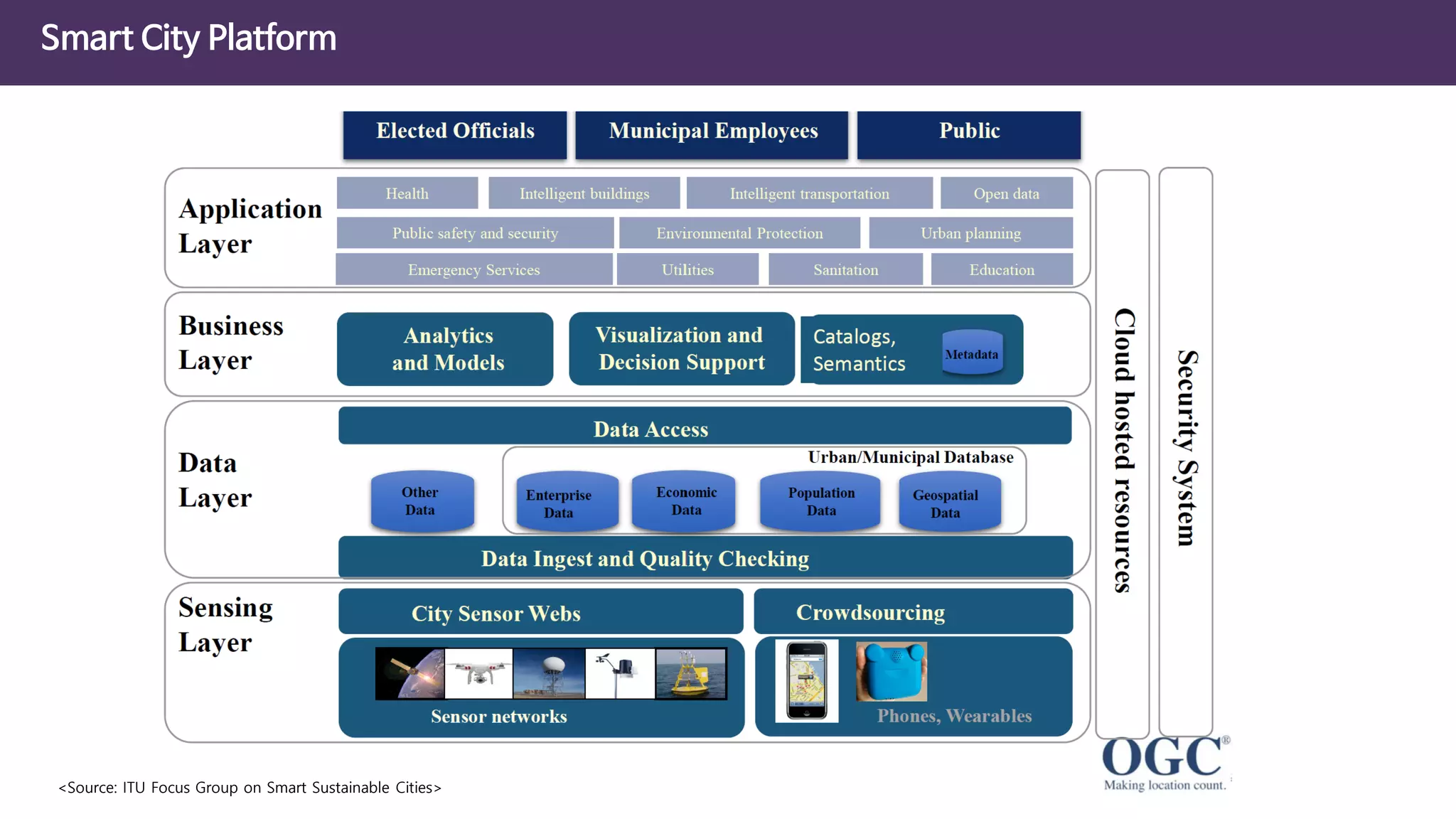
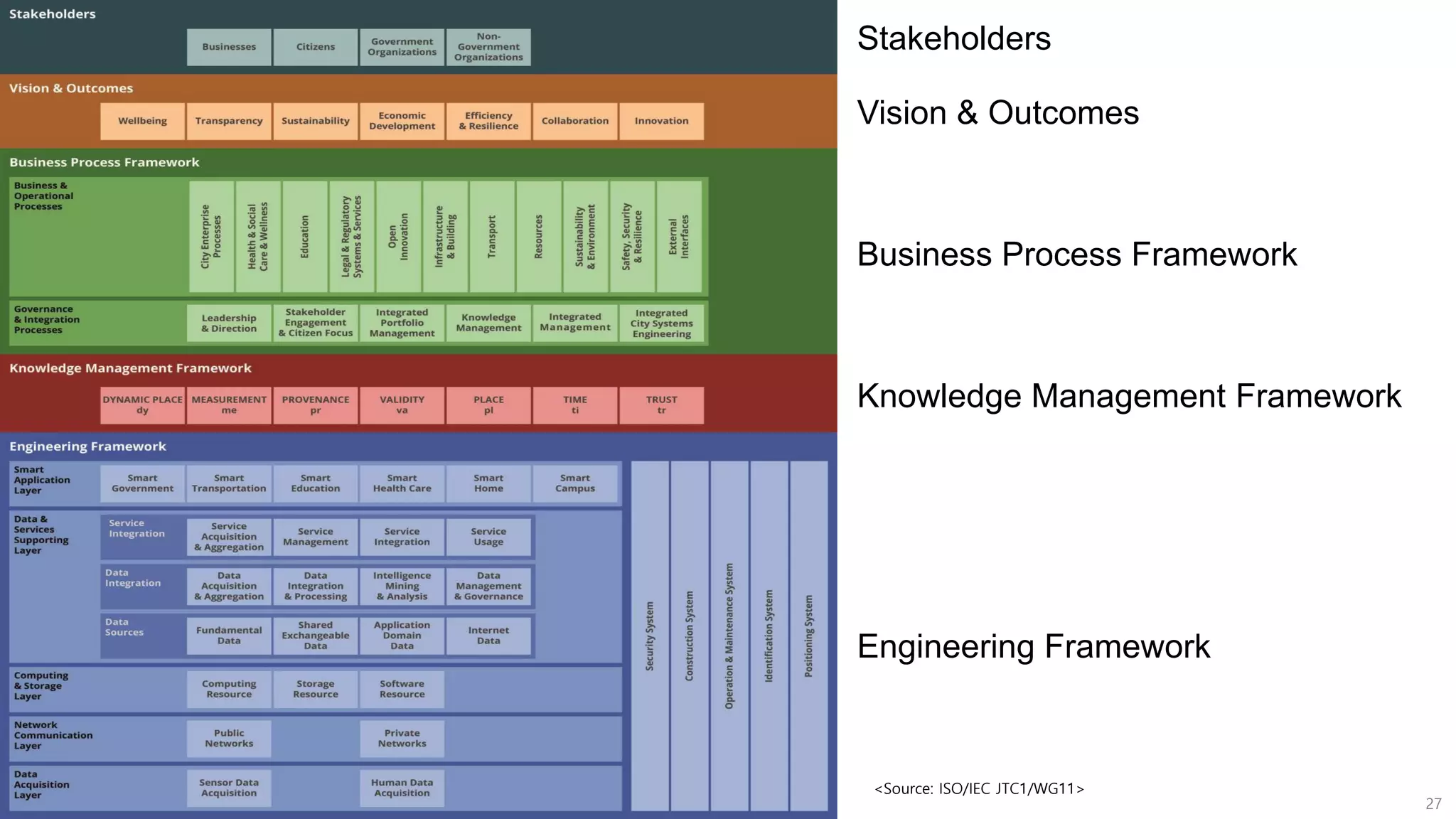
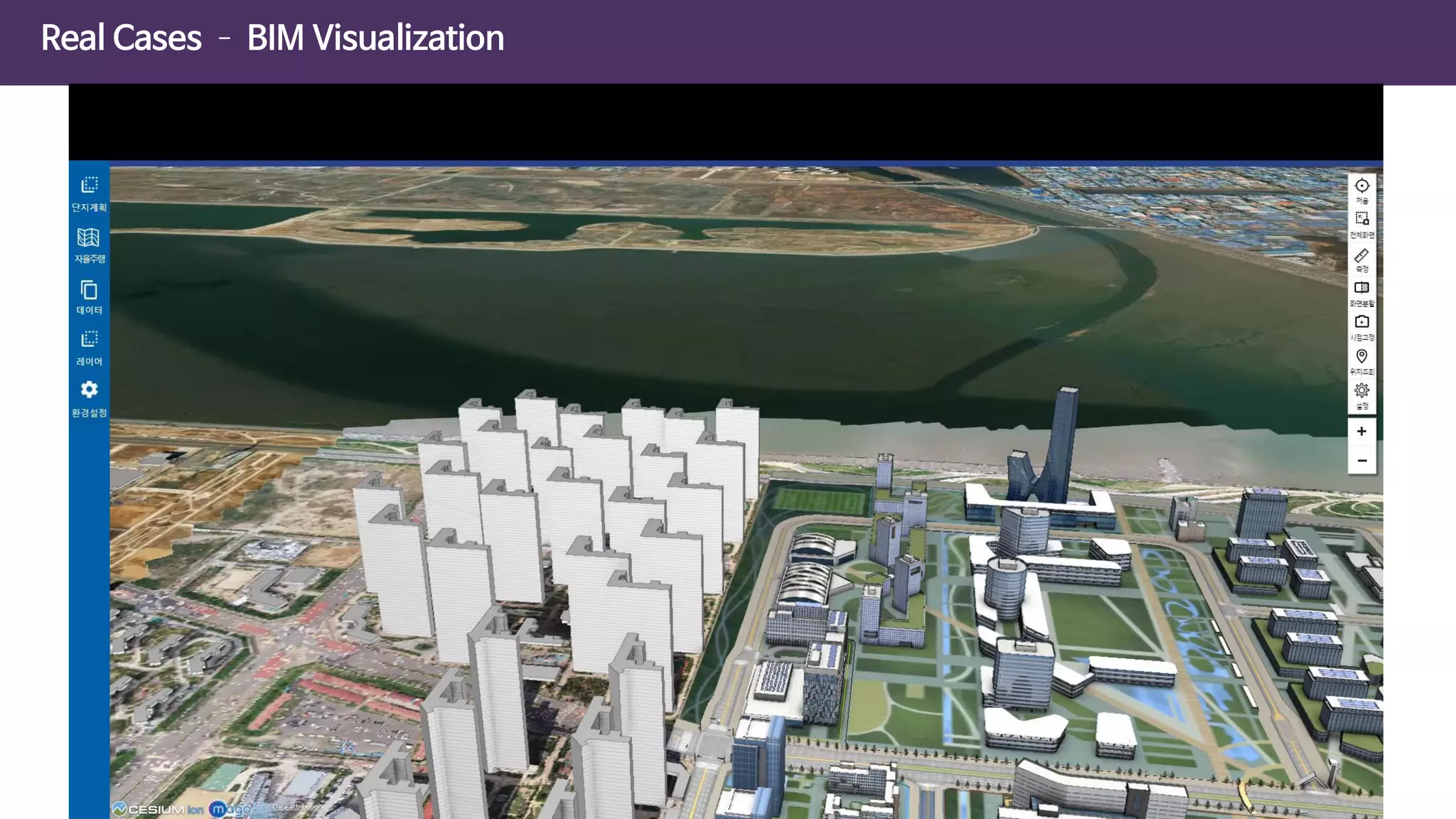
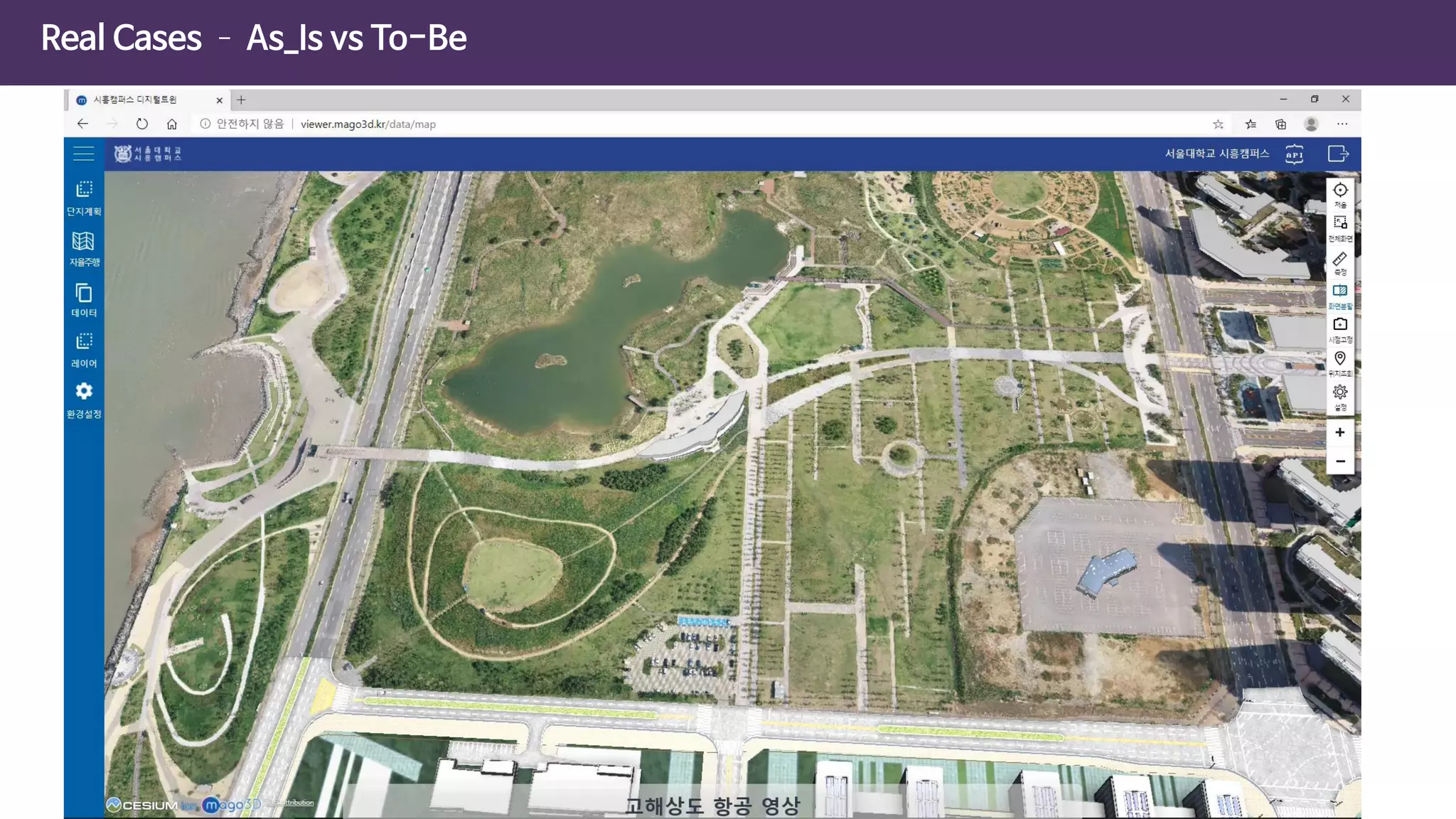
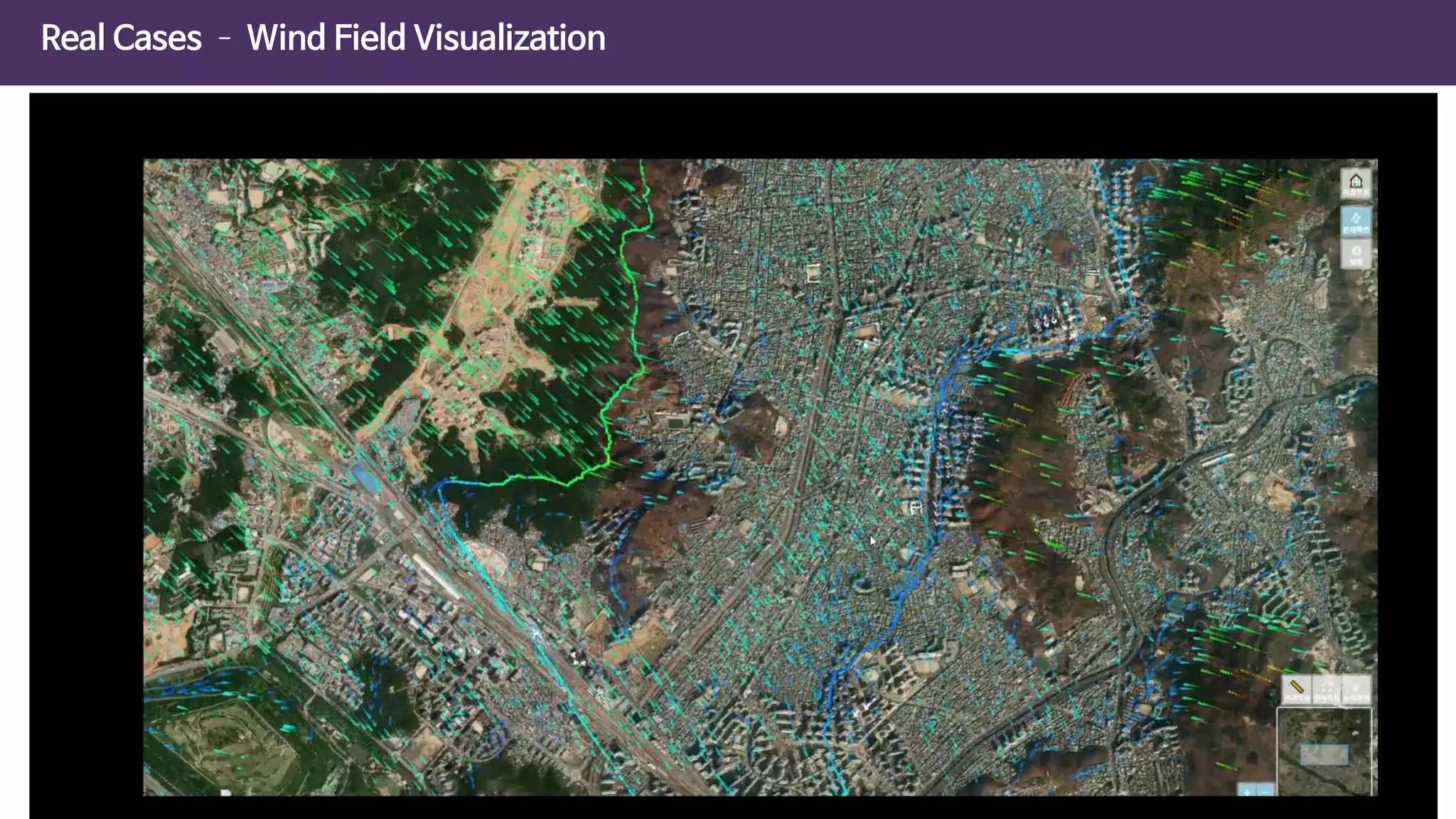
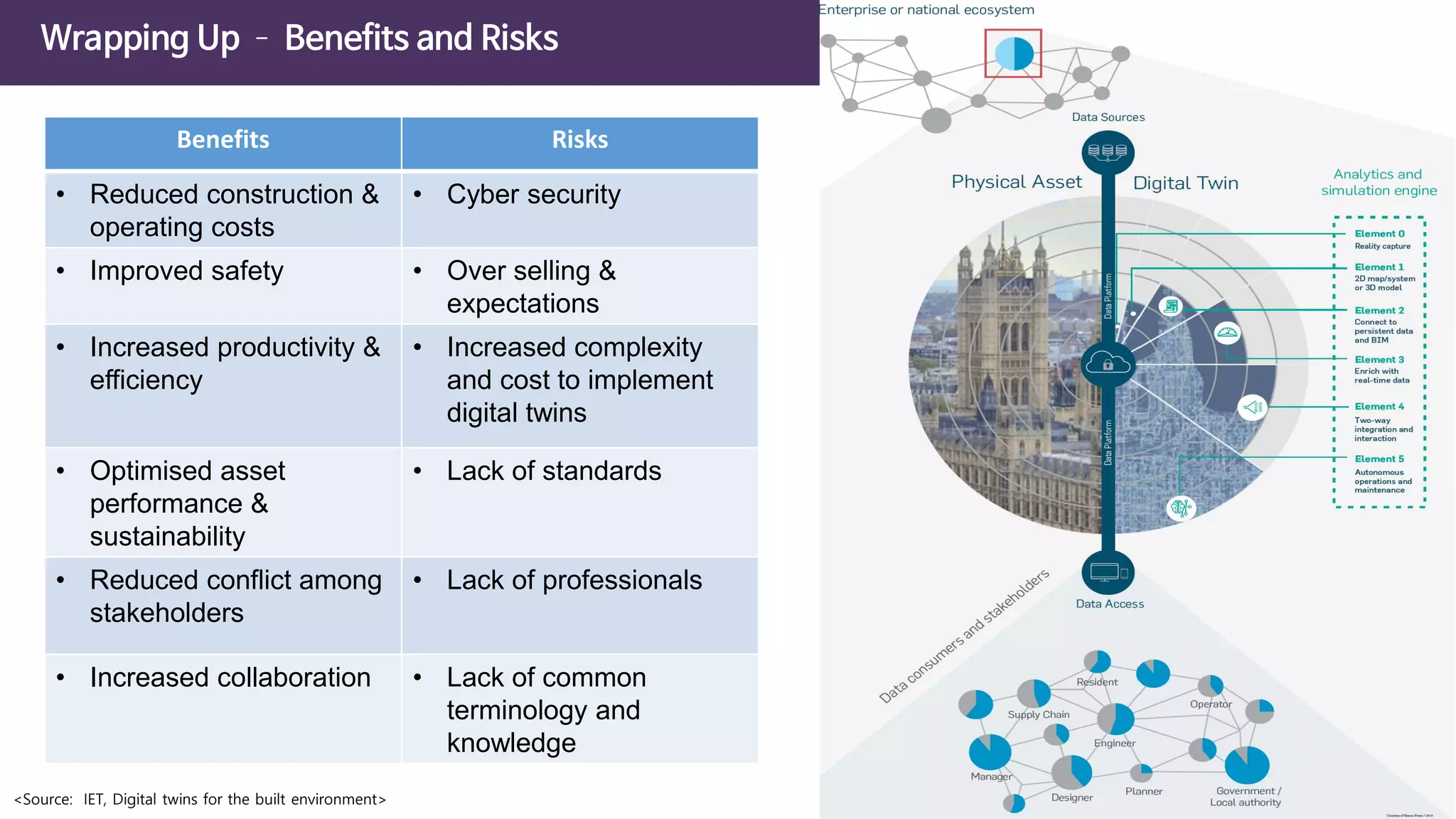
The document discusses the concept of digital twins and their application in smart cities, highlighting their role in urban management and the benefits they can provide such as improved efficiency and reduced costs. It details the various levels of digital twins from basic 3D modeling to real-time data integration and autonomous operations. However, it also addresses the challenges and criticisms associated with implementing these technologies, including the complexity of integration and the need for common standards.