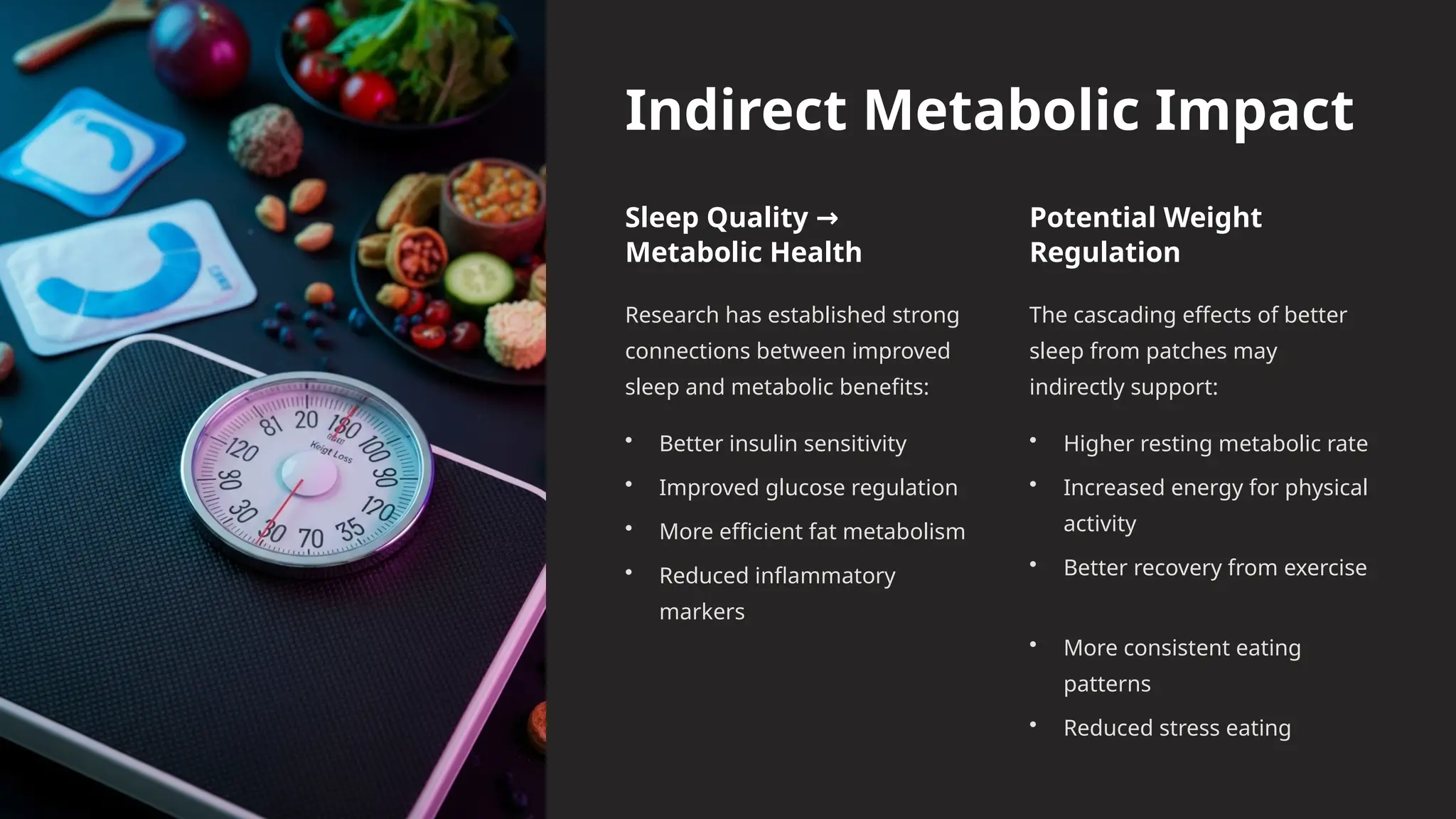
Sleep is one of the most underrated pillars of health. While nutrition and exercise receive enormous attention, sleep often remains neglected. Yet, the science is clear: poor sleep disrupts hormones, impairs memory, weakens the immune system, and increases the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Despite its importance, millions of people worldwide are struggling with insomnia, poor sleep quality, or irregular patterns caused by long work hours, stress, screen exposure, and lifestyle choices.
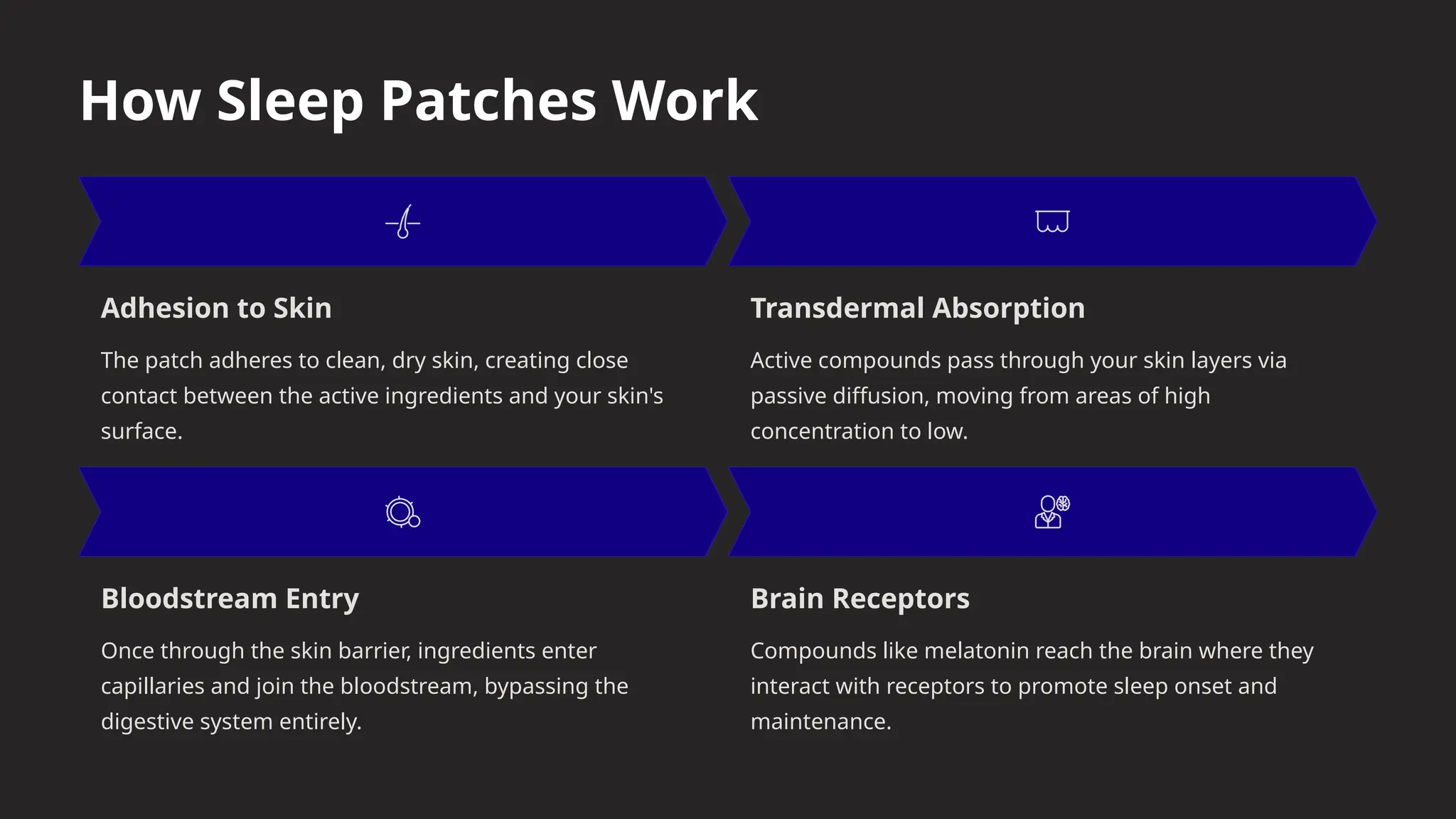
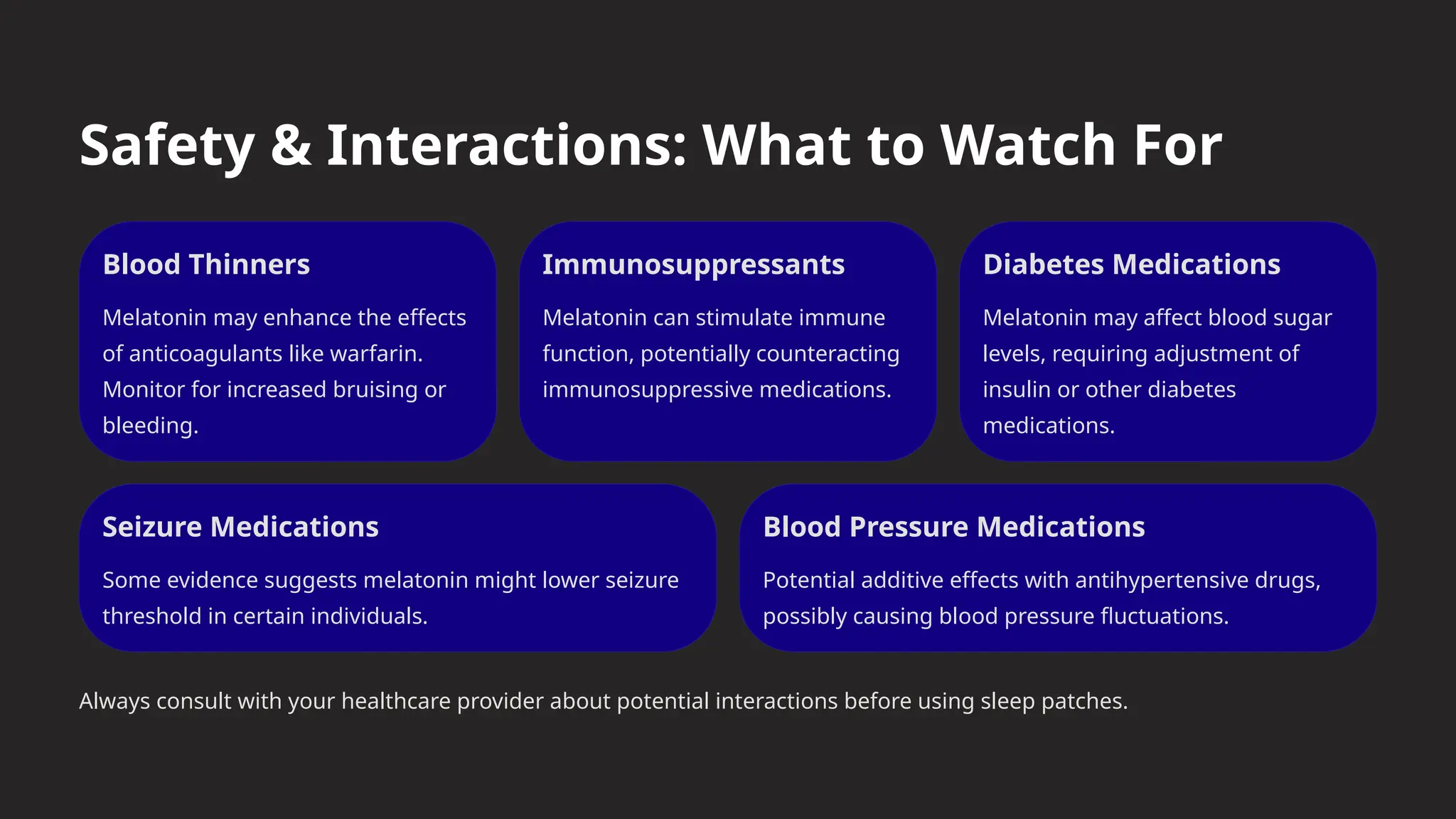
Enter sleep patches—a relatively new innovation in the wellness industry. These small adhesive patches are designed to help individuals fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and wake up refreshed. By delivering active compounds directly through the skin, sleep patches bypass the digestive system, offering an alternative to traditional pills and supplements.
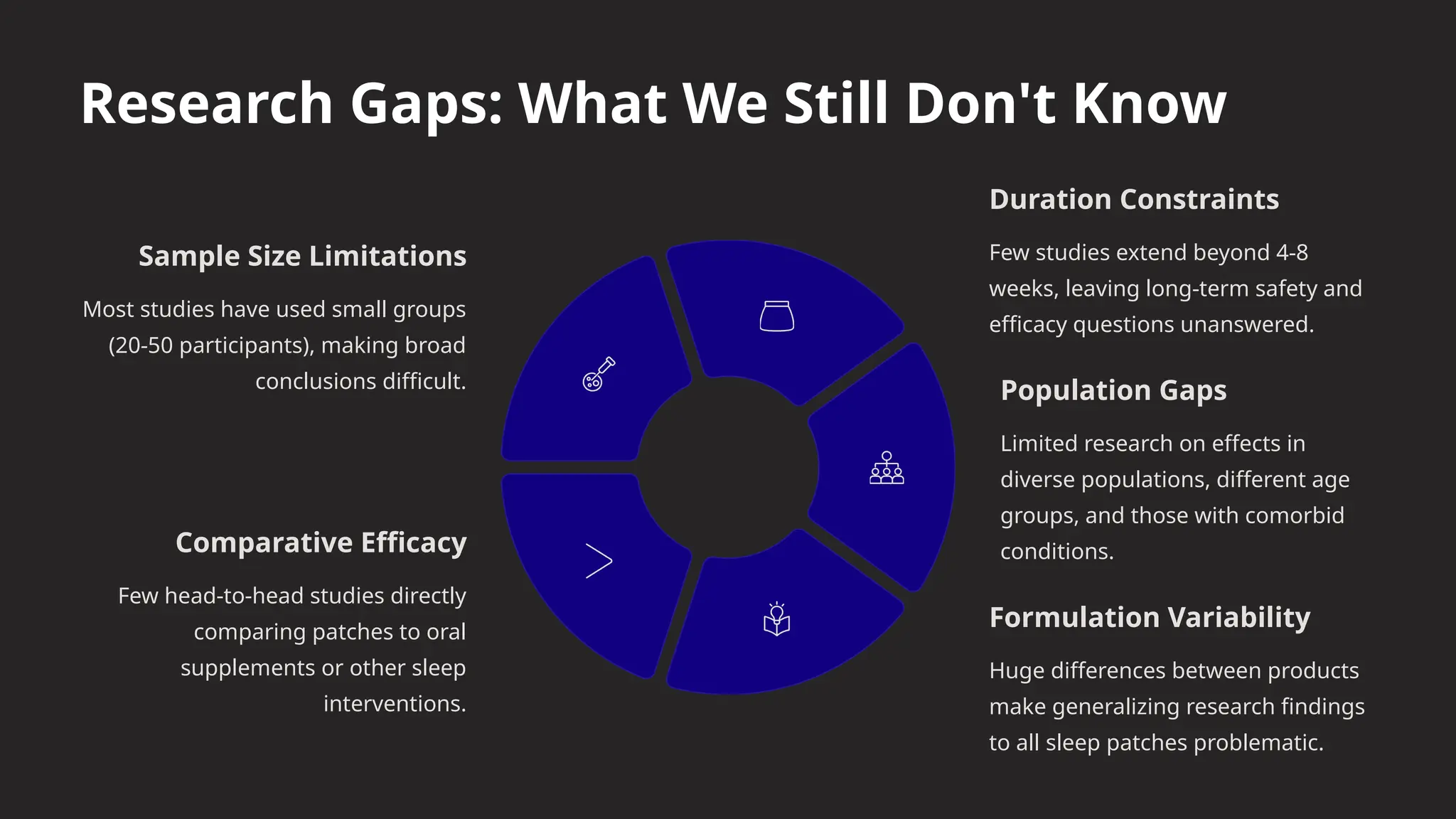
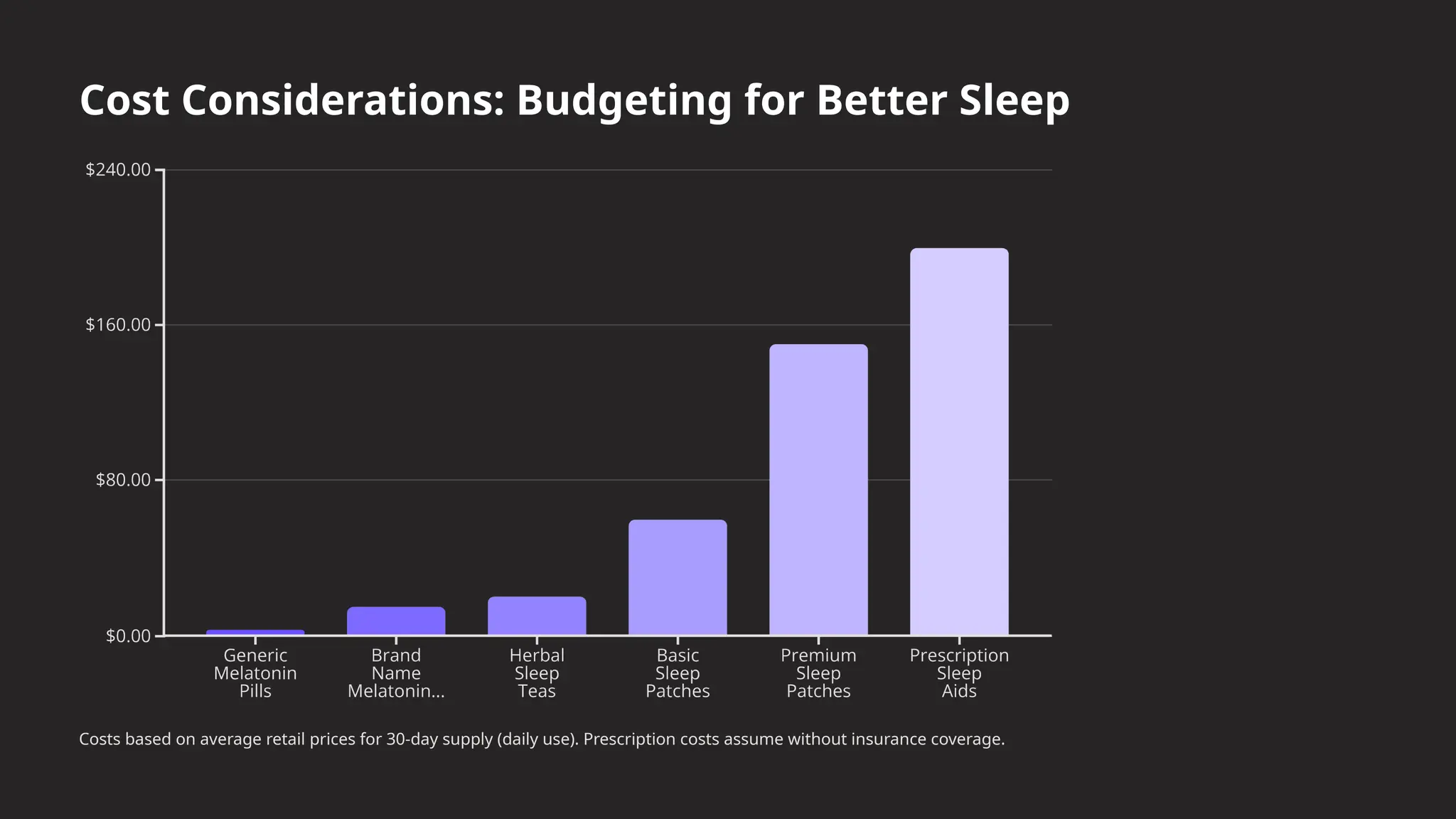
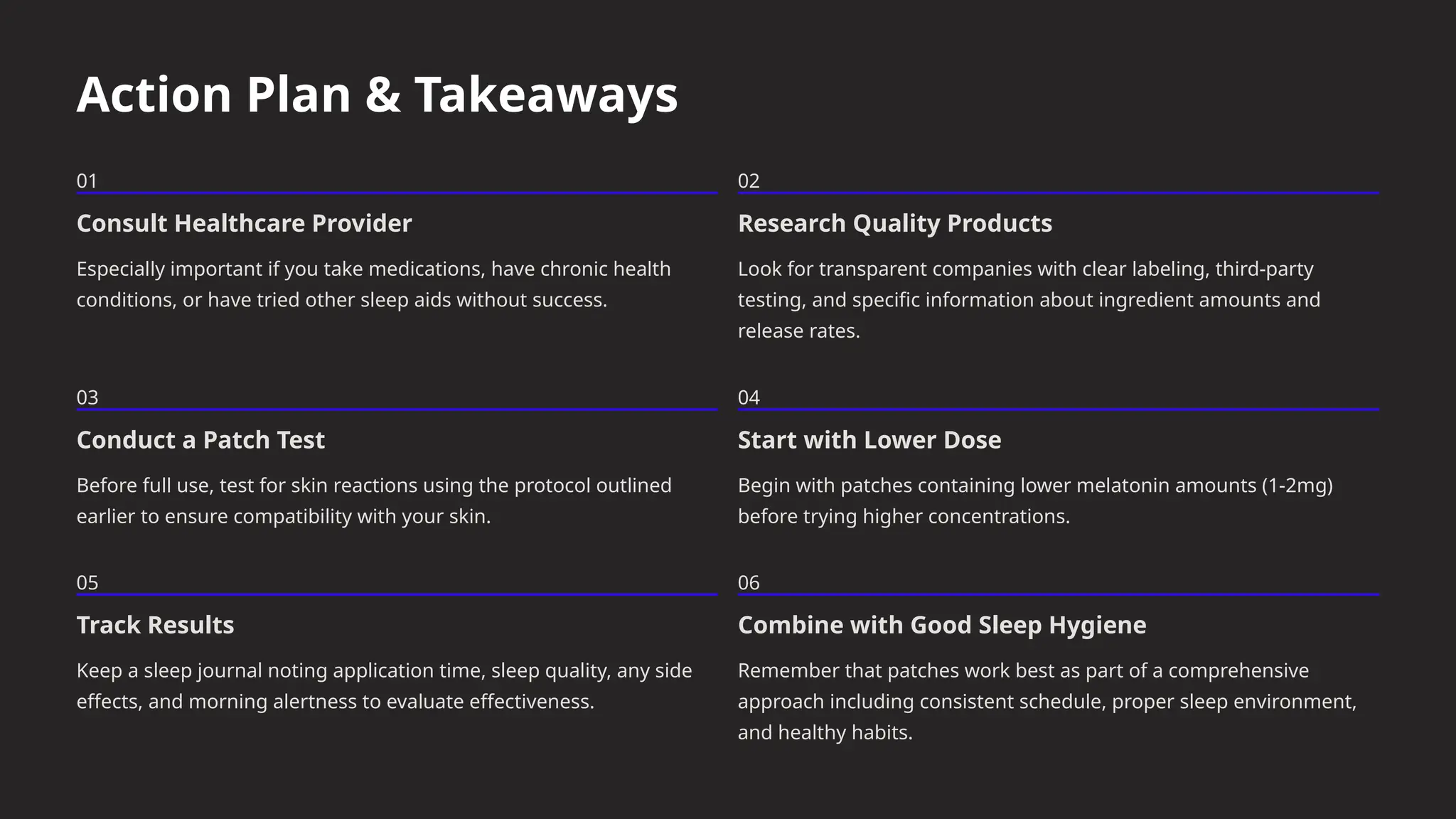
This presentation takes you through the benefits, risks, and real-world impact of sleep patches, helping you understand if they might be the right addition to your daily wellness routine.