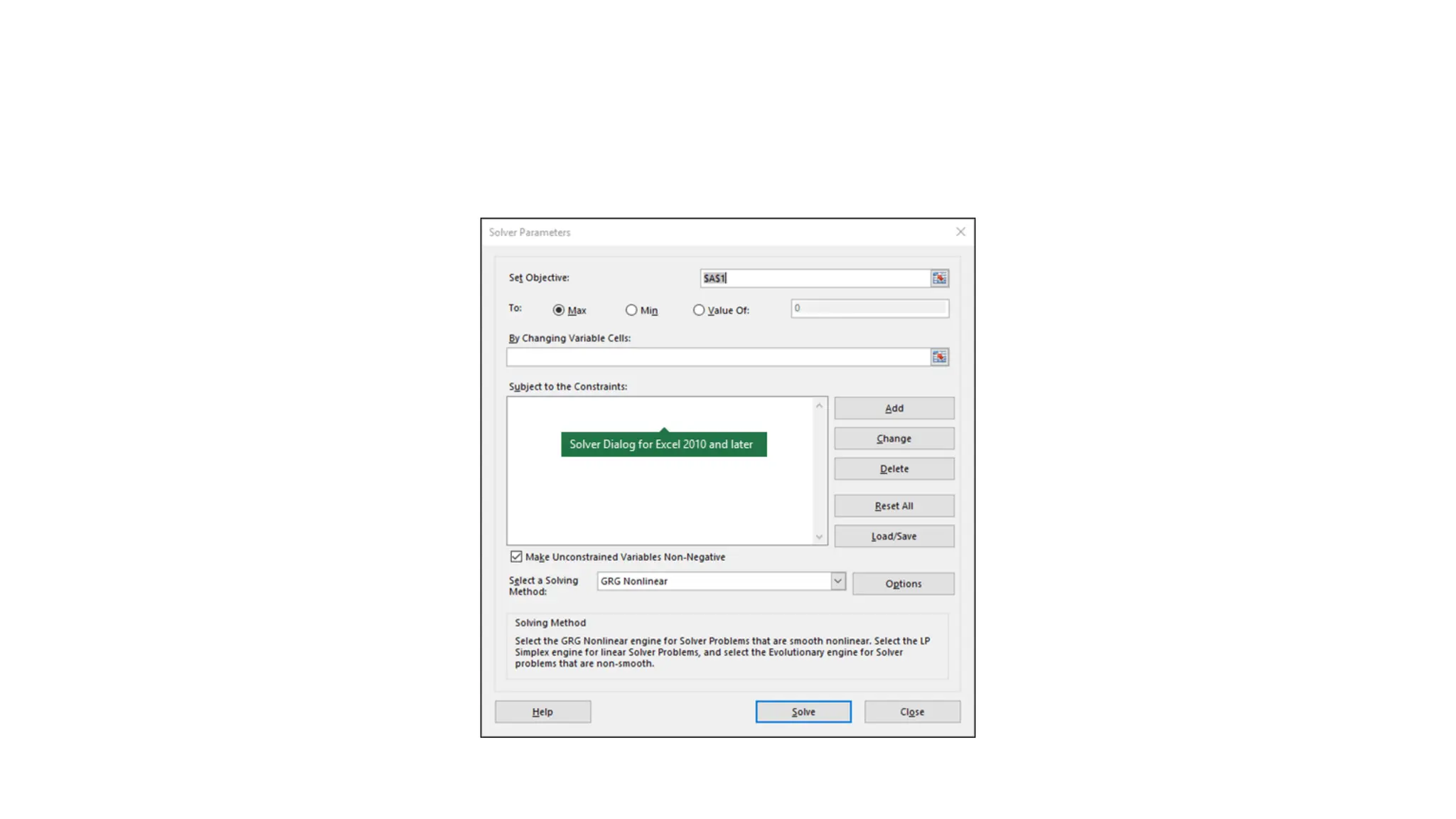
The Microsoft Excel Solver add-in enables what-if analysis by finding optimal values for a specified objective cell while adhering to constraints on other cell values. Users can define decision variable cells that Solver adjusts to achieve the target outcome, such as maximizing profit through budget adjustments. It supports specifying constraints and offers different solving methods for various types of problems.