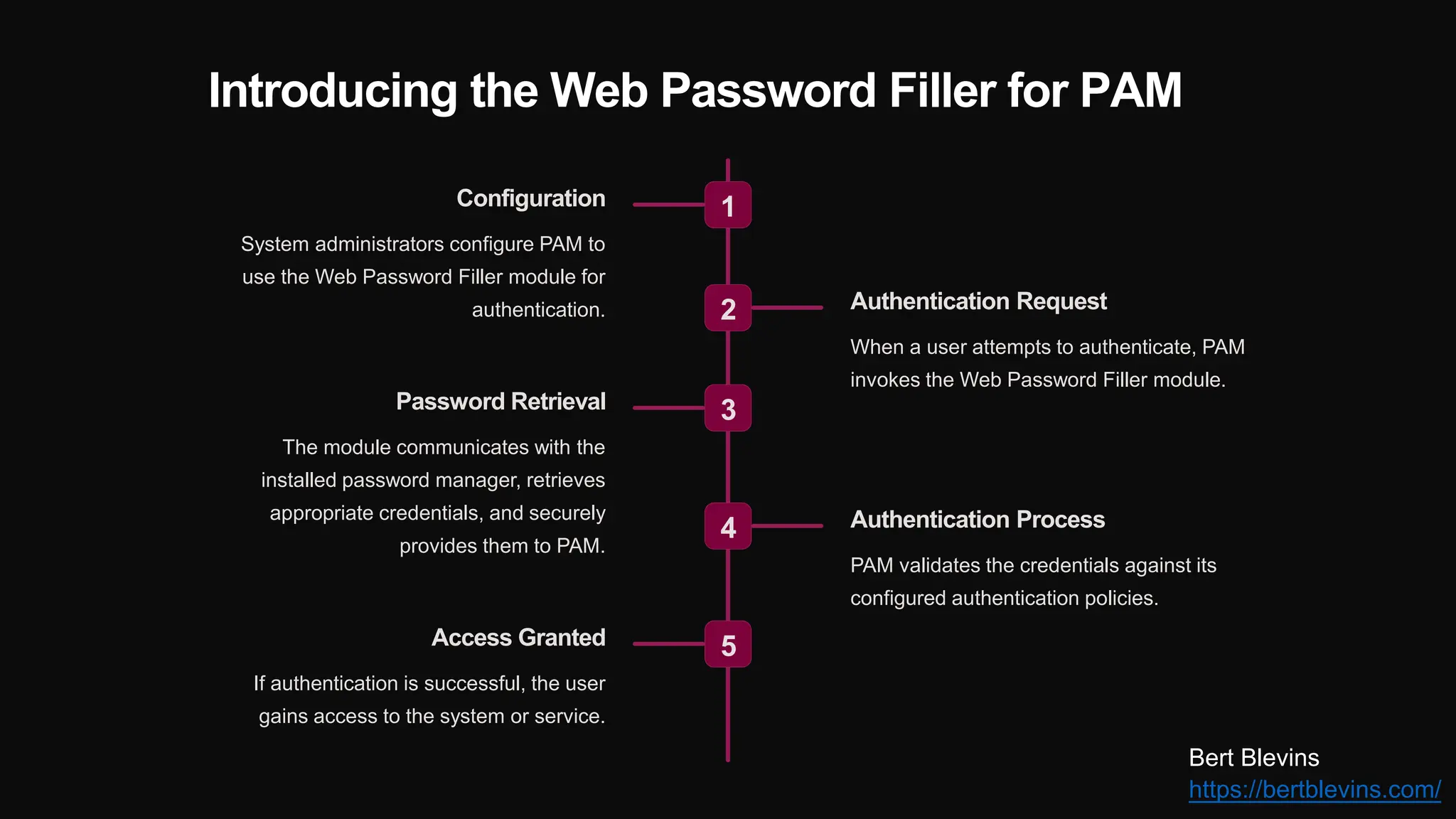
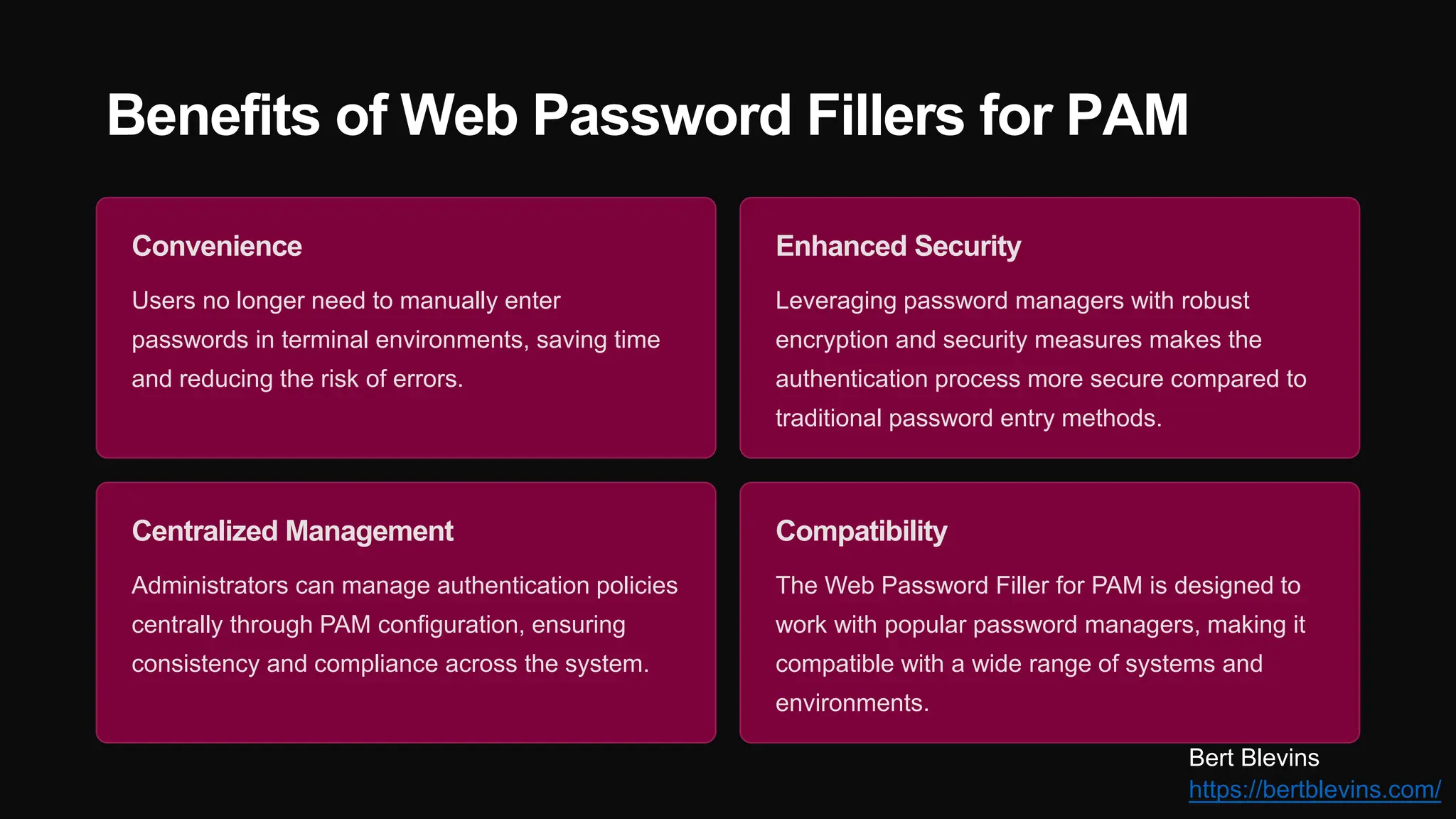
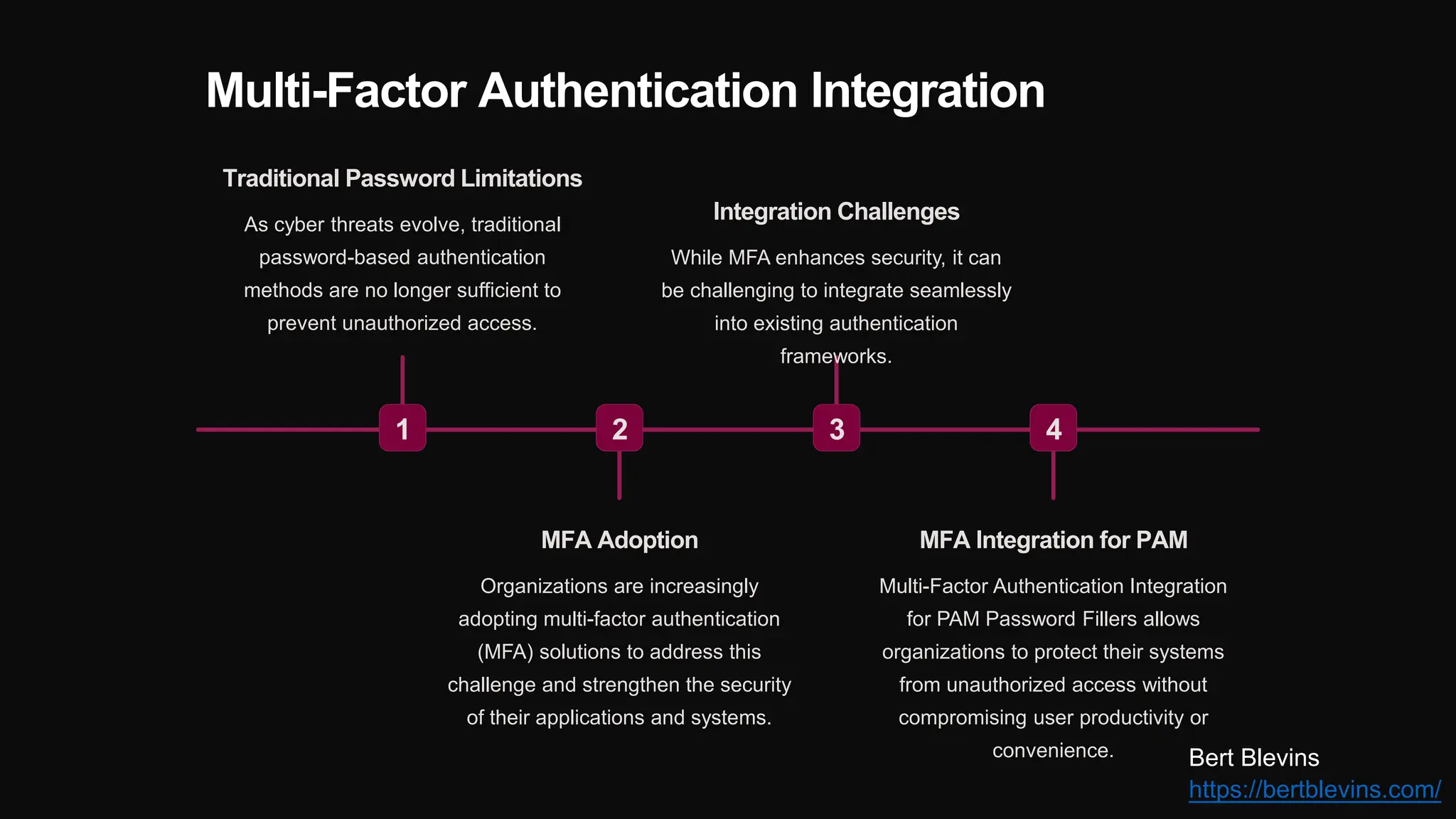
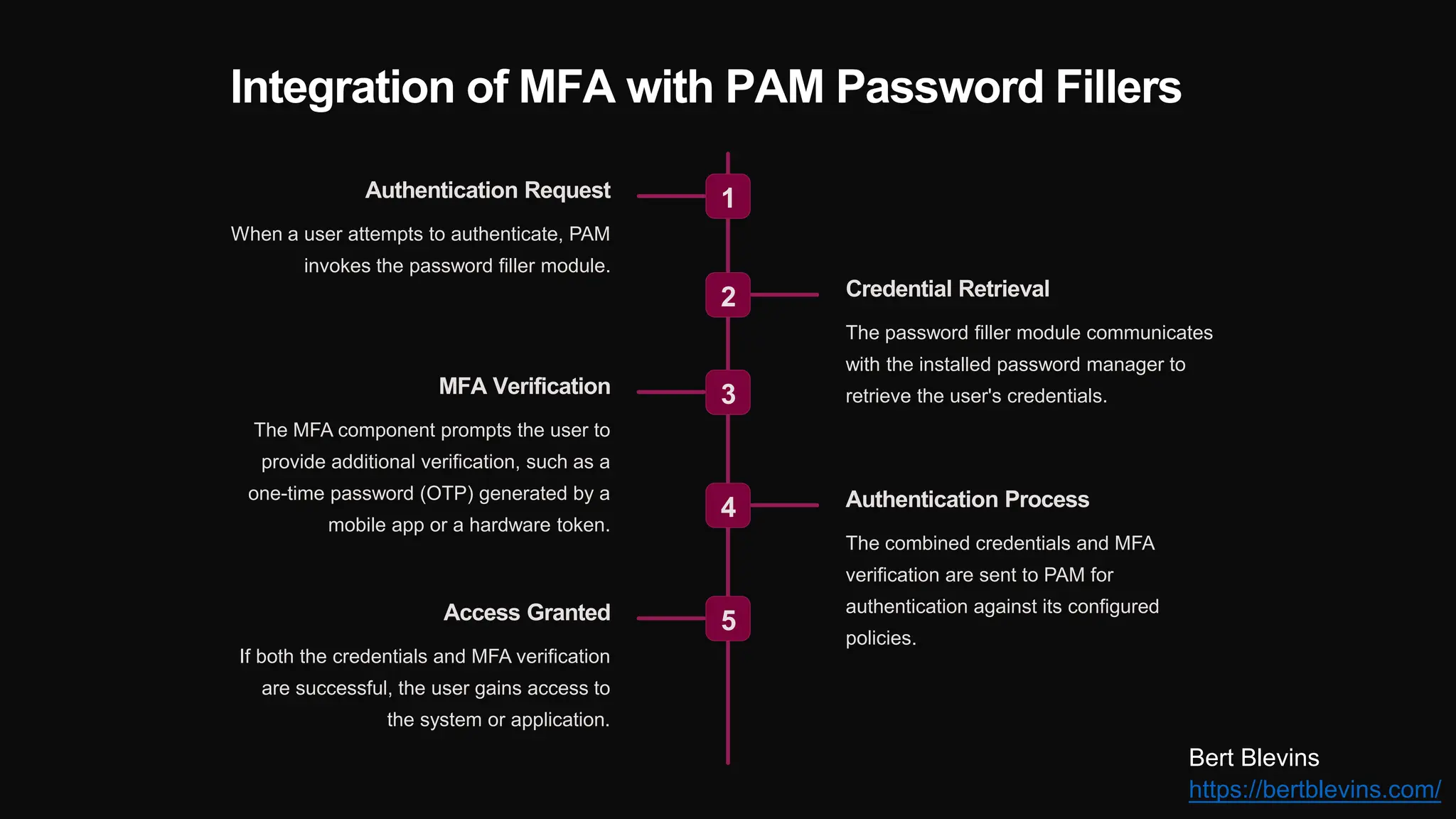
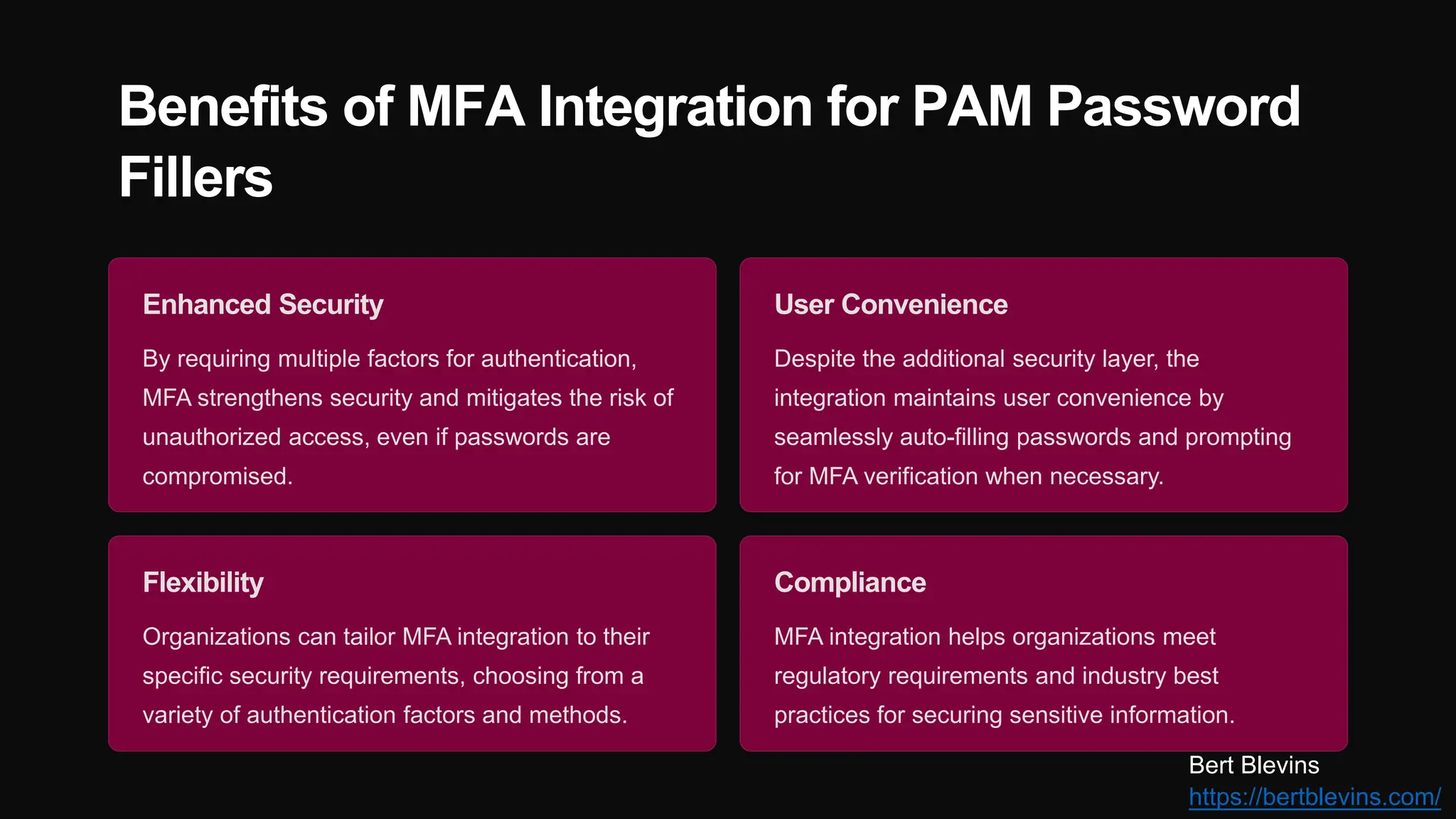
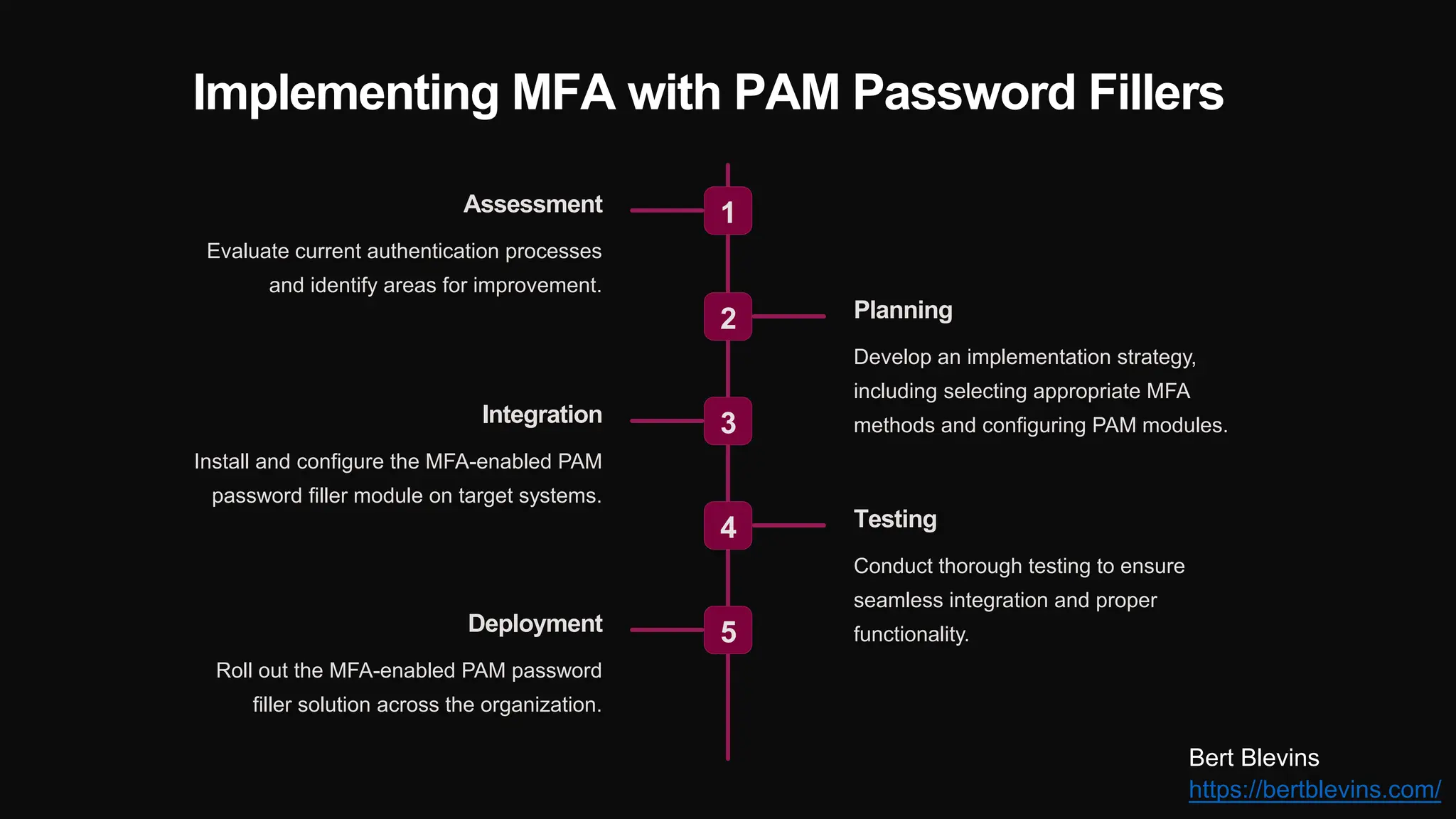
The document discusses the integration of web password fillers with Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) to enhance authentication processes in Linux environments. This integration aims to streamline password management by automating credential retrieval and improving security through multi-factor authentication (MFA), thereby reducing manual input errors and boosting user convenience. Furthermore, it outlines the implementation steps, ongoing maintenance, and emerging trends in authentication to adapt to evolving cyber threats.