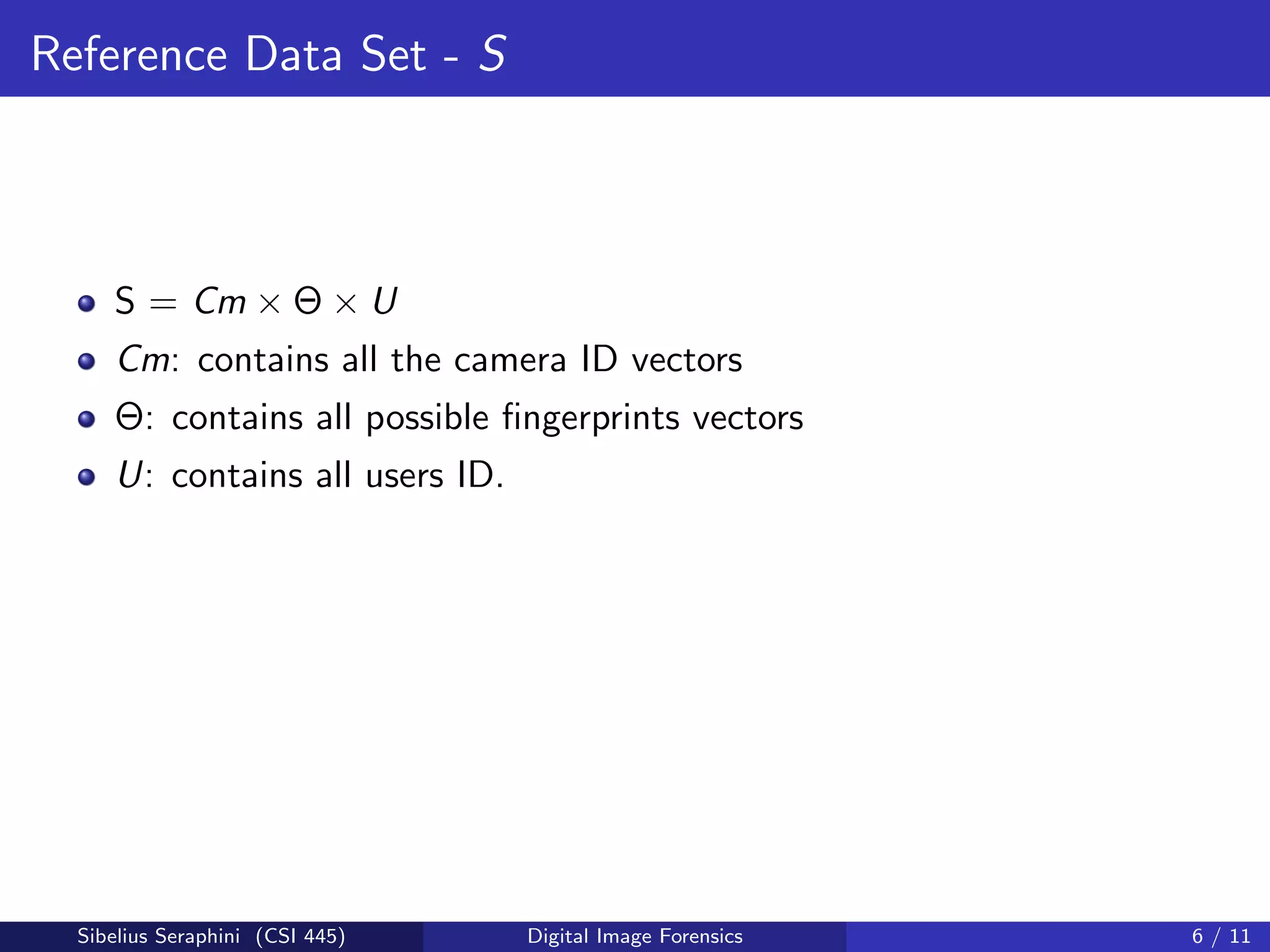
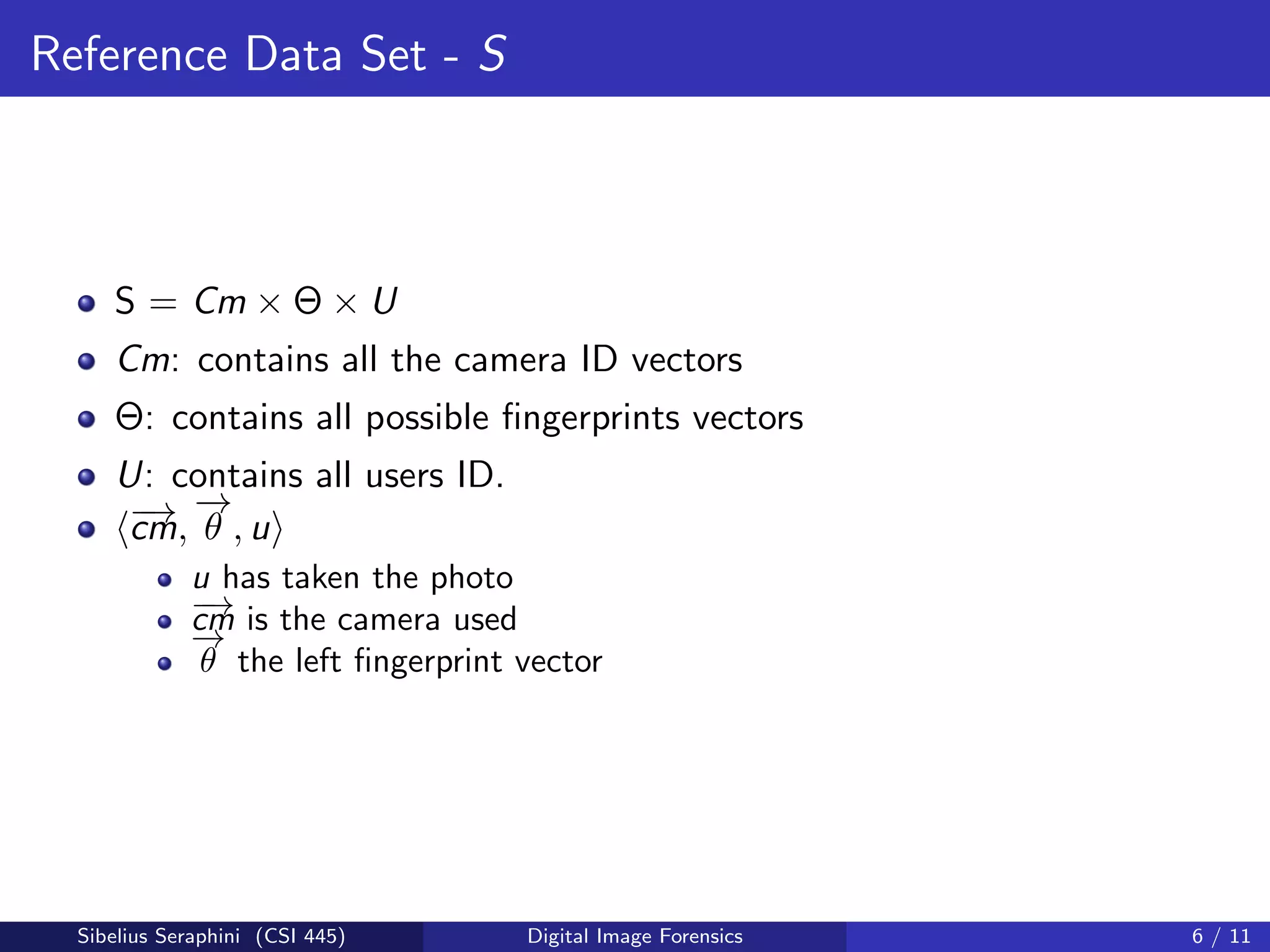
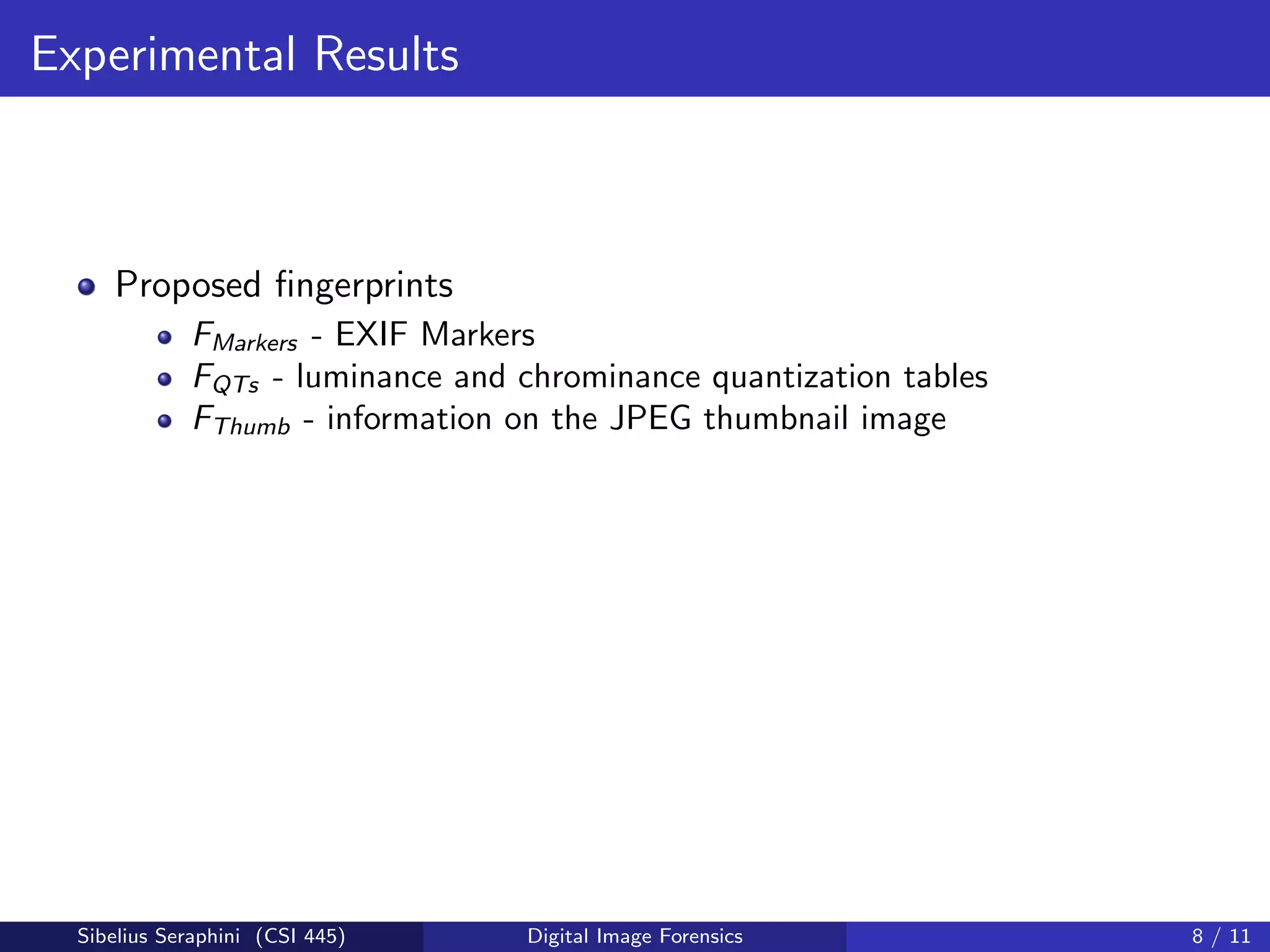
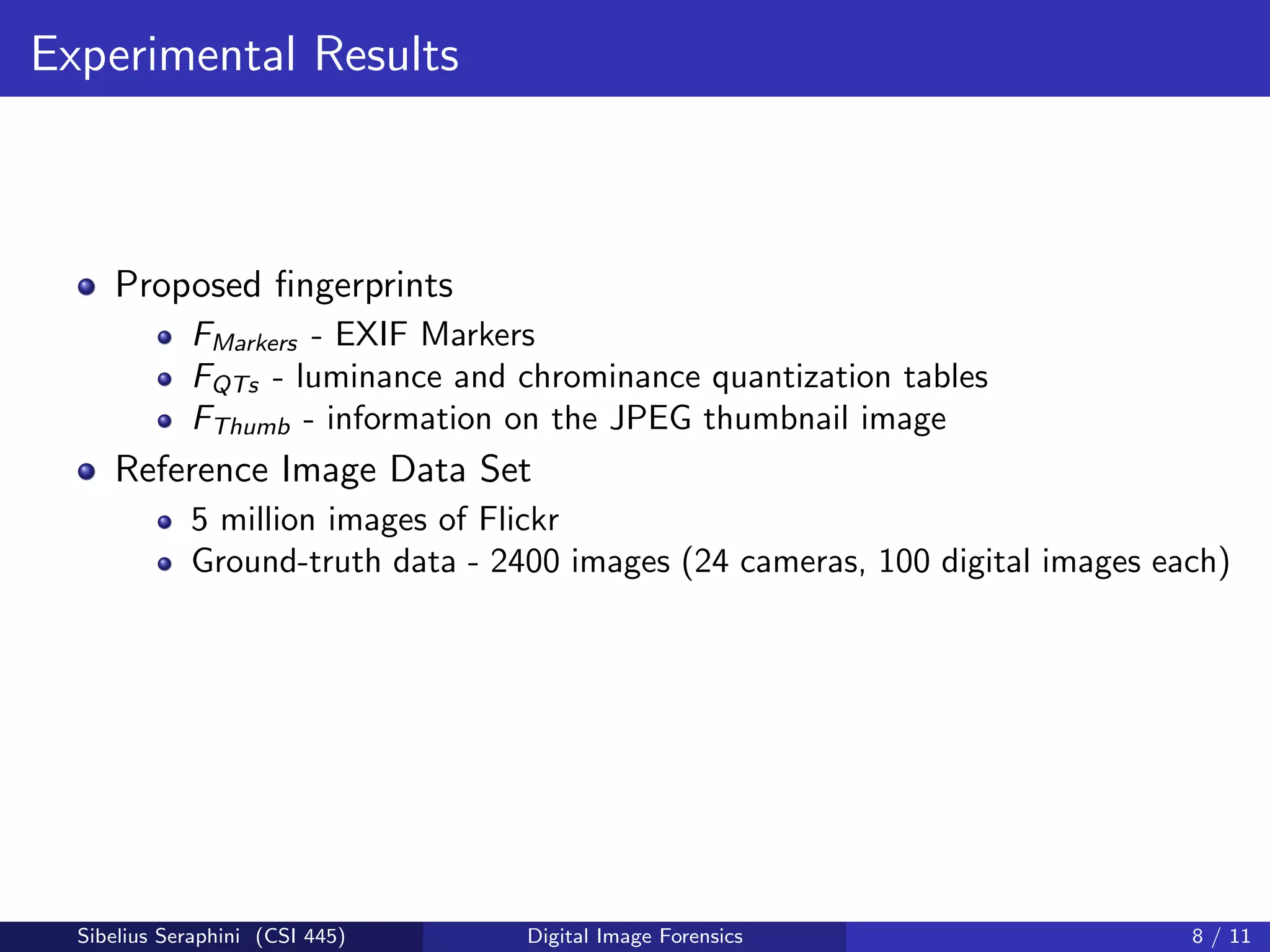
The document discusses a statistical approach to verify the originality of digital images by extracting and comparing image features against a reference set. It addresses the challenge of identifying original images from a database of unguaranteed images and highlights experimental results showing the effectiveness of the proposed methods. The findings suggest that image fingerprints can reliably indicate image authenticity, although limitations exist, such as dependency on reference data sets.