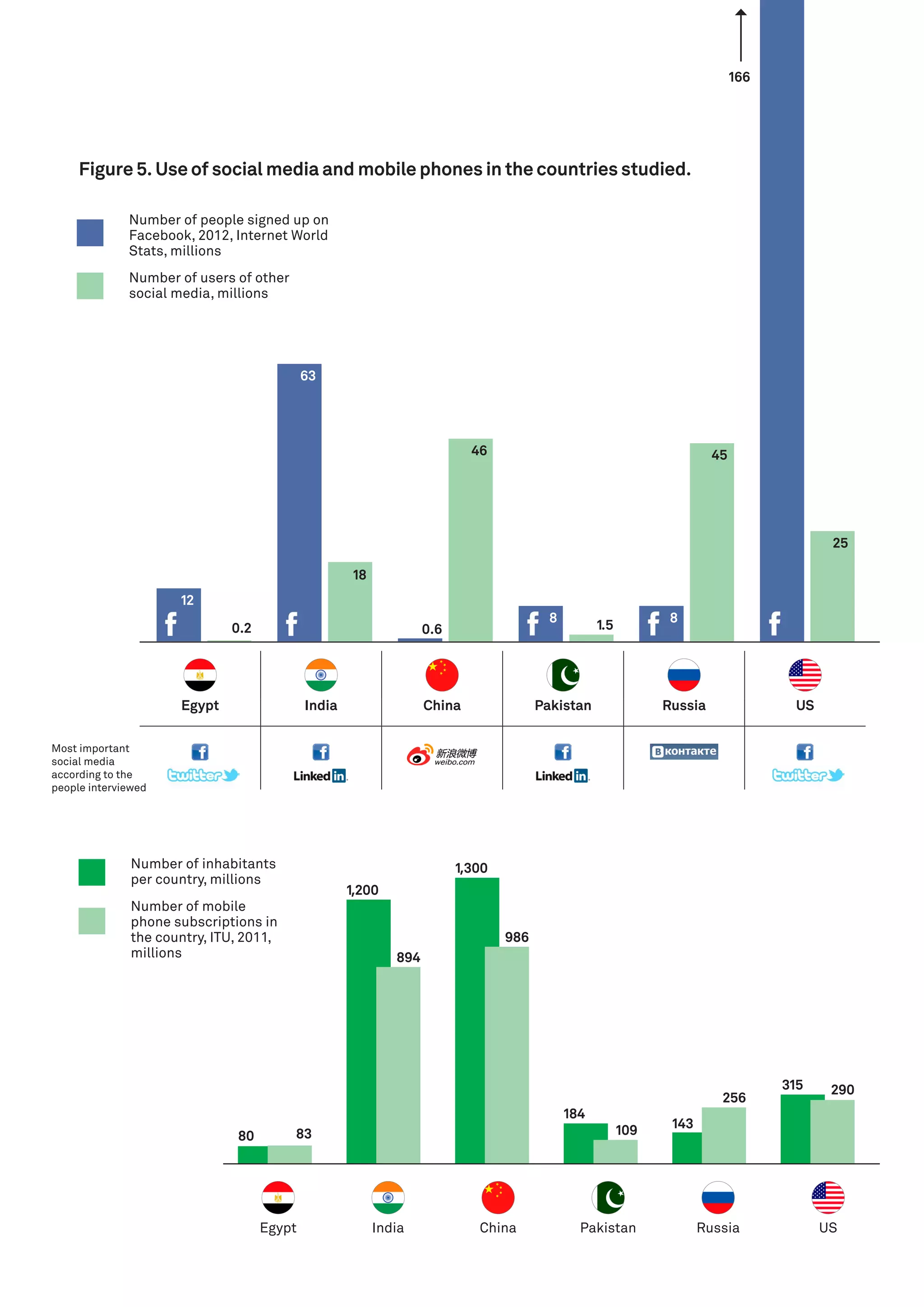
This document summarizes internet freedom in six countries based on interviews with experts. It finds that while the internet has increased access to information and communication, some regimes try to restrict it through censorship, surveillance, and laws. Monitoring organizations report many countries restricting internet freedom, with China often setting trends in control. Experts see potential for the internet to advance democracy but note traditional media also play an important advocacy role.















![18
Human rights are a highly sensitive topic of discussion in
China, since this is indirectly regarded as criticism of the
prevailing political system. In the other countries, however,
it is possible to discuss human rights issues online.
to discuss human rights, though it is easier to discuss social,
cultural and economic rights if caution is exercised. Online
advocacy activities are usually driven by individuals and
journalists rather than organisations.
Development and the fight against poverty can also be a
sensitive topic in China, since this is primarily a government concern. Whether it is regarded as sensitive, however,
depends on how the topic is approached.
In India, it is evident that the internet is becoming an ever
more powerful means of influence. The December 2012
gang rape in New Delhi attracted considerable attention
and drew strong protests. Expressions of protest were posted online using Facebook and WhatsApp, where users replaced their profile images with a black dot symbol.2 Tens of
thousands of Indians have signed an online petition protesting the lack of security for women in the country.3
Innovation can be discussed online in every country in the
study. There seems to be a general understanding of the internet as a communication channel that promotes innovation and new ways of thinking. In countries such as China
and Pakistan, restrictions on freedom of expression give
rise to innovation to some extent as bloggers and activists
try to get around the censorship. For instance, code words
are used to avoid filtering when controversial topics are discussed.
In contrast, issues concerning national security and tense
relations with other countries are a minefield. In China, it
is not possible to bring up the subject of Taiwan or Tibet. In
Russia, Chechnya is a highly sensitive topic. In Pakistan,
the national security situation is generally tense, and the
authorities do not want to attract attention to the situation
in the province of Baluchistan. India also has internal conflicts and security issues that may be risky to mention. Although it is unclear exactly how risky it is to discuss security
issues in Egypt at present, it seems to be subject to less extensive internet censorship than most of the other countries
in the study.
In the US, there is surveillance of suspected terrorists, and
anyone expressing sympathy with terrorist acts could have
problems. Otherwise, people in the US are free to discuss
national security issues online.
Advocacy work today
According to the people United Minds interviewed in China,
there are no Chinese organisations currently fighting for
greater freedom of expression online. The regime would
not tolerate that kind of organisation. It is generally risky
Alok Dixit, a net activist in India, has organised a number
of online offensives. His most recent action, ‘Stop Acid
Attacks’, campaigns against such attacks on women by men
who want to punish them (www.stopacidattacks.org).
Dixit is living proof that it is possible to engage in advocacy
work online, although he and the other people interviewed
feel that the channel is immature in the sense that its full
potential has not been realised.
In Pakistan, an active group of internet activists have
fought strenuously against government efforts to develop
a national internet firewall. A couple of organisations, of
which Bytes for All is the oldest and most influential, are
campaigning for freedom of expression online. Shahzad
Ahmad, the Country Director of Bytes for All, believes
that it is possible to pursue advocacy work online on issues
involving human rights, the fight against poverty, personal
safety, innovation and women’s rights.
For example, a major impact was made by a provocative
music video created by the Pakistani rock band Beygairat
Brigade [Shameless Brigade]. The video criticised the military’s influence in Pakistan and was quickly blocked by
Vimeo, with no reason given (www.vimeo.com/64414932).
The group broke through with another video, Alau Anday
2 articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2012-12-21/
chandigarh/35952817_1_delhi-gangrape-city-student-dot
3 timesofindia.indiatimes.com/tech/social-media/Delhigang-rape-case-FacebookTwitter-fuels-rally-at-India-Gate/
articleshow/17741529.cms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siinternetfreedoma4web-131110211320-phpapp01/75/Si-internet-freedom-a4_web-20-2048.jpg)
![20
[Potatoes and eggs], which joked about the country’s leading politicians and generals (www.vimeo.com/30691910).
In Egypt, the internet played a key role in the overthrow of
the Mubarak regime. As a result, those governing Egypt
today have a complicated relationship with the country’s
internet activists. The activists are considered dangerous
and have to be treated with caution. The people we interviewed in Egypt all affirm that it is possible to undertake
advocacy work online on social issues, as shown by the 2011
revolution. It was not the internet itself that overthrew the
Mubarak regime, but rather tools such as Facebook,
Twitter and YouTube that allowed the protests to spread
more quickly and become more large-scale. 4
In Russia, the internet has developed into one of the most
important channels for providing news, in part because of
the absence of other free media. This makes the internet a
natural channel for anyone who seeks to conduct advocacy
work on social issues and reach a larger audience.
4 Tim Eaton (2012), Online Activism and Revolution in Egypt:
Lessons from Tahir, New Diplomacy Platform
According to the people United Minds interviewed in
Russia, it is possible to carry out advocacy work on issues
concerning human rights, development and the fight
against poverty, and innovation. It is also possible to criticise political leaders, despite the considerable risk of being
reprimanded.
Recently, a mysterious video turned up online in which
Russia’s Prime Minister Dmitri Medvedev was criticised by
former Russian political leaders in interviews. The video
was professionally produced but contained no indication of
who posted it. The aim was clearly to damage Medvedev, and
indirectly Russia’s President, Vladimir Putin. The video
angered Putin; at a press conference where he first requested that journalists turn off their cameras, he sharply criticised the filmmakers (www.lifenews.ru/news/112845). The
internet tabloid Life News, which published a video clip on
its website, was threatened with losing its right to attend
Kremlin press conferences.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siinternetfreedoma4web-131110211320-phpapp01/75/Si-internet-freedom-a4_web-22-2048.jpg)
![21
Vıews of Sweden and ınternet
freedom.
An unfamiliar role model
Sweden is widely recognised for its high degree of freedom
of expression online. Although the general level of knowledge about Sweden is low in many of the countries studied,
the people interviewed have an image of Sweden as a free,
open society.
Human rights activist Nadine Sherif in Egypt:
“Sweden is generally regarded as a role model for how its
citizens are treated. I don’t know about Sweden and internet
freedom, but I have never heard anything bad about Sweden.”
Shahzad Ahmad of the organisation Bytes for All, in Pakistan:
“Scandinavia overall is the best example of civil liberties in
practice, especially when it comes to freedom of
expression.”
The blogger Sana Saleem in Pakistan was more cautious in
identifying role models, but she definitely believed Sweden
was free compared to other countries:
“The models for Pakistan when it comes to freedom of expression are European countries – not the United States in
any respect.”
One of the Chinese respondents:
“I don’t know anything about what the situation is like in
Sweden, but I assume it is very free in relative terms.”
Another Chinese respondent, who had been to Sweden,
was somewhat better informed. She believed that Sweden
was a good role model for other countries:
“I know that Sweden has a really high profile when it comes
to openness and transparency. But if you were to ask typical
Chinese people, most would probably think that the US
was the best role model. Most Chinese don’t know anything
about Sweden, but in my opinion, the US is not the perfect
role model.”
Not as polarising as the US
In Pakistan and Egypt, people have a highly negative view
of the US. Most of the interviewees in these countries see it
as a problem that freedom of expression is so strongly associated with the US.
Blogger Sana Saleem:
“Sadly, freedom of expression is seen in Pakistan as a Western notion. We actually avoid that term, instead using terms
like ‘free flow of information’ or ‘open access’.”
Journalist Nasry Esmat in Egypt:
“When people [in Egypt] think about freedom, they usually
think about the US. The West in general is associated with
freedom, but in the conservative Egyptian mind this is not
necessarily seen as something good. Freedom is to some extent connected to moral decay. Islamists equate freedom to
gay rights, and that is not seen as something good in Egypt –
not something you want to be associated with.”
Pranesh Prakash of the Centre for Internet and Society in
India is involved internationally and was therefore well informed about which countries were driving issues involving
freedom of expression online:
“Sweden is definitely on that list, as well as the Netherlands.”
He did not know exactly what Sweden’s strengths are when
it came to internet freedom, but thought it was a big advantage that Sweden is not as polarising as the US:
“If the Americans suggest something, many disapprove just
because it comes from them. If Sweden takes up the same
proposal, the chances are greater that the debate will be
about the proposal itself.”
Finland a role model for Russia
Somewhat more is known about Sweden in Russia, perhaps
because it is geographically closer than the other countries.
The Russian interviewees affirmed that the Nordic countries were role models for online freedom of expression.
Russian journalist Oksana Chelysheva:
“Finland, Sweden, basically all the Scandinavian countries
– but not the Baltic States.”
However, both she and Ilya Stechkin of Moscow State
University consider Finland to be the main model. In their
view, Finland has traditionally enjoyed a special relation-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siinternetfreedoma4web-131110211320-phpapp01/75/Si-internet-freedom-a4_web-23-2048.jpg)














![36
“They can’t censor everything – both because it costs too
much and because some breathing space is needed. Otherwise, the discontent will grow,” agrees Wu Fang.
His impression is that most average Chinese do not attach
that much importance to freedom of expression on political
issues. “That’s not something they have time to think about.
People care mainly about making money and how they’ll
be able to make a living,” he explains. “For many people,
it is important what music they can listen to, what movies they’re allowed to see and what products they can buy.
They’re less bothered about what they’re permitted to say.”
More permissible issues
Some issues in society can be raised without repercussions.
The government even encourages discussion of certain
problems. This is particularly true of revelations about corrupt local officials, whom leaders in Beijing would like to
see imprisoned.
“People are allowed to criticise corruption, especially in
isolated cases. Pornography can also be criticised,” says
Deng Bo.
“Topics like the fight against poverty, social injustice, environmental destruction, domestic violence against women
and the child sex trade can be discussed online,” affirms
Cheng Lian.
However, there do not seem to be any organisations within
China’s borders which are fighting for greater freedom of
expression online. “You can’t have any organisation like
that, because then the police will come after you,” Wu Fang
explains.
“Some traditional media are trying to stretch the limits.
They might post a news bulletin online, but it will usually
be removed within a few hours,” he adds.
Views on freedom of expression in other
countries
When Wu Fang is asked which countries have more freedom of expression than China, he cites the US, Hong Kong,
Taiwan and Japan. He also mentions Europe but says that
he does not know anything about specific European countries.
Deng Bo thinks there is greater freedom overall in every
country outside China. “However, I haven’t been to Cuba,
so I don’t know about there,” she adds. She thinks Sweden
has transparency and freedom of expression, but does not
know any details.
Cheng Lian: “I think Sweden is a role model when it comes
to openness and transparency. But if you ask average
Chinese people, they would probably answer the US – although I don’t agree on that point.”
How Sweden can help
The respondents have different suggestions for what Sweden can do to help increase freedom of expression in countries like China.
Wu Fang notes that the US supports organisations that
develop proxy servers for Chinese internet users. But that
is not really very effective because a proxy server can be
blocked rather easily. “[The Chinese authorities] have
enough technology and clever people to block any proxy. If
things go really badly, the government could develop a local
internet, just for Chinese people.”
In Deng Bo’s view, Sweden should highlight constructive
examples of how freedom of expression can contribute to
better economic growth. “Show how freedom of opinion
makes it easier for a country to develop, and that countries
that suppress opinions have problems,” she says.
“You should raise the Swedish profile with regard to transparency in the projects you’re already doing, like Sidafunded projects,” suggests Cheng Lian.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siinternetfreedoma4web-131110211320-phpapp01/75/Si-internet-freedom-a4_web-38-2048.jpg)













