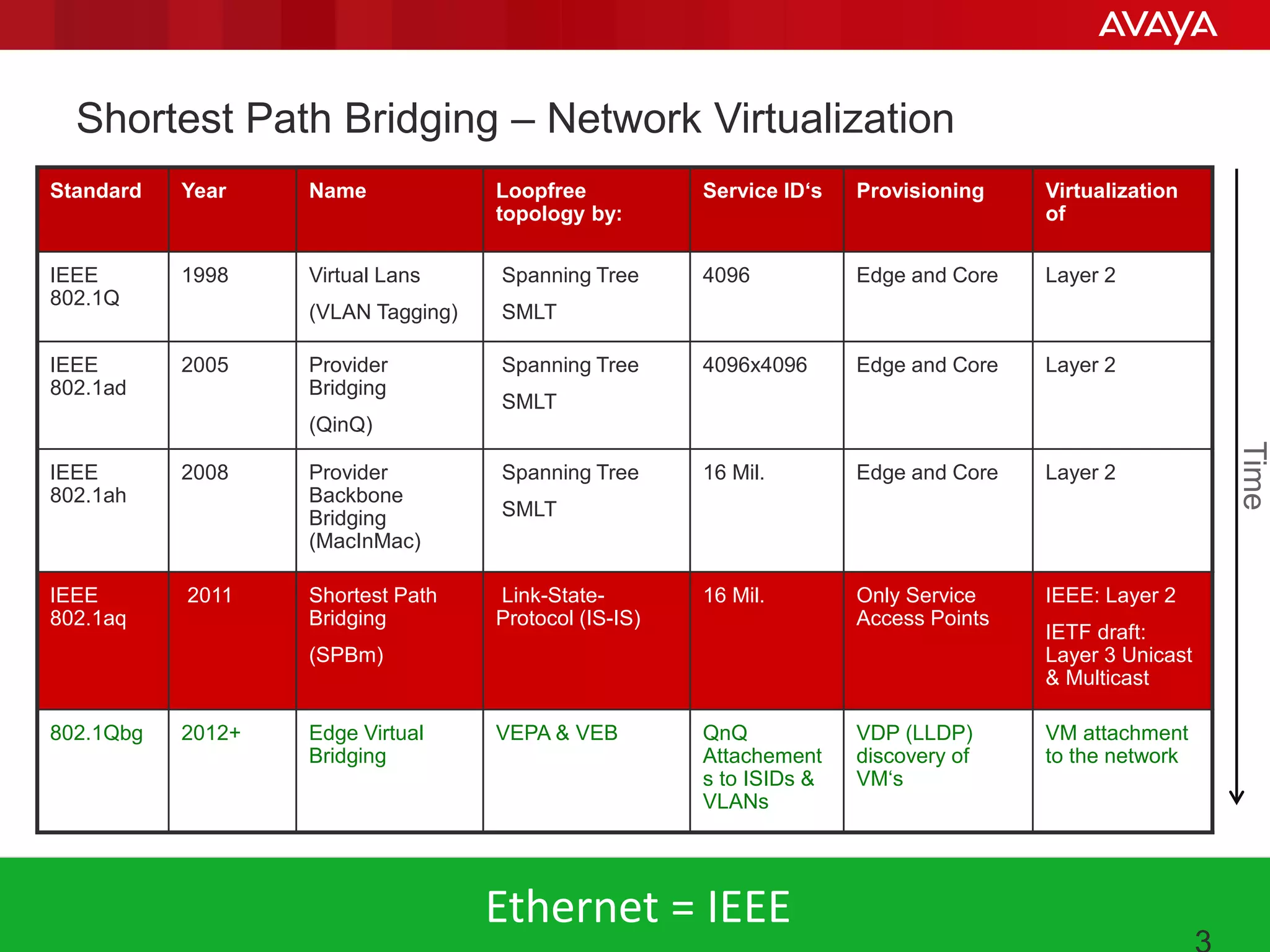
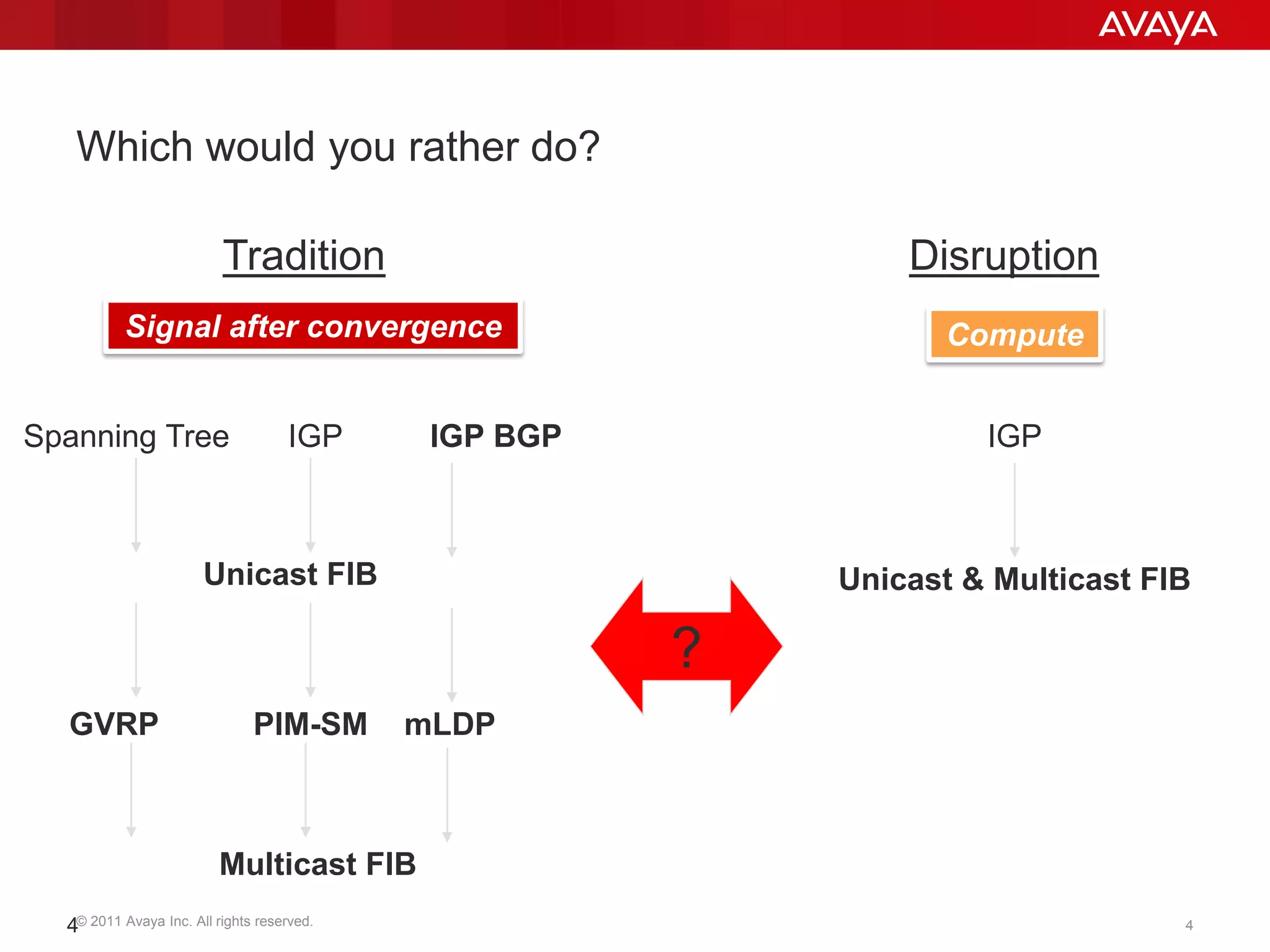
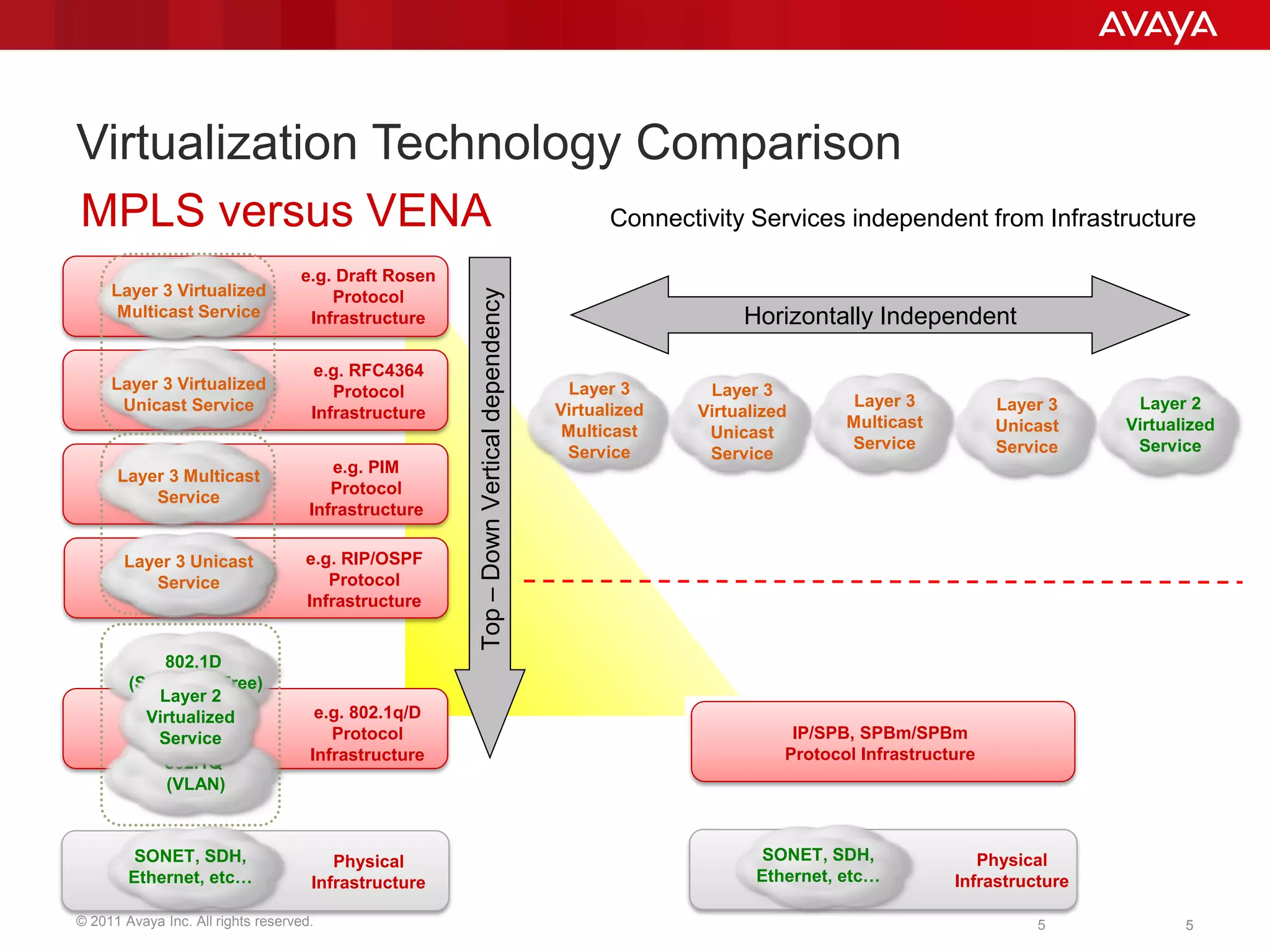
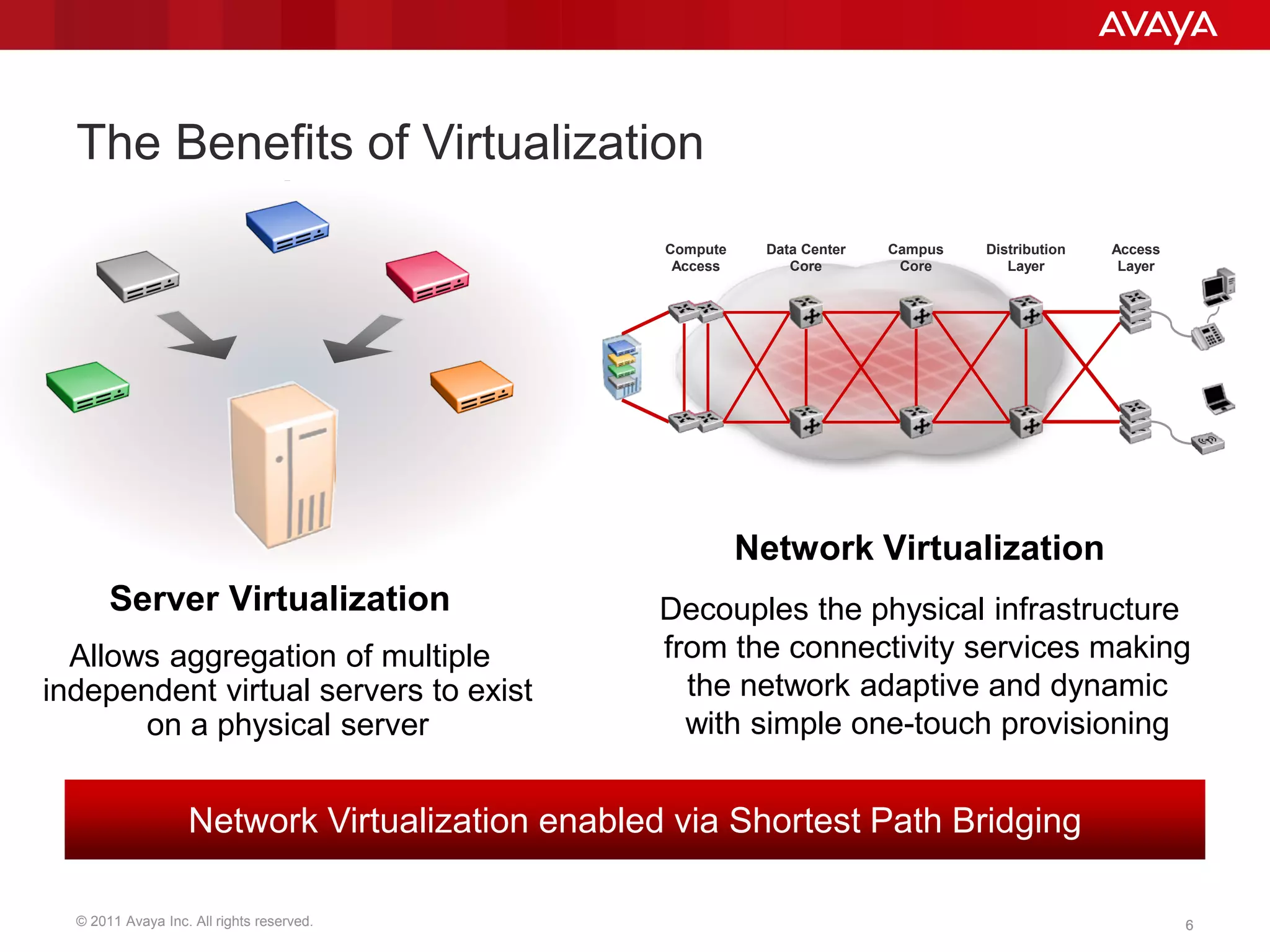
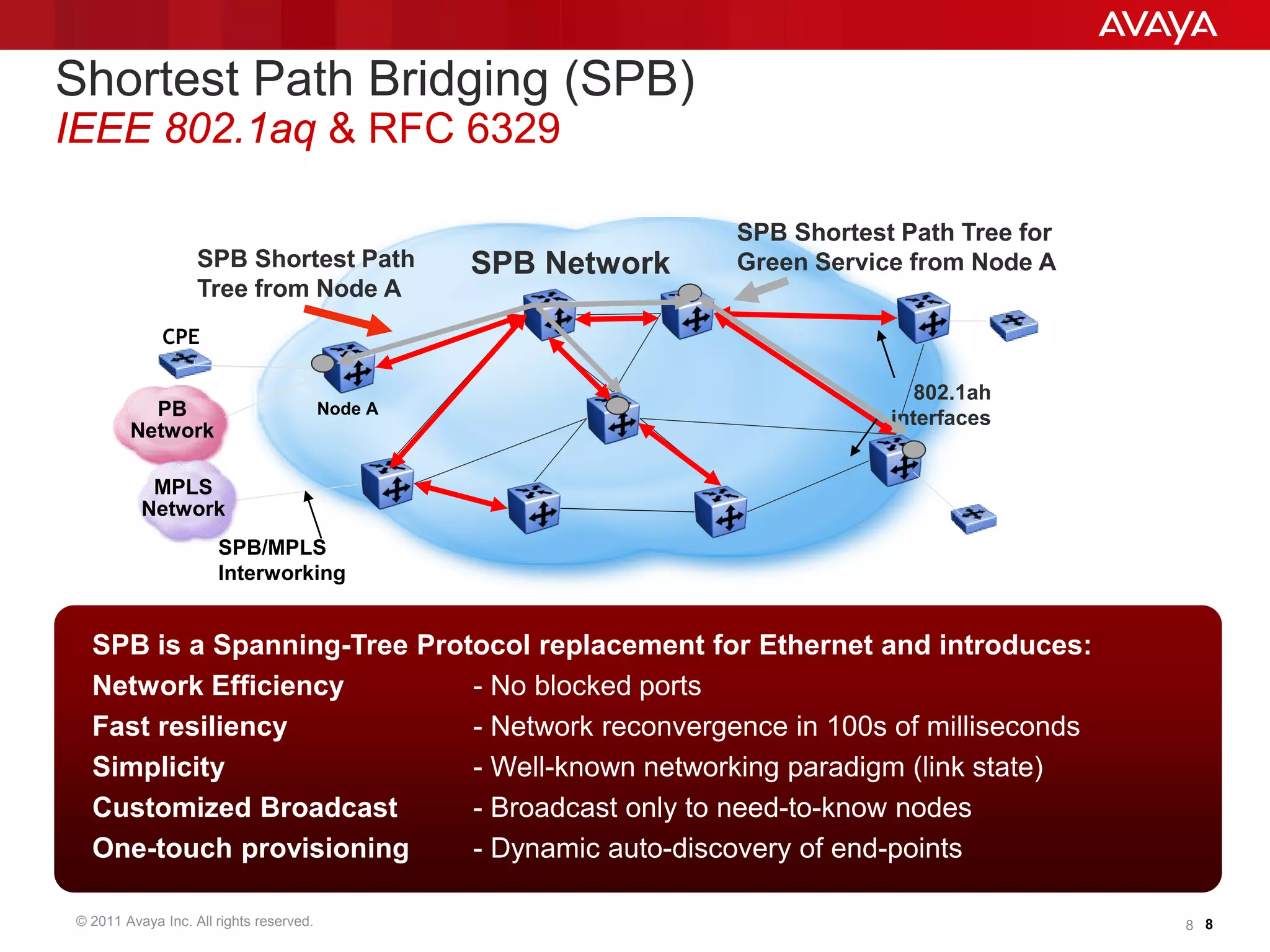
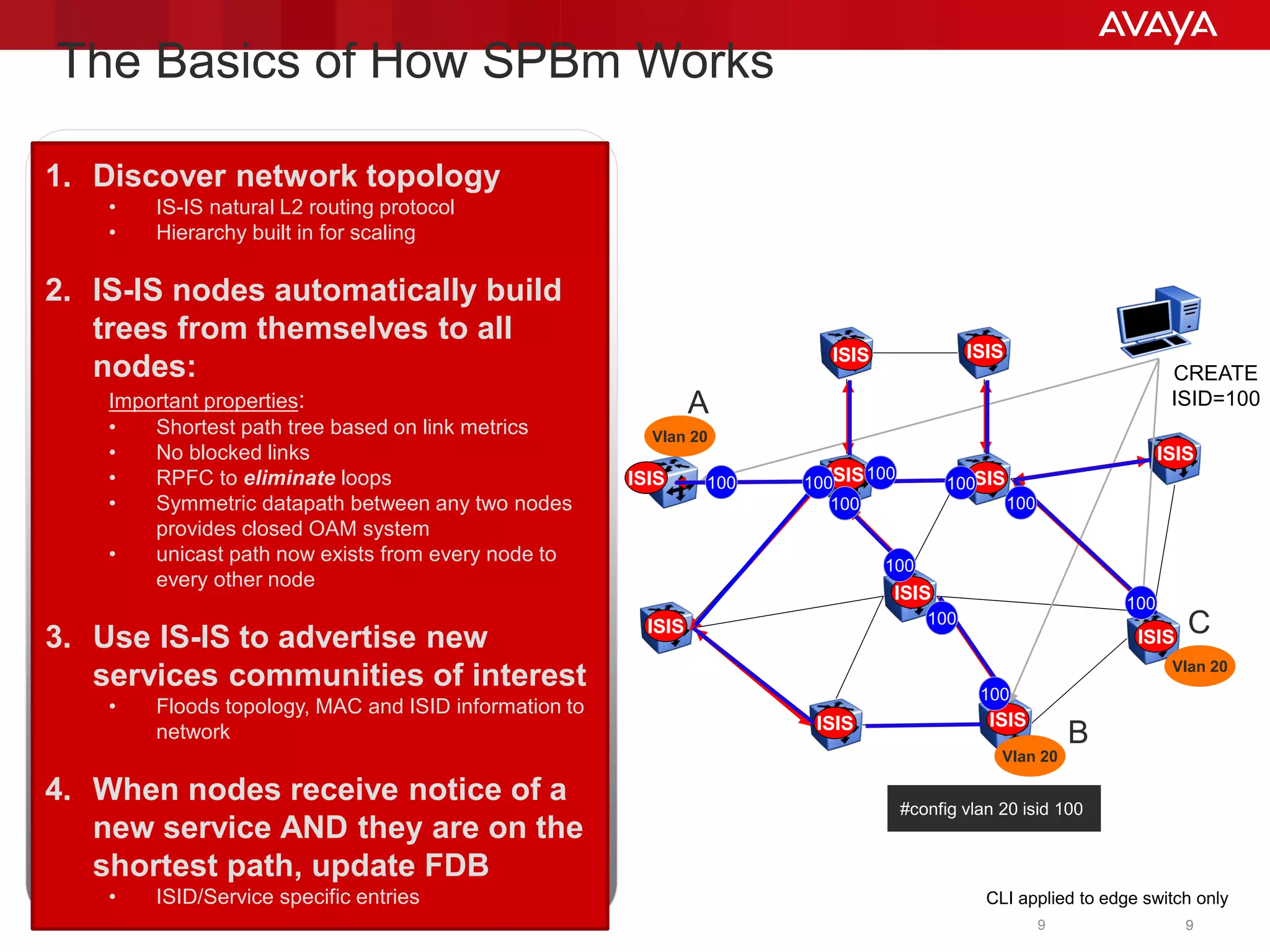
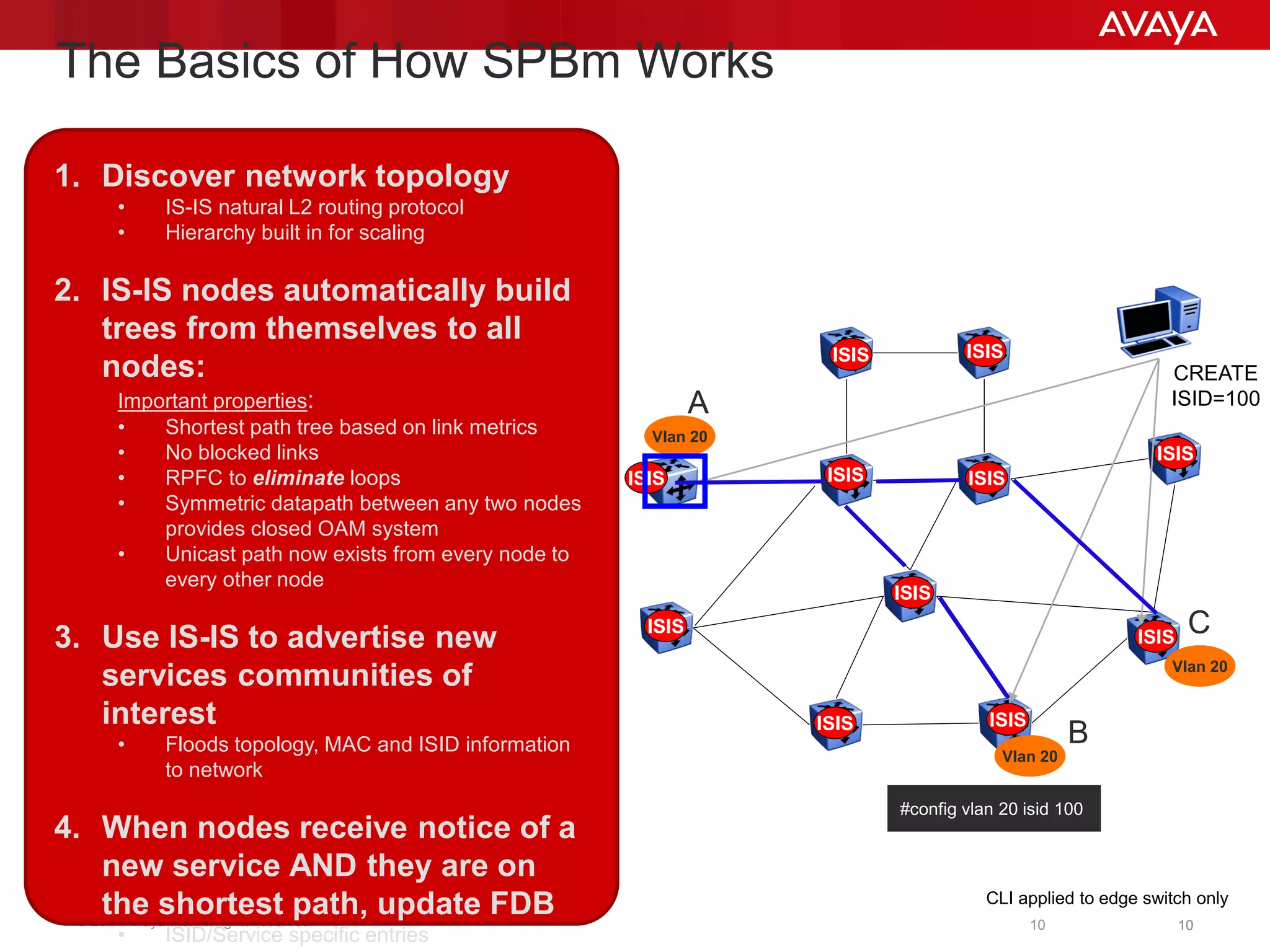
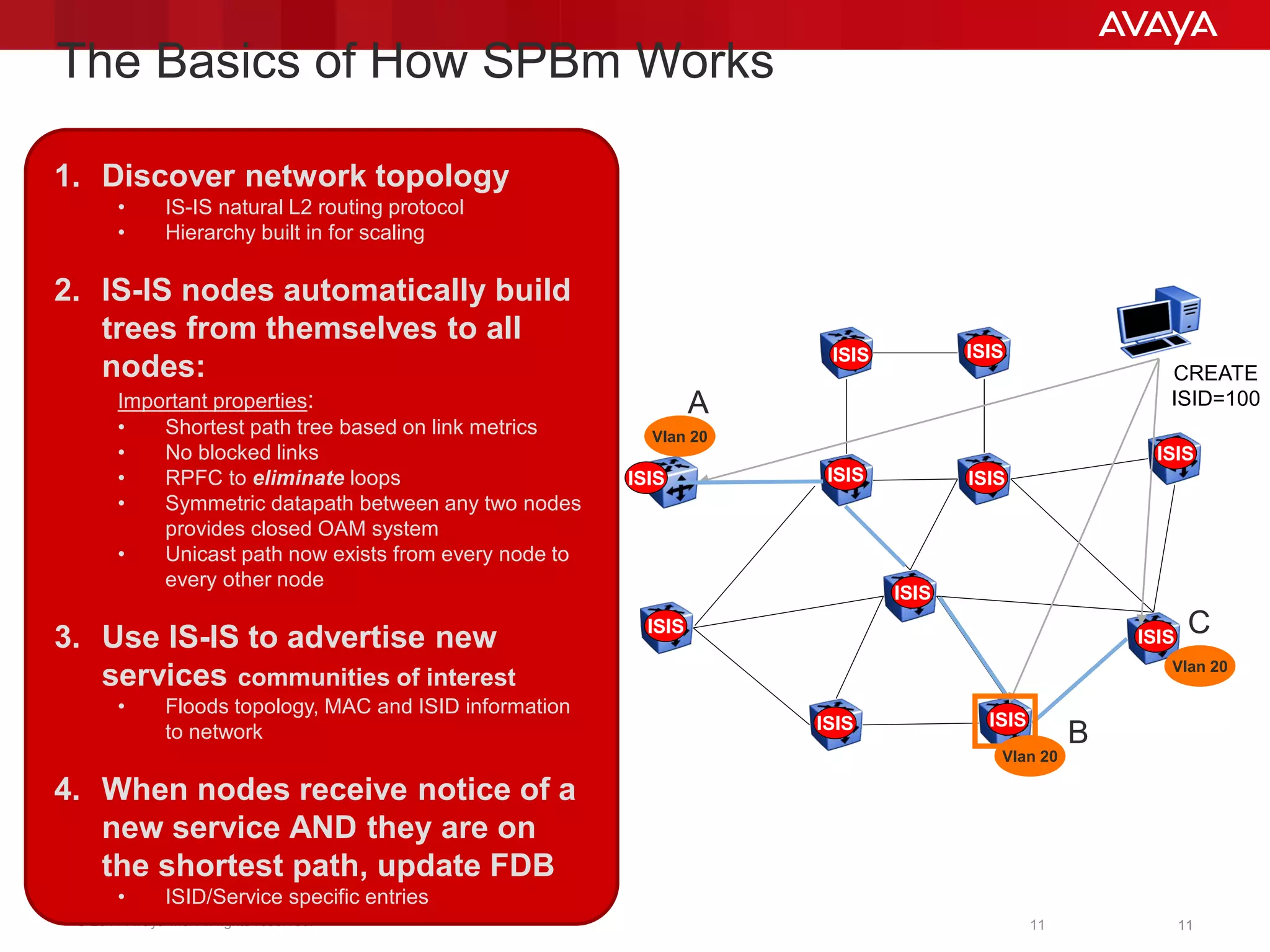
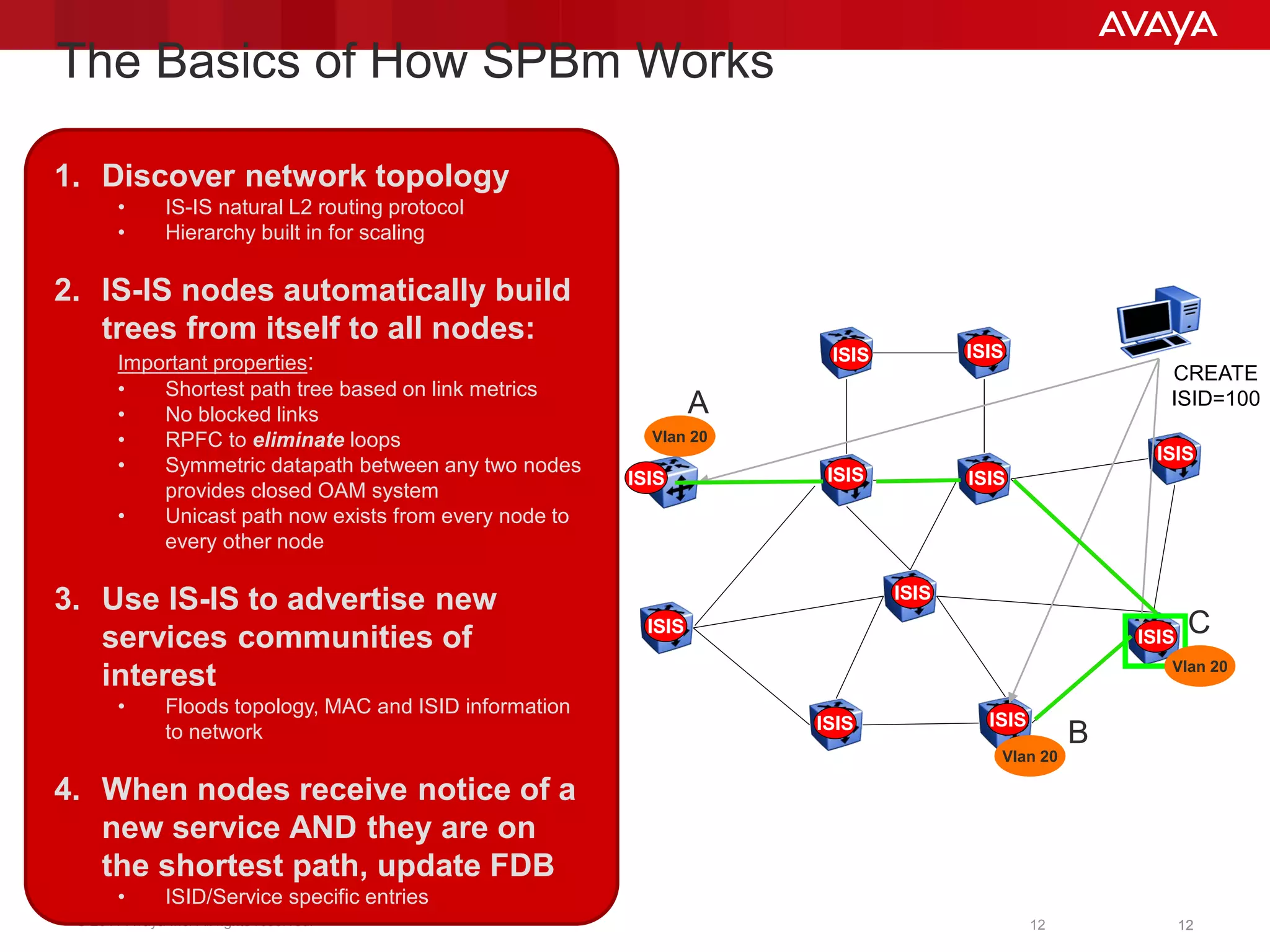
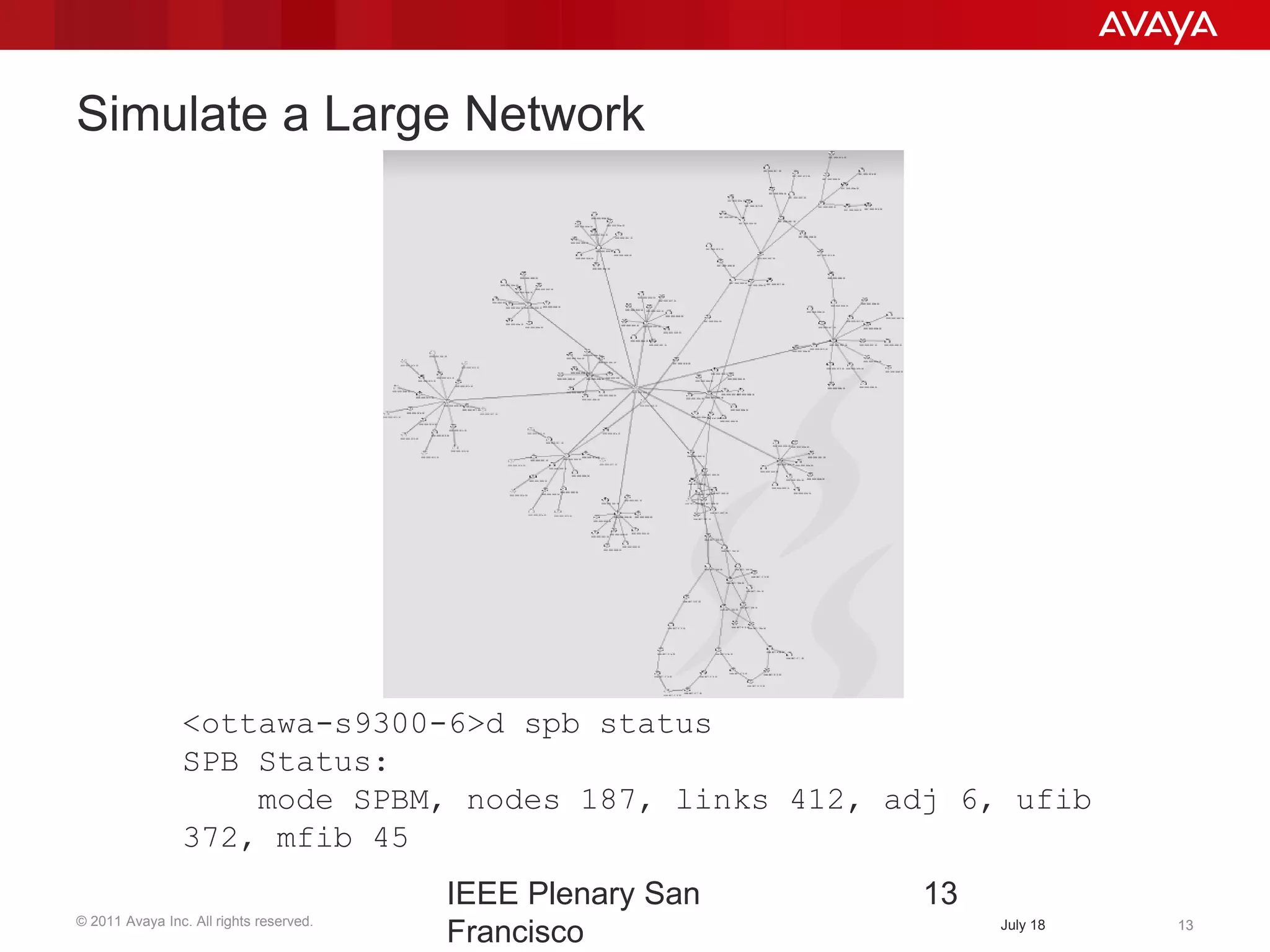
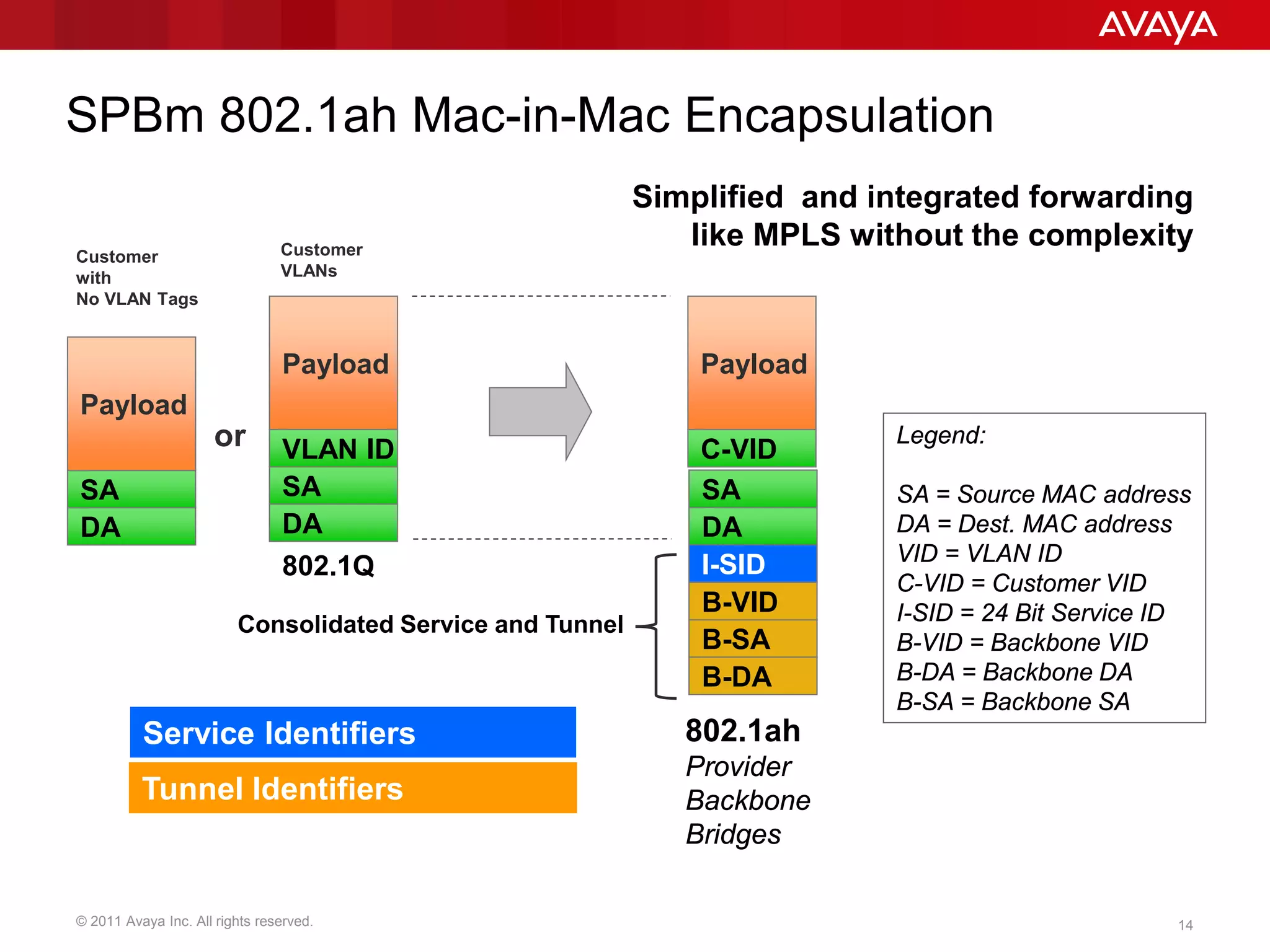
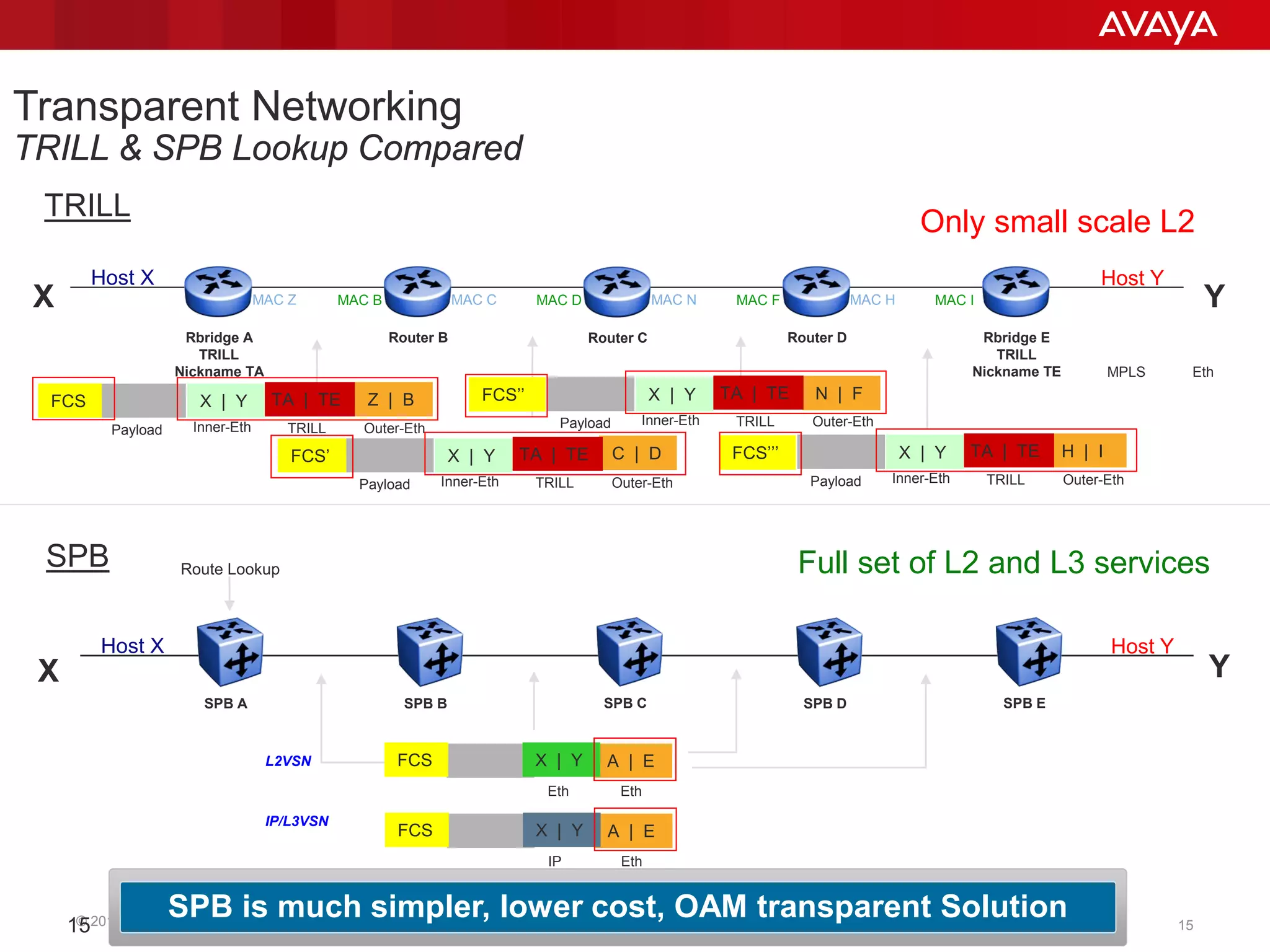
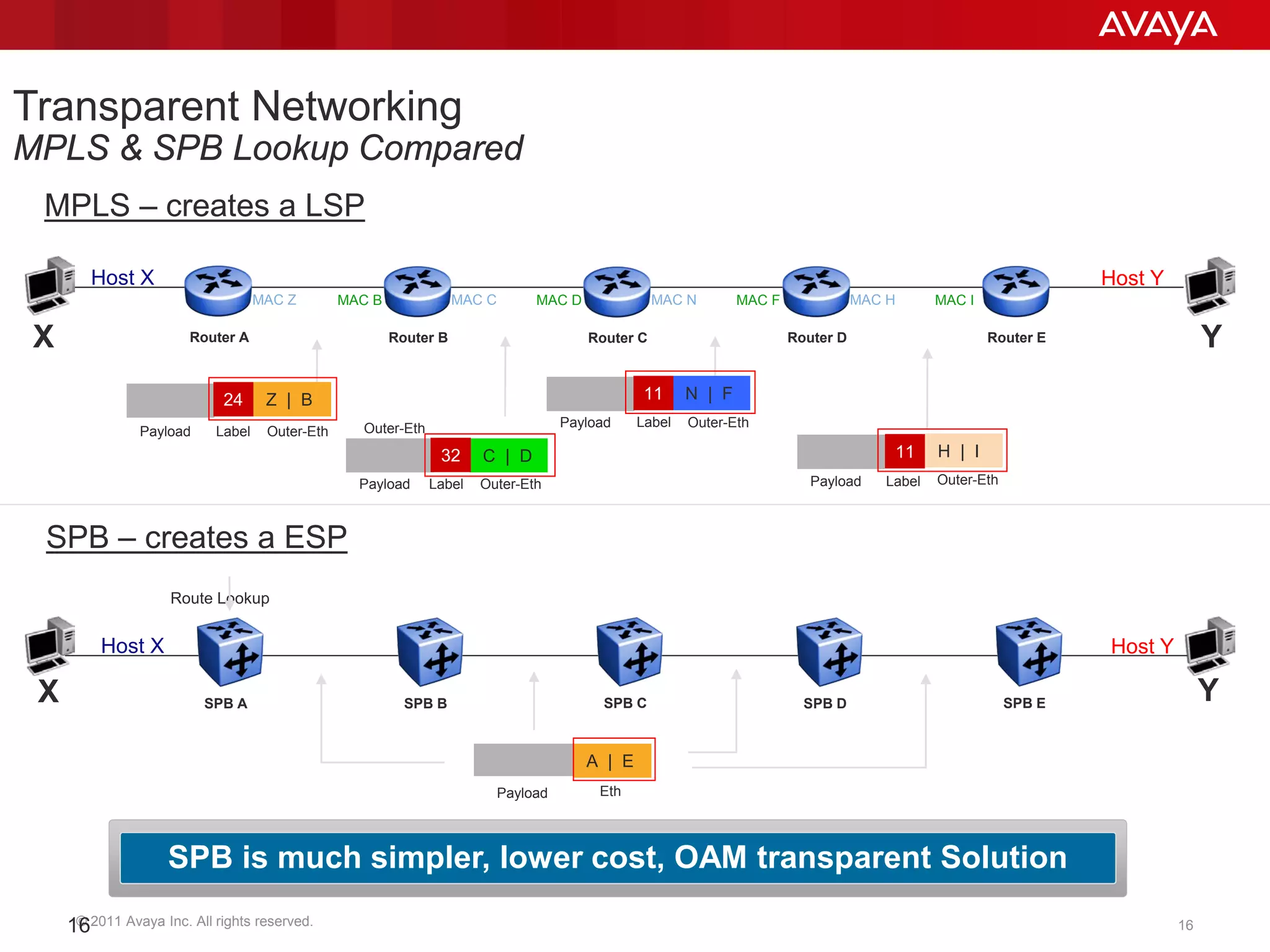
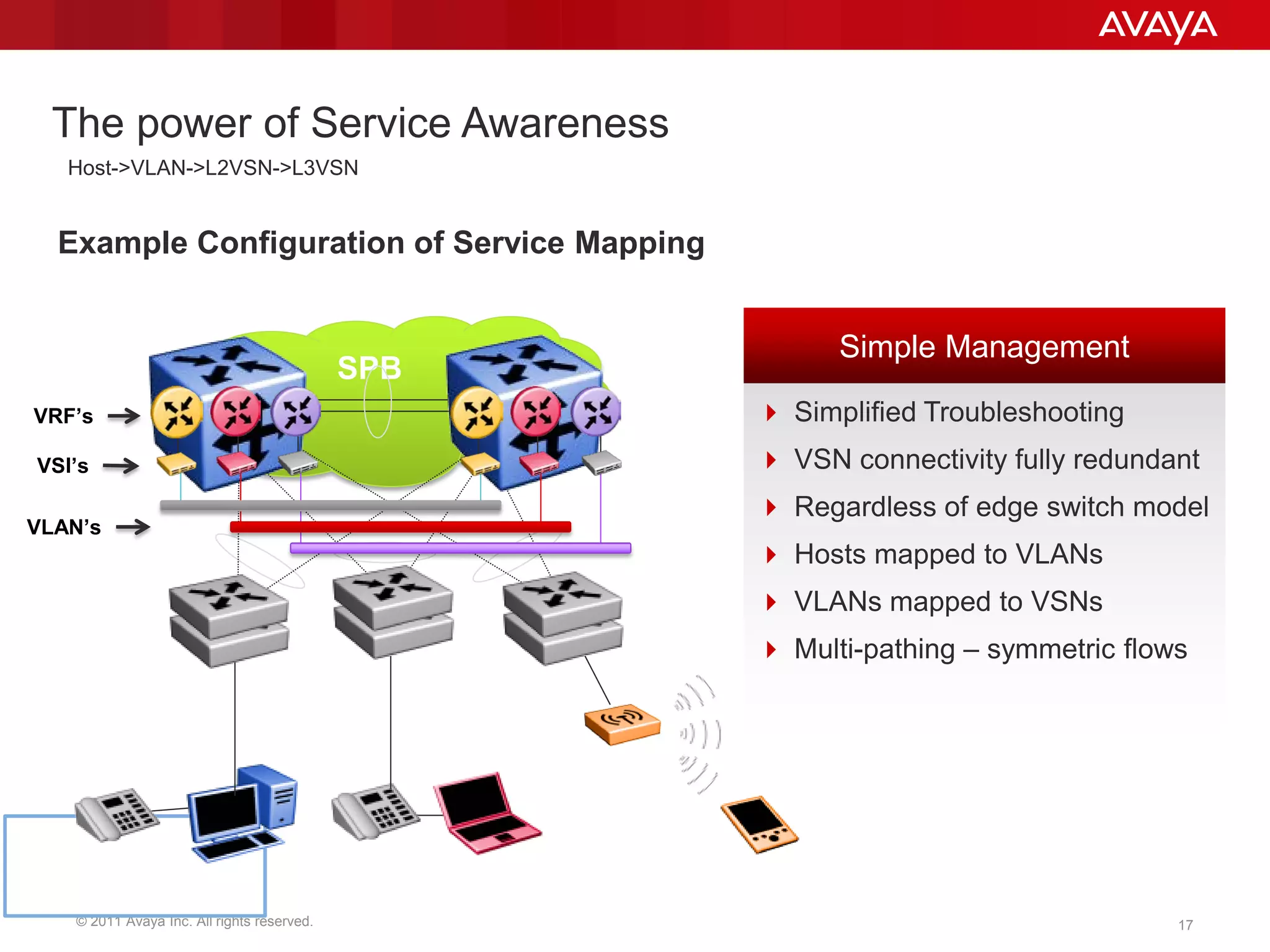
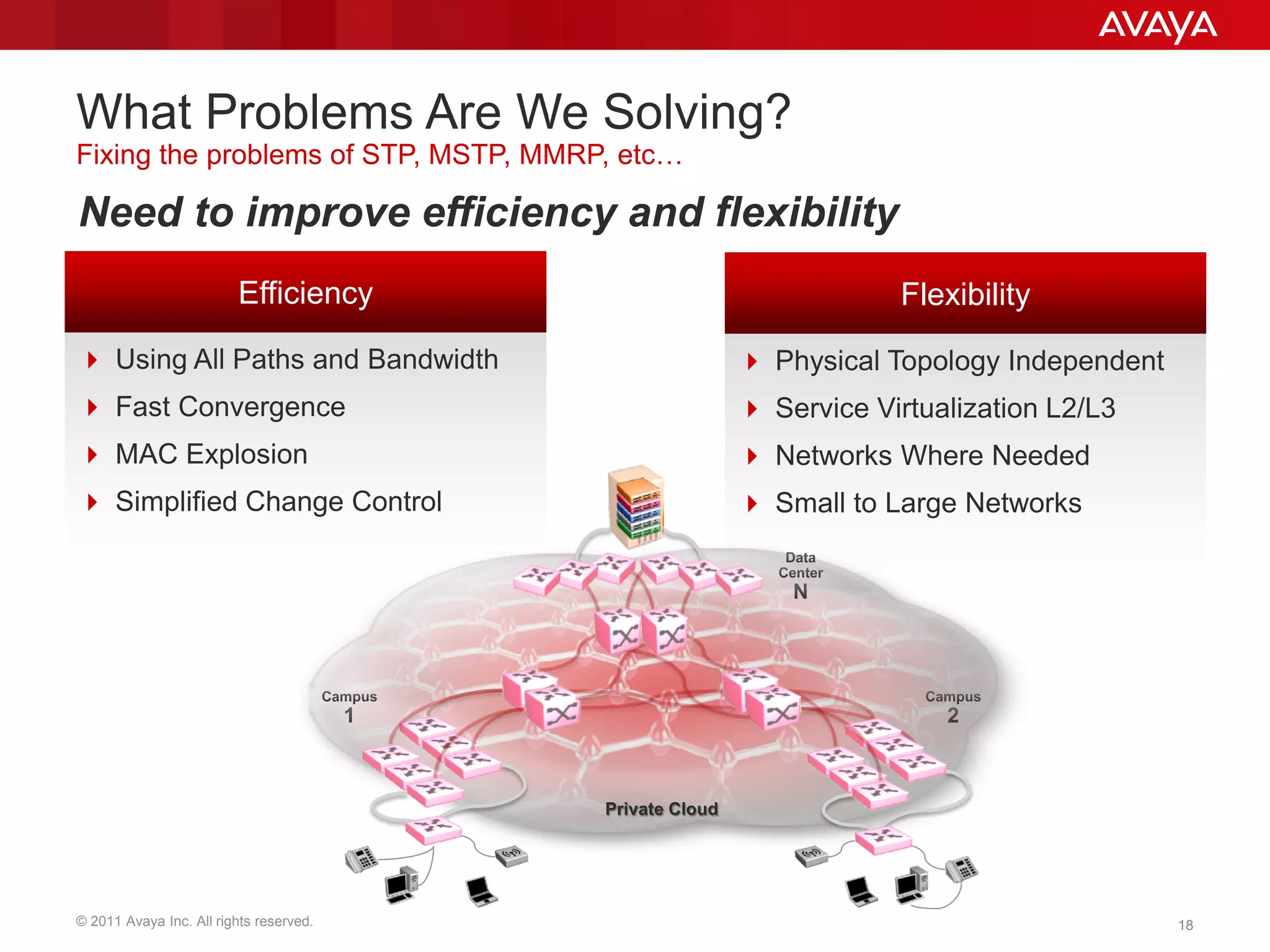
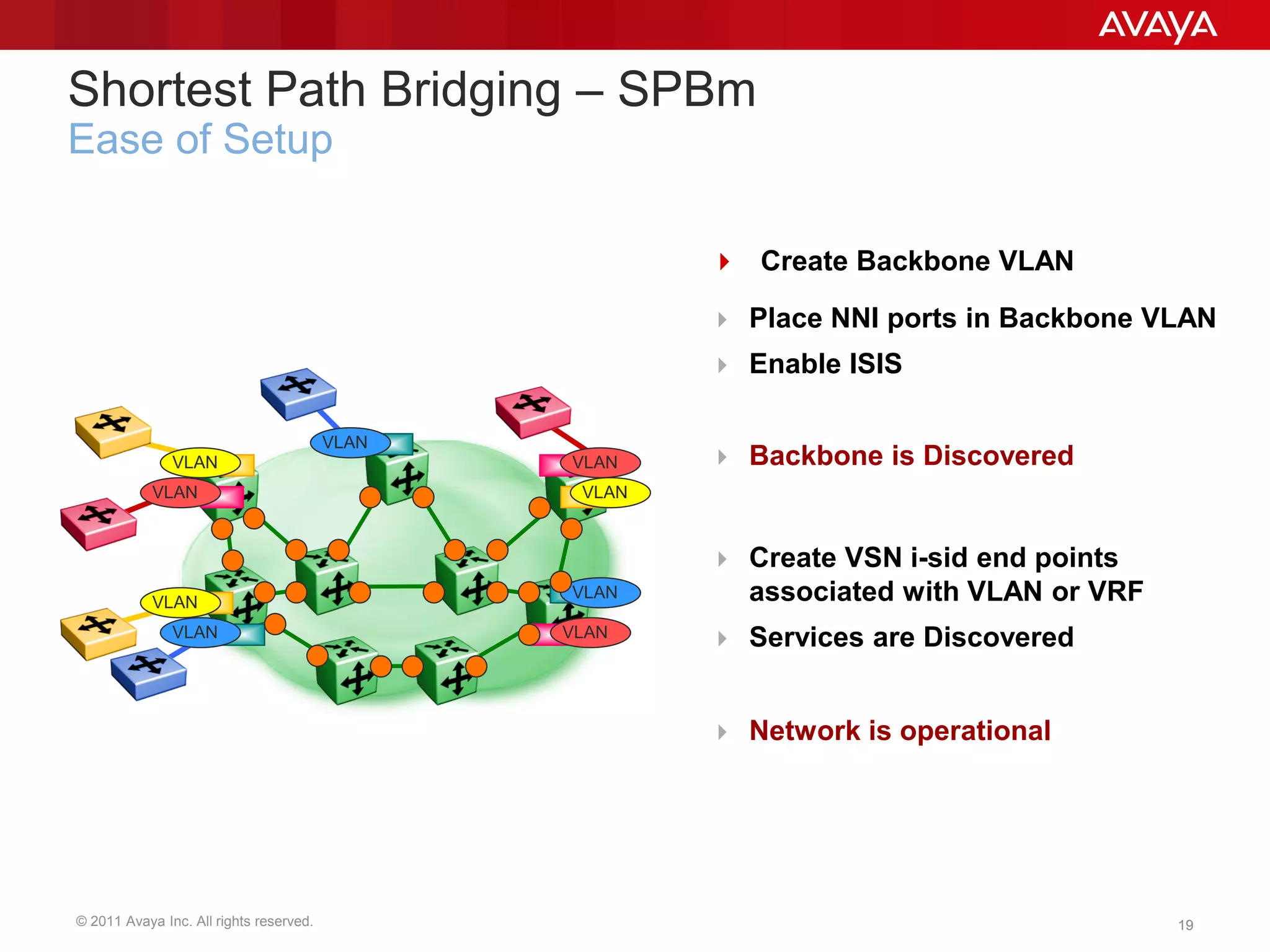
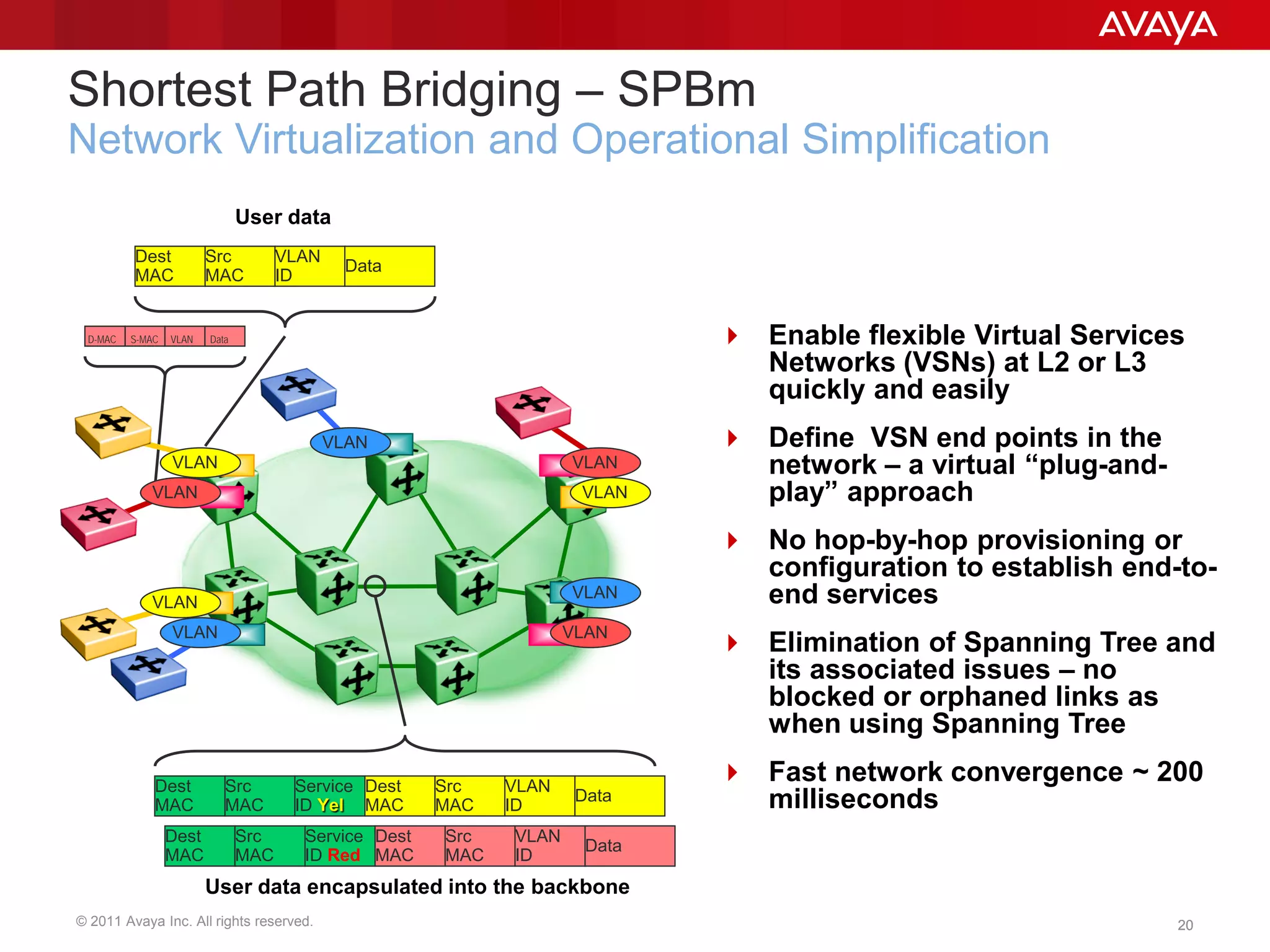
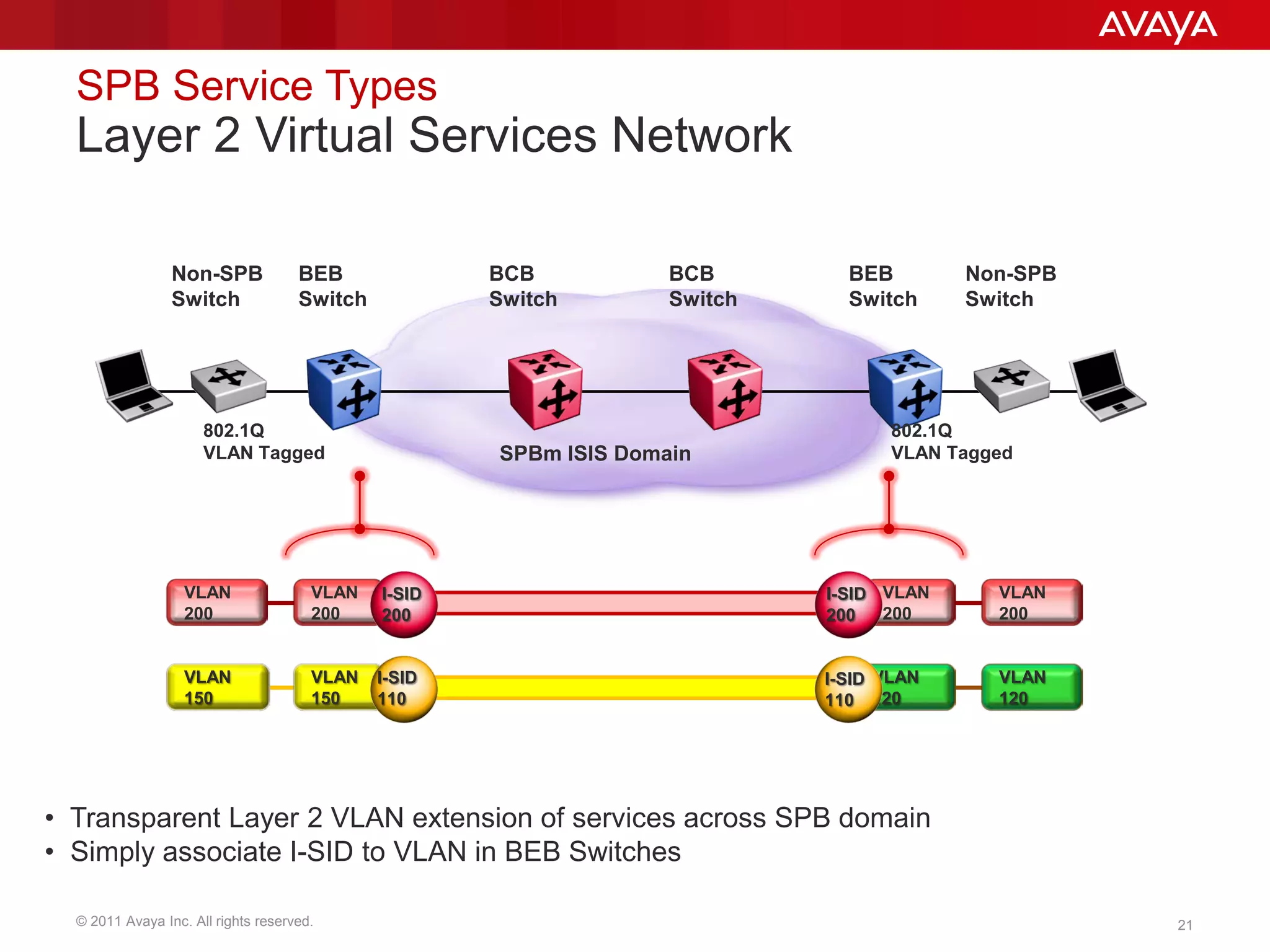
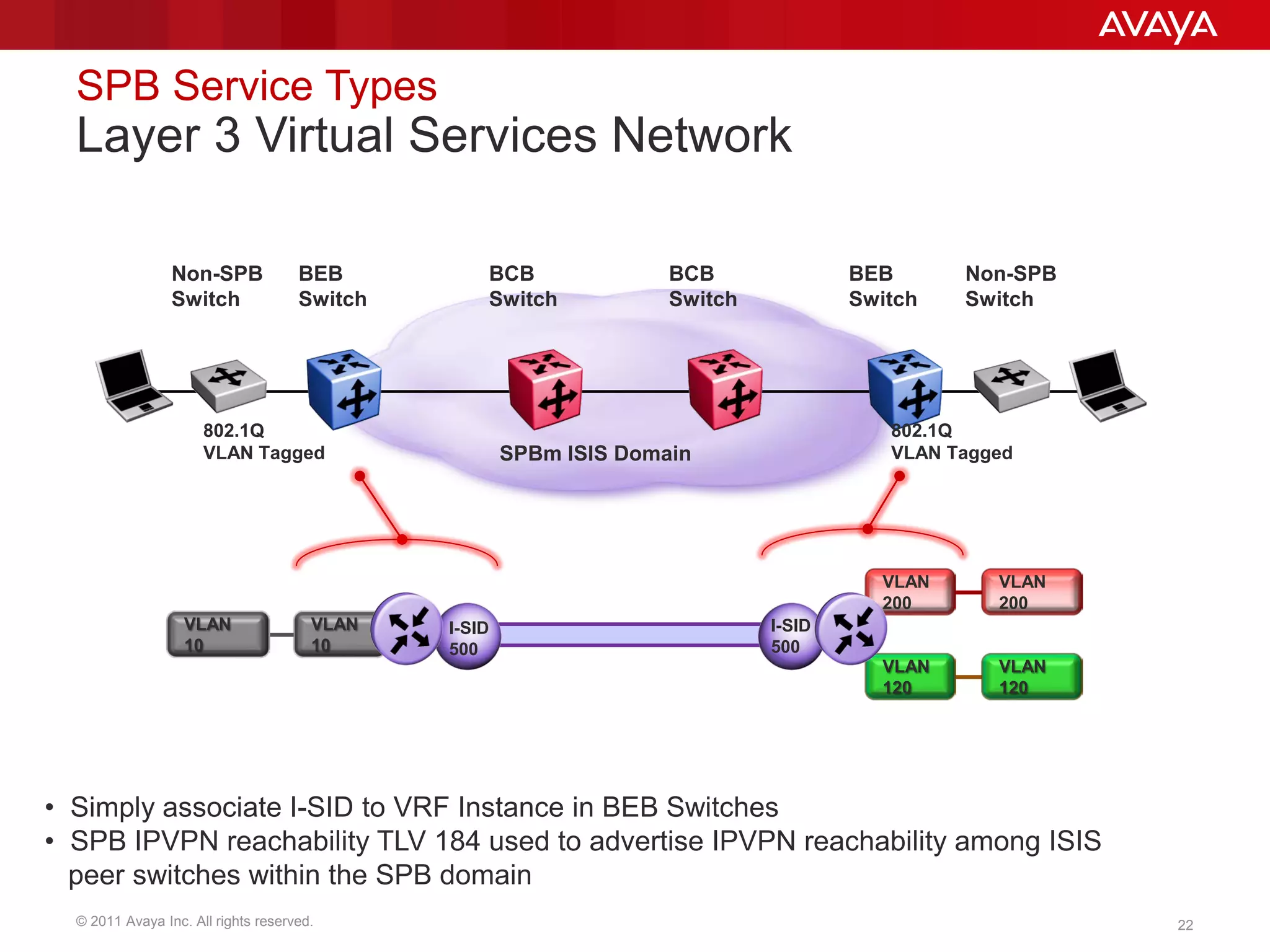
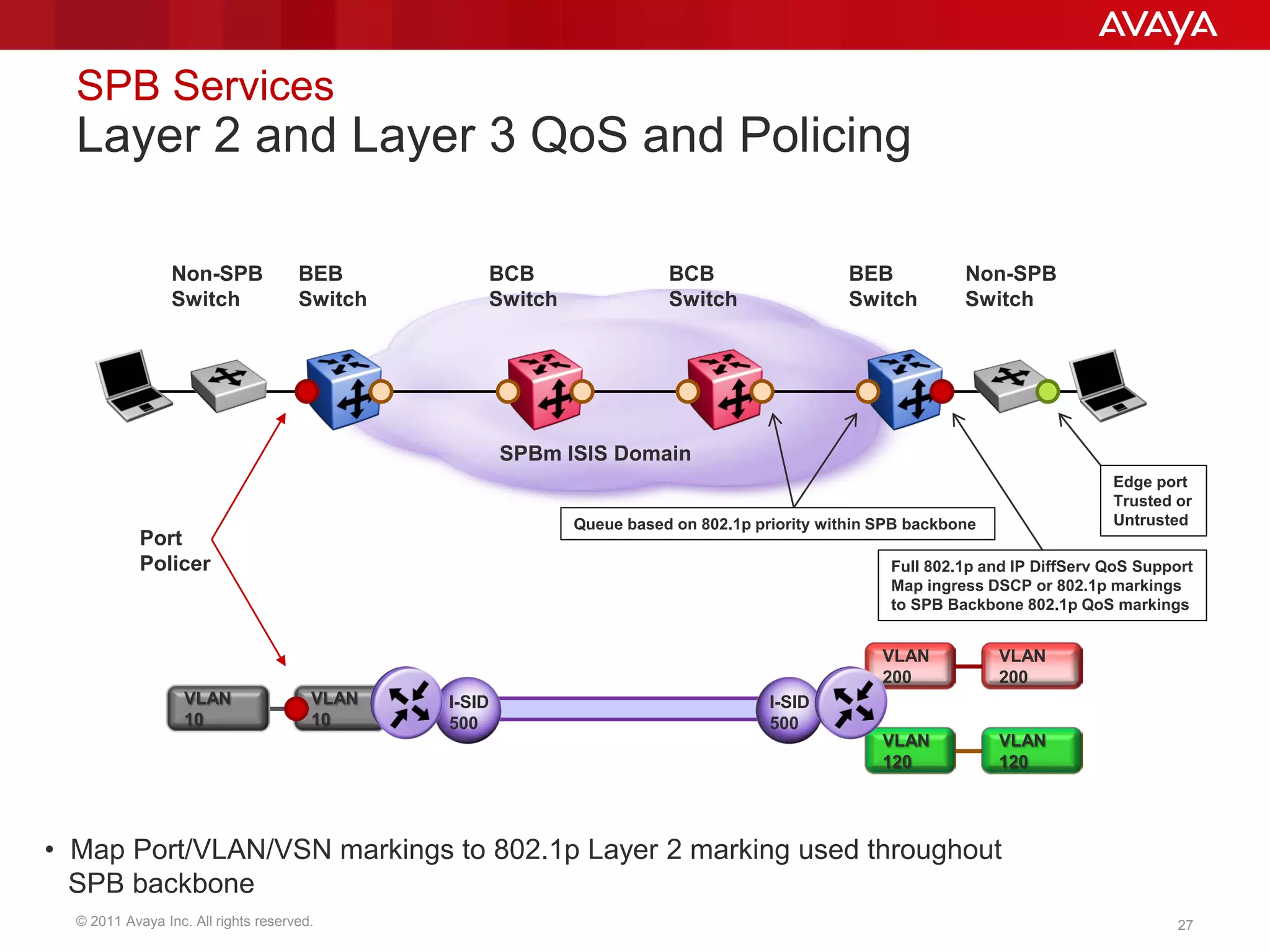
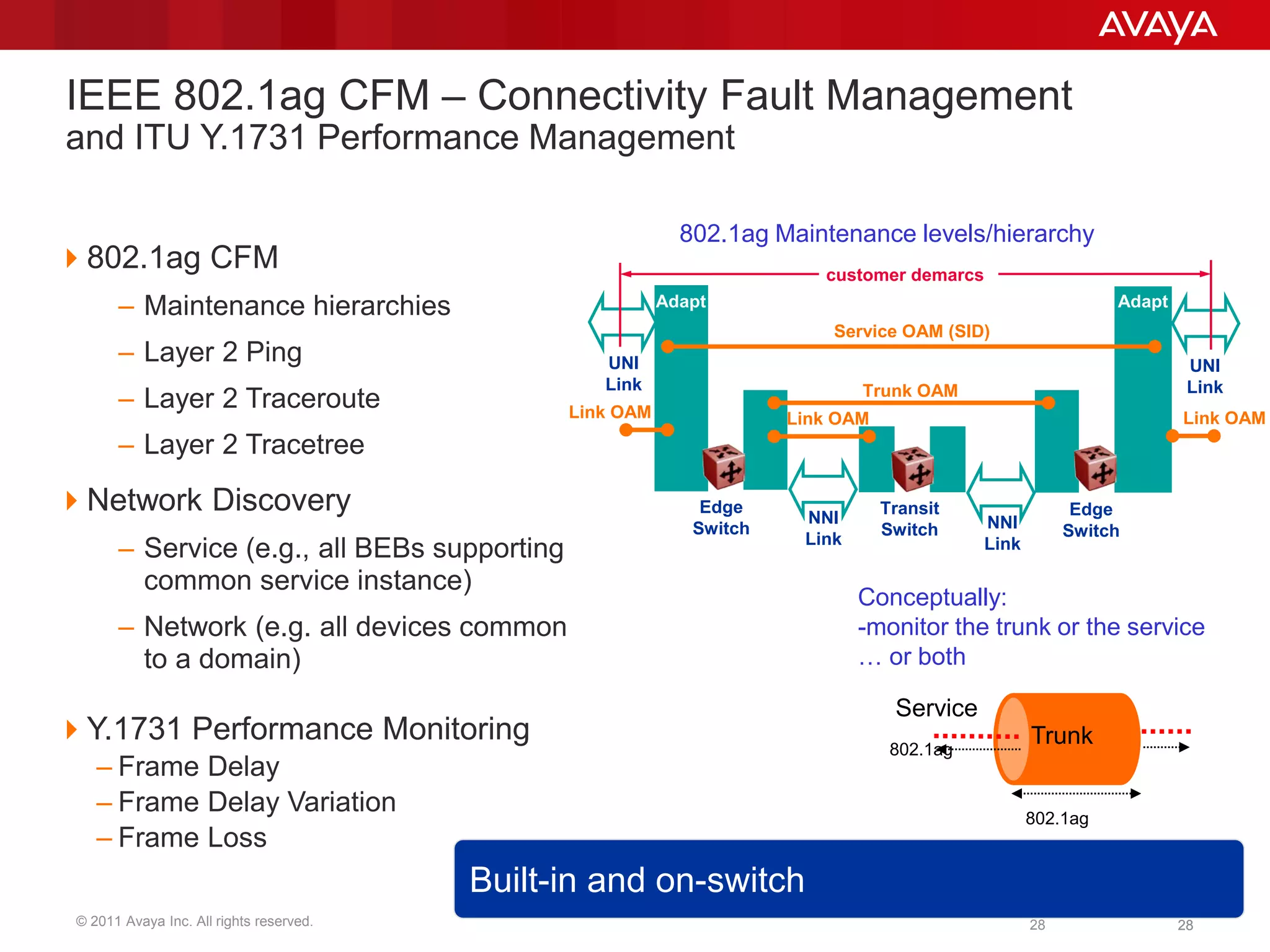
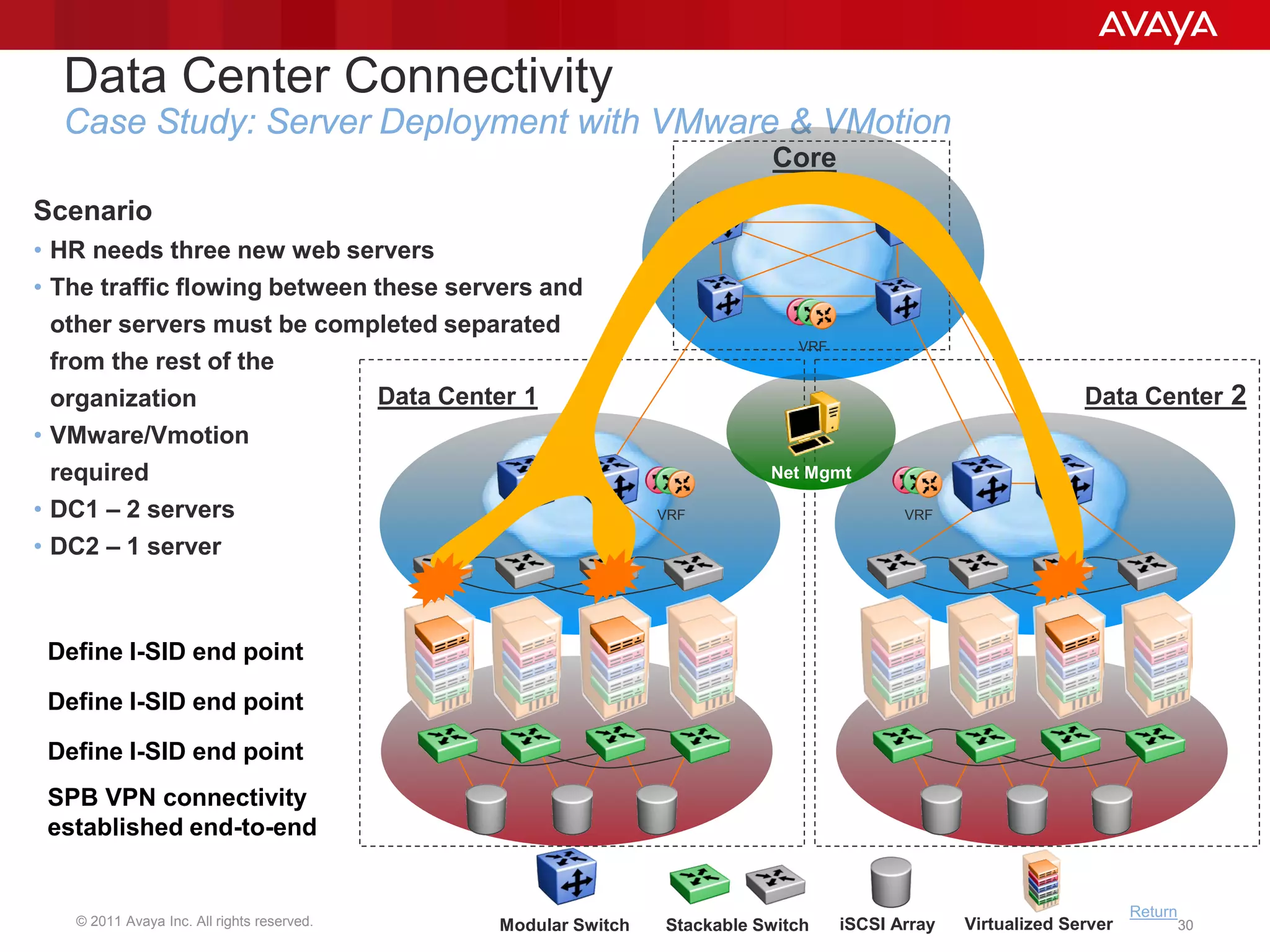
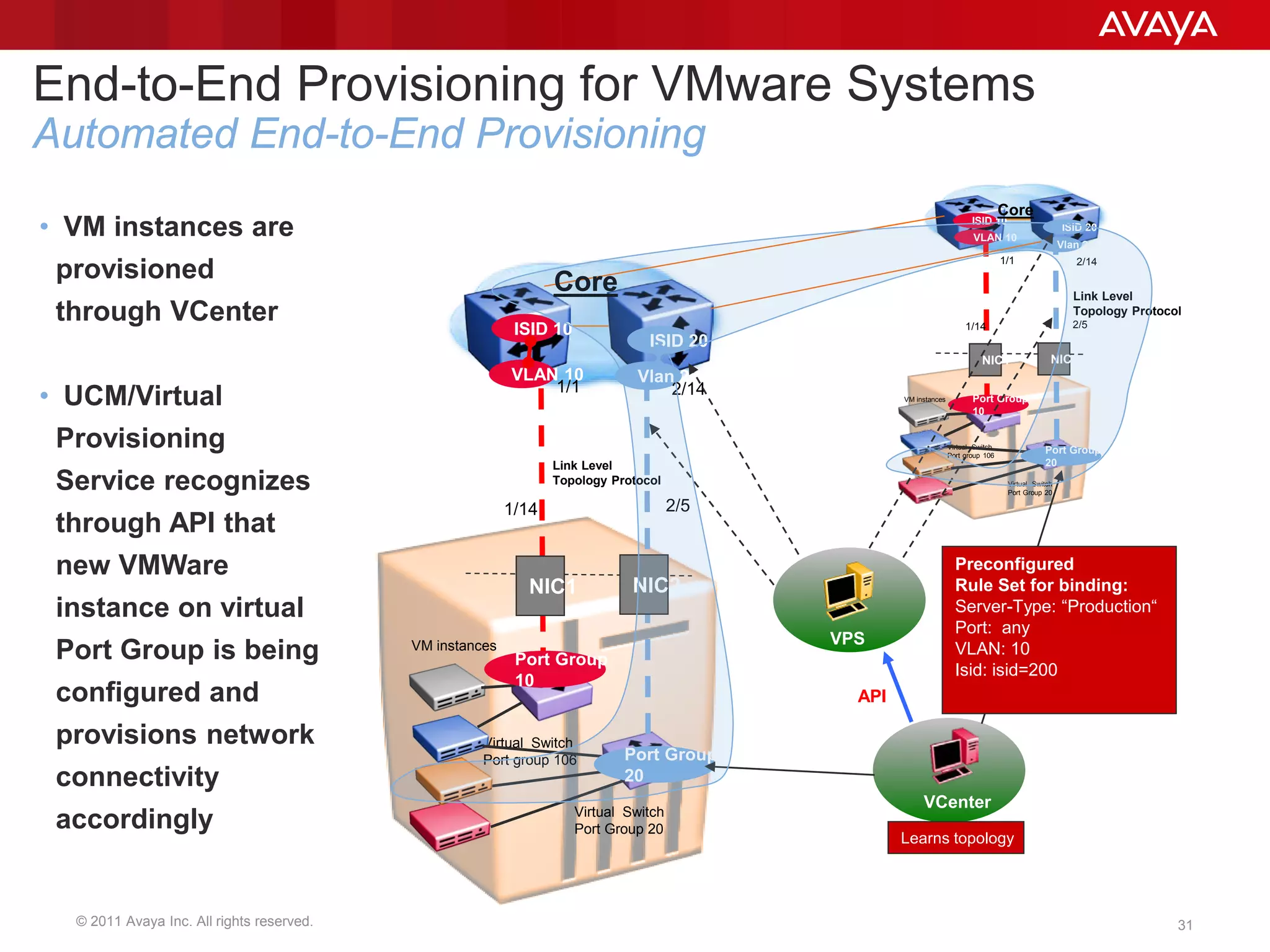
Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) provides several key benefits over traditional spanning tree protocols:
1. SPB eliminates blocked ports by using a link-state protocol (IS-IS) to automatically build shortest path trees to all nodes in the network.
2. It enables much faster reconvergence times of hundreds of milliseconds compared to spanning tree.
3. SPB simplifies network operations through well-known link-state routing paradigms and provides one-touch provisioning of services and end-points.