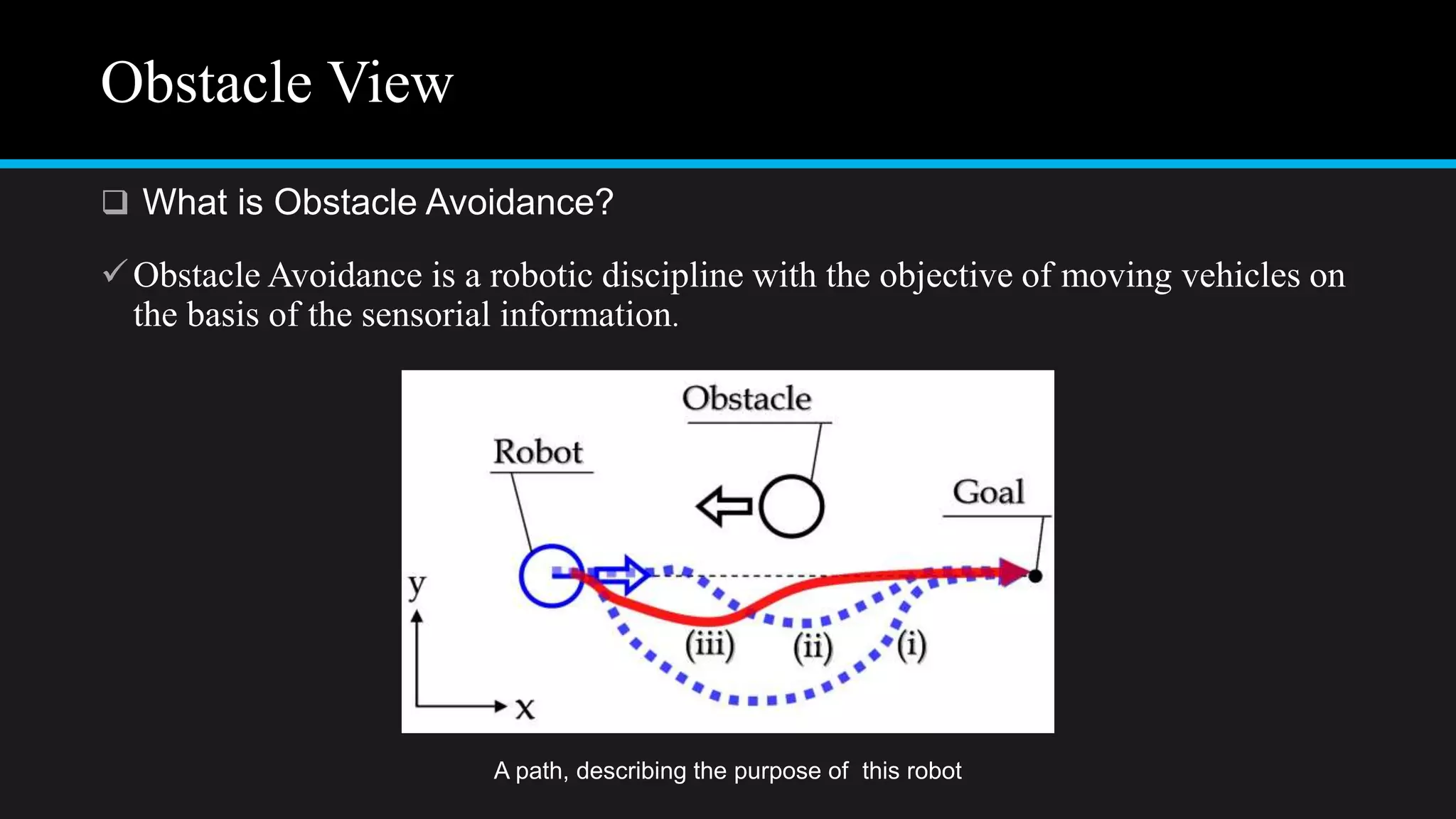
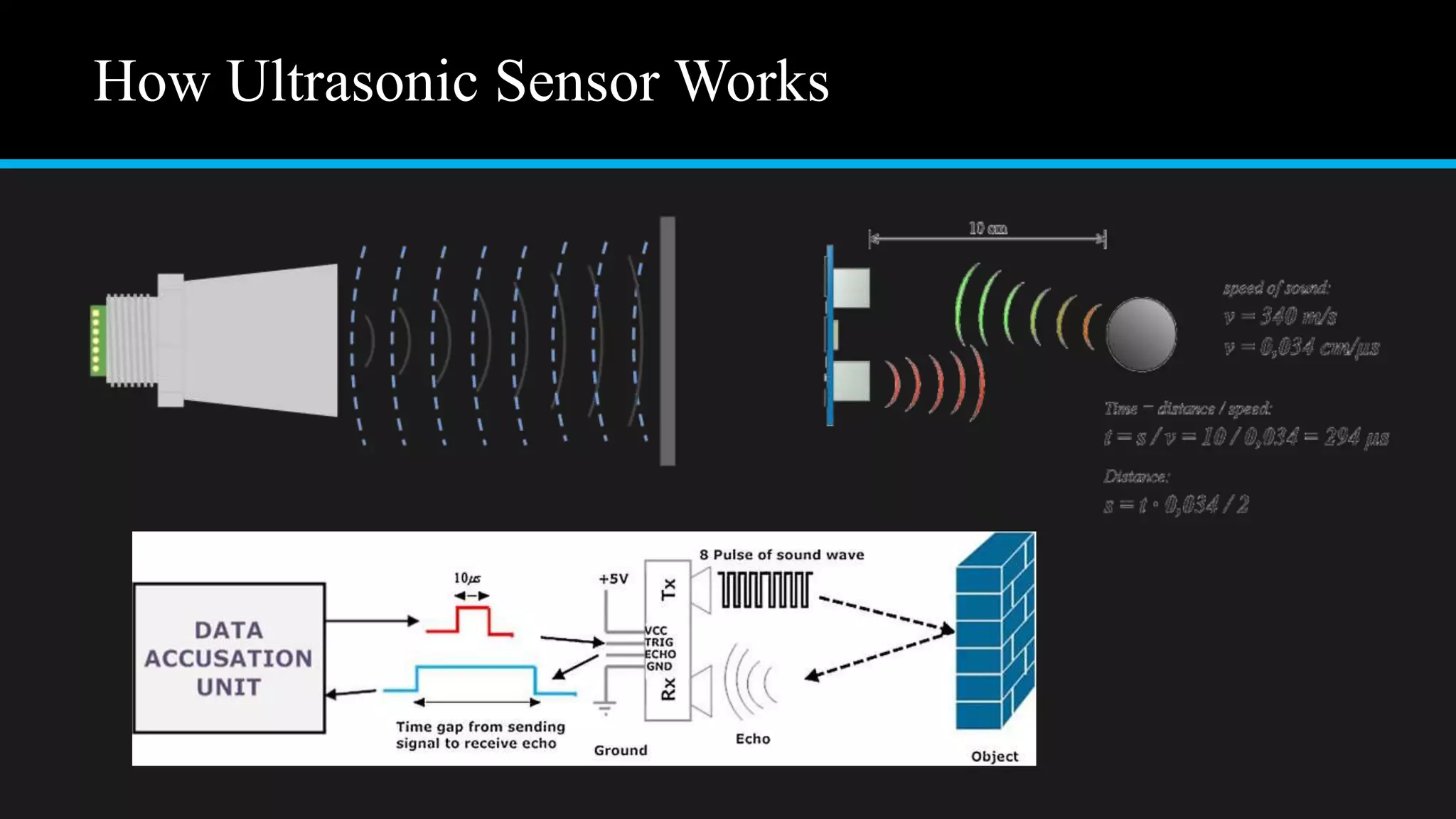
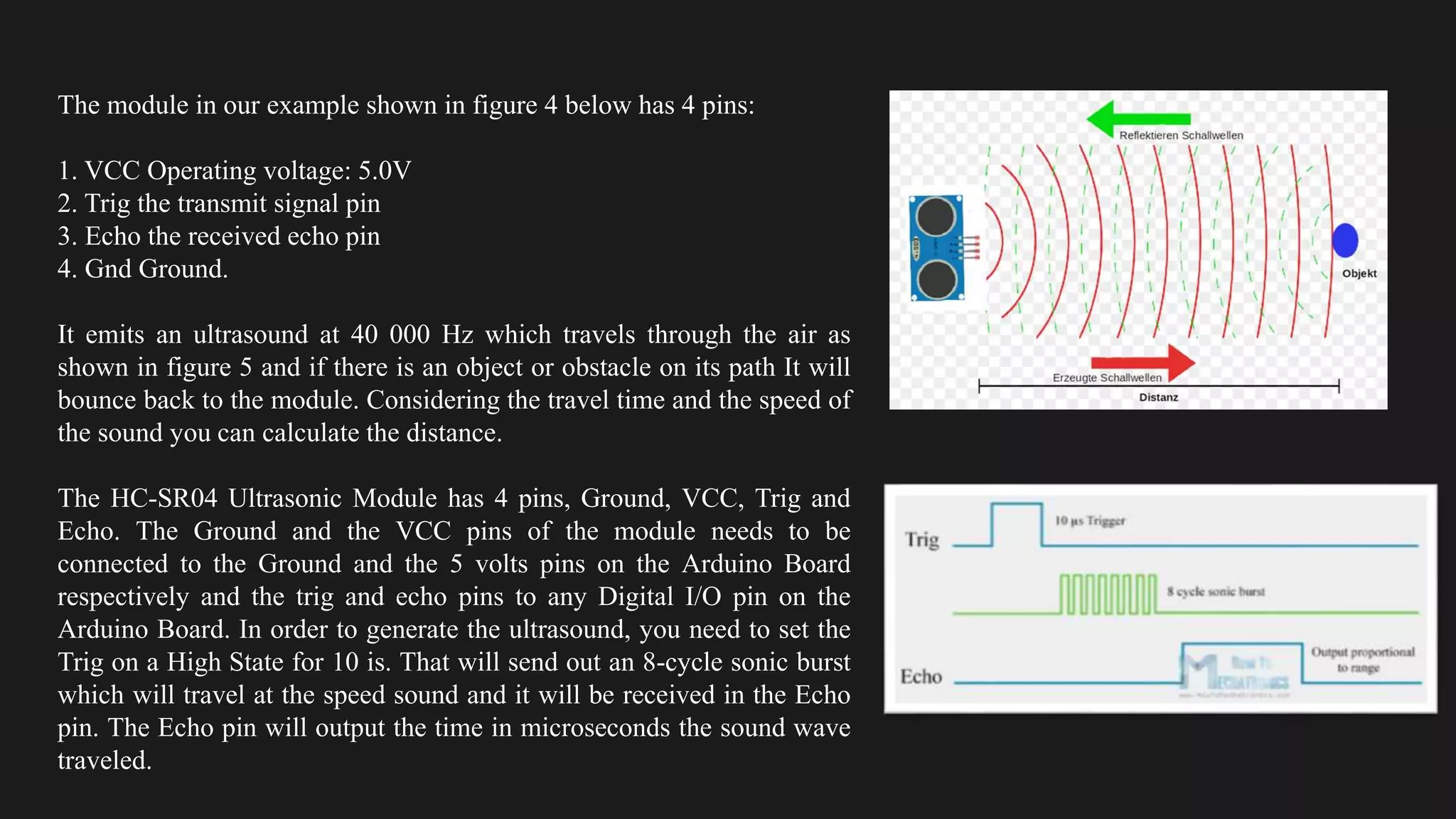
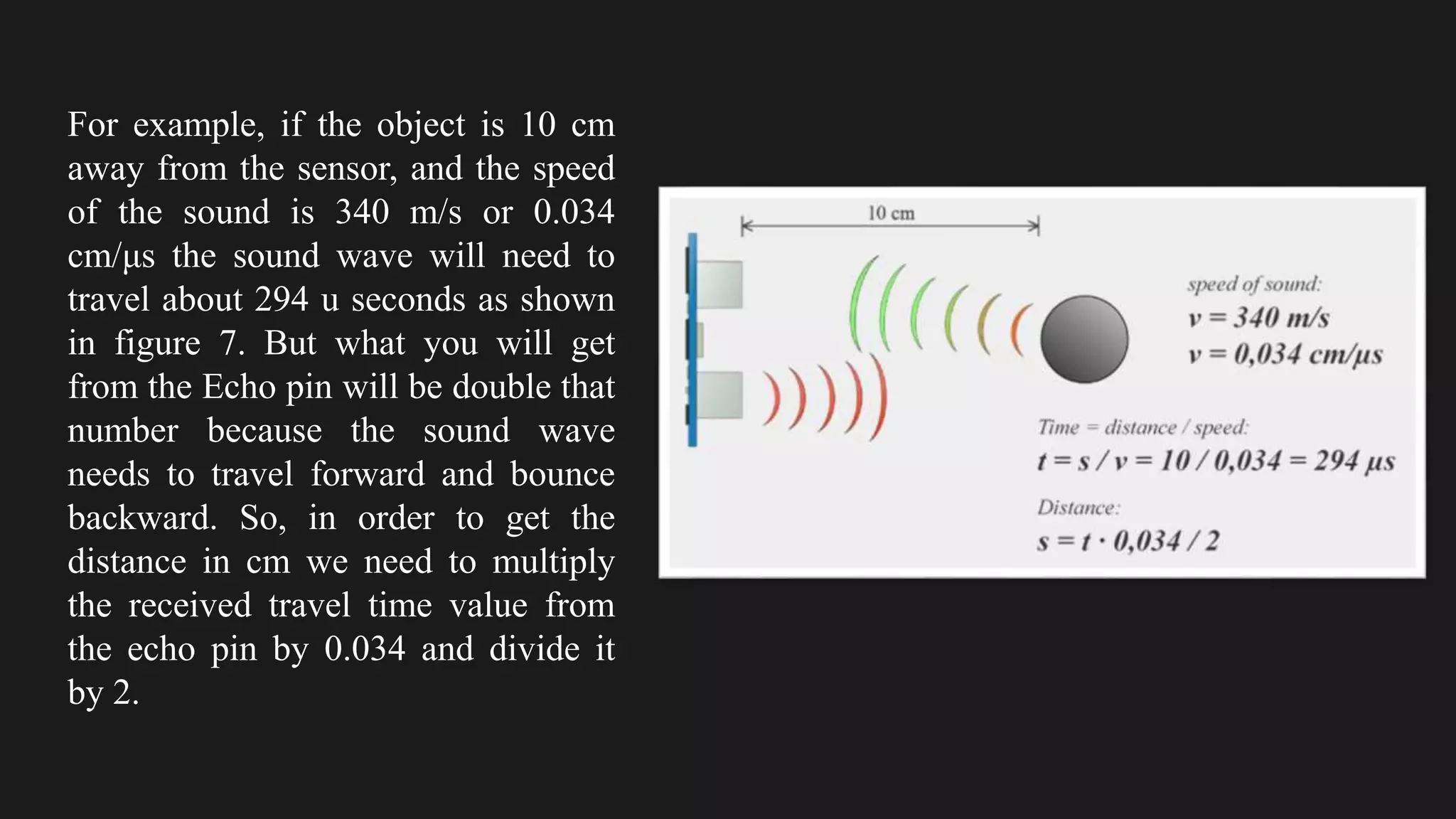
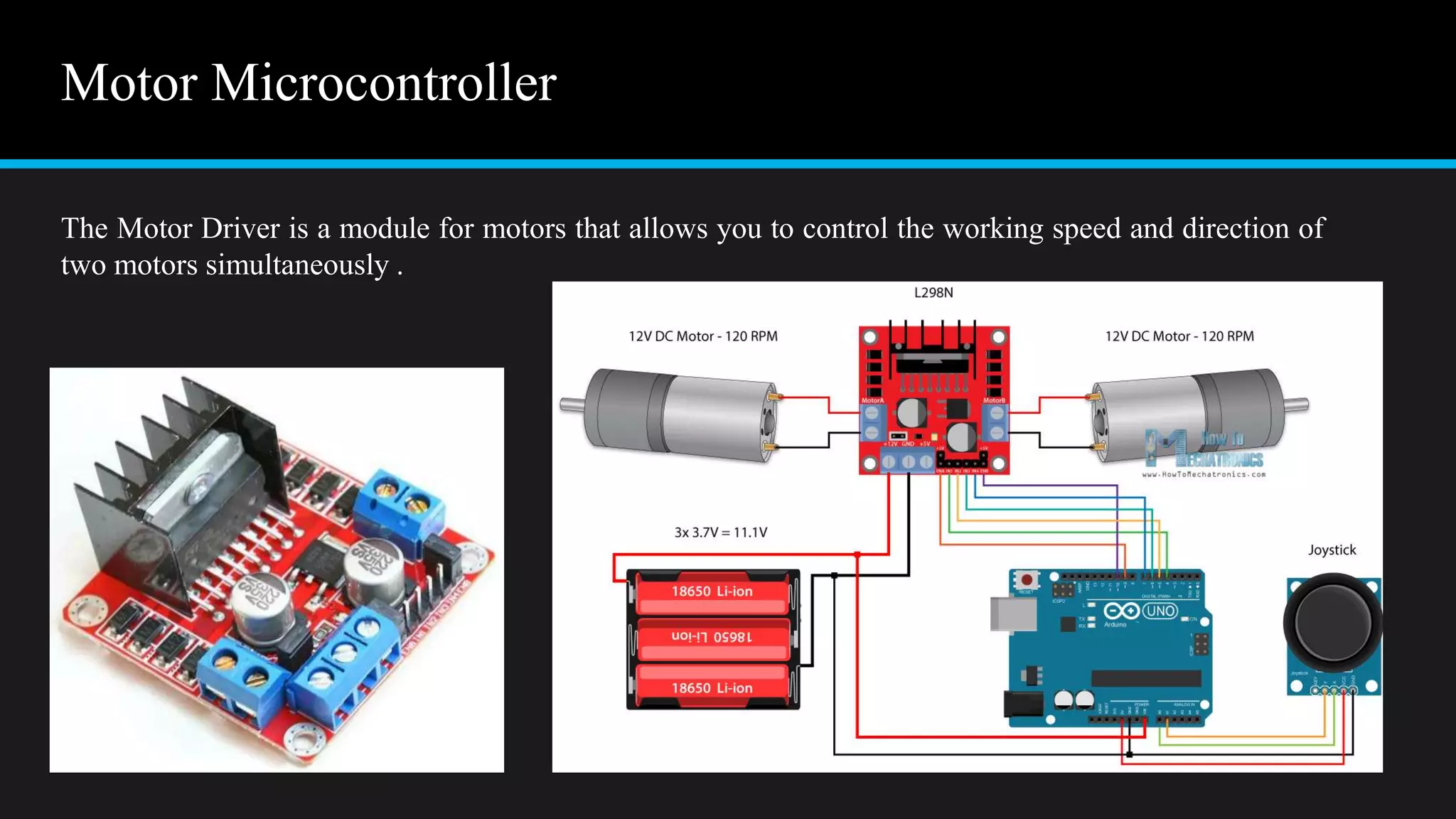
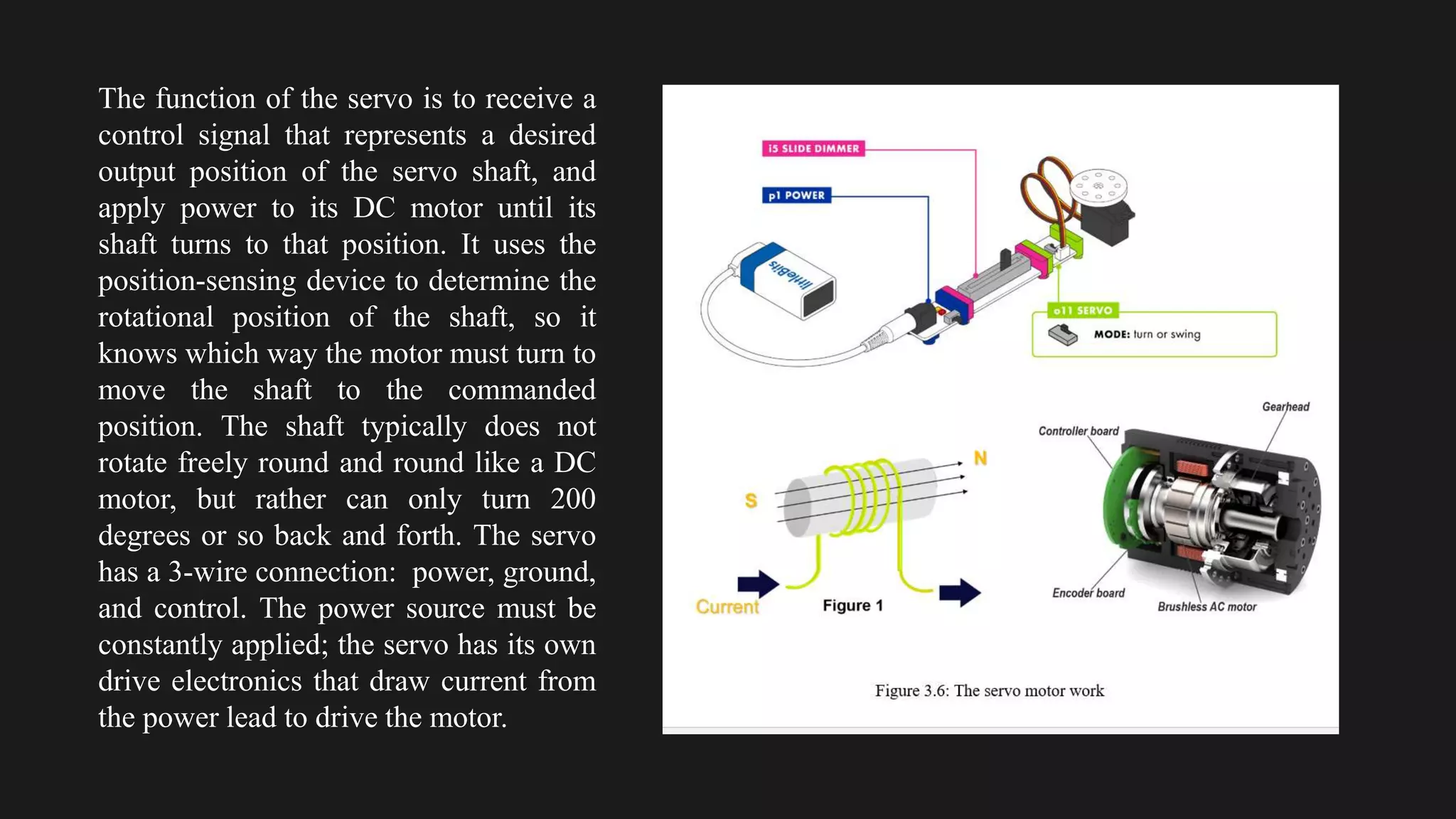
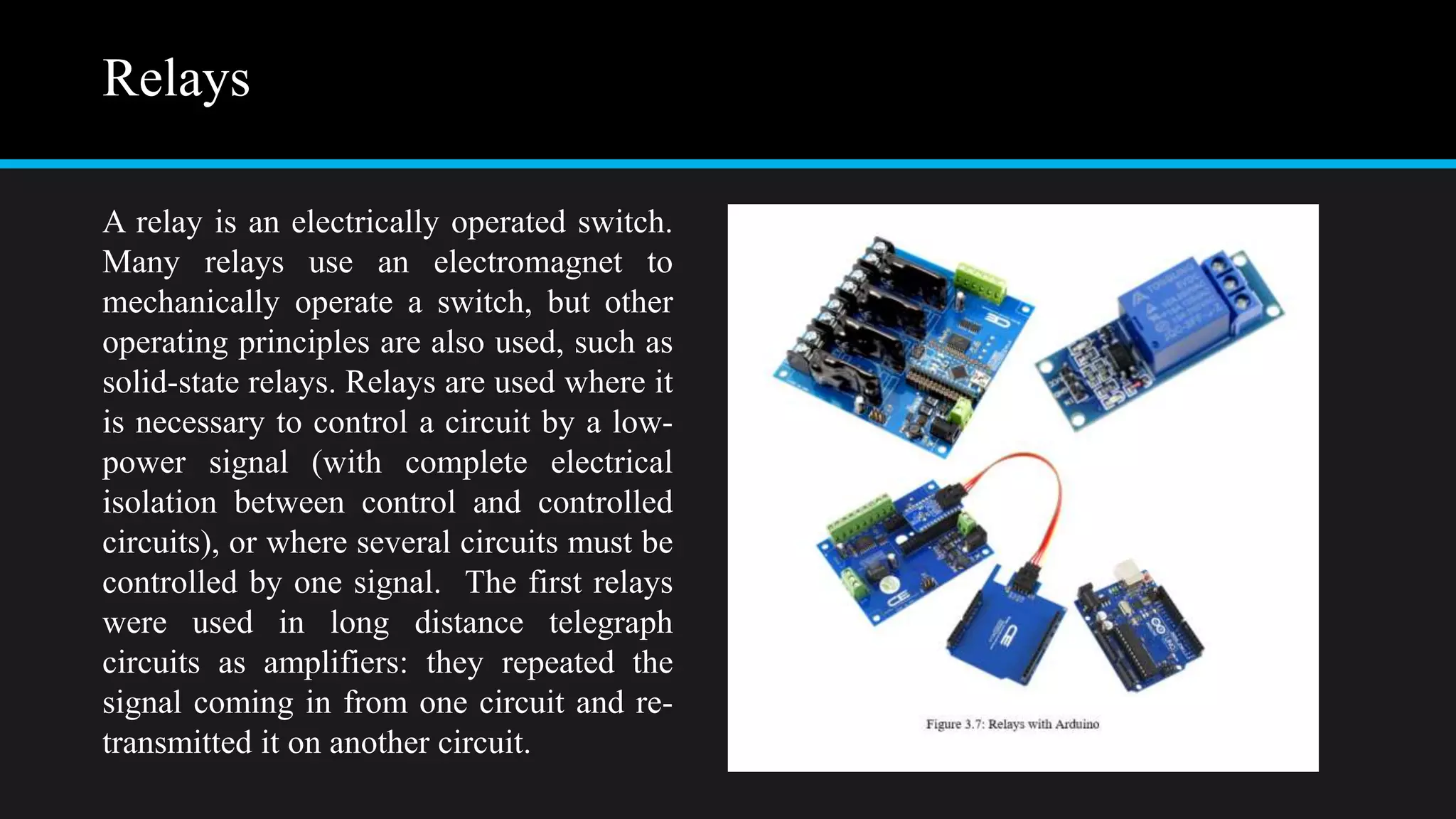
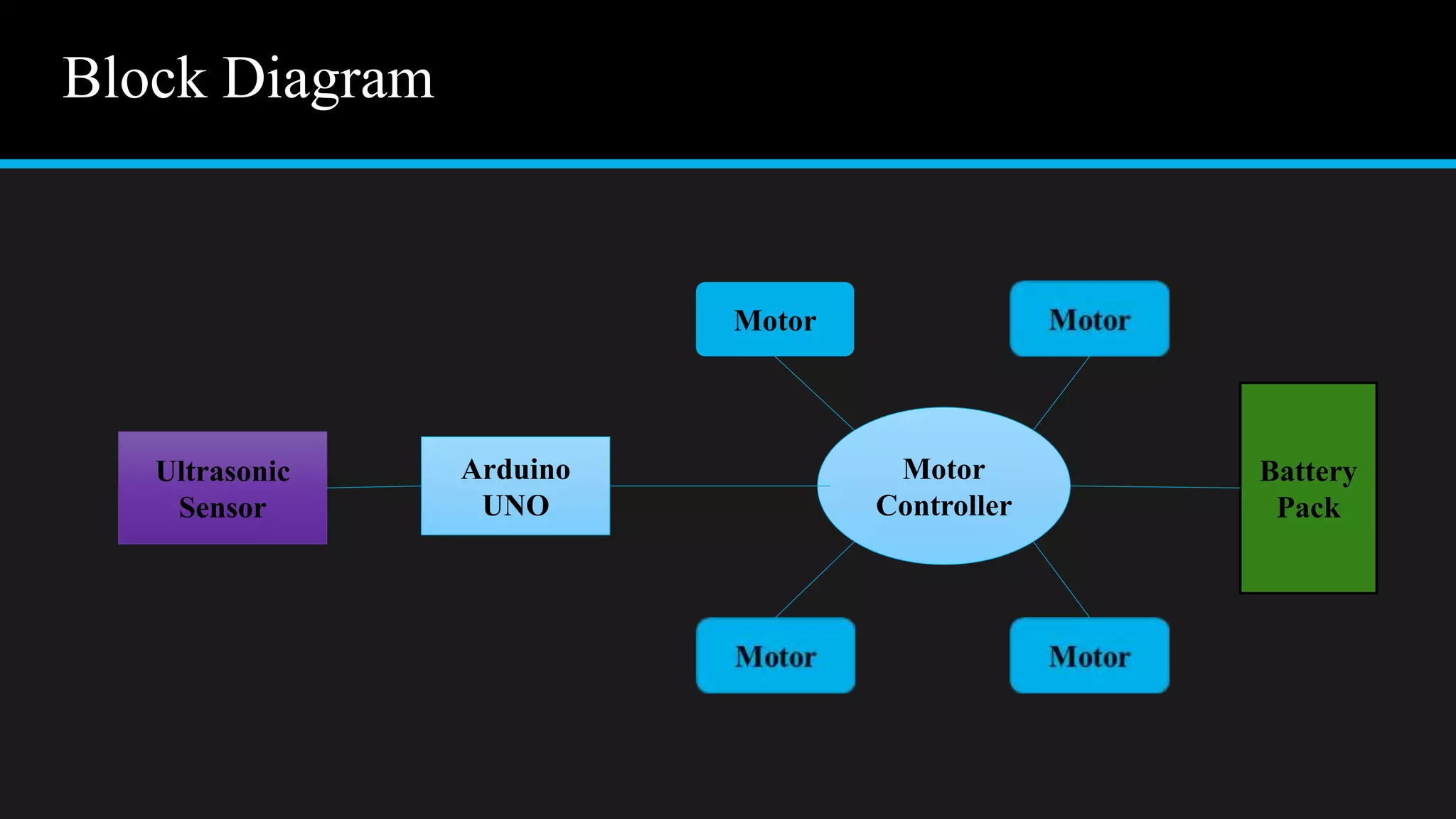
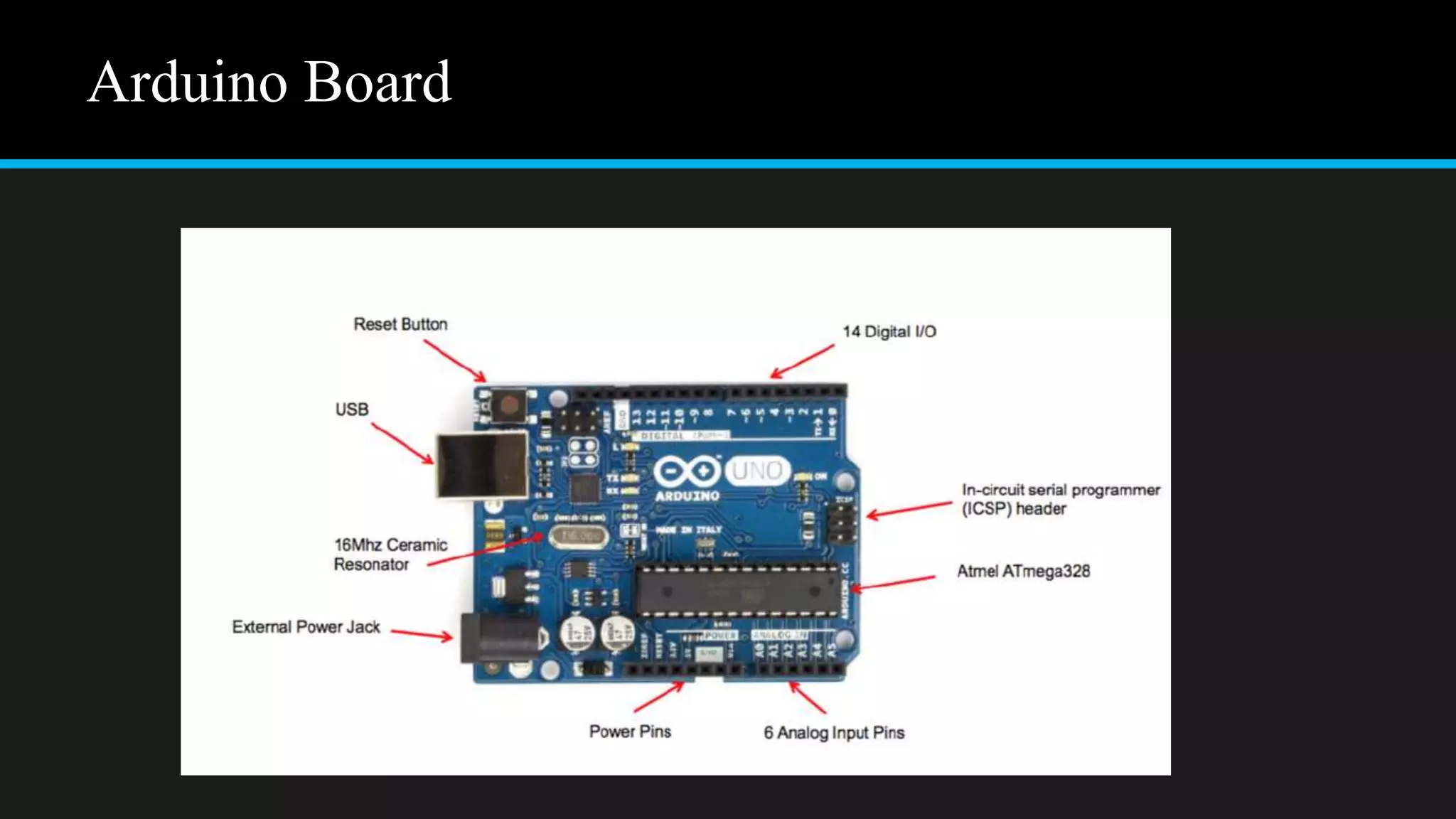
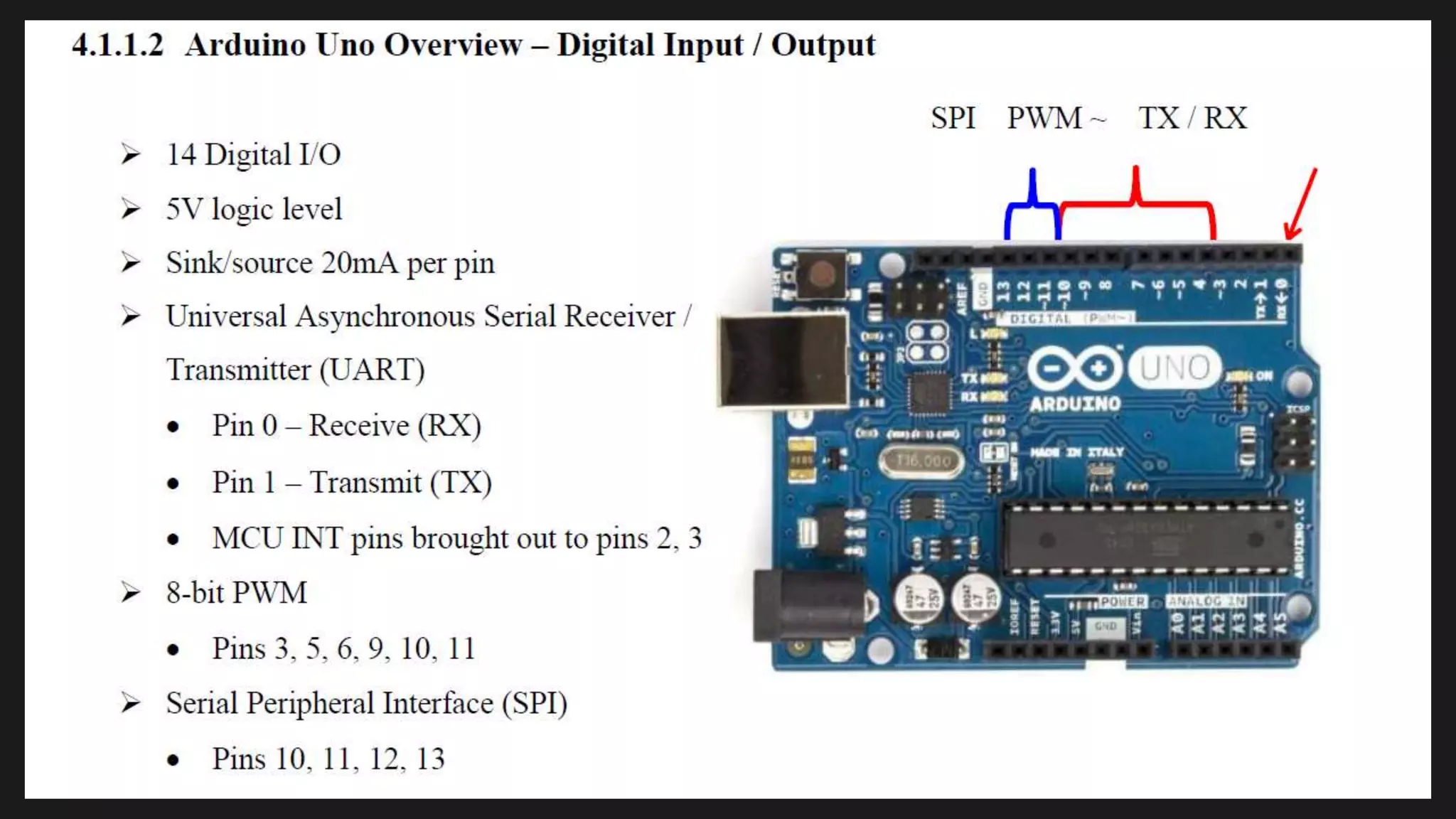
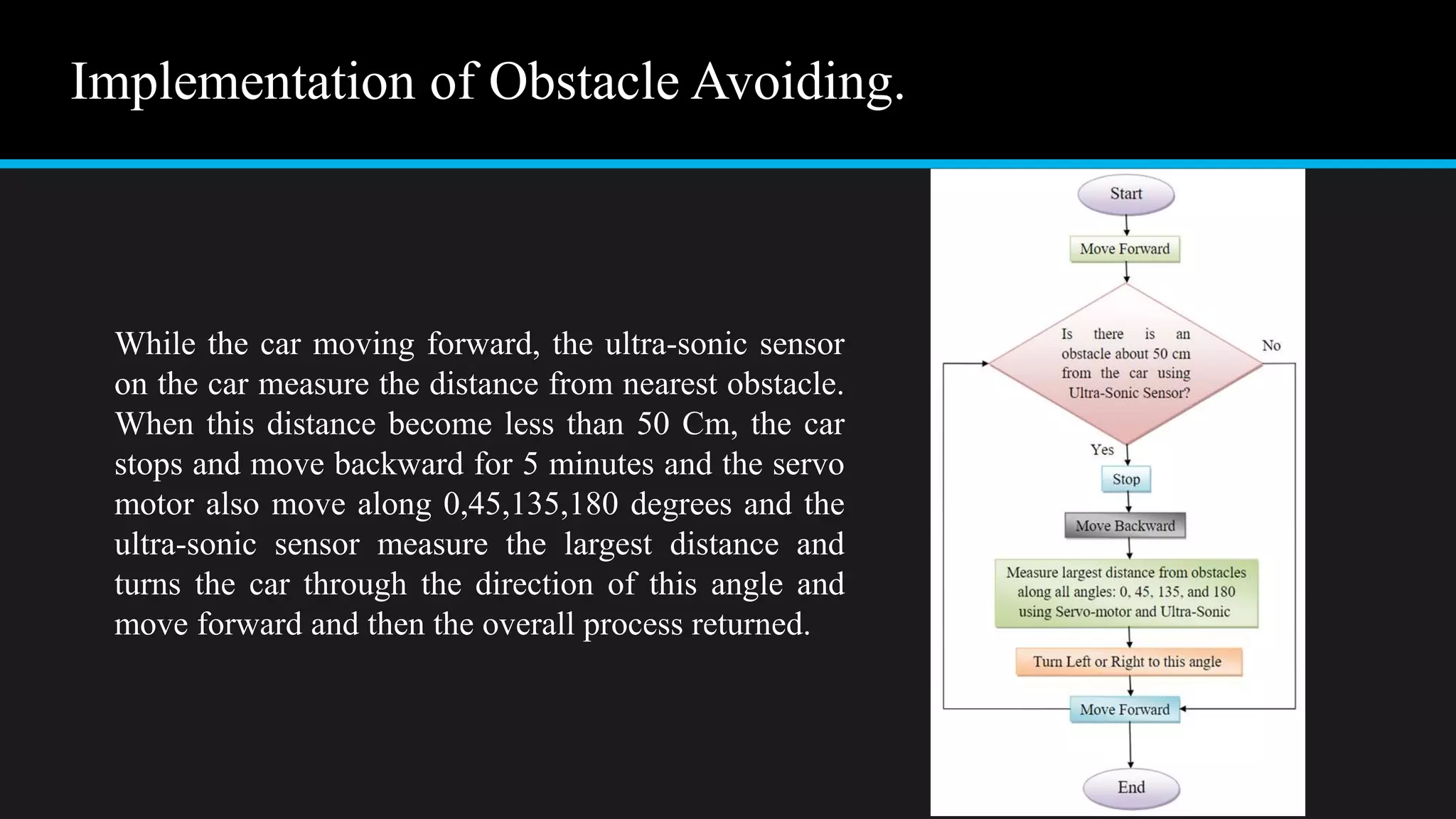
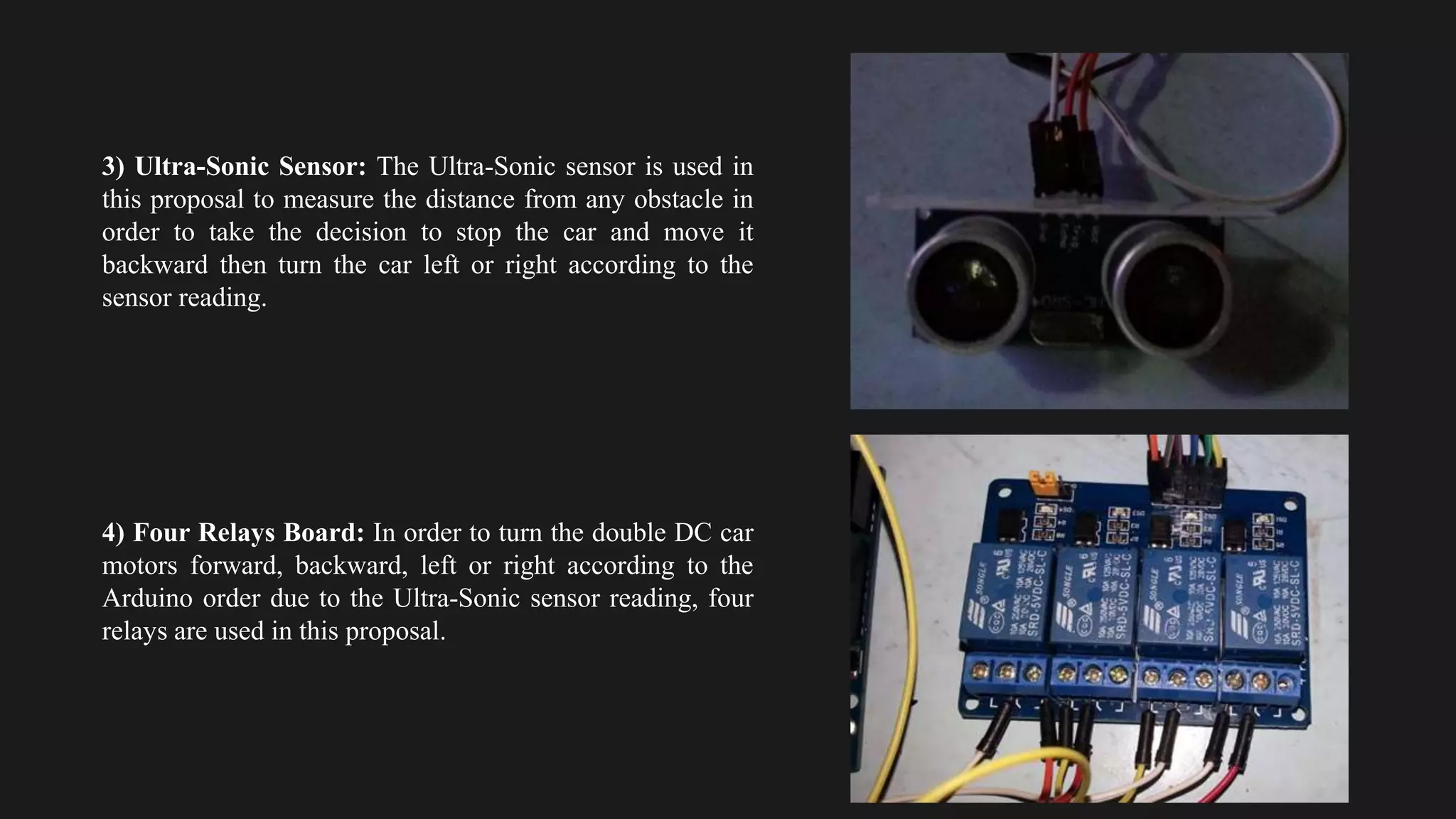
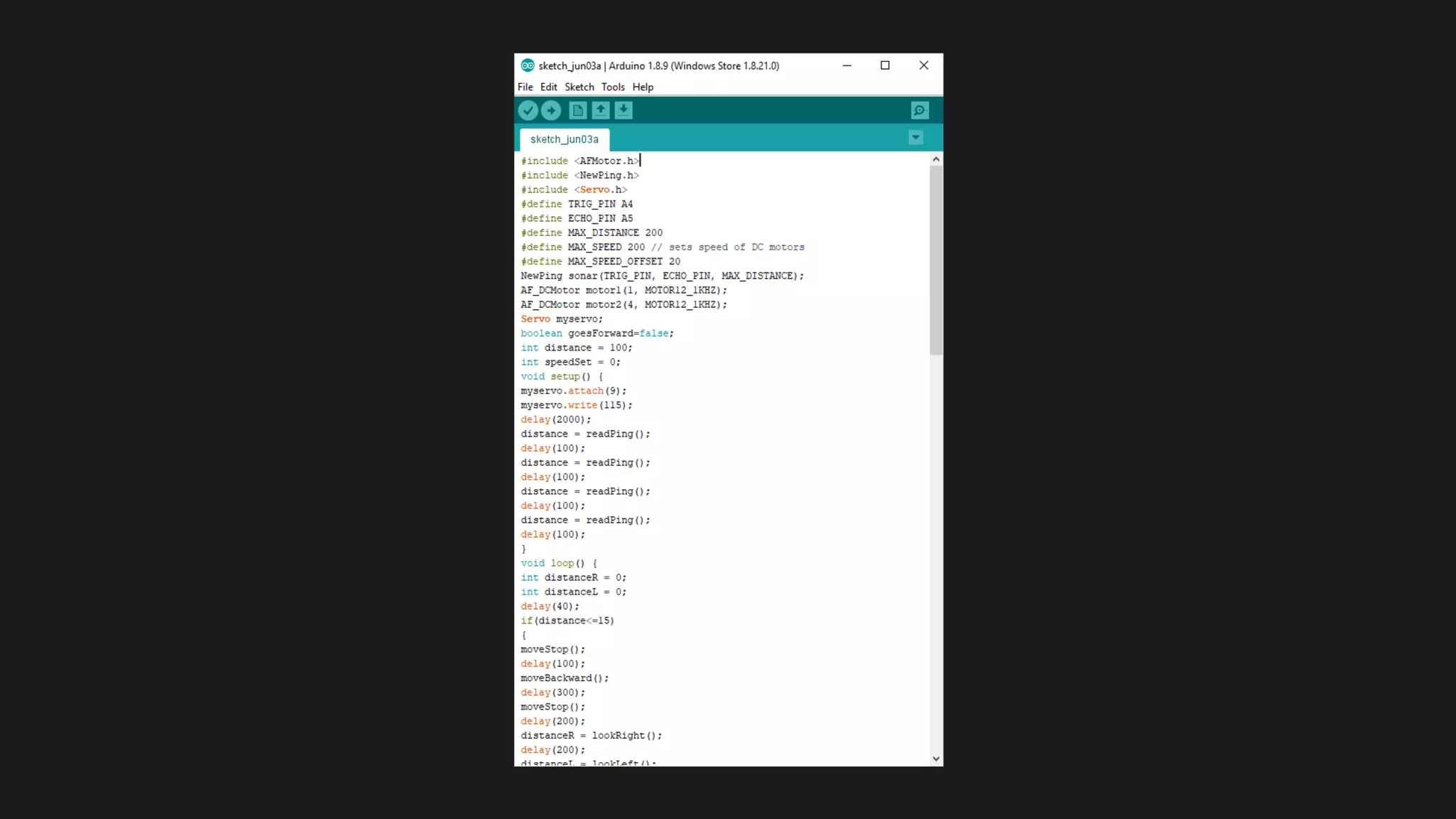
The document provides an overview of an obstacle avoiding robot that uses ultrasonic sensors and an Arduino microcontroller to detect and navigate around obstacles autonomously. It details the components used, including various types of motors, relays, and programming libraries, as well as the implementation steps involved in making the robot functional. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of robotics in everyday life and the educational value of designing and programming such autonomous systems.