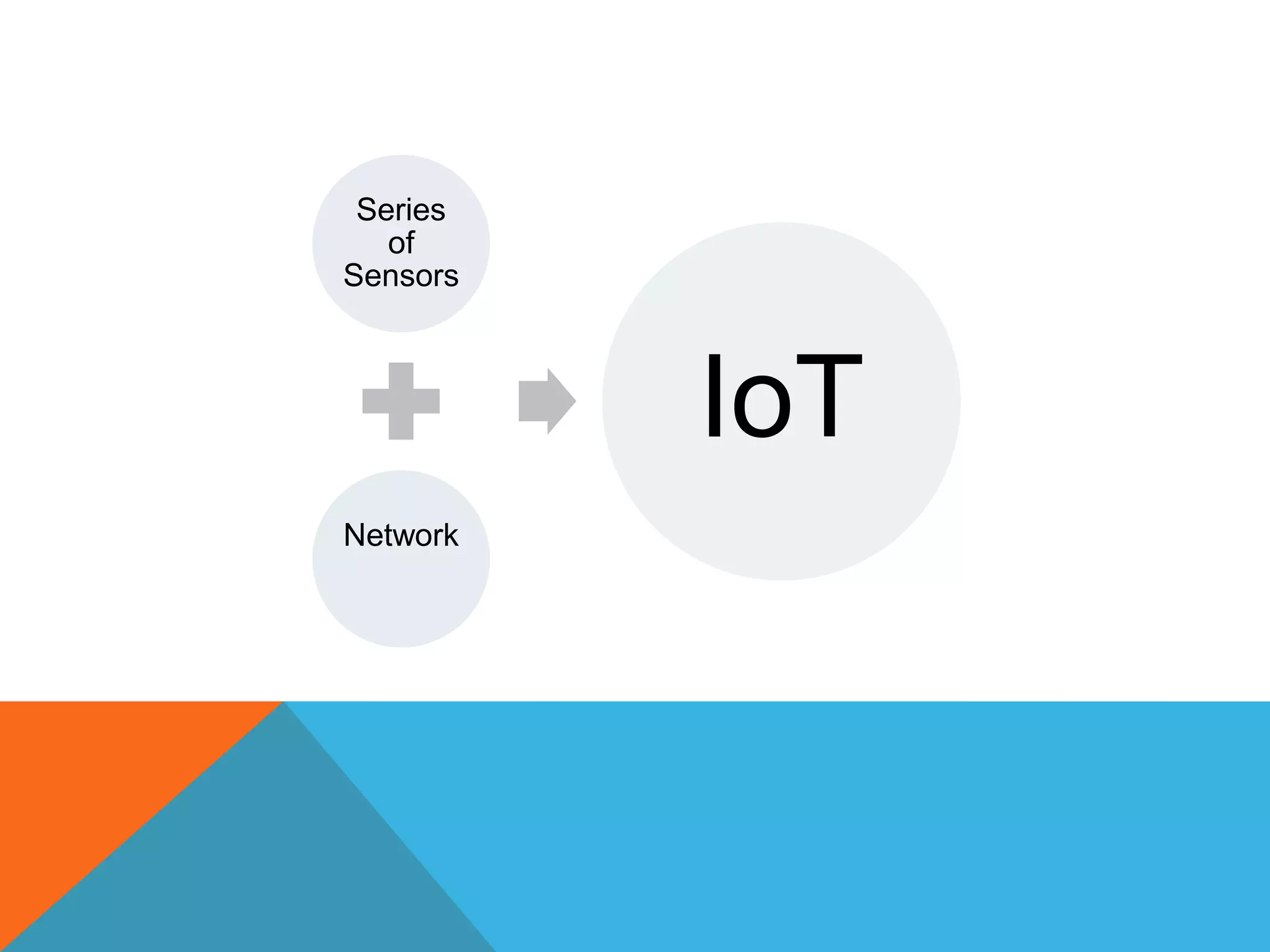
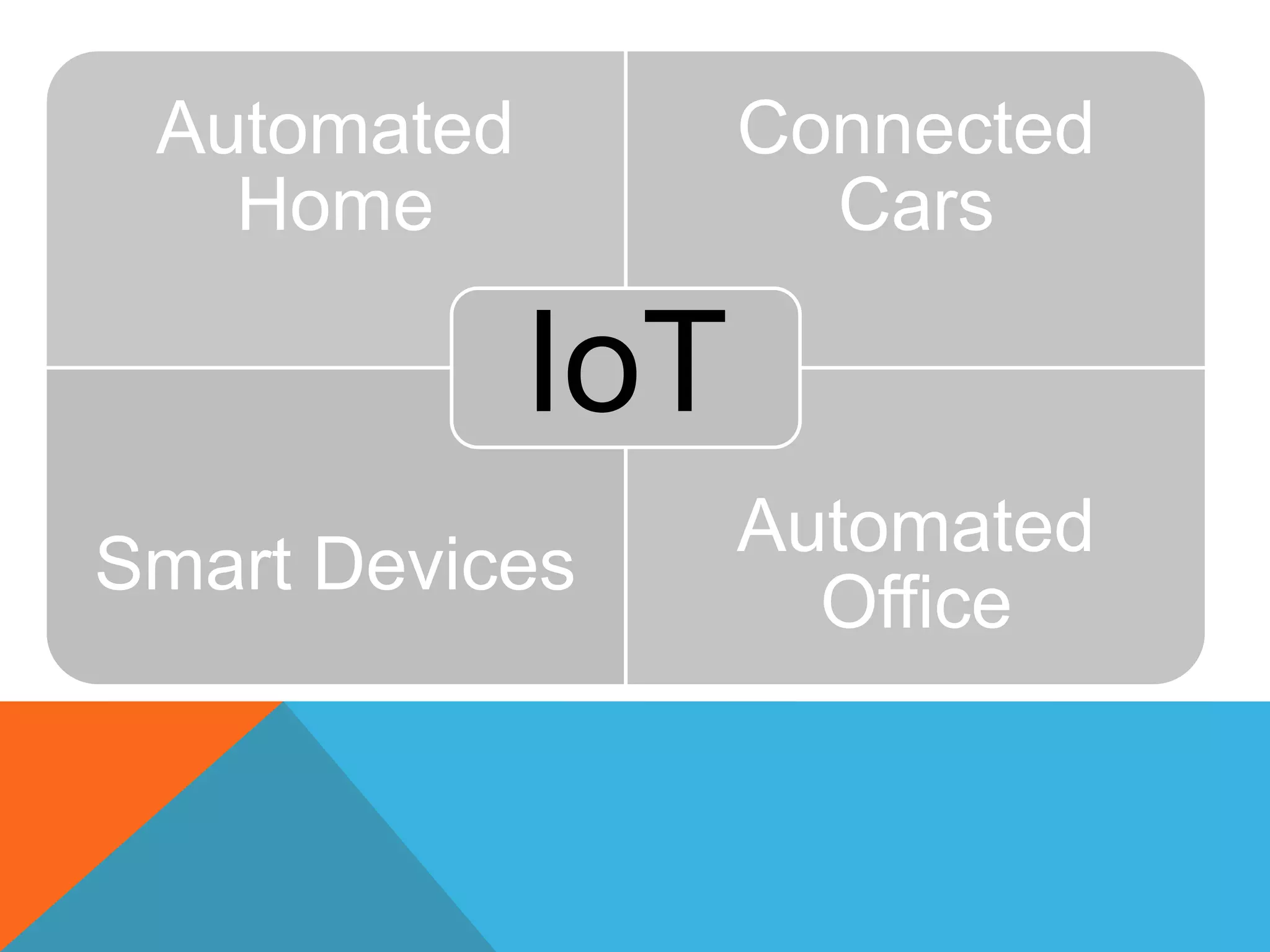
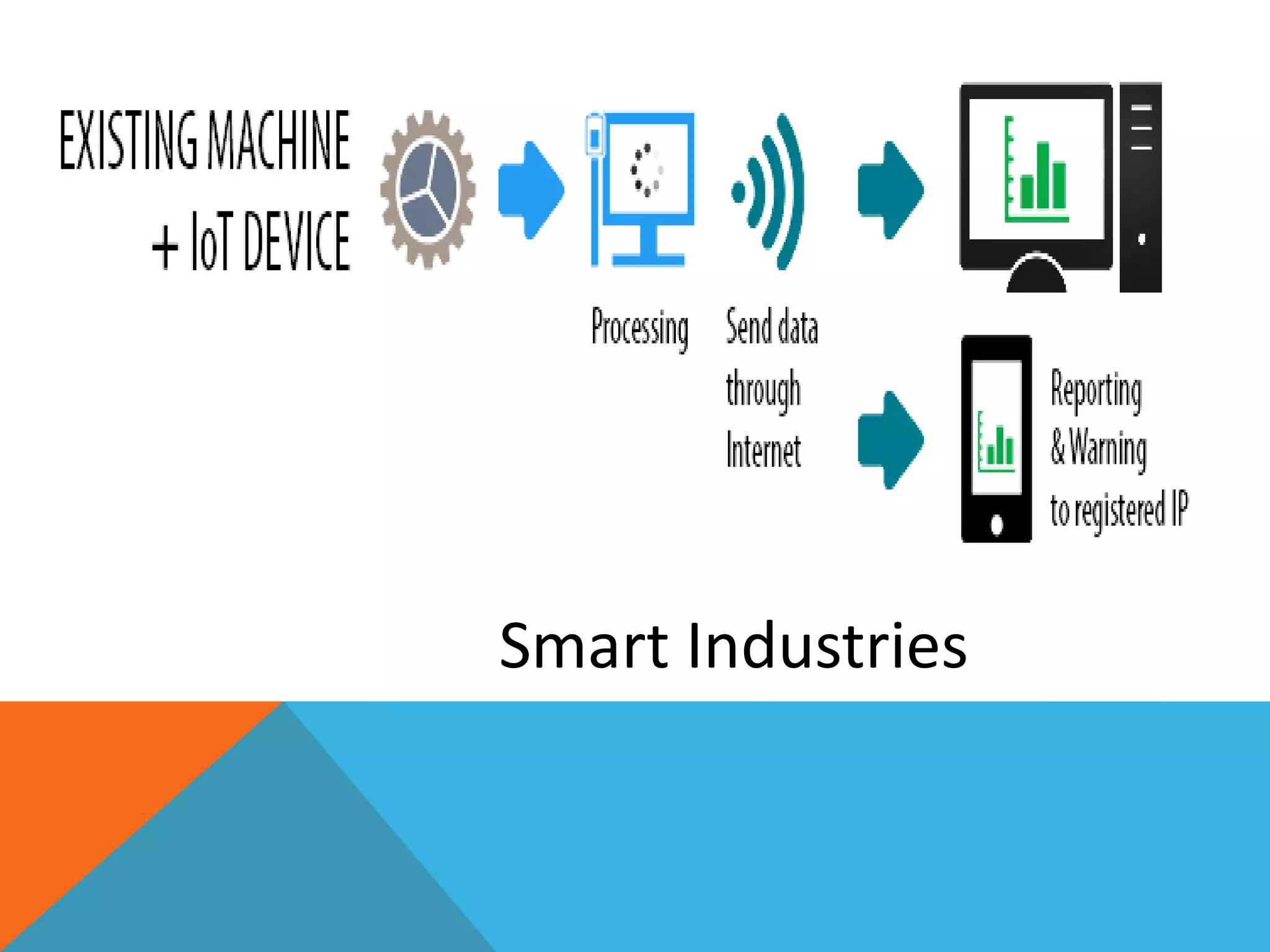
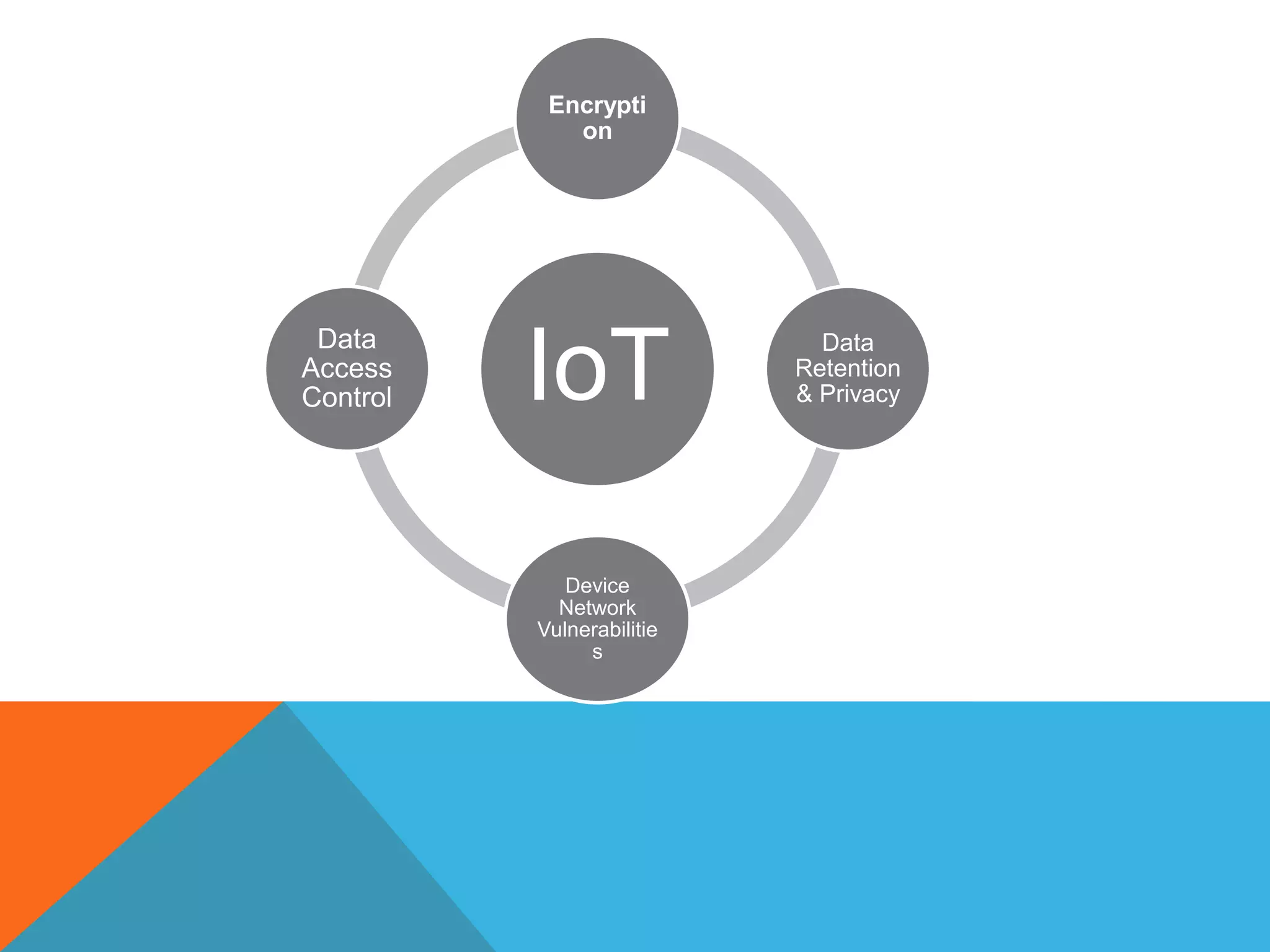
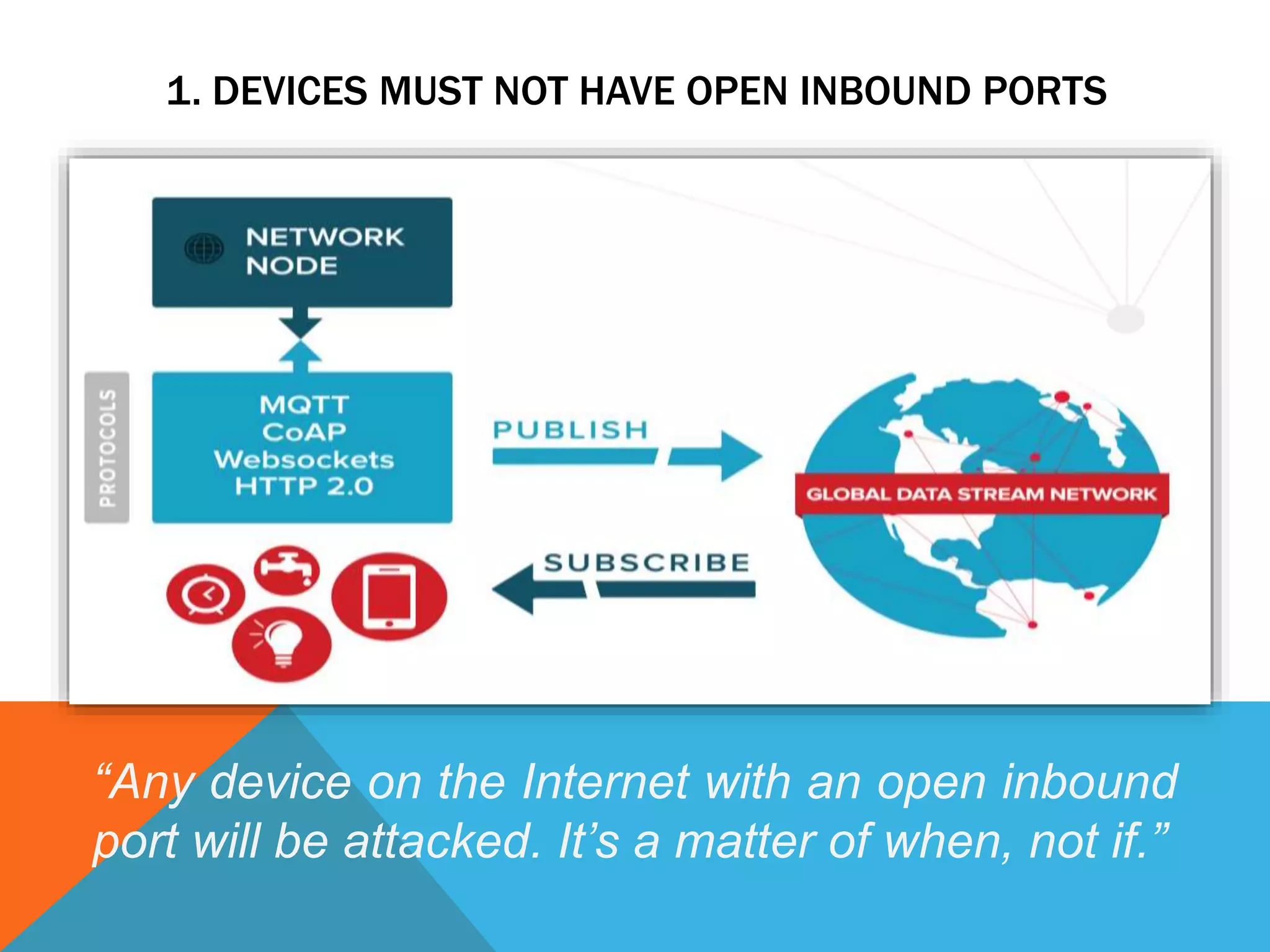
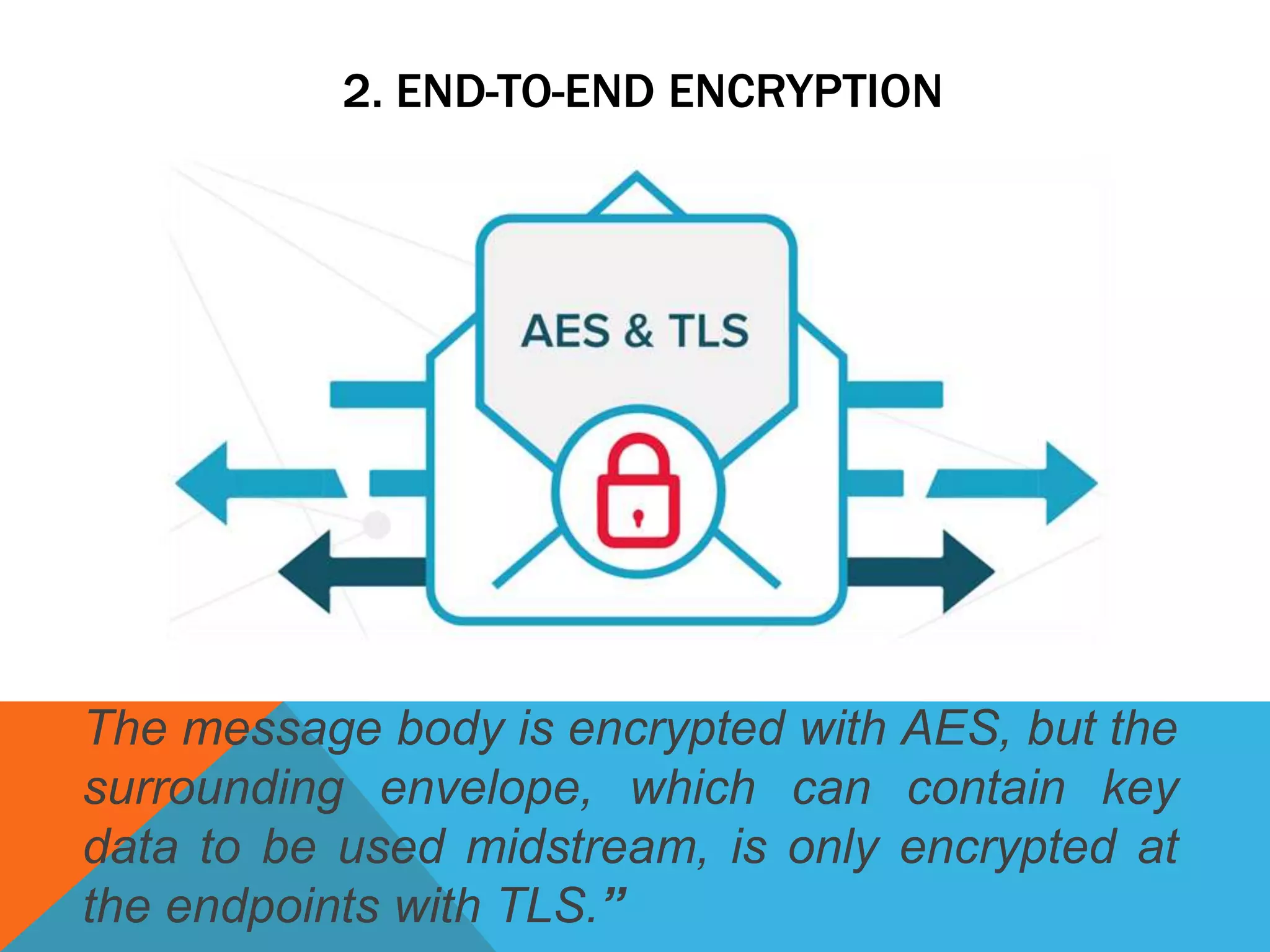
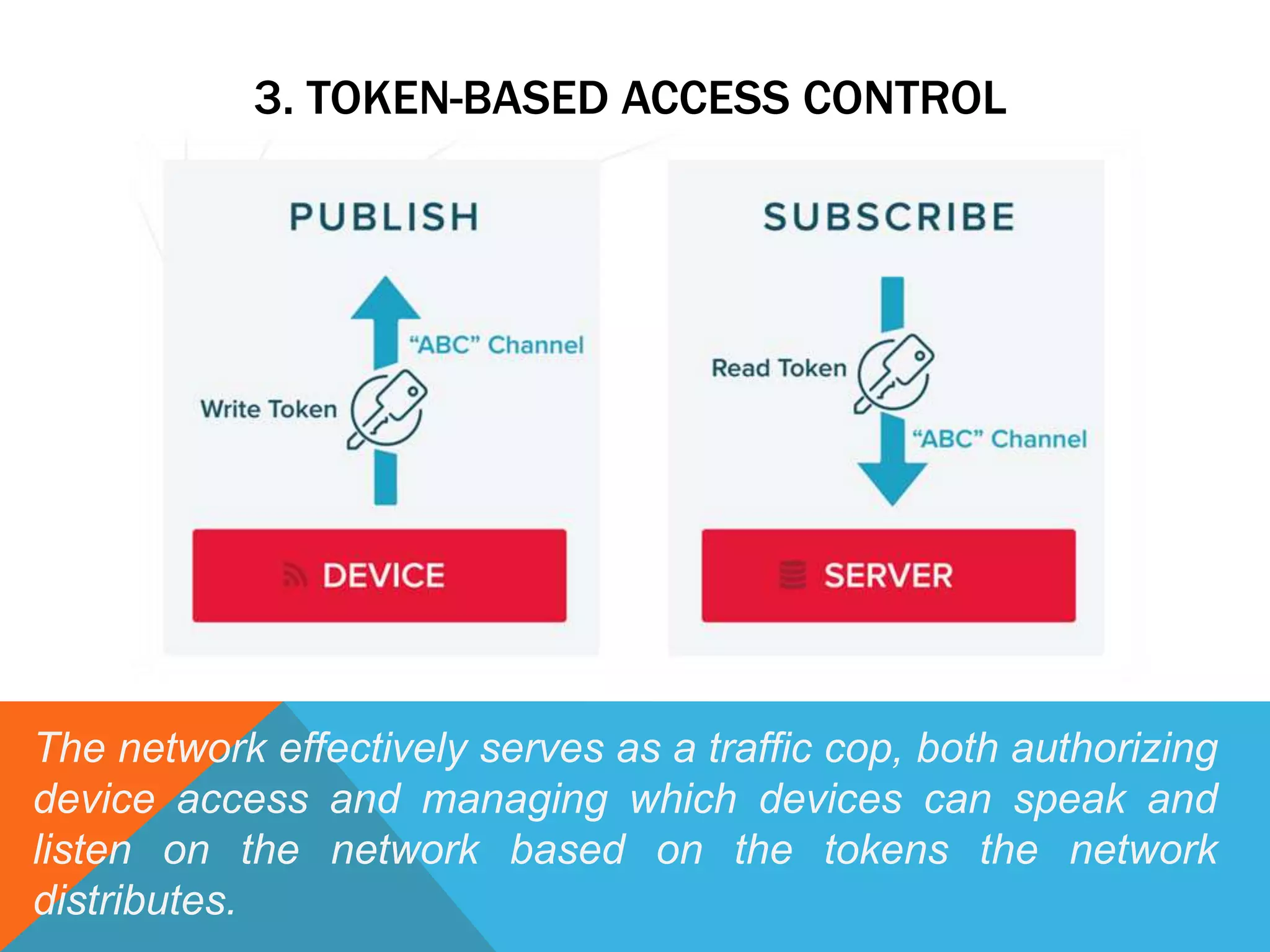
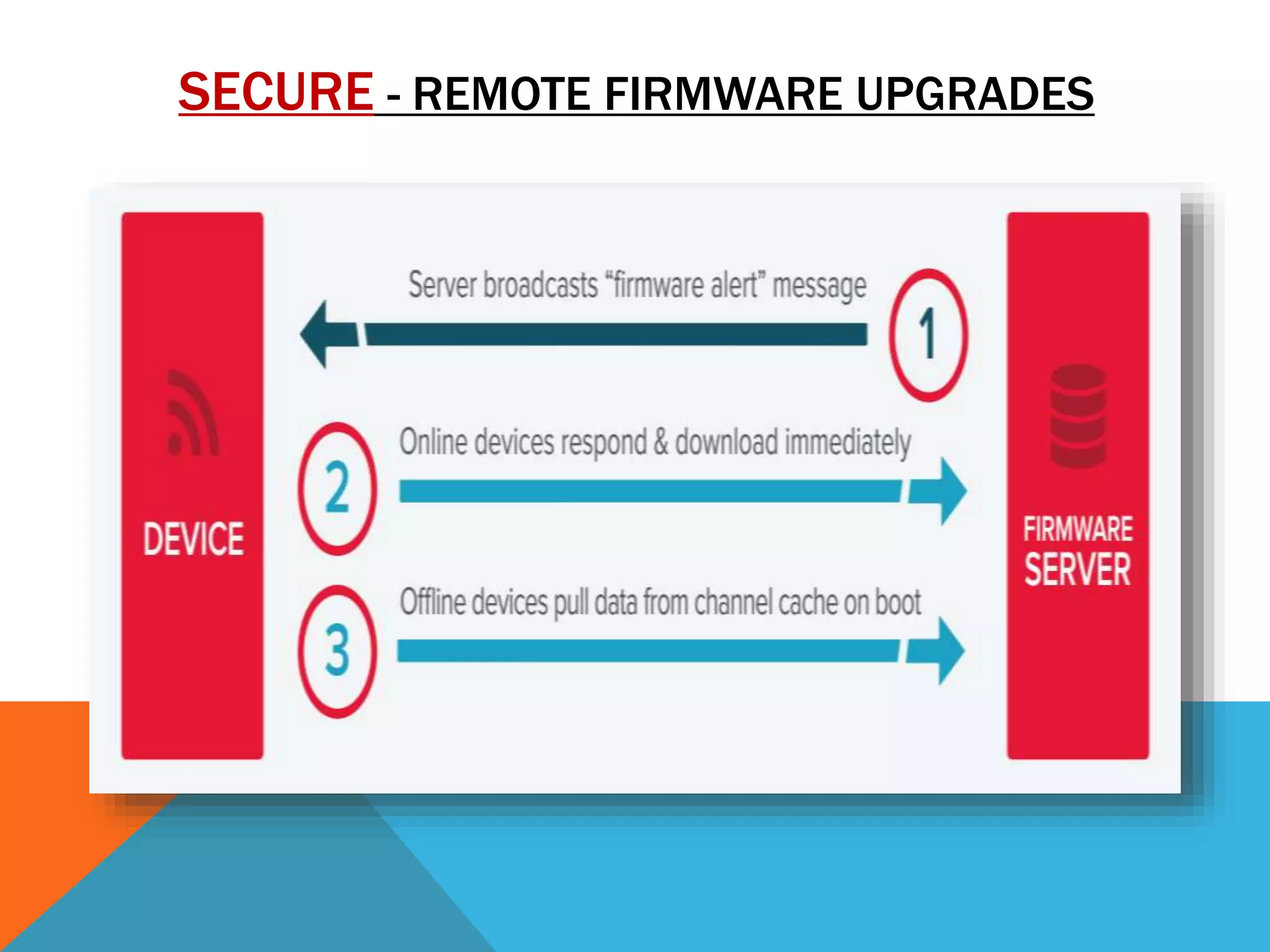
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) and highlights security challenges that hinder its implementation, such as vulnerable devices and flaws in encryption. It outlines potential solutions, including improved access control, end-to-end encryption, and user-friendly setups, to enhance security measures for IoT devices. The conclusion emphasizes the need for cooperation among research communities to address these issues and foster the development of IoT as a sophisticated utility.