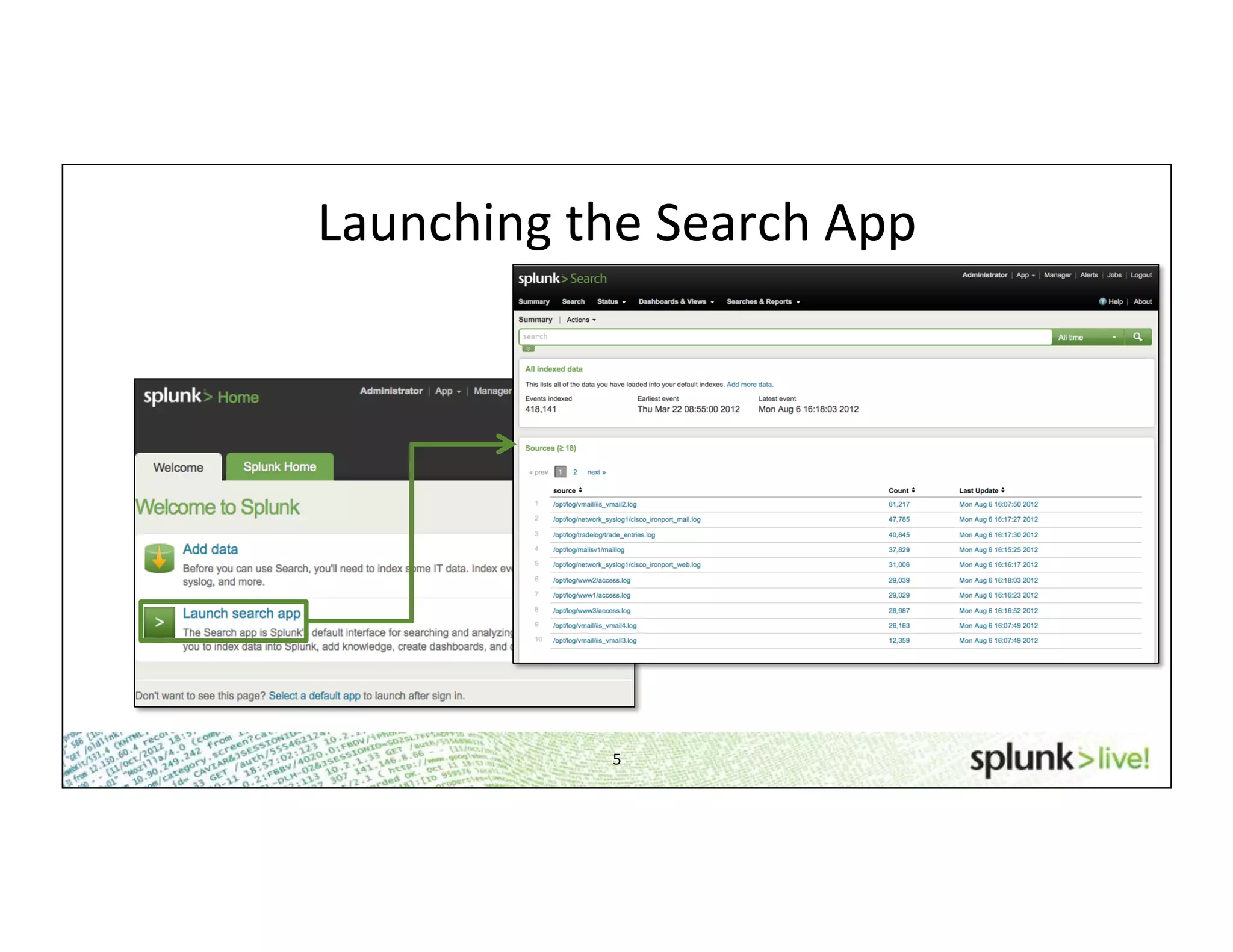
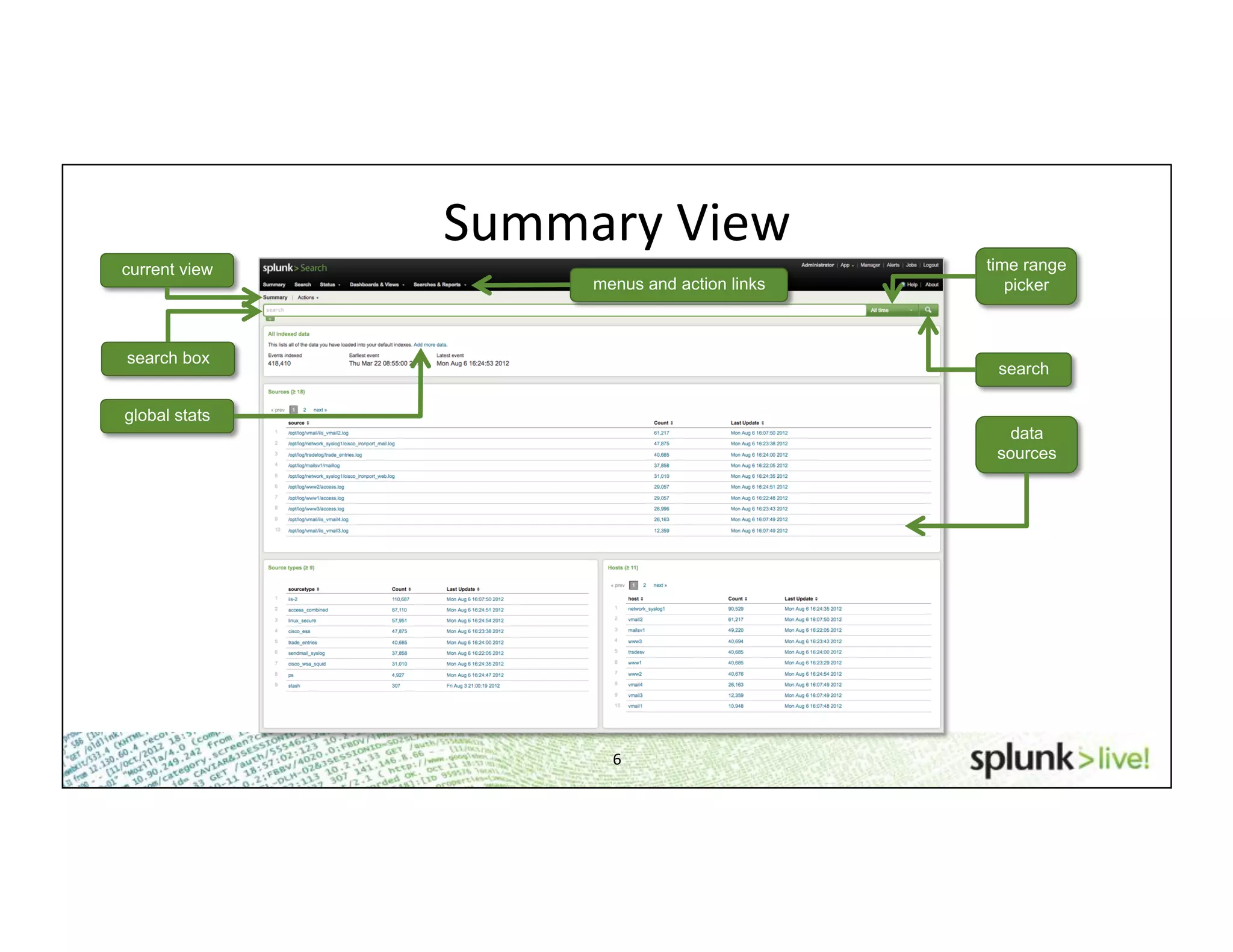
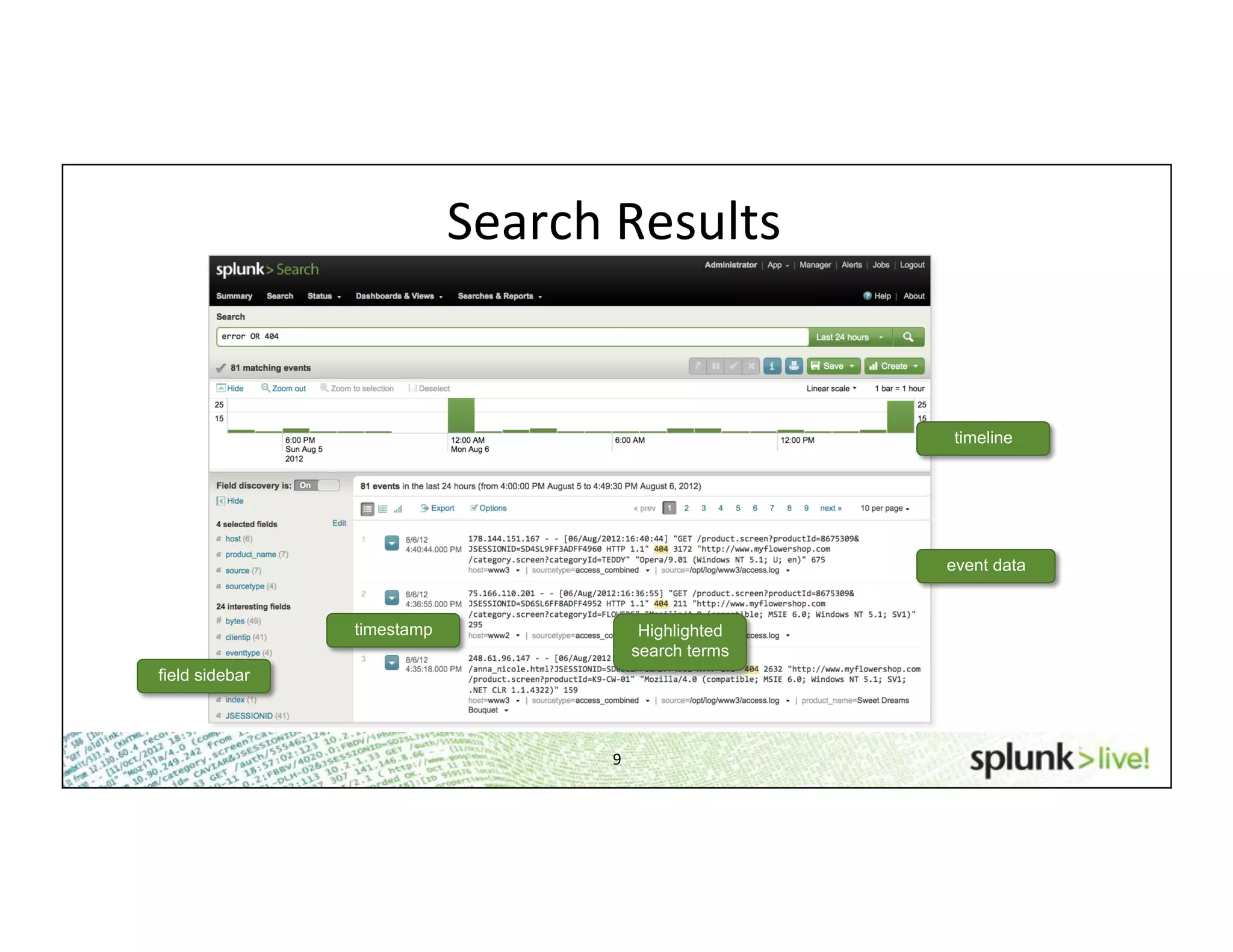
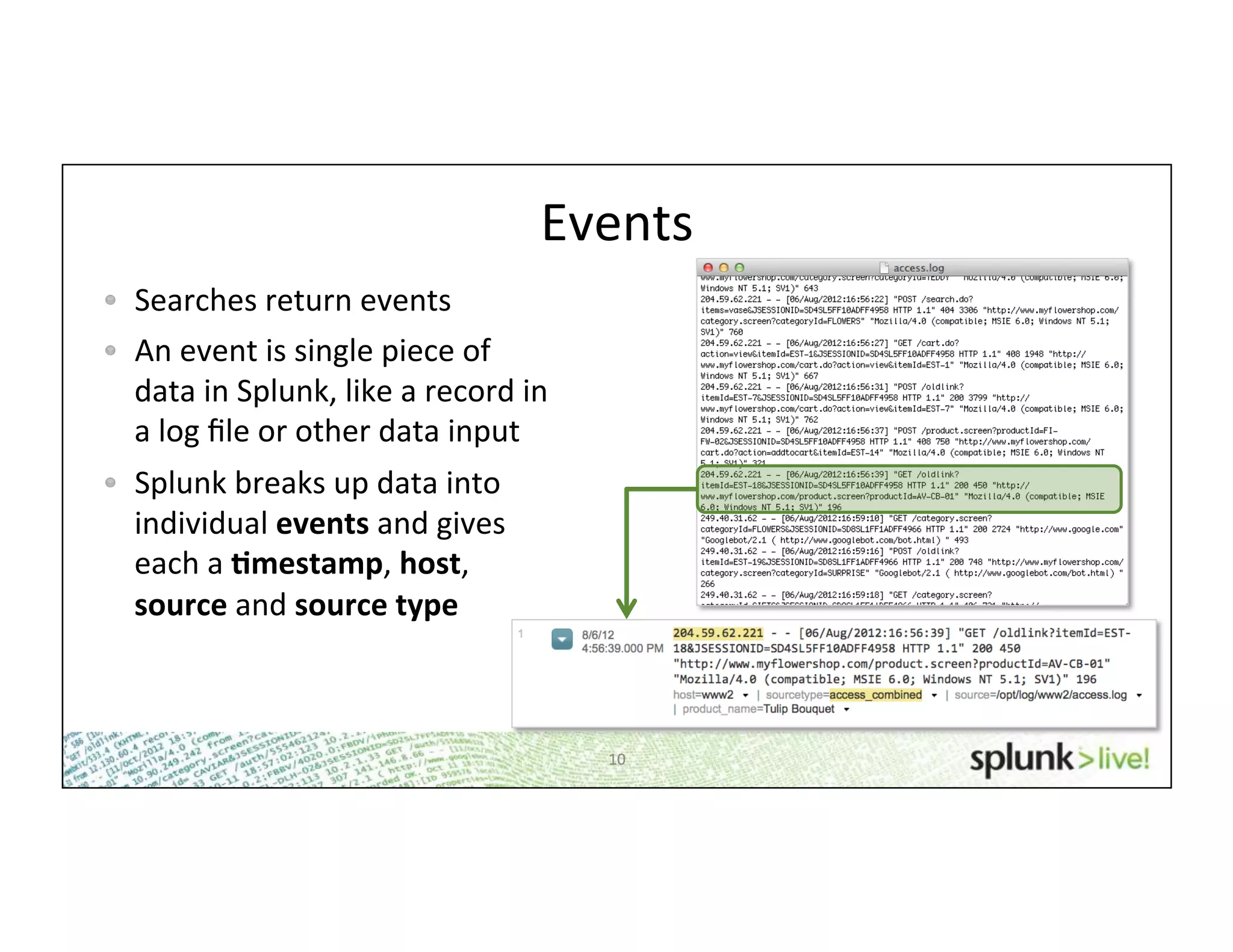
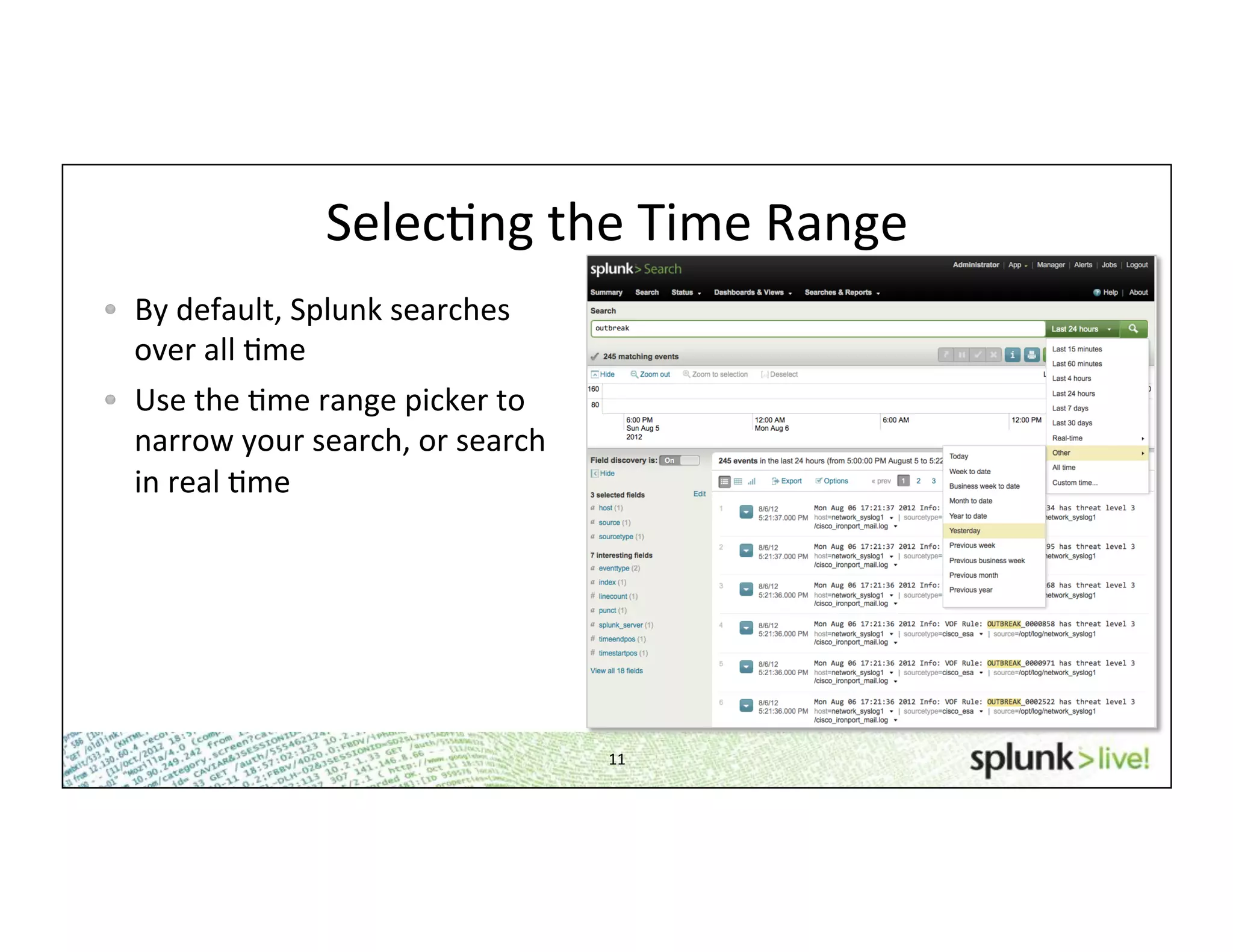
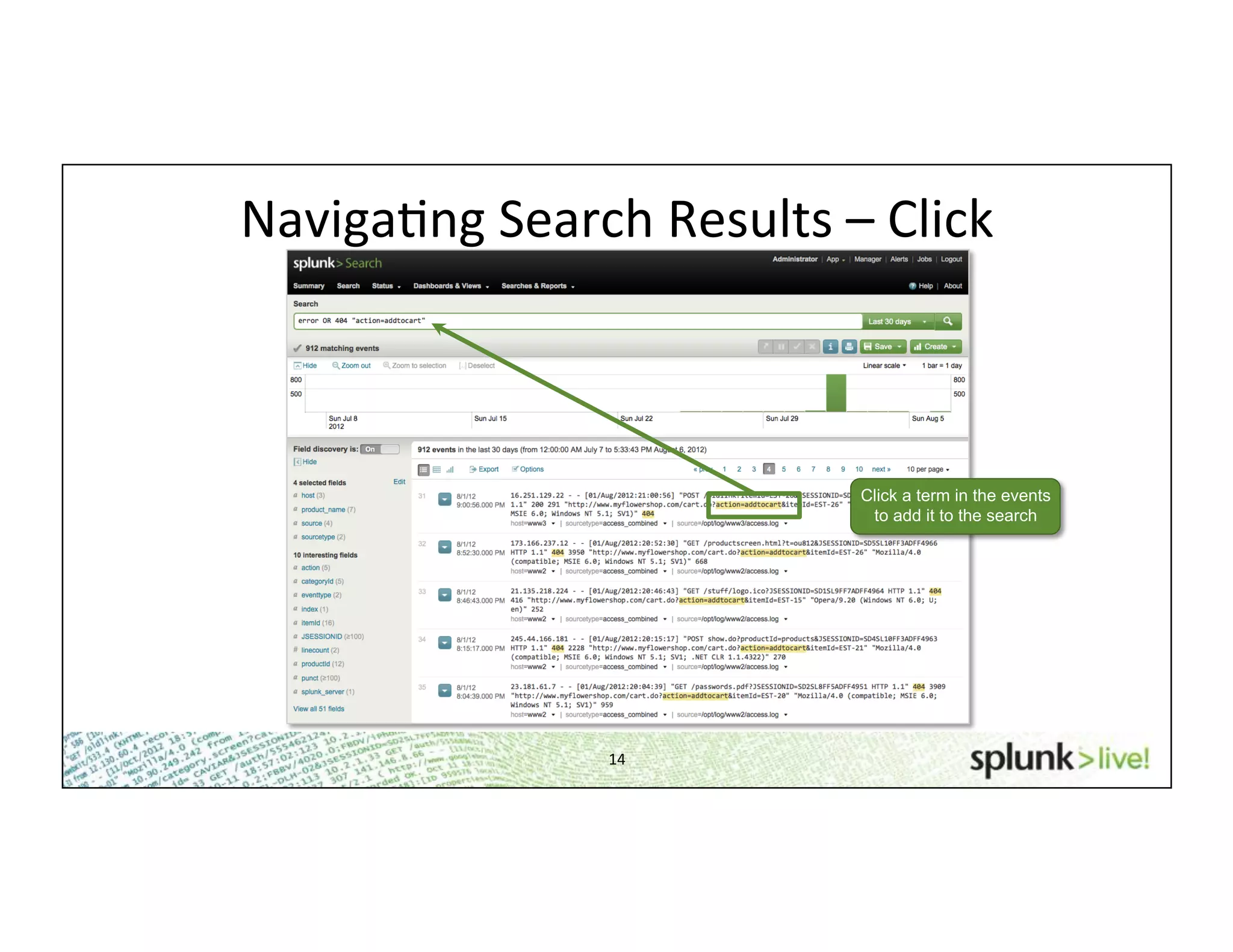
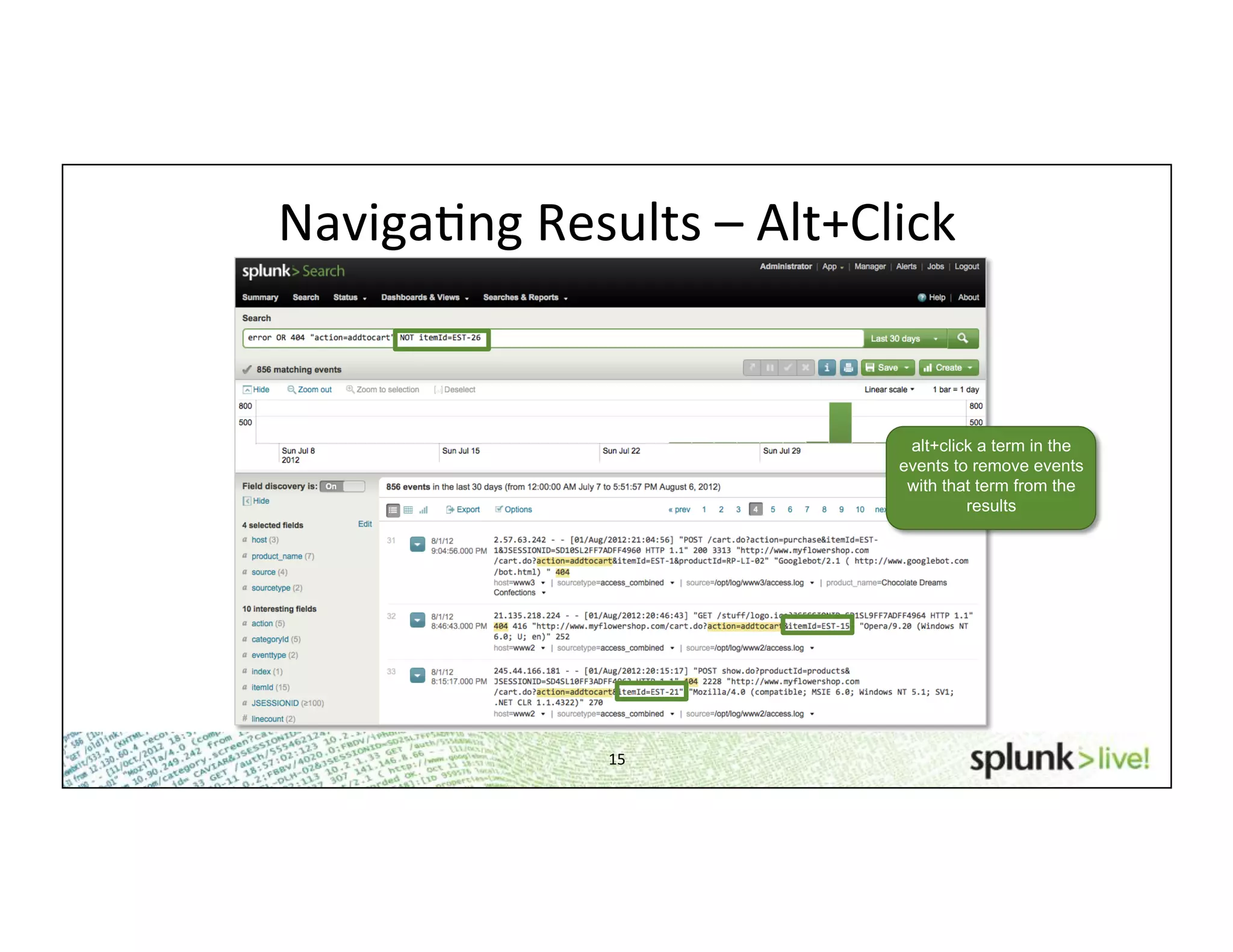
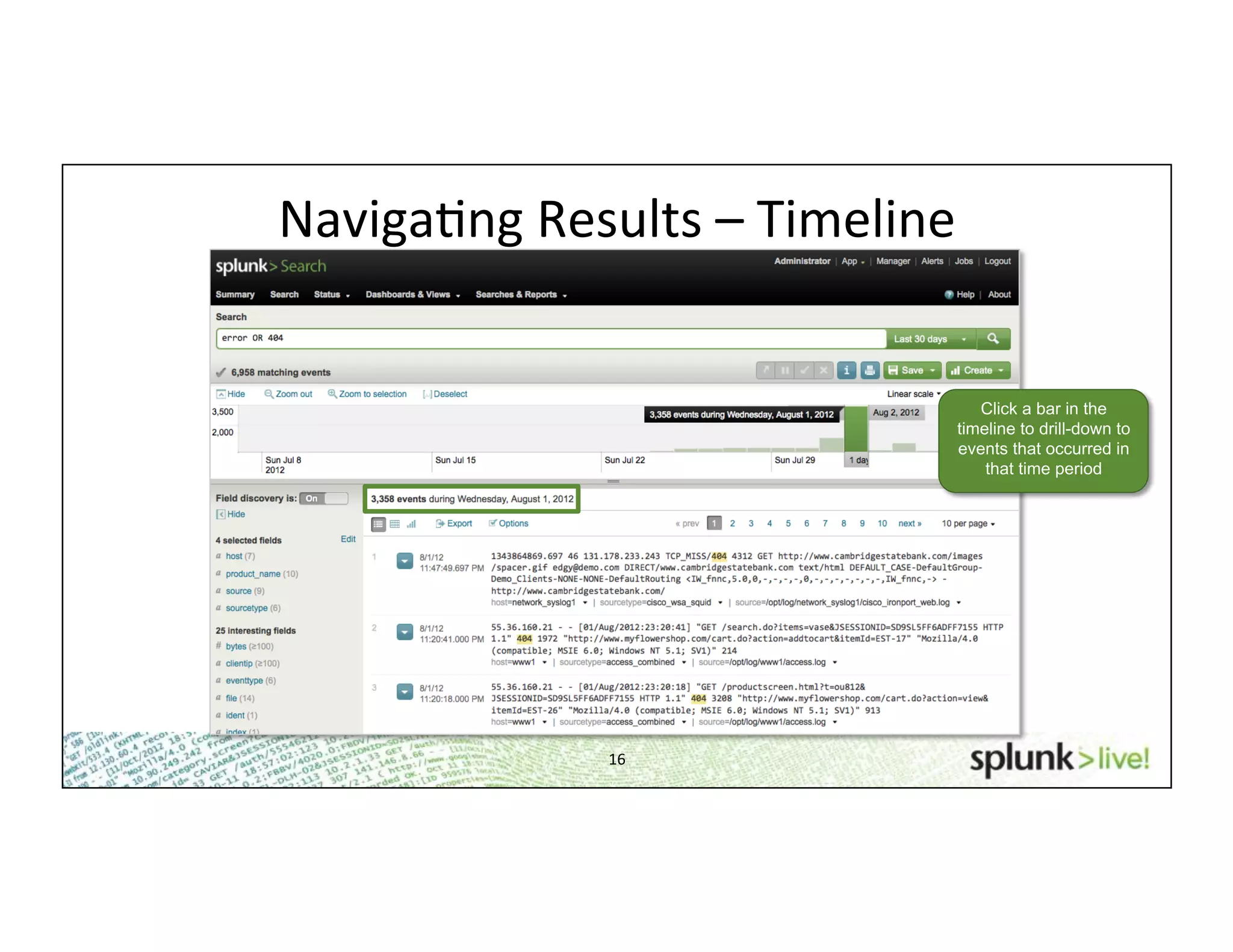
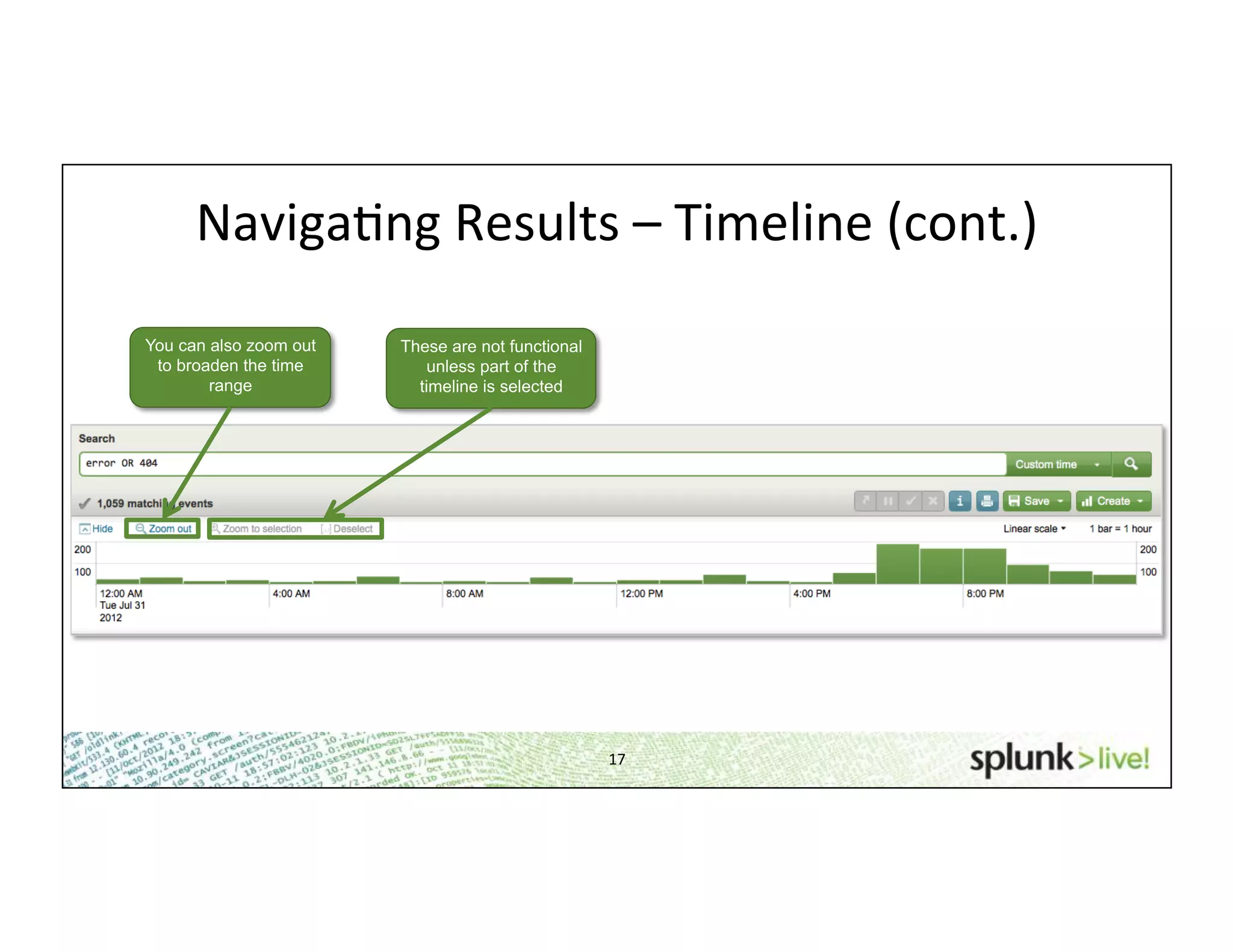
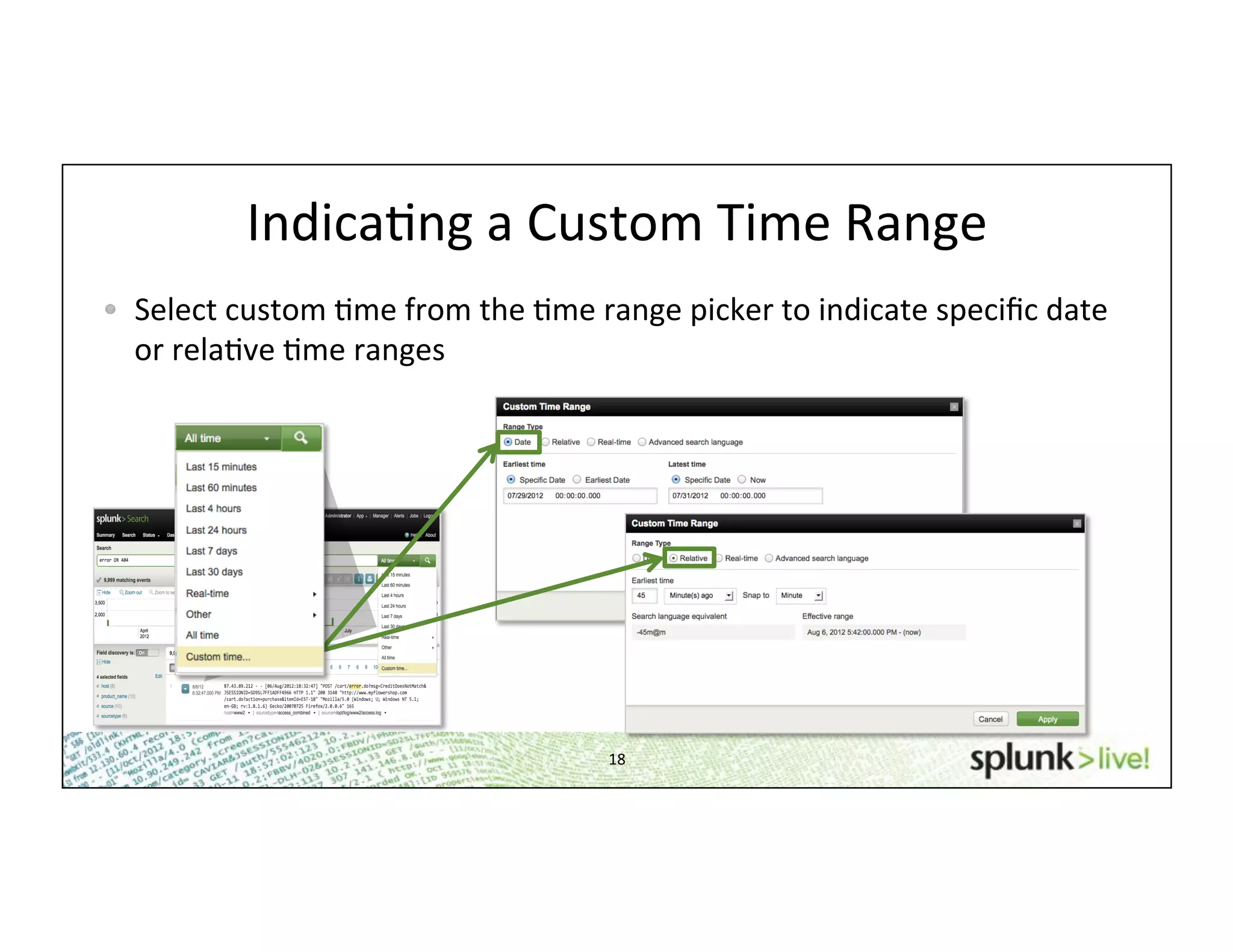
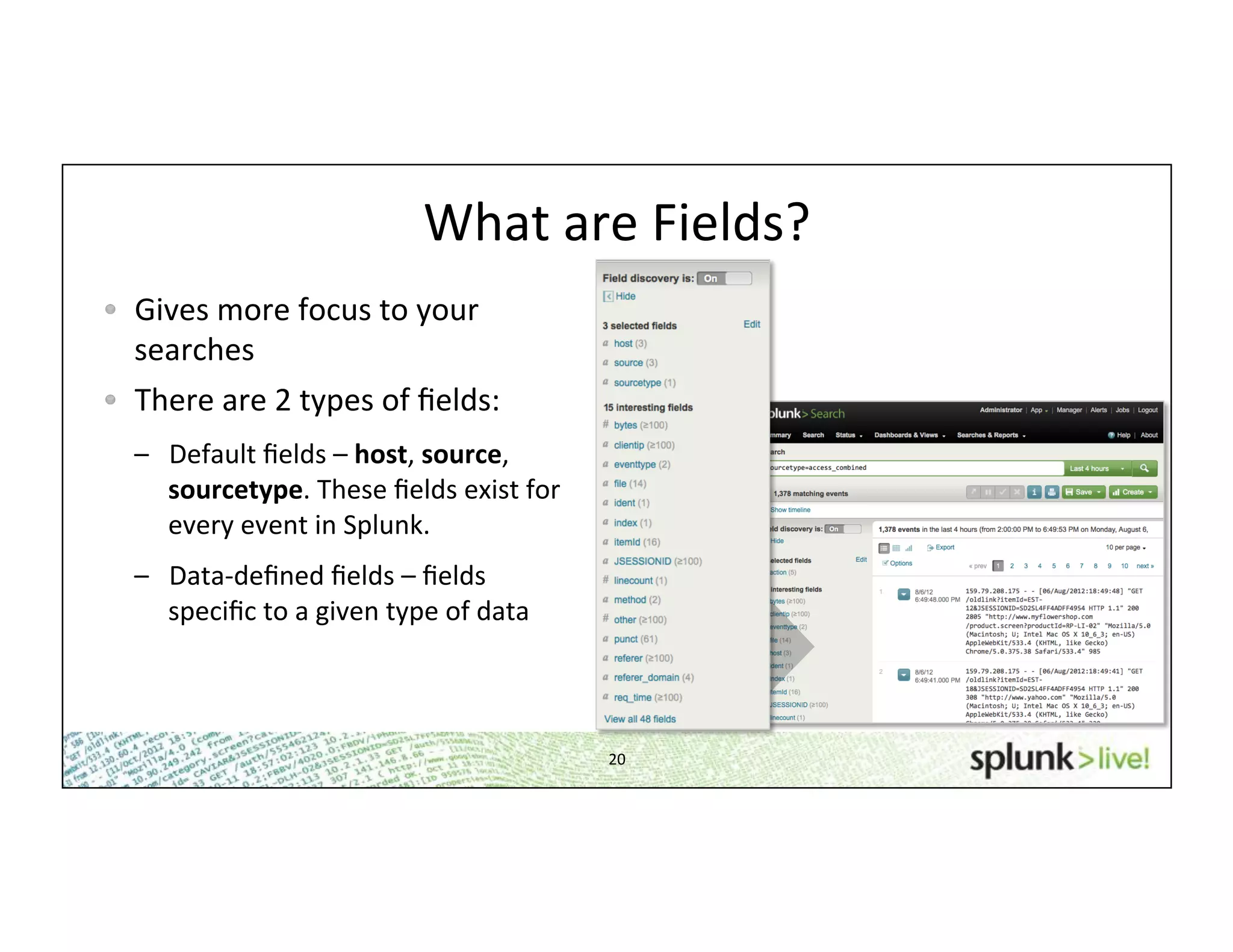
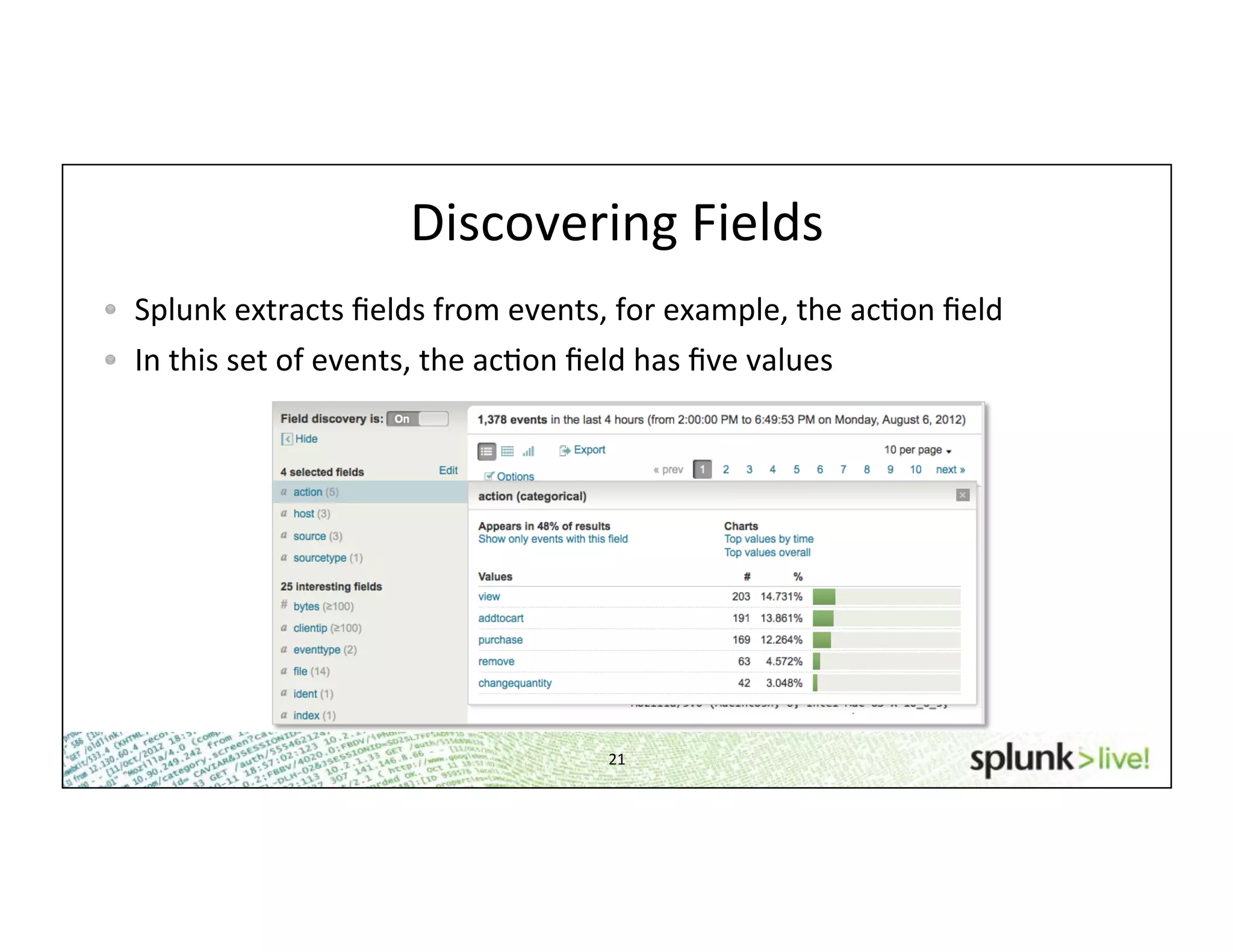
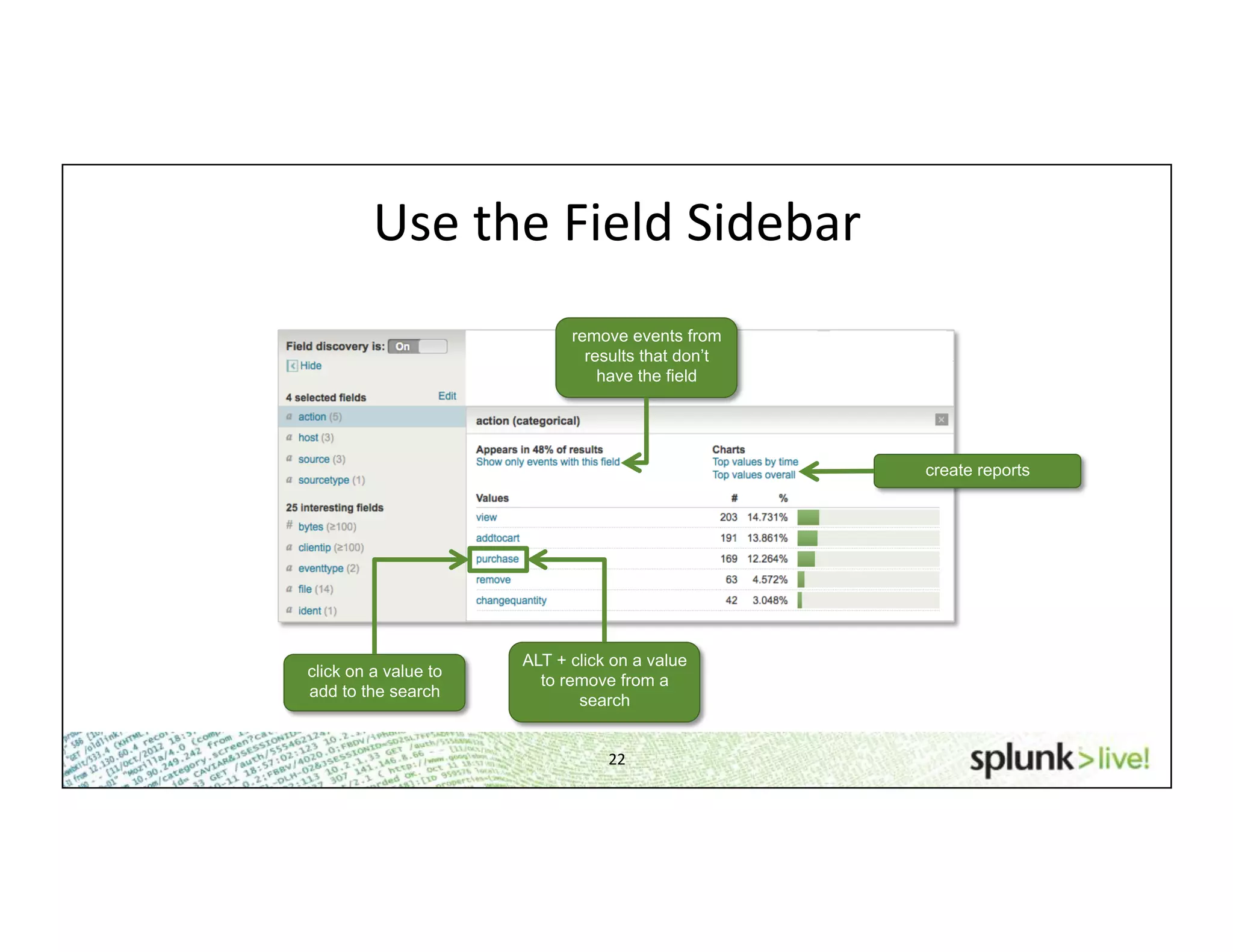
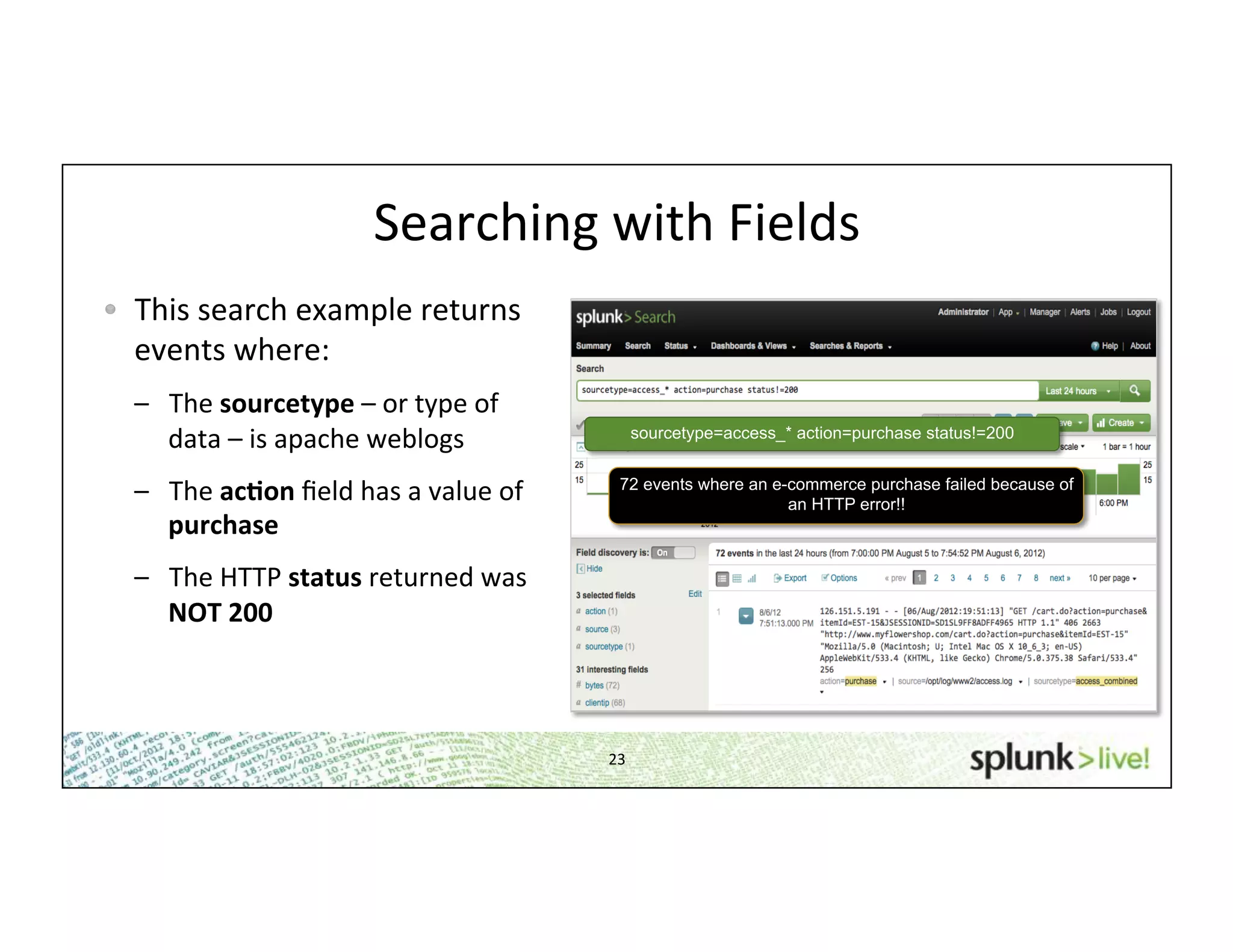
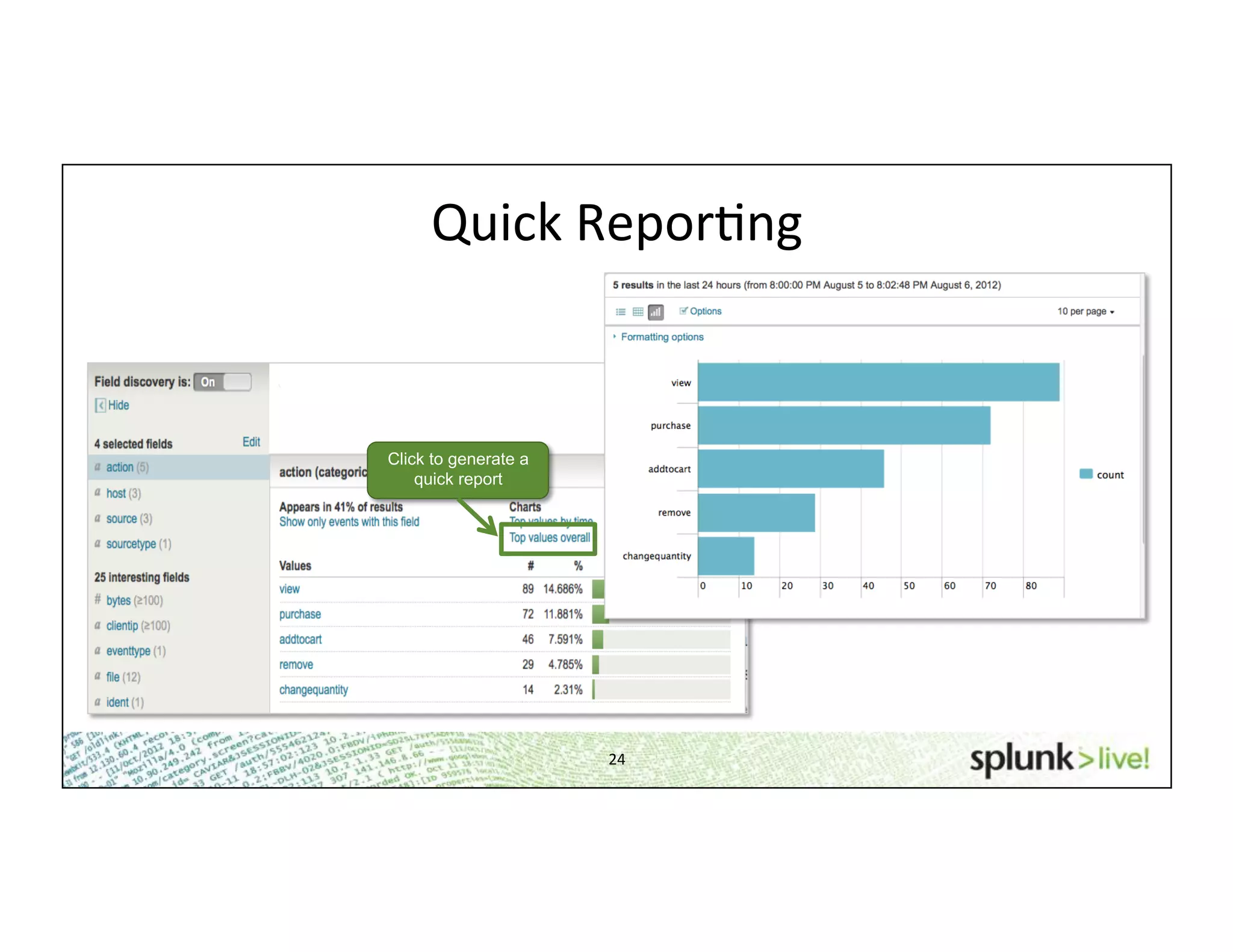
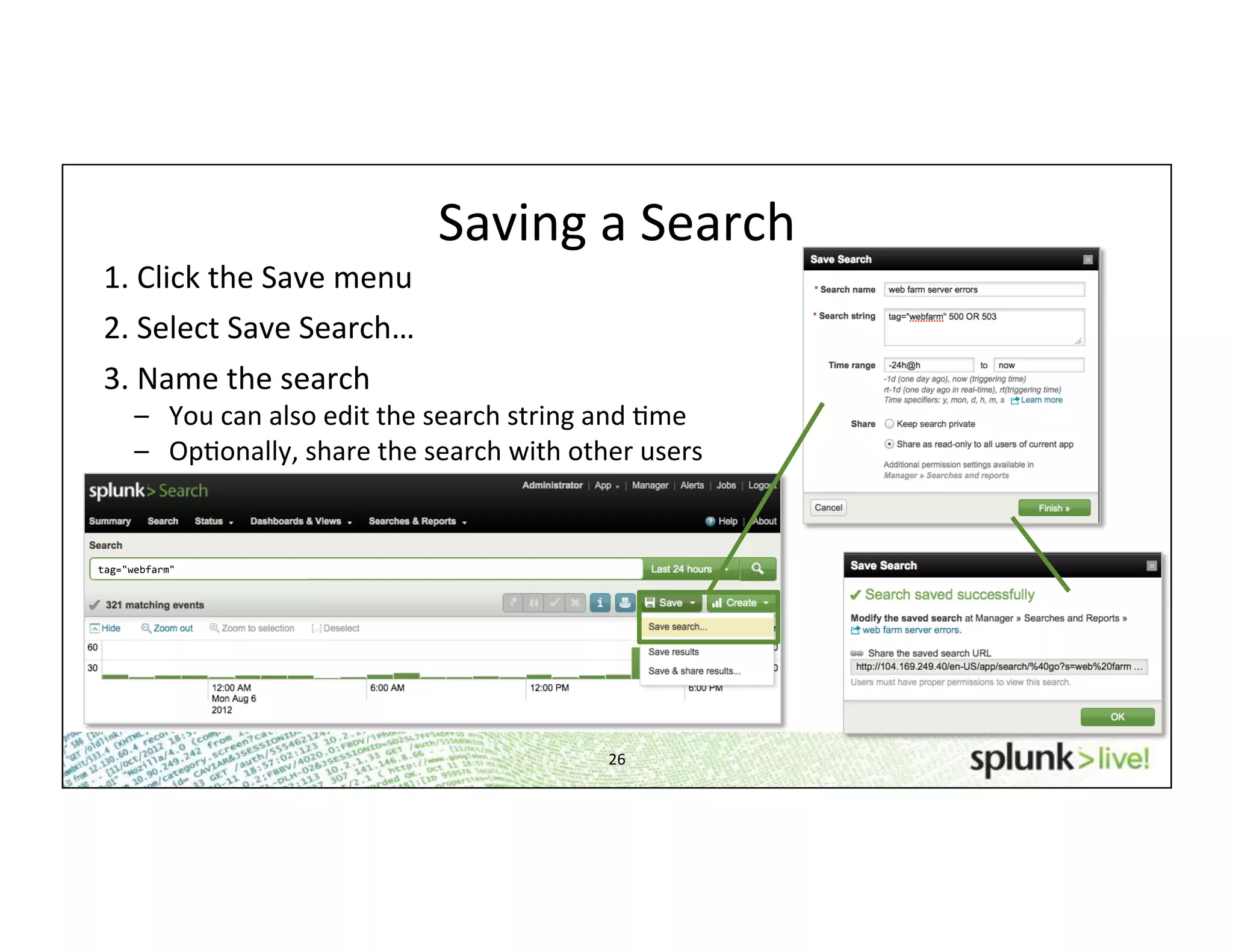
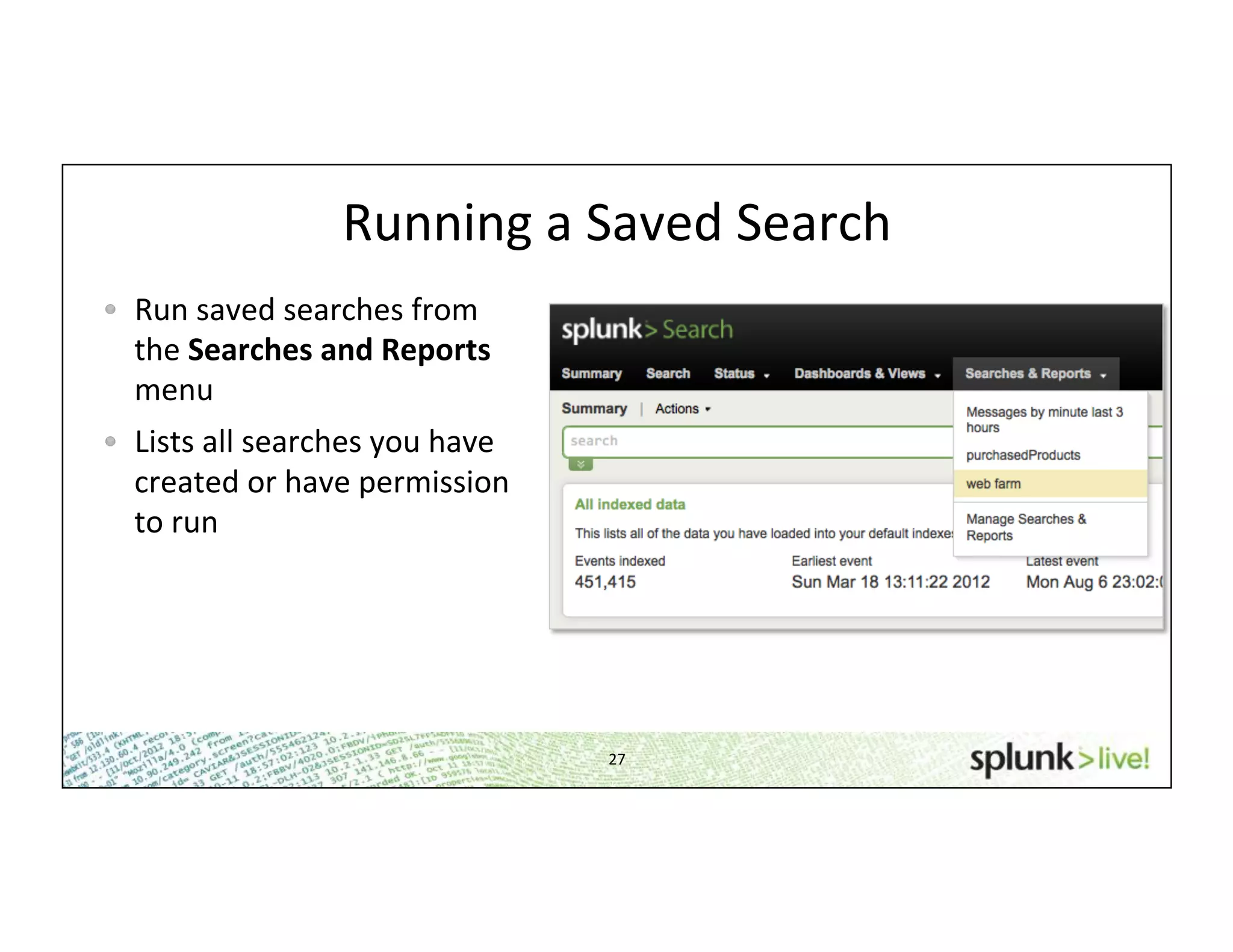
This document provides an agenda and overview for a beginner Splunk search language training. The agenda includes getting started, basic searching, navigating search results, using fields, saving searches, and next steps. It describes the presenter's experience and provides guidance on basic search concepts like wildcards, booleans, phrases, timestamps, and events. It demonstrates how to navigate results through clicking terms, the timeline, and custom time ranges. It also shows how to discover and search using fields as well as save and run saved searches. Finally, it suggests next steps in learning more advanced Splunk features and provides options for additional training.