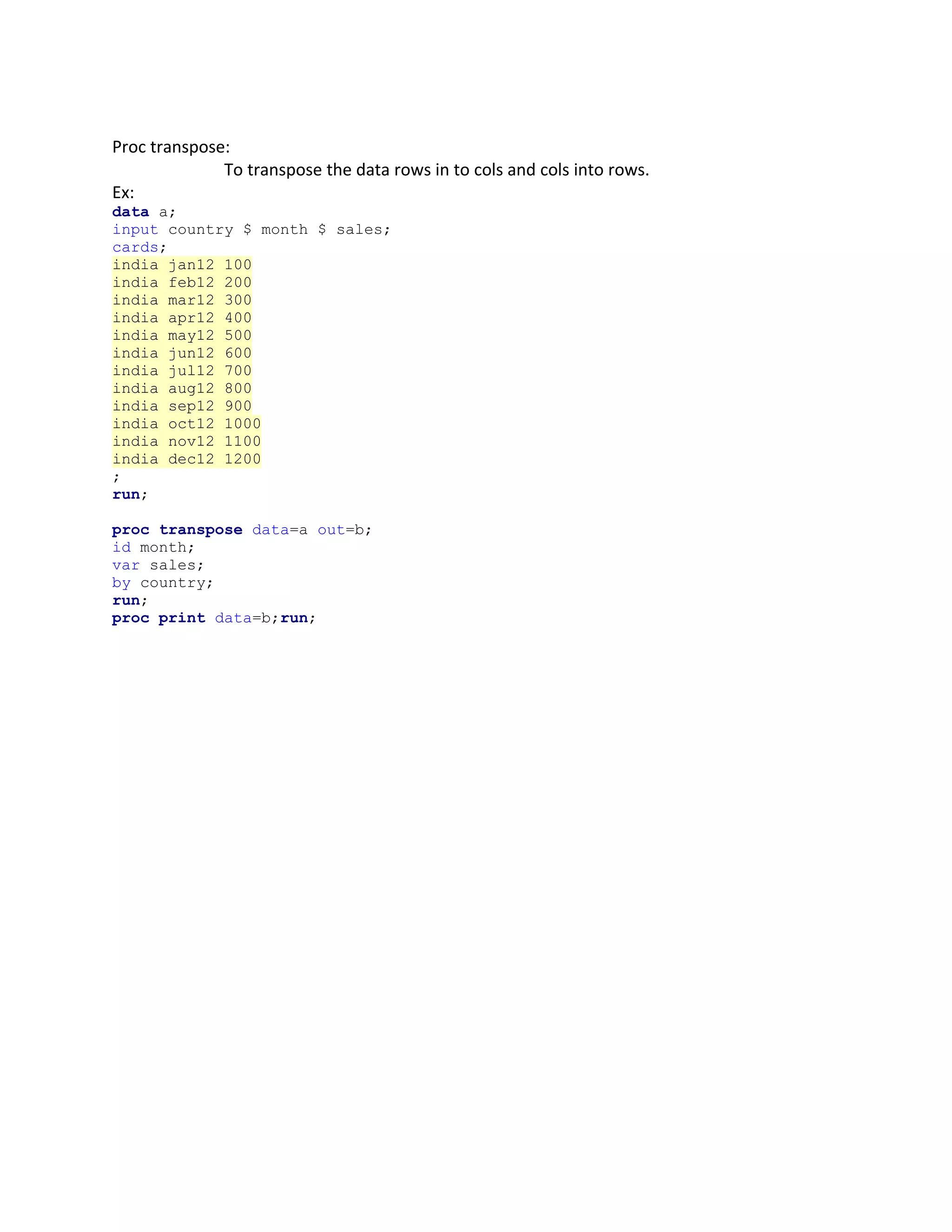
The document describes various SAS commands and functions used for data management and analysis. It provides explanations of commands for reading, writing, importing, exporting, manipulating and transforming SAS data sets as well as functions for working with dates, strings, and transposing data between wide and long formats. Descriptive statistics procedures like PROC MEANS, PROC SUMMARY, and PROC UNIVARIATE are also covered along with differences between merging and joining operations.