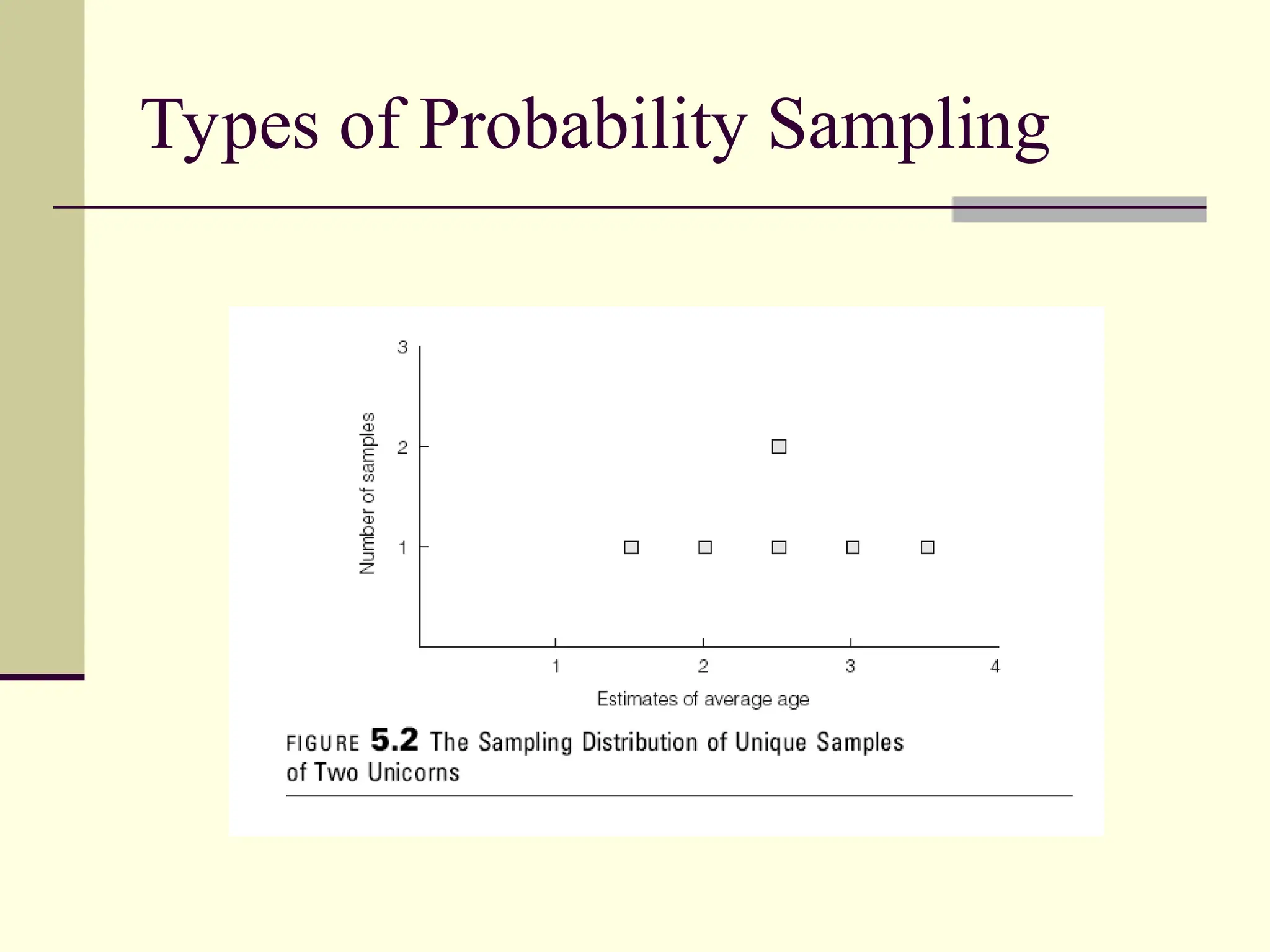
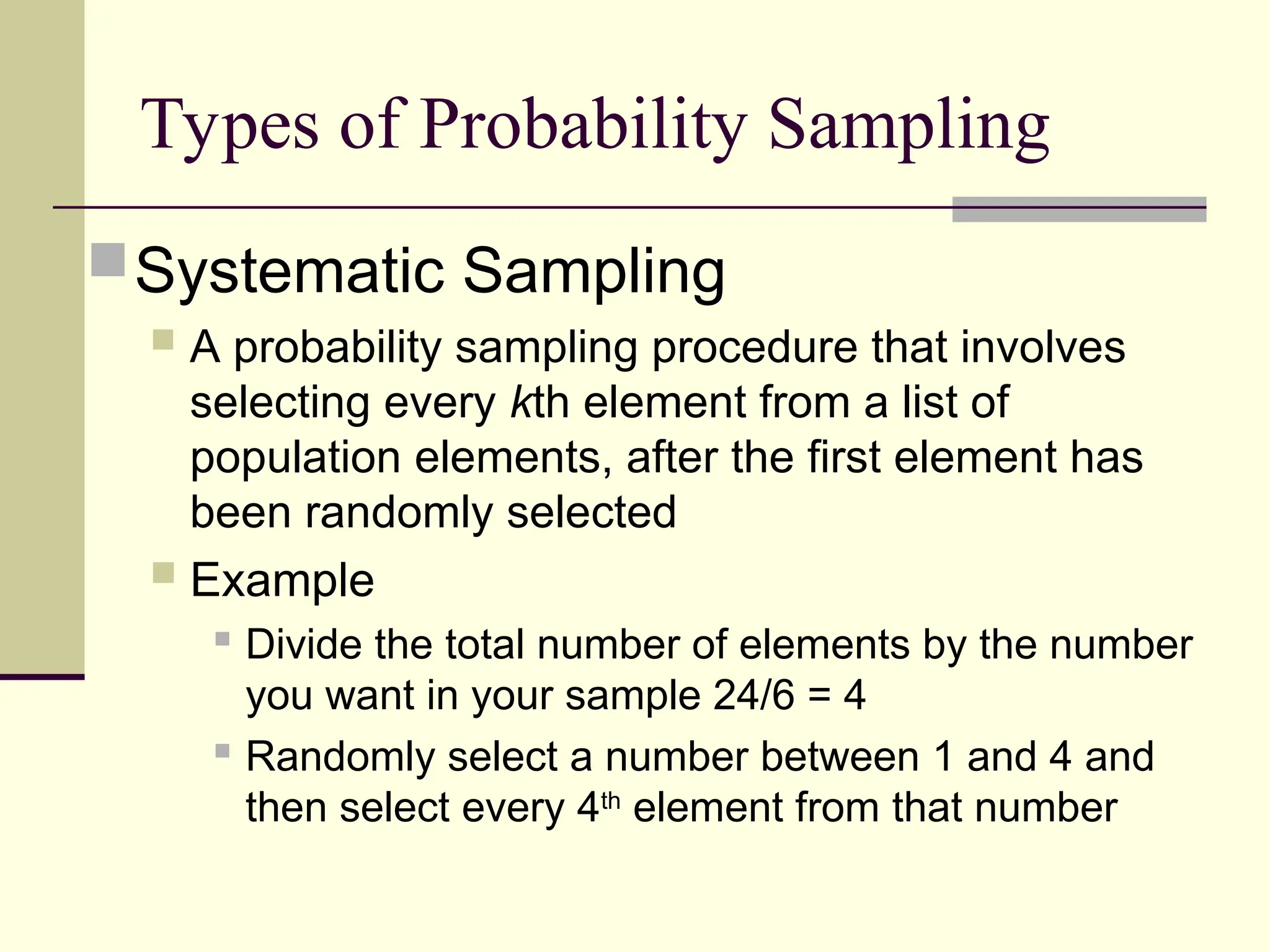
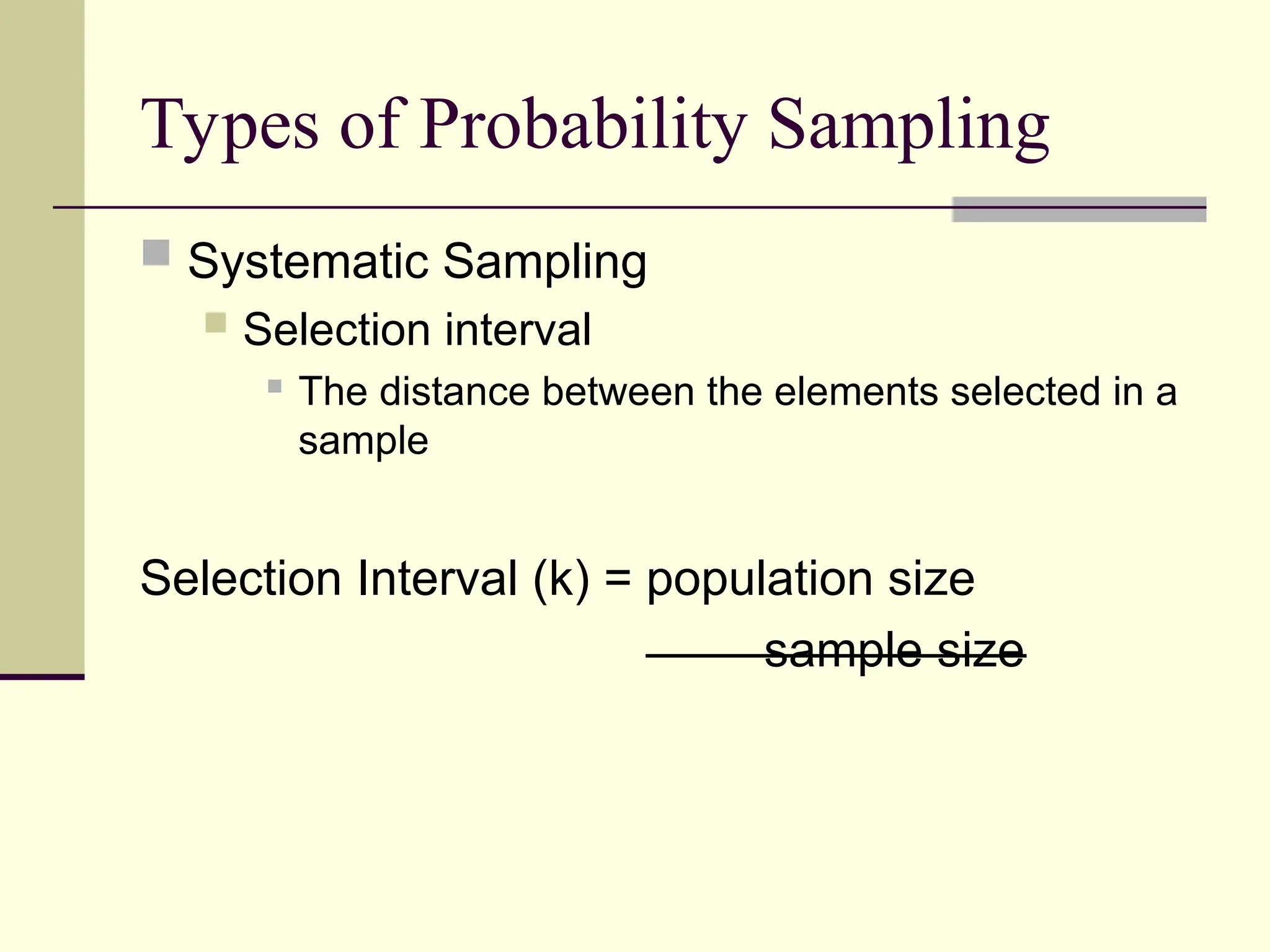
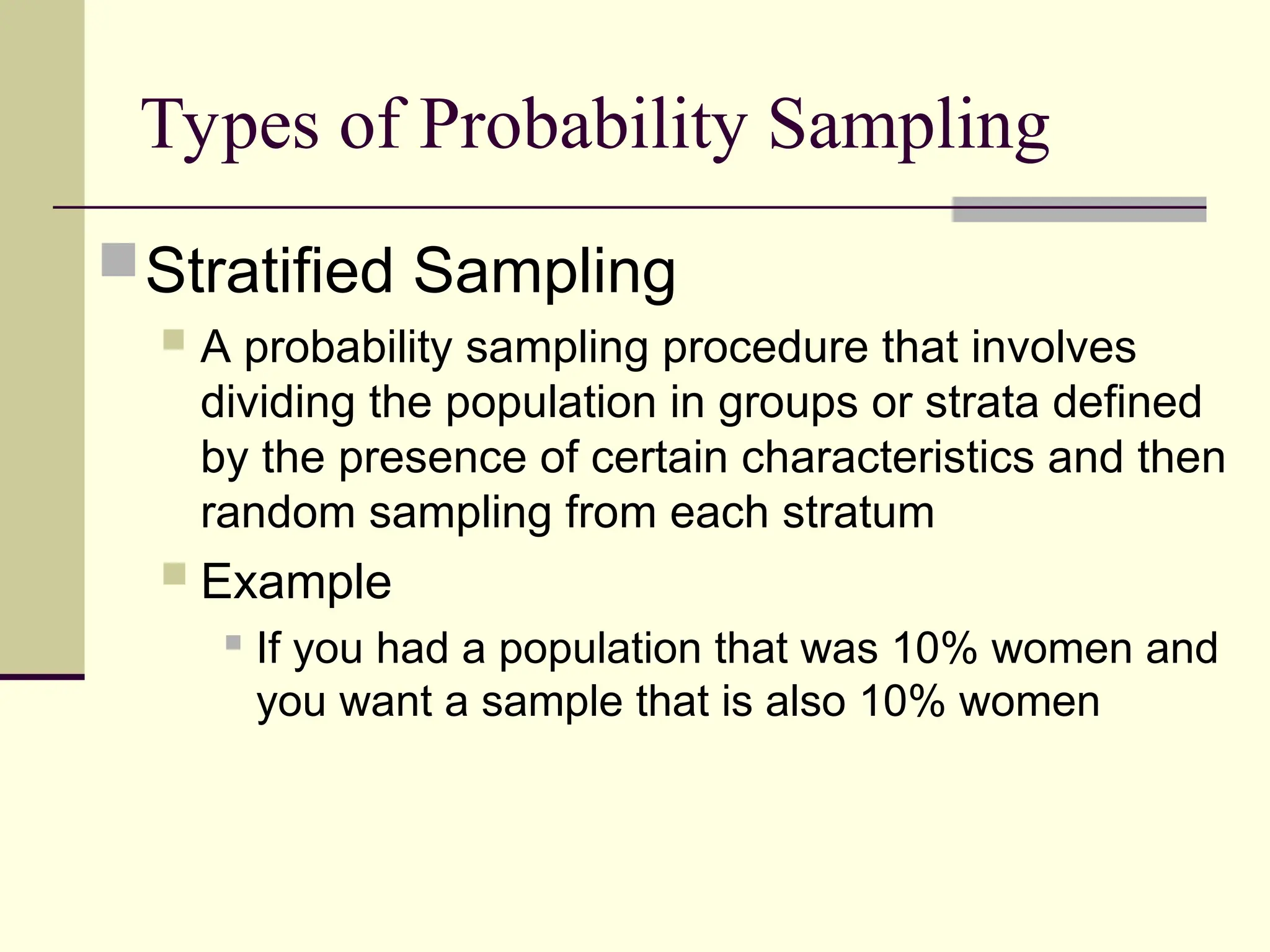
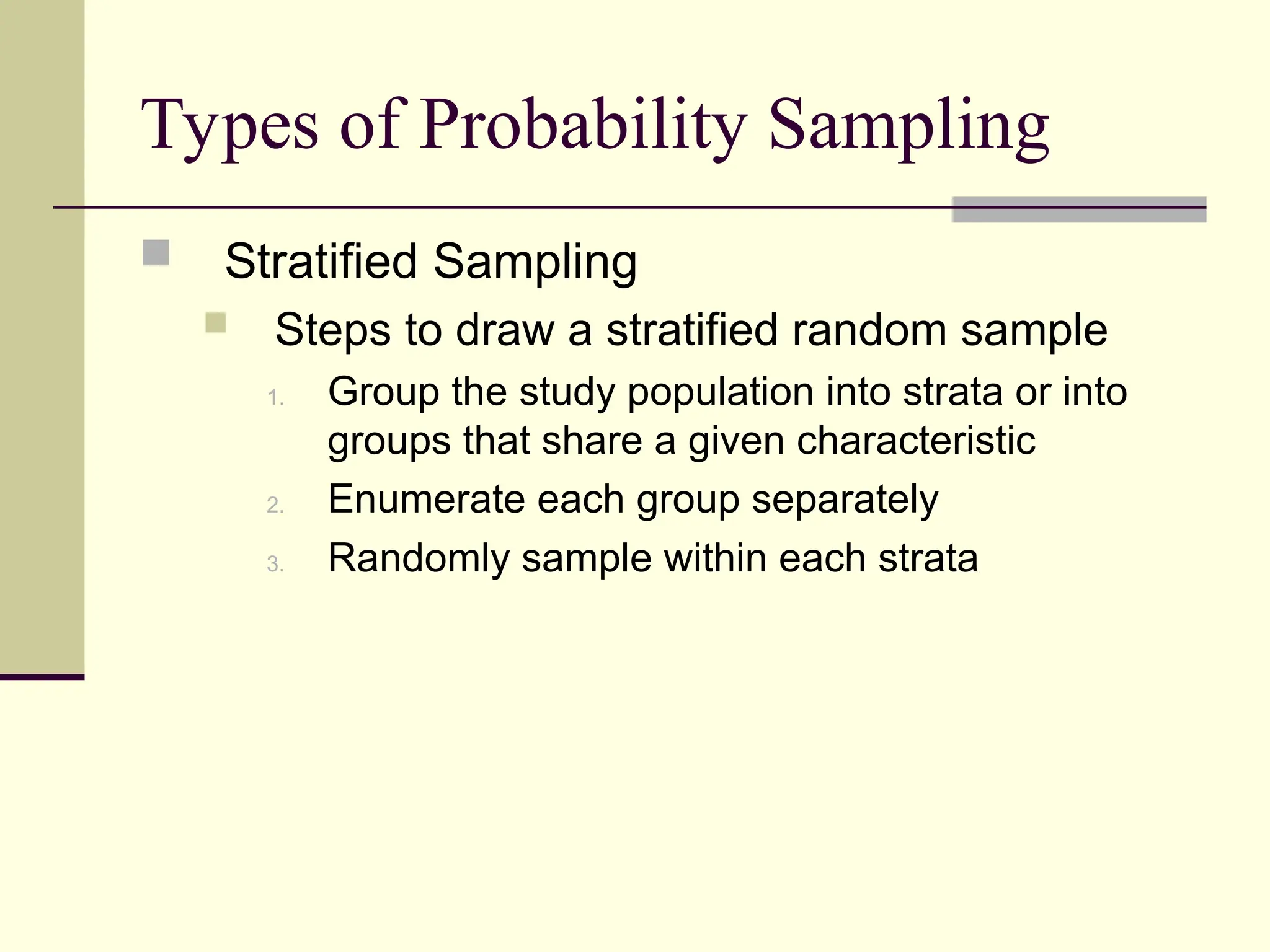
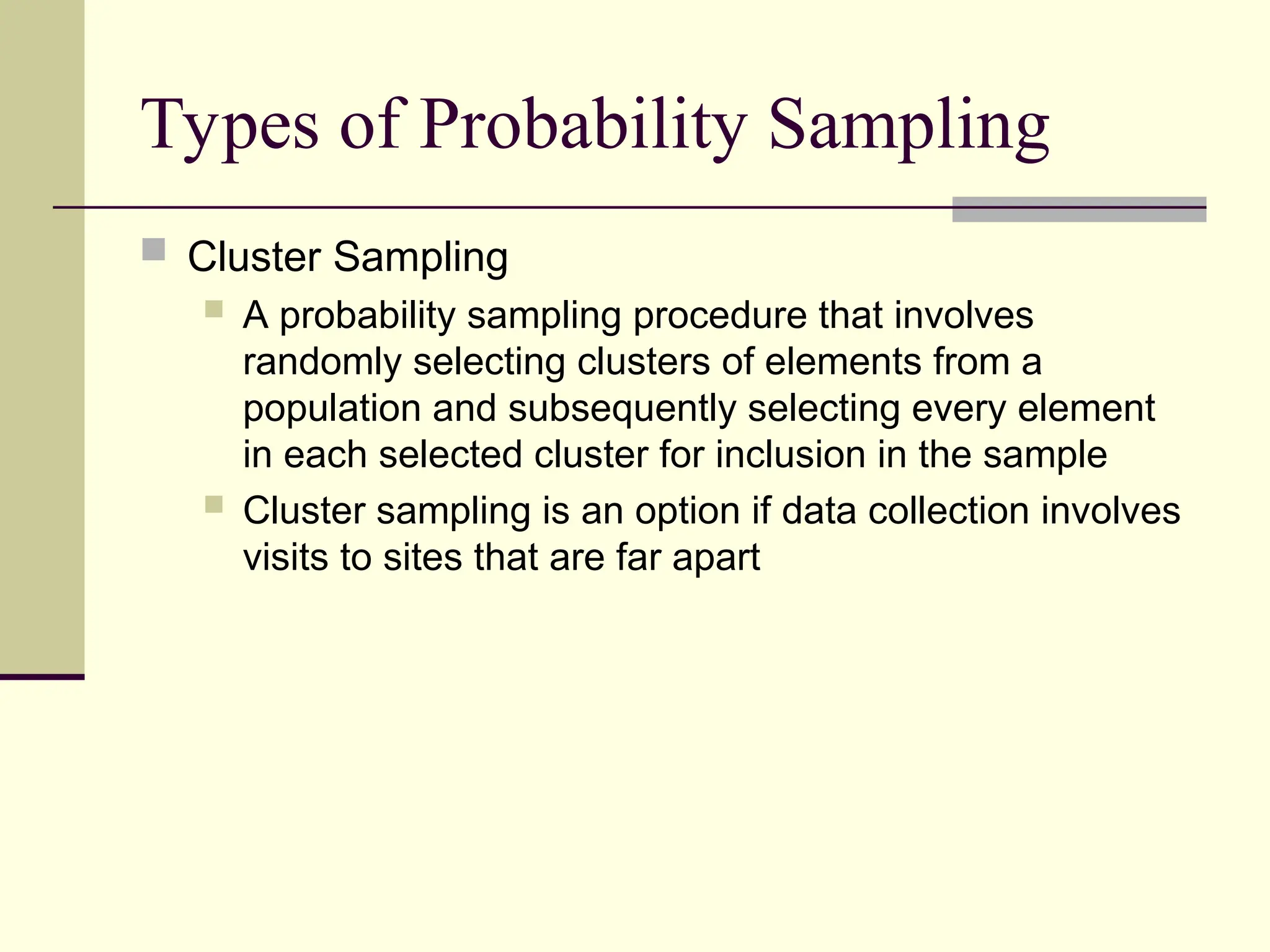
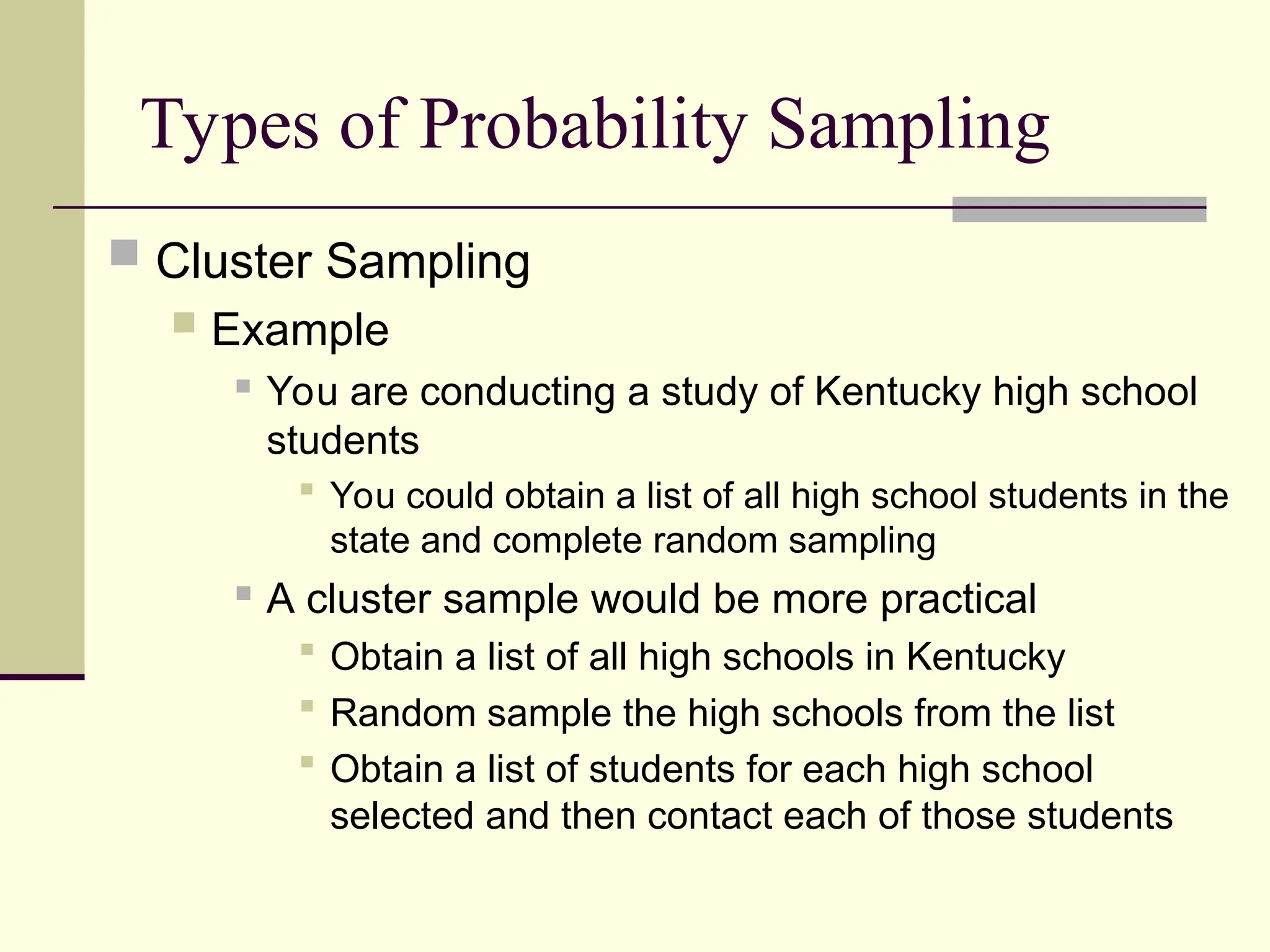
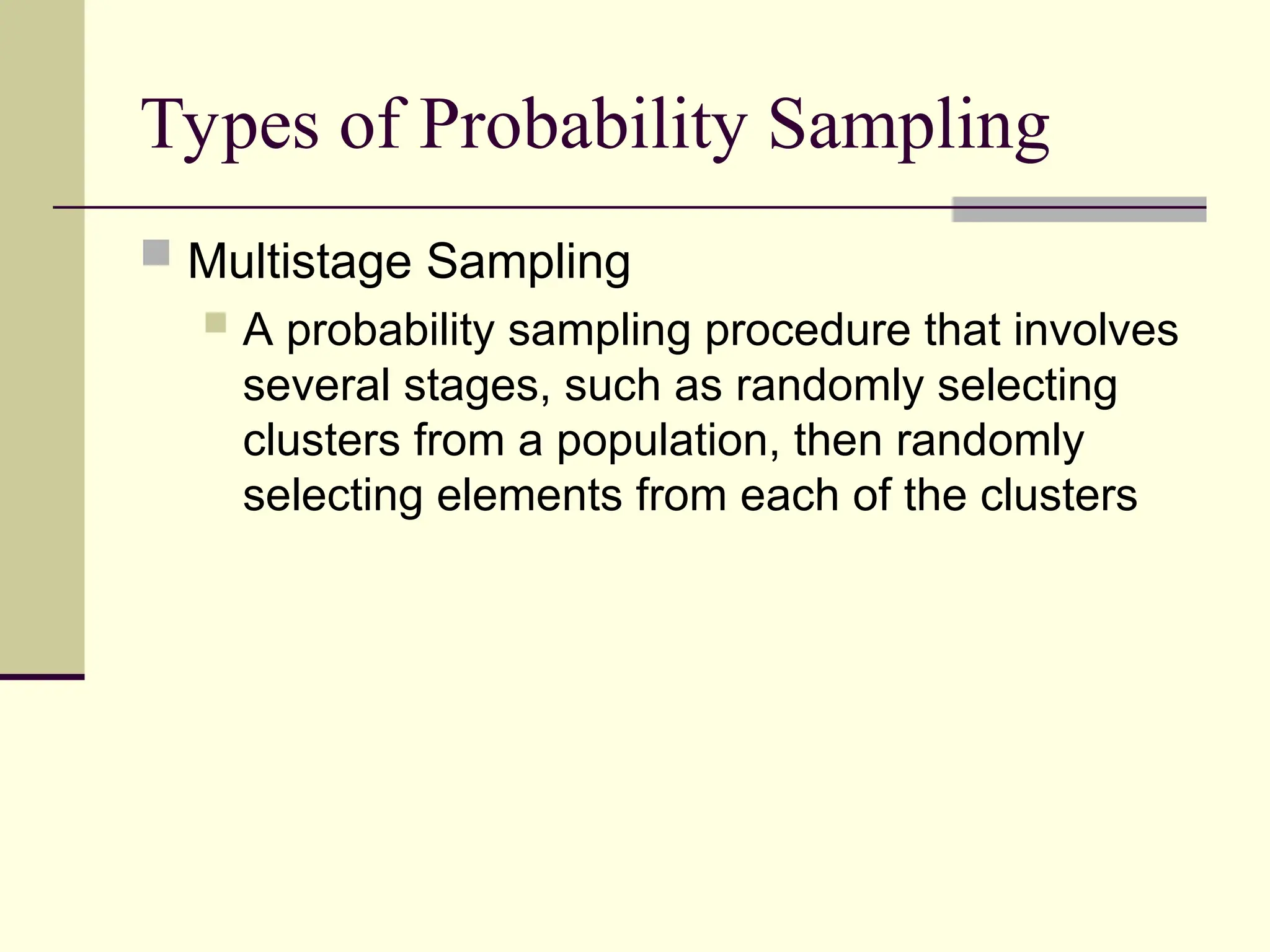
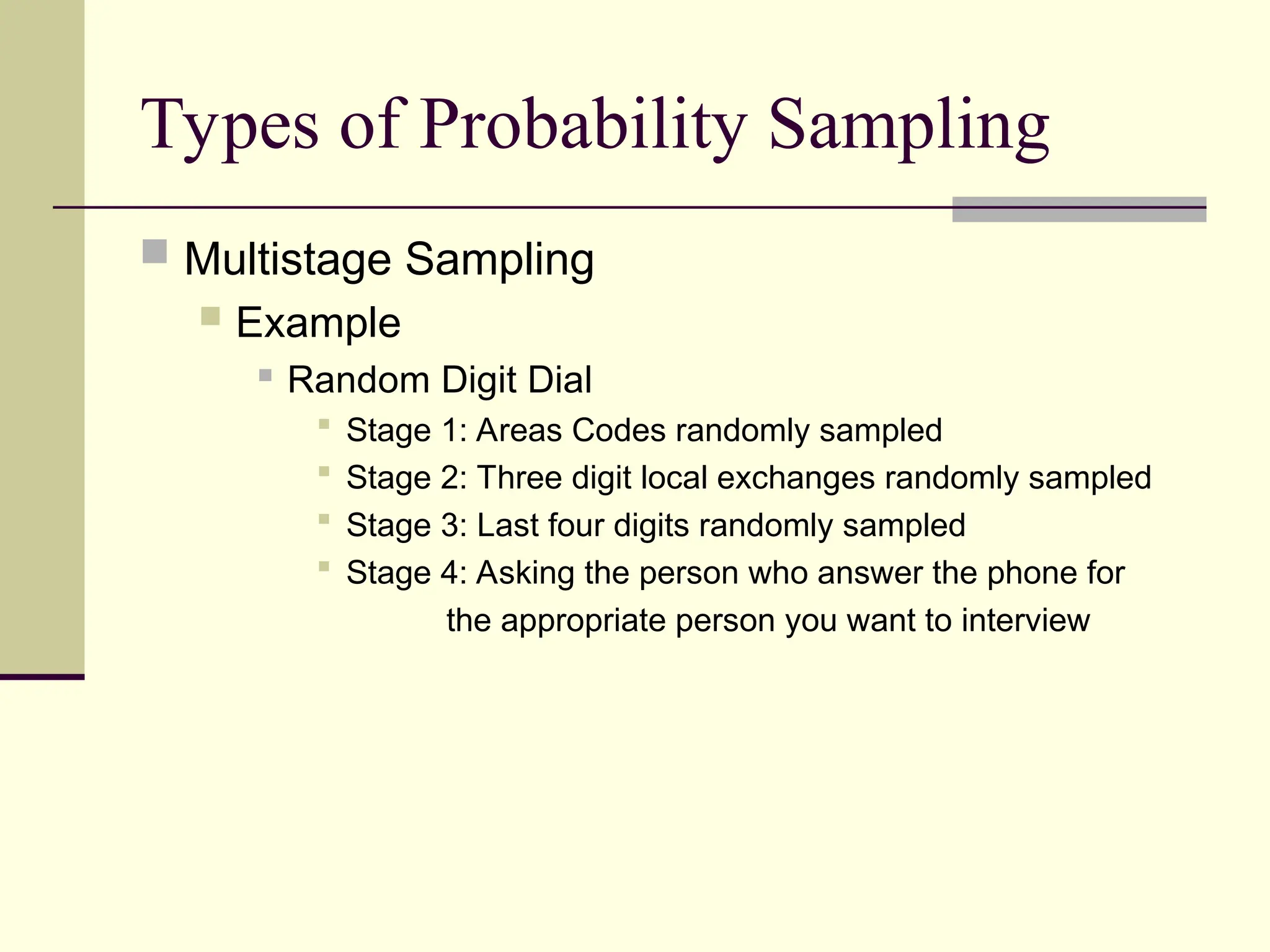
Sampling is the process of selecting individual cases from a larger population to gain insights without studying every member, often used for cost and time efficiency. Different sampling techniques, including probability and nonprobability methods, impact the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the results. Various sources of error, such as coverage error and nonresponse error, can affect sampling accuracy, making careful selection of sampling methods essential.