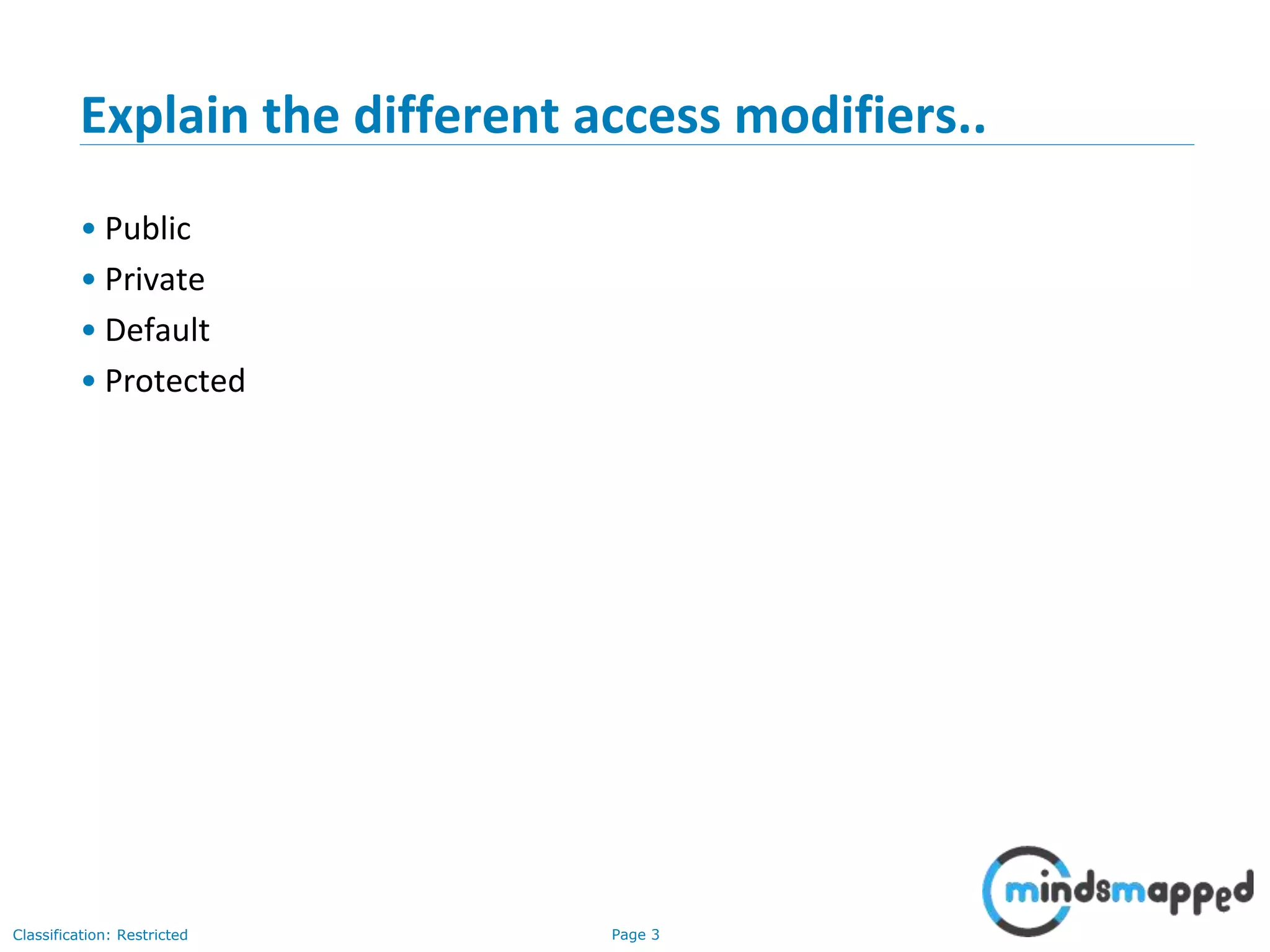
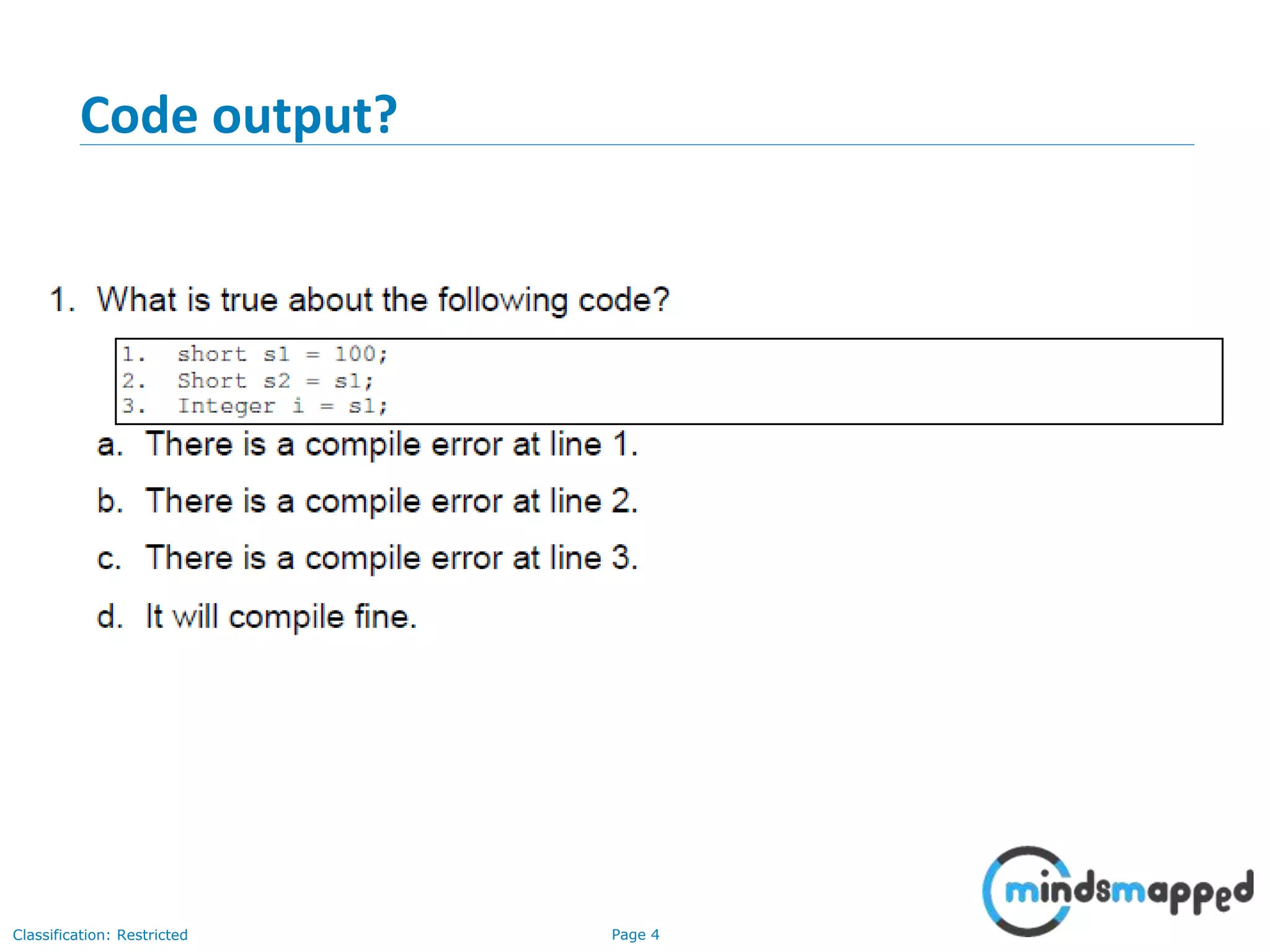
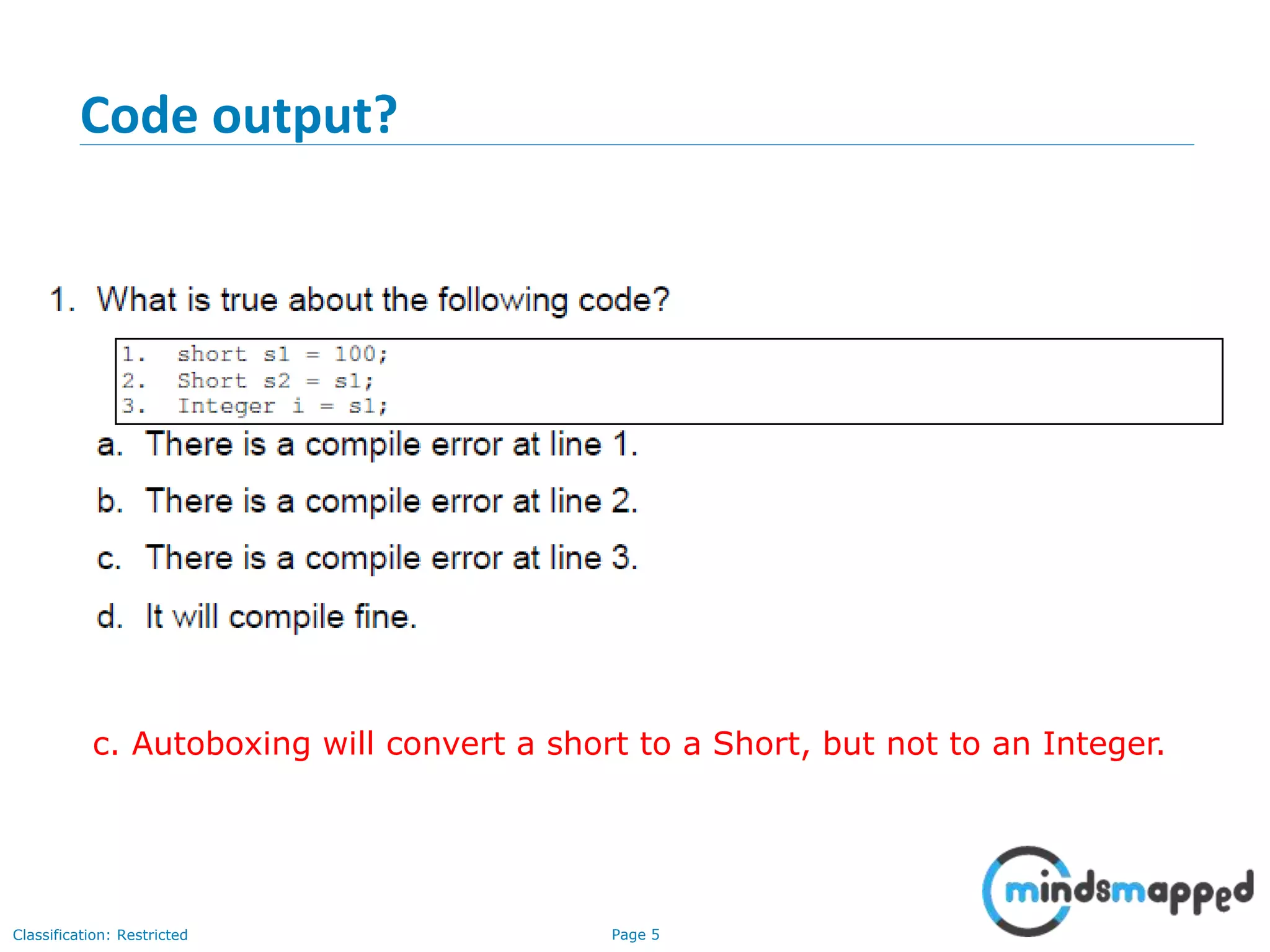
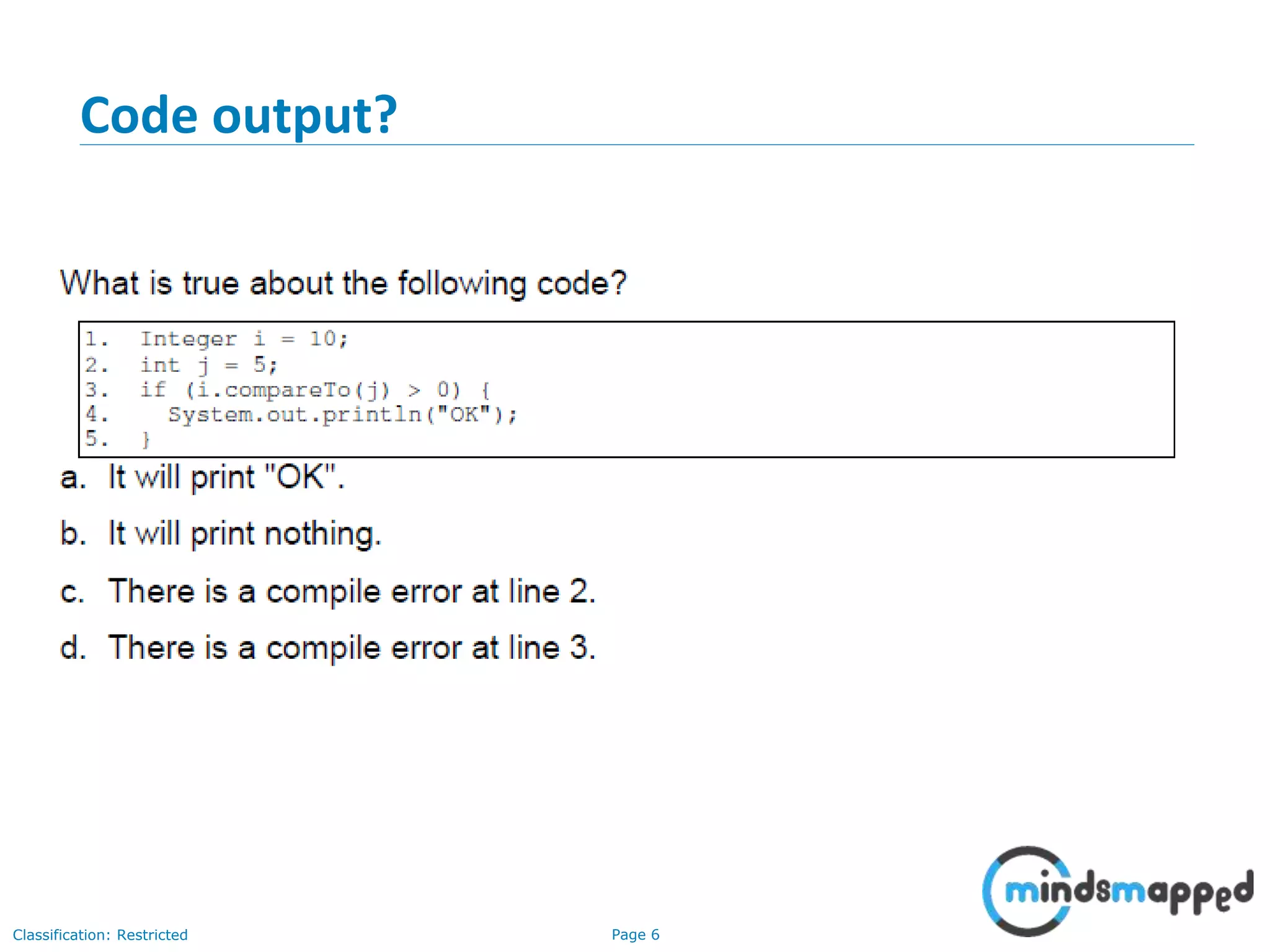
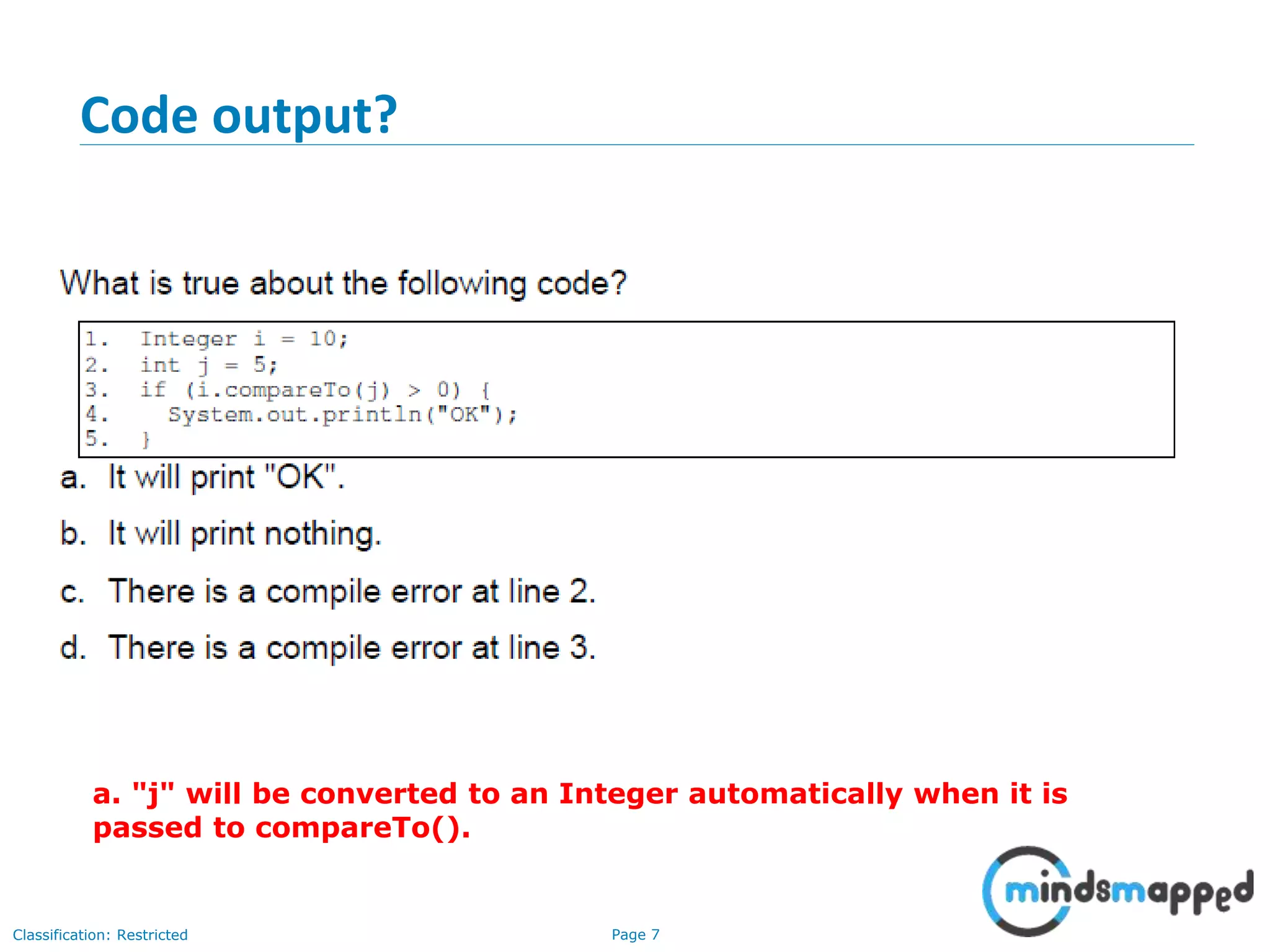
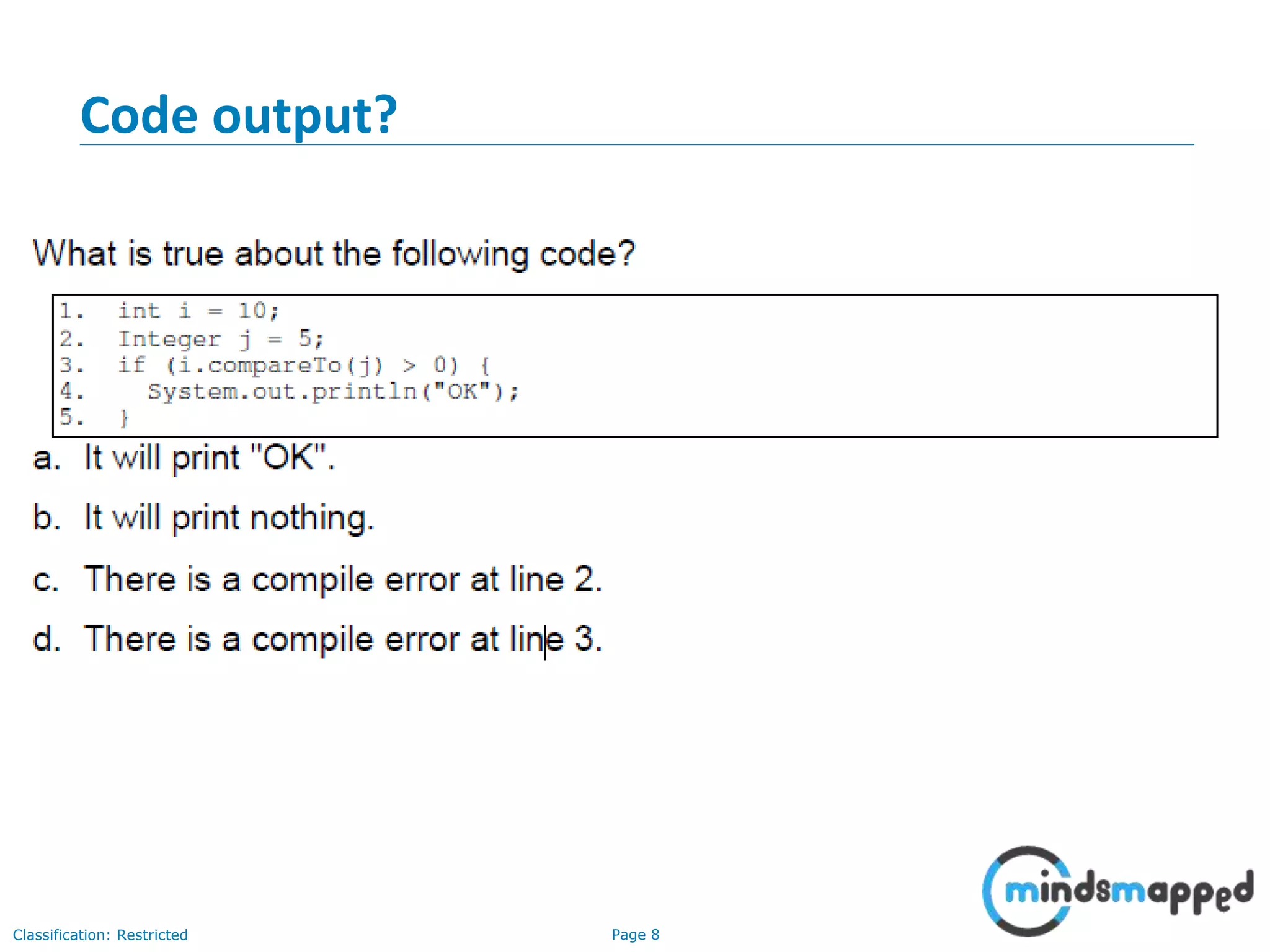
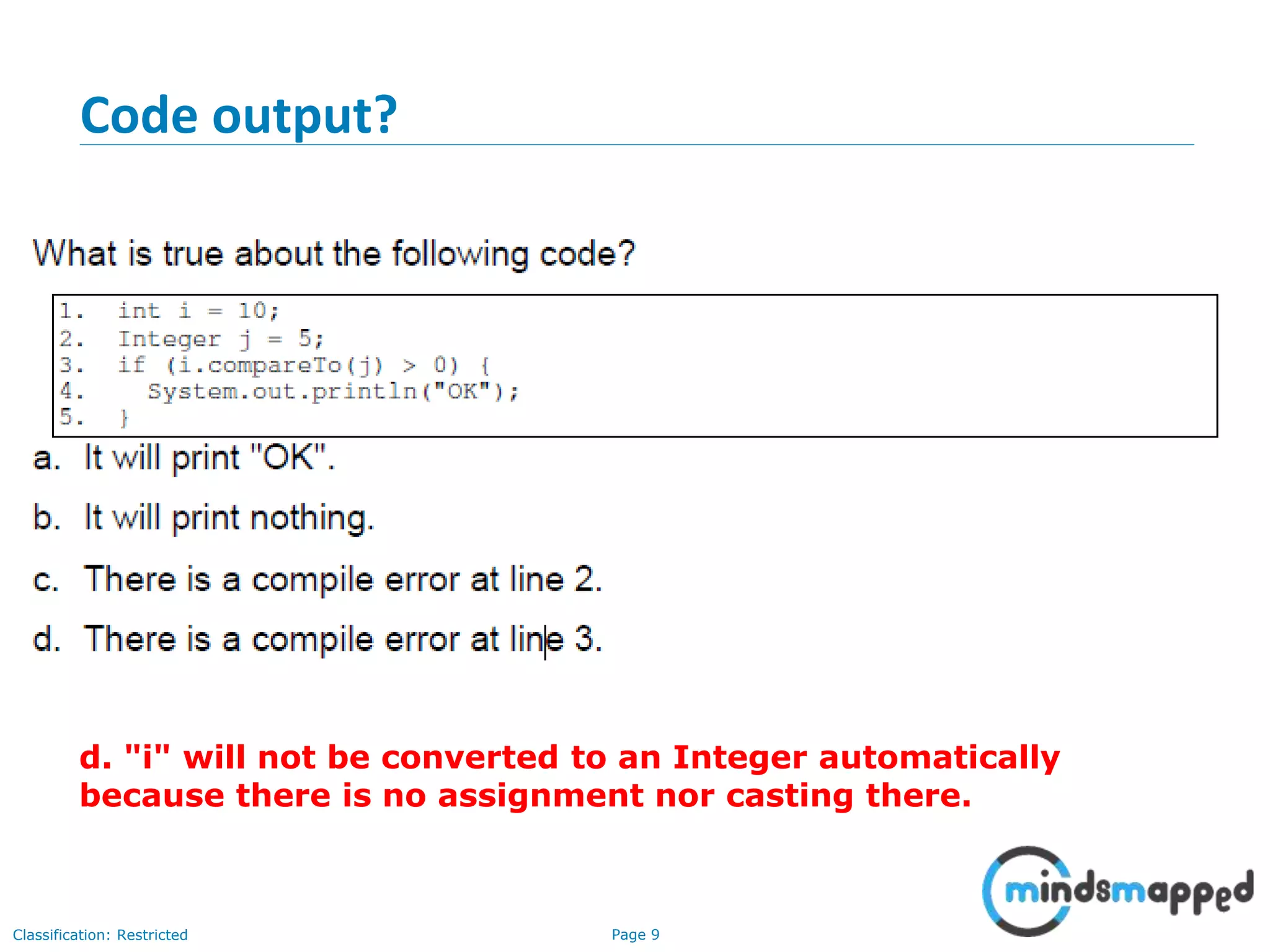
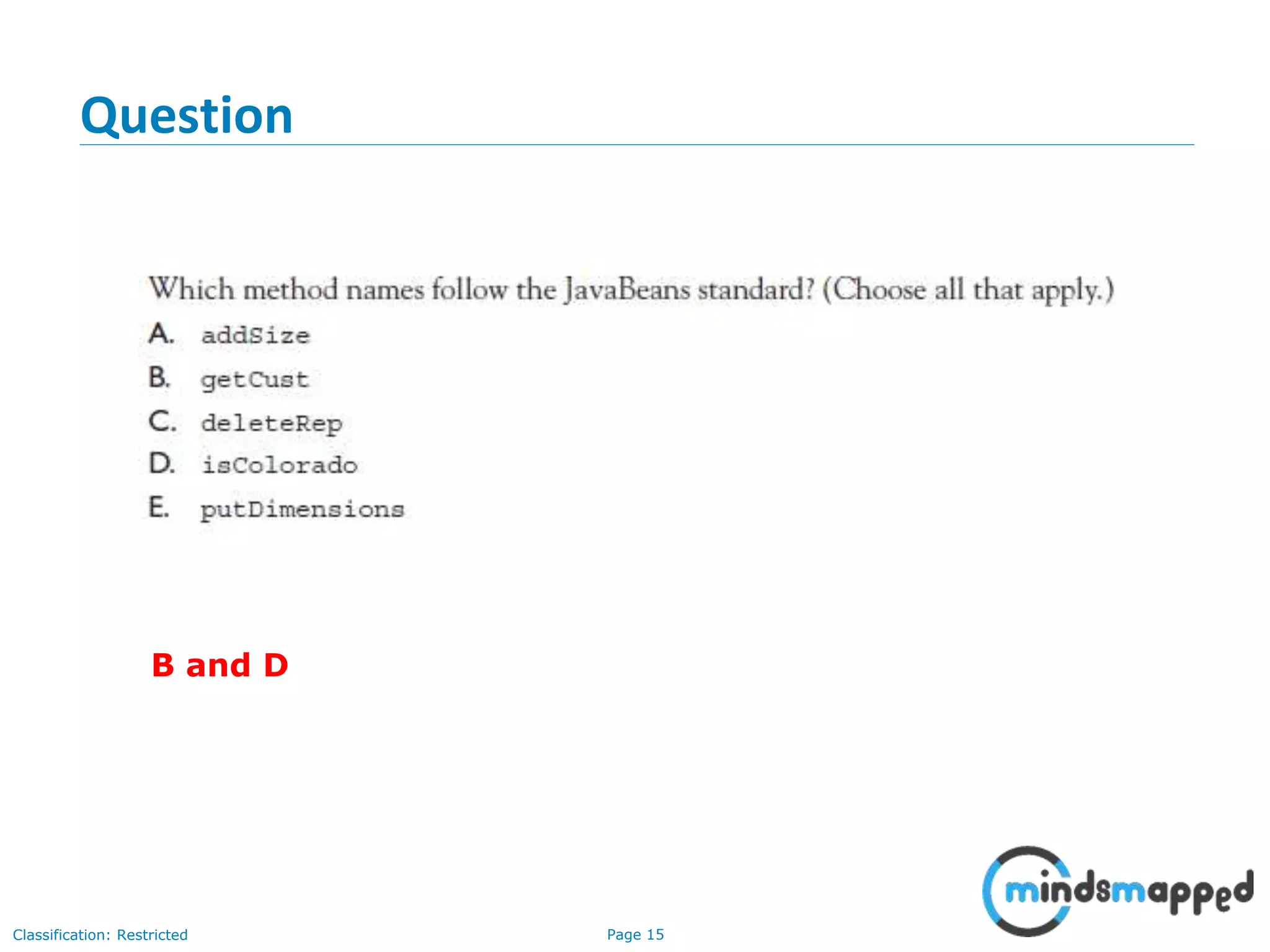
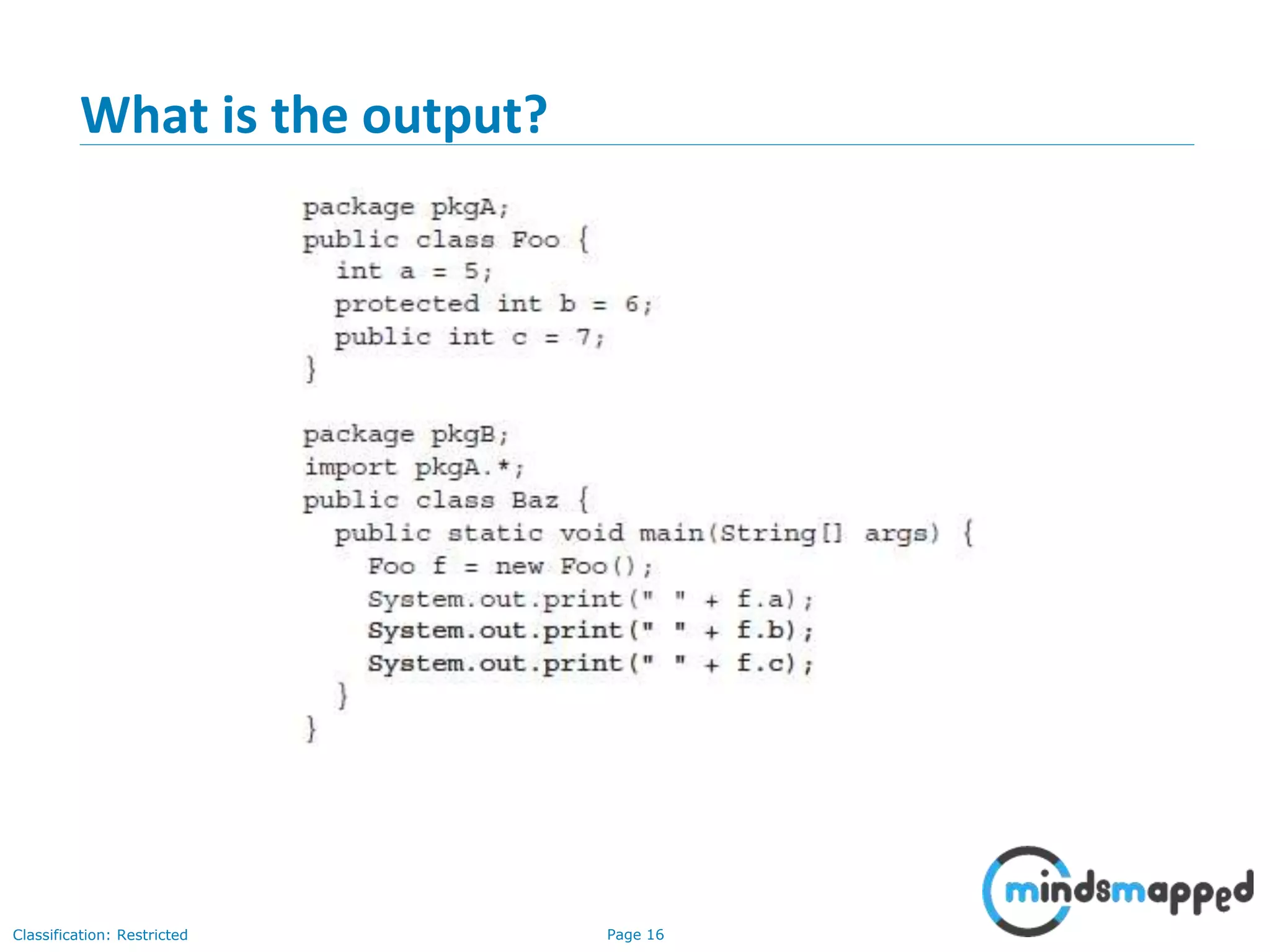
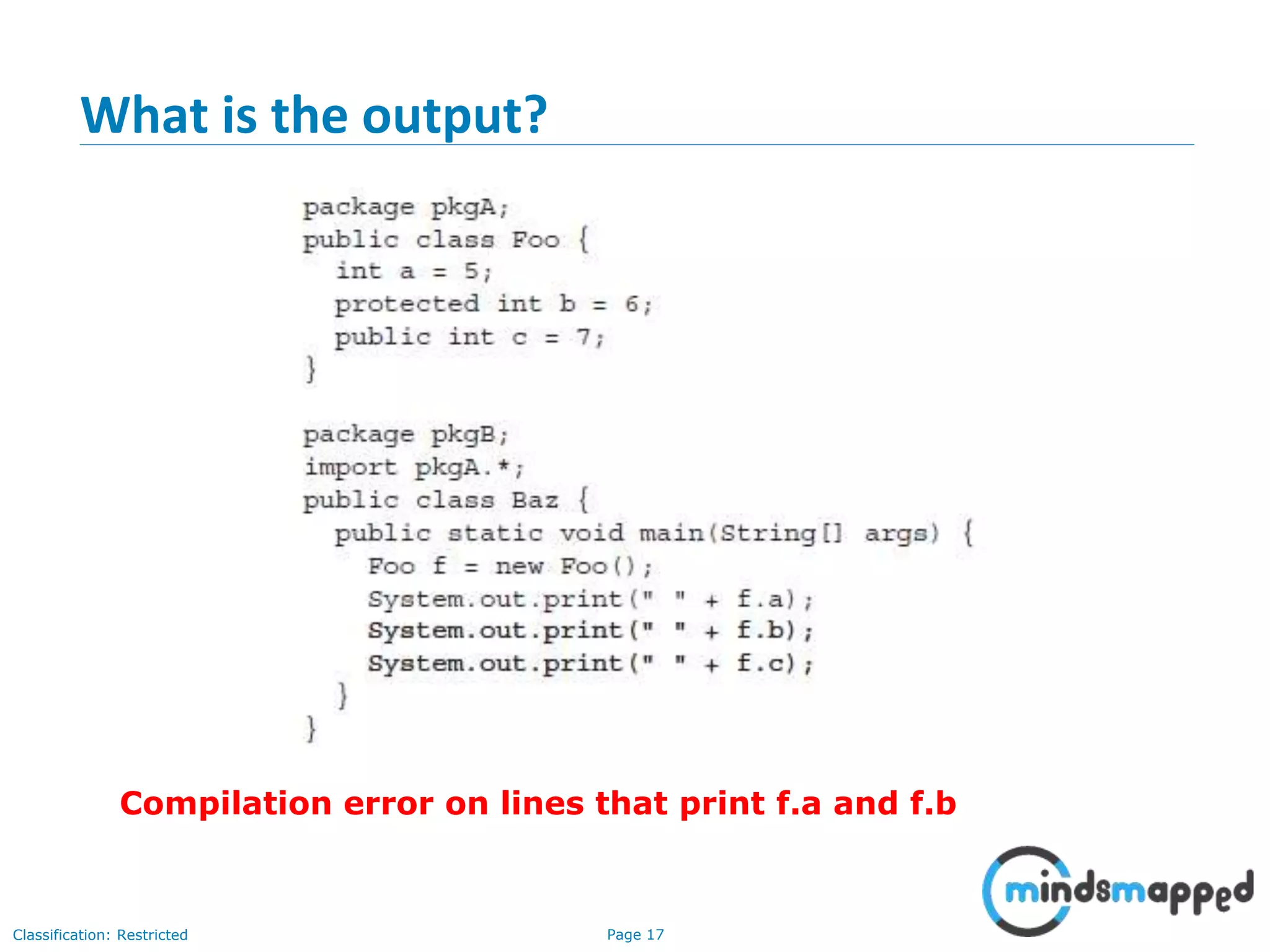
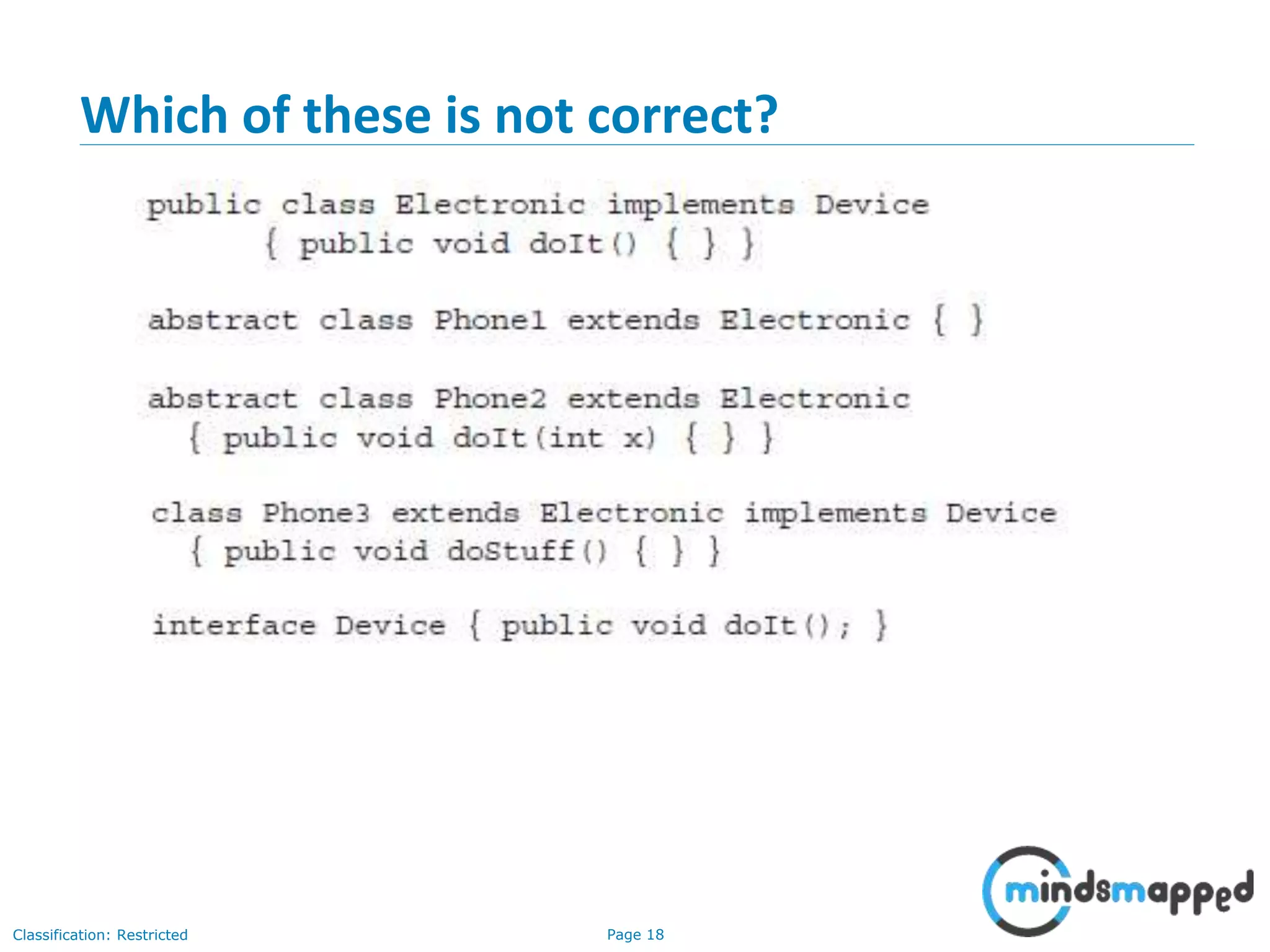
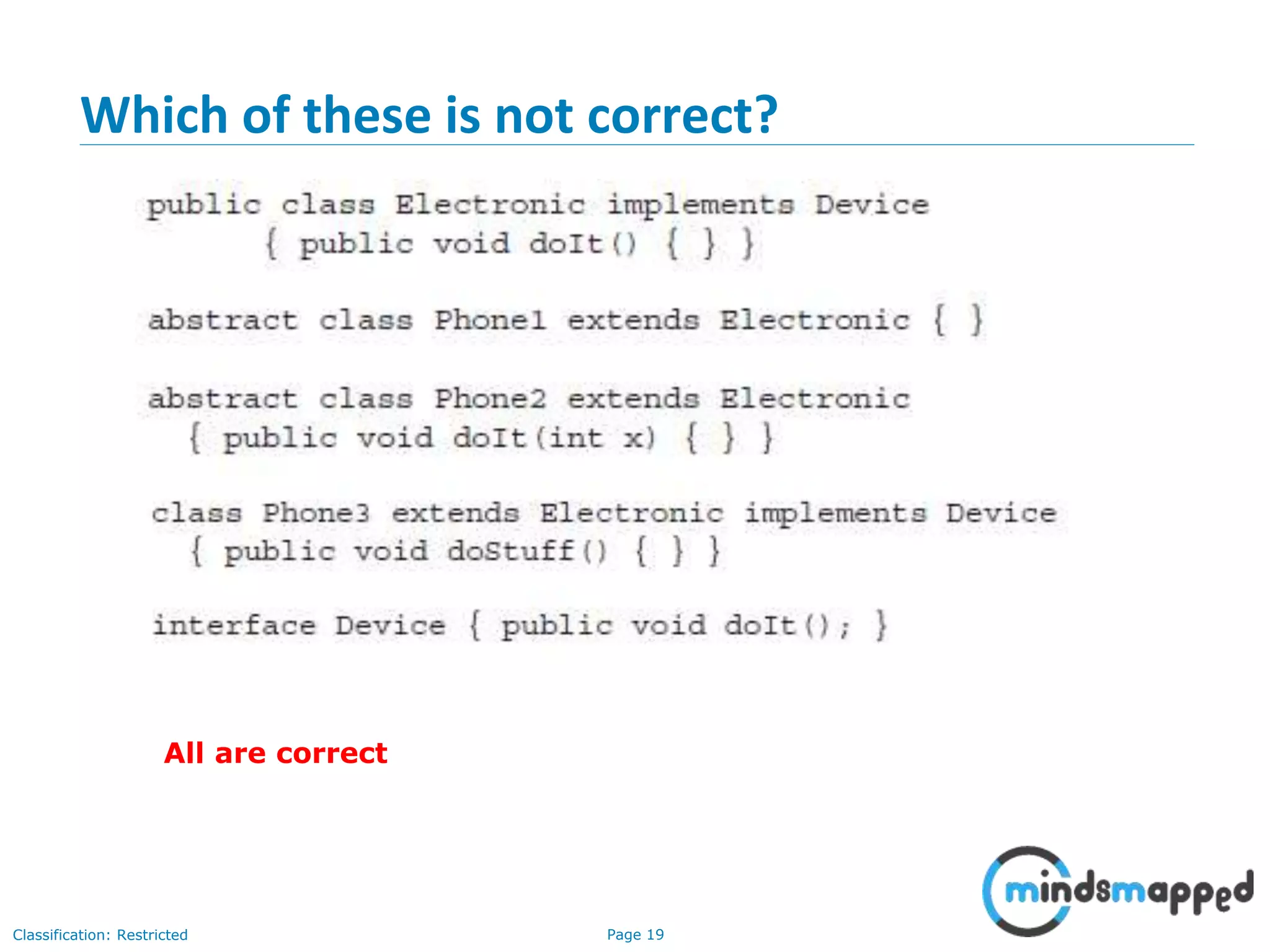
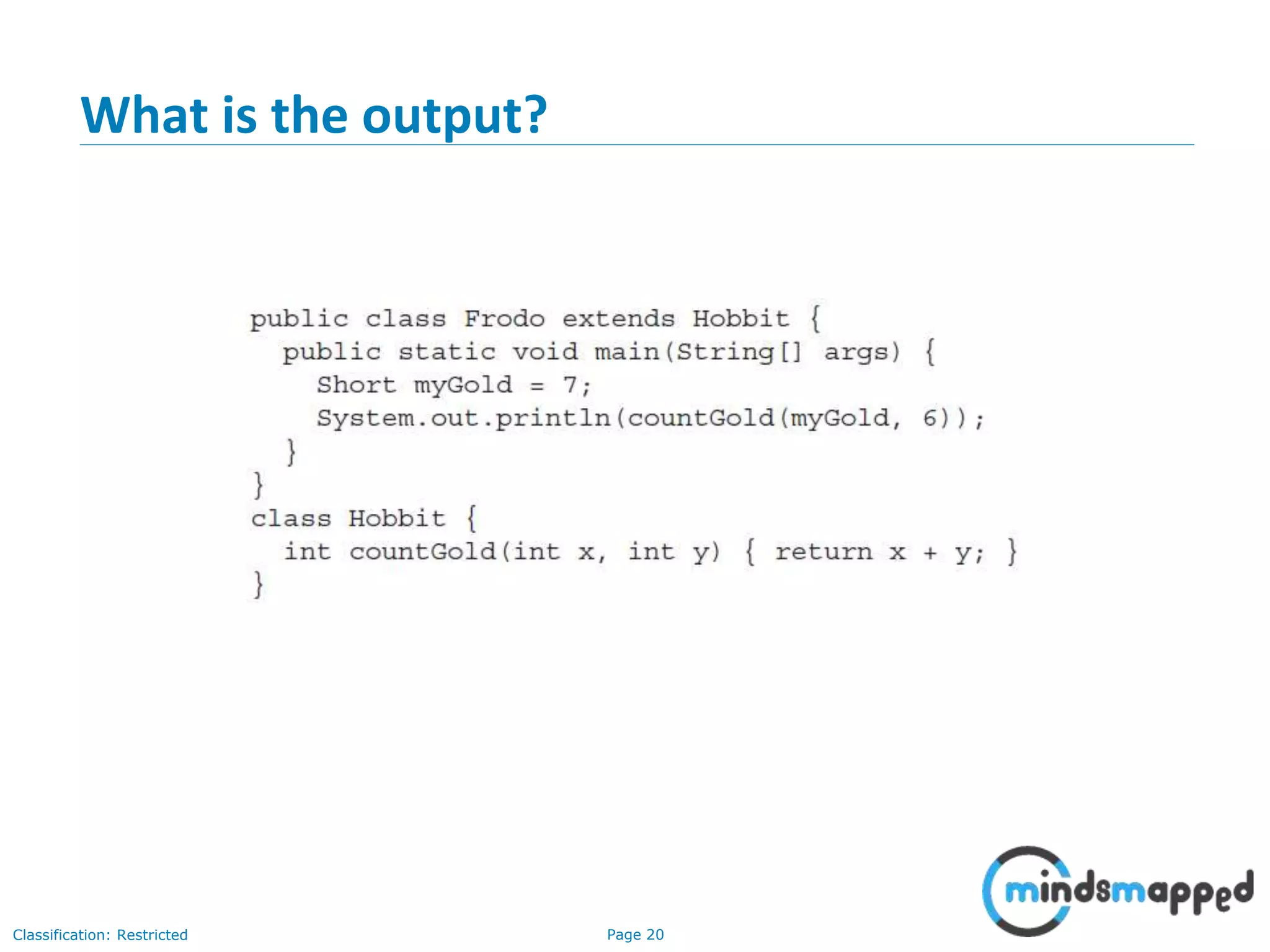
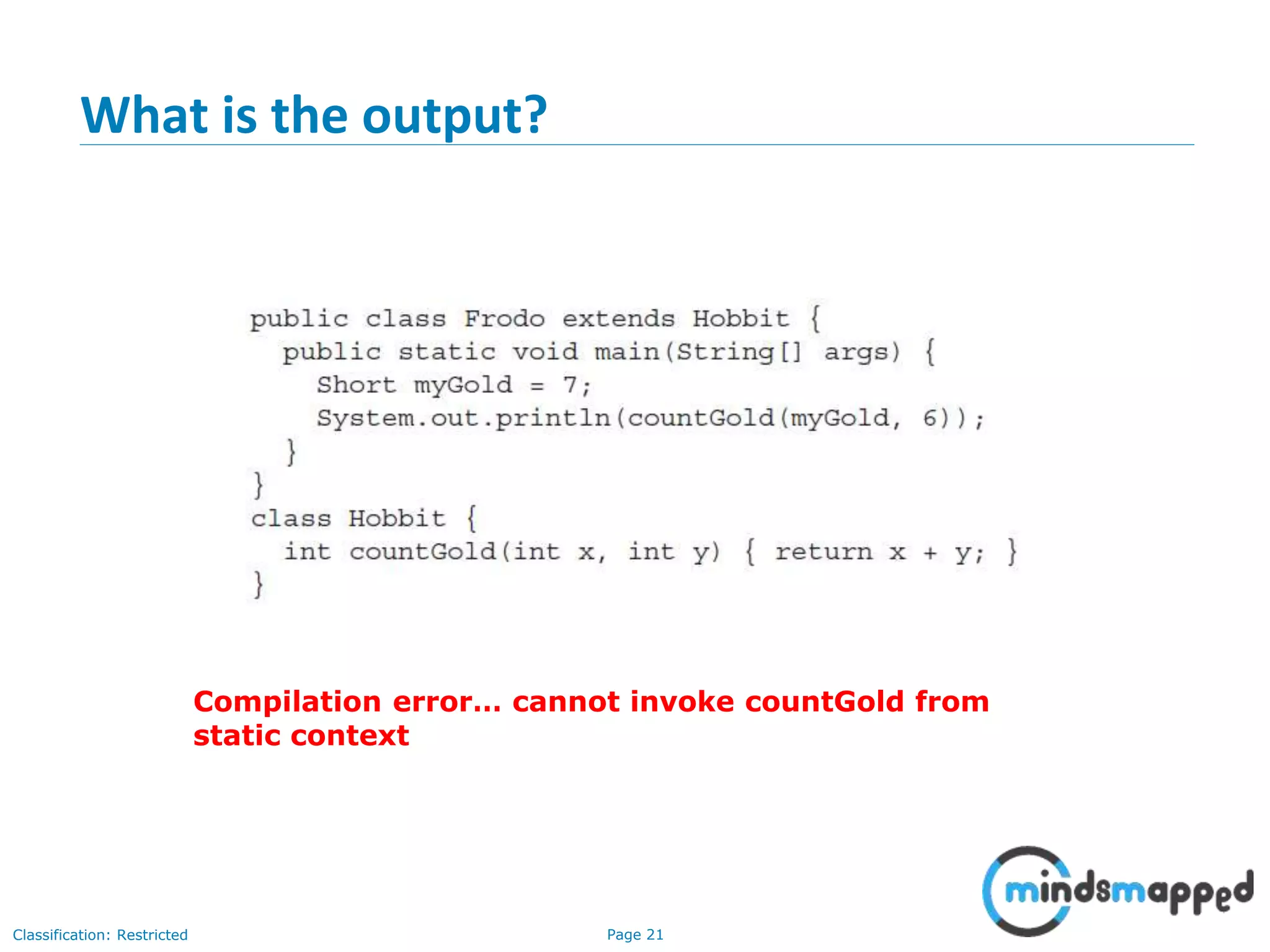
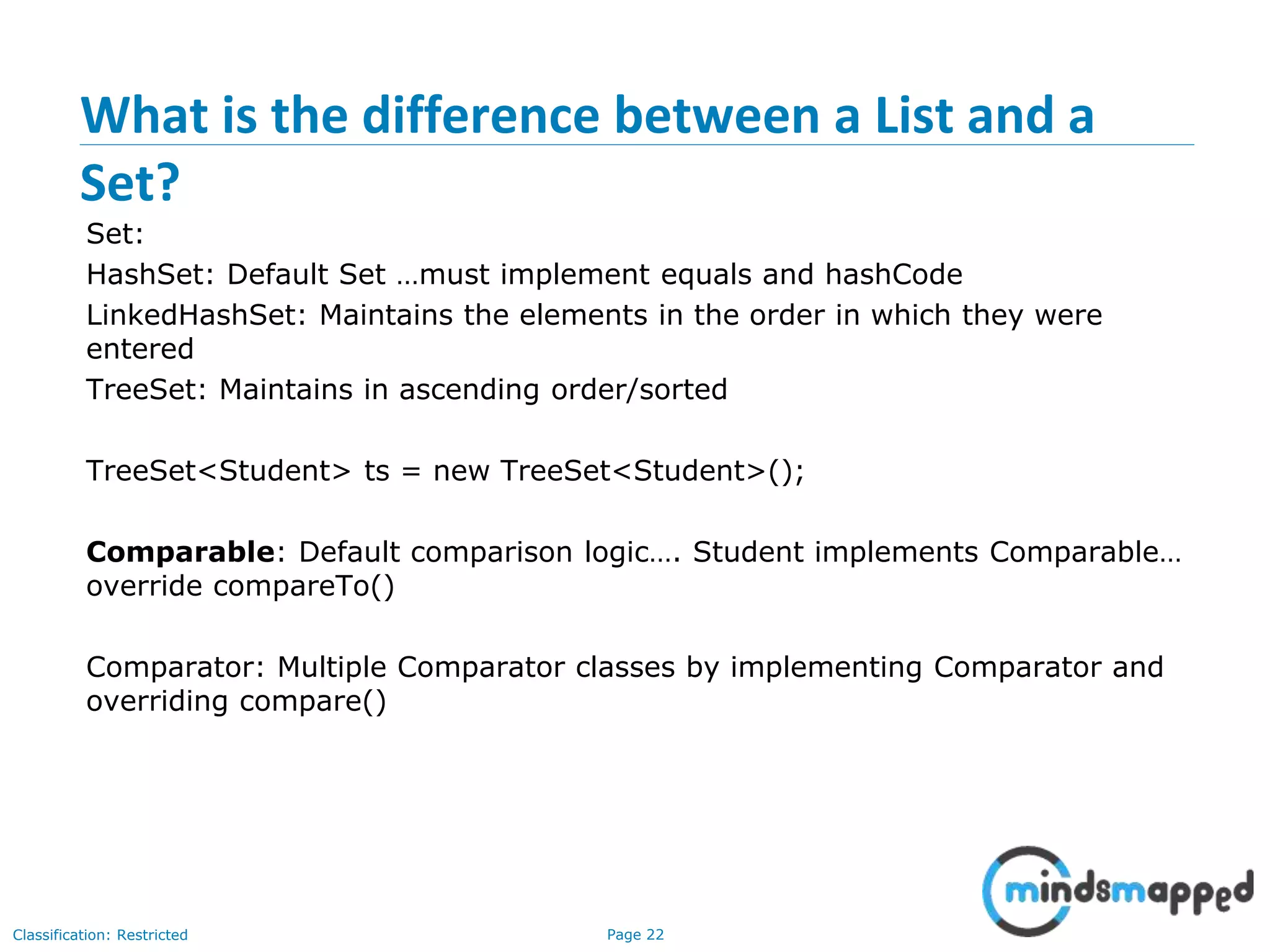
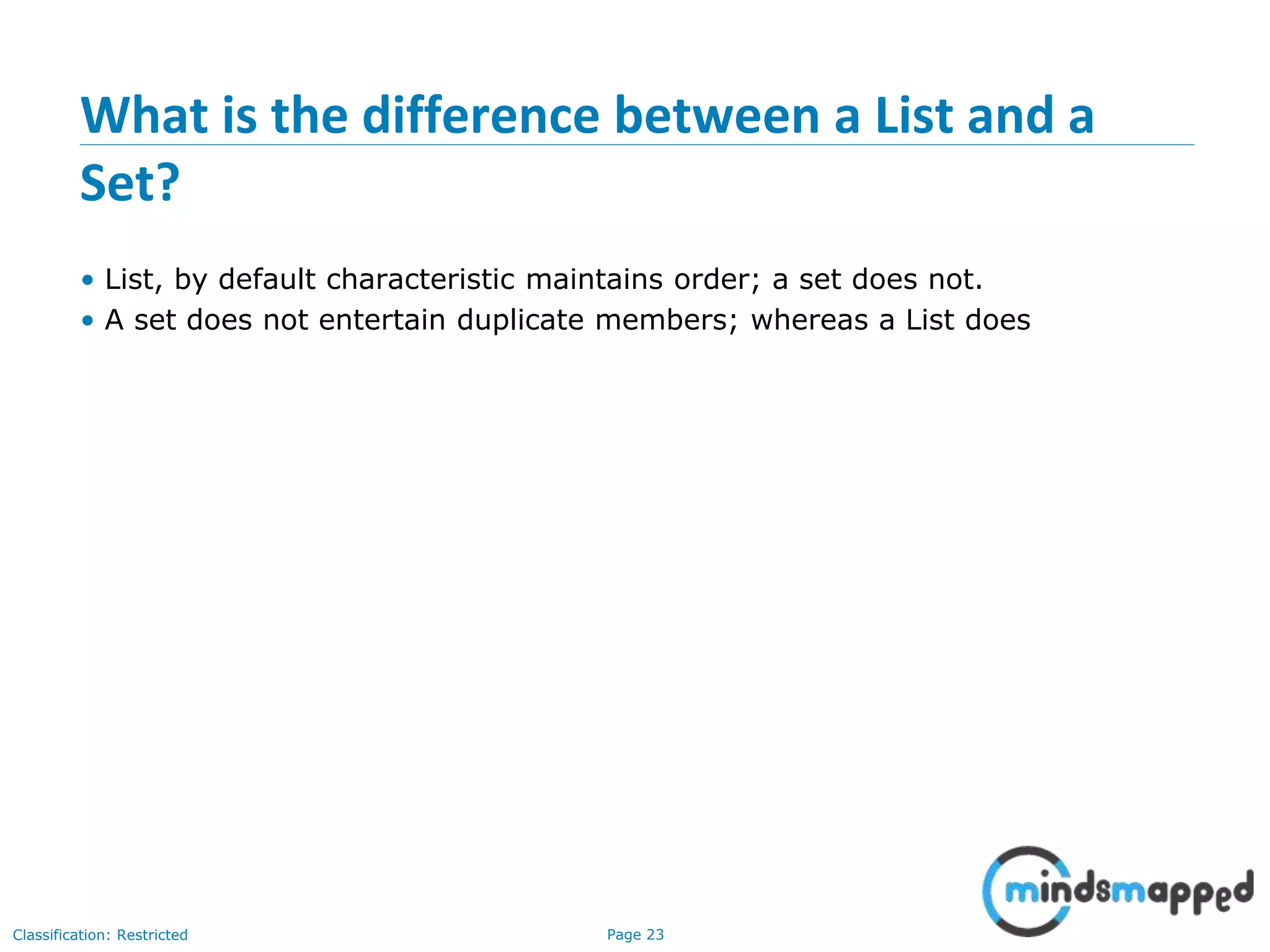
The document is an agenda for Java and JEE training review sessions, covering typical interview preparation, Java access modifiers, and collections concepts like lists and sets. It details various coding scenarios, including autoboxing, method overriding vs. overloading, and common Java errors. The topics to be covered in the next session include maps and their functionalities.