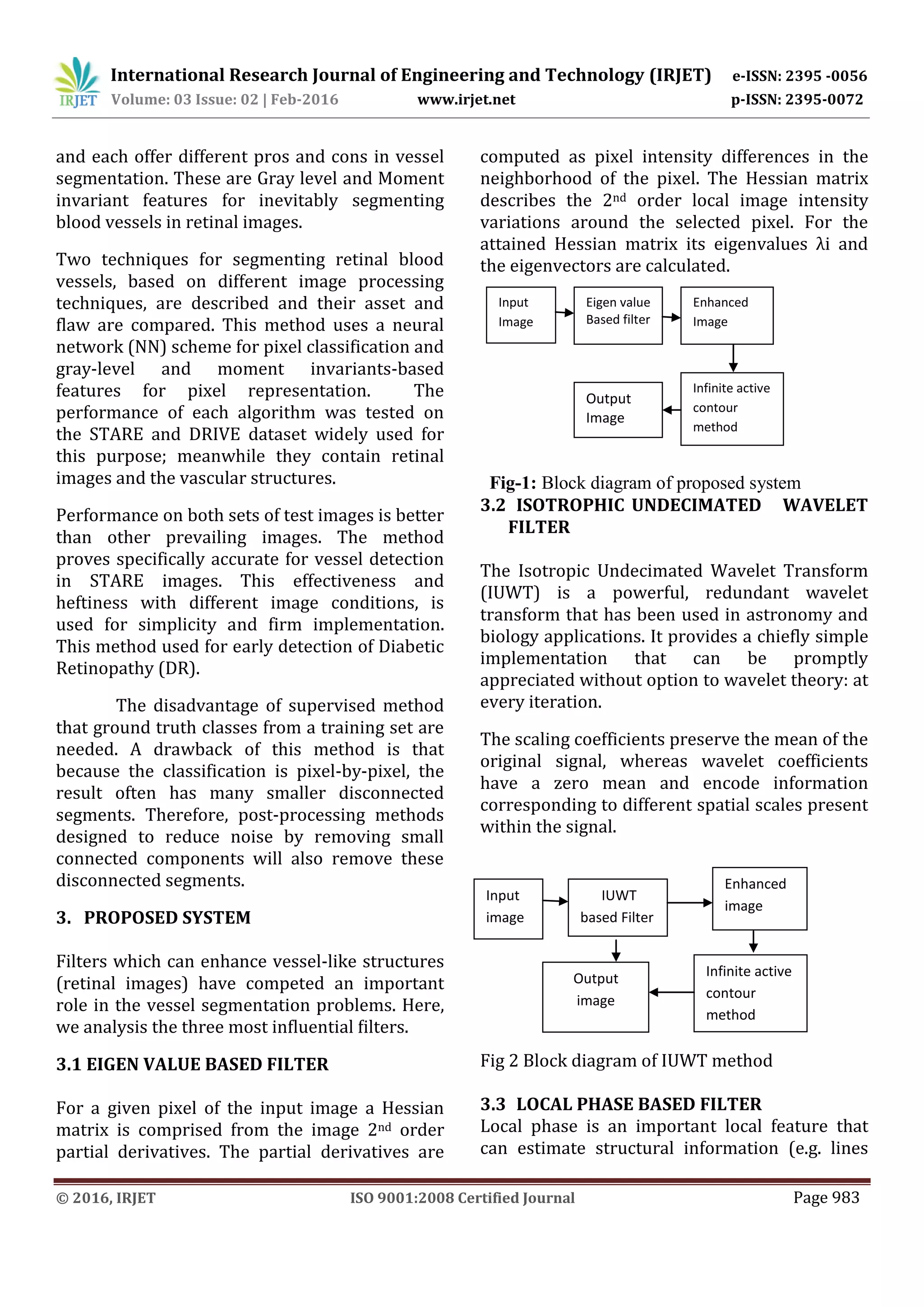
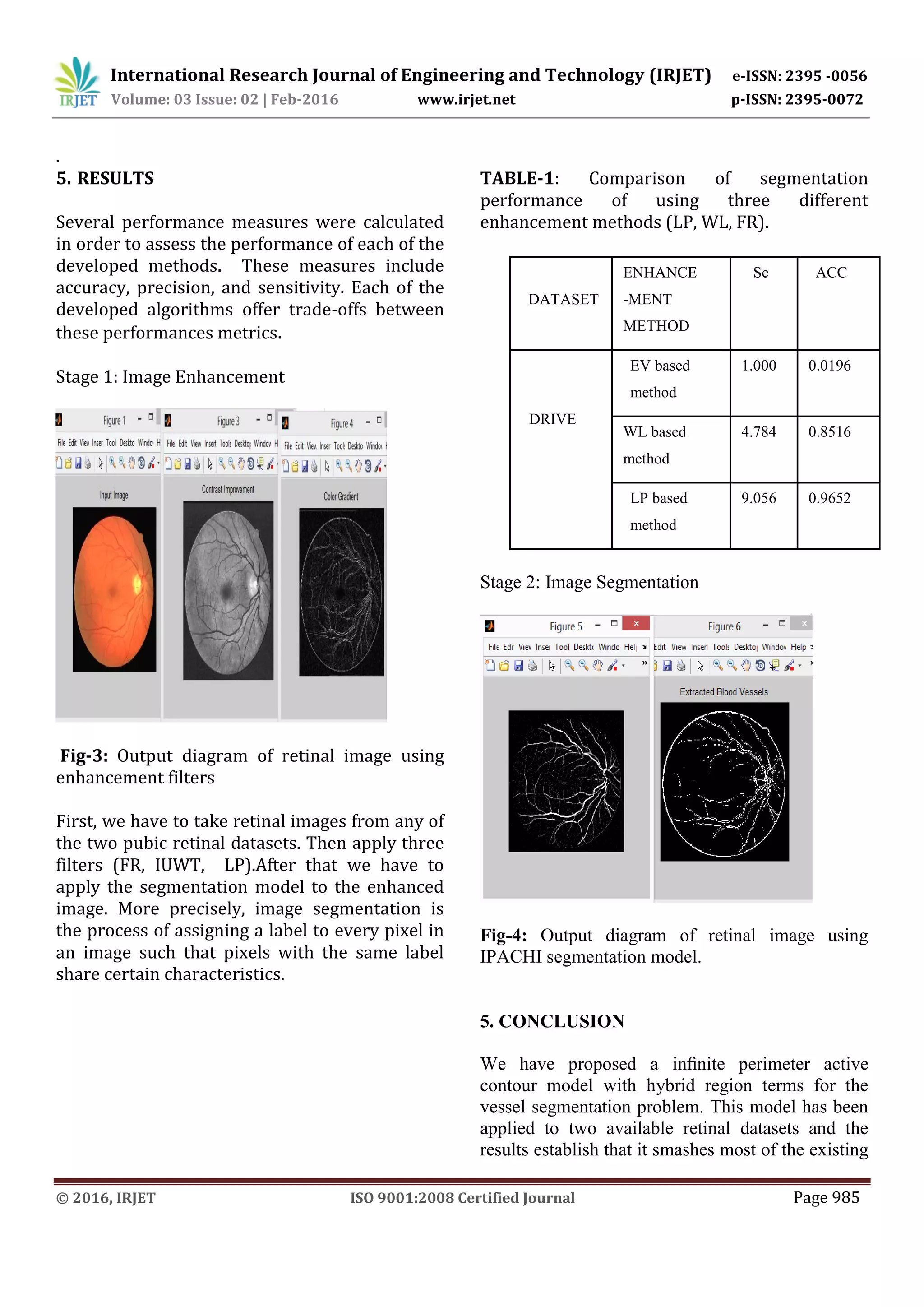
This document proposes a retinal vessel segmentation method using an infinite perimeter active contour model with hybrid region information. It first enhances retinal images using three filters: an eigen value based filter, isotropic undecimated wavelet filter, and local phase based filter. It then segments the vessels from the enhanced images using the proposed infinite active contour model. When tested on two public datasets, the local phase based enhancement achieved the best segmentation accuracy compared to the other filters, with a sensitivity of 9.056% and accuracy of 96.52% on the DRIVE dataset. The proposed segmentation method outperforms most existing approaches in terms of segmentation performance.


![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 03 Issue: 02 | Feb-2016 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2016, IRJET ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 986
methods in terms of segmentation accuracy. Later
vessel segmentation, it is possible to achieve more
progressive analysis, such as measurements of
diameters and lengths of the vessels, classification
of veins and arteries, calculation of arteries venous
ratio, and more prominently study the analytical
and predictive values of these features on eye
disease and a number of systematic diseases.
REFERENCES
[1] Automated Vessel Segmentation Using
Infinite Perimeter Active Contour Model
with Hybrid Region Information with
Application to Retinal Images Yitian Zhao,
Lavdie Rada, Ke Chen, Simon P Harding,
Yalin Zheng, Member IEEE transactions on
medical imaging , vol. 24, no. 10, 2015
[2] Y. Wang, G. Ji, P. Lin, and E. Trucco,
“Retinal vessel segmentation using
multiwavelet kernels and multiscale
hierarchical decomposition,” Pattern
Recogn., vol. 46, pp. 2117–2133, 2013.
[3] B Al-Diri, A. Hunter, and D. Steel, “An
active contour model for segmenting and
measuring retinal vessels,” IEEE Trans.
Med. Image vol. 28, pp. 1488–1497, 2009.
[4] J. Soares and M. Cree, “Retinal vessel
segmentation using the 2D Gabor wavelet
and supervised classification,” IEEE Trans.
Med. Image., vol. 25
[5] Vessel Detection Method Based on
Eigenvalues of the Hessian Matrix, XI
International PhD Workshop OWD 2009,
17–20 October 2009.
[6] A general framework for vessel
segmentation in retinal images,Changhua
Wu, Gady Agam, Peter Stanchev.
[7] K. Sun and S. Jiang, “Local morphology
fitting active contour for automatic vascular
segmentation,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,
vol. 59, pp. 464–473, 2012.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v3i2174-171027091501/75/Retinal-Vessel-Segmentation-using-Infinite-Perimeter-Active-Contour-with-Hybrid-Information-Model-5-2048.jpg)