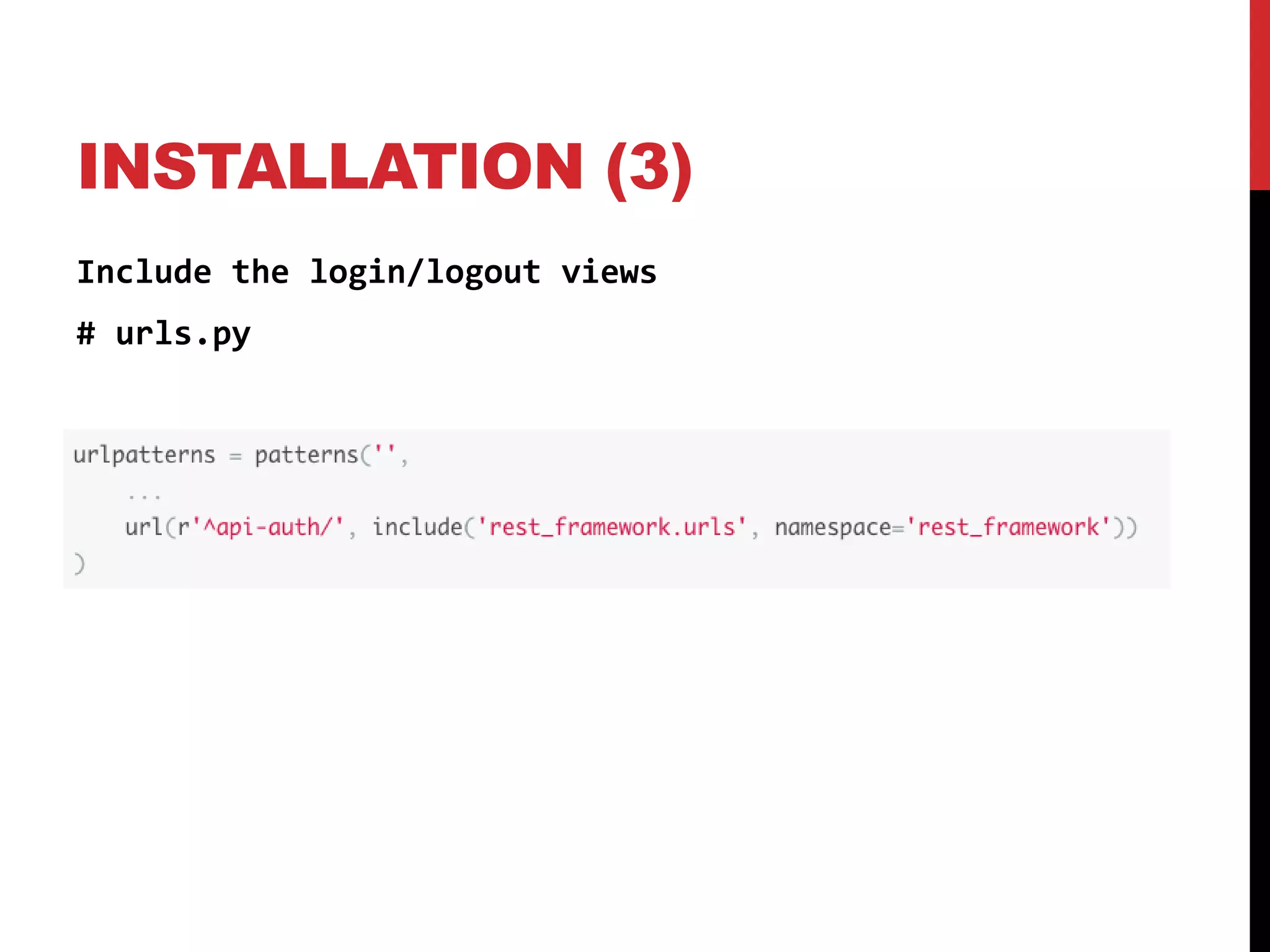
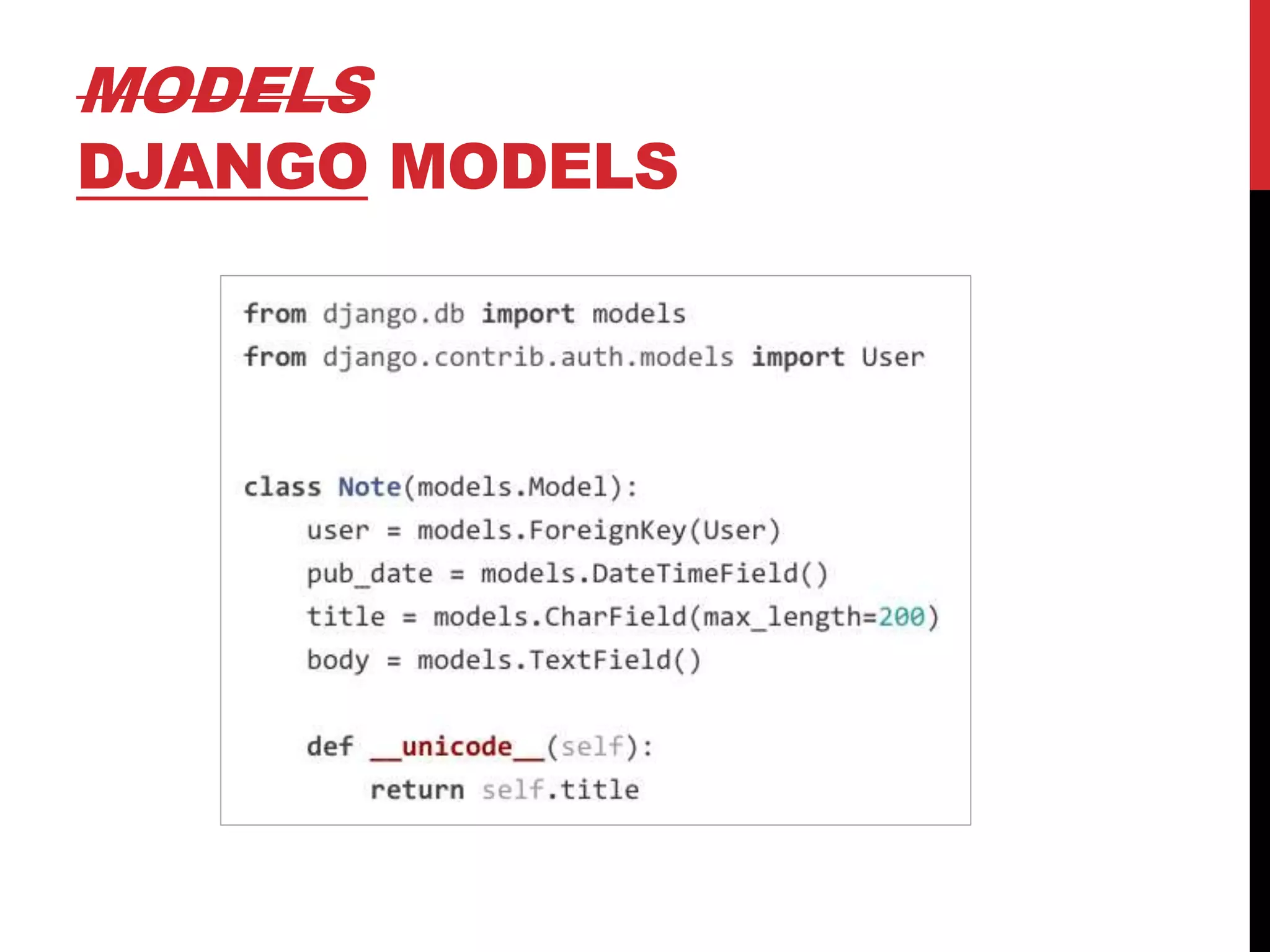
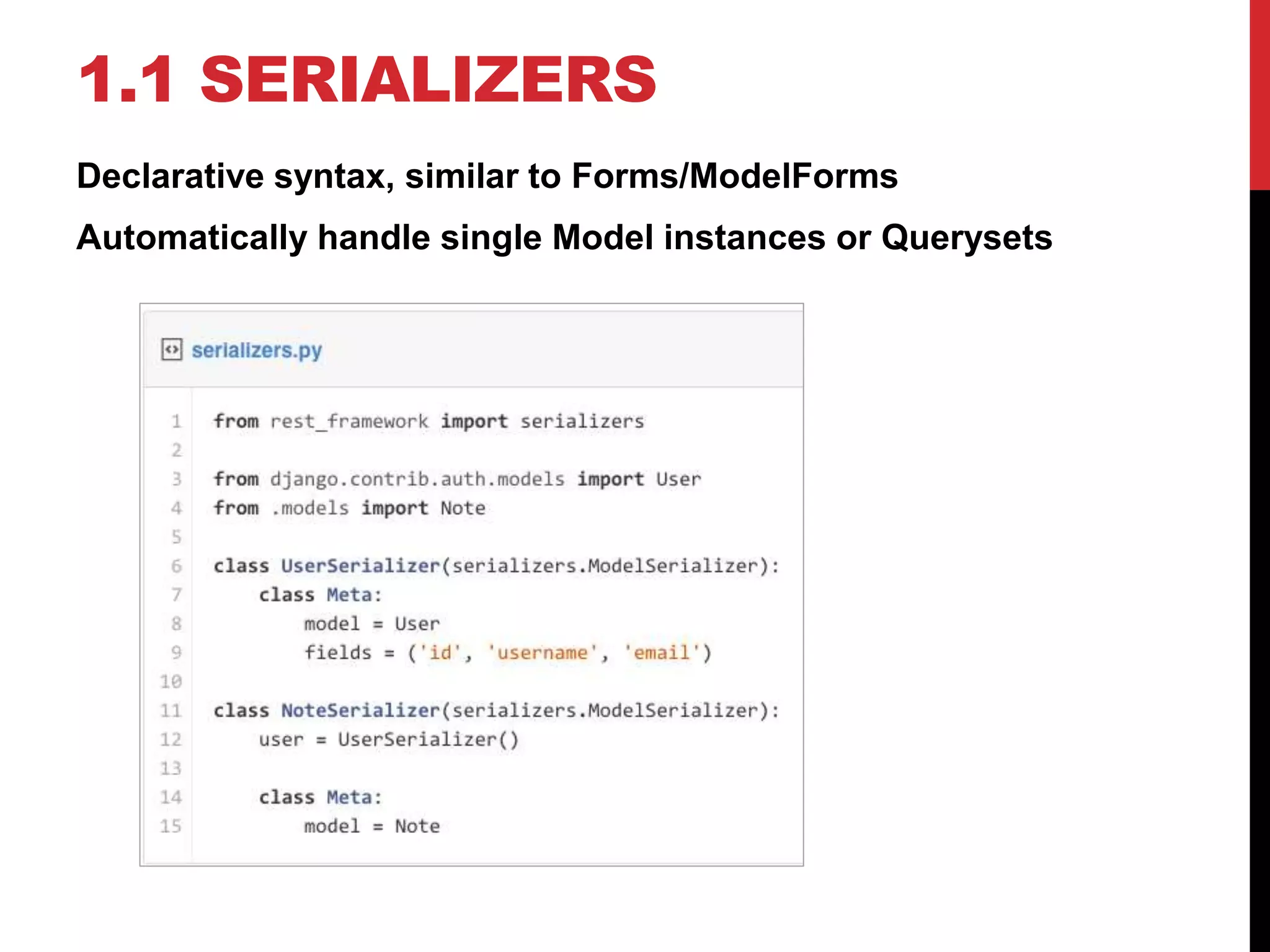
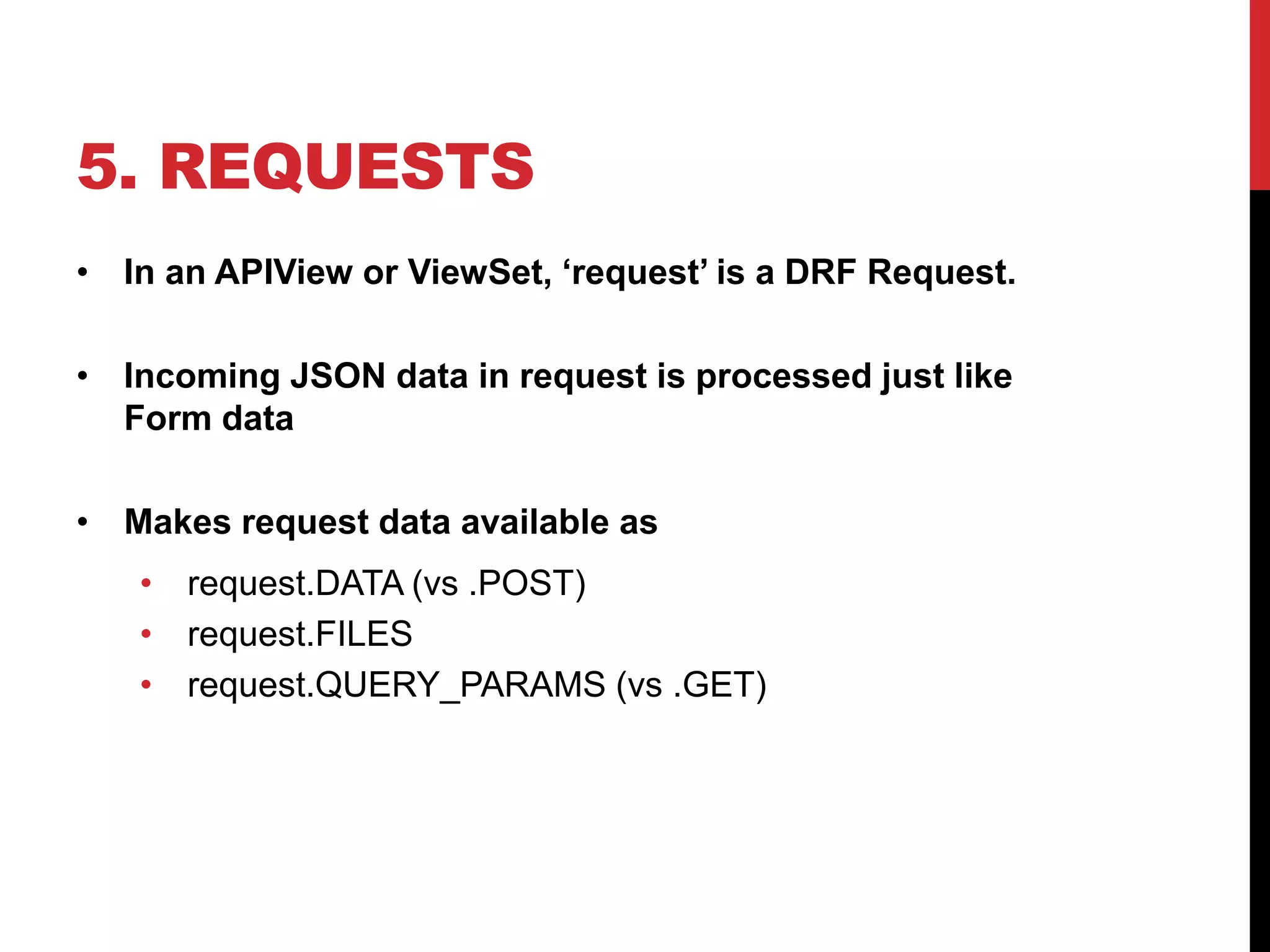
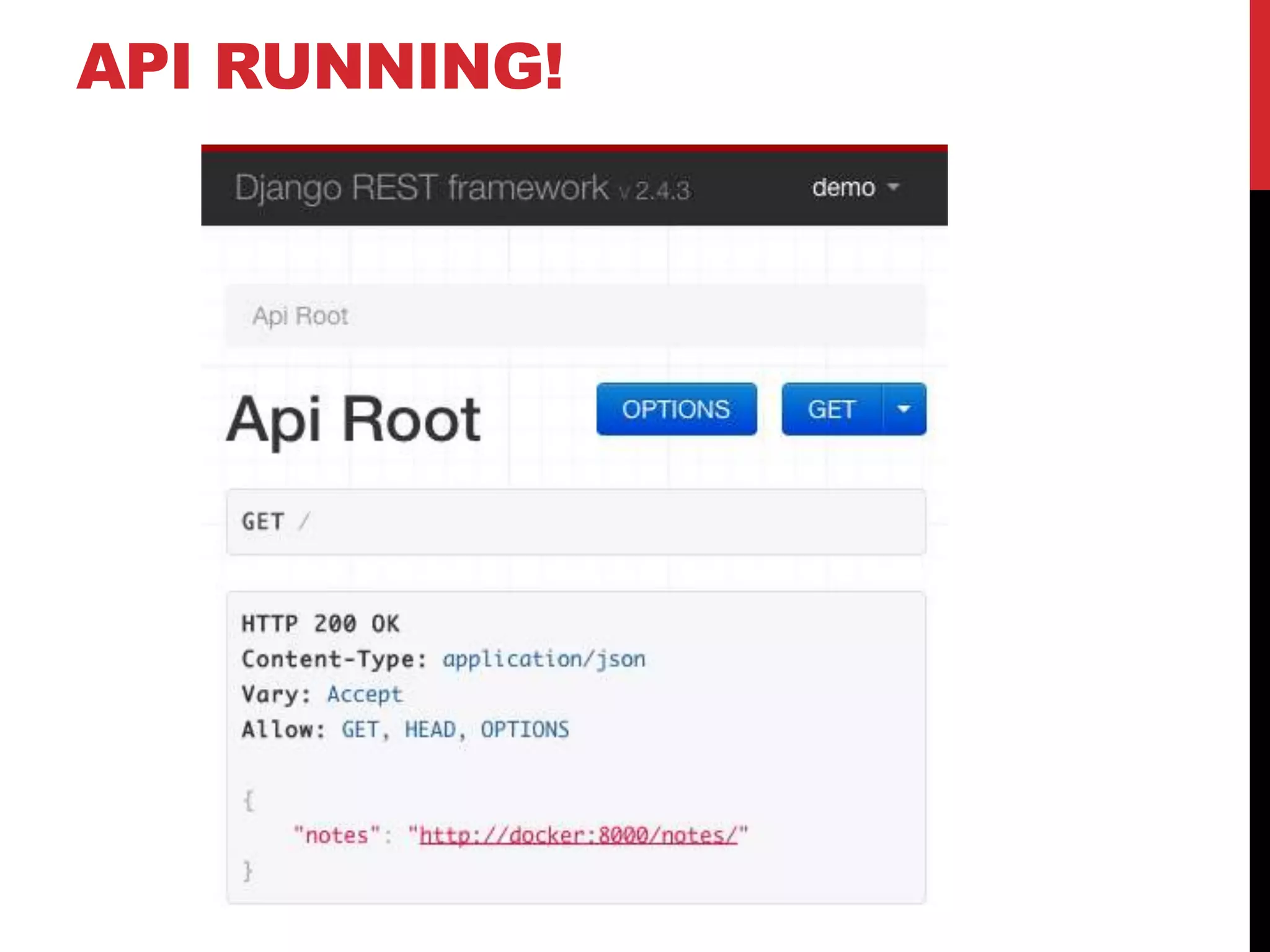
The document provides an overview of Django REST Framework, detailing its components, installation, and functionality for building APIs using REST concepts. It covers core topics such as serializers, API views, viewsets, and URL routing while highlighting the advantages of REST over SOAP. The document also includes customization options and resources for further learning.